An Ultrasound Review of PELVIC PATHOLOGY. Judi M Bender MD January 20, 2016
|
|
|
- Alfred Cunningham
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An Ultrasound Review of PELVIC PATHOLOGY Judi M Bender MD January 20, 2016
2 Pathology to be covered Uterus Cervix Ovary Adnexa Appendicitis Interesting Cases
3 Pathology not covered Pelvic pathology related to pregnancy, congenital or childhood abnormalities or normal variants Pelvic pathology related to non gynecological problems Limited review of normal anatomy
4 Myometrial Pathology Leiomyoma Lipoleiomyoma Leiomyosarcoma Adenomyosis Arteriovenous Malformations
5 Leiomyomas (Fibroids) Most common uterine neoplasm seen in up to 30% of woman over 30 More often seen in Afro-Americans Usually multiple Often asymptomatic but may present with pain/ uterine bleeding Composed of spindle shaped muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue
6 Estrogen dependent and may increase in size in anovulatory cycles, during pregnancy, with Tamoxifen and in post menopausal woman on hormone replacement. Most stabilize or decrease in size after menopause
7 Location Intramural Submucosal Subserosal Appearance Enlarged heterogenic uterus Hypoechoic/heterogenic lesion Acoustic attenuation Focal calcifications/ calcified rim Degeneration/necrosis
8 Intramural Fibroid Confined to myometrium
9 Submucosal Fibroid Projecting into the endometrial cavity
10 Submucosal Fibroid
11 Subserosal fibroid Projecting from the peritoneal surface
12
13 Pedunculated Fibroid
14 Enlarged diffuse leiomyomatous
15
16 Fibroid with acoustic attentuation
17 Calcified fibroid
18 Calcified fibroid
19 Calcified fibroids on plain films
20 Degenerating Fibroid
21 Lipoleiomyomas Very rare benign tumors Consist of variable amounts of lipocytes, smooth muscle and/or fibrous tissues Appears as echogenic, attenuating mass with no flow on color Doppler Usually asymptomatic and do not require surgical removal
22 Lipoleiomyoma
23 Leiomyosarcomas Very rare malignancy which accounts for less than 2% of uterine cancers It may arise from a preexisting leiomyoma Frequently asymptomatic; uterine bleeding may occur Has the ultrasound appearance of a rapidly growing or degenerating leiomyoma with local invasion or distant metastases
24 Leiomyosarcoma
25
26 CT of a leiomyosarcoma
27
28 Adenomyosis The presence of endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium Diffuse form characterized by an enlarged uterus with a diffusely heterogenic myometrium Nodular form compose of nodules (adenomyomas) May present with pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea or menorrhagia
29 Asymmetrically thickened myometrium Subendometrial cysts, echogenic linear striations or echogenic nodules Ill defined endometrial border
30 Adenomyosis Echogenic nodule
31 Subendometrial cysts with indistinct endometrium
32 MRI of Adenomyosis Focal thickening of myometrial junction zone
33 Uterine Arteriovenous Malformations Consist of a vascular plexus of arteries and veins with no intervening capillaries Rare lesions seen in the myometrium and occasionally in the endometrium Most are acquired secondary to trauma, surgery or gestational trophoblastic neoplasm
34 Greyscale images may be nonspecific or may show multiple serpiginous, anechoic structures Color Doppler shows abundant blood flow in the AVM Spectral Doppler shows high velocity low-resistence arterial flow with high velocity venous flow
35
36 Multiple serpiginous anechoic structures
37 AVM in Cesarean scar
38 Endometrial Appearance Normal premenopausal phases Early proliferative Mid cycle secretory Late secretory Post menopausal Endometrial atrophy Endometrial hyperplasia
39 Early proliferative 5-7mm on transvaginal ultrasound
40 Midcycle secretory Up to 11 mm on transvaginal ultrasound
41 Late secretory 7-16mm on transvaginal ultrasound
42 Post menopausal endometrium Endometrium should be </=4mm on transvaginal ultrasound
43 Reasons for post menopausal bleeding Endometrial atrophy Endometrial hyperplasia Endometrial polyps Endometrial carcinoma
