MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE FEMALE GENITAL TRACT I March 12, 2009
|
|
|
- Theodora Hardy
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE FEMALE GENITAL TRACT I March 12, 2009 Faculty Copy GOALS: 1. Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions of the female genital tract. 2. Correlate the structural changes in the organs with clinical manifestations of the diseases. OBJECTIVES: 1. Review the normal gross and histologic anatomy of the uterus, ovary and fallopian tube. 2. Describe the morpholic changes of endometriosis. 3. Describe the morpholic changes of infectious diseases of the female genital tract. 4. Describe the morphologic characteristics of benign neoplasms of the uterus. 5. Describe the morphologic characteristics of malignant neoplasms of the uterus. CASE 1 Review of normal proliferative endometrium CASE 2 CHIEF COMPLAINT: "My husband and I have been trying to have a baby for the past five years." HISTORY: The patient is a 27-year-old woman who presents with the inability to conceive a child during the past five years. She and her husband have regular sexual relations (1-2 times per week) and very much desire to have children. She describes her marriage as loving and warm. Menstrual history: Menarche occurred at age 13. Menstrual cycles have been fairly regular since age 17. Average cycle is days, with menses being 5 days in duration. Menstrual flow has been consistent, requiring 3-4 pads initially and gradually tapering off. She has had premenstrual cramping and cramping pain the first day of menses since her teen years. For the past year or two she has experienced a more diffuse pain throughout her lower pelvis and more severe menstrual pain. Sh has nausea and low back pain during menstruation. Page 1
2 She notes abdominal pain at times during intercourse and when she moves her bowels. Intermittent vaginal spotting occurs but no vaginal discharge. At age 24 she was involved in an automobile accident which required abdominal surgery to stop bleeding from "my intestines. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: Patient is a thin, well nourished woman. She is alert and in no distress. Vital signs: Blood pressure 116/82, Apical heart rate 76/minute and regular, respiratory rate 12/minute, temperature 98.2 F. Abdomen normal bowel sounds, no masses or tenderness. 3.5 cm long parasagital scar in the left lower quadrant represents a healed surgical incision. Several small nodules are felt below the scar (patient says her scar "hurts when I menstruate"). Pelvic exam reveals normal external genitalia. Speculum exam reveals normal vaginal and cervical mucosa. The external os is small and round. Bimanual exam reveals slight tender nodularity in cul-de-sac, recto-vaginal septum and uterosacral ligaments. The uterus is retroverted and of normal size. The right adnexa is tender but the left is not. The rectal exam produces pain when the anterior wall is palpated. 1. What is the major clinical problem? (As far as the patient is concerned) Infertility 2. What are the additional major clinical complaints? Pelvic pain; painful menstruation 3. Develop a differential diagnosis for pelvic pain in a woman. Ruptured ovarian cyst. Twisted ovarian cyst. Ovarian cancer. Ectopic pregnancy Pelvic inflammatory disease. Adenomyosis Endometriosis GI tract conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome and Crohn s disease. Cystitis/urethritis. Chronic pelvic pain without obvious pathology. Premenstrual syndrome. 4. What helps differentiate the cause of pelvic pain? Describe some clinical distinguishing features of causes of pelvic pain. Although all these conditions may result in pain, most are associated with specific pathologic changes in organs and can be differentiated with a good history, physical exam and diagnostic procedures such as ultrasound or laparoscopy. Page 2
3 A twisted ovarian cyst or ruptured cyst is generally sudden in onset, severe and located to one side of the midline. Ovarian cancer pain may be more vague in description but associated with an adnexal mass. The pain of ectopic pregnancy may be severe and located in the lower quadrant of the abdomen. Hypotension and peritoneal signs may be present. Historically, the patient likely missed her last period. PID often produces bilateral pain and may be associated with adnexal masses (tenderness) and vaginal discharge. The pain of adenomyosis and endometriosis often occurs around menstruation. The pain may be associated with clinical findings reflecting other organ involvement, e.g., dyschezia. Infertility often accompanies endometriosis nodules in the parametrial structures and adnexal masses can be palpated. Diseases primarily affecting other organ systems cause pain but should have unique historical and physical findings. For example, irritable bowel syndrome may cause crampy abdominal pain, constipation and may have some psychologic component. For completeness sake, two additional conditions are included, chronic pelvic pain without obvious pathology and premenstrual syndrome. The purpose is to indicate to the students that chronic pelvic pain without structural changes in female organs is real and sometimes debilitating condition. 5. What is this patient s likely diagnosis? Endometriosis 6. Correlate the pathology with the clinical findings in this case. Nodules palpated beneath the patient s healed surgical scar and tender nodularity palpated on bimanual exam and may all represent endometrial deposits. On the virtual microsocopy section, endometrial tissue is present in a healed scar. A histologic diagnosis of endometriosis can be made if 2 of the following 3 features are identified: endometrial glands, stroma, hemosiderin pigment. CASE 3 Page 3
