Biology 152 Tissues Objectives
|
|
|
- Barbara Hines
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology 152 Tissues Objectives Your job in this assignment is to learn 19 tissues that were selected by the Nursing and Allied Health professionals as the most important ones for members of those fields to know. For each assigned tissue, you will want to know: 1) a proper Location for the tissue, and 2) a proper Function for the tissue. Proper is defined as anything that makes that tissue unique from the others! Lastly, I will point out from the tissue by pointing at items on slides during the Practical, so you will want to familiarize yourself with proper definition and locations for those words. To practice, I suggest making study cards (or study sheets) and also to use my online Histology Tutorial (linked on your syllabus or at the bottom of the BIO 152 Homepage). Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue (along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue). Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective absorption, protection, transcellular transport, and detection of sensation. In Greek, "Epi" means, "on, upon," and "Theli" means "tissue." Connective Tissue is a fibrous tissue. It is one of the four traditional classes of tissues (the others being epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissue). Connective Tissue (CT) is found throughout the body. It has 3 main components: cells, fibers (reticular fibers, collagen, and elastin), and extracellular. Connective tissue makes up a variety of physical structures including: tendons, blood, cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, and lymphatic tissue. CT is classified into four subtypes: Proper CT, Cartilage CT, Osseous CT, and Vascular CT. The Proper CT subtype is subdivided into dense regular fibrous CT and loose fibrous CT types. Muscular Tissue (from Latin musculus; diminutive of mus "mouse") is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the embryonic mesodermal layer (along with the skeletal system). Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to produce force and cause motion. Muscles can cause either locomotion of the organism itself or movement of internal organs. Cardiac and smooth muscle contraction occurs without conscious thought and is necessary for survival. Examples are the contraction of the heart and peristalsis which pushes food through the digestive system. Voluntary contraction of the skeletal muscles is used to move the body and can be finely controlled. Examples are movements of the eye, or gross movements like the quadriceps muscle of the thigh. Nervous Tissue is a specialized tissue designed for sensory input, integration, control of muscles and glands, homeostasis, and mental activity. It is the main component of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and nerves) that regulates and controls body functions. It is composed of neurons (which transmit impulses called Action Potentials) and the neuroglial cells (which assist propagation of the nerve impulse, repair damage to neurons, and provide nutrients to the neuron). Neurons receive stimuli using dendrites and then move an impulse down an axon to either a muscle or a gland.
2 Simple Cuboidal Epithelium cuboidal cell Simple Columnar Epithelium cilia columnar cell goblet cell
3 Simple Squamous Epithelium squamous cell Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium keratin keratinocyte melanin melanocyte squamous cell
4 Stratified Squamous Nonkeratinized Epithelium squamous cell Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium cilia columnar cell goblet cell
5 Transitional Epithelium cuboidal cell squamous cell Adipose Connective Tissue adipocyte lipids
6 Areolar (Loose) Connective Tissue collagen fibers elastic fibers fibroblast reticular fibers Dense Regular Fibrous Connective Tissue collagen fibers fibroblast
7 Elastic Cartilage (Connective Tissue) chondrocyte elastin fibers lacuna Fibrocartilage (Connective Tissue) chondrocyte collagen fibers lacuna
8 Hyaline Cartilage (Connective Tissue) chondrocyte reticular fibers Osseous Connective Tissue canaliculi Haversian (Central) Canal lacuna lamella osteocyte
9 Vascular (Blood) Connective Tissue erythrocyte leukocyte plasma thrombocyte Cardiac Muscle Tissue intercalated discs involuntary control striated
10 Skeletal Muscle Tissue striated voluntary control Smooth Muscle Tissue involuntary control nonstriated
11 Nervous Tissue axon (a process) dendrite (a process) neuroglial cell neuron On the practical itself, you will be given the following format: Part 1: Write the correct term for the identified item and then write a definition: Term Definition 1) 2) Part 2: Please provide a function and location for these tissues: Tissue Proper Function Proper Location Adipose Areolar (loose fibrous)
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Location: air sacs of lungs; nephrons of kidney; lining of circulatory system, lymphatic vessels, & ventral body cavity
 Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
Laboratory 3 Histology
 Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System. Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
CHAPTER 5: TISSUES. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY
 SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY
 THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Tissue Types. 1. Epithelial Tissue (or epithelium) is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body
 Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure
 Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
HISTOLOGY: THE FORM AND FUNCTION OF TISSUES
 Biology E-65C Lab #1 HISTOLOGY: THE FORM AND FUNCTION OF TISSUES Objectives: 1. To gain an appreciation of tissue types in terms of their functional significance 2. To gain experience with the use of a
Biology E-65C Lab #1 HISTOLOGY: THE FORM AND FUNCTION OF TISSUES Objectives: 1. To gain an appreciation of tissue types in terms of their functional significance 2. To gain experience with the use of a
Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function
 Name Period Concept 40.1 Animal form and function are correlated at all levels of organization 1. Animals need to exchange materials with their environment. This process occurs as substances dissolved
Name Period Concept 40.1 Animal form and function are correlated at all levels of organization 1. Animals need to exchange materials with their environment. This process occurs as substances dissolved
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Osseous Tissue & Structure. The skeletal system includes: Storage of minerals: calcium salts
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen
 I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE. Striations Present or Absent?
 BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Visit www.ncerthelp.com For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-7
 Chapter-7 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN ANIMALS POINTS TO REMEMBER Tissue : A group of similar cells along with intercellular substances which perform a specific function. Simple epithelium : is composed
Chapter-7 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN ANIMALS POINTS TO REMEMBER Tissue : A group of similar cells along with intercellular substances which perform a specific function. Simple epithelium : is composed
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
h. Large intestine 3
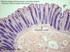 (1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
(1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
Exploring Creation with Advanced Biology ~ Schedule for 2015-2016 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Date:
 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Lecture Exam One Material: Anatomy and Physiology 121 Introduction to Human Body, the Tissue Level of Organization and the Integumentary System
 Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy and physiology are absolutely interrelated subjects in which structures at all levels are defined and also used to understand the dynamic function of a living organism.
Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy and physiology are absolutely interrelated subjects in which structures at all levels are defined and also used to understand the dynamic function of a living organism.
Function of Bones. Bone Tissue and Bones BONE CLASSIFICATION. Long Bones Gross Anatomy. Lab Activity 1 - Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
 Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
 CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
BIO 201 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I with LAB
 BIO 201 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Presented and Approved: January 12, 2012 Effective: 2012-13 FA Prefix & Number BIO 201 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
BIO 201 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Presented and Approved: January 12, 2012 Effective: 2012-13 FA Prefix & Number BIO 201 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
MUSCULAR SYSTEM. A. K. Sengupta 9/9/2010 1/12
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
10/12/2011. Classification of Bones Every adult skeleton contains 206 bones which can be arranged into six broad categories according to shape
 Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
RAD 223. Radiography physiology. Lecture Notes. First lecture: Cell and Tissue
 RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
BONES AND BONE TISSUE
 BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
E. Blood cells production. Blood cells are produced within the cavities of bones.
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
Structural Organisation in Animals
 Chapter 3 Structural Organisation in Animals Introduction Life activities are done by cells, tissues, organs and organ systems in animals. Tissues are a group of similar cells which perform a particular
Chapter 3 Structural Organisation in Animals Introduction Life activities are done by cells, tissues, organs and organ systems in animals. Tissues are a group of similar cells which perform a particular
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Epithelial and Connective Tissues. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Epithelial and Connective Tissues Danil Hammoudi.MD Figure 4.1 4 types of human tissues Epithelium Connective tissue Muscle tissue Skeletal Cardiac Smooth muscles Nerve tissue Tissue derivation Ectoderm
Epithelial and Connective Tissues Danil Hammoudi.MD Figure 4.1 4 types of human tissues Epithelium Connective tissue Muscle tissue Skeletal Cardiac Smooth muscles Nerve tissue Tissue derivation Ectoderm
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Digestive System Digestive Tract
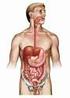 Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Integumentary System Answer Key
 Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook integumentary system answer key in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database the major organs and functions of the integumentary
Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook integumentary system answer key in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database the major organs and functions of the integumentary
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST
 REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes
 Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
This is your Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term.
 This is your Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term. 1 Run for your lives!!! (Just Kidding) Matching - Anatomy or Physiology? A 1. Study of structure A. Anatomy 2. muscle actions B. Physiology 3. Brain Function
This is your Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term. 1 Run for your lives!!! (Just Kidding) Matching - Anatomy or Physiology? A 1. Study of structure A. Anatomy 2. muscle actions B. Physiology 3. Brain Function
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
Human Anatomy & Physiology: Fall Final Exam Review
 Chapter 1: 1. Anatomy is a term which means the study of. A. physiology B. morphology C. cell functions D. human functions 2. The study dealing with the explanations of how an organ works would be an example
Chapter 1: 1. Anatomy is a term which means the study of. A. physiology B. morphology C. cell functions D. human functions 2. The study dealing with the explanations of how an organ works would be an example
CHAPTER 2 : CELL AS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE
 CHAPTER 2 : CELL AS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE Parts of microscope : An instrument that magnifies minute objects so they can be seen easily. It is one of the most important tools of science. Physicians and
CHAPTER 2 : CELL AS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE Parts of microscope : An instrument that magnifies minute objects so they can be seen easily. It is one of the most important tools of science. Physicians and
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
The Functions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46341 1 The Functions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46341 1 The Functions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I.
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
Small & Large Intestines
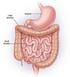 Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin
 Overview Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin Understanding the layered structure of skin is essential to understanding how it functions. The focus of this lesson is for students to discover and
Overview Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin Understanding the layered structure of skin is essential to understanding how it functions. The focus of this lesson is for students to discover and
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems
 Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
