Horngren's Accounting,11e (Miller-Nobles) Chapter 2 Recording Business Transactions. Learning Objective Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc.
|
|
|
- Tobias Armstrong
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Horngren's Accounting,11e (Miller-Nobles) Chapter 2 Recording Business Transactions Learning Objective 2-1 1) Which is a true statement regarding the accounting equation? A) The equation can be stated as assets minus liabilities equals equity. B) The equation consists of three parts: assets, liabilities, and net income. C) The equation is an optional tool for accountants to use. D) The equation does not need to balance during a specific period. Answer: A H2 : What is an Account? (H1) 2) A payment of an expense in advance is called a prepaid expense. Answer: TRUE H2 : Assets 3) An accounts receivable requires the business to pay cash in the future. Answer: FALSE H2 : Assets 4) The account title used for recording the payment of rent in advance for an office building is. A) Prepaid Rent B) Rent Payable C) Rent Revenue D) Rent Expense Answer: A H2 : Assets 1
2 5) Which of the following is an asset account? A) Wages Payable B) Notes Payable C) Unearned Revenue D) Accounts Receivable Answer: D H2 : Assets 6) A customer's promise to pay in the future for services or goods sold is called a(n). A) Accounts Receivable B) Accounts Payable C) Unearned Revenue D) Notes Payable Answer: A H2 : Assets 7) Which of the following is an asset account? A) Salaries Expense B) Accounts Payable C) Service Revenue D) Prepaid Expense Answer: D H2 : Assets 8) Which of the following is an asset account? A) Cash B) Notes Payable C) Dividends D) Unearned Revenue Answer: A H2 : Assets 2
3 9) Provide an explanation for each of the following asset accounts. Account Name Accounts Receivable Explanation Prepaid Expense Notes Receivable Answer: Account Name Accounts Receivable Prepaid Expense Notes Receivable H2 : Assets Explanation A customer's promise to pay in the future for services or goods sold. Often described as "On Account." A payment of an expense in advance. It is considered an asset because the prepayment provides a benefit in the future. A written promise that a customer will pay a fixed amount of money and interest by a certain date in the future. Often more formal than an Accounts Receivable. 10) Liabilities are economic resources that are expected to benefit the business in the future. Answer: FALSE H2 : Liabilities 11) A payable involves a future receipt of cash. Answer: FALSE H2 : Liabilities 3
4 12) Unearned revenue is a liability account. Answer: TRUE H2 : Liabilities 13) represents a debt owed for renting a building currently. A) Prepaid Rent B) Rent Payable C) Rent Revenue D) Rent Expense H2 : Liabilities 14) Which of the following is a liability account? A) Accounts Receivable B) Cash C) Building D) Notes Payable Answer: D H2 : Liabilities 15) Which of the following is a liability account? A) Accounts Payable B) Prepaid Expense C) Salaries Expense D) Service Revenue Answer: A H2 : Liabilities 4
5 16) A liability created when a business collects cash from customers in advance of providing services or delivering goods is called a(n). A) notes receivable B) unearned revenue C) accrued liability D) service revenue H2 : Liabilities 17) Which of the following is a liability account? A) Service Revenue B) Building C) Accounts Receivable D) Unearned Revenue Answer: D H2 : Liabilities 5
6 18) Provide an explanation for each of the follow liability accounts. Account Name Explanation Accounts Payable Accrued Liability Unearned Revenue Answer: Account Name Accounts Payable Explanation A promise made by the business to pay a debt in the future. Arises from a credit purchase. An amount owed but not paid. Accrued Liability Occurs when a company receives cash from a customer but has not provided the product or service. The promise to provide services or Unearned Revenue deliver goods in the future. H2 : Liabilities 19) The owner's claim to the assets of a business is called equity or owner's equity. Answer: TRUE H2 : Equity 20) Owner's withdrawals and expenses increase equity. Answer: FALSE H2 : Equity 6
7 21) Revenues and contributions of the owner in the business increase equity. Answer: TRUE H2 : Equity 22) Nuptial Services Company paid the rent for the current month in cash. Which of the following accounts will be used to record the transaction? A) Prepaid Rent B) Rent Payable C) Rent Revenue D) Rent Expense Answer: D H2 : Equity 23) Amounts earned from delivering goods or services to customers are called. A) notes receivable B) unearned revenues C) equity D) revenues Answer: D H2 : Equity 24) The Owner's Capital account is a separate account in the category of the accounting equation. A) equity B) asset C) liability D) revenue Answer: A H2 : Equity 7
8 25) A chart of accounts is a detailed record of the changes in a particular asset, liability, or equity account during a specified period. Answer: FALSE H2 : Chart of Accounts 26) A chart of accounts is a list of all of a company's accounts with their account numbers. Answer: TRUE H2 : Chart of Accounts 27) Which of the following is provided in a typical chart of accounts? A) Account balance B) Account number C) Dates of transactions D) Transaction amounts H2 : Chart of Accounts 28) A listing of all accounts in numerical order is called a(n). A) Ledger B) Journal C) Income statement D) Chart of accounts Answer: D H2 : Chart of Accounts 29) Companies use a ledger to show all of the increases and decreases in each account along with their balances. Answer: TRUE H2 : Ledger 8
9 30) A chart of accounts provides more detail than a ledger. Answer: FALSE H2 : Ledger 31) Which of the following is the record holding all the accounts, the changes in those accounts, and their balances? A) Source document B) Journal C) Ledger D) Trial balance Answer: C H2 : Ledger Learning Objective 2-2 1) The system of accounting in which every transaction affects at least two accounts is called the doubleentry system. Answer: TRUE H2 : What is Double-Entry Accounting? (H1) 2) Debit refers to the right side of the T-account, and credit refers to the left side. Answer: FALSE H2 : The T-Account 3) A T-account is a summary device with credits posted on the left side of the vertical line. Answer: FALSE H2 : The T-Account 9
10 4) A shortened form of the ledger is called a. A) trial balance B) balance sheet C) chart of accounts D) T-account Answer: D H2 : The T-Account 5) An asset account is increased by a debit. Answer: TRUE H2 : Increases and Decreases in the Accounts 6) A liability account is increased by a debit. Answer: FALSE H2 : Increases and Decreases in the Accounts 7) A debit always means a decrease, and a credit always means an increase. Answer: FALSE H2 : Increases and Decreases in the Accounts 8) Which of the following accounts decreases with a debit? A) Accounts Receivable B) Notes Payable C) Cash D) Rent Expense H2 : Increases and Decreases in the Accounts 10
11 9) "All debits are increases and all credits are decreases." Is this a correct statement? Explain your answer. Answer: This is not a correct statement. The double entry-system of accounting is a system of accounting in which every transaction affects at least two accounts. As transactions are analyzed and recorded, the rules of debits and credits keep the accounting equation in balance. Assets, expenses and dividends are increased with a debit and decreased with a credit. Liabilities, revenues, and common stock are increased with a credit and decreased with a debit. H2 : Increases and Decreases in the Accounts 10) The Owner's Capital account is increased by a debit. Answer: FALSE H2 : Expanding the Rules of Debit and Credit 11) The Owner's Withdrawals account is increased by a debit. Answer: TRUE H2 : Expanding the Rules of Debit and Credit 12) All asset accounts and equity accounts increase with a debit. Answer: FALSE H2 : Expanding the Rules of Debit and Credit 13) The balances in the liability and revenue accounts are increased with a credit. Answer: TRUE H2 : Expanding the Rules of Debit and Credit 11
12 14) Which of the following accounts increases with a credit? A) Cash B) Owner, Capital C) Accounts Receivable D) Prepaid Expense H2 : Expanding the Rules of Debit and Credit 15) Which of the following accounts decreases with a credit? A) Cash B) Owner, Capital C) Accounts Payable D) Notes Payable Answer: A H2 : Expanding the Rules of Debit and Credit 16) Which of the following accounts increases with a debit? A) Cash B) Interest Payable C) Accounts Payable D) Owner, Capital Answer: A H2 : Expanding the Rules of Debit and Credit 17) Which one of the following account groups will decrease with a debit? A) assets and expenses B) revenues and expenses C) liabilities and revenues D) assets and liabilities Answer: C H2 : Expanding the Rules of Debit and Credit 12
