COPD Medications. Mechanism Of Action Indication(s) Common Side Effects Comments
|
|
|
- Reynold O’Neal’
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Short-Acting Beta-2 Agonists (SABAs) Levalbuterol (Xopenex) Albuterol sulfate (ProAir; Ventolin; Proventil) Beta-2 agonists relax bronchial smooth muscle by stimulating beta-2 adrenergic receptors which increases camp and produces functional antagonism to bronchoconstriction. Long-Acting Beta-2 Agonists (LABAs) Treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in patients with reversible obstructive airway disease Decreased serum potassium, tremor, rhinitis, headache, nervousness, Tachycardia, excitement, Decreased serum potassium, tremor, headache, nervousness, -Little effect on heart rate Formoterol (Foradil; Performist) Arformoterol (Brovana) Indacaterol (Arcapta Neohaler) Salmerterol (Serevent Diskus) Beta-2 agonists relax bronchial smooth muscle by stimulating beta-2 adrenergic receptors which increases camp and produces functional antagonism to bronchoconstriction. bronchoconstriction in patients with COPD (including chronic Tachycardia, excitement, Decreased serum potassium, tremor, headache, nervousness -BBW for asthma-related death -Patients using SABAs should be instructed to discontinue routine use of these medications prior to beginning treatment with a LABA -Do not use for acute episodes of COPD. -Do not initiate in patients with significantly worsening or acutely deteriorating COPD. Short-Acting Anticholinergics (SAMAs) Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) Produce bronchodilation via competitive inhibition of cholinergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscles and thus blocking the bronchoconstrictor action bronchospasm in patients with COPD (including chronic Bronchitis, COPD exacerbation, sinusitis, UTI, back pain, dyspnea, cough, flu-like symptoms, URI, xerostomia -Use caution in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, and prostatic hyperplasia -Not indicated for the initial treatment of acute episodes of
2 of vagal efferent impulses. Inhibition of vagal tone results in dilation of the large central airways and small airways Long-Acting Anticholinergics (LAMAs) Aclidinium bromide (Tudorza Pressair) Tiotropium (Spiriva HandiHaler; Spiriva Respimat) Produce bronchodilation via competitive inhibition of cholinergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscles and thus blocking the bronchoconstrictor action of vagal efferent impulses. Inhibition of vagal tone results in dilation of the large central airways and small airways bronchospasm associated with COPD (including Combination Short-Acting Beta-2 Agonist Plus Anticholinergic Albuterol/Ipratropium (Combivent Respimat; Duoneb) See individual mechanisms of action for short-acting Beta-2 agonists and shortacting anticholinergics Treatment of COPD in patients who are on a bronchodilator but continue to have bronchospasms and require a second bronchodilator Headache, nasopharyngitis, cough, diarrhea Xerostomia, URTI, pharyngitis, sinusitis, chest pain, edema, headache, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, constipation, UTI, rhinitis Bronchitis, URTI, Headache, Lung disease, dyspnea, cough bronchospasm -Use caution in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, and prostatic hyperplasia -Not indicated for the initial treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm -Not indicated for the initial treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm -Do not use in patients with allergies to soy or peanut products (All trimesters) -Excessive use may result in tolerance.
3 Combination Long-Acting Beta-2 Agonist Plus Anticholinergic Vilanterol/Umeclidinium (Anoro Ellipta) Methylxanthines Aminophylline Theophylline (SR) (Theo-24) See individual mechanisms of action for long-acting Beta-2 agonists and longacting anticholinergics Relax bronchial smooth muscle and pulmonary blood vessels, stimulate central respiratory drive, and increase diaphragm contractility. airflow obstruction in patients with COPD (including chronic Treatment of symptoms and reversible airway obstruction due to chronic asthma, or other chronic lung diseases Diarrhea, limb pain, pharyingitis, pleuritic pain, sinusitis, UTI, vertigo, headache, arthralgia, nausea, toothache, abdominal pain Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, insomnia, tremor, irritability, restlessness, diuresis, difficulty urinating Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, insomnia, tremor, irritability, restlessness, diuresis, difficulty urinating -BBW for asthma-related death -Contraindicated in patients with severe hypersensitivity to milk proteins. -Paradoxical bronchospasm may occur -A dose-dependent increase in heart rate was reported in healthy subjects; use with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders. -Not recommended for acute symptom relief (All trimesters) -Only available as IV solution -Aminophylline is approximately 79% anhydrous theophylline by weight -Children under 1 year of age and elderly over 60 years of age have reduced theophylline clearance and increased risk of severe and potentially fatal theophylline toxicity -Theophylline-induced nonconvulsive status epilepticus has been reported (rarely) and should be considered in patients who develop CNS abnormalities. -Elderly patients have reduced theophylline clearance and have an increased risk of
