Exercise Theory Performance Standards 2014
|
|
|
- Shanon Elliott
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exercise Theory s 2014 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Alberta Fitness Leadership Certification Association (AFLCA) British Columbia Recreation and Parks Association (BCRPA) Saskatchewan Parks and Recreation Association (SPRA) Manitoba Fitness Council (MFC) Ontario Fitness Council (OFC) Fitness New Brunswick (NBF) Nova Scotia Fitness Association (NSFA) Exercise Theory s National Fitness Leadership Alliance (NFLA) 1
2 Exercise Theory s 2014 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory s Health Related Benefits of Physical Activity (3.5%) The Fitness Leader will be able to describe the benefits of physical activity and its relationship to health and wellness. a. Summarize the health-related benefits of physical activity. b. Describe the potential health impacts of physical inactivity and sedentary lifestyles. c. Identify modifiable lifestyle behaviours and non-modifiable risk factors and how they increase or decrease the risk of chronic disease. Holistic Approach to Physical Activity and Lifestyle (3%) The Fitness Leader will describe and integrate the holistic (whole person wellness) approach to physical activity and lifestyle, identify the elements of the Active Living concept, and discuss the implications for fitness leadership. a. Define holism, describe the benefits as they relate to physical activity, and discuss how to impart this knowledge in a fitness leadership setting. b. Define Active Living. c. Identify common barriers to physical activity. d. Describe and demonstrate ways to encourage participants to commit to exercise and take responsibility for their own health and well-being. National Fitness Leadership Alliance (NFLA) 2
3 Exercise Theory s 2014 Anatomy (15%) The Fitness Leader will demonstrate a basic knowledge of human anatomy. a. Identify the major muscle or muscle groups and the movements they perform, including: trapezius; erector spinae; deltoid (anterior, middle and posterior); rhomboids; pectoralis major; rectus abdominis; internal and external obliques; transverse abdominis; biceps brachii; triceps brachii; the latissimus dorsi; iliopsoas; gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus; hip adductors; hamstrings; quadriceps (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis); gastrocnemius; soleus; and tibialis anterior. b. Identify the types of joints, including; fibrous, cartilaginous and synovial (e.g., ball and socket, saddle, and hinge) and describe how bone structure influences joint function. c. Identify joint structures and connective tissues, including the joint capsule, synovial membrane, articular cartilage, joint cavity, ligaments, and tendons. d. Identify the major bones, including the: cranium, vertebrae (including cervical, thoracic and lumbar areas), scapula, ribs, sternum, humerus, radius, ulna, clavicle, pelvic girdle femur, tibia, fibula, and patella. Movement Mechanics (25%) The Fitness Leader will demonstrate basic knowledge of the biomechanics involved in human movement. a. Identify the movements of the hip, elbow, shoulder girdle, spine, wrist, ankle and knee. b. Identify the major joint actions; including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, medial/ internal and lateral/external rotation, circumduction, hyperextension, dorsiflexion, plantar flexion, pronation, supination, eversion, inversion, lateral flexion, protraction, retraction, elevation, depression, transverse(horizontal) abduction and transverse(horizontal) adduction. c. For the following four exercises (push-up, squat, lunge and abdominal curl), identify the agonist, antagonist, and the type of contraction for each phase of the exercise. d. Define synergist. e. Define and describe muscle actions (e.g., concentric, eccentric, isometric). f. Describe how the following impacts stability: a) size of the base of support, b) height of the centre of gravity and c) location of the centre of gravity in relation to the base of support. g. Using the principle of length of lever, explain how they can be used to vary the intensity of an exercise. National Fitness Leadership Alliance (NFLA) 3
4 Exercise Theory s 2014 Exercise Physiology (12%) The Fitness Leader will demonstrate through verbal and/or written communication a basic knowledge of exercise physiology underlying human movement. a. Identify the average range for resting heart rate as well as the range for target exercise heart rate for an individual of a stated age using the Karvonen Method, and 220- age max heart rate method. b. State whether each of the following increases or decreases during a cardiovascular exercise session: heart rate, blood pressure, stroke volume and respiratory rate. c. Describe how oxygen enters and moves through the body and how carbon dioxide is removed from the muscles. d. Describe venous pooling and how to prevent it. e. Understand blood pressure and normal resting values for diastolic and systolic. f. Describe how blood pressure adapts to cardiovascular conditioning. g. Summarize the key elements (endurance, total time, power) of the three