1 H NMR Spectra of Proteins
|
|
|
- Belinda Byrd
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NMR of Proteins
2 Determining Protein Structures by NMR the process of determining a solution structure by NMR is one of measuring many (hundreds/thousands) of short protonproton distances and angles, and restraining the protein structure with these computationally H H.} d
3 1 H NMR Spectra of Proteins 1D, 1 H NMR spectra of even small proteins are impossible to interpret in any comprehensive manner -normally, only gross statements about secondary structure, tertiary structure, etc. can be made simple 1D 1 H experiment ubiquitin (76 amino acids, 8.5 kda) 2D 1 H COSY experiment cytochrome c, 12.5 kda COSY t 1 t 2 for even moderate sized proteins, addition of a second dimension still does not alleviate spectral crowding and overlap in 1 H spectra
4 nd, heteronuclear NMR Spectra of Proteins Modern NMR spectroscopic studies of proteins rely on multidimensional experiments involving 1 H, 13 C, and 15 N nuclei in isotopically labeled proteins These methods provide for signal selection (selectivity) and a means to reduce signal overlap simple 2D 1 H, 15 N HSQC experiment ubiquitin (76 amino acids, 8.5 kda) In order to measure the distances between protons, we need to find out what protons give rise to the signals in the spectra, I.e. we have to assign the protein (figure out the chemical shifts for all of the protons) The methods used are based on heteronuclear spectra
5 Triple Resonance Approach applicable to uniformly isotopically enriched proteins -uniform 13 C and 15 N labeling: spin 1/2 -three nuclei ( 1 H, 15 N, and 13 C) are involved based on magnetization transfer via (mostly) one bond J couplings -most of these couplings are large compared to linewidths for moderate sized proteins (~20 kda) -magnetization transfer is efficient -indirect ( 1 H) detection provides selective chemical shift correlation -spectral degeneracy minimized
6 Uniform Isotopic Labeling of Proteins Proteins can be uniformly isotopically labeled by recombinant expression using defined media -bacterial expression most common -also yeast, and cell-free systems are being developed -minimal media using 13 C 6 glucose as the sole carbon source and 15 NH 4 Cl (or -SO 4 ) as the sole nitrogen source -normally >98% atom excess -also labeled rich media ($$) -for larger proteins, uniform or fractional 2 H labeling also used - 2 H, 13 C glucose and D 2 O
7 1 J and 2 J Couplings in Proteins - these 1 J and 2 J couplings are uniform throughout polypeptides/proteins - these 1 J and 2 J couplings are virtually conformation independent
8 Prototypical Triple Resonance Experiment: HNCA correlates the chemical shifts of 1 H N, 15 N, 13 C α i and 13 C α i-1
9 Prototypical Triple Resonance Experiment: HNCA both 13 C α i and 13 C α i-1 chemical shifts are correlated -the peak for the intra-residue correlation is usually more intense (11 Hz 1 J NCα coupling vs 7 Hz 2 J NCα coupling) 1 H, 15 N-HSQC HNCA
10 Triple Resonance Approach: A Simple Example 2D HNCA projection 3D HNCA
11 Triple Resonance Approach: A Simple Example
12 Triple Resonance Approach: A Simple Example link the correlated shifts numerically.. or visually
13 Triple Resonance Approach: HNCA/HN(CO)CA Example problems: 13 C α chemical shift degeneracy in proteins 13 C α linewidths/resolution -these preclude complete linkage via 13 C α alone -the same is true for 13 C β, 13 C
14 The Nuclear Overhauser Effect The Nuclear Overhauser Effect or Nuclear Overhauser Enhancement is the change (enhancement) of the signal intensity from a given nucleus as a result of exciting or saturating the resonance frequency of another nucleus It is based on through-space interactions The magnitude of the effect is dependent on distance -enhancement depends on 1/r 6, where r is the internuclear distance -thus, the effect is limited to distances of approximately 5Å or less This provides a means to determine if any two protons in a protein are < 5Å apart The basic experiment used for proteins is called a NOESY cytochrome c, 12.5 kda 2D NOESY t 1 τ m t 2 Even for relatively small proteins, the 2D NOESY spectrum is hampered by severe spectral overlap
15 3D NOE Experiments for Distance Restraints -pulse sequences: combine 2D sequences to get 3D sequences -get increased dimensionality and increased resolution without an increase in the number of signals (peaks) NOESY t 1 τ m t 2 HSQC 1 H 15 N τ τ τ τ t 1 /2 t 1 /2 t 2 decouple 1 H t 1 τ m t 3 τ τ τ τ NOESY-HSQC 15 N t 2 /2 t 2 / decouple
16 3D NOE Experiments for Distance Restraints Left: 2D NOESY Far left: 2D plane of 3D NOESY- HMQC ( 1 H, 13 C) - 1 H signals resolved by 13 C chemical shifts of bound 13 C atoms
17 Structure Calculations the primary structural restraint information for high resolution protein structures are the NOE-based distance restraints -additional restraints include angle restraints based on coupling constants, long range restraints based on dipolar couplings, hydrogen bond restraints calculation of structures involves satisfying structural restraints using simulated annealing/ restrained molecular dynamics -a target/energy function including terms for covalent geometry (known bond lengths and bond angles) and experimental restraints is minimized -the molecule is computationally heated/cooled to attempt to find a global minimum the number of restraints is an important indicator of the quality of final structures
18 Practical Aspects of Protein Structure Determination using NMR
19 Introduction NMR vs X-ray crystallography for protein structure determination in an x-ray diffraction pattern, each datum (reflection) contains information about each atom in the asymmetric unit -each atom contributes information that contributes to the intensity of each reflection in an NMR spectrum, each datum (peak) contains information about only a single interatomic distance or angle -the process of determining a solution structure by NMR is one of measuring many small distances and angles one at a time Why use NMR? can t get a crystal / want to work in solution want to look at binding to other proteins/molecules want to understand stability want to measure fast dynamics processes