4 Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICSs) Beclomethasone (Qvar) Budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler) Fluticasone (Flovent) Improve lung function by acting on multiple cell types and mediators involved in inflammation and airflow obstruction. Off Label: Long term treatment with inhaled corticosteroids added to long-acting bronchodilators is recommended for patients with severe and very severe COPD and frequent exacerbations that are not adequately controlled by long-acting bronchodilators. Long-term monotherapy with inhaled corticosteroids is not recommended. Combination Long-Acting Beta-2 Agonist Plus Corticosteroids Headache, URTI, pharyngitis, rhinitis Headache, dyspepsia, nausea, arthralgia, weakness, back pain, nasopharyngitis, cough, rhinitis, fever -Fatigue, malaise, headache, oral candidiasis, arthralgia, arthritis, musculoskeletal pain, sinus infection, sinusitis, URTI, throat irritation, nasal congestion, nasopharyngitis, rhinitis, bronchitis, pain, voice disorder, nausea and vomiting, influenza, cough, hoarseness toxicity or overdose. -Bronchospasm may occur with wheezing after inhalation (possibly fatal) -Prolonged use of corticosteroids may increase the incidence of secondary infection -Candida albicans infections may occur in the mouth and pharynx; rinsing with water after inhaler use may decrease risk -Rare cases of vasculitis or other systemic eosinophilic conditions can occur -Orally-inhaled corticosteroids may cause a reduction in growth velocity in pediatric patients -Inhaled budesonide is pregnancy Category B Formoterol/Budesonide (Symbicort) Formoterol/Mometasone (Dulera) Salmeterol/Fluticasone (Advair) See individual mechanisms of action for long-acting Beta-2 agonists and corticosteroids airflow obstruction associated with COPD (including chronic Headache, nasopharyngitis, URTI, abdominal distress, oral candidiasis, pharyngolaryngeal pain, LRTI, sinusitis, bronchitis See individual comments on long-acting Beta-2 agonists and corticosteroids
5 Vilanterol/Fluticasone (Breo Ellipta) Generic Systemic Corticosteroids Prednisone (PredniSONE Intensol; Rayos) Methylprednisone (Medrol; Solu-Medrol) Improve lung function by acting on multiple cell types and mediators involved in inflammation and airflow obstruction. Off-Label use only: Systemic corticosteroids given for acute exacerbation of COPD are effective and recommended in the management of this condition. Hypertension, emotional instability, headache, increased intracranial pressure, seizure, impaired wound healing, carbohydrate intolerance, Cushing s syndrome, diabetes mellitus, fluid retention, menstrual irregularities, potassium loss, sodium retention, peptic ulcer, tachycardia, arrhythmias, cardiomegaly, abnormal fat distribution, immune suppression, psychiatric disturbances -Adrenal suppression; especially at high doses for prolonged periods -Prolonged use associated with Kaposi s sarcoma -Acute myopathy has been reported with high dose corticosteroids -Prolonged use may cause cataracts or glaucoma -High doses/long-term use has been associated with increased bone loss and fractures -May affect growth velocity; growth, so use should be routinely monitored in pediatric patients -Pregnancy Category C (methylprednisolone) -Pregnancy category D (prednisone) Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) Inhibitors Roflumilast (Daliresp) Roflumilast and its metabolite selectively inhibit PDE4 leading to an accumulation of camp within inflammatory and structural cells important in the pathogenesis of COPD, To reduce the risk of COPD exacerbations in patients with severe COPD associated with chronic a history of exacerbations Headache, weight loss, diarrhea, nausea, influenza, back pain -Contraindicated in moderate to severe hepatic impairment -Systemic exposure may be increased in patients with mild hepatic impairment -Supraventricular arrhythmias including atrial fibrillation have
6 suppress cytokine release and inhibition of lung infiltration by neutrophils and other leukocytes, attenuate pulmonary remodeling and mucociliary malfunction been reported -Weight loss usually observed within 6 months of initiating therapy and diarrhea within 4 weeks -Use only as adjunctive therapy to bronchodilator therapy Antibiotics Aminopenicillins Amoxicillin/Clavulunate (Augmentin) Macrolides (Azithromycin) Doxycycline Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to one or more of the penicillinbinding proteins (PBPs) Clavulanic acid binds and inhibits beta-lactamases that inactivate amoxicillin. Inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis at the chain elongation step; binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit resulting in blockage of transpeptidation. Inhibits protein synthesis by binding with the 30S and possibly the 50S ribosomal subunit(s) of susceptible bacteria; may also cause alterations in the cytoplasmic membrane. Treatment of COPD exacerbations in patients with 3 cardinal symptoms - increase in dyspnea, sputum volume, and sputum purulence (Evidence B); patients with 2 cardinal symptoms if increased sputum purulence is one (Evidence C); patients who require mechanical ventilation (Evidence B) Diarrhea, nausea, rash, urticaria Diarrhea, nausea, pruritis, rash, abdominal pain, vomiting Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, hepatotoxicity, intracranial hypertension, photosensitivity -Hypersensitivity reactions - Use with caution in patients with renal impairment; dosage adjustment recommended -Pregnancy category B - Macrolides (especially erythromycin) have been associated with rare QT c prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias - Use with caution in patients with severe renal impairment -Pregnancy category B - May induce hyperpigmentation in many organs, including nails, bone, skin -Pregnancy category D
7 References: 1. Lexicomp [internet database]. Hudson, OH: Wolters Kluwer. Updated Periodically. Accessed 28 Apr Micromedex 2.0 Healthcare Series [internet database]. Greenwood Village, CO: Truven Health Analytics, Inc. Updated Periodically. Accessed 24 Apr Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Updated 2014). Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease, Inc. Updated 2014.