13 18) Which of the following statements is true of expenses? A) Expenses increase equity, so an expense account's normal balance is a credit balance. B) Expenses decrease equity, so an expense account's normal balance is a credit balance. C) Expenses increase equity, so an expense account's normal balance is a debit balance. D) Expenses decrease equity, so an expense account's normal balance is a debit balance. Answer: D H2 : Expanding the Rules of Debit and Credit 19) An account that normally has a debit balance may occasionally have a credit balance. Answer: TRUE H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 20) The normal balance of an account is the increase side of the account. Answer: TRUE H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 21) Which one of the following account groups normally has a credit balance? A) assets and liabilities B) equity and assets C) liabilities and revenues D) assets and expenses Answer: C H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 22) Which one of the following account groups normally has a debit balance? A) assets and expenses B) revenues and expenses C) liabilities and revenues D) assets and liabilities Answer: A H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 13
14 23) Accounts Receivable is a(n) account and has a normal balance. A) liability; debit B) asset; debit C) liability; credit D) asset; credit AACSB: Analytical thinking H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 24) Accounts Payable is a(n) account and has a normal balance. A) liability; debit B) asset; debit C) liability; credit D) asset; credit Answer: C H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 25) Cash is a(n) account and has a normal balance. A) asset; debit B) liability; credit C) liability; debit D) asset; credit Answer: A H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 26) Which of the following statements is true of the Owner's Capital account? A) It is an equity account that has a normal credit balance. B) It is a liability account that has a normal credit balance. C) It is a liability account that has a normal debit balance. D) It is an equity account that has a normal debit balance. Answer: A H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 14
15 27) For Office Supplies, the category of account and its normal balance is. A) liabilities and a debit balance B) assets and a debit balance C) liabilities and a credit balance D) assets and a credit balance H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 28) The Salaries Payable account is a(n). A) liability account with a normal debit balance B) asset account with a normal debit balance C) liability account with a normal credit balance D) asset account with a normal credit balance Answer: C H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 29) For Expenses, the category of account and its normal balance is. A) equity and a credit balance B) assets and a debit balance C) assets and a credit balance D) equity and a debit balance Answer: D H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 30) For Revenues, the category of account and its normal balance is. A) equity and a credit balance B) assets and a debit balance C) assets and a credit balance D) equity and a debit balance Answer: A H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 15
16 31) For Owner's Capital, the category of account and its normal balance is. A) equity and a credit balance B) assets and a debit balance C) equity and a debit balance D) assets and a credit balance Answer: A H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 32) Owner's Withdrawals is a(n) account that has a normal balance. A) liability; credit B) equity; debit C) liability; debit D) equity; credit H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 33) Which of the following statements is true of revenues? A) Revenues decrease equity, so a revenue account's normal balance is a credit balance. B) Revenues decrease equity, so a revenue account's normal balance is a debit balance. C) Revenues increase equity, so a revenue account's normal balance is a debit balance. D) Revenues increase equity, so a revenue account's normal balance is a credit balance. Answer: D H2 : The Normal Balance of an Account 34) The T-account is a summary device that is shaped like a capital T with debits posted on the right side of the vertical line and credits posted on the left side of the vertical line. Answer: FALSE H2 : Determining the Balance of a T-Account 16
17 35) The T-account is a summary device that is shaped like a capital T with debits posted on the left side of the vertical line and credits posted on the right side of the vertical line. Answer: TRUE H2 : Determining the Balance of a T-Account 36) In reviewing the T-account for Accounts Receivable, you find that the beginning balance is zero, the total increases are $4,900 and the total decreases are $2,400. This means that the ending balance of the account is a credit balance of $2,500. Answer: FALSE H2 : Determining the Balance of a T-Account 37) In reviewing the T-account for Accounts Payable, you find that the beginning balance is zero, the total increases are $7,400 and the total decreases are $4,900. This means that the ending balance of the account is a credit balance of $2,500. Answer: TRUE H2 : Determining the Balance of a T-Account 38) The Accounts Receivable account of Rosewood Company has the following postings: Calculate the ending balance of the account. A) $33,000 debit B) $27,000 debit C) $6,000 credit D) $21,000 debit Answer: D H2 : Determining the Balance of a T-Account 17
18 39) The Accounts Payable account of Golden Company has the following postings: Calculate the ending balance of the account. A) $12,000 credit B) $16,000 debit C) $16,000 credit D) $6,000 debit Answer: C H2 : Determining the Balance of a T-Account Learning Objective 2-3 1) Source documents provide the evidence and data for accounting transactions. Answer: TRUE H2 : Source Documents - The Origin of the Transactions 2) Which of the following is a source document that provides the evidence and data for accounting transactions? A) Journal B) Sales invoice C) Ledger D) Trial balance H2 : Source Documents - The Origin of the Transactions 3) Debits in the journal are always posted as debits in the ledger. Answer: TRUE 18
19 4) The process of transferring data from the ledger to the journal is called posting. Answer: FALSE 5) A compound journal entry has more than two accounts, but the total dollar value of the debits still must equal total dollar value of the credits. Answer: TRUE 6) When a business makes a cash payment, the Cash account is debited. Answer: FALSE 7) When a business collects cash, the Cash account is debited. Answer: TRUE 8) When a business records an accrued utility liability, the Utilities Expense account is credited. Answer: FALSE 9) When a business records the earning of service revenue, the Service Revenue account is credited. Answer: TRUE 19
20 10) Transactions are first record in a. A) chart of accounts B) trial balance C) journal D) ledger Answer: C 11) Journalizing a transaction involves. A) calculating the balance in an account using journal entries B) posting the account balances in the chart of accounts C) preparing a summary of account balances D) recording the data only in the journal Answer: D 12) Posting a transaction means. A) calculating the balance in an account B) transferring data from the journal to the ledger C) preparing a summary of account balances D) finding the account number in the chart of accounts 13) After initially recording a transaction, the data is then transferred to the. A) chart of accounts B) ledger C) trial balance D) journal 20