20 Introduction Some things you should know before you talk to an NMR spectroscopist about determining a structure Protein production Protein purity Isotopic labeling NMR samples / conditions / tubes Simple spectra / evaluation (stability, tertiary structure) Protein size / magnet size
21 Protein production protein sample(s) in theory, as little as a few mg of protein is sufficient -best if the protein sample for NMR is > 1 mm in practice, tens of milligrams (or more) are usually necessary, as are multiple samples -multiple samples if your protein is not stable -multiple samples with different isotopic labeling schemes many very good bacterial expression vectors/cell strains are available for expression in bacteria -good track record, easily automated expression in eukaryotic cells more complicated (yeast, insect, human cells) are cell-free systems currently available (i.e. Roche Rapid Translation System (RTS)).good for specific isotope labeling, not good for uniform isotopic labeling
22 Protein purity protein samples should always be as pure as possible in practice, for small proteins, small amounts of high molecular weight contaminants are OK SDS-PAGE molecular weight markers sample
23 Isotopic labeling of protein for NMR protein must be uniformly isotopically labeled with 13 C and 15 N not difficult these days: bacterial expression cell strains grow well on minimal media (D-glucose (U- 13 C 6, 98-99%) and 15 NH 4 Cl (98-99%) as sole carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively) for 1L medium, $300 for glucose (2 $150/g), and $30 for 15 NH 4 Cl (1 $30/g) there are also alternatives to minimal media (i.e. isotopically labeled rich media), but they are much more expensive
24 Isotopic labeling of protein for NMR in practice, often multiple samples with other isotopic labeling schemes are necessary 15 N only for certain angle (φ, ψ) measurements -also, usually used for initial evaluation of sample/spectra 13 C, 15 N plus partial or uniform deuteration for large proteins -requires growth in minimal media in D 2 O -cells must be adapted to growth on D 2 O samples with only specific amino acid types labeled assist in NMR resonance assignment -cells grown on medium with all unlabeled amino acids except for the one of interest -more common for larger proteins samples made with a mixture of 10% U- 13 C 6 glucose and 90% unlabeled glucose are used for stereospecific -CH 3 assignment -pror methyl groups of Valine and Leucine
25 Isotopic labeling of protein for NMR isotopic labeling to identify specific amino acid types, groups, or to assign stereospecificity 15 N-Gly only labeled protein uniformly 15 N labeled protein ε 13 CΗ 3 -Met only labeled protein uniformly 13 C labeled protein Left: sample prepared by growth on 100% uniformly 13 C-labeled glucose Right: sample prepared by growth on 10% uniformly 13 C-labeled glucose and 90% unlabeled glucose
26 The NMR sample buffer: no C- or N-bound protons phosphate is the best. deuterated Tris, deuterated acetate, deuterated imidazole, etc., are OK (can be expensive) salts K +, Na +, Cl -, SO 4 2-, etc., all OK (no protons) too much salt leads to decreased S/N ph: neutral or lower is best must minimize the rate of exchange of amide protons with solvent solvent 90% H 2 O, 10% D 2 O (for instrumental lock)
27 The NMR sample temperature sample dependent: usually 25 to 35 C bacteriostatic agents sodium azide used widely put it all together in a good quality, clean NMR tube standard NMR tube is 5 mm diameter (for use in a 5 mm NMR probe).volume of sample is ~ ul (~1 mm protein) magnetic susceptibility matched tubes, Shigemi tubes, permit lower volume samples to be used (i.e. less sample, or more concentrated sample), usually without deleterious effects (but the tubes are complicated) volume of sample is ul
28 Initial NMR spectra / evaluation 1D 1 H NMR spectrum of a small organic compound F(ω) = x x f (t)e iωt dt f (t) = 1 2π x x F(ω)e iωt dω 1D 1 H NMR spectrum of a small protein for even small proteins, 1D spectra are complicated and cannot be analyzed comprehensively 1D spectra can be useful, however, for evaluating the suitability/stability of a protein sample ubiquitin (76 amino acids, 8.5 kda)
29 Initial NMR spectra / evaluation 1D 1 H NMR spectrum of a small protein for properly folded small proteins -peaks should be sharp -peaks should show good chemical shift dispersion (i.e. tertiary structure intact) for unfolded proteins -peaks are usually broad (many protons in each peak) -chemical shift dispersion poor (leading to the broad peaks) acid-unfolded ubiquitin ubiquitin, neutral ph
30 Initial NMR spectra / evaluation sample stability can takes weeks of instrument time to acquire all data for structure determination sample has to be stable for the amount of time necessary to acquire all of the data (at the data acquisition temperature), plus the time between experiments (all data is rarely acquired all at once) protein x, t = 0 properly folded protein x, t = 2 weeks (at room temperature) partially unfolded
31 Initial NMR spectra / evaluation simple 2D 1 H, 15 N correlation NMR spectra of proteins reduce complex spectra to simple ones based on isotope editing reduce/eliminate spectral overlap/spectral degeneracy correlate amide 1 H- 15 N pairs ubiquitin (76 amino acids, 8.5 kda) simple 2D 1 H, 15 N HSQC experiment this spectrum demonstrates 1). that you can express your protein, 2). That you can isotopically label your protein, 3). That your protein is pure (1 peak per amino acid), 4) that your protein is folded (tertiary structure / good chemical shift dispersion), 5). etc. granting agencies need to see this spectrum or similar (akin to a crystal and a diffraction pattern)
32 Initial NMR spectra / evaluation tertiary structure and sample stability chemical shift dispersion and peakwidths reflect tertiary structure c: apomyoglobin b and a: acid unfolded apomyoglobin protein x, t = 0 properly folded protein x, t = 2 weeks (at room temperature) partially unfolded
