SELF-PREPARATION FOR THE BIOLOGY ASSESSMENT TEST MODULE 5: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
|
|
|
- Sabina Pearson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SELF-PREPARATION FOR THE BIOLOGY ASSESSMENT TEST MODULE 5: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
2 Mitosis and meiosis: Two types of eukaryotic cell division According to the Cell Theory, new cells are created by the division of existing cells There are two types of eukaryotic cell division: Mitosis and meiosis Examples in the human body: Mitosis is done to make more of a specific body cell Meiosis is done by certain cells in ovaries or testes to create gametes (eggs or sperm)
3 Interphase: Preparations for mitosis or meiosis A eukaryotic cell has a laundry list of preparations it must do to ready for mitosis or meiosis. The time spent completing the preparations is called Interphase An important preparation is the duplication of chromosomes. The two chromosome copies, called sister chromatids, remain together until late in cell division. Another preparation is the formation of a protein structure called the spindle, which begins in late Interphase
4 Mitosis: Introduction In mitosis, a eukaryotic cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells Human somatic (body) cells divide by mitosis at some point in their lives, though at different rates Some cells, such as skin cells, divide rapidly Some cells, such as nerve cells, divide extremely slowly There are two major events in the process of mitosis: 1. Equal division of the cell s chromosomes 2. Division of the cell s cytoplasm Many other cell structures are divided in the process of mitosis, but these slides will focus on the above two events.
5 Mitosis: Overview of the process Mitosis may be divided into the following stages: Prophase - Start of mitosis Prometaphase - Setting up chromosome alignment Metaphase - Chromosomes line up in middle of cell Anaphase - Sister chromatids separate Telophase - Final steps of chromosome division Cytokinesis - Division of cytoplasm
6 Prophase The chromosomes condense Nuclear envelope begins to break down The spindle continues to form: Two centrosomes migrate to opposite sides of the cell, while long spindle fibers extend out of them
7 Prometaphase: Preparation for chromosome alignment Nuclear envelope disappears Chromosomes are fully condensed Some spindle fibers attach to sister chromatids. The location on a chromatid where the attachment occurs is called the centromere.
8 Metaphase: Chromosomes align in middle of cell Spindle fibers help chromosomes move so that they align in the middle of the cell
9 Anaphase: Separating sister chromatids Sister chromatids (identical chromosome copies) are separated from each other The spindle fibers shorten The chromatids are pulled to opposite sides of the cell. Once they begin to separate, each chromatid is considered a chromosome.
10 Telophase: Final events of mitosis Chromosomes become less condensed Spindle fibers are fully disassembled The nuclear envelope reforms
11 Cytokinesis: Dividing the cytoplasm In animal cells, the cell membrane is pinched off to divide the cell into two The two daughter cells are identical to each other Each daughter cell is also identical to the original cell
12 Summary of mitosis Before mitosis is Interphase, where the cell carries out preparations for cell division. Important preparations include chromosome replication and the start of spindle formation. The phases of mitosis are: Pretty People Meet And Talk Prophase Prometaphase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Mitosis results in daughter cells that are identical
13 Meiosis: Introduction In meiosis, a eukaryotic cell produces daughter cells that are very different from it and from each other Regions of DNA in a chromosome have been shuffled by a process called crossing over Whole chromosomes have been shuffled by a process called independent assortment Each daughter cell has half the number of chromosomes as the original one In the human body, specific cells in the ovaries and testes divide by meiosis. The daughter cells they produce are gametes (eggs or sperm).
14 Meiosis: Overview of the process Meiosis consists of two rounds of cell division: Meiosis I and Meiosis II Each round has its own Prophase, Prometaphase (left out for simplicity), Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase and cytokinesis For example, Prophase I is the Prophase of Meiosis I, while Prophase II is the Prophase of Meiosis II.
15 Meiosis: Overview of the process Animal cells have two sets of chromosomes, one set from each parent. An organism with two chromosome sets is diploid, or 2n Prior to meiosis, each chromosome is duplicated so that it consists of two sister chromatids The next few slides focus on some of the major events that occur in the process of meiosis.