21 14) The accounting process of transferring a transaction from the journal to the ledger is called. A) journalizing B) posting C) compounding D) sourcing 15) The first step in the journalizing and posting process is to. A) post the journal entry to the ledger B) identify the accounts involved and the account type C) decide whether each account increases or decreases D) record the transaction in the journal 16) Which of the following is the order of steps to journalize an entry? A) Identify the accounts and the account type Decide whether each account increases or decreases, then apply the rules of debits and credits Record the transaction B) Identify the accounts and the account type Record the transaction Decide whether each account increases or decreases, then apply the rules of debits and credits C) Record the transaction Identify the accounts and the account type Decide whether each account increases or decreases, then apply the rules of debits and credits D) Decide whether each account increases or decreases, then apply the rules of debits and credits Identify the accounts and the account type Record the transaction Answer: A 17) Which of the following is the final step in the journalizing and posting process? A) Posting the accounts to the ledger. B) Identifying each account affected and its type. C) Determining whether the accounting equation is in balance. D) Determining whether each account has increased or decreased. Answer: C 21
22 18) Which of the following sequences is the normal sequence of flow of accounting data? A) Ledger Journal Source document B) Journal Source document Ledger C) Source document Journal Ledger D) Source document Ledger Journal Answer: C 19) A business renders services to a client and issues a sales invoice. The amount will be collected from the customer at a later time. Which of the following is true at the time the invoice is issued? A) Equity will decrease. B) Total liabilities will increase. C) Total assets will decrease. D) Net income will increase. Answer: D 20) Stewart Candle Company received a cash contribution of $40,000 from the owner of the business. Which of the following accounts will be debited? A) Accounts Receivable B) Cash C) Stewart, Capital D) Accounts Payable 22
23 21) Whitney Chemicals Company received cash contribution of $40,000 from the owner of the business. Which of the following accounts will be credited? A) Accounts Receivable B) Cash C) Owner, Capital D) Accounts Payable Answer: C 22) A business purchases equipment for $8,000 cash. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Owner, Capital D) Equipment Answer: D 23) A business purchases equipment for $8,000 cash. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Owner, Capital D) Equipment Answer: A 23
24 24) A business makes a cash payment of $12,000 to a supplier for supplies purchased two weeks earlier. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Supplies D) Accounts Receivable 25) A business makes a cash payment of $12,000 to a creditor. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Bank D) Accounts Receivable Answer: A 26) A business renders services to a customer for $26,000 on account. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Receivable C) Service Revenue D) Accounts Payable 24
25 27) A business renders services to a customer for $26,000 on account. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Cash B) Accounts Receivable C) Service Revenue D) Accounts Payable Answer: C 28) A business renders services for $26,000 and collects cash from the customer. Which of the following accounts will be debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Receivable C) Service Revenue D) Accounts Payable Answer: A 29) A business prepays four months' office rent. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Rent Expense B) Cash C) Prepaid Rent D) Unearned Rent Answer: C 25
26 30) A business receives $40,000 for services that it will perform over the next four months. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Service Revenue D) Unearned Revenue Answer: D 31) Beetles Company recorded the following journal entry on March 2, Cash 10,500 Unearned Revenue 10,500 From the journal entry above, identify the transaction on March 2, A) Beetles purchased goods worth $10,500 and signed a one-year note for the same. B) Beetles sold goods for $10,500 cash. C) Beetles received $10,500 for services to be performed in a later period. D) Beetles paid $10,500 for services to be received at a later date. Answer: C 32) A business pays $500 cash for office supplies. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Office Supplies D) Utilities Expense Answer: C 26
27 33) A business pays $500 cash for office supplies. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Office Supplies D) Utilities Expense Answer: A 34) A business purchases $500 of office supplies on account. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Office Supplies D) Utilities Expense Answer: C 35) A business purchases $500 of office supplies on account. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Office Supplies D) Service Revenue 27
28 36) A business makes a cash payment to a supplier for office supplies that were purchased earlier on account. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Office Supplies D) Utilities Expense 37) A business makes a cash payment to a supplier on account for office supplies that were purchased earlier. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Office Supplies D) Utilities Expense Answer: A 38) A business collects cash from a customer for services that were performed one month earlier. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Receivable C) Service Revenue D) Accounts Payable Answer: A 28
29 39) A business collects cash from a customer for services that were preformed one month earlier. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Cash B) Accounts Receivable C) Service Revenue D) Accounts Payable 40) A business borrows cash by signing a note payable. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Notes Payable B) Accounts Payable C) Notes Receivable D) Cash Answer: D 41) A business borrows cash by signing a note payable. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Notes Payable B) Accounts Payable C) Notes Receivable D) Cash Answer: A 29
30 42) A business repays the amount borrowed on a note with cash. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Notes Payable D) Notes Receivable Answer: C 43) A business repays the amount borrowed on a note with cash. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Accounts Payable B) Cash C) Notes Payable D) Notes Receivable 44) A business makes a payment in cash for advertising expense. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Accounts Payable C) Accounts Receivable D) Advertising Expense Answer: D 30
31 45) A business makes a payment in cash for advertising expense. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Notes Payable B) Accounts Receivable C) Cash D) Advertising Expense Answer: C 46) The owner withdrew cash from the business. Which of the following accounts is debited? A) Cash B) Owner, Withdrawals C) Accounts Payable D) Common Stock 47) The owner withdrew cash from the business. Which of the following accounts is credited? A) Common Stock B) Dividends C) Cash D) Accounts Payable Answer: C 31
32 48) An accounting entry that is characterized by having multiple debits and/or multiple credits is called a entry. A) balanced B) posted C) chart of accounts D) compound journal Answer: D 49) A business makes a payment of $1,400 on a note payable. Which of the following journal entries would be recorded? A) Cash is credited and Notes Payable is debited for $1,400. B) Notes Payable is credited and Cash is debited for $1,400. C) Cash is credited and Financing Expense is debited for $1,400. D) Cash is debited and Financing Revenue is credited for $1,400. Answer: A 50) A business purchases equipment by paying $6,081 in cash and issuing a note payable of $12,291. Which of the following occurs? A) Cash is credited for $6,081, Equipment is credited for $18,372, and Notes Payable is debited for $12,291. B) Cash is credited for $6,081, Equipment is debited for $18,372, and Notes Payable is credited for $12,291. C) Cash is debited for $6,081, Equipment is debited for $12,291,and Notes Payable is credited for $18,372. D) Cash is debited for $6,081, Equipment is credited for $12,291, and Notes Payable is debited for $6,
33 51) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if a business purchased $800 of office supplies on account? A) Accounts Payable 800 Office Supplies 800 B) Office Supplies 800 Accounts Payable 800 C) Office Supplies 800 Cash 800 D) Cash 800 Office Supplies
34 52) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if a business renders service and receives cash of $900 from the customer? A) Service Revenue 900 Cash 900 B) Service Revenue 900 Accounts Payable 900 C) Cash 900 Service Revenue 900 D) Service Revenue 900 Accounts Receivable 900 Answer: C 34