44 Postmenopausal atrophy If< than 4mm, postmenopausal bleeding is usually attributed to atrophy May see small amount of fluid or cystic changes
45 Endometrial Hyperplasia Diffuse but may not involve the entire endometrium Histologically may +/- cellular atypia (25% with atypia progress to cancer) -need Bx to determine Develops from unopposed estrogen stimulation- hormone replacement, persistent anovulatory cycles, PCO, obesity, estrogen producing ovarian cancers
46 Diffuse Diffusely thickened and echogenic
47 Tamoxifen Therapy Has estrogenic effect on postmenopausal women-causes endometrial thickening and cystic changes-increased risk of polyps/ca
48 Endometrial Polyps Localized overgrowths of endometrial tissue covered by endothelium 20% of polyps are multiple Malignant degeneration is uncommon May be diffuse, focal, pedunculated, stalked or contain cysts Best evaluated with sonohysterography
49 Echogenic polyp
50 Echogenic polyp Color Doppler shows vascular flow
51 Small single polyp
52 Multiple polyps
53 Cystic changes in Endometrial Polyp
54 Sonohysterography Helps determine if endometrial lesion is polyp or submucosal fibroid
55 Endometrial Carcinoma Most common gynecologic malignancy occurring in 3% of women 75-80% of this cancer occurs in postmenopausal woman Accounts for less than 1.5% of cancer deaths in women because > 75% of endometrial cancers are confined to the uterus.
56 Subtypes of endometrial cancer Type I (80%) Well differentiated with slow progression seen in woman PTEN gene mutation in 30-80% Arises in setting of hyperplasia/elevated estrogen Type II (20%) Less differentiated and spreads early in woman P53 mutation in up to 50% Arises in setting of endometrial atrophy
57 Appearance of endometrial cancer May resemble hyperplasia/polyps with uniformed thickened echogenic endometrium More commonly the endometrium is heterogenic with poorly defined borders
58
59
60 Fluid filled endometrium with an irregular vasculized wall, polypoid lesions and ascitis
61 Endometritis Endometrium may appear thickened, irregular and may or may not contain fluid Gas may be seen in the endometrial canal May occur postpartum, following surgery or with PID
62 Thickened heterogenic endometrium Secondary to PID
63 Poorly defined endometrium with gas Following myomectomy for leiomyoma
64 Endometrial Adhesions Endometrium may appear normal on transabdominal and transvaginal US Best seen in secretory phase when the endometrium is more hyperechoic Sonohysterography demonstrates adhesions as bridging bands of tissue that distort the endometrial cavity
65 Transvaginal Bright hyperechoic scar tissue in the endometrial canal
66 Sonohysterogram Demonstrates synechiae also known as Asherman s syndrome
67
68 Hydro/Hematometrocolpos Accumulation of secretions and/or blood in the uterus and/or vagina with the location depending on the amount of obstruction. When congenital due to imperforate hymen,vaginal septum,atresia, rudimentory uterine horn When acquired due to endometrial or cervical tumors or postradiation fibrosis
69 Hydrometacolpos Secondary to imperforate hymen
70 Hematometrocolpos Secondary to cervical tumor
71 Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices Appear as echogenic linear structures in the endometrial cavity in the body of the uterus Should see acoustic shadowing and two parallel echoes representing the anterior and posterior surfaces of the IUCD
72 3D US image IUCD correctly positioned in the fundus and body of the endometrial canal
73 Malpositioned IUCD IUCD in endocervical canal
74 IUCD in the posterior wall of the uterus
75 Cervical Lesions Nabothian cysts Cervical polyps Cervical leiomyomas Cervical carcinoma
76 Nabothian cysts Common finding Measure few mm to 4 cm May have internal echoes from hemorrhage or infection
77 Cervical Polyps Hyperechoic lesion with vascular flow Frequent cause of vaginal bleeding
78 Cervical Leiomyoma Pedunculated fibroids can prolapse into vagina Can be obstructive at childbirth
79 Cervical Carcinoma May resemble a cervical Fibroid Usually diagnosed clinically
