Transistors. Lesson #8 Chapter 4. BME 372 Electronics I J.Schesser
|
|
|
- Angelica Alexander
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Transistors Lesson #8 Chapter 4 225
2 Configurations of the BJT Common Emitter and Emitter Follower B Base ib o Collector C o vce v BE o E Emitter npn i C i E 226
3 Configurations of the BJT Common Collector Common Base B o Base ib v BE Emitter E o o C vce Collector npn i E i c 227
4 Characteristics of the BJT npn Common Emitter Configuration i C 25 i B 10mA 100μA i B mA 50μA v BE V v CE Baseemitter junction looks like a forward biased diode Collectoremitter is a family of curves which are a function of base current 228
5 i i i E B C i i i C C E i B (1 ) i i 1 1 B E BJT Equations i B B o Base ib Collector C o vce v BE o E Emitter I c =β i B =α i E Since α is less than unity then β will be greater than unity and there is current gain from base to collector. i E 229
6 Example Calculate the values of β and α from the transistor shown in the previous graphs. i C β = i c / i b = 5m/50µ = 100 5mA α = β /(β1) = 100/101 =.99 10mA 100μA i B 50μA 20V v CE 230
7 BJT Analysis R C 2k R B V in 50k 1.6V 10V V CC V BB Here is a common emitter BJT amplifier: What are the steps? 231
8 BJT Analysis Inputs and Outputs R C 2k i C R B V in 50k 1.6V i b V BE V CE 10V V CC V BB We would want to know the collector current (i c ), collectoremitter voltage (V CE ), and the voltage across R C. To get this we need to fine the base current (i b ) and the baseemitter voltage (V BE ). 232
9 BJT Analysis Input Equation R C 2k i C R B V in 50k 1.6V i B V BE V CE 10V V CC V BB To start, let s write KVL around the base circuit. V in (t) V BB = i B (t)r B V BE (t) 233
10 BJT Analysis Output Equations R C 2k i C R B V in 50k 1.6V i B V BE V CE 10V V CC V BB Likewise, we can write KVL around the collector circuit. V CC = i C (t)r C V CE (t) 234
11 BJT Analysis Use Superposition: DC & AC sources Note that both equations are written so as to calculate the transistor parameters (i.e., base current, baseemitter voltage, collector current, and the collectoremitter voltage) for both the DC signal and the AC signal sources. Let s use superposition, calculate the parameters for each separately, and add up the results First, the DC analysis to calculate the DC Qpoint Short Circuit any AC voltage sources Open Circuit any AC current sources Next, the AC analysis to calculate gains of the amplifier. Depends on how we perform AC analysis Graphical Method Equivalent circuit method for small AC signals 235
12 BJT DC Analysis Using KVL for the input and output circuits and the transistor characteristics, the following steps apply: 1. Draw the load lines on the transistor characteristics 2. For the input characteristics determine the Q point for the input circuit from the intersection of the load line and the characteristic curve (Note that some transistor do not need an input characteristic curve.) 3. From the output characteristics, find the intersection of the load line and characteristic curve determined from the Q point found in step 2, determine the Q point for the output circuit. 236
13 V BE = 0; i B = V BB / R B = 1.6 /50k = 32 A BJT DC Analysis BaseEmitter Circuit Q point i B amps I BQ = 20 A Q POINT V BEQ = 0.6 V v BE volts i B = 0; V BE = V BB = 1.6 V First let s set V in (t) =0 to get the Qpoint for the BJT. We start with the base circuit. V BB = i B R B V BE And the intercepts occur at i B = 0; V BE = V BB = 1.6 V and at V BE = 0; i B = V BB / R B = 1.6 /50k = 32 A The Load Line intersects the Baseemitter characteristics at V BEQ = 0.6 V and I BQ = 20 A 237
14 BJT DC Analysis CollectorEmitter Circuit Q point i C amps 7.E03 6.E03 5.E03 4.E03 VCC RC 5 ma i B =50 μa 40 μa 30 μa I CQ 2. 5 ma 3.E03 2.E03 1.E03 0.E00 V CEQ = 5.9 V v CE volts Q POINT 0 μa 20 μa 10 μa VCC 10 Now that we have the Qpoint for the base circuit, let s proceed to the collector circuit. v V CC = i C R C V CE The intercepts occur at i C = 0; V CE = V CC = 10 V; and at V CE = 0; i C = V CC / R C = 10 /2k = 5mA The Load Line intersects the Collectoremitter characteristic, i B =20mA at V CEQ = 5.9 V and I CQ = 2.5mA β = 2.5m/20m =
15 BJT DC Analysis Summary Calculating the Qpoint for BJT is the first step in analyzing the circuit To summarize: We ignored the AC (variable) source Short circuit the voltage sources Open Circuit the current sources We applied KVL to the baseemitter circuit and using load line analysis on the baseemitter characteristics, we obtained the base current Qpoint We then applied KVL to the collectoremitter circuit and using load line analysis on the collectoremitter characteristics, we obtained the collector current and voltage Qpoint This process is also called DC Analysis We now proceed to perform AC Analysis 239