33 Size (of the protein) matters the rotational correlation time (τ c ) scales with protein size larger τ c : peak broadening and decreased S/N larger proteins have more atoms, therefore more peaks in the spectra more peaks: increased peak overlap/chemical shift degeneracy ubiquitin (76 amino acids, 8.5 kda) AlgH (189 amino acids, 20.2 kda) EPSP synthase (427 amino acids, 46.2 kda)
34 Size (of the magnet) matters 1 H, 15 N-HSQC (TROSY) spectra of EPSP synthase (46 kda) at 600 and 800 MHz higher field means higher sensitivity (increased S/N), increased resolution (decreased peak overlap), and a bonus increase in S/N in TROSY experiments 600 MHz 800 MHz
35 ligand binding NMR: beyond structure slow dynamics / local and global stability (hydrogen exchange) residue mutational affects fast dynamics (ps/ns) via nuclear relaxation S 2 residue
36 END
Lecture #7 (2D NMR) Utility of Resonance Assignments
 Lecture #7 (2D NMR) Basics of multidimensional NMR (2D NMR) 2D NOESY, COSY and TOCSY 2/23/15 Utility of Resonance Assignments Resonance Assignments: Assignment of frequency positions of resonances (peaks)
Lecture #7 (2D NMR) Basics of multidimensional NMR (2D NMR) 2D NOESY, COSY and TOCSY 2/23/15 Utility of Resonance Assignments Resonance Assignments: Assignment of frequency positions of resonances (peaks)
VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND
 Figure from: http://www.embl.de/nmr/sattler/teaching Why NMR (instead of X ray crystallography) a great number of macromolecules won't crystallize) natural environmant (water) ligand binding and inter
Figure from: http://www.embl.de/nmr/sattler/teaching Why NMR (instead of X ray crystallography) a great number of macromolecules won't crystallize) natural environmant (water) ligand binding and inter
NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
 NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an effect whereby magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic (EM) energy. This energy is at a specific resonance
NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an effect whereby magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic (EM) energy. This energy is at a specific resonance
NMR Spectroscopy in Notre Dame
 NMR Spectroscopy in Notre Dame University of Notre Dame College of Science Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Facility http://www.nd.edu/~nmr Reservation system for spectrometers
NMR Spectroscopy in Notre Dame University of Notre Dame College of Science Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Facility http://www.nd.edu/~nmr Reservation system for spectrometers
13C NMR Spectroscopy
 13 C NMR Spectroscopy Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for structural determination. A nucleus with an odd number of protons, an odd number
13 C NMR Spectroscopy Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for structural determination. A nucleus with an odd number of protons, an odd number
NMR for Physical and Biological Scientists Thomas C. Pochapsky and Susan Sondej Pochapsky Table of Contents
 Preface Symbols and fundamental constants 1. What is spectroscopy? A semiclassical description of spectroscopy Damped harmonics Quantum oscillators The spectroscopic experiment Ensembles and coherence
Preface Symbols and fundamental constants 1. What is spectroscopy? A semiclassical description of spectroscopy Damped harmonics Quantum oscillators The spectroscopic experiment Ensembles and coherence
Introduction to NMR spectroscopy. Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics I.Phan & J. Kopp
 Introduction to NMR spectroscopy Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics I.Phan & J. Kopp NMR: the background Complex technique. Requires knowledge in: Mathematics Physics Chemistry Biology (Medicin) Involves
Introduction to NMR spectroscopy Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics I.Phan & J. Kopp NMR: the background Complex technique. Requires knowledge in: Mathematics Physics Chemistry Biology (Medicin) Involves
NMR SPECTROSCOPY. Basic Principles, Concepts, and Applications in Chemistry. Harald Günther University of Siegen, Siegen, Germany.
 NMR SPECTROSCOPY Basic Principles, Concepts, and Applications in Chemistry Harald Günther University of Siegen, Siegen, Germany Second Edition Translated by Harald Günther JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester
NMR SPECTROSCOPY Basic Principles, Concepts, and Applications in Chemistry Harald Günther University of Siegen, Siegen, Germany Second Edition Translated by Harald Günther JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester
Spin-Lattice Relaxation Times
 Spin-Lattice Relaxation Times Reading Assignment: T. D. W. Claridge, High Resolution NMR Techniques in Organic Chemistry, Chapter 2; E. Breitmaier, W. Voelter, Carbon 13 NMR Spectroscopy,3rd Ed., 3.3.2.
Spin-Lattice Relaxation Times Reading Assignment: T. D. W. Claridge, High Resolution NMR Techniques in Organic Chemistry, Chapter 2; E. Breitmaier, W. Voelter, Carbon 13 NMR Spectroscopy,3rd Ed., 3.3.2.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to characterize organic molecules by identifying carbonhydrogen frameworks within
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to characterize organic molecules by identifying carbonhydrogen frameworks within
4. It is possible to excite, or flip the nuclear magnetic vector from the α-state to the β-state by bridging the energy gap between the two. This is a
 BASIC PRINCIPLES INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (NMR) 1. The nuclei of certain atoms with odd atomic number, and/or odd mass behave as spinning charges. The nucleus is the center of positive
BASIC PRINCIPLES INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (NMR) 1. The nuclei of certain atoms with odd atomic number, and/or odd mass behave as spinning charges. The nucleus is the center of positive
List the 3 main types of subatomic particles and indicate the mass and electrical charge of each.
 Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction NMR is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination. It is used to study a wide variety of nuclei: 1 H 13 C 15 N 19 F 31 P 2
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction NMR is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination. It is used to study a wide variety of nuclei: 1 H 13 C 15 N 19 F 31 P 2
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 CHEM 334L Organic Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy In this laboratory exercise we will learn how to use the Chemistry Department's Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
CHEM 334L Organic Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy In this laboratory exercise we will learn how to use the Chemistry Department's Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination
 Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination Introduction Knowing the exact 3D-structure of bio-molecules is essential for any attempt to understand
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination Introduction Knowing the exact 3D-structure of bio-molecules is essential for any attempt to understand
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance notes
 Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance notes Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a spectrometric technique which provides information
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance notes Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a spectrometric technique which provides information
PROTON NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY (H-NMR)
 PROTON NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY (H-NMR) WHAT IS H-NMR SPECTROSCOPY? References: Bruice 14.1, 14.2 Introduction NMR or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a technique used to determine
PROTON NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY (H-NMR) WHAT IS H-NMR SPECTROSCOPY? References: Bruice 14.1, 14.2 Introduction NMR or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a technique used to determine
Chemical Exchange in NMR Spectroscopy
 COURSE#1022: Biochemical Applications of NMR Spectroscopy http://www.bioc.aecom.yu.edu/labs/girvlab/nmr/course/ Chemical Exchange in NMR Spectroscopy LAST UPDATE: 3/28/2012 1 References Bain, A. D. (2003).
COURSE#1022: Biochemical Applications of NMR Spectroscopy http://www.bioc.aecom.yu.edu/labs/girvlab/nmr/course/ Chemical Exchange in NMR Spectroscopy LAST UPDATE: 3/28/2012 1 References Bain, A. D. (2003).
Protein Dynamics by NMR. Why NMR is the best!
 Protein Dynamics by NMR Why NMR is the best! Key Points NMR dynamics divided into 2 regimes: fast and slow. How protein mobons affect NMR parameters depend on whether they are faster or slower than the
Protein Dynamics by NMR Why NMR is the best! Key Points NMR dynamics divided into 2 regimes: fast and slow. How protein mobons affect NMR parameters depend on whether they are faster or slower than the
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR is probably the most useful and powerful technique for identifying and characterizing organic compounds. Felix Bloch and Edward Mills Purcell were awarded the 1952 Nobel
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR is probably the most useful and powerful technique for identifying and characterizing organic compounds. Felix Bloch and Edward Mills Purcell were awarded the 1952 Nobel
Signal Manipulation. time domain NMR signal in MHz range is converted to khz (audio) range by mixing with the reference ( carrier ) frequency
 NMR Spectroscopy: 3 Signal Manipulation time domain NMR signal in MHz range is converted to khz (audio) range by mixing with the reference ( carrier ) frequency Ref in (MHz) mixer Signal in (MHz) Signal
NMR Spectroscopy: 3 Signal Manipulation time domain NMR signal in MHz range is converted to khz (audio) range by mixing with the reference ( carrier ) frequency Ref in (MHz) mixer Signal in (MHz) Signal
NMR and other Instrumental Techniques in Chemistry and the proposed National Curriculum.
 NMR and other Instrumental Techniques in Chemistry and the proposed National Curriculum. Dr. John Jackowski Chair of Science, Head of Chemistry Scotch College Melbourne john.jackowski@scotch.vic.edu.au
NMR and other Instrumental Techniques in Chemistry and the proposed National Curriculum. Dr. John Jackowski Chair of Science, Head of Chemistry Scotch College Melbourne john.jackowski@scotch.vic.edu.au
Molecular Models in Biology
 Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
The Four Questions to Ask While Interpreting Spectra. 1. How many different environments are there?
 1 H NMR Spectroscopy (#1c) The technique of 1 H NMR spectroscopy is central to organic chemistry and other fields involving analysis of organic chemicals, such as forensics and environmental science. It
1 H NMR Spectroscopy (#1c) The technique of 1 H NMR spectroscopy is central to organic chemistry and other fields involving analysis of organic chemicals, such as forensics and environmental science. It
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
 INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR) Theory and Interpretation of IR spectra ASSIGNED READINGS Introduction to technique 25 (p. 833-834 in lab textbook) Uses of the Infrared Spectrum (p. 847-853) Look over pages
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR) Theory and Interpretation of IR spectra ASSIGNED READINGS Introduction to technique 25 (p. 833-834 in lab textbook) Uses of the Infrared Spectrum (p. 847-853) Look over pages
Tetramethylsilane (TMS) Trimethylsilyl d 4. -propionic acid (TMSP) Dioxane. O - Na + Dimethylfura n. Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate. Sodium Maleate CH 3
 Practical Aspects of Quantitative NMR Experiments This discussion presumes that you already have an understanding of the basic theory of NMR. There are a number of issues that should be considered when
Practical Aspects of Quantitative NMR Experiments This discussion presumes that you already have an understanding of the basic theory of NMR. There are a number of issues that should be considered when
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction: The NMR Spectrum serves as a great resource in determining the structure of an organic compound by revealing the hydrogen and carbon skeleton.
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction: The NMR Spectrum serves as a great resource in determining the structure of an organic compound by revealing the hydrogen and carbon skeleton.