80 Benign Ovarian Cysts Functional Cysts Follicular Corpus Luteal Hemorrhagic Cysts Theca-luteal Cysts Postmenopausal Cysts Endometriomas
81 Normal ovarian follicles -during the proliferative phase
82 Dominant follicle on Day 10 which can reach cm at time of ovulation
83 Follicular cyst Result of mature follicle failing to ovulate or involute; Cyst must be > than 2.5 cm; usually regress on own
84 Corpus Luteal Cyst Result from failure of absorption or from excess bleeding into the corpus luteum Have thicker walls with crenulated appearance
85 Hemorrhagic cysts Internal hemorrhage from granulose cells lining functional or corpus luteal cysts Appearance depends on age and amount of hemorrhage ranging from hyperechoic with posterior acoustic enhancement to reticular pattern with internal echoes to fluid-fluid line No flow seen within cyst on Doppler
86 Acute hemorrhagic cyst Echogenic free fluid in pelvis indicates a leaking or ruptured cyst woman with these cysts complain of pelvic pain
87 Hemorrhagic Cysts Septations with internal echoes and no flow
88
89
90 Theca-luteal cysts Largest of functional cysts Associated with high levels of HCG Seen in gestational trophoblastic disease and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome with infertility drug therapy These cysts are bilateral, multilocular and very large
91 Theca-luteal cysts Cysts may hemorrhage, rupture or undergo torsion
92 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome Complication of ovulation induction Mild form associated with lower abdominal pain, up to 5 cm ovaries, mild ascitis nausea Severe form associated with severe abdominal pain and distention, 10cm or larger ovaries with multiple cysts, ascitis, pleural effusions, low BP,oliguria and electrolyte imbalance
93
94 Postmenopausal Cysts Unilocular <7cm in diameter and without septations or solid components can be followed by US <3cm simple cysts seen in 15% of postmenopausal woman May disappear or change in size
95
96 Ovarian Remnant Cysts Small simple to larger complex cysts can infrequently arise from a small amount of residual ovarian tissue following a bilateral oophrectomy Usually the remnant of ovarian tissue is secondary to a surgery complicated by adhesions, endometriosis, PID or tumor
97 Followup of Ovarian cysts in Premenopausal Women Simple Cysts 1.<3cm=Normal finding cm=certainly benign, No F/U cm=Likely benign; yearly F/U 4. >7cm=further evaluation with MRI or surgery Hemorrhagic Cysts 1.<5cm=Describe; No F/u 2. >5cm=F/U in 6-12 weeks
98 Followup of Ovarian Cysts in Post menopausal Women Simple Cysts 1.<1cm=inconsequential;No F/U cm=Yearly F/U 3. >7cm=Further evaluate with MRI or surgery Hemorrhagic Cysts Perimenopausal=F/U US in 6-12 wks Postmenopausal=Abnormal; Surgery
99 Endometriomas Localized form of endometriosis Well defined uni/multilocular cystic mass with diffuse low level internal echoes usually found in the ovary; often bilateral May have marginal echogenic nodules or fluid-fluid level Show little change over time with no pain or chronic menstraul pain Endometriomas > 9 cm show <1% malignant transformation Cause decrease ovarian function and fertility
100
101
102 Polycystic Ovarian Disease PCOD is an endocrine disorder which causes elevated LH and depressed FSH levels which results in hypersecretion of androgens and chronic anovulation. Common cause of infertility and early pregnancy loss Increased risk for Type 2 DM, CAD, CVA, HTN and Hyperlipidemia Spectrum ranges from thin menstruating woman to obese, hirsute amenorrhic females(stein-leventhal syndrome)
103 PCOD Appearance Threshold ovarian volume > 10cm There are 12 or more follicles measuring 2-9mm in diameter Need to have only one ovary meet either of the criteria to establish the presence of polycystic ovaries Increased echogenicity of ovarian stroma
104
105