16 BJT AC Analysis How do we handle the variable source V in (t)? When the variations of V in (t) are large we will use the baseemitter and collectoremitter characteristics using a similar graphical technique as we did for obtaining the Qpoint When the variations of V in (t) are small we will shortly use a linear approach using the BJT small signal equivalent circuit. 240
17 BJT AC Analysis Let s assume that V in (t) = 0.2 sin(ωt). Then the voltage sources at the base vary from a maximum of = 1.8 V to a minimum of = 1.4 V We can then draw two load lines corresponding the maximum and minimum values of the input sources The current intercepts then become for the: Maximum value: 1.8 / 50k = 36 µa Minimum value: 1.4 / 50k = 28 µa 241
18 BJT AC Analysis BaseEmitter Circuit i B amps I BQ = 20μA V BEQ = 0.6 V v BE volts From this graph, we find: At Maximum Input Voltage: V BE = 0.63 V, i B = 24μa At Minimum Input Voltage: V BE = 0.59 V, i B = 15μa Recall: At Qpoint: V BE = 0.6 V, i B = 20μa Note the asymmetry around the Qpoint of the Max and Min Values for the base current and voltage which is due to the nonlinearity of the baseemitter characteristics Δi Bmax =2420=4μa; Δi Bmin =2015=5μa load line for minimum input voltage load line for maximum input voltage 242
19 BJT AC Analysis BaseEmitter Circuit i B amps load line for minimum input voltage I BQ = 20 A V BEQ = 0.6 V load line for maximum input voltage v BE volts vin ib 243
20 BJT CharacteristicsCollector Circuit i C amps 7.E03 6.E03 i B =50 μa 5.E03 4.E03 40 μa 30 μa I CQ E03 ma 2.E03 1.E03 0.E00 V CEQ = 5.9 V Q POINT v CE volts Using these maximum and minimum values for the base current on the collect circuit load line, we find: Note that in addition to the asymmetry around the Qpoint there is an inversion between the input voltage and the collector to emitter voltage μa At Maximum Input Voltage: V CE = 5 V, i C = 2.7ma At Minimum Input Voltage: V CE = 7 V, i C = 1.9ma Recall: At Qpoint: V CE = 5.9 V, i C = 2.5ma 24 μa 20 μa 15 μa 10 μa
21 BJT CharacteristicsCollector Circuit i C amps 7.E03 6.E03 i B =50 μa I CQ E03 4.E03 3.E03 ma 2.E03 1.E03 0.E00 V CEQ = 5.9 V v CE volts 40 μa 30 μa 24 μa Q POINT 20 μa 15 μa 10 μa 0 μa ic ib vin vce 245
22 BJT AC Analysis Amplifier Gains From the values calculated from the base and collector circuits we can calculate the amplifier gains: β = 125 Current gain = Δi c / Δi b = ( ) m / (24 15) μ = 0.8/ = 88.9 Voltage gain = V o / V i = ΔV CE / ΔV BE = (5 7) / (.63.59) = 2/0.04 = 50 Voltage gain = V o / V s = ΔV CE / ΔV in = (5 7) /.4 = 2 /.4 = 5 246
23 BJT AC Analysis Summary Once we complete DC analysis, we analyze the circuit from an AC point of view. AC analysis can be performed via a graphical processes Find the maximum and minimum values of the input parameters (e.g., base current for a BJT) Use the transistor characteristics to calculate the output parameters (e.g., collector current for a BJT). Calculate the gains for the amplifier 247
24 BJT Characteristics Distortion i C amps 7.E03 6.E03 5.E03 i B =50 μa 40 μa I CQ 2. 5 ma 4.E03 3.E03 2.E03 1.E03 0.E00 V CEQ = 5.9 V Note that even though the input (base current) is symmetrical about its Qpoint, the output voltage is uneven v CE volts Q POINT 0 μa 30 μa 20 μa 10 μa 24 μa 15 μa This is due to the nonlinear spacing of the characteristic curves and leads to signal distortion 248
25 The pnp Transistor Basically, the pnp transistor is similar to the npn except the parameters have the opposite sign. The collector and base currents flows out of the transistor; while the emitter current flows into the transistor The baseemitter and collectoremitter voltages are negative Otherwise the analysis is identical to the npn 249
26 PNP Bipolar Junction Transistors Base Collector ptype ntype ptype Two junctions CollectorBase and EmitterBase Biasing v BE Forward Biased v CB Reverse Biased Collector B o Base ib v BE C o o E v CE Emitter i C i E V in R B 50k 1.6V R C 2k 10V V CC pnp Emitter 250
27 Homework Probs. 4.4, 4.5, 4.8, 4.10, 4.14, 4.15, 4.19, 4.20, 4.21, 4.22, 251
Bipolar Junction Transistors
 Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
Voltage Divider Bias
 Voltage Divider Bias ENGI 242 ELEC 222 BJT Biasing 3 For the Voltage Divider Bias Configurations Draw Equivalent Input circuit Draw Equivalent Output circuit Write necessary KVL and KCL Equations Determine
Voltage Divider Bias ENGI 242 ELEC 222 BJT Biasing 3 For the Voltage Divider Bias Configurations Draw Equivalent Input circuit Draw Equivalent Output circuit Write necessary KVL and KCL Equations Determine
Bipolar Junction Transistor Basics
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
Transistors. NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor
 Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers
 BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
W04 Transistors and Applications. Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören
 W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
CIRCUITS LABORATORY. In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low
 CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Transistor Biasing. The basic function of transistor is to do amplification. Principles of Electronics
 192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
AMPLIFIERS BJT BJT TRANSISTOR. Types of BJT BJT. devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level
 AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor
 The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
BJT Circuit Configurations
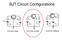 BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
Transistor Models. ampel
 Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
TOSHIBA Transistor Silicon PNP Epitaxial Type (PCT Process) 2SA1020
 2SA12 TOSHIBA Transistor Silicon PNP Epitaxial Type (PCT Process) 2SA12 Power Amplifier Applications Power Switching Applications Unit: mm Low Collector saturation voltage: V CE (sat) =.5 V (max) (I C
2SA12 TOSHIBA Transistor Silicon PNP Epitaxial Type (PCT Process) 2SA12 Power Amplifier Applications Power Switching Applications Unit: mm Low Collector saturation voltage: V CE (sat) =.5 V (max) (I C
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS
 CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
 LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET. BFQ34 NPN 4 GHz wideband transistor. Product specification File under Discrete Semiconductors, SC14
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET File under Discrete Semiconductors, SC4 September 995 DESCRIPTION PINNING NPN transistor encapsulated in a 4 lead SOTA envelope with a ceramic cap. All leads are isolated
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET File under Discrete Semiconductors, SC4 September 995 DESCRIPTION PINNING NPN transistor encapsulated in a 4 lead SOTA envelope with a ceramic cap. All leads are isolated
05 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) basics
 The first bipolar transistor was realized in 1947 by Brattain, Bardeen and Shockley. The three of them received the Nobel prize in 1956 for their invention. The bipolar transistor is composed of two PN
The first bipolar transistor was realized in 1947 by Brattain, Bardeen and Shockley. The three of them received the Nobel prize in 1956 for their invention. The bipolar transistor is composed of two PN
3 The TTL NAND Gate. Fig. 3.1 Multiple Input Emitter Structure of TTL
 3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
Amplifier Teaching Aid
 Amplifier Teaching Aid Table of Contents Amplifier Teaching Aid...1 Preface...1 Introduction...1 Lesson 1 Semiconductor Review...2 Lesson Plan...2 Worksheet No. 1...7 Experiment No. 1...7 Lesson 2 Bipolar
Amplifier Teaching Aid Table of Contents Amplifier Teaching Aid...1 Preface...1 Introduction...1 Lesson 1 Semiconductor Review...2 Lesson Plan...2 Worksheet No. 1...7 Experiment No. 1...7 Lesson 2 Bipolar
Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2010, 2011 and 2012
 1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
Lecture 060 Push-Pull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 060-1. ECE 6412 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems II P.E. Allen - 2002
 Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Common-Emitter Amplifier
 Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D186 Supersedes data of 1999 Apr 23 2001 Oct 10 FEATURES High current (max. 1 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V). APPLICATIONS Audio and video amplifiers. PINNING
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D186 Supersedes data of 1999 Apr 23 2001 Oct 10 FEATURES High current (max. 1 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V). APPLICATIONS Audio and video amplifiers. PINNING
Supplement Reading on Diode Circuits. http://www.inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/ edu/~ee40/fa09/handouts/ee40_mos_circuit.pdf
 EE40 Lec 18 Diode Circuits Reading: Chap. 10 of Hambley Supplement Reading on Diode Circuits http://www.inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/ edu/~ee40/fa09/handouts/ee40_mos_circuit.pdf Slide 1 Diodes Circuits Load
EE40 Lec 18 Diode Circuits Reading: Chap. 10 of Hambley Supplement Reading on Diode Circuits http://www.inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/ edu/~ee40/fa09/handouts/ee40_mos_circuit.pdf Slide 1 Diodes Circuits Load
Lecture-7 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) Part-I Continued
 1 Lecture-7 ipolar Junction Transistors (JT) Part-I ontinued 1. ommon-emitter (E) onfiguration: Most JT circuits employ the common-emitter configuration shown in Fig.1. This is due mainly to the fact that
1 Lecture-7 ipolar Junction Transistors (JT) Part-I ontinued 1. ommon-emitter (E) onfiguration: Most JT circuits employ the common-emitter configuration shown in Fig.1. This is due mainly to the fact that
The basic cascode amplifier consists of an input common-emitter (CE) configuration driving an output common-base (CB), as shown above.
 Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
BD238. Low voltage PNP power transistor. Features. Applications. Description. Low saturation voltage PNP transistor
 Low voltage PNP power transistor Features Low saturation voltage PNP transistor Applications Audio, power linear and switching applications Description The device is manufactured in planar technology with
Low voltage PNP power transistor Features Low saturation voltage PNP transistor Applications Audio, power linear and switching applications Description The device is manufactured in planar technology with
Lecture 17. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.
 Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier
 Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Configuration Common Base Configuration Small Signal Analysis Design Example Amplifier Input and Output Impedances
Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Configuration Common Base Configuration Small Signal Analysis Design Example Amplifier Input and Output Impedances
Differential Amplifier Offset. Causes of dc voltage and current offset Modeling dc offset R C
 ESE39 ntroduction to Microelectronics Differential Amplifier Offset Causes of dc voltage and current offset Modeling dc offset mismatch S mismatch β mismatch transistor mismatch dc offsets in differential
ESE39 ntroduction to Microelectronics Differential Amplifier Offset Causes of dc voltage and current offset Modeling dc offset mismatch S mismatch β mismatch transistor mismatch dc offsets in differential
TWO PORT NETWORKS h-parameter BJT MODEL
 TWO PORT NETWORKS h-parameter BJT MODEL The circuit of the basic two port network is shown on the right. Depending on the application, it may be used in a number of different ways to develop different
TWO PORT NETWORKS h-parameter BJT MODEL The circuit of the basic two port network is shown on the right. Depending on the application, it may be used in a number of different ways to develop different
2N6387, 2N6388. Plastic Medium-Power Silicon Transistors DARLINGTON NPN SILICON POWER TRANSISTORS 8 AND 10 AMPERES 65 WATTS, 60-80 VOLTS
 2N6388 is a Preferred Device Plastic MediumPower Silicon Transistors These devices are designed for generalpurpose amplifier and lowspeed switching applications. Features High DC Current Gain h FE = 2500
2N6388 is a Preferred Device Plastic MediumPower Silicon Transistors These devices are designed for generalpurpose amplifier and lowspeed switching applications. Features High DC Current Gain h FE = 2500
TOSHIBA Transistor Silicon NPN Epitaxial Type (PCT Process) 2SC2383
 TOSHIBA Transistor Silicon NPN Epitaxial Type (PCT Process) SC8 Color TV Vertical Deflection Output Applications Color TV Class-B Sound Output Applications Unit: mm High breakdown voltage: V CEO = 6 V
TOSHIBA Transistor Silicon NPN Epitaxial Type (PCT Process) SC8 Color TV Vertical Deflection Output Applications Color TV Class-B Sound Output Applications Unit: mm High breakdown voltage: V CEO = 6 V
Vdc. Vdc. Adc. W W/ C T J, T stg 65 to + 200 C
 2N6284 (NPN); 2N6286, Preferred Device Darlington Complementary Silicon Power Transistors These packages are designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. Features High
2N6284 (NPN); 2N6286, Preferred Device Darlington Complementary Silicon Power Transistors These packages are designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. Features High
TOSHIBA Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor Silicon N Channel IGBT GT60J323
 GT6J2 TOSHIBA Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor Silicon N Channel IGBT GT6J2 Current Resonance Inverter Switching Application Unit: mm Enhancement mode type High speed : t f =.6 μs (typ.) (I C = 6A) Low
GT6J2 TOSHIBA Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor Silicon N Channel IGBT GT6J2 Current Resonance Inverter Switching Application Unit: mm Enhancement mode type High speed : t f =.6 μs (typ.) (I C = 6A) Low
AT-41486 Up to 6 GHz Low Noise Silicon Bipolar Transistor
 AT- Up to 6 GHz Low Noise Silicon Bipolar Transistor Data Sheet Description Avago s AT- is a general purpose NPN bipolar transistor that offers excellent high frequency performance. The AT- is housed in
AT- Up to 6 GHz Low Noise Silicon Bipolar Transistor Data Sheet Description Avago s AT- is a general purpose NPN bipolar transistor that offers excellent high frequency performance. The AT- is housed in
Objectives The purpose of this lab is build and analyze Differential amplifiers based on NPN transistors (or NMOS transistors).
 1 Lab 03: Differential Amplifiers (BJT) (20 points) NOTE: 1) Please use the basic current mirror from Lab01 for the second part of the lab (Fig. 3). 2) You can use the same chip as the basic current mirror;
1 Lab 03: Differential Amplifiers (BJT) (20 points) NOTE: 1) Please use the basic current mirror from Lab01 for the second part of the lab (Fig. 3). 2) You can use the same chip as the basic current mirror;
45 V, 100 ma NPN/PNP general-purpose transistor
 Rev. 4 18 February 29 Product data sheet 1. Product profile 1.1 General description NPN/PNP general-purpose transistor pair in a very small SOT363 (SC-88) Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) plastic package.
Rev. 4 18 February 29 Product data sheet 1. Product profile 1.1 General description NPN/PNP general-purpose transistor pair in a very small SOT363 (SC-88) Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) plastic package.