35 53) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if a business purchased office supplies on account in a previous accounting period and now makes a cash payment of $750 to the supplier to settle the account? A) Cash 750 Accounts Payable 750 B) Accounts Payable 750 Cash 750 C) Cash 750 Office Supplies 750 D) Accounts Payable 750 Office Supplies
36 54) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if Christy Jones Company received a $3,000 cash contribution from the owner? A) Cash 3,000 C. Jones, Capital 3,000 B) Accounts Payable 3,000 Cash 3,000 C) C. Jones, Capital 3,000 Cash 3,000 D) C. Jones, Capital 3,000 Accounts Payable 3,000 Answer: A 55) A business purchased land for $250,000 cash. Record the transaction in the journal. Answer: Land 250,000 Cash 250,000 Purchased land for cash. 36
37 56) A business renders services to its customer for $50,000 on account. Record the transaction in the journal. Answer: Accounts Receivable 50,000 Service Revenue 50,000 Performed services on account. 57) A business paid salaries of $6,000 in cash. Record the transaction in the journal. Answer: Salaries Expense 6,000 Cash 6,000 Paid salaries. 37
38 58) For each transaction, identify which account is debited and which account is credited. Use proper account titles. Transaction Debit Credit Received cash on account from a customer Paid cash to the owner as a withdrawal Purchased office supplies on account Received cash from customers for services to be performed next month Paid employee's salary Answer: Transaction Debit Credit Received cash on account from a customer Cash Accounts Receivable Paid cash to the owner as a withdrawal Owner, Withdrawals Cash Purchased office supplies on account Office Supplies Accounts Payable Received cash from customers for services to be performed next month Cash Unearned Revenue Paid employee's salary Salaries Expense Cash 38
39 59) For each transaction, identify which account is debited and which account is credited. Use proper account titles. Transaction Debit Credit Received a bill for utilities to be paid next month Performed services on account Paid cash for a 12-month insurance policy, coverage starting next month Paid rent for the current month Borrowed cash from the bank for business use; a note was signed Answer: Transaction Debit Credit Received a bill for utilities to be paid next month Utilities Expense Utilities Payable Performed services on account Account Receivable Service Revenue Paid cash for a 12-month insurance policy, coverage starting next month Prepaid Insurance Cash Paid rent for the current month Rent Expense Cash Borrowed cash from the bank for business use; a note was signed Cash Notes Payable 60) After posting the journal entries from the journal to the ledger, the accounting equation should be in balance. Answer: TRUE H2 : The Ledger Accounts After Posting 39
40 61) A business purchases $3,500 of office supplies for cash. Which of the following sets of ledger accounts reflects the posting of this transaction? A) B) C) D) Answer: D H2 : The Ledger Accounts After Posting 62) The following transactions for the month of March have been journalized and posted to the proper accounts. Mar. 1 The business received a $9,000 cash contribution from the owner. Mar. 2 Paid the first month's rent of $900. Mar. 3 Purchased equipment by paying $4,000 cash and executing a note payable for $5,000. Mar. 4 Purchased office supplies for $710 cash. Mar. 5 Billed a client for $9,000 of design services completed. Mar. 6 Received $7,600 on account for the services previously recorded. What is the balance in Cash? A) $11,890 B) $10,990 C) $14,990 D) $12,600 Explanation: B) Cash is increased by the March 1 transaction of $9,000 and the March 6 amount of $7,600 and decreased by the March 2 payment of $900, March 3 payment of $4,000, and March 4 payment of $710 for a final cash balance of $10,990. Diff: 3 H2 : The Ledger Accounts After Posting 40
41 63) Sharon Foods Company reported the following transactions for September a) The business received a $21,000 cash contribution from the owner. It was credited to Sharon, Capital. b) The business purchased office equipment for $9,000 for which $4,000 cash was paid and the balance was put on a note payable. c) Paid insurance expense of $1,500 cash. d) Paid the September utility bill for $800 cash. e) Paid $1,600 cash for September rent. f) The business had sales of $12,000 in September. Of these sales, 40% were cash sales, and the balance was credit sales. g) The business paid $8,000 cash for office furniture. What are the total liabilities at the end of September, 2017? A) $12,000 B) $1,500 C) $5,000 D) $9,000 Answer: C Explanation: C) H2 : The Ledger Accounts After Posting 41
42 64) The following transactions for the month of March have been journalized and posted to the proper accounts. Mar. 1 The business received a $9,000 cash contribution from the owner. Mar. 2 Paid the first month's rent of $600. Mar. 3 Purchased equipment by paying $4,000 cash and executing a note payable for $5,000. Mar. 4 Purchased office supplies for $600 cash. Mar. 5 Billed a client for $10,000 of design services completed. Mar. 6 Received $8,000 on account for the services previously recorded. What is the balance in Accounts Receivable? A) $8,000 B) $2,000 C) $5,000 D) $10,000 Explanation: B) Accounts Receivable is increased (debited) by the March 5 amount of $10,000 and decreased (credited) by the March 6 amount of $8,000. Diff: 3 H2 : The Ledger Accounts After Posting 42
43 65) The following transactions for March have been journalized and posted to the proper accounts. Mar. 1 The business received a $10,000 cash contribution from the owner. Mar. 2 Paid the first month's rent of $800. Mar. 3 Purchased equipment by paying $4,000 cash and executing a note payable for $6,000. Mar. 4 Purchased office supplies for $500 cash. Mar. 5 Billed a client for $14,000 of design services completed. Mar. 6 Received $6,000 on account for the services previously recorded. What is the ending balance in the Service Revenue account? A) $16,000 B) $10,000 C) $14,000 D) $6,000 Answer: C Explanation: C) Service Revenue 14,000 Mar. 5 14,000 Bal. Diff: 3 H2 : The Ledger Accounts After Posting 43
44 66) A business has the following transactions: * The business receives $15,000 cash and issues common stock to stockholders. * The business purchases $600 of office supplies on account. * The business purchases $3,000 of furniture on account. * The business renders services to various clients totaling $15,000 on account. * The business pays $1,500 for salaries expense and $4,500 for rent expense. * The business pays $800 to a supplier for the office supplies purchased earlier. * The business collects $4,000 from one of its clients for services rendered earlier in the month. At the end of the month, all journal entries are posted to the ledger. Accounts Receivable will appear as which of the following? A) Accounts Receivable 4,000 15,000 11,000 Bal. B) Accounts Receivable 15,000 Bal. 15,000 C) Accounts Receivable 15,000 4,000 Bal. 11,000 D) Accounts Receivable 15,000 4,000 11,000 Bal. Answer: C H2 : The Ledger Accounts After Posting 44
45 67) A business has the following transactions: * The business received $16,000 cash and issued common stock to stockholders. * The business purchases $600 of office supplies on account. * The business purchases $3,000 of furniture on account. * The business renders services to various clients totaling $10,000 on account. * The business pays out $1,500 for salaries expense and $3,500 for rent expense. * The business pays $800 to supplier for the office supplies purchased earlier. * The business collects $4,000 from one of its clients for services rendered earlier in the month. At the end of the month, all journal entries are posted to the ledger. Accounts Payable will appear as which of the following? A) Accounts Payable ,000 2,800 Bal. B) Accounts Payable 600 3,000 10,000 Bal. C) Accounts Payable 600 3, Bal. 2,800 D) Accounts Payable 600 3, ,400 Bal. H2 : The Ledger Accounts After Posting 45
46 68) When using a four-column account, the posting reference column allows the user of the financial data to trace the amounts in the journal back to the ledger. Answer: FALSE H2 : The Four-Column Account: An Alternative to the T-Account 69) In a computerized environment, the posting process is completed automatically when the user enters the journal entry. Answer: TRUE H2 : The Four-Column Account: An Alternative to the T-Account 70) A posting reference column is used. A) while preparing the trial balance using the ledger B) when the information is transferred from the journal to the ledger C) when the information is transferred from the ledger to the post-closing trial balance D) while preparing the balance sheet using the trial balance H2 : The Four-Column Account: An Alternative to the T-Account Learning Objective 2-4 1) The trial balance is also known as the balance sheet. Answer: FALSE LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 2) The trial balance verifies the equality of debits and credits at a point in time. Answer: TRUE LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 46