106 Ovarian Torsion Partial or complete rotation of the ovarian pedicle on its axis which compromises the lymphatic and venous drainage causing edema leading to loss of arterial perfusion and infarction May occur in normal ovaries or with an ovarian mass More common in childhood/reproductive years with increased risk during pregnancy
107 Ultrasound Findings Enlarged ovary with multiple cortical follicles Sparse or lack of flow in the ovary on Color Doppler Free fluid often present
108
109 Nonshadowing Echogenic Ovarian Foci (EOF) EOF in otherwise normal ovaries are caused by a specular reflection from walls of tiny unresolved benign cysts Can be peripheral, central or diffuse Average size = 1.8 mm Benign and require no further imaging followup
110
111 Psammomatous Calcification
112 Ovarian Neoplasms Surface epithelial-stromal 65-75% Germ cell 15-20% Sex cord-stromal 5-10% Metastatic 5-10%
113 Surface epithelial-stromal Tumors Account for 65-75% of ovarian malignancies Five categories 1. Serous cystadenoma/carcinoma 2. Mucinous cystadenoma/carcinoma 3. Endometrioid carcinoma 4. Clear cell carcinoma 5. Transitional cell carcinoma
114 Serous Cystadenomas Account for 20-25% of all benign ovarian neoplasms Peak incidence in woman age % bilateral Large thin walled unilocular cystic mass May contain septations or mural nodules
115
116
117
118 Serous Cystadenocarcinomas Account for 40-50% of all malignant ovarian neoplasms Most often seen in peri /post menopausal women 50% are bilateral Very large multilocular cystic mass with multiple papillary projections arising from the walls and septae May contain echogenic solid material
119
120
121 Mucinous cystadenomas Account for 20-25% of all benign ovarian neoplasms Peak incidence in women % are bilateral 15-30cm cystic masses with multiple thin septae and low level echoes caused by mucoid material
122
123 Mucinous cystadenocarcinomas Account for 5-10% of primary ovarian neoplasms Most often seen in woman % are bilateral Appearance is similar to mucinous cystadenoma but with septal nodularity Can see pseudomyxoma peritonei secondary to intraperitoneal spread
124
125 Germ Cell Tumors Derived from the primitive cells of the embryonic gonad Three categories of germ cell tumors 1. Teratoma Dermoid Immature 2. Dysgerminoma 3. Yolk sac tumor
126 Dermoids Account for 95% of germ cell tumors AKA a mature cystic teratoma Occur in women of child bearing age Usually unilocular, few are multilocular and 15% are bilateral Compose of ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm Up to 60% contain Ca+ Presence of fluid fat level is diagnostic
127
128 Tip of the Iceberg sign Echogenic mass of hair and secum which obscures the posterior wall of the lesion
129 Fat fluid level
130 Dermoid mesh Hair fibers in cystic portion
131
132 Sex cord-stromal Tumors Derived from the sex cords of the embryonic gonad and/or the ovarian stroma Three categories 1. Granulosa cell tumor 2. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor 3. Thecoma and fibroma
133 Thecoma and Fibroma Tumors Arise from the ovarian stroma and contain thecal and fibrous tissue On US appear as a hypoechoic mass with marked posterior attenuation of the sound beam
134
135 Metastatic Tumors Three categories 1. Genital primary- Uterus 2. Extragenital primary Stomach Colon Breast 3. Lymphoma
136 Krukenberg Tumor Metastasis from the colon
137 Extraovarian Lesions Hydrosalpinx Pyosalpinx/Tubo-ovarian Abcess Endometriosis Carcinoma Peritoneal inclusion cysts Para-ovarian cysts
138 Hydrosalpinx Distally blocked fallopian tube filled with serous or clear fluid; 2 to infection/endometriosis
139 Pyosalpinx Low level internal echoes in dilated fluid filled tube
140 Tubo-ovarian Abcess Enlarged complex cystic multiloculated mass
141 Tubo-ovarian Abcess May have irregular margins and scattered internal echoes
142 Endometrial implants Diffuse endometriosis presents as minute implants on the pelvis organs and their ligaments
143 Peritoneal Inclusion Cyst Occur primarily in premenopausal women with hx of previous surgery, PID, trauma or endometriosis
144 Peritoneal inclusion cyst Ovary is entrapped in fluid
145