16 Prophase I Meiosis I: Major events Nuclear envelope disassembles Spindle forms Chromosomes condense and pair up Crossing over occurs: Paired chromosomes exchange DNA Metaphase I Chromosomes remain paired Spindle fibers push chromosome pairs to middle of the cell Anaphase I Spindle fibers shorten Paired chromosomes are separated
17 Meiosis I: Major events Telophase I Spindle fibers disassemble Chromosomes become less condensed Nuclear envelope might reform Cytokinesis The cell divides into two Each daughter cell only has one set of chromosomes they are each haploid, or n
18 Prophase II Meiosis II: Major events Nuclear envelope disassembles (if reformed in Meiosis I) Spindle forms Chromosomes condense Metaphase II Spindle fibers chromosomes to middle of the cell Anaphase II Sister chromatids are separated
19 Meiosis II: Major events Telophase II Spindle fibers disassemble Chromosomes become less condensed Nuclear envelope reforms Cytokinesis Cell divides into two Each daughter cell is haploid, or n
20 Meiosis creates genetic variety Meiosis ensures that gametes will be genetically different from each other If there is genetic variation in gametes, each offspring will also be at least a little different from each other and from their parents. These new gene combinations may be better than the combinations of previous generations!
21 Meiosis: Crossing over In crossing over, paired chromosomes exchange DNA with each other Location of DNA exchange This exchange can occur at one or multiple locations along the paired chromosomes Must be an equal exchange! Argrid / Wikimedia Commons / CC-BY-SA-3.0 / GFDL
22 Meiosis: Independent assortment Chromosomes pairs are pushed to the middle of the cell in Metaphase I The alignment chromosomes in each pair is random This random alignment affects which chromosome in the pair will get into a daughter cell when they are separated in Anaphase I
23 Summary of meiosis Before mitosis is Interphase, where the cell carries out preparations for cell division. Important preparations include chromosome replication and the start of spindle formation. Consists of two rounds of cell division, Meiosis I and II. Each cell division has its own Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase
24 Summary of meiosis Chromosome variety is created by crossing over and independent assortment Meiosis results in daughter cells that differ from each other and from the original cell because of the genetic variety created by crossing over and independent assortment
25 Mitosis and meiosis: Similarities Chromosomes are replicated in advance of mitosis or meiosis, during Interphase A spindle forms to help separate chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis Both mitosis and meiosis can be divided up into different phases
26 Mitosis and meiosis: Differences Mitosis 1. Occurs in somatic (body) cells 2. Consists of one round of cell division 3. Results in identical daughter cells Meiosis 1. Occurs in sex cells to form gametes 2. Consists of two rounds of cell division 3. Results in daughter cells that have half the number of chromosomes. Chromosomes differ per gamete due to crossing over and independent assortment.
27 SELF-PREPARATION FOR THE BIOLOGY ASSESSMENT TEST END OF MODULE 5: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
List, describe, diagram, and identify the stages of meiosis.
 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this topic we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells: meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell division, mitosis
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this topic we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells: meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell division, mitosis
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis
 The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis Learning objective This learning material is about the life cycle of a cell and the series of stages by which genetic materials are duplicated and partitioned to produce
The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis Learning objective This learning material is about the life cycle of a cell and the series of stages by which genetic materials are duplicated and partitioned to produce
1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells
 Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
www.njctl.org PSI Biology Mitosis & Meiosis
 Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Meiosis is a special form of cell division.
 Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS
 CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis
 Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Sexual Reproduction. The specialized cells that are required for sexual reproduction are known as. And come from the process of: GAMETES
 Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
5. The cells of a multicellular organism, other than gametes and the germ cells from which it develops, are known as
 1. True or false? The chi square statistical test is used to determine how well the observed genetic data agree with the expectations derived from a hypothesis. True 2. True or false? Chromosomes in prokaryotic
1. True or false? The chi square statistical test is used to determine how well the observed genetic data agree with the expectations derived from a hypothesis. True 2. True or false? Chromosomes in prokaryotic
1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes?
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Chapter 3. Cell Division. Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.
 Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257
 CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257 SECTION 9-1 CELLULAR GROWTH Page 244 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is it beneficial for cells to remain small? MAIN IDEA Cells grow until they reach their size limit,
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257 SECTION 9-1 CELLULAR GROWTH Page 244 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is it beneficial for cells to remain small? MAIN IDEA Cells grow until they reach their size limit,
Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA
 Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis
 Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis 1. Chromosomes 2. Diploid life cycle 3. Cell cycle 4. Mitosis 5. Meiosis 6. Parallel behavior of genes and chromosomes Basic morphology of chromosomes telomere short arm
Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis 1. Chromosomes 2. Diploid life cycle 3. Cell cycle 4. Mitosis 5. Meiosis 6. Parallel behavior of genes and chromosomes Basic morphology of chromosomes telomere short arm
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis
 BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
The Somatic Cell Cycle
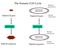 The Somatic Cell Cycle Maternal chromosome Diploid Zygote Diploid Zygote Paternal chromosome MITOSIS MITOSIS Maternal chromosome Diploid organism Diploid organism Paternal chromosome Int terpha ase The
The Somatic Cell Cycle Maternal chromosome Diploid Zygote Diploid Zygote Paternal chromosome MITOSIS MITOSIS Maternal chromosome Diploid organism Diploid organism Paternal chromosome Int terpha ase The
If and when cancer cells stop dividing, they do so at random points, not at the normal checkpoints in the cell cycle.
 Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body s control mechanisms. Cancer cells do not stop dividing when
Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body s control mechanisms. Cancer cells do not stop dividing when
The illustrations below reflect other scientists results in identifying and counting the stages of the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula.
 Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis In this lecture Cell division Chromosomes The cell cycle Mitosis PPMAT Apoptosis What is cell division? Cells divide in order to reproduce themselves The cell cycle
Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis In this lecture Cell division Chromosomes The cell cycle Mitosis PPMAT Apoptosis What is cell division? Cells divide in order to reproduce themselves The cell cycle
From DNA to Protein
 Nucleus Control center of the cell contains the genetic library encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins determines which specific proteins
Nucleus Control center of the cell contains the genetic library encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins determines which specific proteins
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction
 Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A Chromosome and Sister Chromatids Key Points About Chromosome Structure A chromosome consists of DNA that is wrapped around proteins (histones) and condensed Each
Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A Chromosome and Sister Chromatids Key Points About Chromosome Structure A chromosome consists of DNA that is wrapped around proteins (histones) and condensed Each
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
Cellular Reproduction
 9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
Workshop: Cellular Reproduction via Mitosis & Meiosis
 Workshop: Cellular Reproduction via Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction In this workshop you will examine how cells divide, including how they partition their genetic material (DNA) between the two resulting
Workshop: Cellular Reproduction via Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction In this workshop you will examine how cells divide, including how they partition their genetic material (DNA) between the two resulting
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB)
 Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9
 Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
CELL DIVISION. STAGES OF MITOTIC DIVISION (Diag. C1)
 1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis
 K.Muma Bio 6 Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis Study Objectives: Appendix C: DNA replication and Mitosis 1. Describe the structure of DNA and where it is found. 2. Explain complimentary base pairing:
K.Muma Bio 6 Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis Study Objectives: Appendix C: DNA replication and Mitosis 1. Describe the structure of DNA and where it is found. 2. Explain complimentary base pairing:
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Reproduction Growth and development Tissue removal Example
Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Reproduction Growth and development Tissue removal Example
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Sexual Reproduction. and Meiosis. Sexual Reproduction
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Guided Notes: Chapter 9 Cellular Reproduction
 Guided Notes: Cellular Reproduction When do cells divide? Cells grow and function normally until they become too. Cell size is because increases faster than This means that there is not enough area on
Guided Notes: Cellular Reproduction When do cells divide? Cells grow and function normally until they become too. Cell size is because increases faster than This means that there is not enough area on
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 12 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Concept Outline 12.1 Meiosis produces haploid cells from diploid cells. Discovery of Reduction Division. Sexual reproduction does not increase chromosome number because
12 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Concept Outline 12.1 Meiosis produces haploid cells from diploid cells. Discovery of Reduction Division. Sexual reproduction does not increase chromosome number because
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction
 Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Cell Division Simulation: Bacteria Activity One
 Cell Division Simulation: Bacteria Activity One Introduction All living things are made of cells. Some living things, like plants and animals, are made of millions of cells. But some living things are
Cell Division Simulation: Bacteria Activity One Introduction All living things are made of cells. Some living things, like plants and animals, are made of millions of cells. But some living things are
Teacher s Guide. Mitosis. Grades 5-9 MTTV
 Teacher s Guide Mitosis Grades 5-9 MTTV CREDITS Program Production Sunburst Visual Media Teacher s Guide Terry Gates Print Material Design Cecile Foshee 2004 Sunburst Visual Media, a division of Global
Teacher s Guide Mitosis Grades 5-9 MTTV CREDITS Program Production Sunburst Visual Media Teacher s Guide Terry Gates Print Material Design Cecile Foshee 2004 Sunburst Visual Media, a division of Global
1. Identify each phase of mitosis on the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula. 3. Explain differences in mitosis between plant and animal cells.