Content Map For Career & Technology
 Content Strand: Applied Academics CT-ET1-1 analysis of electronic A. Fractions and decimals B. Powers of 10 and engineering notation C. Formula based problem solutions D. Powers and roots E. Linear equations
Content Strand: Applied Academics CT-ET1-1 analysis of electronic A. Fractions and decimals B. Powers of 10 and engineering notation C. Formula based problem solutions D. Powers and roots E. Linear equations
Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads.
 Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
Diodes and Transistors
 Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
EN: This Datasheet is presented by the m anufacturer. Please v isit our website for pricing and availability at www.hest ore.hu.
 EN: This Datasheet is presented by the m anufacturer. Please v isit our website for pricing and availability at www.hest ore.hu. 2N3055, MJ2955 Complementary power transistors Features Datasheet - production
EN: This Datasheet is presented by the m anufacturer. Please v isit our website for pricing and availability at www.hest ore.hu. 2N3055, MJ2955 Complementary power transistors Features Datasheet - production
Features: Characteristic Symbol Rating Unit. Collector-Emitter Voltage V CEO 100 Collector-Base Voltage I C
 Designed for use in general purpose power amplifier and switching applications. Features: Collector-Emitter Sustaining Voltage V CEO(sus) = 100V (Minimum) - TIP35C, TIP36C DC Current Gain h FE = 25 (Minimum)
Designed for use in general purpose power amplifier and switching applications. Features: Collector-Emitter Sustaining Voltage V CEO(sus) = 100V (Minimum) - TIP35C, TIP36C DC Current Gain h FE = 25 (Minimum)
BJT AC Analysis. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
2N4921G, 2N4922G, 2N4923G. Medium-Power Plastic NPN Silicon Transistors 1.0 AMPERE GENERAL PURPOSE POWER TRANSISTORS 40 80 VOLTS, 30 WATTS
 ,, Medium-Power Plastic NPN Silicon Transistors These highperformance plastic devices are designed for driver circuits, switching, and amplifier applications. Features Low Saturation Voltage Excellent
,, Medium-Power Plastic NPN Silicon Transistors These highperformance plastic devices are designed for driver circuits, switching, and amplifier applications. Features Low Saturation Voltage Excellent
Lecture 12: DC Analysis of BJT Circuits.
 Whites, 320 Lecture 12 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 12: D Analysis of JT ircuits. n this lecture we will consider a number of JT circuits and perform the D circuit analysis. For those circuits with an active mode
Whites, 320 Lecture 12 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 12: D Analysis of JT ircuits. n this lecture we will consider a number of JT circuits and perform the D circuit analysis. For those circuits with an active mode
Low Noise, Matched Dual PNP Transistor MAT03
 a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
MJD112 (NPN), MJD117 (PNP) Complementary Darlington Power Transistors. DPAK For Surface Mount Applications
 MJD (NPN), MJD7 (PNP) Complementary Darlington Power Transistors For Surface Mount Applications Designed for general purpose power and switching such as output or driver stages in applications such as
MJD (NPN), MJD7 (PNP) Complementary Darlington Power Transistors For Surface Mount Applications Designed for general purpose power and switching such as output or driver stages in applications such as
Figure 1. Diode circuit model
 Semiconductor Devices Non-linear Devices Diodes Introduction. The diode is two terminal non linear device whose I-V characteristic besides exhibiting non-linear behavior is also polarity dependent. The
Semiconductor Devices Non-linear Devices Diodes Introduction. The diode is two terminal non linear device whose I-V characteristic besides exhibiting non-linear behavior is also polarity dependent. The
Peak Atlas DCA. Semiconductor Component Analyser Model DCA55. User Guide
 GB55-7 Peak Atlas DCA Semiconductor Component Analyser Model DCA55 User Guide Peak Electronic Design Limited 2000/2007 In the interests of development, information in this guide is subject to change without
GB55-7 Peak Atlas DCA Semiconductor Component Analyser Model DCA55 User Guide Peak Electronic Design Limited 2000/2007 In the interests of development, information in this guide is subject to change without
BC327, BC327-16, BC327-25, BC327-40. Amplifier Transistors. PNP Silicon. These are Pb Free Devices* http://onsemi.com. Features MAXIMUM RATINGS
 BC327, BC327-16, BC327-25, BC327-4 Amplifier Transistors PNP Silicon Features These are PbFree Devices* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter Voltage V CEO 45 Vdc CollectorEmitter Voltage
BC327, BC327-16, BC327-25, BC327-4 Amplifier Transistors PNP Silicon Features These are PbFree Devices* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter Voltage V CEO 45 Vdc CollectorEmitter Voltage
TIP31, TIP32 High Power Bipolar Transistor
 Features: Collector-Emitter sustaining voltage - V CEO(sus) = 60V (Minimum) - TIP31A, TIP32A = 100V (Minimum) - TIP31C,. Collector-Emitter saturation voltage - V CE(sat) = 1.2V (Maximum) at I C = 3.0A.