146 Paraovarian Cysts Cystic dilatation in the vestiges of the Wolffian or Mullerian ducts in the broad ligament These cysts are separate from the ovary and fallopian tubes Nonfunctional in nature Can measure from 1-8 cm in size
147 Acute Appendicitis Secondary to obstruction of the appendiceal lumen. Presents as a blind ending, aperistaltic and noncompressible tubular structure arising from the cecum =/> 7mm in diameter Advanced cases may perforate and cause an abcess
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155 Interesting cases
156 HX: 28 year old female with pelvic and RLQ pain
157
158
159
160
161
162 DX: Acute appendicitis and 6 week IUP
163 HX: 16 yr old amenorhegic female
164
165
166
167
168 Dx: Amenorrhegic female successfully tx with hormones Hormone imbalance may be at the level of the pituitary/hypothalamus or be related to gonadal end organ failure
169 Hx: 48 yr old female with excessive uterine bleeding Hx of IDDM, LUE DVT tx with Xerelto Heavy menstraul bleeding which started 9 days ago Hgb=5
170
171
172
173
174 Dx: DUB secondary to med Pelvic exam revealed no cervical or vaginal mass Tx with Provera and blood transfusion
175 Hx: 29 yr old female with acute onset of LLQ pain
176
177
178
179 Dx: Torsed mucinous cystadenoma of the left ovary
180 Hx: 50 yr old female with RLQ pain
181
182
183
184 Dx:Mucinous adenoma of the appendix/ left ovarian cystadenoma
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries. Simple Cystic Masses
 Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
ProSono Copyright 2006. Ovarian Pathology
 Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Benign Ovarian Masses
 Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine
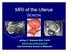 MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management
 Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
POSTMENOPAUSAL ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO
 POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
良 性 附 屬 器 腫 瘤 簡 介. Benign adnexal mass
 良 性 附 屬 器 腫 瘤 簡 介 Benign adnexal mass Prepubertal Age Group Adolescent Age Group Reproductive Age Group Postmenopausal Age Group Prepubertal Age Group Differential Diagnosis Diagnosis and Management Prepubertal
良 性 附 屬 器 腫 瘤 簡 介 Benign adnexal mass Prepubertal Age Group Adolescent Age Group Reproductive Age Group Postmenopausal Age Group Prepubertal Age Group Differential Diagnosis Diagnosis and Management Prepubertal
The menstrual cycle Hypophysis
 Normal endometrium Tumors of the uterine corpus by MB The endometrium comprises the zona functionalis zf (superficial two thirds) ) and the zona basalis zb (deep one third) The zf responds to hormonal
Normal endometrium Tumors of the uterine corpus by MB The endometrium comprises the zona functionalis zf (superficial two thirds) ) and the zona basalis zb (deep one third) The zf responds to hormonal
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
The Radiologic Evaluation of the Ovary
 September 2000 The Radiologic Evaluation of the Ovary Aradhana M. Venkatesan,, Harvard Medical School Year- IV MD 1 Menu of Tests Trans-abdominal pelvic ultrasound Trans-vaginal pelvic ultrasound Pelvic
September 2000 The Radiologic Evaluation of the Ovary Aradhana M. Venkatesan,, Harvard Medical School Year- IV MD 1 Menu of Tests Trans-abdominal pelvic ultrasound Trans-vaginal pelvic ultrasound Pelvic
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
Variations in Appearance of Endometriomas
 CME rticle Variations in ppearance of Endometriomas Elizabeth sch,, Deborah Levine, MD Objective. ecause of the range of patient ages with endometriosis, the persistence of endometriomas, and the degradation
CME rticle Variations in ppearance of Endometriomas Elizabeth sch,, Deborah Levine, MD Objective. ecause of the range of patient ages with endometriosis, the persistence of endometriomas, and the degradation
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps
 Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S.
 Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Why would you need a hysterectomy?
 Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors
 From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors Uterine Fibroid Tumors A woman s fibroisis condition usually associated with estrogen dominance. Uterine
From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors Uterine Fibroid Tumors A woman s fibroisis condition usually associated with estrogen dominance. Uterine
Ovarian Cysts Made Simple Michael East. Oxford Clinic
 Ovarian Cysts Made Simple Michael East Oxford Clinic Objectives of this talk To understand risk of malignancy and thus not fear it Practical advice for follow up of asymptomatic cysts Practical advice
Ovarian Cysts Made Simple Michael East Oxford Clinic Objectives of this talk To understand risk of malignancy and thus not fear it Practical advice for follow up of asymptomatic cysts Practical advice
Uterine Fibroids. More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth.
 Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013
 Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
What are the differences between fibroid and ovarian cyst?
 DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report
 Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report Abstract Ovarian cancer is a very common cancer among women. It is an extremely diverse disease requiring several treatment options. Occasionally ovarian cancer is diagnosed
Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report Abstract Ovarian cancer is a very common cancer among women. It is an extremely diverse disease requiring several treatment options. Occasionally ovarian cancer is diagnosed
How To Treat A Uterine Sarcoma
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts
 Image Presentation Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts Kiran A. Jain, MD Objective. To present the spectrum of sonographic findings associated with hemorrhagic ovarian cysts. Methods. Experience
Image Presentation Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts Kiran A. Jain, MD Objective. To present the spectrum of sonographic findings associated with hemorrhagic ovarian cysts. Methods. Experience
Guideline on the management of ovarian masses. Gynaecologists, radiologists, sonographers, nurses. Ovarian masses, ovarian cysts, management
 Guideline on the management of ovarian masses. A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Written by: Gynaecology Services Gynaecologists, radiologists, sonographers, nurses Management
Guideline on the management of ovarian masses. A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Written by: Gynaecology Services Gynaecologists, radiologists, sonographers, nurses Management
SUBSEROSAL FIBROIDS TREATMENT
 INTRODUCTION Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are the most common pelvic mass found in women. Fibroids are benign tumors that arise from the uterine muscular tissue (myometrium). They occur
INTRODUCTION Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are the most common pelvic mass found in women. Fibroids are benign tumors that arise from the uterine muscular tissue (myometrium). They occur
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit
 R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit Ectoservikal squamous epithelium Endoservical columnar epithelium Dilated cystic endoservical glands lymphoplasmocytes R18:Squamous cell carcinoma insitu Neoplastic epithelium
R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit Ectoservikal squamous epithelium Endoservical columnar epithelium Dilated cystic endoservical glands lymphoplasmocytes R18:Squamous cell carcinoma insitu Neoplastic epithelium
K Raja/N Varol FPA 2013. FPA Sydney August 31 2013
 FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding)
 Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
worry When to Cervical Abnormalities CME Workshop What s the situation? What are the trends? By Dianne Miller, MD, FRCSC In this article:
 CME Workshop When to worry Cervical Abnormalities By Dianne Miller, MD, FRCSC What s the situation? Over 600,000 Papanicolaou s (Pap) smears were performed in British Columbia in 2000. Approximately 13,400
CME Workshop When to worry Cervical Abnormalities By Dianne Miller, MD, FRCSC What s the situation? Over 600,000 Papanicolaou s (Pap) smears were performed in British Columbia in 2000. Approximately 13,400
Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization
 September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
HEALTH UPDATE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
 HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
The position of hysteroscopy in current fertility practice is under debate.