47 3) A trial balance is the list of only a company's debit accounts along with their account numbers at a point in time. Answer: FALSE LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 4) A trial balance is a list of all of the accounts of a company with their balances at a point in time. Answer: TRUE LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 5) In a trial balance, total debits must always equal total credits. Answer: TRUE LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 6) The trial balance is an internal document used only by employees of the company. Answer: TRUE LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 7) A trial balance summarizes the ledger by listing all the accounts with their balances at a point in time. Answer: TRUE LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 8) The trial balance reports the balances of assets, liabilities, and equity. Answer: TRUE LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 47
48 9) Which of the following is used by both internal and external users? A) Chart of Accounts B) Trial Balance C) Balance Sheet D) Costing Reports Answer: C LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 10) Which of the following statements is true of a trial balance? A) A trial balance has the same format as a balance sheet. B) A trial balance presents data in debit and credit format. C) A trial balance shows the total amounts of assets and liabilities, but not equity. D) A trial balance is prepared after the balance sheet. LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 11) Which of the following sequences states the order in which accounts are listed on a trial balance? A) Equity Assets Liabilities B) Liabilities Assets Equity C) Assets Equity Liabilities D) Assets Liabilities Equity Answer: D LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 12) Which of the following statements is true of a trial balance? A) A trial balance is the first step in the accounting cycle. B) A trial balance is also known as a balance sheet. C) A trial balance is a list of all accounts with their balances. D) A trial balance is also known as the chart of accounts. Answer: C LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 48
49 13) The following are the current month's balances for Toys Galore before preparing the trial balance. Accounts Payable $5,000 Revenue 3,000 Cash 5,000 Expenses 18,500 Furniture 11,000 Accounts Receivable 11,000 R. Schwartz, Capital? Notes Payable 6,500 What amount should be shown for R. Schwartz, Capital on the trial balance? A) $56,000 B) $31,000 C) $11,500 D) $27,000 Explanation: B) In a trial balance, the total of debits must match the total of credits. Therefore, the balance of the Capital account can be determined by totaling the debit and the credit balances and calculating the balancing amount. Debit Credit Cash $5,000 Accounts Receivable 11,000 Furniture 11,000 Accounts Payable $5,000 Notes Payable 6,500 R. Schwartz, Capital? Revenues 3,000 Expenses 18,500 Total $45,500 $14,500 Owner, Capital = $45,500 - $14,500 = $31,000 LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 49
50 14) The following are the current month's balances for Jackson Company. Accounts Payable $8,000 Revenue 12,000 Cash 4,000 Expenses 1,600 Furniture 12,000 Accounts Receivable 14,000 B. Jackson, Capital 9,250 Notes Payable 4,500 Calculate the total amount of credits for the trial balance. A) $24,500 B) $21,750 C) $25,750 D) $33,750 Answer: D Explanation: D) Accounts Payable $8,000 Revenue 12,000 B. Jackson, Capital 9,250 Notes Payable 4,500 Total credit amounts $33,750 LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 50
51 15) The following are the current month's balances for Global Enterprises. Accounts Payable $10,000 Revenue 8,000 Cash 6,000 Expenses 1,600 Furniture 11,000 Accounts Receivable 15,000 Owner, Capital 7,250 Notes Payable 6,500 What is the total amount of debits for the trial balance? A) $26,000 B) $27,600 C) $32,000 D) $33,600 Answer: D Explanation: D) Cash $6,000 Expenses 1,600 Furniture 11,000 Accounts Receivable 15,000 Total debits $33,600 LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 51
52 16) The following transactions have been journalized and posted to the proper accounts. Prepare a trial balance at the end of the first month using the following details: a) Received a $15,000 cash contribution from the owner. b) Paid the first month's rent with $800 cash. c) Purchased equipment by paying $4,000 cash and executing a note payable for $4,000. d) Purchased office supplies for $200 cash. The supplies remain at the end of the month. e) Billed clients for a total of $7,000 for design services rendered. f) Received $1,000 cash from clients for services rendered above. Answer: Account Title Debit Credit Cash $11,000 Accounts Receivable 6,000 Office Supplies 200 Equipment 8,000 Notes Payable $4,000 Owner, Capital 15,000 Service Revenue 7,000 Rent Expense 800 Total $26,000 $26,000 Explanation: Note: Cash balance is calculated as: Owner's contribution $15,000 Rent paid (800) Cash paid for equipment (4,000) Office supplies purchased (200) Cash received from clients 1,000 Cash balance $11,000 Diff: 3 LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 52
53 17) Melody Instruments Company sells musical instruments. On December 31, 2017, after its first month of business, Melody Instruments had the following balances in its accounts, listed alphabetically. Accounts Receivable $5,000 Accounts Payable 15,000 Advertising Expense 2,000 Building 16,500 Cash? L. Melody, Capital 50,000 L. Melody, Withdrawals 1,200 Equipment 2,000 Land 70,000 Notes Payable 60,000 Office Supplies 3,400 Salaries Expense 4,000 Service Revenue 72,000 Utilities Expense 4,100 Determine the balance in the cash account and prepare the trial balance. 53
54 Answer: In the given problem, the cash balance is the difference between the debit and credit columns of the Trial Balance. Melody Instruments Company Trial Balance December 31, 2017 Account Title Debit Credit Cash $88,800 Accounts Receivable 5,000 Office Supplies 3,400 Equipment 2,000 Building 16,500 Land 70,000 Accounts Payable $15,000 Notes Payable 60,000 L. Melody, Capital 50,000 L. Melody, Withdrawals 1,200 Service Revenue 72,000 Utilities Expense 4,100 Salaries Expense 4,000 Advertising Expense 2,000 Total $197,000 $197,000 Cash balance = $197,000 - $108,200 = $88,800 Diff: 3 LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 54
55 18) At the end of a month, a business shows the following balances in its ledger. Use this data to prepare a trial balance. Answer: Trial Balance Last Day of the Month Account Title Debit Credit Cash $5,000 Accounts Receivable 1,200 Office Supplies 200 Land 20,000 Accounts Payable $1,300 Owner, Capital 1,000 Service Revenue 35,500 Rent Expense 4,500 Salaries Expense 6,000 Utility Expense 900 Total $37,800 $37,800 LO: 2-4 H2 : What is the Trial Balance (H1) 55
56 19) Data from a trial balance is used to prepare the income statement, statement of owner's equity, and the balance sheet. Answer: TRUE LO: 2-4 H2 : Preparing Financial Statements from the Trial Balance 20) The trial balance is one of the three basic financial statements that are issued to external users of the business. Answer: FALSE LO: 2-4 H2 : Preparing Financial Statements from the Trial Balance 21) Which of the following is a financial statement that presents a business's accounting equation? A) Chart of Accounts B) Trial Balance C) Income Statement D) Balance Sheet Answer: D LO: 2-4 H2 : Preparing Financial Statements from the Trial Balance 22) When is a trial balance usually prepared? A) after each entry is journalized B) before the financial statements are prepared C) after the financial statements are prepared D) at the beginning of an accounting period LO: 2-4 H2 : Preparing Financial Statements from the Trial Balance 56