energy systems, (aerobic, lactic acid and ATP-CP) and their primary fuel (glycogen/glucose, fats, ATP-CP). Identify the primary system used in various physical activities. h. Describe the long-term training adaptations of the following fitness components: cardiovascular endurance, muscular endurance, muscular strength and flexibility. i. Identify and describe how environmental factors (heat, humidity, cold) can affect the body's response to physical activity. Principles of Exercise Conditioning (18%) The Fitness Leader will demonstrate a basic knowledge of exercise conditioning principles. a. Describe the FITT Principle: frequency, intensity, time (duration), and type of exercise for improving each of the following health related components of fitness: flexibility, cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, and muscular endurance. b. Show how using the talk test, rating of perceived exertion, the Borg scale, and training heart rate can be used to monitor and adjust intensity. c. Identify the pros and cons associated with static, dynamic and ballistic stretching and when each is most appropriate. d. Describe the importance of developing a balanced muscle conditioning program for the muscles surrounding the major joints. e. Identify and describe the anatomical limitations to joint range of motion (flexibility). f. Describe established training methods and principles. (SAID, progressive overload, maintenance, FITT, reversibility, ceiling effect, symmetry). National Fitness Leadership Alliance (NFLA) 4
5 Exercise Theory s 2014 Exercise Analysis and Risk Management (10%) The Fitness Leader will exemplify and demonstrate safety in all aspects of planning and delivering of fitness programs as well as demonstrate methods for preventing and managing injuries. a. Describe why and how to use the following pre-screening tools: PAR-Q+ and eparmed-x. b. For the following exercises: push-up, squat, lunge and abdominal curl, analyze each for purpose, potential risks to joint structures, and modifications or alternative exercises. c. Describe the signs and symptoms of overtraining. d. Know the signs and symptoms that would warrant modifying or stopping an exercise session. e. Understand the importance of knowing the set of emergency procedures for the facility (i.e., location of the first aid kit, emergency exits, emergency protocols, location of telephone and street address) f. Explain the RICE principle (i.e., rest, immobilize, cold and elevation). g. Describe and demonstrate neutral posture while standing. Basic Nutrition (3.5%) The Fitness Leader will be able to explain Eating Well with Canada's Food Guide. a. Using Eating Well with Canada's Food Guide, list the 4 food groups and describe the main principles of the guide, e.g., choosing healthy options, choosing variety and using water to satisfy your thirst. b. Know the differences between the unsaturated, saturated and trans-fat and give a food example of each. c. Know when you should refer a participant to a Registered Dietitian. Body Composition (3%) The Fitness Leader will identify safe and effective strategies for obtaining and maintaining a healthy body composition. a. Explain the energy-in/energy-out concept. National Fitness Leadership Alliance (NFLA) 5
6 Exercise Theory s 2014 b. Understand that the combination of food intake and physical activity is most effective in maintaining a healthy body composition. c. Demonstrate an understanding of Body Mass Index (BMI), and this measurement s limitations. (e.g., it does not differentiate between lean and fat mass) d. Demonstrate an understanding of waist girth and its use as a predictor of the health related risks of obesity. e. Explain how changes in body composition (lean and fat tissue changes) influence basal metabolic rate and subsequent energy balance. f. Define atrophy and hypertrophy. Program Planning (5%) The Fitness Leader will design an effective physical activity/exercise program using established training methods and principles. a. Demonstrate the ability to provide exercise modifications based on clients needs. b. Apply the principles of the Canadian Physical Activity Guidelines. Leadership Skills (2.5%) The Fitness Leader will understand principles of adult learning, communication skills, and leadership models. a. Understand the principles of adult learning and how they relate to an exercise environment. b. Understand how to use effective communication when working with a variety of participants. (ex. non-verbal, verbal) c. Describe and apply the principles of effective leadership styles: leader centred dictator, and laissez-faire. d. Identify intrinsic and extrinsic factors that may motivate adults to participate in physical activity. e. Understand the principles of adult learning. National Fitness Leadership Alliance (NFLA) 6
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES
 Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation:
 EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
The skeletal and muscular systems
 anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Deltoid Trapezius. Identify the muscle pair(s) that work together to produce the movements listed above.
 Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
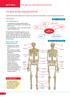 SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Anatomy for Sport and Exercise
 Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise and Health. Unit Accreditation Number A/600/9051
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Rehabilitation with Pilates
 Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice
 Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis
 Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
Strength Training for the Runner
 Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE
 UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM
 EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
Practice Chapter 6. Figure 6.3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb
 2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
Personal Trainer Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities (1/01/12)
 1. Core Knowledge A. Kinesiology: Anatomy and Biomechanics B. Exercise Physiology C. Basic Nutrition and Weight Management D. Human Behavior 2. Health and Medical Review; and Fitness Assessment A. Health
1. Core Knowledge A. Kinesiology: Anatomy and Biomechanics B. Exercise Physiology C. Basic Nutrition and Weight Management D. Human Behavior 2. Health and Medical Review; and Fitness Assessment A. Health
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson
 Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle
 Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
SAMPLE WORKOUT Full Body
 SAMPLE WORKOUT Full Body Perform each exercise: 30 secs each x 2 rounds or 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps Monday & Wednesday or Tuesday & Thursday Standing Squat Muscles: glutes (butt), quadriceps (thigh) Stand
SAMPLE WORKOUT Full Body Perform each exercise: 30 secs each x 2 rounds or 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps Monday & Wednesday or Tuesday & Thursday Standing Squat Muscles: glutes (butt), quadriceps (thigh) Stand
Women s Home Workout Bible
 Women s Home Workout Bible CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM #125. Check your receipt for course expiration date.. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. How to Complete this Program
Women s Home Workout Bible CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM #125. Check your receipt for course expiration date.. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. How to Complete this Program
Strength Training. Designed Specifically for Novice/Junior/Senior Skaters and Coaches
 Strength Training Designed Specifically for Novice/Junior/Senior Skaters and Coaches Strength Training Instructor Guidelines Instructor Qualifications A. Degree in exercise, physical education or sports
Strength Training Designed Specifically for Novice/Junior/Senior Skaters and Coaches Strength Training Instructor Guidelines Instructor Qualifications A. Degree in exercise, physical education or sports
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
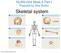 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Structure & Function of the Knee. One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity.
 Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
The Muscular System General & Anatomy
 The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength
 A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM # 140. Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 2012 by Exercise
A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM # 140. Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 2012 by Exercise
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. 4. Name the three types of fibrous joints and give an example of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Chapter 5. The Shoulder Joint. The Shoulder Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Avoiding Meniscus Surgery
 Avoiding Meniscus Surgery Robert Tarantino February 9, 2008 2007 NY CTTC-1 1 WARNING THIS MATERIAL DOES NOT CONSTITUTE MEDICAL ADVICE. IT IS INTENDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. PLEASE CONSULT A PHYSICIAN
Avoiding Meniscus Surgery Robert Tarantino February 9, 2008 2007 NY CTTC-1 1 WARNING THIS MATERIAL DOES NOT CONSTITUTE MEDICAL ADVICE. IT IS INTENDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. PLEASE CONSULT A PHYSICIAN
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014
 PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation.
 Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome and the Pilates Client
 Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome and the Pilates Client Aliza Nizet Comprehensive Teacher Training Course Body Arts and Science International Mind & Body Wellness Studio January 26 May 18, 2008 1 Abstract
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome and the Pilates Client Aliza Nizet Comprehensive Teacher Training Course Body Arts and Science International Mind & Body Wellness Studio January 26 May 18, 2008 1 Abstract
GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011
 GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011 Tick off list of revision topics Section 1 Reasons for taking part physical, social, mental Influences people, image, cultural, resources, health and well-being, socio-economic
GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011 Tick off list of revision topics Section 1 Reasons for taking part physical, social, mental Influences people, image, cultural, resources, health and well-being, socio-economic
Chair Exercises and Lifting Weights
 Chair Exercises and Lifting Weights Why are chair exercises and lifting weights important? Physical activity is one of the most important things you can do to maintain your diabetes control as well as
Chair Exercises and Lifting Weights Why are chair exercises and lifting weights important? Physical activity is one of the most important things you can do to maintain your diabetes control as well as
AMERICAN COUNCIL ON EXERCISE PERSONAL TRAINER UNIVERSITY CURRICULUM LAB MANUAL
 AMERICAN COUNCIL ON EXERCISE PERSONAL TRAINER UNIVERSITY CURRICULUM LAB MANUAL LAB ACTIVITY #1: SOCIAL SUPPORT STRATEGIES ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION An important coping strategy for relapse prevention is for
AMERICAN COUNCIL ON EXERCISE PERSONAL TRAINER UNIVERSITY CURRICULUM LAB MANUAL LAB ACTIVITY #1: SOCIAL SUPPORT STRATEGIES ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION An important coping strategy for relapse prevention is for
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
Muscle Organization and Function. Chapter 10: The Muscular System. Parallel (Fusiform) Muscles. Organization of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
 Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
Massage and Movement
 Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Clinical Care Program
 Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP
 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B.
 Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
CHAPTER 9: THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463
 Phase I Passive Range of Motion Phase (postop week 1-2) Minimize shoulder pain and inflammatory response Achieve gradual restoration of gentle active range of motion Enhance/ensure adequate scapular function
Phase I Passive Range of Motion Phase (postop week 1-2) Minimize shoulder pain and inflammatory response Achieve gradual restoration of gentle active range of motion Enhance/ensure adequate scapular function
9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS
 Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Muscle Energy Technique. Applied to the Shoulder
 Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
NDT Treatment Planning Worksheet
 Child s Name: Kalab DOB: 01/01/02 Diagnosis: CP-Right-sided Heimplegia DOE: May 29, 2009 Therapist s Name: Mary Rose Franjoine Discipline: PT Current Participation: Attends his neighborhood school with
Child s Name: Kalab DOB: 01/01/02 Diagnosis: CP-Right-sided Heimplegia DOE: May 29, 2009 Therapist s Name: Mary Rose Franjoine Discipline: PT Current Participation: Attends his neighborhood school with
The Time Constrained Athlete:
 The Time Constrained Athlete: Developing a 15 Minute Rehabilitation Program Joshua Stone, MA, ATC, NASM-CPT, CES, PES Sports Medicine Program Manager National Academy of Sports Medicine Agenda 1. Time
The Time Constrained Athlete: Developing a 15 Minute Rehabilitation Program Joshua Stone, MA, ATC, NASM-CPT, CES, PES Sports Medicine Program Manager National Academy of Sports Medicine Agenda 1. Time
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
Figure 6.1. 2) The A band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 188
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
Chapter 4 Exercise Metabolism and Bioenergetics:
 CPT Study Guide, Version 4 On the actual exam, you will be tested in the following subject areas (exam breakdown): Basic and Applied Sciences Assessment Exercise Technique and Training Instruction Program
CPT Study Guide, Version 4 On the actual exam, you will be tested in the following subject areas (exam breakdown): Basic and Applied Sciences Assessment Exercise Technique and Training Instruction Program
Biomechanics. State of equilibrium is when the sum (or net effect) of forces acting on a body equals zero
 Biomechanics Kinesiology is the science of, or study of, human motion. It brings together the fields of anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, physics and geometry relating them to human movement. Bio refers
Biomechanics Kinesiology is the science of, or study of, human motion. It brings together the fields of anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, physics and geometry relating them to human movement. Bio refers
American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine James McCrossin MS ATC, CSCS Philadelphia Flyers April 23 rd, 2015
 American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine James McCrossin MS ATC, CSCS Philadelphia Flyers April 23 rd, 2015 Coming together is a beginning; keeping together is progress; working together is success.
American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine James McCrossin MS ATC, CSCS Philadelphia Flyers April 23 rd, 2015 Coming together is a beginning; keeping together is progress; working together is success.
Evaluation, Treatment, and Exercise Rx for Muscle Imbalance in the Lower Extremities April 5, 2014 AOCPMR Midyear Meetingr Rebecca Fishman, D.O.
 Evaluation, Treatment, and Exercise Rx for Muscle Imbalance in the Lower Extremities April 5, 2014 AOCPMR Midyear Meetingr Rebecca Fishman, D.O. Biomechanics of the Lumbar Spine and Lower Extremities Lower
Evaluation, Treatment, and Exercise Rx for Muscle Imbalance in the Lower Extremities April 5, 2014 AOCPMR Midyear Meetingr Rebecca Fishman, D.O. Biomechanics of the Lumbar Spine and Lower Extremities Lower
2002 Functional Design Systems
 1. Proprioceptive sensitivity has to do with not being too sensitive but being sensitive enough. 2. The hammies have a lot to do with all three planes of function. 3. In upright function, knee flexion
1. Proprioceptive sensitivity has to do with not being too sensitive but being sensitive enough. 2. The hammies have a lot to do with all three planes of function. 3. In upright function, knee flexion
Muscular System Teacher s lecture notes, curriculum and guides 2012
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines
 USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
PILATES Fatigue Posture and the Medical Technology Field
 PILATES Fatigue Posture and the Medical Technology Field Marybeth Kane May 2014 Course: 2014, Pacific Palisades, CA 1 ABSTRACT A medical laboratory scientist (MLS) (also referred to as a medical technologist
PILATES Fatigue Posture and the Medical Technology Field Marybeth Kane May 2014 Course: 2014, Pacific Palisades, CA 1 ABSTRACT A medical laboratory scientist (MLS) (also referred to as a medical technologist
Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany the OCR resource
 Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany the OCR resource Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training activity which supports
Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany the OCR resource Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training activity which supports