 Mitosis Objectives Having completed the lab on mitosis, you should be able to: 1. Identify each phase of mitosis on the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula. 2. Describe the events during each phase
Mitosis Objectives Having completed the lab on mitosis, you should be able to: 1. Identify each phase of mitosis on the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula. 2. Describe the events during each phase
CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
Cell Division and Mitosis DNA. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. 2. Meiosis occurs in the reproductive organs, producing four haploid sex cells.
 ell Division and Mitosis 1. he life cycle of a cell has two parts growth and development, and cell division. 2. In mitosis, the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four continuous
ell Division and Mitosis 1. he life cycle of a cell has two parts growth and development, and cell division. 2. In mitosis, the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four continuous
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY
 MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
Sample Questions for Exam 3
 Sample Questions for Exam 3 1. All of the following occur during prometaphase of mitosis in animal cells except a. the centrioles move toward opposite poles. b. the nucleolus can no longer be seen. c.
Sample Questions for Exam 3 1. All of the following occur during prometaphase of mitosis in animal cells except a. the centrioles move toward opposite poles. b. the nucleolus can no longer be seen. c.
Look for these related items from Learning Resources :
 Look for these related items from Learning Resources : LER 1901 Cross Section Plant Cell LER 1902 Cross Section Heart Model LER 1903 Cross Section Brain Model LER 2437 Cross Section Earth Model For a dealer
Look for these related items from Learning Resources : LER 1901 Cross Section Plant Cell LER 1902 Cross Section Heart Model LER 1903 Cross Section Brain Model LER 2437 Cross Section Earth Model For a dealer
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1
 Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Describe the cell cycle. 2. Identify stages of mitosis from prepared
LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Describe the cell cycle. 2. Identify stages of mitosis from prepared
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions. Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions!
 AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
The Cell Cycle: A series of modeling activities
 The Cell Cycle: A series of modeling activities Cancer Education Project University of Rochester Premise: Students learn best when exposed to a variety of activities Overview 1. Information Gathering:
The Cell Cycle: A series of modeling activities Cancer Education Project University of Rochester Premise: Students learn best when exposed to a variety of activities Overview 1. Information Gathering:
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
8 kcal/mole of ATP 2 ATP 16 kcal 16 kcal/2 moles of ATP 686 kcal/mole of glucose 2.3%
 4. The cell s supply of ADP, P i, and NAD + is finite (limited). What happens to cellular respiration when all of the cell s NAD + has been converted to NADH? If NAD is unavailable, the cell is unable
4. The cell s supply of ADP, P i, and NAD + is finite (limited). What happens to cellular respiration when all of the cell s NAD + has been converted to NADH? If NAD is unavailable, the cell is unable
Addition by Division TEACHER NOTES SCIENCE NSPIRED
 Science Objectives Students will identify the changes that occur in cells during each phase of the cell cycle. Students will correlate these changes to the duration of time cells spend in each phase. While
Science Objectives Students will identify the changes that occur in cells during each phase of the cell cycle. Students will correlate these changes to the duration of time cells spend in each phase. While
The chromosomes are structures in living cells that contain
 Brooker Widmaier Graham Stiling: III. Nucleic Acid Structure and DNA Replication 15. Eukaryotic Chromosomes, Mitosis, 47 EUKARYOTIC CHROMOSOMES, MITOSIS, AND MEIOSIS C HAPTER O UTLINE 15.1 Molecular Structure