Proton NMR. One Dimensional H-NMR. Cl S. Common types of NMR experiments: 1-H NMR
 Common types of NMR experiments: 1- NMR Proton NMR ne Dimensional -NMR a. Experiment igh field proton NMR (400Mz). single-pulse experiment. b. Spectral nterpretation i. Number of multiplets gives the different
Common types of NMR experiments: 1- NMR Proton NMR ne Dimensional -NMR a. Experiment igh field proton NMR (400Mz). single-pulse experiment. b. Spectral nterpretation i. Number of multiplets gives the different
Molecular Spectroscopy
 Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
NMR and IR spectra & vibrational analysis
 Lab 5: NMR and IR spectra & vibrational analysis A brief theoretical background 1 Some of the available chemical quantum methods for calculating NMR chemical shifts are based on the Hartree-Fock self-consistent
Lab 5: NMR and IR spectra & vibrational analysis A brief theoretical background 1 Some of the available chemical quantum methods for calculating NMR chemical shifts are based on the Hartree-Fock self-consistent
(c) How would your answers to problem (a) change if the molecular weight of the protein was 100,000 Dalton?
 Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Chapter 13 Spectroscopy NMR, IR, MS, UV-Vis
 Chapter 13 Spectroscopy NMR, IR, MS, UV-Vis Main points of the chapter 1. Hydrogen Nuclear Magnetic Resonance a. Splitting or coupling (what s next to what) b. Chemical shifts (what type is it) c. Integration
Chapter 13 Spectroscopy NMR, IR, MS, UV-Vis Main points of the chapter 1. Hydrogen Nuclear Magnetic Resonance a. Splitting or coupling (what s next to what) b. Chemical shifts (what type is it) c. Integration
Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) And. NMR Metabolomics
 Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) And NMR Metabolomics Acknowledgment: Some slides from talks by Natalia Serkova, Wimal Pathmasiri, and from many internet sources (e.g., U of Oxford, Florida
Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) And NMR Metabolomics Acknowledgment: Some slides from talks by Natalia Serkova, Wimal Pathmasiri, and from many internet sources (e.g., U of Oxford, Florida
BUILDING BLOCKS FOR MULTIDIMENSIONAL NMR AND SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR BIOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS OF NMR
 09-Pochapsky-09-cpp 3/7/06 2:9 pm Page 24 9 BUILDING BLOCKS FOR MULTIDIMENSIONAL NMR AND SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR BIOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS OF NMR The development of multidimensional NMR (three or more
09-Pochapsky-09-cpp 3/7/06 2:9 pm Page 24 9 BUILDING BLOCKS FOR MULTIDIMENSIONAL NMR AND SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR BIOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS OF NMR The development of multidimensional NMR (three or more
Determining the Structure of an Organic Compound
 Determining the Structure of an Organic Compound The analysis of the outcome of a reaction requires that we know the full structure of the products as well as the reactants In the 19 th and early 20 th
Determining the Structure of an Organic Compound The analysis of the outcome of a reaction requires that we know the full structure of the products as well as the reactants In the 19 th and early 20 th
Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition
 Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition T. W. Graham Solomons Craig B. Fryhle Welcome to CHM 22 Organic Chemisty II Chapters 2 (IR), 9, 3-20. Chapter 2 and Chapter 9 Spectroscopy (interaction of molecule with
Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition T. W. Graham Solomons Craig B. Fryhle Welcome to CHM 22 Organic Chemisty II Chapters 2 (IR), 9, 3-20. Chapter 2 and Chapter 9 Spectroscopy (interaction of molecule with
Question 4.2: Write Lewis dot symbols for atoms of the following elements: Mg, Na, B, O, N, Br.
 Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in a chemical species. Various theories
Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in a chemical species. Various theories
Trans Fats. What is a trans fat? Trans fatty acids, or trans fats as they are known, are certain
 Trans Fats What is a trans fat? Trans fatty acids, or trans fats as they are known, are certain fats found in such foodstuffs as vegetable shortenings, margarines, crackers, candies baked goods and many
Trans Fats What is a trans fat? Trans fatty acids, or trans fats as they are known, are certain fats found in such foodstuffs as vegetable shortenings, margarines, crackers, candies baked goods and many
Used to determine relative location of atoms within a molecule Most helpful spectroscopic technique in organic chemistry Related to MRI in medicine
 Structure Determination: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance CHEM 241 UNIT 5C 1 The Use of NMR Spectroscopy Used to determine relative location of atoms within a molecule Most helpful spectroscopic technique in
Structure Determination: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance CHEM 241 UNIT 5C 1 The Use of NMR Spectroscopy Used to determine relative location of atoms within a molecule Most helpful spectroscopic technique in
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ( 1 H-NMR) Spectroscopy
 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ( 1 H-NMR) Spectroscopy Theory behind NMR: In the late 1940 s, physical chemists originally developed NMR spectroscopy to study different properties of atomic nuclei,
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ( 1 H-NMR) Spectroscopy Theory behind NMR: In the late 1940 s, physical chemists originally developed NMR spectroscopy to study different properties of atomic nuclei,
Solving Spectroscopy Problems
 Solving Spectroscopy Problems The following is a detailed summary on how to solve spectroscopy problems, key terms are highlighted in bold and the definitions are from the illustrated glossary on Dr. Hardinger
Solving Spectroscopy Problems The following is a detailed summary on how to solve spectroscopy problems, key terms are highlighted in bold and the definitions are from the illustrated glossary on Dr. Hardinger
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Wade Textbook
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Wade Textbook Background Is a nondestructive structural analysis technique Has the same theoretical basis as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Referring to MRI as nuclear
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Wade Textbook Background Is a nondestructive structural analysis technique Has the same theoretical basis as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Referring to MRI as nuclear
Time out states and transitions
 Time out states and transitions Spectroscopy transitions between energy states of a molecule excited by absorption or emission of a photon hn = DE = E i - E f Energy levels due to interactions between
Time out states and transitions Spectroscopy transitions between energy states of a molecule excited by absorption or emission of a photon hn = DE = E i - E f Energy levels due to interactions between
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are
 This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy cont... Recommended Reading:
 Applied Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy cont... Recommended Reading: Banwell and McCash Chapter 7 Skoog, Holler Nieman Chapter 19 Atkins, Chapter 18 Relaxation processes We need
Applied Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy cont... Recommended Reading: Banwell and McCash Chapter 7 Skoog, Holler Nieman Chapter 19 Atkins, Chapter 18 Relaxation processes We need
Hydrogen Bonds The electrostatic nature of hydrogen bonds
 Hydrogen Bonds Hydrogen bonds have played an incredibly important role in the history of structural biology. Both the structure of DNA and of protein a-helices and b-sheets were predicted based largely
Hydrogen Bonds Hydrogen bonds have played an incredibly important role in the history of structural biology. Both the structure of DNA and of protein a-helices and b-sheets were predicted based largely
Practical guide for quantitative 1D NMR integration Eugenio Alvarado, University of Michigan, 05/10/10