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients. Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources
 Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
GEORGIA MEDICAID FEE-FOR-SERVICE ASTHMA and COPD AGENTS PA SUMMARY
 GEORGIA MEDICAID FEE-FOR-SERVICE ASTHMA and COPD AGENTS PA SUMMARY Preferred Anticholinergics and Combinations Atrovent HFA (ipratropium) Combivent Respimat (ipratropium/albuterol) Ipratropium neb inhalation
GEORGIA MEDICAID FEE-FOR-SERVICE ASTHMA and COPD AGENTS PA SUMMARY Preferred Anticholinergics and Combinations Atrovent HFA (ipratropium) Combivent Respimat (ipratropium/albuterol) Ipratropium neb inhalation
Stacie L. Penkova, PharmD, MHSA, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Manager Critical Care Pharmacy Specialist Drug Information Coordinator Pharmacology Summit
 Stacie L. Penkova, PharmD, MHSA, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Manager Critical Care Pharmacy Specialist Drug Information Coordinator Pharmacology Summit July 26, 2014 Objectives Classify asthma by severity Prescribe
Stacie L. Penkova, PharmD, MHSA, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Manager Critical Care Pharmacy Specialist Drug Information Coordinator Pharmacology Summit July 26, 2014 Objectives Classify asthma by severity Prescribe
COPD. (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (Emphysema) (Chronic Bronchitis) Education For Our Community
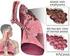 COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (Emphysema) (Chronic Bronchitis) Education For Our Community Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Definition Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (Emphysema) (Chronic Bronchitis) Education For Our Community Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Definition Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
AECOPD: Management and Prevention
 AECOPD: Management and Prevention Neil MacIntyre MD Duke University Medical Center Durham NC AECOPD: Management and Prevention AECOPD: Definitions and impact Acute management of AECOPD Preventing AECOPD.
AECOPD: Management and Prevention Neil MacIntyre MD Duke University Medical Center Durham NC AECOPD: Management and Prevention AECOPD: Definitions and impact Acute management of AECOPD Preventing AECOPD.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
MEDICATION GUIDE. SYMBICORT 80/4.5 (budesonide 80 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol
 MEDICATION GUIDE SYMBICORT 80/4.5 (budesonide 80 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol SYMBICORT 160/4.5 (budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation
MEDICATION GUIDE SYMBICORT 80/4.5 (budesonide 80 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol SYMBICORT 160/4.5 (budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation
YOU VE BEEN REFERRED TO AN ASTHMA SPECIALIST...
 YOU VE BEEN REFERRED TO AN ASTHMA SPECIALIST... ...HERE S WHAT TO EXPECT You have been referred to an allergist because you have or may have asthma. The health professional who referred you wants you to
YOU VE BEEN REFERRED TO AN ASTHMA SPECIALIST... ...HERE S WHAT TO EXPECT You have been referred to an allergist because you have or may have asthma. The health professional who referred you wants you to
CCHCS Care Guide: Asthma
 GOALS SHORTNESS OF BREATH, WHEEZE, COUGH NIGHT TIME AWAKENINGS ACTIVITY INTERFERENCE SABA* USE FOR SYMPTOM CONTROL FEV1* OR PEAK FLOW EXACERBATIONS REQUIRING ORAL STEROIDS < 2 DAYS / WEEK 2 TIMES / MONTH
GOALS SHORTNESS OF BREATH, WHEEZE, COUGH NIGHT TIME AWAKENINGS ACTIVITY INTERFERENCE SABA* USE FOR SYMPTOM CONTROL FEV1* OR PEAK FLOW EXACERBATIONS REQUIRING ORAL STEROIDS < 2 DAYS / WEEK 2 TIMES / MONTH
medicineupdate to find out more about this medicine
 medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Seretide for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease What this medicine is 1 What this medicine treats 2 Other medicines available for this condition
medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Seretide for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease What this medicine is 1 What this medicine treats 2 Other medicines available for this condition
Drug therapy SHORT-ACTING BETA AGONISTS SHORT-ACTING ANTICHOLINERGICS LONG-ACTING BETA AGONISTS LONG-ACTING ANTICHOLINERGICS
 Drug therapy 6 6.1 What is the role of bronchodilators in COPD? 52 SHORT-ACTING BETA AGONISTS 6.2 How do short-acting beta agonists work? 52 6.3 What are the indications for their use? 52 6.4 What is the
Drug therapy 6 6.1 What is the role of bronchodilators in COPD? 52 SHORT-ACTING BETA AGONISTS 6.2 How do short-acting beta agonists work? 52 6.3 What are the indications for their use? 52 6.4 What is the
Inhaled and Oral Corticosteroids
 Inhaled and Oral Corticosteroids Corticosteroids (steroids) are medicines that are used to treat many chronic diseases. Corticosteroids are very good at reducing inflammation (swelling) and mucus production
Inhaled and Oral Corticosteroids Corticosteroids (steroids) are medicines that are used to treat many chronic diseases. Corticosteroids are very good at reducing inflammation (swelling) and mucus production
RSPT 1410 Common Respiratory Drugs
 1 RSPT 1410 Wilkins: Chapter 32 2 Classifications Respiratory therapists administer several different class of drugs: (adrenergic) Parasympatholytics (anticholinergic) Mucoactives (mucolytic) Antiasthmatics
1 RSPT 1410 Wilkins: Chapter 32 2 Classifications Respiratory therapists administer several different class of drugs: (adrenergic) Parasympatholytics (anticholinergic) Mucoactives (mucolytic) Antiasthmatics
Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and asthma
 Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
Understanding COPD. An educational health series from