Features: Collector-Emitter sustaining voltage - V CEO(sus) = 60V (Minimum) - TIP31A, TIP32A = 100V (Minimum) - TIP31C,. Collector-Emitter saturation voltage - V CE(sat) = 1.2V (Maximum) at I C = 3.0A.
40 V, 200 ma NPN switching transistor
 Rev. 01 21 July 2009 Product data sheet BOTTOM VIEW 1. Product profile 1.1 General description NPN single switching transistor in a SOT883 (SC-101) leadless ultra small Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) plastic
Rev. 01 21 July 2009 Product data sheet BOTTOM VIEW 1. Product profile 1.1 General description NPN single switching transistor in a SOT883 (SC-101) leadless ultra small Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) plastic
SEMICONDUCTOR APPLICATION NOTE
 SEMICONDUCTOR APPLICATION NOTE Order this document by AN7A/D Prepared by: Francis Christian INTRODUCTION The optical coupler is a venerable device that offers the design engineer new freedoms in designing
SEMICONDUCTOR APPLICATION NOTE Order this document by AN7A/D Prepared by: Francis Christian INTRODUCTION The optical coupler is a venerable device that offers the design engineer new freedoms in designing
BD241A BD241C. NPN power transistors. Features. Applications. Description. NPN transistors. Audio, general purpose switching and amplifier transistors
 BD241A BD241C NPN power transistors Features. NPN transistors Applications Audio, general purpose switching and amplifier transistors Description The devices are manufactured in Planar technology with
BD241A BD241C NPN power transistors Features. NPN transistors Applications Audio, general purpose switching and amplifier transistors Description The devices are manufactured in Planar technology with
Bob York. Transistor Basics - BJTs
 ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
PHOTOTRANSISTOR OPTOCOUPLERS
 MCT2 MCT2E MCT20 MCT27 WHITE PACKAGE (-M SUFFIX) BLACK PACKAGE (NO -M SUFFIX) DESCRIPTION The MCT2XXX series optoisolators consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode driving a silicon phototransistor
MCT2 MCT2E MCT20 MCT27 WHITE PACKAGE (-M SUFFIX) BLACK PACKAGE (NO -M SUFFIX) DESCRIPTION The MCT2XXX series optoisolators consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode driving a silicon phototransistor
Lecture 21: Junction Field Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 21 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 21: Junction Fiel Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier As mentione in Lecture 16, there are two major families of transistors. We ve worke with BJTs
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 21 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 21: Junction Fiel Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier As mentione in Lecture 16, there are two major families of transistors. We ve worke with BJTs
DATA SHEET. BST50; BST51; BST52 NPN Darlington transistors DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product specification Supersedes data of 2001 Feb 20.
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D109 Supersedes data of 2001 Feb 20 2004 Dec 09 FEATURES High current (max. 0.5 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V) Integrated diode and resistor. APPLICATIONS
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D109 Supersedes data of 2001 Feb 20 2004 Dec 09 FEATURES High current (max. 0.5 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V) Integrated diode and resistor. APPLICATIONS
DATA SHEET. BC875; BC879 NPN Darlington transistors DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product specification Supersedes data of 1999 May 28.
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D186 Supersedes data of 1999 May 28 2004 Nov 05 FEATURES High DC current gain (min. 1000) High current (max. 1 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V) Integrated
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D186 Supersedes data of 1999 May 28 2004 Nov 05 FEATURES High DC current gain (min. 1000) High current (max. 1 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V) Integrated
The two simplest atoms. Electron shells and Orbits. Electron shells and Orbits
 EET140/ET1 Electronics Semiconductors and Diodes Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology Department Prepared by textbook based on Electronics Devices by Floyd, Prentice Hall, 7 th edition.
EET140/ET1 Electronics Semiconductors and Diodes Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology Department Prepared by textbook based on Electronics Devices by Floyd, Prentice Hall, 7 th edition.
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 Class B Amplifier (Push-Pull Emitter Follower) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
Class B Amplifier (Push-Pull Emitter Follower) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
Transistor amplifiers: Biasing and Small Signal Model
 Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FT are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly. Then, similar FT
Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FT are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly. Then, similar FT
Diode Circuits. Operating in the Reverse Breakdown region. (Zener Diode)
 Diode Circuits Operating in the Reverse Breakdown region. (Zener Diode) In may applications, operation in the reverse breakdown region is highly desirable. The reverse breakdown voltage is relatively insensitive
Diode Circuits Operating in the Reverse Breakdown region. (Zener Diode) In may applications, operation in the reverse breakdown region is highly desirable. The reverse breakdown voltage is relatively insensitive
TIP41, TIP41A, TIP41B, TIP41C (NPN); TIP42, TIP42A, TIP42B, TIP42C (PNP) Complementary Silicon Plastic Power Transistors
 TIP41, TIP41A, TIP41B, TIP41C (NPN); TIP42, TIP42A, TIP42B, TIP42C (PNP) Complementary Silicon Plastic Power Transistors Designed for use in general purpose amplifier and switching applications. Features
TIP41, TIP41A, TIP41B, TIP41C (NPN); TIP42, TIP42A, TIP42B, TIP42C (PNP) Complementary Silicon Plastic Power Transistors Designed for use in general purpose amplifier and switching applications. Features
Taping code. Reel size (mm) 2SCR513P MPT3 4540 T100 180 12 1,000 NC
 2SCR53P NPN.0A 50 Middle Power Transistor Datasheet Outline Parameter alue MPT3 CEO 50 I C.0A Base Collector Emitter Features ) Suitable for Middle Power Driver 2) Complementary PNP Types : 2SAR53P 3)
2SCR53P NPN.0A 50 Middle Power Transistor Datasheet Outline Parameter alue MPT3 CEO 50 I C.0A Base Collector Emitter Features ) Suitable for Middle Power Driver 2) Complementary PNP Types : 2SAR53P 3)
Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design
 Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design 1 Some Random Observations Conditions for stabilized voltage source biasing Emitter resistance, R E, is needed. Base voltage source will have finite
Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design 1 Some Random Observations Conditions for stabilized voltage source biasing Emitter resistance, R E, is needed. Base voltage source will have finite
Basic DC Motor Circuits. Living with the Lab Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu
 Basic DC Motor Circuits Living with the Lab Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu DC Motor Learning Objectives Explain the role of a snubber diode Describe how PWM controls DC motor
Basic DC Motor Circuits Living with the Lab Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu DC Motor Learning Objectives Explain the role of a snubber diode Describe how PWM controls DC motor
BJT Amplifier Circuits
 JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
Basic DC Motor Circuits
 Basic DC Motor Circuits Living with the Lab Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu DC Motor Learning Objectives Explain the role of a snubber diode Describe how PWM controls DC motor
Basic DC Motor Circuits Living with the Lab Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu DC Motor Learning Objectives Explain the role of a snubber diode Describe how PWM controls DC motor
2STBN15D100. Low voltage NPN power Darlington transistor. Features. Application. Description
 Low voltage NPN power Darlington transistor Features Good h FE linearity High f T frequency Monolithic Darlington configuration with integrated antiparallel collector-emitter diode TAB Application Linear
Low voltage NPN power Darlington transistor Features Good h FE linearity High f T frequency Monolithic Darlington configuration with integrated antiparallel collector-emitter diode TAB Application Linear
Electronics. Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit. LD Physics Leaflets P4.2.1.1
 Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS IN ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
2N6056. NPN Darlington Silicon Power Transistor DARLINGTON 8 AMPERE SILICON POWER TRANSISTOR 80 VOLTS, 100 WATTS
 NPN Darlington Silicon Power Transistor The NPN Darlington silicon power transistor is designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. High DC Current Gain h FE = 3000
NPN Darlington Silicon Power Transistor The NPN Darlington silicon power transistor is designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. High DC Current Gain h FE = 3000
Figure 1: Common-base amplifier.
 The Common-Base Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of a single stage common-base amplifier. The object is to solve for the small-signal voltage gain, input resistance, and output
The Common-Base Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of a single stage common-base amplifier. The object is to solve for the small-signal voltage gain, input resistance, and output
TLP504A,TLP504A 2. Programmable Controllers AC / DC Input Module Solid State Relay. Pin Configurations (top view) 2002-09-25
 TOSHIBA Photocoupler GaAs Ired & Photo Transistor TLP4A,TLP4A 2 TLP4A,TLP4A 2 Programmable Controllers AC / DC Input Module Solid State Relay Unit in mm The TOSHIBA TLP4A and TLP4A 2 consists of a photo
TOSHIBA Photocoupler GaAs Ired & Photo Transistor TLP4A,TLP4A 2 TLP4A,TLP4A 2 Programmable Controllers AC / DC Input Module Solid State Relay Unit in mm The TOSHIBA TLP4A and TLP4A 2 consists of a photo
Regulated D.C. Power Supply
 442 17 Principles of Electronics Regulated D.C. Power Supply 17.1 Ordinary D.C. Power Supply 17.2 Important Terms 17.3 Regulated Power Supply 17.4 Types of Voltage Regulators 17.5 Zener Diode Voltage Regulator
442 17 Principles of Electronics Regulated D.C. Power Supply 17.1 Ordinary D.C. Power Supply 17.2 Important Terms 17.3 Regulated Power Supply 17.4 Types of Voltage Regulators 17.5 Zener Diode Voltage Regulator
BUX48/48A BUV48A/V48AFI
 BUX48/48A BU48A/48AFI HIGH POWER NPN SILICON TRANSISTORS STMicroelectronics PREFERRED SALESTYPES NPN TRANSISTOR HIGH OLTAGE CAPABILITY HIGH CURRENT CAPABILITY FAST SWITCHING SPEED APPLICATIONS SWITCH MODE
BUX48/48A BU48A/48AFI HIGH POWER NPN SILICON TRANSISTORS STMicroelectronics PREFERRED SALESTYPES NPN TRANSISTOR HIGH OLTAGE CAPABILITY HIGH CURRENT CAPABILITY FAST SWITCHING SPEED APPLICATIONS SWITCH MODE
2N2222A. Small Signal Switching Transistor. NPN Silicon. MIL PRF 19500/255 Qualified Available as JAN, JANTX, and JANTXV. http://onsemi.com.