 Practical guide for quantitative 1D NMR integration Eugenio Alvarado, University of Michigan, 05/10/10 The purpose of this manuscript is not to present a discussion about quantitative NMR, but to offer
Practical guide for quantitative 1D NMR integration Eugenio Alvarado, University of Michigan, 05/10/10 The purpose of this manuscript is not to present a discussion about quantitative NMR, but to offer
CHAPTER 6 Chemical Bonding
 CHAPTER 6 Chemical Bonding SECTION 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding OBJECTIVES 1. Define Chemical bond. 2. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonding.. 4. Explain
CHAPTER 6 Chemical Bonding SECTION 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding OBJECTIVES 1. Define Chemical bond. 2. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonding.. 4. Explain
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
 18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Chapter 11 Structure Determination: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. 11.1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 11 Structure Determination: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 11.1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Many atomic nuclei behave
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 11 Structure Determination: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 11.1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Many atomic nuclei behave
Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectrscopy
 CHEM 331L Physical Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0 Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectrscopy In this laboratory exercise we will measure a chemical equilibrium constant using key proton
CHEM 331L Physical Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0 Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectrscopy In this laboratory exercise we will measure a chemical equilibrium constant using key proton
Elements in the periodic table are indicated by SYMBOLS. To the left of the symbol we find the atomic mass (A) at the upper corner, and the atomic num
 . ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
. ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
Structure Determination
 5 Structure Determination Most of the protein structures described and discussed in this book have been determined either by X-ray crystallography or by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Although
5 Structure Determination Most of the protein structures described and discussed in this book have been determined either by X-ray crystallography or by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Although
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display
 Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
UNIT 2 PRACTICE EXAM (Part 1: General Chemistry)
 UIT 2 PRACTICE EXAM (Part 1: General Chemistry) 1. Which would be the best definition of an ionic bond? a. The attraction between the partial positive region of one molecule and the partial negative region
UIT 2 PRACTICE EXAM (Part 1: General Chemistry) 1. Which would be the best definition of an ionic bond? a. The attraction between the partial positive region of one molecule and the partial negative region
Name Lab #3: Solubility of Organic Compounds Objectives: Introduction: soluble insoluble partially soluble miscible immiscible
 Lab #3: Solubility of rganic Compounds bjectives: - Understanding the relative solubility of organic compounds in various solvents. - Exploration of the effect of polar groups on a nonpolar hydrocarbon
Lab #3: Solubility of rganic Compounds bjectives: - Understanding the relative solubility of organic compounds in various solvents. - Exploration of the effect of polar groups on a nonpolar hydrocarbon
NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds (#1e)
 NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds (#1e) 1 H NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds Erich Hückel s study of aromaticity in the 1930s produced a set of rules for determining whether a compound is aromatic.
NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds (#1e) 1 H NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds Erich Hückel s study of aromaticity in the 1930s produced a set of rules for determining whether a compound is aromatic.
The Experiment Some nuclei have nuclear magnetic moments; just as importantly, some do not
 Chemistry 2600 Lecture Notes Chapter 15 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Page 1 of 23 Structure Determination in Organic Chemistry: NMR Spectroscopy Three main techniques are used to determine the
Chemistry 2600 Lecture Notes Chapter 15 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Page 1 of 23 Structure Determination in Organic Chemistry: NMR Spectroscopy Three main techniques are used to determine the
Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Dr. Dean L. Olson, NMR Lab Director School of Chemical Sciences University of Illinois Called figures, equations, and tables are from Principles
Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Dr. Dean L. Olson, NMR Lab Director School of Chemical Sciences University of Illinois Called figures, equations, and tables are from Principles
Determination of Molecular Structure by MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY
 Determination of Molecular Structure by MOLEULAR SPETROSOPY hemistry 3 B.Z. Shakhashiri Fall 29 Much of what we know about molecular structure has been learned by observing and analyzing how electromagnetic
Determination of Molecular Structure by MOLEULAR SPETROSOPY hemistry 3 B.Z. Shakhashiri Fall 29 Much of what we know about molecular structure has been learned by observing and analyzing how electromagnetic
Chemistry Diagnostic Questions
 Chemistry Diagnostic Questions Answer these 40 multiple choice questions and then check your answers, located at the end of this document. If you correctly answered less than 25 questions, you need to
Chemistry Diagnostic Questions Answer these 40 multiple choice questions and then check your answers, located at the end of this document. If you correctly answered less than 25 questions, you need to
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
NMR SPECTROSCOPY A N I N T R O D U C T I O N T O... Self-study booklet NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE. 4 3 2 1 0 δ PUBLISHING
 A N I N T R O D U T I O N T O... NMR SPETROSOPY NULEAR MAGNETI RESONANE 4 3 1 0 δ Self-study booklet PUBLISING NMR Spectroscopy NULEAR MAGNETI RESONANE SPETROSOPY Origin of Spectra Theory All nuclei possess
A N I N T R O D U T I O N T O... NMR SPETROSOPY NULEAR MAGNETI RESONANE 4 3 1 0 δ Self-study booklet PUBLISING NMR Spectroscopy NULEAR MAGNETI RESONANE SPETROSOPY Origin of Spectra Theory All nuclei possess
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts
 AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture
 CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
HOMEWORK PROBLEMS: IR SPECTROSCOPY AND 13C NMR. The peak at 1720 indicates a C=O bond (carbonyl). One possibility is acetone:
 HMEWRK PRBLEMS: IR SPECTRSCPY AND 13C NMR 1. You find a bottle on the shelf only labeled C 3 H 6. You take an IR spectrum of the compound and find major peaks at 2950, 1720, and 1400 cm -1. Draw a molecule
HMEWRK PRBLEMS: IR SPECTRSCPY AND 13C NMR 1. You find a bottle on the shelf only labeled C 3 H 6. You take an IR spectrum of the compound and find major peaks at 2950, 1720, and 1400 cm -1. Draw a molecule
Macromolecular Structure Determination: Comparison of Crystallography and NMR
 Macromolecular Structure Determination: Comparison of Crystallography and NMR J Mitchell Guss, University of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia Glenn F King, University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington,
Macromolecular Structure Determination: Comparison of Crystallography and NMR J Mitchell Guss, University of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia Glenn F King, University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington,
PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes.