 Understanding COPD An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best integrated and
Understanding COPD An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best integrated and
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis
 COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
Medications. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to medications for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Introduction
 Patient Education A guide to medications for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Do you know how each of your inhalers works to help your breathing? Do you know the correct order in which to use
Patient Education A guide to medications for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Do you know how each of your inhalers works to help your breathing? Do you know the correct order in which to use
Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg
![Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg](/thumbs/33/15949075.jpg) Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg (mometasone furoate 100 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 5 mcg inhalation aerosol) DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg (mometasone furoate 200 mcg and formoterol
Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg (mometasone furoate 100 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 5 mcg inhalation aerosol) DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg (mometasone furoate 200 mcg and formoterol
Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations
 December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
RES/006/APR16/AR. Speaker : Dr. Pither Sandy Tulak SpP
 RES/006/APR16/AR Speaker : Dr. Pither Sandy Tulak SpP Definition of Asthma (GINA 2015) Asthma is a common and potentially serious chronic disease that imposes a substantial burden on patients, their families
RES/006/APR16/AR Speaker : Dr. Pither Sandy Tulak SpP Definition of Asthma (GINA 2015) Asthma is a common and potentially serious chronic disease that imposes a substantial burden on patients, their families
COPD PROTOCOL CELLO. Leiden
 COPD PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives and medication of COPD. The Cello way of working can be viewed on
COPD PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives and medication of COPD. The Cello way of working can be viewed on
Protocol in depth Asthma/COPD. [email protected]
 Protocol in depth Asthma/COPD [email protected] Asthma/COPD Narrowing of airways (an H4 histamine response causing inflammation and mucous production), leading to wheezing on inspiration and exhalation.
Protocol in depth Asthma/COPD [email protected] Asthma/COPD Narrowing of airways (an H4 histamine response causing inflammation and mucous production), leading to wheezing on inspiration and exhalation.
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History
 Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg
![Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg](/thumbs/40/20820124.jpg) Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg (mometasone furoate 100 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 5 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg (mometasone furoate 200 mcg and formoterol
Medication Guide DULERA [dew-lair-ah] 100 mcg/5 mcg (mometasone furoate 100 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 5 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol DULERA 200 mcg/5 mcg (mometasone furoate 200 mcg and formoterol
Objectives COPD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 4/19/2011
 Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema
 Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema YOUR PATIENT GUIDE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CHEST PHYSICIANS AND THE CHEST FOUNDATION Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema YOUR PATIENT
Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema YOUR PATIENT GUIDE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CHEST PHYSICIANS AND THE CHEST FOUNDATION Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema YOUR PATIENT
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
RESPIRATORY MEDICATIONS
 RESPIRATORY MEDICATIONS Purpose: To define and describe medications administered by Respiratory Therapy to patients. Sympathetic receptors: 1. Alpha receptors: - found primarily in blood vessels - stimulation
RESPIRATORY MEDICATIONS Purpose: To define and describe medications administered by Respiratory Therapy to patients. Sympathetic receptors: 1. Alpha receptors: - found primarily in blood vessels - stimulation
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers
 Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
COPD. What is COPD? How many people have COPD in Canada? Who gets COPD?
 What is COPD? COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. It is a long-term lung disease that makes it difficult for air to move into and out of the lungs. COPD is used to describe a few lung
What is COPD? COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. It is a long-term lung disease that makes it difficult for air to move into and out of the lungs. COPD is used to describe a few lung
Salbutamol 1mg/ml Nebuliser Solution. Salbutamol 2mg/ml Nebuliser Solution PL 36390/0035 PL 36390/0036
 Salbutamol 1mg/ml Nebuliser Solution Salbutamol 2mg/ml Nebuliser Solution PL 36390/0035 PL 36390/0036 UKPAR TABLE OF CONTENTS Lay summary Page 2 Scientific discussion Page 3 Steps taken for assessment
Salbutamol 1mg/ml Nebuliser Solution Salbutamol 2mg/ml Nebuliser Solution PL 36390/0035 PL 36390/0036 UKPAR TABLE OF CONTENTS Lay summary Page 2 Scientific discussion Page 3 Steps taken for assessment
Before prescribing for COPD management, the patient should have had appropriate assessment, including spirometry, as per NICE guidelines.