4 CHIEF COMPLAINT: I'm bleeding from my vagina. HISTORY: The patient is a 69 year-old woman who presents with intermittent vaginal bleeding of 9 months duration. Initially she noted spotting of bright red blood which seemed to occur several times each month. No particular activity precipitates the bleeding and she experiences no other symptoms. She states, "I just thought my period came back." She is twelve years post-menopause. She has never been pregnant. After three months of spotting, she sought care from a physician who placed her on "estrogen pills to control my bleeding." He also gave her "iron pills. The vaginal bleeding continued and contained small clots. The bleeding was always irregular She sought a second opinion because the bleeding progressed. She has been treated for diabetes mellitus, type 2 since age 52. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: The patient is obese, alert and in no distress. Vital signs: Blood pressure 146/90, pulse 90/minute, respiratory rate 18/minute, temperature 98 F. Abdomen is soft and round. Organomegaly and masses are not palpable. Pelvic exam reveals external genitalia consistent with the age of the patient. The vaginal introitus is narrowed and only admits two fingers. A small speculum allows visualization of the cervix. The ectocervix is smooth. Blood is noted in the os. Bimanual exam reveals a symmetrically enlarged, non-tender uterus. The adnexae are not palpable. A rectocele or cystocele are not present. LAB TESTS: Hemoglobin 9.8 grams/dl Hematocrit 30% MCV 79 fl 1. What is the major clinical problem? (As far as the patient is concerned) Vaginal bleeding (Abnormal uterine bleeding) 2. Develop a differential diagnosis for this problem. Endometrial polyp Endometrial hyperplasia Endometrial carcinoma Leiomyoma (submucosal) Ectopic pregnancy Abnormalities of pregnancy: spontaneous abortion, gestational trophoblastic disease, third trimester hemorrhage (abruptio placenta, placenta previa) Endocervical polyp Cervical carcinoma Dysfunctional uterine bleeding Abnormal uterine bleeding is a common gynecologic problem. Many of these cases during the reproductive years represent a condition known as dysfunctional uterine bleeding. This condition will be discussed by the gynecologists but must be included in the differential diagnosis. There are generally no pathologic changes. Page 4
5 3. What factors may help differentiate the cause of bleeding? Various historical and physical examination findings will help differentiate causes of uterine bleeding: age, reproductive years, obvious pregnancy, timing in cycle, associated findings such as pain, palpable mass or visible lesion on cervix, PAP smear findings. 4. What are the common causes of abnormal uterine bleeding in post-menopausal women? Exogenous estrogens (30%) Atrophic endometritis/vaginitis (30%) Endometrial cancer (15%) Endometrial/ endocervical polyps (10%) Endometrial hyperplasia (5%) 5. What condition must be ruled out in a postmenopausal woman? How? Endometrial cancer; endometrial biopsy 6. A biopsy was peformed on this patient and is found on the virtual microscopy slide. What is your diagnosis? Compare to normal uterus/endometrium (case 1) Endometrial carcinoma (Confluent glands lined by malignant stratified columnar epithelial cells without intervening stroma) 7. List the risk factors for this disease in this patient. Late menopause Nulligravida Diabetes Obesity Hypertension 8. From this patient's history, explain what was wrong with her initial treatment. Why? The initial physician placed the patient on hormone therapy without determining the exact cause of the uterine bleeding. Delay in diagnosis could lead to tumor invasion and metastases. 9. Define the following terms: A. Menorrhagia: cyclic menstrual bleeding that is excessive in amount or duration. B. Hypomenorrhea: decreased menstrual flow; menstrual flow that is less than the norm of 3 to 7 days in duration C. Hypermenorrhea: increased menstrual flow; menstrual flow that is longer than the norm of 3 to 7 days in duration D. Polymenorrhea: regular bleedng that occurs at an interval less than 21 days Page 5
6 E. Oligomenorrhea: bleeding that occurs at an interval greater than 35 days. F. Metrorrhagia: uterine bleeding between periods. G. Menometrorrhagia: uterine bleeding that is irregular in frequency and excessive in amount. H. Postmenopausal bleeding: bleeding occurring more than one year following menopause. CASE 4 CHIEF COMPLAINT: None HISTORY: A 38-year-old woman undergoes a routine, annual gynecologic examination. Her gestational history is as follows: gravida 4, para 3 with one spontaneous abortion. She menstruates every days for 2-4 days. Page 6