 1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
F321 THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS. ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important are... in the nucleus of an atom
 Atomic Structure F32 TE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important are... Mass / kg Charge / C Relative mass Relative Charge PROTON NEUTRON ELECTRON
Atomic Structure F32 TE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important are... Mass / kg Charge / C Relative mass Relative Charge PROTON NEUTRON ELECTRON
For example: (Example is from page 50 of the Thinkbook)
 SOLVING COMBINED SPECTROSCOPY PROBLEMS: Lecture Supplement: page 50-53 in Thinkbook CFQ s and PP s: page 216 241 in Thinkbook Introduction: The structure of an unknown molecule can be determined using
SOLVING COMBINED SPECTROSCOPY PROBLEMS: Lecture Supplement: page 50-53 in Thinkbook CFQ s and PP s: page 216 241 in Thinkbook Introduction: The structure of an unknown molecule can be determined using
Performance and advantages of qnmr measurements
 Return to Web Version This is the first of a series of articles related to the launch of new organic CRMs certified by quantitative NMR under double accreditation. In this issue, we focus on CRMs intended
Return to Web Version This is the first of a series of articles related to the launch of new organic CRMs certified by quantitative NMR under double accreditation. In this issue, we focus on CRMs intended
INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL EXCHANGE WITH THE MEXICO PROGRAM
 ITRODUCTIO TO CEMICAL EXCAGE WIT TE MEXICO PROGRAM TE PEOMEO May, 2001 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 Figure 1 Consider the molecule in figure 1: 3-dimethylamino-7-methyl-1,2,4- benzotriazine. As it is drawn,
ITRODUCTIO TO CEMICAL EXCAGE WIT TE MEXICO PROGRAM TE PEOMEO May, 2001 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 Figure 1 Consider the molecule in figure 1: 3-dimethylamino-7-methyl-1,2,4- benzotriazine. As it is drawn,
Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain.
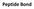 Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Nuclear Structure. particle relative charge relative mass proton +1 1 atomic mass unit neutron 0 1 atomic mass unit electron -1 negligible mass
 Protons, neutrons and electrons Nuclear Structure particle relative charge relative mass proton 1 1 atomic mass unit neutron 0 1 atomic mass unit electron -1 negligible mass Protons and neutrons make up
Protons, neutrons and electrons Nuclear Structure particle relative charge relative mass proton 1 1 atomic mass unit neutron 0 1 atomic mass unit electron -1 negligible mass Protons and neutrons make up
Background A nucleus with an odd atomic number or an odd mass number has a nuclear spin that can be observed by NMR spectrometers.
 NMR Spectroscopy I Reading: Wade chapter, sections -- -7 Study Problems: -, -7 Key oncepts and Skills: Given an structure, determine which protons are equivalent and which are nonequivalent, predict the
NMR Spectroscopy I Reading: Wade chapter, sections -- -7 Study Problems: -, -7 Key oncepts and Skills: Given an structure, determine which protons are equivalent and which are nonequivalent, predict the
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers:
 Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
Chemistry Department
 Chemistry Department NMR/Instrumentation Facility Users Guide - Rules, safety and system information Prepared by Leila Maurmann The NMR/Instrumentation facility at the Chemistry Department at Kansas State
Chemistry Department NMR/Instrumentation Facility Users Guide - Rules, safety and system information Prepared by Leila Maurmann The NMR/Instrumentation facility at the Chemistry Department at Kansas State
ATOMS AND BONDS. Bonds
 ATOMS AND BONDS Atoms of elements are the simplest units of organization in the natural world. Atoms consist of protons (positive charge), neutrons (neutral charge) and electrons (negative charge). The
ATOMS AND BONDS Atoms of elements are the simplest units of organization in the natural world. Atoms consist of protons (positive charge), neutrons (neutral charge) and electrons (negative charge). The
Infrared Spectroscopy: Theory
 u Chapter 15 Infrared Spectroscopy: Theory An important tool of the organic chemist is Infrared Spectroscopy, or IR. IR spectra are acquired on a special instrument, called an IR spectrometer. IR is used
u Chapter 15 Infrared Spectroscopy: Theory An important tool of the organic chemist is Infrared Spectroscopy, or IR. IR spectra are acquired on a special instrument, called an IR spectrometer. IR is used
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility
 Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
How To Understand The Physics Of Ft Nmr
 Basic Practical NMR Concepts: A Guide for the Modern Laboratory Description: This handout is designed to furnish you with a basic understanding of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy as it pertains
Basic Practical NMR Concepts: A Guide for the Modern Laboratory Description: This handout is designed to furnish you with a basic understanding of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy as it pertains
8.1 Relaxation in NMR Spectroscopy
 8.1 Relaxation in NMR Spectroscopy Copyright ans J. Reich 2010 All Rights Reserved University of Wisconsin An understanding of relaxation processes is important for the proper measurement and interpretation
8.1 Relaxation in NMR Spectroscopy Copyright ans J. Reich 2010 All Rights Reserved University of Wisconsin An understanding of relaxation processes is important for the proper measurement and interpretation
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson
 Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
PHYSIOLOGY AND MAINTENANCE Vol. II - On The Determination of Enzyme Structure, Function, and Mechanism - Glumoff T.