 The position of hysteroscopy in current fertility practice is under debate. The procedure is well tolerated. No consensus on effectiveness of HSC in improving prognosis of subfertile women. systematic
The position of hysteroscopy in current fertility practice is under debate. The procedure is well tolerated. No consensus on effectiveness of HSC in improving prognosis of subfertile women. systematic
1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound
 Indications/Goals: 1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound Geoffrey E. Hayden, MD Director of Emergency Ultrasonography Vanderbilt Emergency Medicine Primary objective is to identify an intrauterine pregnancy Secondary
Indications/Goals: 1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound Geoffrey E. Hayden, MD Director of Emergency Ultrasonography Vanderbilt Emergency Medicine Primary objective is to identify an intrauterine pregnancy Secondary
DISCLOSURE OBJECTIVES IN THE INEREST OF TIME LAPAROSCOPY AND AN APPROACH TO THE ADNEXAL MASS
 LAPAROSCOPY AND AN APPROACH TO THE ADNEXAL MASS DISCLOSURE I do not have any financial relationship with commercial interests. Michael Traynor Michael Traynor MD MPH Northwest Permanente, PC KAISER PERMANENTE
LAPAROSCOPY AND AN APPROACH TO THE ADNEXAL MASS DISCLOSURE I do not have any financial relationship with commercial interests. Michael Traynor Michael Traynor MD MPH Northwest Permanente, PC KAISER PERMANENTE
DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM
 DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM NEPHRITIS, NEPHROTIC SYNDROME ANS NEPHROSIS (580 589.9) 580 ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.0 WITH LESION OF PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.4 WITH LESION OF RAPIDLY
DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM NEPHRITIS, NEPHROTIC SYNDROME ANS NEPHROSIS (580 589.9) 580 ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.0 WITH LESION OF PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.4 WITH LESION OF RAPIDLY
BELIEVE MIDWIFERY SERVICES, LLC
 , LLC TITLE: ADENOMYOSIS EFFECTIVE DATE: May, 2012 POLICY STATEMENT Adenomyosis is a common benign gynecologic disorder that any certified nurse-midwife who provides gynecologic care is likely to see on
, LLC TITLE: ADENOMYOSIS EFFECTIVE DATE: May, 2012 POLICY STATEMENT Adenomyosis is a common benign gynecologic disorder that any certified nurse-midwife who provides gynecologic care is likely to see on
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Transvaginal Sonographic Guidance of Puncture Procedures: Minimally Invasive Surgery
 : Safety and Efficacy Frances R. Batzer, MD, MBE Clinical Professor, Obstetrics & Gynecology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Safety and Efficacy Learning Objectives Describe patient
: Safety and Efficacy Frances R. Batzer, MD, MBE Clinical Professor, Obstetrics & Gynecology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Safety and Efficacy Learning Objectives Describe patient
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels. Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College
 From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
Uterus myomatosus. 10-May-15. Clinical presentation. Incidence. Causes? 3 out of 4 women. Growth rate vary. Most common solid pelvic tumor in women
 Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Polyps. Hyperplasias. CAP 2011: Course AP104. The High Risk Benign Endometrium. Mutter and Nucci 1
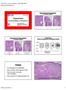 Course AP104 Endometrial Hyperplasia A morphologic Definition Hyperplasias Hormonal Effect or Precancer? George L. Mutter, MD Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA Endometrial
Course AP104 Endometrial Hyperplasia A morphologic Definition Hyperplasias Hormonal Effect or Precancer? George L. Mutter, MD Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA Endometrial
Hysterectomy. The time to take care of yourself
 Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
Renal Cysts What should I do now?
 Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
CHAPTER 10 Uterine Synechiae
 CHAPTER 10 Uterine Synechiae Uterine synechiae are intrauterine adhesions. They may involve small focal areas of the endometrium (Figures 10.1a e), or they can be so extensive that they obliterate the
CHAPTER 10 Uterine Synechiae Uterine synechiae are intrauterine adhesions. They may involve small focal areas of the endometrium (Figures 10.1a e), or they can be so extensive that they obliterate the
Ovarian Cancer. in Georgia, 1999-2003. Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health
 Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
OVARIAN CYSTS, MASSES and other pains OBJECTIVES FETAL AND NEONATAL OVARIAN CYSTS 11/26/2012. Anne Marie Priebe, DO
 OVARIAN CYSTS, MASSES and other pains Anne Marie Priebe, DO Fellow, Adolescent Gynecology Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, MO OBJECTIVES Describe the normal anatomical and physiologic development
OVARIAN CYSTS, MASSES and other pains Anne Marie Priebe, DO Fellow, Adolescent Gynecology Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, MO OBJECTIVES Describe the normal anatomical and physiologic development
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids?