57 23) The following are the current month's balances for Adams Marketing Company. Accounts Payable $8,000 Revenue 11,000 Cash 7,000 Expenses 1,500 Furniture 10,000 Accounts Receivable 16,000 Adams, Capital 8,250 Notes Payable 5,500 What is the net income for Adams Marketing for the current month? A) $11,000 B) $9,500 C) $12,500 D) $18,000 Explanation: B) Revenue $11,000 Expenses (1,500) Net Income $9,500 LO: 2-4 H2 : Preparing Financial Statements from the Trial Balance 24) Balancing errors can be detected by computing the difference between total debits and total credits on the trial balance. Answer: TRUE LO: 2-4 H2 : Correcting Trial Balance Errors 25) If the total debits equal the total credits on the trial balance, the individual account balances will be error free. Answer: FALSE LO: 2-4 H2 : Correcting Trial Balance Errors 57
58 26) A journal entry for a $70 payment for rent expense was posted as a debit to Salaries Expense and a credit to Cash. Which of the following statements correctly states the effect of the error on the trial balance? A) The sum of the credits will equal the sum of the debits. B) The sum of the debits will exceed the sum of the credits by $70. C) The sum of the debits will exceed the sum of the credits by $140. D) The sum of the credits will exceed the sum of the debits by $140. Answer: A LO: 2-4 H2 : Correcting Trial Balance Errors 27) A journal entry for a $270 payment to purchase office supplies was erroneously recorded as a debit to Office Supplies for $520 and a credit to Cash for $270. Which of the following statements correctly states the effect of the error on the trial balance? A) The sum of the credits will exceed the sum of the debits by $250. B) The sum of the debits will exceed the sum of the credits by $270. C) The sum of the debits will exceed the sum of the credits by $250. D) The sum of the debits will exceed the sum of the credits by $520. Answer: C LO: 2-4 H2 : Correcting Trial Balance Errors Learning Objective 2-5 1) The debt ratio shows the proportion of assets financed with debt. Answer: TRUE LO: 2-5 H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 2) Grace Paper Company has a debt ratio of 25%, which means that 75% of the assets are financed by creditors. Answer: FALSE LO: 2-5 H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 58
59 3) The higher the debt ratio, the lower the risk. Answer: FALSE LO: 2-5 H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 4) Which of the following is the correct formula to calculate the debt ratio? A) Debt ratio = Total liabilities Total assets B) Debt ratio = Total liabilities + Total assets C) Debt ratio = Total liabilities - Total assets D) Debt ratio = Total liabilities / Total assets Answer: D LO: 2-5 H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 5) The percentage of assets that are financed with liabilities can be calculated using the. A) accounting equation B) debt ratio C) journal D) ledger LO: 2-5 AACSB: Interpersonal relations and teamwork H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 6) The ability of a company to repay its liabilities can be determined from its. A) bankers B) creditors C) debt ratio D) journal Answer: C LO: 2-5 H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 59
60 7) Mitchell Florists reported assets of $1,400 and equity of $350. What is its debt ratio? (Round your percentage answer to two decimal places.) A) 75.00% B) 25.00% C) % D) 80.00% Answer: A Explanation: A) Total liabilities = $1,400 $350 = $1,050 Debt ratio = Total liabilities / Total assets Debt ratio = $1,050 / $1,400 = 0.75 or 75.00% LO: 2-5 H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 8) Camile Plastics Company had the following total assets, liabilities, and equity as of December 31. Assets $430,000 Liabilities 133,000 Equity 297,000 What is the company's debt ratio as of December 31? (Round your percentage answer to two decimal places.) A) 30.93% B) 69.07% C) % D) 44.78% Answer: A Explanation: A) Debt ratio = Total liabilities / Total assets Debt ratio = $133,000 / $430,000 = or 30.93% LO: 2-5 H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 9) Which of the following factors is assessed using the debt ratio? A) expenses B) revenues C) risk D) income Answer: C LO: 2-5 H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 60
61 10) Calculate the debt ratio using the following trial balance of Harmony Instruments Company as of December 31, Harmony Instruments, Inc. Trial Balance December 31, 2017 Account Title Debit Credit Cash $88,800 Accounts Receivable 5,000 Office Supplies 3,400 Equipment 2,000 Building 16,500 Land 70,000 Accounts Payable $15,000 Notes Payable 60,000 H. Harmony, Capital 50,000 H. Harmony, Withdrawals 1,200 Service Revenue 72,000 Utilities Expense 4,100 Salaries Expense 4,000 Advertising Expense 2,000 Total $197,000 $197,000 Answer: Accounts Payable $15,000 Notes Payable 60,000 Total Liabilities $75,000 Accounts Receivable $5,000 Building 16,500 Cash 88,800 Equipment 2,000 Land 70,000 Office Supplies 3,400 Total assets $185,700 Debt ratio = Total liabilities / Total assets Debt ratio = $75,000 / $185,700 = 0.40 or 40% Diff: 3 LO: 2-5 H2 : How Do You Use the Debt Ratio to Evaluate Business Performance? (H1) 61
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
Accounting Notes. Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value
 Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
Chapter 2. Analyzing transactions
 1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
Basic Accounting Principles
 Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca)
 Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca) Further valuable accounting and bookkeeping website resources are listed at the end of this document. A business is one
Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca) Further valuable accounting and bookkeeping website resources are listed at the end of this document. A business is one
Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT. 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr APPLE COMPUTER, INC.
 2 Chapter 40878 9/25/07 3:18 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr SPOTLIGHT APPLE COMPUTER, INC. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes,
2 Chapter 40878 9/25/07 3:18 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr SPOTLIGHT APPLE COMPUTER, INC. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes,
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS. Lecture Outline
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
Which of the following accounts impact equity? (Check all that apply.) Owner, Withdrawal. Expenses. Liabilities. Owner, Capital. Revenue.
 Which of the following accounts impact equity? (Check all that apply.) a Owner, Withdrawal & Expenses a Liabilities Owner, Capital & Revenue Assets ) ) ) ) The correct answer is shown. The T- account for
Which of the following accounts impact equity? (Check all that apply.) a Owner, Withdrawal & Expenses a Liabilities Owner, Capital & Revenue Assets ) ) ) ) The correct answer is shown. The T- account for
1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000.
 Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Preparing Financial Statements
 Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
Chapter 1. Introduction to Accounting and Business
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings
 Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
ACCT1115. Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013
 ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
2 Transaction Analysis
 29366_06_ch2_p053-110 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT A P P L E C O M P U T E R, I N C. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes, which along
29366_06_ch2_p053-110 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT A P P L E C O M P U T E R, I N C. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes, which along
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs
 ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
How To Calculate A Trial Balance For A Company
 THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
Review of Accounting Principles
 Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Accounting Cycle. Matching Principle
 CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
The Work Sheet and the Closing Process
 C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET
 Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
Accrual Accounting Process
 Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance
 6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
The General Journal and the General Ledger
 4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems. Functional Area Systems. Lecture 4
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments
 Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
EXERCISES. Does not normally require adjustment. Normally requires adjustment (AE).
 EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries -
 COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives
 CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
Authored for ENMU Tutoring Services. By Jessica Huff
 By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions
 Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Baseline Assessment. Date Accounting 1
 Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
Definition of Accounting
 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. True-False Statements
 CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
Chapter 4: Accounting Records
 Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
CHAPTER 2 THE RECORDING PROCESS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. True-False Statements. Multiple Choice Questions
 CHAPTER 2 THE RECORDING PROCESS sg st SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 3 K 25.
CHAPTER 2 THE RECORDING PROCESS sg st SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 3 K 25.
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS
 C H A P T E R 1 0 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS I N T R O D U C T I O N Historically, profit-oriented businesses have used the accrual basis of accounting in which the income statement,
C H A P T E R 1 0 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS I N T R O D U C T I O N Historically, profit-oriented businesses have used the accrual basis of accounting in which the income statement,
Learning Module 3 Journal Entries
 Learning Module 3 Journal Entries The Accounting Equation Balance Sheet Income Statement = + + - Assets Liabilities Owners' Equity Revenue Expenses Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Recording journal
Learning Module 3 Journal Entries The Accounting Equation Balance Sheet Income Statement = + + - Assets Liabilities Owners' Equity Revenue Expenses Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Recording journal
A = L + OE. Transaction 1 Assets = Liabilitites + Owners equity + 1,000,000 Cash + 1,000,000 Common stock
 FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS Henry Jarva Aalto University, Spring 2015 Student name: EXERCISE 1. Provide journal entries for Transactions 5 8, Adjusting Entries 2 7, and prepare Exhibit 1. 2. Calculate
FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS Henry Jarva Aalto University, Spring 2015 Student name: EXERCISE 1. Provide journal entries for Transactions 5 8, Adjusting Entries 2 7, and prepare Exhibit 1. 2. Calculate
Advanced Accounting. Chapter 4: Financial Reporting for a Departmentalized Business
 Advanced Accounting Chapter 4: Financial Reporting for a Departmentalized Business Financial statements are used to summarize financial info and then are used to evaluate the financial position and progress
Advanced Accounting Chapter 4: Financial Reporting for a Departmentalized Business Financial statements are used to summarize financial info and then are used to evaluate the financial position and progress
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed
 Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL
 CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping
 Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
T Accounts, Debits and Credits, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements
 2 T Accounts, Debits and Credits, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM maintains an office for the practice of veterinary medicine. The account balances as of September 1 are given
2 T Accounts, Debits and Credits, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM maintains an office for the practice of veterinary medicine. The account balances as of September 1 are given
Gold Run Snowmobile. Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries For The Quarter Ended December 31. Final Project Evaluation. 5 th Edition.
 Gold Run Snowmobile 5 th Edition Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries For The Quarter Ended December 31 and the Final Project Evaluation Page 1 ADJUSTING ENTRIES FOR THE QUARTER Using a copy of the December
Gold Run Snowmobile 5 th Edition Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries For The Quarter Ended December 31 and the Final Project Evaluation Page 1 ADJUSTING ENTRIES FOR THE QUARTER Using a copy of the December
Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures
 Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle
 Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
When to Debit and Credit in Accounting
 When to Debit and Credit in Accounting Journal entries show a firm s transactions throughout a period of time; for example, when a company purchases supplies a journal entry will show the amount of supplies
When to Debit and Credit in Accounting Journal entries show a firm s transactions throughout a period of time; for example, when a company purchases supplies a journal entry will show the amount of supplies
Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle
 Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
Financial Statements Tutorial
 Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Completing the Accounting Cycle
 C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and
 Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
Accounting Skills Assessment Practice Exam Page 1 of 10
 NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
EasyPC Training. Accounting Basics
 EasyPC Training Accounting Basics Contents Accounting Basics... 3 The Accounting Equation... 3 Assets... 3 Liabilities... 3 Owner s Equity... 3 The Balance Sheet... 5 Double Entry Bookkeeping... 6 Ledger
EasyPC Training Accounting Basics Contents Accounting Basics... 3 The Accounting Equation... 3 Assets... 3 Liabilities... 3 Owner s Equity... 3 The Balance Sheet... 5 Double Entry Bookkeeping... 6 Ledger
Debits and Credits CHAPTER
 3 CHAPTER Debits and Credits As you learned in the last chapter, accountants use the accounting equation to analyze a firm s transactions and determine the effects of those transactions on the firm s assets,
3 CHAPTER Debits and Credits As you learned in the last chapter, accountants use the accounting equation to analyze a firm s transactions and determine the effects of those transactions on the firm s assets,
Accounting II Second Semester Final
 Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
PROFESSOR S NAME ACC 255 FALL 2011 COVER SHEET FOR COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8)
 COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) Page 137 NAME ANSWER KEY PROFESSOR S NAME SECTION SCORE ACC 255 FALL 2011 COVER SHEET FOR COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) INSTRUCTIONS: COMPLETE ALL
COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) Page 137 NAME ANSWER KEY PROFESSOR S NAME SECTION SCORE ACC 255 FALL 2011 COVER SHEET FOR COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) INSTRUCTIONS: COMPLETE ALL
Glossary of Accounting Terms
 Glossary of Accounting Terms Account - Something to which transactions are assigned. Accounts in MYOB are in one of eight categories: Asset Liability Equity Income Cost of sales Expense Other income Other
Glossary of Accounting Terms Account - Something to which transactions are assigned. Accounts in MYOB are in one of eight categories: Asset Liability Equity Income Cost of sales Expense Other income Other
CHAPTER 10 Financial Statements NOTE
 NOTE In practice, accruals accounts and prepayments accounts are implied rather than drawn up. It is common for expense accounts to show simply a balance c/d and a balance b/d. The accrual or prepayment
NOTE In practice, accruals accounts and prepayments accounts are implied rather than drawn up. It is common for expense accounts to show simply a balance c/d and a balance b/d. The accrual or prepayment
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT ACCOUNTING-BASIC - PILOT. Test Code: 4100 Version: 01
 JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT ACCOUNTING-BASIC - PILOT Test Code: 4100 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Journalizing Apply the accounting equation to journalize
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT ACCOUNTING-BASIC - PILOT Test Code: 4100 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Journalizing Apply the accounting equation to journalize
Objective Evidence. Unit of Measurement. Accounting Period Cycle. Business Entity. Going Concern. Adequate Disclosure. Matching Expenses with Revenue
 Accounting Concept: A source document is prepared for each transaction Objective Evidence Accounting Concept: Business transactions are stated in numbers that have common values; that is, using a common
Accounting Concept: A source document is prepared for each transaction Objective Evidence Accounting Concept: Business transactions are stated in numbers that have common values; that is, using a common
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle. Appendix 4A: Reversing entries
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
Bean Counter's Accounting and Bookkeeping "Cheat Sheet"
 Page 1 of 6 Bean Counter's ing and Bookkeeping "Cheat Sheet" Provided by: Bean Counter Source Documents ( Invoices, Checks, etc.) Journals -Transactions first recorded using Debits and s General Ledger
Page 1 of 6 Bean Counter's ing and Bookkeeping "Cheat Sheet" Provided by: Bean Counter Source Documents ( Invoices, Checks, etc.) Journals -Transactions first recorded using Debits and s General Ledger
Statement of Cash Flows
 THE CONTENT AND VALUE OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS The cash flow statement reconciles beginning and ending cash by presenting the cash receipts and cash disbursements of an enterprise for an accounting
THE CONTENT AND VALUE OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS The cash flow statement reconciles beginning and ending cash by presenting the cash receipts and cash disbursements of an enterprise for an accounting
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 16
 Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
TOPIC LEARNING OBJECTIVE
 Topic Mapping 1 Transaction Analysis Understand the effect of various types of transactions on the accounting equation, accounting journal and accounting ledger. Concepts and Skills Accounting Equation
Topic Mapping 1 Transaction Analysis Understand the effect of various types of transactions on the accounting equation, accounting journal and accounting ledger. Concepts and Skills Accounting Equation
The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201
 The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201 Content Accounting definition Accounting equation Accounting elements Asset, Liabilities, & Equity Transactions Accounts Receivable vs Accounts Payable Retained Earnings
The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201 Content Accounting definition Accounting equation Accounting elements Asset, Liabilities, & Equity Transactions Accounts Receivable vs Accounts Payable Retained Earnings
COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE
 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Review the seven basic steps of the accounting cycle. Prepare a work sheet. Prepare financial statements
4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Review the seven basic steps of the accounting cycle. Prepare a work sheet. Prepare financial statements
Analyzing Business Transactions Using T Accounts
 pri639_ch03_053-088.qxd 9/7/3 4:54 PM Page 53 Analyzing Business Transactions Using T Accounts Chapter 3 When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 876, and gave birth to www.att.com the company
pri639_ch03_053-088.qxd 9/7/3 4:54 PM Page 53 Analyzing Business Transactions Using T Accounts Chapter 3 When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 876, and gave birth to www.att.com the company
CHAPTER 3. BE3-2 Advertising. Dec. 31 Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 to adjust. BE3-3 Bere Co.
 CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
Accounting for Accruals and Deferrals
 CHAPTER 2 Accounting for Accruals and Deferrals LEARNING OBJECTIVES After you have mastered the material in this chapter, you will be able to: SECTION 1: SHOW HOW ACCRUALS AFFECT FINANCIAL STATEMENTS LO
CHAPTER 2 Accounting for Accruals and Deferrals LEARNING OBJECTIVES After you have mastered the material in this chapter, you will be able to: SECTION 1: SHOW HOW ACCRUALS AFFECT FINANCIAL STATEMENTS LO
A Simple Model. The Accounting Equation
 An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines
 Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines PART 1 Chapter 1 ACCOUNTING FOR A SERVICE BUSINESS ORGANIZED AS A PROPRIETORSHIP Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting
Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines PART 1 Chapter 1 ACCOUNTING FOR A SERVICE BUSINESS ORGANIZED AS A PROPRIETORSHIP Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting
Financial Accounting. (Exam)
 Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
Time Period Assumption
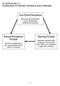 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
Debits and Credits: Analyzing and Recording Business Transactions
 63802_02_ch2_p039-076 2/26/09 11:30 AM Page 39 2 Debits and Credits: Analyzing and Recording Business Transactions DID YOU KNOW? In 2006 20% of sales came from Staples brands. The company plans to increase
63802_02_ch2_p039-076 2/26/09 11:30 AM Page 39 2 Debits and Credits: Analyzing and Recording Business Transactions DID YOU KNOW? In 2006 20% of sales came from Staples brands. The company plans to increase
b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize revenue until next year after the games are played.
 CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
RECORDING OF TRANSACTIONS (JOURNAL ENTRIES, LEDGER AND TRIAL BALANCE)
 Source Document : RECORDING OF TRANSACTIONS (JOURNAL ENTRIES, LEDGER AND TRIAL BALANCE) A document which provides evidence of the transactions is called the Source Document such as Cash memo, Invoice etc.
Source Document : RECORDING OF TRANSACTIONS (JOURNAL ENTRIES, LEDGER AND TRIAL BALANCE) A document which provides evidence of the transactions is called the Source Document such as Cash memo, Invoice etc.
Income Measurement and Profitability Analysis
 PROFITABILITY ANALYSIS The following financial statements for Spencer Company will be used to demonstrate the calculation of the various ratios in profitability analysis. Spencer Company Comparative Balance
PROFITABILITY ANALYSIS The following financial statements for Spencer Company will be used to demonstrate the calculation of the various ratios in profitability analysis. Spencer Company Comparative Balance
Learning Objectives: Quick answer key: Question # Multiple Choice True/False. 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information.
 0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
HERE'S A TIP. Double Entry Accounting. Debits and Credits
 Double Entry Accounting Because every business transaction affects at least two accounts, our accounting system is known as a double entry system. (You can refer to the company's chart of accounts to select
Double Entry Accounting Because every business transaction affects at least two accounts, our accounting system is known as a double entry system. (You can refer to the company's chart of accounts to select
Chapter 14. 1 Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall.
 Chapter 14 1 Identify the purposes of the statement of cash flows Distinguish among operating, investing, and financing cash flows Prepare the statement of cash flows by the indirect method Identify noncash
Chapter 14 1 Identify the purposes of the statement of cash flows Distinguish among operating, investing, and financing cash flows Prepare the statement of cash flows by the indirect method Identify noncash
4. Business Accounting
 4. Business Accounting Nobody was ever meant to remember or invent what he did with every cent. Robert Frost Questions 1. What is the purpose of accounting? 2. What are the main types of accounting? 3.
4. Business Accounting Nobody was ever meant to remember or invent what he did with every cent. Robert Frost Questions 1. What is the purpose of accounting? 2. What are the main types of accounting? 3.
'i*,; V' Your answer is correct! Match the Item on the left wlth the definition on the rtght.
 Match the Item on the left wlth the definition on the rtght. V' Your answer is correct! ~ Income statement """' ~ Reports a business's revenues and expenses for a period of time. ~ Balance sheet 1rt1 ~
Match the Item on the left wlth the definition on the rtght. V' Your answer is correct! ~ Income statement """' ~ Reports a business's revenues and expenses for a period of time. ~ Balance sheet 1rt1 ~
E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions?
 E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions? Listed below are eight transactions. In each case, identify whether the transaction is an example of financing, investing or operating
E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions? Listed below are eight transactions. In each case, identify whether the transaction is an example of financing, investing or operating
Accg100 Accounting 1A. Lecture Notes
 Accg100 Accounting 1A Lecture Notes Semester 2, 2012 1 Table of Contents Lecture Notes Page Week 1: Introduction to Accounting, Ethics, 3 Business Entities, Financial Statements Week 2: Accounting for
Accg100 Accounting 1A Lecture Notes Semester 2, 2012 1 Table of Contents Lecture Notes Page Week 1: Introduction to Accounting, Ethics, 3 Business Entities, Financial Statements Week 2: Accounting for
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers
 Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis
 1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
SMART TOUCH LEARNING Balance Sheet May 31, 2013 $ 4,800. $ 48,700 Accounts receivable 2,600. 900 Inventory 30,500. 100 Supplies.
 3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I
 Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J
 Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II
 Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER IN ACCOUNTANCY. Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER IN ACCOUNTANCY Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Note: The question paper is divided into two sections A and B. Attempt all questions of Section A and any one question of Section
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER IN ACCOUNTANCY Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Note: The question paper is divided into two sections A and B. Attempt all questions of Section A and any one question of Section