 Formulary Guidance for Management of COPD patients Before prescribing for COPD management, the patient should have had appropriate assessment, including spirometry, as per NICE guidelines. For inhaler
Formulary Guidance for Management of COPD patients Before prescribing for COPD management, the patient should have had appropriate assessment, including spirometry, as per NICE guidelines. For inhaler
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids
 Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL
 Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT. BEST PRACTICE: DISEASE MANAGEMENT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease NURSE TRACK
 IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BEST PRACTICE: DISEASE MANAGEMENT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease NURSE TRACK Best Practice Intervention Packages were designed for use by any In-Home Provider Agency
IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BEST PRACTICE: DISEASE MANAGEMENT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease NURSE TRACK Best Practice Intervention Packages were designed for use by any In-Home Provider Agency
Chapter 13. Sympathetic Nervous System. Basic Functions of the Nervous System. Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System
 Chapter 13 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Basic Functions of the Recognizing changes in Internal environment External environment Processing and integrating changes Reacting to changes Upper Saddle River,
Chapter 13 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Basic Functions of the Recognizing changes in Internal environment External environment Processing and integrating changes Reacting to changes Upper Saddle River,
PATIENT HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE Radiation Oncology (Patient Label)
 REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS SAFETY: Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? ALLERGIES: Do you have any allergies to medications? If, please
REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS SAFETY: Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? ALLERGIES: Do you have any allergies to medications? If, please
understanding the professional guidelines
 SEVERE ASTHMA understanding the professional guidelines This guide includes information on what the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the American Thoracic Society (ATS) have said about severe asthma.
SEVERE ASTHMA understanding the professional guidelines This guide includes information on what the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the American Thoracic Society (ATS) have said about severe asthma.
salmeterol xinafoate/fluticasone propionate dry powder for inhalation salmeterol xinafoate/fluticasone propionate inhalation aerosol
 Pr ADVAIR DISKUS salmeterol xinafoate/fluticasone propionate dry powder for inhalation Pr ADVAIR 100 DISKUS 50 mcg salmeterol (as the xinafoate salt) and 100 mcg fluticasone propionate Pr ADVAIR 250 DISKUS
Pr ADVAIR DISKUS salmeterol xinafoate/fluticasone propionate dry powder for inhalation Pr ADVAIR 100 DISKUS 50 mcg salmeterol (as the xinafoate salt) and 100 mcg fluticasone propionate Pr ADVAIR 250 DISKUS
DRUG UTILISATION STUDY IN BRONCHIAL ASTHMA IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Applications ISSN 0976-2639, Online ISSN 2278 6023 Vol 3, Issue 2, 2012, pp 297-305 http://www.bipublication.com DRUG UTILISATION STUDY IN BRONCHIAL ASTHMA IN A
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Applications ISSN 0976-2639, Online ISSN 2278 6023 Vol 3, Issue 2, 2012, pp 297-305 http://www.bipublication.com DRUG UTILISATION STUDY IN BRONCHIAL ASTHMA IN A
Understanding and Controlling Asthma Attacks. Information for parents
 Understanding and Controlling Asthma Attacks Information for parents Your child was recently seen by a doctor for asthma. This guide will help you gain a better understanding about your child's recent
Understanding and Controlling Asthma Attacks Information for parents Your child was recently seen by a doctor for asthma. This guide will help you gain a better understanding about your child's recent
Prof. Florian Gantner. Vice President Respiratory Diseases Research Boehringer Ingelheim
 Prof. Florian Gantner Vice President Respiratory Diseases Research Boehringer Ingelheim Research and Development in Practice: COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Facts Main cause of COPD
Prof. Florian Gantner Vice President Respiratory Diseases Research Boehringer Ingelheim Research and Development in Practice: COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Facts Main cause of COPD
RSPT 2317 Non-steroidal anti-asthma agents
 RSPT 2317 Non-steroidal Anti-asthma Agents Mechanisms of Inflammation in Asthma Mechanisms of Inflammation in Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways It is divided into extrinsic
RSPT 2317 Non-steroidal Anti-asthma Agents Mechanisms of Inflammation in Asthma Mechanisms of Inflammation in Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways It is divided into extrinsic
DRUG INTERACTIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW. Council on Family Health
 DRUG INTERACTIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Council on Family Health Drug Interactions There are more opportunities today than ever before to learn about your health and to take better care of yourself. It
DRUG INTERACTIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Council on Family Health Drug Interactions There are more opportunities today than ever before to learn about your health and to take better care of yourself. It
Tests. Pulmonary Functions
 Pulmonary Functions Tests Static lung functions volumes Dynamic lung functions volume and velocity Dynamic Tests Velocity dependent on Airway resistance Resistance of lung tissue to change in shape Dynamic
Pulmonary Functions Tests Static lung functions volumes Dynamic lung functions volume and velocity Dynamic Tests Velocity dependent on Airway resistance Resistance of lung tissue to change in shape Dynamic
Asthma & COPD Medication List
 Asthma & COPD Medication List LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS (used for prevention / control of asthma, NOT treatment of acute exacerbations) a. INHALED CORTICOSTEROIDS (ICS) Drug of choice for all levels
Asthma & COPD Medication List LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS (used for prevention / control of asthma, NOT treatment of acute exacerbations) a. INHALED CORTICOSTEROIDS (ICS) Drug of choice for all levels
EMS Information Bulletin- #060
 BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES EMS Information Bulletin- #060 DATE: October 27, 2008 SUBJECT: TO: FROM: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Basic Life Support Pennsylvania EMS Organizations &
BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES EMS Information Bulletin- #060 DATE: October 27, 2008 SUBJECT: TO: FROM: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Basic Life Support Pennsylvania EMS Organizations &
Interpretation of Laboratory Values
 Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Glucocorticoids, Inhaled Therapeutic Class Review (TCR)
 Glucocorticoids, Inhaled Therapeutic Class Review (TCR) July 31, 2015 No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
Glucocorticoids, Inhaled Therapeutic Class Review (TCR) July 31, 2015 No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
Key Points. Autonomic Nervous System Drugs. Autonomic effects Sympathetic. Drugs can modify ANS activity by: Autonomic Nervous System
 Key Points Autonomic Nervous System Drugs Autonomic drugs work at the synapses, Drugs either suppress or magnify the sympathetic or parasympathetic effect, Drugs don t work on a single target organ so
Key Points Autonomic Nervous System Drugs Autonomic drugs work at the synapses, Drugs either suppress or magnify the sympathetic or parasympathetic effect, Drugs don t work on a single target organ so
Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema
 Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema Your Patient workbook AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CHEST PHYSICIANS AND THE CHEST FOUNDATION Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema your patient
Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema Your Patient workbook AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CHEST PHYSICIANS AND THE CHEST FOUNDATION Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema your patient
PATIENT HISTORY FORM
 PATIENT HISTORY FORM If you are new to the office, have not been seen in over one (1) year, or are returning for a new problem, please complete this form in full. If there have been any changes since your
PATIENT HISTORY FORM If you are new to the office, have not been seen in over one (1) year, or are returning for a new problem, please complete this form in full. If there have been any changes since your
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim)
 EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. ADRENALINE (TARTRATE) STEROP 1 mg/1 ml Solution for injection. Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (TARTRATE) STEROP 1 mg/1 ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (TARTRATE) STEROP 1 mg/1 ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
PATIENT INFORMATION ABOUT TREATMENTS FOR ASTHMA AND ALLERGIC RHINITIS, PRESCRIPTIONS & OVER THE COUNTER MEDICINE
 PATIENT INFORMATION ABOUT TREATMENTS FOR ASTHMA AND ALLERGIC RHINITIS, PRESCRIPTIONS & OVER THE COUNTER MEDICINE The content of this booklet was developed by Allergy UK. MSD reviewed this booklet to comment
PATIENT INFORMATION ABOUT TREATMENTS FOR ASTHMA AND ALLERGIC RHINITIS, PRESCRIPTIONS & OVER THE COUNTER MEDICINE The content of this booklet was developed by Allergy UK. MSD reviewed this booklet to comment
Asthma in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence. Presented by Frederick Lloyd, MD Palo Alto Medical Foundation Palo Alto, California
 Asthma in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Presented by Frederick Lloyd, MD Palo Alto Medical Foundation Palo Alto, California Major Health Problem in Childhood Afflicts 2.7 million children in the USA
Asthma in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Presented by Frederick Lloyd, MD Palo Alto Medical Foundation Palo Alto, California Major Health Problem in Childhood Afflicts 2.7 million children in the USA
Emory Eye Center New Patient Questionnaire
 Patient Name: Date: Current Address: Current Phone: Date of Birth: Primary Care Physician: Referring Physician: (First & Last Name) (First & Last Name) Pharmacy Name: Phone #: ( ) Please answer all questions
Patient Name: Date: Current Address: Current Phone: Date of Birth: Primary Care Physician: Referring Physician: (First & Last Name) (First & Last Name) Pharmacy Name: Phone #: ( ) Please answer all questions
patient group direction
 DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
Seretide Diskus 50/100 Seretide Diskus 50/250 Seretide Diskus 50/500
 The format of this leaflet was determined by the Ministry of Health and its content was checked and approved in November 2009 TITLE Salmeterol-Fluticasone Propionate (Salmeterol-FP) SCOPE Trade Name Salmeterol
The format of this leaflet was determined by the Ministry of Health and its content was checked and approved in November 2009 TITLE Salmeterol-Fluticasone Propionate (Salmeterol-FP) SCOPE Trade Name Salmeterol
Breathe Easy: Asthma and FMLA
 This article was published in the FMLA Policy, Practice, and Legal Update newsletter, by Business & Legal Reports, Inc. (BLR). BLR is a nationally recognized publisher of regulatory and legal compliance
This article was published in the FMLA Policy, Practice, and Legal Update newsletter, by Business & Legal Reports, Inc. (BLR). BLR is a nationally recognized publisher of regulatory and legal compliance
COPD Prescribing Guidelines
 South Staffordshire Area Prescribing Group COPD Prescribing Guidelines Inhaler choices in this guideline are different from previous versions produced by the APG. It is not expected patients controlled
South Staffordshire Area Prescribing Group COPD Prescribing Guidelines Inhaler choices in this guideline are different from previous versions produced by the APG. It is not expected patients controlled
Pulmonary Disorders. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Pulmonary Disorders Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Characterized by decreased expiratory airflow Reduction in expiratory
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Pulmonary Disorders Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Characterized by decreased expiratory airflow Reduction in expiratory
COPD MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL STANFORD COORDINATED CARE
 I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines f the collabative management of patients with a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are not adequately controlled and to define the roles and
I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines f the collabative management of patients with a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are not adequately controlled and to define the roles and
Medications for COPD: A Review of Effectiveness
 Medications for COPD: A Review of Effectiveness GIL C. GRIMES, MD; JOHN L. MANNING, MD; PARITA PATEL, MD; and R. MARC VIA, MD Texas A&M University Health Science Center, Temple, Texas Chronic obstructive
Medications for COPD: A Review of Effectiveness GIL C. GRIMES, MD; JOHN L. MANNING, MD; PARITA PATEL, MD; and R. MARC VIA, MD Texas A&M University Health Science Center, Temple, Texas Chronic obstructive
Enhancing the Child s Voice in Clinical Care and Research
 Enhancing the Child s Voice in Clinical Care and Research Bryce B. Reeve, Ph.D. Associate Professor, Health Policy and Management Member, Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center [email protected] Standardized,
Enhancing the Child s Voice in Clinical Care and Research Bryce B. Reeve, Ph.D. Associate Professor, Health Policy and Management Member, Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center [email protected] Standardized,
PLAN OF ACTION FOR. Physician Name Signature License Date
 PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
MEDICATION INFORMATION: CONTROLLER MEDICATIONS
 FRANK J. TWAROG, M.D., Ph.D. CURTIS T. MOODY, M.D. ADULT AND PEDIATRIC ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES Brookline Concord (617) 735-8750 (978) 369-3567 MEDICATION INFORMATION: CONTROLLER MEDICATIONS Asthma medications
FRANK J. TWAROG, M.D., Ph.D. CURTIS T. MOODY, M.D. ADULT AND PEDIATRIC ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES Brookline Concord (617) 735-8750 (978) 369-3567 MEDICATION INFORMATION: CONTROLLER MEDICATIONS Asthma medications
Medicines Use Review Supporting Information for Asthma Patients
 Medicines Use Review Supporting Information for Asthma Patients What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. The inflammation causes an associated increase in airway hyper-responsiveness,
Medicines Use Review Supporting Information for Asthma Patients What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. The inflammation causes an associated increase in airway hyper-responsiveness,
Upstate University Health System Medication Exam - Version A
 Upstate University Health System Medication Exam - Version A Name: ID Number: Date: Unit: Directions: Please read each question below. Choose the best response for each of the Multiple Choice and Medication
Upstate University Health System Medication Exam - Version A Name: ID Number: Date: Unit: Directions: Please read each question below. Choose the best response for each of the Multiple Choice and Medication
Your health care provider may prescribe bronchodilators such as albuterol for emergency relief if an acute asthma attack occurs.
 Patient Information ASMANEX TWISTHALER 220 mcg (mometasone furoate inhalation powder) ASMANEX TWISTHALER 110 mcg (mometasone furoate inhalation powder) FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY Please read this leaflet
Patient Information ASMANEX TWISTHALER 220 mcg (mometasone furoate inhalation powder) ASMANEX TWISTHALER 110 mcg (mometasone furoate inhalation powder) FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY Please read this leaflet
Medication and Devices for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Medication and Devices for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients with COPD take a wide variety of medicines to manage their symptoms these include: Inhaled Short Acting Bronchodilators
Medication and Devices for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients with COPD take a wide variety of medicines to manage their symptoms these include: Inhaled Short Acting Bronchodilators
White, circular, biconvex, uncoated tablets with a score line on one side, plain on the other.
 Nausicalm Cyclizine hydrochloride Ph. Eur. 50 mg Presentation White, circular, biconvex, uncoated tablets with a score line on one side, plain on the other. Uses Actions The active ingredient-cyclizine
Nausicalm Cyclizine hydrochloride Ph. Eur. 50 mg Presentation White, circular, biconvex, uncoated tablets with a score line on one side, plain on the other. Uses Actions The active ingredient-cyclizine
SERETIDE Fluticasone propionate/salmeterol xinafoate Consumer Medicine Information
 SERETIDE Fluticasone propionate/salmeterol xinafoate Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using Seretide. This leaflet answers some
SERETIDE Fluticasone propionate/salmeterol xinafoate Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using Seretide. This leaflet answers some
Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa )
 Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa ) ESCA: For the treatment of Alzheimer s disease. SECONDARY CARE SECTION TO BE COMPLETED BY INITIATING DOCTOR
Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa ) ESCA: For the treatment of Alzheimer s disease. SECONDARY CARE SECTION TO BE COMPLETED BY INITIATING DOCTOR
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system
 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
MEDICATION GUIDE REMICADE (Rem-eh-kaid) (infliximab) Read the Medication Guide that comes with REMICADE before you receive the first treatment, and
 MEDICATION GUIDE REMICADE (Rem-eh-kaid) (infliximab) Read the Medication Guide that comes with REMICADE before you receive the first treatment, and before each time you get a treatment of REMICADE. This
MEDICATION GUIDE REMICADE (Rem-eh-kaid) (infliximab) Read the Medication Guide that comes with REMICADE before you receive the first treatment, and before each time you get a treatment of REMICADE. This
NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only)
 PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
5. Aerosol Drug Delivery Devices: Pressurized Metered-Dose Inhalers
 Table of Contents Introduction 1. Aerosol Drug Delivery: the Basics 2. Aerosol Drugs: the Major Categories 3. Aerosol Drug Delivery Devices: Small-Volume Nebulizers 4. Aerosol Drug Delivery Devices: Inhalers
Table of Contents Introduction 1. Aerosol Drug Delivery: the Basics 2. Aerosol Drugs: the Major Categories 3. Aerosol Drug Delivery Devices: Small-Volume Nebulizers 4. Aerosol Drug Delivery Devices: Inhalers
Welcome COPD MANAGEMENT PROGRAM. Reproduced with permission of UofL Pulmonary s COPD Management Program
 Welcome COPD MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4: Section 5: Section 6: Section 7: Section 8: Section 9: What is COPD? How the Lungs work. Managing your COPD. Exercise Breathing
Welcome COPD MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4: Section 5: Section 6: Section 7: Section 8: Section 9: What is COPD? How the Lungs work. Managing your COPD. Exercise Breathing
SOUTH TAMPA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CENTER
 SOUTH TAMPA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CENTER PATIENT/CARE GIVER QUESTIONNAIRE DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Patient's Name: City: State: Zip Code: Phone: Marital Status: Spouse/Care Giver Name: Phone (H) (W) Occupation:
SOUTH TAMPA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CENTER PATIENT/CARE GIVER QUESTIONNAIRE DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Patient's Name: City: State: Zip Code: Phone: Marital Status: Spouse/Care Giver Name: Phone (H) (W) Occupation:
Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia
 Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Lower Respiratory Tract Dr T Avenant Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Definitions Recurrent pneumonia more than two episodes of pneumonia in 18 months Persistent pneumonia
Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Lower Respiratory Tract Dr T Avenant Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Definitions Recurrent pneumonia more than two episodes of pneumonia in 18 months Persistent pneumonia
The patient s response to therapy within the first hour in the Emergency Room is one of the most reliable ways to predict need for hospitalization.
 Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
UpRight Aceclofenac 100 mg and Paracetamol 500 mg fixed dose combination
 For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only UpRight Aceclofenac 100 mg and Paracetamol 500 mg fixed dose combination DESCRIPTION UPRIGHT is a fixed dose combination
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only UpRight Aceclofenac 100 mg and Paracetamol 500 mg fixed dose combination DESCRIPTION UPRIGHT is a fixed dose combination
Adrenal Insufficiency. Adrenal cortex secretions. Adrenal Insufficiency. Adrenal Insufficiency. Acute Adrenal Insufficiency
 Adrenal cortex secretions Cortisol secretion Diurnal pattern 24 hour secretion = Stress = demands 30 mg 300 mg to meet physiological Adrenal Insufficiency PRIMARY ADDISON S DISEASE Autoimmune Infection
Adrenal cortex secretions Cortisol secretion Diurnal pattern 24 hour secretion = Stress = demands 30 mg 300 mg to meet physiological Adrenal Insufficiency PRIMARY ADDISON S DISEASE Autoimmune Infection
The Annual Direct Care of Asthma
 The Annual Direct Care of Asthma The annual direct health care cost of asthma in the United States is approximately $11.5 billion; indirect costs (e.g. lost productivity) add another $4.6 billion for a
The Annual Direct Care of Asthma The annual direct health care cost of asthma in the United States is approximately $11.5 billion; indirect costs (e.g. lost productivity) add another $4.6 billion for a
- Canine Chronic Bronchitis cannot be cured, but can be controlled
 MD-096A-0211 1 2 - The symptoms of asthma can mimic other diseases such as heartworm, pneumonia and congestive heart failure (Padrid, Use of Inhaled Medications to Treat Respiratory Diseases in Dogs and
MD-096A-0211 1 2 - The symptoms of asthma can mimic other diseases such as heartworm, pneumonia and congestive heart failure (Padrid, Use of Inhaled Medications to Treat Respiratory Diseases in Dogs and