 da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding
 :{ic0fp'16 ACOFP 53 rd Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding Michele Tartaglia, DO Michele Tartaglia, DO, FACOOG, CS Assistant Professor and Residency Program Director
:{ic0fp'16 ACOFP 53 rd Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding Michele Tartaglia, DO Michele Tartaglia, DO, FACOOG, CS Assistant Professor and Residency Program Director
1. AMOUNT OF FSH PRESENT
 The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
The Adnexal Mass and Early Ovarian Cancer
 The Adnexal Mass and Early Ovarian Cancer Fred Ueland, MD University of Kentucky Gynecologic Oncology Never give in. Never give in. Never, never, never, never- in nothing great or small, large or petty-
The Adnexal Mass and Early Ovarian Cancer Fred Ueland, MD University of Kentucky Gynecologic Oncology Never give in. Never give in. Never, never, never, never- in nothing great or small, large or petty-
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
 Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer starts when cells in the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer starts when cells in the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the
Ovarian cancer. A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment
 Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Endometriosis: An Overview
 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
 Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
All you need to know about Endometriosis. Nordica Fertility Centre, Lagos, Asaba, Abuja
 All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
Ovarian Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
Once a woman has had a hysterectomy, she will no longer have menstrual periods and cannot have a child. She no longer needs to use contraception.
 Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
AB N O R M A LUT E R I N E BL E E D I N G
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE AB N O R M A LUT E R I N E BL E E D I N G A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE AB N O R M A LUT E R I N E BL E E D I N G A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the
Ovarian masses - CT imaging
 Dr. Sujata Patnaik Review Article Ovarian masses - CT imaging Sujatha Patnaik 1 1 Department of Radiology, Nizam s Institute of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India *Corresponding author:
Dr. Sujata Patnaik Review Article Ovarian masses - CT imaging Sujatha Patnaik 1 1 Department of Radiology, Nizam s Institute of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India *Corresponding author:
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Objective. Indications for IUDs. IUDs 3 types. ParaGard IUD. Mirena IUD. Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Inert
 Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Anna S. Lev-Toaff, MD FACR Department of Radiology Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Leading Edge in Diagnostic
Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Anna S. Lev-Toaff, MD FACR Department of Radiology Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Leading Edge in Diagnostic
Introduction to Gynecologic Oncology
 Objectives Cervical Dysplasia and Cancer Introduction to Gynecologic Oncology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Western Ontario Discuss the incidence and risk factors for cervical dysplasia
Objectives Cervical Dysplasia and Cancer Introduction to Gynecologic Oncology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Western Ontario Discuss the incidence and risk factors for cervical dysplasia
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Surgical Staging of Endometrial Cancer
 Surgical Staging of Endometrial Cancer I. Endometrial Cancer Surgical Staging Overview Uterine cancer types: carcinomas type I and type II, sarcomas, carcinosarcomas Hysterectomy with BSO Surgical Staging
Surgical Staging of Endometrial Cancer I. Endometrial Cancer Surgical Staging Overview Uterine cancer types: carcinomas type I and type II, sarcomas, carcinosarcomas Hysterectomy with BSO Surgical Staging
Update on Abnormal Uterine Bleeding. Susan M. Sheridan, M.D., F.A.C.O.G Casper Obstetrical and Gynecological Associates Casper, WY
 Update on Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Susan M. Sheridan, M.D., F.A.C.O.G Casper Obstetrical and Gynecological Associates Casper, WY Defining Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) Normal menstrual cycle Frequency
Update on Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Susan M. Sheridan, M.D., F.A.C.O.G Casper Obstetrical and Gynecological Associates Casper, WY Defining Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) Normal menstrual cycle Frequency
Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas: A multidisciplinary approach to the prevention and early detection of invasive pancreatic cancer.
 This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass. Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic. Secondary / adaptation due to other cause.
 Disorders of Growth Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic Secondary / adaptation due to other cause. Neoplastic. Primary growth abnormality. Non-Neoplastic
Disorders of Growth Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic Secondary / adaptation due to other cause. Neoplastic. Primary growth abnormality. Non-Neoplastic
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Ovarian Cancer. What is ovarian cancer?
 Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer, and can spread to other areas of the body.
Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer, and can spread to other areas of the body.

 details >>> HERE
details >>> HERE  Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE