Solution to Selected Questions: CHAPTER 12 MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND OLIGOPOLY
|
|
|
- Melinda Bell
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chulalongkorn University: BBA International Program, Faculty of Commerce and Accountancy 900 (Section ) Chairat Aemkulwat Economics I: Microeconomics Spring 05 Solution to Selected Questions: CHAPTER MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND OLIGOPOLY Suppose all firms in a monopolistically competitive industry were merged into one large firm Would that new firm produce as many different brands? Would it produce only a single brand? Explain Monopolistic competition is defined by product differentiation Each firm earns economic profit by distinguishing its brand from all other brands This distinction can arise from underlying differences in the product or from differences in advertising If these competitors merge into a single firm, the resulting monopolist would not produce as many brands, since too much brand competition is internecine (mutually destructive) However, it is unlikely that only one brand would be produced after the merger Producing several brands with different prices and characteristics is one method of splitting the market into sets of customers with different price elasticities The monopolist can sell to more consumers and maximize overall profit by producing multiple brands and practicing a form of price discrimination 3 A monopolist can produce at a constant average (and marginal) cost of AC = MC = $5 It faces a market demand curve given by Q = 53 P a Calculate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for this monopolist Also calculate its profits First solve for the inverse demand curve, P = 53 Q Then the marginal revenue curve has the same intercept and twice the slope: MR = 53 Q Marginal cost is a constant $5 Setting MR = MC, find the optimal quantity: 53 Q = 5, or Q = 4 Substitute Q = 4 into the demand function to find price: P = 53 4 = $9 Assuming fixed costs are zero, profits are equal to = TR TC = (9)(4) (5)(4) = $576 b Suppose a second firm enters the market Let Q be the output of the first firm and Q be the output of the second Market demand is now given by Q + Q = 53 P Assuming that this second firm has the same costs as the first, write the profits of each firm as functions of Q and Q
2 When the second firm enters, price can be written as a function of the output of both firms: P = 53 Q Q We may write the profit functions for the two firms: and PQ CQ 53 Q Q Q 5Q, or 48Q Q QQ PQ CQ 53 Q Q Q 5Q, or 48Q Q QQ c Suppose (as in the Cournot model) that each firm chooses its profit-maximizing level of output on the assumption that its competitor s output is fixed Find each firm s reaction curve (ie, the rule that gives its desired output in terms of its competitor s output) Under the Cournot assumption, each firm treats the output of the other firm as a constant in its maximization calculations Therefore, Firm chooses Q to maximize in part (b) with Q being treated as a constant The change in with respect to a change in Q is 48 Q Q Q 0, or Q Q 4 This equation is the reaction function for Firm, which generates the profitmaximizing level of output, given the output of Firm Because the problem is symmetric, the reaction function for Firm is Q Q 4 d Calculate the Cournot equilibrium (ie, the values of Q and Q for which each firm is doing as well as it can given its competitor s output) What are the resulting market price and profits of each firm? Solve for the values of Q and Q that satisfy both reaction functions by substituting Firm s reaction function into the function for Firm : By symmetry, Q = 6 Q 4 4 Q, or Q 6 To determine the price, substitute Q and Q into the demand equation: P = = $ Profit for Firm is therefore i = PQ i C(Q i ) = i = ()(6) (5)(6) = $56 Firm s profit is the same, so total industry profit is + = $56 + $56 = $5 e Suppose there are N firms in the industry, all with the same constant marginal cost, MC = $5 Find the Cournot equilibrium How much will each firm produce, what will be the market price, and how much profit will each firm earn? Also, show that as N becomes large, the market price approaches the price that would prevail under perfect competition If there are N identical firms, then the price in the market will be P 53 Q Q Q N Profits for the i th firm are given by
3 i PQ i CQ i, i 53Q i Q Q i Q Q i Q i Q N Q i 5Q i Differentiating to obtain the necessary first-order condition for profit maximization, Solving for Q i, i Q i 53 Q Q Qi QN 5 0 Q i 4 Q Q i Q i Q N If all firms face the same costs, they will all produce the same level of output, ie, Q i = Q* Therefore, Q* 4 N Q*, or Q* 48 N Q*, or 48 N Q* 48, or Q* N Now substitute Q = NQ* for total output in the demand function: P 53 N 48 N Total profits are T = PQ C(Q) = P(NQ*) 5(NQ*) or or T = 53 N 48 N T = 48 N N 48 N 5N 48 N + or 48 N N 48 N T = 48 Notice that with N firms N N N 48 N N =, 304 N N and that, as N increases (N ) Similarly, with Q 48 N N Q = 48 3
4 as N, Finally, P N N P = = 5, N T,304, N so as N, T = $0 In perfect competition, we know that profits are zero and price equals marginal cost Here, T = $0 and P = MC = 5 Thus, when N approaches infinity, this market approaches a perfectly competitive one 5 Two firms compete in selling identical widgets They choose their output levels Q and Q simultaneously and face the demand curve P = 30 Q where Q = Q + Q Until recently, both firms had zero marginal costs Recent environmental regulations have increased Firm s marginal cost to $5 Firm s marginal cost remains constant at zero True or false: As a result, the market price will rise to the monopoly level Surprisingly, this is true However, it occurs only because the marginal cost for Firm is $5 or more If the market were monopolized before the environmental regulations, the marginal revenue for the monopolist would be MR = 30 Q Profit maximization implies MR = MC, or 30 Q = 0 Therefore, Q = 5, and (using the demand curve) P = $5 The situation after the environmental regulations is a Cournot game where Firm 's marginal costs are zero and Firm 's marginal costs are $5 We need to find the best response functions: Firm s revenue is PQ (30 Q Q )Q 30Q Q Q Q, and its marginal revenue is given by: MR 30 Q Q Profit maximization implies MR = MC or 30 Q Q 0 Q 5 Q, which is Firm s best response function Firm s revenue function is symmetric to that of Firm and hence MR 30 Q Q Profit maximization implies MR = MC, or 4
5 30 Q Q 5 Q 75 Q, which is Firm s best response function Cournot equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the best response functions Substituting for Q in the response function for Firm yields: Q 75 05(5 Q ) Thus Q = 0 and Q = 5 P = 30 Q Q = $5, which is the monopoly price 7 Suppose that two competing firms, A and B, produce a homogeneous good Both firms have a marginal cost of MC $50 Describe what would happen to output and price in each of the following situations if the firms are at (i) Cournot equilibrium, (ii) collusive equilibrium, and (iii) Bertrand equilibrium a Because Firm A must increase wages, its MC increases to $80 (i) In a Cournot equilibrium you must think about the effect on the reaction functions, as illustrated in Figure 5 of the text When Firm A experiences an increase in marginal cost, its reaction function will shift inward The quantity produced by Firm A will decrease and the quantity produced by Firm B will increase Total quantity produced will decrease and price will increase (ii) In a collusive equilibrium, the two firms will collectively act like a monopolist When the marginal cost of Firm A increases, Firm A will reduce its production to zero, because Firm B can produce at a lower marginal cost Because Firm B can produce the entire industry output at a marginal cost of $50, there will be no change in output or price However, the firms will have to come to some agreement on how to share the profit earned by B (iii) Before the increase in Firm A s costs, both firms would charge a price equal to marginal cost (P $50) because the good is homogeneous After Firm A s marginal cost increases, Firm B will raise its price to $7999 (or some price just below $80) and take all sales away from Firm A Firm A would lose money on each unit sold at any price below its marginal cost of $80, so it will produce nothing b The marginal cost of both firms increases (i) Again refer to Figure 5 The increase in the marginal cost of both firms will shift both reaction functions inward Both firms will decrease quantity produced and price will increase (ii) When marginal cost increases, both firms will produce less and price will increase, as in the monopoly case (iii) Price will increase to the new level of marginal cost and quantity will decrease c The demand curve shifts to the right (i) This is the opposite of the case in part b In this situation, both reaction functions will shift outward and both will produce a higher quantity Price will tend to increase (ii) Both firms will increase the quantity produced as demand and marginal revenue increase Price will also tend to increase (iii) Both firms will supply more output Given that marginal cost remains the same, the price will not change 5
6 Two firms compete by choosing price Their demand functions are Q = 0 P + P and Q = 0 + P P where P and P are the prices charged by each firm, respectively, and Q and Q are the resulting demands Note that the demand for each good depends only on the difference in prices; if the two firms colluded and set the same price, they could make that price as high as they wanted, and earn infinite profits Marginal costs are zero a Suppose the two firms set their prices at the same time Find the resulting Nash equilibrium What price will each firm charge, how much will it sell, and what will its profit be? (Hint: Maximize the profit of each firm with respect to its price) To determine the Nash equilibrium in prices, first calculate the reaction function for each firm, then solve for price With zero marginal cost, profit for Firm is: 0P P P P P Q P 0 P P Marginal revenue is the slope of the total revenue function (here it is the derivative of the profit function with respect to P because total cost is zero): MR = 0 P + P At the profit-maximizing price, MR = 0 Therefore, 0 P P This is Firm s reaction function Because Firm is symmetric to Firm, its 0 P reaction function is P Substituting Firm s reaction function into that of Firm : 0 P 0 P P 0 5, so P = $0 4 By symmetry, P = $0 To determine the quantity produced by each firm, substitute P and P into the demand functions: Q = = 0 and Q = = 0 Profits for Firm are P Q = $400, and, by symmetry, profits for Firm are also $400 b Suppose Firm sets its price first and then Firm sets its price What price will each firm charge, how much will it sell, and what will its profit be? If Firm sets its price first, it takes Firm s reaction function into account Firm s profit function is: P 0 P 0 P 30P P To determine the profit-maximizing price, find the change in profit with respect to a change in price: 6
7 d dp 30 P Set this expression equal to zero to find the profit-maximizing price: 30 P = 0, or P = $30 Substitute P in Firm s reaction function to find P : 0 30 P $5 At these prices, Q = = 5 and Q = = 5 Profits are = (30)(5) = $450 and = (5)(5) = $65 If Firm must set its price first, Firm is able to undercut Firm and gain a larger market share However, both firms make greater profits than they did in part (a), where they chose prices simultaneously c Suppose you are one of these firms and that there are three ways you could play the game: (i) Both firms set price at the same time; (ii) You set price first; or (iii) Your competitor sets price first If you could choose among these options, which would you prefer? Explain why Your first choice should be (iii), and your second choice should be (ii) (Compare the Nash profits in part (a), $400, with profits in part (b), $450 and $65) From the reaction functions, we know that the price leader provokes a price increase in the follower By being able to move second, however, the follower increases price by less than the leader, and hence undercuts the leader Both firms enjoy increased profits, but the follower does better 7
Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
 Chapter Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Review Questions. What are the characteristics of a monopolistically competitive market? What happens to the equilibrium price and quantity in such a market
Chapter Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Review Questions. What are the characteristics of a monopolistically competitive market? What happens to the equilibrium price and quantity in such a market
Oligopoly: How do firms behave when there are only a few competitors? These firms produce all or most of their industry s output.
 Topic 8 Chapter 13 Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition Econ 203 Topic 8 page 1 Oligopoly: How do firms behave when there are only a few competitors? These firms produce all or most of their industry
Topic 8 Chapter 13 Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition Econ 203 Topic 8 page 1 Oligopoly: How do firms behave when there are only a few competitors? These firms produce all or most of their industry
Economics 203: Intermediate Microeconomics I Lab Exercise #11. Buy Building Lease F1 = 500 F1 = 750 Firm 2 F2 = 500 F2 = 400
 Page 1 March 19, 2012 Section 1: Test Your Understanding Economics 203: Intermediate Microeconomics I Lab Exercise #11 The following payoff matrix represents the long-run payoffs for two duopolists faced
Page 1 March 19, 2012 Section 1: Test Your Understanding Economics 203: Intermediate Microeconomics I Lab Exercise #11 The following payoff matrix represents the long-run payoffs for two duopolists faced
Price competition with homogenous products: The Bertrand duopoly model [Simultaneous move price setting duopoly]
![Price competition with homogenous products: The Bertrand duopoly model [Simultaneous move price setting duopoly] Price competition with homogenous products: The Bertrand duopoly model [Simultaneous move price setting duopoly]](/thumbs/24/4353364.jpg) ECON9 (Spring 0) & 350 (Tutorial ) Chapter Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly (Part ) Price competition with homogenous products: The Bertrand duopoly model [Simultaneous move price setting duopoly]
ECON9 (Spring 0) & 350 (Tutorial ) Chapter Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly (Part ) Price competition with homogenous products: The Bertrand duopoly model [Simultaneous move price setting duopoly]
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 9. Basic Oligopoly Models
 Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 9 Basic Oligopoly Models Overview I. Conditions for Oligopoly? II. Role of Strategic Interdependence III. Profit Maximization in Four Oligopoly Settings
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 9 Basic Oligopoly Models Overview I. Conditions for Oligopoly? II. Role of Strategic Interdependence III. Profit Maximization in Four Oligopoly Settings
Chapter 9 Basic Oligopoly Models
 Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 9 Basic Oligopoly Models McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Overview I. Conditions for Oligopoly?
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 9 Basic Oligopoly Models McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Overview I. Conditions for Oligopoly?
12 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
 12 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Read Pindyck and Rubinfeld (2012), Chapter 12 09/04/2015 CHAPTER 12 OUTLINE 12.1 Monopolistic Competition 12.2 Oligopoly 12.3 Price Competition 12.4 Competition
12 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Read Pindyck and Rubinfeld (2012), Chapter 12 09/04/2015 CHAPTER 12 OUTLINE 12.1 Monopolistic Competition 12.2 Oligopoly 12.3 Price Competition 12.4 Competition
Market Structure: Duopoly and Oligopoly
 WSG10 7/7/03 4:24 PM Page 145 10 Market Structure: Duopoly and Oligopoly OVERVIEW An oligopoly is an industry comprising a few firms. A duopoly, which is a special case of oligopoly, is an industry consisting
WSG10 7/7/03 4:24 PM Page 145 10 Market Structure: Duopoly and Oligopoly OVERVIEW An oligopoly is an industry comprising a few firms. A duopoly, which is a special case of oligopoly, is an industry consisting
Mikroekonomia B by Mikolaj Czajkowski. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Mikroekonomia B by Mikolaj Czajkowski Test 12 - Oligopoly Name Group MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The market structure in which
Mikroekonomia B by Mikolaj Czajkowski Test 12 - Oligopoly Name Group MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The market structure in which
Microeconomics. Lecture Outline. Claudia Vogel. Winter Term 2009/2010. Part III Market Structure and Competitive Strategy
 Microeconomics Claudia Vogel EUV Winter Term 2009/2010 Claudia Vogel (EUV) Microeconomics Winter Term 2009/2010 1 / 25 Lecture Outline Part III Market Structure and Competitive Strategy 12 Monopolistic
Microeconomics Claudia Vogel EUV Winter Term 2009/2010 Claudia Vogel (EUV) Microeconomics Winter Term 2009/2010 1 / 25 Lecture Outline Part III Market Structure and Competitive Strategy 12 Monopolistic
CHAPTER 10 MARKET POWER: MONOPOLY AND MONOPSONY
 CHAPTER 10 MARKET POWER: MONOPOLY AND MONOPSONY EXERCISES 3. A monopolist firm faces a demand with constant elasticity of -.0. It has a constant marginal cost of $0 per unit and sets a price to maximize
CHAPTER 10 MARKET POWER: MONOPOLY AND MONOPSONY EXERCISES 3. A monopolist firm faces a demand with constant elasticity of -.0. It has a constant marginal cost of $0 per unit and sets a price to maximize
INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS COMPONENT: THE INTERACTIVE TEXTBOOK
 UNIT EC407, LEVEL 2 INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS COMPONENT: THE INTERACTIVE TEXTBOOK Semester 1 1998/99 Lecturer: K. Hinde Room: 427 Northumberland Building Tel: 0191 2273936 email: [email protected] Web Page:
UNIT EC407, LEVEL 2 INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS COMPONENT: THE INTERACTIVE TEXTBOOK Semester 1 1998/99 Lecturer: K. Hinde Room: 427 Northumberland Building Tel: 0191 2273936 email: [email protected] Web Page:
Market Structure: Perfect Competition and Monopoly
 WSG8 7/7/03 4:34 PM Page 113 8 Market Structure: Perfect Competition and Monopoly OVERVIEW One of the most important decisions made by a manager is how to price the firm s product. If the firm is a profit
WSG8 7/7/03 4:34 PM Page 113 8 Market Structure: Perfect Competition and Monopoly OVERVIEW One of the most important decisions made by a manager is how to price the firm s product. If the firm is a profit
The Basics of Game Theory
 Sloan School of Management 15.010/15.011 Massachusetts Institute of Technology RECITATION NOTES #7 The Basics of Game Theory Friday - November 5, 2004 OUTLINE OF TODAY S RECITATION 1. Game theory definitions:
Sloan School of Management 15.010/15.011 Massachusetts Institute of Technology RECITATION NOTES #7 The Basics of Game Theory Friday - November 5, 2004 OUTLINE OF TODAY S RECITATION 1. Game theory definitions:
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 8. Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets
 Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 8 Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets I. Perfect Competition Overview Characteristics and profit outlook. Effect
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 8 Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets I. Perfect Competition Overview Characteristics and profit outlook. Effect
c. Given your answer in part (b), what do you anticipate will happen in this market in the long-run?
 Perfect Competition Questions Question 1 Suppose there is a perfectly competitive industry where all the firms are identical with identical cost curves. Furthermore, suppose that a representative firm
Perfect Competition Questions Question 1 Suppose there is a perfectly competitive industry where all the firms are identical with identical cost curves. Furthermore, suppose that a representative firm
Oligopoly: Cournot/Bertrand/Stackelberg
 Outline Alternative Market Models Wirtschaftswissenschaften Humboldt Universität zu Berlin March 5, 2006 Outline 1 Introduction Introduction Alternative Market Models 2 Game, Reaction Functions, Solution
Outline Alternative Market Models Wirtschaftswissenschaften Humboldt Universität zu Berlin March 5, 2006 Outline 1 Introduction Introduction Alternative Market Models 2 Game, Reaction Functions, Solution
Economics II: Micro Fall 2009 Exercise session 5. Market with a sole supplier is Monopolistic.
 Economics II: Micro Fall 009 Exercise session 5 VŠE 1 Review Optimal production: Independent of the level of market concentration, optimal level of production is where MR = MC. Monopoly: Market with a
Economics II: Micro Fall 009 Exercise session 5 VŠE 1 Review Optimal production: Independent of the level of market concentration, optimal level of production is where MR = MC. Monopoly: Market with a
CHAPTER 6 MARKET STRUCTURE
 CHAPTER 6 MARKET STRUCTURE CHAPTER SUMMARY This chapter presents an economic analysis of market structure. It starts with perfect competition as a benchmark. Potential barriers to entry, that might limit
CHAPTER 6 MARKET STRUCTURE CHAPTER SUMMARY This chapter presents an economic analysis of market structure. It starts with perfect competition as a benchmark. Potential barriers to entry, that might limit
ECON 312: Oligopolisitic Competition 1. Industrial Organization Oligopolistic Competition
 ECON 312: Oligopolisitic Competition 1 Industrial Organization Oligopolistic Competition Both the monopoly and the perfectly competitive market structure has in common is that neither has to concern itself
ECON 312: Oligopolisitic Competition 1 Industrial Organization Oligopolistic Competition Both the monopoly and the perfectly competitive market structure has in common is that neither has to concern itself
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MBA 640 Survey of Microeconomics Fall 2006, Quiz 6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A monopoly is best defined as a firm that
MBA 640 Survey of Microeconomics Fall 2006, Quiz 6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A monopoly is best defined as a firm that
Chapter 7 Monopoly, Oligopoly and Strategy
 Chapter 7 Monopoly, Oligopoly and Strategy After reading Chapter 7, MONOPOLY, OLIGOPOLY AND STRATEGY, you should be able to: Define the characteristics of Monopoly and Oligopoly, and explain why the are
Chapter 7 Monopoly, Oligopoly and Strategy After reading Chapter 7, MONOPOLY, OLIGOPOLY AND STRATEGY, you should be able to: Define the characteristics of Monopoly and Oligopoly, and explain why the are
A Detailed Price Discrimination Example
 A Detailed Price Discrimination Example Suppose that there are two different types of customers for a monopolist s product. Customers of type 1 have demand curves as follows. These demand curves include
A Detailed Price Discrimination Example Suppose that there are two different types of customers for a monopolist s product. Customers of type 1 have demand curves as follows. These demand curves include
All these models were characterized by constant returns to scale technologies and perfectly competitive markets.
 Economies of scale and international trade In the models discussed so far, differences in prices across countries (the source of gains from trade) were attributed to differences in resources/technology.
Economies of scale and international trade In the models discussed so far, differences in prices across countries (the source of gains from trade) were attributed to differences in resources/technology.
Oligopoly and Strategic Pricing
 R.E.Marks 1998 Oligopoly 1 R.E.Marks 1998 Oligopoly Oligopoly and Strategic Pricing In this section we consider how firms compete when there are few sellers an oligopolistic market (from the Greek). Small
R.E.Marks 1998 Oligopoly 1 R.E.Marks 1998 Oligopoly Oligopoly and Strategic Pricing In this section we consider how firms compete when there are few sellers an oligopolistic market (from the Greek). Small
How To Understand The Theory Of Economic Theory
 MICROECONOMICS II. ELTE Faculty of Social Sciences, Department of Economics Microeconomics II. MARKET THEORY AND MARKETING, PART 3 Author: Supervised by February 2011 Prepared by:, using Jack Hirshleifer,
MICROECONOMICS II. ELTE Faculty of Social Sciences, Department of Economics Microeconomics II. MARKET THEORY AND MARKETING, PART 3 Author: Supervised by February 2011 Prepared by:, using Jack Hirshleifer,
Midterm Exam #1 - Answers
 Page 1 of 9 Midterm Exam #1 Answers Instructions: Answer all questions directly on these sheets. Points for each part of each question are indicated, and there are 1 points total. Budget your time. 1.
Page 1 of 9 Midterm Exam #1 Answers Instructions: Answer all questions directly on these sheets. Points for each part of each question are indicated, and there are 1 points total. Budget your time. 1.
Chapter 6 Competitive Markets
 Chapter 6 Competitive Markets After reading Chapter 6, COMPETITIVE MARKETS, you should be able to: List and explain the characteristics of Perfect Competition and Monopolistic Competition Explain why a
Chapter 6 Competitive Markets After reading Chapter 6, COMPETITIVE MARKETS, you should be able to: List and explain the characteristics of Perfect Competition and Monopolistic Competition Explain why a
Table of Contents MICRO ECONOMICS
 economicsentrance.weebly.com Basic Exercises Micro Economics AKG 09 Table of Contents MICRO ECONOMICS Budget Constraint... 4 Practice problems... 4 Answers... 4 Supply and Demand... 7 Practice Problems...
economicsentrance.weebly.com Basic Exercises Micro Economics AKG 09 Table of Contents MICRO ECONOMICS Budget Constraint... 4 Practice problems... 4 Answers... 4 Supply and Demand... 7 Practice Problems...
Figure: Computing Monopoly Profit
 Name: Date: 1. Most electric, gas, and water companies are examples of: A) unregulated monopolies. B) natural monopolies. C) restricted-input monopolies. D) sunk-cost monopolies. Use the following to answer
Name: Date: 1. Most electric, gas, and water companies are examples of: A) unregulated monopolies. B) natural monopolies. C) restricted-input monopolies. D) sunk-cost monopolies. Use the following to answer
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The four-firm concentration ratio equals the percentage of the value of accounted for by the four
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The four-firm concentration ratio equals the percentage of the value of accounted for by the four
ECON 103, 2008-2 ANSWERS TO HOME WORK ASSIGNMENTS
 ECON 103, 2008-2 ANSWERS TO HOME WORK ASSIGNMENTS Due the Week of June 23 Chapter 8 WRITE [4] Use the demand schedule that follows to calculate total revenue and marginal revenue at each quantity. Plot
ECON 103, 2008-2 ANSWERS TO HOME WORK ASSIGNMENTS Due the Week of June 23 Chapter 8 WRITE [4] Use the demand schedule that follows to calculate total revenue and marginal revenue at each quantity. Plot
Competition and Regulation. Lecture 2: Background on imperfect competition
 Competition and Regulation Lecture 2: Background on imperfect competition Monopoly A monopolist maximizes its profits, choosing simultaneously quantity and prices, taking the Demand as a contraint; The
Competition and Regulation Lecture 2: Background on imperfect competition Monopoly A monopolist maximizes its profits, choosing simultaneously quantity and prices, taking the Demand as a contraint; The
Final Exam 15 December 2006
 Eco 301 Name Final Exam 15 December 2006 120 points. Please write all answers in ink. You may use pencil and a straight edge to draw graphs. Allocate your time efficiently. Part 1 (10 points each) 1. As
Eco 301 Name Final Exam 15 December 2006 120 points. Please write all answers in ink. You may use pencil and a straight edge to draw graphs. Allocate your time efficiently. Part 1 (10 points each) 1. As
Economics 201 Fall 2010 Introduction to Economic Analysis Problem Set #6 Due: Wednesday, November 3
 Economics 201 Fall 2010 Introduction to Economic Analysis Jeffrey Parker Problem Set #6 Due: Wednesday, November 3 1. Cournot Duopoly. Bartels and Jaymes are two individuals who one day discover a stream
Economics 201 Fall 2010 Introduction to Economic Analysis Jeffrey Parker Problem Set #6 Due: Wednesday, November 3 1. Cournot Duopoly. Bartels and Jaymes are two individuals who one day discover a stream
Chapter 13 Market Structure and Competition
 Chapter 13 Market Structure and Competition Solutions to Review Questions 1. Explain why, at a Cournot equilibrium with two firms, neither firm would have any regret about its output choice after it observes
Chapter 13 Market Structure and Competition Solutions to Review Questions 1. Explain why, at a Cournot equilibrium with two firms, neither firm would have any regret about its output choice after it observes
1 Cournot Oligopoly with n firms
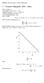 BEE07, Microeconomics, Dieter Balkenborg Cournot Oligopoly with n firms firmi soutput: q i totaloutput: q=q +q + +q n opponent soutput: q i =q q i =Σ j i q i constantmarginalcostsoffirmi: c i inverse demand
BEE07, Microeconomics, Dieter Balkenborg Cournot Oligopoly with n firms firmi soutput: q i totaloutput: q=q +q + +q n opponent soutput: q i =q q i =Σ j i q i constantmarginalcostsoffirmi: c i inverse demand
CHAPTER 12 MARKETS WITH MARKET POWER Microeconomics in Context (Goodwin, et al.), 2 nd Edition
 CHAPTER 12 MARKETS WITH MARKET POWER Microeconomics in Context (Goodwin, et al.), 2 nd Edition Chapter Summary Now that you understand the model of a perfectly competitive market, this chapter complicates
CHAPTER 12 MARKETS WITH MARKET POWER Microeconomics in Context (Goodwin, et al.), 2 nd Edition Chapter Summary Now that you understand the model of a perfectly competitive market, this chapter complicates
Week 7 - Game Theory and Industrial Organisation
 Week 7 - Game Theory and Industrial Organisation The Cournot and Bertrand models are the two basic templates for models of oligopoly; industry structures with a small number of firms. There are a number
Week 7 - Game Theory and Industrial Organisation The Cournot and Bertrand models are the two basic templates for models of oligopoly; industry structures with a small number of firms. There are a number
9.1 Cournot and Bertrand Models with Homogeneous Products
 1 Chapter 9 Quantity vs. Price Competition in Static Oligopoly Models We have seen how price and output are determined in perfectly competitive and monopoly markets. Most markets are oligopolistic, however,
1 Chapter 9 Quantity vs. Price Competition in Static Oligopoly Models We have seen how price and output are determined in perfectly competitive and monopoly markets. Most markets are oligopolistic, however,
PART A: For each worker, determine that worker's marginal product of labor.
 ECON 3310 Homework #4 - Solutions 1: Suppose the following indicates how many units of output y you can produce per hour with different levels of labor input (given your current factory capacity): PART
ECON 3310 Homework #4 - Solutions 1: Suppose the following indicates how many units of output y you can produce per hour with different levels of labor input (given your current factory capacity): PART
Models of Imperfect Competition
 Models of Imperfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Models of Imperfect Competition So far, we have discussed two forms of market competition that are difficult to observe in practice Perfect
Models of Imperfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Models of Imperfect Competition So far, we have discussed two forms of market competition that are difficult to observe in practice Perfect
Economics Chapter 7 Market Structures. Perfect competition is a in which a large number of all produce.
 Economics Chapter 7 Market Structures Perfect competition is a in which a large number of all produce. There are Four Conditions for Perfect Competition: 1. 2. 3. 4. Barriers to Entry Factors that make
Economics Chapter 7 Market Structures Perfect competition is a in which a large number of all produce. There are Four Conditions for Perfect Competition: 1. 2. 3. 4. Barriers to Entry Factors that make
Pricing and Output Decisions: i Perfect. Managerial Economics: Economic Tools for Today s Decision Makers, 4/e By Paul Keat and Philip Young
 Chapter 9 Pricing and Output Decisions: i Perfect Competition and Monopoly M i l E i E i Managerial Economics: Economic Tools for Today s Decision Makers, 4/e By Paul Keat and Philip Young Pricing and
Chapter 9 Pricing and Output Decisions: i Perfect Competition and Monopoly M i l E i E i Managerial Economics: Economic Tools for Today s Decision Makers, 4/e By Paul Keat and Philip Young Pricing and
Practice Questions Week 8 Day 1
 Practice Questions Week 8 Day 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The characteristics of a market that influence the behavior of market participants
Practice Questions Week 8 Day 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The characteristics of a market that influence the behavior of market participants
Chapter 11 Pricing Strategies for Firms with Market Power
 Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 11 Pricing Strategies for Firms with Market Power McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Overview I. Basic
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 11 Pricing Strategies for Firms with Market Power McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Overview I. Basic
ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS
 ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 23-1 Briefly indicate the basic characteristics of pure competition, pure monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly. Under which of these market classifications
ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 23-1 Briefly indicate the basic characteristics of pure competition, pure monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly. Under which of these market classifications
MPP 801 Monopoly Kevin Wainwright Study Questions
 MPP 801 Monopoly Kevin Wainwright Study Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The marginal revenue facing a monopolist A) is
MPP 801 Monopoly Kevin Wainwright Study Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The marginal revenue facing a monopolist A) is
Cooleconomics.com Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly. Contents:
 Cooleconomics.com Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Contents: Monopolistic Competition Attributes Short Run performance Long run performance Excess capacity Importance of Advertising Socialist Critique
Cooleconomics.com Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Contents: Monopolistic Competition Attributes Short Run performance Long run performance Excess capacity Importance of Advertising Socialist Critique
Thus MR(Q) = P (Q) Q P (Q 1) (Q 1) < P (Q) Q P (Q) (Q 1) = P (Q), since P (Q 1) > P (Q).
 A monopolist s marginal revenue is always less than or equal to the price of the good. Marginal revenue is the amount of revenue the firm receives for each additional unit of output. It is the difference
A monopolist s marginal revenue is always less than or equal to the price of the good. Marginal revenue is the amount of revenue the firm receives for each additional unit of output. It is the difference
Examples on Monopoly and Third Degree Price Discrimination
 1 Examples on Monopoly and Third Degree Price Discrimination This hand out contains two different parts. In the first, there are examples concerning the profit maximizing strategy for a firm with market
1 Examples on Monopoly and Third Degree Price Discrimination This hand out contains two different parts. In the first, there are examples concerning the profit maximizing strategy for a firm with market
Profit maximization in different market structures
 Profit maximization in different market structures In the cappuccino problem as well in your team project, demand is clearly downward sloping if the store wants to sell more drink, it has to lower the
Profit maximization in different market structures In the cappuccino problem as well in your team project, demand is clearly downward sloping if the store wants to sell more drink, it has to lower the
Economics 431 Fall 2003 1st midterm Answer Key
 Economics 431 Fall 003 1st midterm Answer Key 1) (7 points) Consider an industry that consists of a large number of identical firms. In the long run competitive equilibrium, a firm s marginal cost must
Economics 431 Fall 003 1st midterm Answer Key 1) (7 points) Consider an industry that consists of a large number of identical firms. In the long run competitive equilibrium, a firm s marginal cost must
Monopoly WHY MONOPOLIES ARISE
 In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: Why do monopolies arise? Why is MR < P for a monopolist? How do monopolies choose their P and Q? How do monopolies affect society s well-being?
In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: Why do monopolies arise? Why is MR < P for a monopolist? How do monopolies choose their P and Q? How do monopolies affect society s well-being?
Learning Objectives. Chapter 6. Market Structures. Market Structures (cont.) The Two Extremes: Perfect Competition and Pure Monopoly
 Chapter 6 The Two Extremes: Perfect Competition and Pure Monopoly Learning Objectives List the four characteristics of a perfectly competitive market. Describe how a perfect competitor makes the decision
Chapter 6 The Two Extremes: Perfect Competition and Pure Monopoly Learning Objectives List the four characteristics of a perfectly competitive market. Describe how a perfect competitor makes the decision
4. Market Structures. Learning Objectives 4-63. Market Structures
 1. Supply and Demand: Introduction 3 2. Supply and Demand: Consumer Demand 33 3. Supply and Demand: Company Analysis 43 4. Market Structures 63 5. Key Formulas 81 2014 Allen Resources, Inc. All rights
1. Supply and Demand: Introduction 3 2. Supply and Demand: Consumer Demand 33 3. Supply and Demand: Company Analysis 43 4. Market Structures 63 5. Key Formulas 81 2014 Allen Resources, Inc. All rights
N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Economics. Chapter 15. MONOPOLY
 N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Economics Chapter 15. MONOPOLY Solutions to Problems and Applications 1. The following table shows revenue, costs, and profits, where quantities are in thousands, and total
N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Economics Chapter 15. MONOPOLY Solutions to Problems and Applications 1. The following table shows revenue, costs, and profits, where quantities are in thousands, and total
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chap 13 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly These questions may include topics that were not covered in class and may not be on the exam. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
Chap 13 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly These questions may include topics that were not covered in class and may not be on the exam. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
Understanding Economics 2nd edition by Mark Lovewell and Khoa Nguyen
 Understanding Economics 2nd edition by Mark Lovewell and Khoa Nguyen Chapter 5 Perfect Competition Chapter Objectives! In this chapter you will: " Consider the four market structures, and the main differences
Understanding Economics 2nd edition by Mark Lovewell and Khoa Nguyen Chapter 5 Perfect Competition Chapter Objectives! In this chapter you will: " Consider the four market structures, and the main differences
Do not open this exam until told to do so.
 Do not open this exam until told to do so. Department of Economics College of Social and Applied Human Sciences K. Annen, Winter 004 Final (Version ): Intermediate Microeconomics (ECON30) Solutions Final
Do not open this exam until told to do so. Department of Economics College of Social and Applied Human Sciences K. Annen, Winter 004 Final (Version ): Intermediate Microeconomics (ECON30) Solutions Final
Chapter 15: Monopoly WHY MONOPOLIES ARISE HOW MONOPOLIES MAKE PRODUCTION AND PRICING DECISIONS
 Chapter 15: While a competitive firm is a taker, a monopoly firm is a maker. A firm is considered a monopoly if... it is the sole seller of its product. its product does not have close substitutes. The
Chapter 15: While a competitive firm is a taker, a monopoly firm is a maker. A firm is considered a monopoly if... it is the sole seller of its product. its product does not have close substitutes. The
An increase in the number of students attending college. shifts to the left. An increase in the wage rate of refinery workers.
 1. Which of the following would shift the demand curve for new textbooks to the right? a. A fall in the price of paper used in publishing texts. b. A fall in the price of equivalent used text books. c.
1. Which of the following would shift the demand curve for new textbooks to the right? a. A fall in the price of paper used in publishing texts. b. A fall in the price of equivalent used text books. c.
Cournot s model of oligopoly
 Cournot s model of oligopoly Single good produced by n firms Cost to firm i of producing q i units: C i (q i ), where C i is nonnegative and increasing If firms total output is Q then market price is P(Q),
Cournot s model of oligopoly Single good produced by n firms Cost to firm i of producing q i units: C i (q i ), where C i is nonnegative and increasing If firms total output is Q then market price is P(Q),
Chapter 16 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
 Chapter 16 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Market Structure Market structure refers to the physical characteristics of the market within which firms interact It is determined by the number of firms
Chapter 16 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Market Structure Market structure refers to the physical characteristics of the market within which firms interact It is determined by the number of firms
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 11 Monopoly practice Davidson spring2007 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A monopoly industry is characterized by 1) A)
Chapter 11 Monopoly practice Davidson spring2007 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A monopoly industry is characterized by 1) A)
MODULE 64: INTRODUCTION TO OLIGOPOLY Schmidty School of Economics. Wednesday, December 4, 2013 9:20:15 PM Central Standard Time
 MODULE 64: INTRODUCTION TO OLIGOPOLY Schmidty School of Economics Learning Targets I Can Understand why oligopolists have an incentive to act in ways that reduce their combined profit. Explain why oligopolies
MODULE 64: INTRODUCTION TO OLIGOPOLY Schmidty School of Economics Learning Targets I Can Understand why oligopolists have an incentive to act in ways that reduce their combined profit. Explain why oligopolies
BEE2017 Intermediate Microeconomics 2
 BEE2017 Intermediate Microeconomics 2 Dieter Balkenborg Sotiris Karkalakos Yiannis Vailakis Organisation Lectures Mon 14:00-15:00, STC/C Wed 12:00-13:00, STC/D Tutorials Mon 15:00-16:00, STC/106 (will
BEE2017 Intermediate Microeconomics 2 Dieter Balkenborg Sotiris Karkalakos Yiannis Vailakis Organisation Lectures Mon 14:00-15:00, STC/C Wed 12:00-13:00, STC/D Tutorials Mon 15:00-16:00, STC/106 (will
Final Exam (Version 1) Answers
 Final Exam Economics 101 Fall 2003 Wallace Final Exam (Version 1) Answers 1. The marginal revenue product equals A) total revenue divided by total product (output). B) marginal revenue divided by marginal
Final Exam Economics 101 Fall 2003 Wallace Final Exam (Version 1) Answers 1. The marginal revenue product equals A) total revenue divided by total product (output). B) marginal revenue divided by marginal
Equilibrium: Illustrations
 Draft chapter from An introduction to game theory by Martin J. Osborne. Version: 2002/7/23. [email protected] http://www.economics.utoronto.ca/osborne Copyright 1995 2002 by Martin J. Osborne.
Draft chapter from An introduction to game theory by Martin J. Osborne. Version: 2002/7/23. [email protected] http://www.economics.utoronto.ca/osborne Copyright 1995 2002 by Martin J. Osborne.
AGEC 105 Spring 2016 Homework 7. 1. Consider a monopolist that faces the demand curve given in the following table.
 AGEC 105 Spring 2016 Homework 7 1. Consider a monopolist that faces the demand curve given in the following table. a. Fill in the table by calculating total revenue and marginal revenue at each price.
AGEC 105 Spring 2016 Homework 7 1. Consider a monopolist that faces the demand curve given in the following table. a. Fill in the table by calculating total revenue and marginal revenue at each price.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Economics 103 Spring 2012: Multiple choice review questions for final exam. Exam will cover chapters on perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition and oligopoly up to the Nash equilibrium
Economics 103 Spring 2012: Multiple choice review questions for final exam. Exam will cover chapters on perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition and oligopoly up to the Nash equilibrium
CHAPTER 11 PRICE AND OUTPUT IN MONOPOLY, MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION, AND PERFECT COMPETITION
 CHAPTER 11 PRICE AND OUTPUT IN MONOPOLY, MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION, AND PERFECT COMPETITION Chapter in a Nutshell Now that we understand the characteristics of different market structures, we ask the question
CHAPTER 11 PRICE AND OUTPUT IN MONOPOLY, MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION, AND PERFECT COMPETITION Chapter in a Nutshell Now that we understand the characteristics of different market structures, we ask the question
AP Microeconomics Chapter 12 Outline
 I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. The significance of resource pricing. B. How the marginal revenue productivity of a resource relates to a firm s demand for that resource.
I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. The significance of resource pricing. B. How the marginal revenue productivity of a resource relates to a firm s demand for that resource.
Chapter 8. Competitive Firms and Markets
 Chapter 8. Competitive Firms and Markets We have learned the production function and cost function, the question now is: how much to produce such that firm can maximize his profit? To solve this question,
Chapter 8. Competitive Firms and Markets We have learned the production function and cost function, the question now is: how much to produce such that firm can maximize his profit? To solve this question,
Pure Competition urely competitive markets are used as the benchmark to evaluate market
 R. Larry Reynolds Pure Competition urely competitive markets are used as the benchmark to evaluate market P performance. It is generally believed that market structure influences the behavior and performance
R. Larry Reynolds Pure Competition urely competitive markets are used as the benchmark to evaluate market P performance. It is generally believed that market structure influences the behavior and performance
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK SET #4
 Sloan School of Management 15.010/15.011 Massachusetts Institute of Technology SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK SET #4 1. a. If the markets are open to free trade, the monopolist cannot keep the markets separated.
Sloan School of Management 15.010/15.011 Massachusetts Institute of Technology SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK SET #4 1. a. If the markets are open to free trade, the monopolist cannot keep the markets separated.
Pre-Test Chapter 23 ed17
 Pre-Test Chapter 23 ed17 Multiple Choice Questions 1. The kinked-demand curve model of oligopoly: A. assumes a firm's rivals will ignore a price cut but match a price increase. B. embodies the possibility
Pre-Test Chapter 23 ed17 Multiple Choice Questions 1. The kinked-demand curve model of oligopoly: A. assumes a firm's rivals will ignore a price cut but match a price increase. B. embodies the possibility
Rutgers University Economics 102: Introductory Microeconomics Professor Altshuler Fall 2003
 Rutgers University Economics 102: Introductory Microeconomics Professor Altshuler Fall 2003 Answers to Problem Set 11 Chapter 16 2. a. If there were many suppliers of diamonds, price would equal marginal
Rutgers University Economics 102: Introductory Microeconomics Professor Altshuler Fall 2003 Answers to Problem Set 11 Chapter 16 2. a. If there were many suppliers of diamonds, price would equal marginal
 1 Monopoly Why Monopolies Arise? Monopoly is a rm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutes. The fundamental cause of monopoly is barriers to entry: A monopoly remains the only seller
1 Monopoly Why Monopolies Arise? Monopoly is a rm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutes. The fundamental cause of monopoly is barriers to entry: A monopoly remains the only seller
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 11 Perfect Competition - Sample Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Perfect competition is an industry with A) a
Chapter 11 Perfect Competition - Sample Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Perfect competition is an industry with A) a
Employment and Pricing of Inputs
 Employment and Pricing of Inputs Previously we studied the factors that determine the output and price of goods. In chapters 16 and 17, we will focus on the factors that determine the employment level
Employment and Pricing of Inputs Previously we studied the factors that determine the output and price of goods. In chapters 16 and 17, we will focus on the factors that determine the employment level
Chapter. Perfect Competition CHAPTER IN PERSPECTIVE
 Perfect Competition Chapter 10 CHAPTER IN PERSPECTIVE In Chapter 10 we study perfect competition, the market that arises when the demand for a product is large relative to the output of a single producer.
Perfect Competition Chapter 10 CHAPTER IN PERSPECTIVE In Chapter 10 we study perfect competition, the market that arises when the demand for a product is large relative to the output of a single producer.
Equilibrium of a firm under perfect competition in the short-run. A firm is under equilibrium at that point where it maximizes its profits.
 Equilibrium of a firm under perfect competition in the short-run. A firm is under equilibrium at that point where it maximizes its profits. Profit depends upon two factors Revenue Structure Cost Structure
Equilibrium of a firm under perfect competition in the short-run. A firm is under equilibrium at that point where it maximizes its profits. Profit depends upon two factors Revenue Structure Cost Structure
Solution to Homework Set 7
 Solution to Homework Set 7 Managerial Economics Fall 011 1. An industry consists of five firms with sales of $00 000, $500 000, $400 000, $300 000, and $100 000. a) points) Calculate the Herfindahl-Hirschman
Solution to Homework Set 7 Managerial Economics Fall 011 1. An industry consists of five firms with sales of $00 000, $500 000, $400 000, $300 000, and $100 000. a) points) Calculate the Herfindahl-Hirschman
CHAPTER 11: MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND OLIGOPOLY
 CHAPTER 11: MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND OLIGOPOLY Introduction While perfect competition and monopoly represent the extremes of market structures, most American firms are found in the two market structures
CHAPTER 11: MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND OLIGOPOLY Introduction While perfect competition and monopoly represent the extremes of market structures, most American firms are found in the two market structures
or, put slightly differently, the profit maximizing condition is for marginal revenue to equal marginal cost:
 Chapter 9 Lecture Notes 1 Economics 35: Intermediate Microeconomics Notes and Sample Questions Chapter 9: Profit Maximization Profit Maximization The basic assumption here is that firms are profit maximizing.
Chapter 9 Lecture Notes 1 Economics 35: Intermediate Microeconomics Notes and Sample Questions Chapter 9: Profit Maximization Profit Maximization The basic assumption here is that firms are profit maximizing.
The Analysis of the Article Microsoft's Aggressive New Pricing Strategy Using. Microeconomic Theory
 2 The Analysis of the Article Microsoft's Aggressive New Pricing Strategy Using Microeconomic Theory I. Introduction: monopolistic power as a means of getting high profits II. The review of the article
2 The Analysis of the Article Microsoft's Aggressive New Pricing Strategy Using Microeconomic Theory I. Introduction: monopolistic power as a means of getting high profits II. The review of the article
R&D cooperation with unit-elastic demand
 R&D cooperation with unit-elastic demand Georg Götz This draft: September 005. Abstract: This paper shows that R&D cooperation leads to the monopoly outcome in terms of price and quantity if demand is
R&D cooperation with unit-elastic demand Georg Götz This draft: September 005. Abstract: This paper shows that R&D cooperation leads to the monopoly outcome in terms of price and quantity if demand is
b. Cost of Any Action is measure in foregone opportunities c.,marginal costs and benefits in decision making
 1 Economics 130-Windward Community College Review Sheet for the Final Exam This final exam is comprehensive in nature and in scope. The test will be divided into two parts: a multiple-choice section and
1 Economics 130-Windward Community College Review Sheet for the Final Exam This final exam is comprehensive in nature and in scope. The test will be divided into two parts: a multiple-choice section and
Marginal cost. Average cost. Marginal revenue 10 20 40
 Economics 101 Fall 2011 Homework #6 Due: 12/13/2010 in lecture Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework
Economics 101 Fall 2011 Homework #6 Due: 12/13/2010 in lecture Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework
13 MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND OLIGOPOLY. Chapter. Key Concepts
 Chapter 13 MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND OLIGOPOLY Key Concepts Monopolistic Competition The market structure of most industries lies between the extremes of perfect competition and monopoly. Monopolistic
Chapter 13 MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND OLIGOPOLY Key Concepts Monopolistic Competition The market structure of most industries lies between the extremes of perfect competition and monopoly. Monopolistic
ECON101 STUDY GUIDE 7 CHAPTER 14
 ECON101 STUDY GUIDE 7 CHAPTER 14 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An oligopoly firm is similar to a monopolistically competitive
ECON101 STUDY GUIDE 7 CHAPTER 14 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An oligopoly firm is similar to a monopolistically competitive
A2 Micro Business Economics Diagrams
 A2 Micro Business Economics Diagrams Advice on drawing diagrams in the exam The right size for a diagram is ½ of a side of A4 don t make them too small if needed, move onto a new side of paper rather than
A2 Micro Business Economics Diagrams Advice on drawing diagrams in the exam The right size for a diagram is ½ of a side of A4 don t make them too small if needed, move onto a new side of paper rather than
ECON 600 Lecture 5: Market Structure - Monopoly. Monopoly: a firm that is the only seller of a good or service with no close substitutes.
 I. The Definition of Monopoly ECON 600 Lecture 5: Market Structure - Monopoly Monopoly: a firm that is the only seller of a good or service with no close substitutes. This definition is abstract, just
I. The Definition of Monopoly ECON 600 Lecture 5: Market Structure - Monopoly Monopoly: a firm that is the only seller of a good or service with no close substitutes. This definition is abstract, just
Chapter 11. T he economy that we. The World of Oligopoly: Preliminaries to Successful Entry. 11.1 Production in a Nonnatural Monopoly Situation
 Chapter T he economy that we are studying in this book is still extremely primitive. At the present time, it has only a few productive enterprises, all of which are monopolies. This economy is certainly
Chapter T he economy that we are studying in this book is still extremely primitive. At the present time, it has only a few productive enterprises, all of which are monopolies. This economy is certainly
OLIGOPOLY. Nature of Oligopoly. What Causes Oligopoly?
 CH 11: OLIGOPOLY 1 OLIGOPOLY When a few big firms dominate the market, the situation is called oligopoly. Any action of one firm will affect the performance of other firms. If one of the firms reduces
CH 11: OLIGOPOLY 1 OLIGOPOLY When a few big firms dominate the market, the situation is called oligopoly. Any action of one firm will affect the performance of other firms. If one of the firms reduces
BPE_MIC1 Microeconomics 1 Fall Semester 2011
 Masaryk University - Brno Department of Economics Faculty of Economics and Administration BPE_MIC1 Microeconomics 1 Fall Semester 2011 Final Exam - 05.12.2011, 9:00-10:30 a.m. Test A Guidelines and Rules:
Masaryk University - Brno Department of Economics Faculty of Economics and Administration BPE_MIC1 Microeconomics 1 Fall Semester 2011 Final Exam - 05.12.2011, 9:00-10:30 a.m. Test A Guidelines and Rules:
Monopoly and Monopsony Labor Market Behavior
 Monopoly and Monopsony abor Market Behavior 1 Introduction For the purposes of this handout, let s assume that firms operate in just two markets: the market for their product where they are a seller) and
Monopoly and Monopsony abor Market Behavior 1 Introduction For the purposes of this handout, let s assume that firms operate in just two markets: the market for their product where they are a seller) and
MICROECONOMICS II. "B"
 MICROECONOMICS II. "B" Sponsored by a Grant TÁMOP-4.1.2-08/2/A/KMR-2009-0041 Course Material Developed by Department of Economics, Faculty of Social Sciences, Eötvös Loránd University Budapest (ELTE) Department
MICROECONOMICS II. "B" Sponsored by a Grant TÁMOP-4.1.2-08/2/A/KMR-2009-0041 Course Material Developed by Department of Economics, Faculty of Social Sciences, Eötvös Loránd University Budapest (ELTE) Department
Chapter 13 Oligopoly 1
 Chapter 13 Oligopoly 1 4. Oligopoly A market structure with a small number of firms (usually big) Oligopolists know each other: Strategic interaction: actions of one firm will trigger re-actions of others
Chapter 13 Oligopoly 1 4. Oligopoly A market structure with a small number of firms (usually big) Oligopolists know each other: Strategic interaction: actions of one firm will trigger re-actions of others