 ON THE DETERMINATION OF ENZYME STRUCTURE, FUNCTION, AND MECHANISM University of Oulu, Finland Keywords: enzymes, protein structure, X-ray crystallography, bioinformatics Contents 1. Introduction 2. Structure
ON THE DETERMINATION OF ENZYME STRUCTURE, FUNCTION, AND MECHANISM University of Oulu, Finland Keywords: enzymes, protein structure, X-ray crystallography, bioinformatics Contents 1. Introduction 2. Structure
Spin-lattice and spin-spin relaxation
 Spin-lattice and spin-spin relaation Sequence of events in the NMR eperiment: (i) application of a 90 pulse alters the population ratios, and creates transverse magnetic field components (M () ); (ii)
Spin-lattice and spin-spin relaation Sequence of events in the NMR eperiment: (i) application of a 90 pulse alters the population ratios, and creates transverse magnetic field components (M () ); (ii)
The Unified Scale for Referencing in NMR: New IUPAC Recommendations revised (cgf): 26 July 2010
 The Unified Scale for Referencing in NMR: New IUPAC Recommendations revised (cgf): 26 July 2010 In 2001, IUPAC set new definitions and standards for NMR referencing, 1 and updated these in 2008. 2 A significant
The Unified Scale for Referencing in NMR: New IUPAC Recommendations revised (cgf): 26 July 2010 In 2001, IUPAC set new definitions and standards for NMR referencing, 1 and updated these in 2008. 2 A significant
Lecture 26: Overview of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) structure
 Lecture 26: Overview of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) structure Nucleic acids play an important role in the storage and expression of genetic information. They are divided into
Lecture 26: Overview of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) structure Nucleic acids play an important role in the storage and expression of genetic information. They are divided into
Chemical Bonds and Groups - Part 1
 hemical Bonds and Groups - Part 1 ARB SKELETS arbon has a unique role in the cell because of its ability to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Thus carbon atoms can join to form chains.
hemical Bonds and Groups - Part 1 ARB SKELETS arbon has a unique role in the cell because of its ability to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Thus carbon atoms can join to form chains.
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids
 Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Application Note AN4
 TAKING INVENTIVE STEPS IN INFRARED. MINIATURE INFRARED GAS SENSORS GOLD SERIES UK Patent App. No. 2372099A USA Patent App. No. 09/783,711 World Patents Pending INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY Application Note AN4
TAKING INVENTIVE STEPS IN INFRARED. MINIATURE INFRARED GAS SENSORS GOLD SERIES UK Patent App. No. 2372099A USA Patent App. No. 09/783,711 World Patents Pending INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY Application Note AN4
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding. Modified by Dr. Daniela Radu
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding Modified by Dr. Daniela Radu What is Organic Chemistry? Living things are made of organic chemicals Proteins that make
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding Modified by Dr. Daniela Radu What is Organic Chemistry? Living things are made of organic chemicals Proteins that make
Preliminary MFM Quiz
 Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure
 FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure Warren Gallagher A. Introduction to protein structure The first structures of proteins at an atomic resolution were determined in the late 1950 s. 1 From that time to
FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure Warren Gallagher A. Introduction to protein structure The first structures of proteins at an atomic resolution were determined in the late 1950 s. 1 From that time to
Test Bank - Chapter 4 Multiple Choice
 Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes
 Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
NMR practice times. Mo 2---8 pm Jim 2-4:30 Ning 4:30-7. Tues 2--- 8 pm Jianing 2-4:30 Ting 4:30-7. Fri 10- --- 7 Donia 10-12:00 Ilya 2-4
 NMR practice times 1 Mo 2---8 pm Jim 2-4:30 Ning 4:30-7 Tues 2--- 8 pm Jianing 2-4:30 Ting 4:30-7 Wed 4:30---8 John 5:00-7:30 Fri 10- --- 7 Donia 10-12:00 Ilya 2-4 Samples are listed in the homework along
NMR practice times 1 Mo 2---8 pm Jim 2-4:30 Ning 4:30-7 Tues 2--- 8 pm Jianing 2-4:30 Ting 4:30-7 Wed 4:30---8 John 5:00-7:30 Fri 10- --- 7 Donia 10-12:00 Ilya 2-4 Samples are listed in the homework along
A Grignard reagent formed would deprotonate H of the ethyl alcohol OH.
 216 S11-E2 Page 2 Name Key I. (9 points) Answer in the boxes below the following questions for the Grignard reagent C 3 -Mg. (1) (2 points) Is the carbon atom associated with magnesium electrophilic or
216 S11-E2 Page 2 Name Key I. (9 points) Answer in the boxes below the following questions for the Grignard reagent C 3 -Mg. (1) (2 points) Is the carbon atom associated with magnesium electrophilic or
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