7 She experienced three or four episodes of metrorrhagia in the previous year, but no hypermenorrhea. She has a persistent, mild leukorrhea. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: The patient is a moderately obese woman who is alert and in no distress. Vital signs are as follows: blood pressure 136/84, apical heart rate 80/minute and regular, respiratory rate 14/minute, temperature 97.9 F. Examination of the abdomen: It is soft and slightly round; no organomegaly. Pelvic examination reveals normal external genitalia. Speculum exam reveals normal vaginal and cervical mucosa. Bimanual exam reveals an asymmetrically enlarged uterus. The uterus is the size of a 2-3 month gestation and is freely movable. The uterus contains multiple nodules of varying size which are not tender. The adnexae are not palpable. 1. What is the clinical problem? Enlarged, nodular uterus 2. Describe the gross pathology. Uterus with sharply circumscrbied, discrete, round, firm gray-white tumors. They are usually found in the myometrium of the corpus. They can occur in the myometrium (intramural) just beneath the endometrium (submucosal), and beneath the serosa (submucosal). 3. Describe the histologic findings on the virtual microscopy slide. Whorled pattern of smooth muscle bundles 4. What is the diagnosis? Leiomyoma 5. What are potential symptoms of this condition? Abnormal bleeding (submucosal leiomyomas) Pain if blood supply to a leiomyoma is disrupted If large, leiomyomas can compress adjacent organs (such as the bladder resulting in urinary frequency) Impaired fertility CASE 5 (no virtual micoscopy images) HISTORY: The patient is a 25 year-old woman who presents with bilateral lower abdominal pain of 3 days duration. The pain is sometimes sharp but more often dull; it is moderate in intensity and continuous. Movement accentuates the pain which remains localized to the right and left lower quadrants of the abdomen. In addition to the abdominal pain, Page 7
8 the patient has noticed a yellow-white vaginal discharge for two weeks. She also has mild dysuria but no urgency or frequency. The patient relates that she had similar health problems in the past for which she had been treated. Treatment did not require hospitalization. Her gestational history is gravida 0. She is sexually active and does not regularly use condoms. Her last menstrual period was 12 days ago. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: The abdomen is scaphoid and soft. Palpation reveals mild point tenderness in the right and left lower quadrants but no rebound tenderness. No organomegaly. The bowel sounds are normoactive. Pelvic exam reveals normal external genitalia. The vaginal mucosa is hyperemic and covered by a thin, yellow-white exudate. The same exudate flows from the cervical os. Bimanual examination of the corpus/cervix uteri demonstrates normal size but adnexal pain on motion of the cervix. The adnexae are tender by palpation. 1. Develop a differential diagnosis. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Cervicitis Endometriosis Ectopic Pregnancy Urinary tract infection Appendicitis LABORATORY DATA: WBC 13,700/mm3 (reference rage 4,500-11,000/mm3). Urine HCG - negative Gram stain of the vaginal discharge reveals numerous polymorophuclear cells and intracellular, Gram negative diplococci. 2. What is the clinical diagnosis? Pelvic Inflammatory Disease an acute infection of the upper genital tract structures in women involving any or all of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries Findings may include endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, peritonitis, perihepatitis and tubo-ovarian abscess. 3. What microorganism is the most likely etiologic agent in this case? What are other etiologic agents? Neisseria gonorrhoeae Chlamydia trachomatis Genital mycoplasma Enterobacteriaceae Mixed-polymicrobial Page 8
9 4. Describe the pathology. There is marked acute inflammation of the fallopian tube. Grossly, the fimbriated ends of the fallopian tubes are distended with purulent material and adherent to adjacent structures. The serosa is hyperemic and covered with a fibrinous exudate. The inflammation extends to the ovaries. This acute inflammation is superimposed on chronic inflammatory changes. 5. What is the diagnosis? Acute salpingitis 6. What are potential complications of this disease process? Peritonitis Bacteremia Adhesions between pelvic organs and bowel resulting in bowel obstruction Infertility a consequence of chronic PID Page 9
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
K Raja/N Varol FPA 2013. FPA Sydney August 31 2013
 FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Medical criteria for IUCD s Based on the WHO MEC (2004- Annexure 3) system a woman s eligibility for IUCD insertion falls in 4 categories. These categ
 CLIENT ASSESSMENT Ensure that the woman is not pregnant Determine the length and direction of uterus. Ensure that she does not have gonorrhea and chlamydia, and is not a high risk case of STI s Identify
CLIENT ASSESSMENT Ensure that the woman is not pregnant Determine the length and direction of uterus. Ensure that she does not have gonorrhea and chlamydia, and is not a high risk case of STI s Identify
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors
 From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors Uterine Fibroid Tumors A woman s fibroisis condition usually associated with estrogen dominance. Uterine
From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors Uterine Fibroid Tumors A woman s fibroisis condition usually associated with estrogen dominance. Uterine
Endometriosis: An Overview
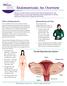 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S.
 Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination
 Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
All you need to know about Endometriosis. Nordica Fertility Centre, Lagos, Asaba, Abuja
 All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
Why would you need a hysterectomy?
 Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps
 Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group
 Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
What could endometriosis mean for me?
 Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
 Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management
 Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Hysterectomy. The time to take care of yourself
 Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries. Simple Cystic Masses
 Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
PRENATAL/WOMEN S HEALTH ROTATION
 PRENATAL/WOMEN S HEALTH ROTATION Course Title: Women s Health Rotation Course Description and goals: This is a 4- week rotation designed to educate the student about the diagnosis, management and treatment
PRENATAL/WOMEN S HEALTH ROTATION Course Title: Women s Health Rotation Course Description and goals: This is a 4- week rotation designed to educate the student about the diagnosis, management and treatment
Timby/Smith: Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 9/E
 Timby/Smith: Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 9/E Chapter 59: Caring for Female Clients With Disorders of the Pelvic Reproductive Structures Slide 1 A Nurse s Role in All Reproductive Disorders Nurse
Timby/Smith: Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 9/E Chapter 59: Caring for Female Clients With Disorders of the Pelvic Reproductive Structures Slide 1 A Nurse s Role in All Reproductive Disorders Nurse
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding)
 Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
This is Jaydess. Patient Information. What is Jaydess? How does Jaydess work?
 , Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
, Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A.
 Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
OVARIAN CANCER IS A MAJOR CAUSE OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN WOMEN. Name of Student HTHSCI 1110 WEBER STATE UNIVERSITY.
 Ovarian Cancer 2 OVARIAN CANCER IS A MAJOR CAUSE OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN WOMEN by Name of Student HTHSCI 1110 WEBER STATE UNIVERSITY Ogden, Utah Instructor s Name Date Ovarian Cancer 2 Background
Ovarian Cancer 2 OVARIAN CANCER IS A MAJOR CAUSE OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN WOMEN by Name of Student HTHSCI 1110 WEBER STATE UNIVERSITY Ogden, Utah Instructor s Name Date Ovarian Cancer 2 Background
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer?
 Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
How do I know if I need to have surgery?
 How do I know if I need to have surgery? Deciding whether or not to have surgery for your bladder, bowel and/or prolapse problems is an individual decision. The success or failure of someone else's operation
How do I know if I need to have surgery? Deciding whether or not to have surgery for your bladder, bowel and/or prolapse problems is an individual decision. The success or failure of someone else's operation
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Specimen collection and transport for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae testing
 Specimen collection and transport for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae testing Overview Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) infections are two of the most common sexually
Specimen collection and transport for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae testing Overview Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) infections are two of the most common sexually
BELIEVE MIDWIFERY SERVICES, LLC
 , LLC TITLE: ADENOMYOSIS EFFECTIVE DATE: May, 2012 POLICY STATEMENT Adenomyosis is a common benign gynecologic disorder that any certified nurse-midwife who provides gynecologic care is likely to see on
, LLC TITLE: ADENOMYOSIS EFFECTIVE DATE: May, 2012 POLICY STATEMENT Adenomyosis is a common benign gynecologic disorder that any certified nurse-midwife who provides gynecologic care is likely to see on
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Uterine Fibroids. More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth.
 Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
WOOD COUNTY SCHOOL OF PRACTICAL NURSING. Medical/Surgical Nursing: Reproductive
 WOOD COUNTY SCHOOL OF PRACTICAL NURSING Medical/Surgical Nursing: Reproductive Time: 19 Hours Theory; 1 Hour Pharmacology IV, (1 Diet Therapy - Integrated.) Placement: Nursing IV. Instructor: Toni Tennant,
WOOD COUNTY SCHOOL OF PRACTICAL NURSING Medical/Surgical Nursing: Reproductive Time: 19 Hours Theory; 1 Hour Pharmacology IV, (1 Diet Therapy - Integrated.) Placement: Nursing IV. Instructor: Toni Tennant,
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids?
 da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM
 DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM NEPHRITIS, NEPHROTIC SYNDROME ANS NEPHROSIS (580 589.9) 580 ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.0 WITH LESION OF PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.4 WITH LESION OF RAPIDLY
DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM NEPHRITIS, NEPHROTIC SYNDROME ANS NEPHROSIS (580 589.9) 580 ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.0 WITH LESION OF PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.4 WITH LESION OF RAPIDLY
Update on Abnormal Uterine Bleeding. Susan M. Sheridan, M.D., F.A.C.O.G Casper Obstetrical and Gynecological Associates Casper, WY
 Update on Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Susan M. Sheridan, M.D., F.A.C.O.G Casper Obstetrical and Gynecological Associates Casper, WY Defining Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) Normal menstrual cycle Frequency
Update on Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Susan M. Sheridan, M.D., F.A.C.O.G Casper Obstetrical and Gynecological Associates Casper, WY Defining Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) Normal menstrual cycle Frequency
Once a woman has had a hysterectomy, she will no longer have menstrual periods and cannot have a child. She no longer needs to use contraception.
 Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
POSTMENOPAUSAL ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO
 POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair
 Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Uterus myomatosus. 10-May-15. Clinical presentation. Incidence. Causes? 3 out of 4 women. Growth rate vary. Most common solid pelvic tumor in women
 Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
3 Lower Abdominal Pain in the First Trimester of Pregnancy
 3 Lower Abdominal Pain in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Sisty J. Moshi INTRODUCTION Abdominal pain in pregnancy is very common. Many of the complications of early pregnancy present with some form of
3 Lower Abdominal Pain in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Sisty J. Moshi INTRODUCTION Abdominal pain in pregnancy is very common. Many of the complications of early pregnancy present with some form of
worry When to Cervical Abnormalities CME Workshop What s the situation? What are the trends? By Dianne Miller, MD, FRCSC In this article:
 CME Workshop When to worry Cervical Abnormalities By Dianne Miller, MD, FRCSC What s the situation? Over 600,000 Papanicolaou s (Pap) smears were performed in British Columbia in 2000. Approximately 13,400
CME Workshop When to worry Cervical Abnormalities By Dianne Miller, MD, FRCSC What s the situation? Over 600,000 Papanicolaou s (Pap) smears were performed in British Columbia in 2000. Approximately 13,400
MHRI IUD Protocol. Migraine with aura Current DVT or PE History of or current breast cancer Active viral hepatitis Severe cirrhosis or liver tumors
 Table of Contents A. Indications B. Contraindications C. Prior to Insertion D. Insertion E. Follow-Up Visit F. Removal G. Re-Insertion H. Complications/Side Effects I. Appendices MHRI IUD Protocol A. Indications
Table of Contents A. Indications B. Contraindications C. Prior to Insertion D. Insertion E. Follow-Up Visit F. Removal G. Re-Insertion H. Complications/Side Effects I. Appendices MHRI IUD Protocol A. Indications
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Get the Facts, Be Informed, Make YOUR Best Decision. Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Ectopic Pregnancy. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
The Centre For Women s Reproductive Care HYSTERECTOMY
 The Centre For Women s Reproductive Care Baringa Private Hospital, 31 Mackays Rd Coffs Harbour NSW 2450 Harvey Ward MB ChB, BSc(Med), FCOG (SA), MMed (O&G), FRANZCOG Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Phone:
The Centre For Women s Reproductive Care Baringa Private Hospital, 31 Mackays Rd Coffs Harbour NSW 2450 Harvey Ward MB ChB, BSc(Med), FCOG (SA), MMed (O&G), FRANZCOG Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Phone:
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
Saint Mary s Hospital. Hysterectomy. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Hysterectomy Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What is a hysterectomy? 4 Why is a hysterectomy necessary? 4 How common is it? 7 Things to consider before having a hysterectomy
Saint Mary s Hospital Hysterectomy Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What is a hysterectomy? 4 Why is a hysterectomy necessary? 4 How common is it? 7 Things to consider before having a hysterectomy
Considering a Hysterectomy?
 Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Pelvic Prolapse
Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Pelvic Prolapse
What are the differences between fibroid and ovarian cyst?
 DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
Cancer Facts for Women
 2006, American Cancer Society, Inc. No.200700-Rev.03/08 The American Cancer Society is the nationwide community-based voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer as a major health problem
2006, American Cancer Society, Inc. No.200700-Rev.03/08 The American Cancer Society is the nationwide community-based voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer as a major health problem
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Simple evaluation and management in premenopausal women
 Objectives Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Simple evaluation and management in premenopausal women Provide a framework to evaluate abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) Review medical and surgical management options
Objectives Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Simple evaluation and management in premenopausal women Provide a framework to evaluate abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) Review medical and surgical management options
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
The menstrual cycle Hypophysis
 Normal endometrium Tumors of the uterine corpus by MB The endometrium comprises the zona functionalis zf (superficial two thirds) ) and the zona basalis zb (deep one third) The zf responds to hormonal
Normal endometrium Tumors of the uterine corpus by MB The endometrium comprises the zona functionalis zf (superficial two thirds) ) and the zona basalis zb (deep one third) The zf responds to hormonal
PILLS & RING INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS ON COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION INCLUDING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS & NUVA RING
 PILLS & RING INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS ON COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION INCLUDING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS & NUVA RING What is combined hormonal contraception? Birth control which contains two hormones
PILLS & RING INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS ON COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION INCLUDING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS & NUVA RING What is combined hormonal contraception? Birth control which contains two hormones
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
A potential treatment for your abnormal uterine bleeding
 TRUCLEAR System A potential treatment for your abnormal uterine bleeding Do You Suffer from Abnormal Uterine Bleeding? What is a Hysteroscopy? What is the TRUCLEAR Procedure? What Happens Before Your
TRUCLEAR System A potential treatment for your abnormal uterine bleeding Do You Suffer from Abnormal Uterine Bleeding? What is a Hysteroscopy? What is the TRUCLEAR Procedure? What Happens Before Your
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up
 Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up What is a Pap Smear? A Pap smear (also known as the Pap test) is a medical procedure in which a sample of cells from a woman's cervix (the end of the
Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up What is a Pap Smear? A Pap smear (also known as the Pap test) is a medical procedure in which a sample of cells from a woman's cervix (the end of the
ENDOMETRIOSIS He who knows endometriosis knows gynecology." Sir William Osler
 ENDOMETRIOSIS He who knows endometriosis knows gynecology." Sir William Osler Dr. Sahni BS DHMS Hons, PGRT (BOM), FF Hom Deputy Chief Medical Officer (H), ONGC Hospital Panvel-410221, Navi Mumbai, INDIA
ENDOMETRIOSIS He who knows endometriosis knows gynecology." Sir William Osler Dr. Sahni BS DHMS Hons, PGRT (BOM), FF Hom Deputy Chief Medical Officer (H), ONGC Hospital Panvel-410221, Navi Mumbai, INDIA
Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair
 Women s Service Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair Information for patients Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a vaginal hysterectomy.
Women s Service Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair Information for patients Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a vaginal hysterectomy.
Physician. Patient HYSTERECTOMY HYSTERECTOMY. Treatment Options Risks and Benefits Experience and Skill
 HYSTERECTOMY Physician Treatment Options Risks and Benefits Experience and Skill Patient Personal Preferences Values and Concerns Lifestyle Choices HYSTERECTOMY Shared Decision Making A process of open
HYSTERECTOMY Physician Treatment Options Risks and Benefits Experience and Skill Patient Personal Preferences Values and Concerns Lifestyle Choices HYSTERECTOMY Shared Decision Making A process of open
Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines your uterus (the endometrium)
Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines your uterus (the endometrium)
SUBSEROSAL FIBROIDS TREATMENT
 INTRODUCTION Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are the most common pelvic mass found in women. Fibroids are benign tumors that arise from the uterine muscular tissue (myometrium). They occur
INTRODUCTION Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are the most common pelvic mass found in women. Fibroids are benign tumors that arise from the uterine muscular tissue (myometrium). They occur
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine
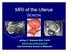 MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Gonorrhoea. Looking after your sexual health
 Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
LIPPES LOOP TRADEMARK. your intrauterine contraceptive
 LIPPES LOOP TRADEMARK your intrauterine contraceptive LIPPES LOOP Patient Information This brochure provides information on the use of In trauterine Contraceptive Devices (lud s). There are other birth
LIPPES LOOP TRADEMARK your intrauterine contraceptive LIPPES LOOP Patient Information This brochure provides information on the use of In trauterine Contraceptive Devices (lud s). There are other birth