 Small Signal Switching Transistor NPN Silicon Features MILPRF19/ Qualified Available as JAN, JANTX, and JANTXV COLLECTOR MAXIMUM RATINGS (T A = unless otherwise noted) Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
Small Signal Switching Transistor NPN Silicon Features MILPRF19/ Qualified Available as JAN, JANTX, and JANTXV COLLECTOR MAXIMUM RATINGS (T A = unless otherwise noted) Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
BJT Amplifier Circuits
 JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
Field-Effect (FET) transistors
 Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
MPS2222, MPS2222A. NPN Silicon. Pb Free Packages are Available* http://onsemi.com. Features MAXIMUM RATINGS MARKING DIAGRAMS THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
 , is a Preferred Device General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* COLLECTOR 3 MAXIMUM RATINGS CollectorEmitter Voltage CollectorBase Voltage Rating Symbol Value Unit
, is a Preferred Device General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* COLLECTOR 3 MAXIMUM RATINGS CollectorEmitter Voltage CollectorBase Voltage Rating Symbol Value Unit
DATA SHEET. MMBT3904 NPN switching transistor DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product data sheet Supersedes data of 2002 Oct 04. 2004 Feb 03.
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET dbook, halfpage M3D088 Supersedes data of 2002 Oct 04 2004 Feb 03 FEATURES Collector current capability I C = 200 ma Collector-emitter voltage V CEO = 40 V. APPLICATIONS
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET dbook, halfpage M3D088 Supersedes data of 2002 Oct 04 2004 Feb 03 FEATURES Collector current capability I C = 200 ma Collector-emitter voltage V CEO = 40 V. APPLICATIONS
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
DATA SHEET. PBSS5540Z 40 V low V CEsat PNP transistor DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product data sheet Supersedes data of 2001 Jan 26. 2001 Sep 21.
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET fpage M3D87 PBSS554Z 4 V low V CEsat PNP transistor Supersedes data of 21 Jan 26 21 Sep 21 FEATURES Low collector-emitter saturation voltage High current capability Improved
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET fpage M3D87 PBSS554Z 4 V low V CEsat PNP transistor Supersedes data of 21 Jan 26 21 Sep 21 FEATURES Low collector-emitter saturation voltage High current capability Improved
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 15. BJT Structure and Fabrication
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 15 Lecture Outline Now move on to bipolar junction transistor (BJT) Strategy for next few lectures similar to diode: structure and processing, basic operation,
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 15 Lecture Outline Now move on to bipolar junction transistor (BJT) Strategy for next few lectures similar to diode: structure and processing, basic operation,
BD434/436/438. Symbol Parameter Value Units V CBO Collector-Base Voltage : BD434 : BD436 : BD438
 Medium Power Linear and Switching Applications Complement to BD433, BD435 and BD437 respectively 1 TO26 1. Emitter 2.Collector 3.Base PNP Epitaxial Silicon Transistor Absolute Maximum Ratings T C =25 C
Medium Power Linear and Switching Applications Complement to BD433, BD435 and BD437 respectively 1 TO26 1. Emitter 2.Collector 3.Base PNP Epitaxial Silicon Transistor Absolute Maximum Ratings T C =25 C
BDX33/A/B/C. Symbol Parameter Value Units V CBO Collector-Base Voltage : BDX33 : BDX33A : BDX33B : BDX33C
 Power Linear and Switching Applications High Gain General Purpose Power Darlington TR Complement to BDX34/34A/34B/34C respectively 1 TO-220 1.Base 2.Collector 3.Emitter NPN Epitaxial Silicon Transistor
Power Linear and Switching Applications High Gain General Purpose Power Darlington TR Complement to BDX34/34A/34B/34C respectively 1 TO-220 1.Base 2.Collector 3.Emitter NPN Epitaxial Silicon Transistor
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET BC856; BC857; BC858
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET Supersedes data of 23 Apr 9 24 Jan 16 FEATURES Low current (max. 1 ma) Low voltage (max. 65 V). APPLICATIONS General purpose switching and amplification. PINNING PIN
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET Supersedes data of 23 Apr 9 24 Jan 16 FEATURES Low current (max. 1 ma) Low voltage (max. 65 V). APPLICATIONS General purpose switching and amplification. PINNING PIN
Theory of Transistors and Other Semiconductor Devices
 Theory of Transistors and Other Semiconductor Devices 1. SEMICONDUCTORS 1.1. Metals and insulators 1.1.1. Conduction in metals Metals are filled with electrons. Many of these, typically one or two per
Theory of Transistors and Other Semiconductor Devices 1. SEMICONDUCTORS 1.1. Metals and insulators 1.1.1. Conduction in metals Metals are filled with electrons. Many of these, typically one or two per