Brooker Widmaier Graham Stiling: III. Nucleic Acid Structure and DNA Replication 15. Eukaryotic Chromosomes, Mitosis, 47 EUKARYOTIC CHROMOSOMES, MITOSIS, AND MEIOSIS C HAPTER O UTLINE 15.1 Molecular Structure
Test Two Study Guide
 Test Two Study Guide 1. Describe what is happening inside a cell during the following phases (pictures may help but try to use words): Interphase: : Consists of G1 / S / G2. Growing stage, cell doubles
Test Two Study Guide 1. Describe what is happening inside a cell during the following phases (pictures may help but try to use words): Interphase: : Consists of G1 / S / G2. Growing stage, cell doubles
Use of the Microscope and Cytology
 Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
LAB 09 Cell Division
 LAB 09 Cell Division Introduction: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic information to the next generation. Cell division in individual bacteria and
LAB 09 Cell Division Introduction: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic information to the next generation. Cell division in individual bacteria and
1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Cells CHAPTER. 1.2.1 Prokaryotic Cells. 1.2.2 Eukaryotic Cells
 C HAPTER 1CELLS AND CELL DIVISION CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction In genetics, we view cells as vessels for the genetic material. Our main interest is in the chromosomes and their environment. This being said,
C HAPTER 1CELLS AND CELL DIVISION CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction In genetics, we view cells as vessels for the genetic material. Our main interest is in the chromosomes and their environment. This being said,
Classify chromosomes in a karyotype according to size and centromere position. Identify metacentric, submetacentric and acrocentric chromosomes
 Mitosis, Meiosis and the Cell Cycle Prof. Alfred Cuschieri University of Malta Department of Anatomy Objectives By the end of the session the student shoud be able to: Define the meaning of chromosomes
Mitosis, Meiosis and the Cell Cycle Prof. Alfred Cuschieri University of Malta Department of Anatomy Objectives By the end of the session the student shoud be able to: Define the meaning of chromosomes
Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis
 Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis Why do cells divide? Lab today focuses on cellular division, also known as cellular reproduction. To become more familiar with why cells divide, the types of cell
Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis Why do cells divide? Lab today focuses on cellular division, also known as cellular reproduction. To become more familiar with why cells divide, the types of cell
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome.
 Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance. Ch. 3
 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Ch. 3 THE CHROMOSOME THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND SEX CHROMOSOMES! The chromosome theory of inheritance describes how the transmission of chromosomes account for the Mendelian
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Ch. 3 THE CHROMOSOME THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND SEX CHROMOSOMES! The chromosome theory of inheritance describes how the transmission of chromosomes account for the Mendelian
How Well Do You Know Your Cells?
 How Well Do You Know Your Cells? Complete each sentence below with words from the box. One word will not be used. cells cell membrane cell walls chloroplasts cytoplasm Hooke Leeuwenhoek mitochondria nucleus
How Well Do You Know Your Cells? Complete each sentence below with words from the box. One word will not be used. cells cell membrane cell walls chloroplasts cytoplasm Hooke Leeuwenhoek mitochondria nucleus
The Case of the Dividing Cell: Mitosis and Meiosis in the Cellular Court. Part I The First Day of Testimony
 The Case of the Dividing Cell: Mitosis and Meiosis in the Cellular Court Part I The First Day of Testimony by Clyde Freeman Herreid Department of Biological Sciences University at Buffalo, State University
The Case of the Dividing Cell: Mitosis and Meiosis in the Cellular Court Part I The First Day of Testimony by Clyde Freeman Herreid Department of Biological Sciences University at Buffalo, State University
Objective: On a team of no more than (2). Build to illustrate a 3D model of a PLANT or ANIMAL cell. 10 pts.
 THE CELL model: Activity 4.1 Science / Biology Objective: On a team of no more than (2). Build to illustrate a 3D model of a PLANT or ANIMAL cell. - Your models should clearly demonstrate the following
THE CELL model: Activity 4.1 Science / Biology Objective: On a team of no more than (2). Build to illustrate a 3D model of a PLANT or ANIMAL cell. - Your models should clearly demonstrate the following
Bio 101 Section 001: Practice Questions for First Exam
 Do the Practice Exam under exam conditions. Time yourself! MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. The substrate fits in the of an enzyme: (A) allosteric site (B) active site (C) reaction groove (D) Golgi body (E) inhibitor
Do the Practice Exam under exam conditions. Time yourself! MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. The substrate fits in the of an enzyme: (A) allosteric site (B) active site (C) reaction groove (D) Golgi body (E) inhibitor
AP Biology 2011 Scoring Guidelines Form B
 AP Biology 2011 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to college success and opportunity. Founded
AP Biology 2011 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to college success and opportunity. Founded
Time For Mitosis. Materials. Procedure. Name
 Time For Mitosis Name Do all phases of mitosis require the same amount of time for completion? This question can be answered by counting the number of onion root tip cells in the four phases of mitosis
Time For Mitosis Name Do all phases of mitosis require the same amount of time for completion? This question can be answered by counting the number of onion root tip cells in the four phases of mitosis
Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number
 Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Know the principles and terminology associated with variations
Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Know the principles and terminology associated with variations
Contains chromatin that makes chromosomes (DNA and protein)
 1 Eukaryotic Large ribosomes Mitochondria Nucleus Linear DNA Prokaryotic Small ribosomes No mitochondria No Nucleus Circular DNA Plasmid / Flagellum Nucleus Nucleolus Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi
1 Eukaryotic Large ribosomes Mitochondria Nucleus Linear DNA Prokaryotic Small ribosomes No mitochondria No Nucleus Circular DNA Plasmid / Flagellum Nucleus Nucleolus Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi
June examination memorandum G12 ~ Life Sciences LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 JUNE EXAMINATION 2014 MEMORANDUM
 LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 JUNE EXAMINATION 2014 MEMORANDUM LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 JUNE EXAMINATION 2014 MEMORANDUM TOTAL: 150 SECTION A QUESTION 1 1.1 1.1.1 A 1.1.2 C 1.1.3 C 1.1.4 D 1.1.5 D 1.1.6 B 1.1.7
LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 JUNE EXAMINATION 2014 MEMORANDUM LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 JUNE EXAMINATION 2014 MEMORANDUM TOTAL: 150 SECTION A QUESTION 1 1.1 1.1.1 A 1.1.2 C 1.1.3 C 1.1.4 D 1.1.5 D 1.1.6 B 1.1.7
the plant & animal cell
 6.1 Basic unit of life Biology Biology Structure & functions of 06 the plant & animal cell In 1665, Robert Hooke observed a section of a cork using a microscope prepared by him. He discovered a structure
6.1 Basic unit of life Biology Biology Structure & functions of 06 the plant & animal cell In 1665, Robert Hooke observed a section of a cork using a microscope prepared by him. He discovered a structure
Laboratory Observing the Cell Cycle of Onion Root Tip Cells
 Laboratory Observing the Cell Cycle of Onion Root Tip Cells Background: Because of their rapid growth, the cells of the root tips of plants undergo rapid cell division. Ornamental onion root tips cells
Laboratory Observing the Cell Cycle of Onion Root Tip Cells Background: Because of their rapid growth, the cells of the root tips of plants undergo rapid cell division. Ornamental onion root tips cells
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
Cell Structure and Function
 CHAPTER 3 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Vocabulary Practice cell theory vacuole concentration gradient cytoplasm lysosome osmosis organelle centriole isotonic prokaryotic cell cell wall hypertonic eukaryotic
CHAPTER 3 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Vocabulary Practice cell theory vacuole concentration gradient cytoplasm lysosome osmosis organelle centriole isotonic prokaryotic cell cell wall hypertonic eukaryotic
Practice Problems 4. (a) 19. (b) 36. (c) 17
 Chapter 10 Practice Problems Practice Problems 4 1. The diploid chromosome number in a variety of chrysanthemum is 18. What would you call varieties with the following chromosome numbers? (a) 19 (b) 36
Chapter 10 Practice Problems Practice Problems 4 1. The diploid chromosome number in a variety of chrysanthemum is 18. What would you call varieties with the following chromosome numbers? (a) 19 (b) 36
Chapter 3. Chapter Outline. Chapter Outline 9/11/10. Heredity and Evolu4on
 Chapter 3 Heredity and Evolu4on Chapter Outline The Cell DNA Structure and Function Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis The Genetic Principles Discovered by Mendel Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Misconceptions
Chapter 3 Heredity and Evolu4on Chapter Outline The Cell DNA Structure and Function Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis The Genetic Principles Discovered by Mendel Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Misconceptions
Chromosome Mapping Assignment INSTRUCTIONS
 INSTRUCTIONS PROCEDURE A: 1) Examine the diagram of perch chromosomes supplied. They have been removed from the nucleus of the white blood cell after replication. 2) Cut out each chromosome map of these
INSTRUCTIONS PROCEDURE A: 1) Examine the diagram of perch chromosomes supplied. They have been removed from the nucleus of the white blood cell after replication. 2) Cut out each chromosome map of these
7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST. Part I: Cells. 1. The cell grows to its mature size during. a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d.
 7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST Part I: Cells 1. The cell grows to its mature size during a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d. interphase 2. The final stage of the cell cycle is called a. interphase
7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST Part I: Cells 1. The cell grows to its mature size during a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d. interphase 2. The final stage of the cell cycle is called a. interphase
the!sun!to!sugars.!this!is!called!! photosynthesis.!the!byproduct!of!those! Nucleus! sugars!is!our!oxygen.!
 Cytoplasm ANIMAL CELL Vacuoles Mitochondria Chromosomes GolgiApparatus Chloroplast+ TheChloroplastiswhatmakesthefood inthecell.they reonlyfoundinplant cellsandsomeprotists.everygreen plantyouseeisconvertingenergyfrom
Cytoplasm ANIMAL CELL Vacuoles Mitochondria Chromosomes GolgiApparatus Chloroplast+ TheChloroplastiswhatmakesthefood inthecell.they reonlyfoundinplant cellsandsomeprotists.everygreen plantyouseeisconvertingenergyfrom
Answer: 2. Uracil. Answer: 2. hydrogen bonds. Adenine, Cytosine and Guanine are found in both RNA and DNA.
 Answer: 2. Uracil Adenine, Cytosine and Guanine are found in both RNA and DNA. Thymine is found only in DNA; Uracil takes its (Thymine) place in RNA molecules. Answer: 2. hydrogen bonds The complementary
Answer: 2. Uracil Adenine, Cytosine and Guanine are found in both RNA and DNA. Thymine is found only in DNA; Uracil takes its (Thymine) place in RNA molecules. Answer: 2. hydrogen bonds The complementary
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes
 Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
02-SciProbe9-Chap02 2/8/07 12:12 PM Page 32 32 NEL
 32 UNIT A REPRODUCTION Chapter 2 Cell Growth and Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction Chapter 4 Human Reproduction Unit Preview Your body is made of many trillions of cells that came from a single
32 UNIT A REPRODUCTION Chapter 2 Cell Growth and Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction Chapter 4 Human Reproduction Unit Preview Your body is made of many trillions of cells that came from a single
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100
 Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity
 12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
High School Science Lesson Plan: Biology
 High School Science Lesson Plan: Biology Introduction Each lesson in the Adolescent Literacy Toolkit is designed to support students through the reading/learning process by providing instruction before,
High School Science Lesson Plan: Biology Introduction Each lesson in the Adolescent Literacy Toolkit is designed to support students through the reading/learning process by providing instruction before,
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9700 BIOLOGY
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers
MCAS Biology. Review Packet
 MCAS Biology Review Packet 1 Name Class Date 1. Define organic. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2. All living things are made up of 6 essential elements: SPONCH. Name the six elements of life. S N P C O H 3. Elements
MCAS Biology Review Packet 1 Name Class Date 1. Define organic. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2. All living things are made up of 6 essential elements: SPONCH. Name the six elements of life. S N P C O H 3. Elements
The correct answer is c A. Answer a is incorrect. The white-eye gene must be recessive since heterozygous females have red eyes.
 1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns
 Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
