Treatment options for acute uncomplicated cystitis in adults. Kurt G. Naber*
|
|
|
- Prudence Griffith
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2000) 46, Suppl. S1, Treatment options for acute uncomplicated cystitis in adults JAC Kurt G. Naber* Urological Clinic, Hospital St Elisabeth, Straubing, Teaching Hospital of the Technical University of Munich, Germany Urinary tract infection (UTI) is classified as uncomplicated if it occurs in a patient with a structurally and functionally normal urinary tract. Acute uncomplicated cystitis is observed chiefly in women. It needs, however, to be differentiated depending on whether it occurs in premenopausal, postmenopausal or pregnant women. Only a small number of year old, otherwise healthy men suffer acute uncomplicated cystitis. In premenopausal, non-pregnant women, single-dose antimicrobial therapy is generally less effective than the same antibiotic used for longer duration. However, most antimicrobial agents given for 3 days are as effective as those given for longer duration, and adverse events tend to be found more often with longer treatment. Trimethoprim (or co-trimoxazole) can be recommended as first-line empirical therapy only in communities with resistance rates of uropathogens to trimethoprim of < 10 20%. Otherwise fluoroquinolones are recommended. Alternatives are fosfomycin trometamol or β-lactams, such as second- or third-generation oral cephalosprins or pivmecillinam, especially when fluoroquinolones are contraindicated or a high proportion (>10%) of Escherichia coli strains in the community are already resistant to fluoroquinolones, as in Spain, for example. Recurrent UTIs are common among young, healthy women even though they generally have anatomically and physiologically normal urinary tracts. The following prophylactic antimicrobial regimens are recommended: (i) the use of long-term, low-dose prophylactic antimicrobials taken at bedtime; (ii) post-coital prophylaxis for women in whom episodes of infection are associated with sexual intercourse. Other prophylactic methods are not as yet as effective as antimicrobial prophylaxis. Introduction For optimal management of urinary tract infections (UTIs), it is necessary to classify them according to the status of the patient (symptomatic or asymptomatic), the status of the urinary tract (uncomplicated or complicated), the pattern of infection (isolated, recurrent or unresolved) and the site of infection (cystitis, pyelonephritis or prostatitis). A UTI is classified as uncomplicated if it occurs in a patient with a structurally and functionally normal urinary tract. A UTI is classified as complicated if there are functional or anatomical abnormalities within the urinary tract or underlying diseases that predispose to UTI, such as diabetes mellitus or AIDS. Acute uncomplicated cystitis is observed chiefly in women. It needs, however, to be differentiated depending on whether it occurs in premenopausal, postmenopausal or pregnant women. Recurrent cystitis is common in young, healthy women, even though they generally have anatomically and physiologically normal urinary tracts. Whether UTI in pregnancy should be classified as uncomplicated or complicated remains debatable. Although data dealing specifically with UTIs in healthy postmenopausal women without genitourinary abnormalities are limited, it is likely that most UTIs in this group of women are uncomplicated. Data on uncomplicated UTI in healthy adult men are also sparse and much less is known about optimal diagnosis and therapy. Aetiological spectrum Escherichia coli is the causative pathogen in c.70 95% of cases and Staphylococcus saprophyticus in between 5% and 20% of cases. Occasionally, other Enterobacteriaceae, such as Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella spp., or *Corresponding author. Tel: ; Fax: ; naberk@klinikum-straubing.de 2000 The British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 23
2 K. G. Naber enterococci are isolated from patients with UTIs. In as many as 10 15% of symptomatic patients, there are low levels of bacteriuria ( cfu/ml), which cannot be detected with routine culture methods, which use 1 L of urine per agar plate. 1 Treatment options There seem to be no long-term adverse effects with respect to renal function or increased mortality associated with acute uncomplicated cystitis in non-pregnant women, even in those with frequent recurrences. 1 Untreated cystitis rarely progresses to symptomatic upper UTI. Thus, the significance of uncomplicated lower UTI in non-pregnant women is limited to the morbidity produced by the symptoms of UTI, although these may substantially disrupt the lives of affected individuals. In fact, 50 70% of lower UTIs clear spontaneously if untreated, although symptoms may persist for several months. 1 Knowledge of the antimicrobial susceptibility profile of uropathogens causing uncomplicated UTIs in the community should guide therapeutic decisions, although the trend away from routinely culturing samples from patients with uncomplicated cystitis may lead to the lack of such data. The resistance pattern of E. coli strains causing uncomplicated UTI, however, varies considerably between regions and countries, so no general recommendations are suitable. Acute uncomplicated cystitis in premenopausal, non-pregnant women Short courses of antimicrobial agents are highly effective in the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis in premenopausal women. 2 Short-course regimens are desirable because they improve compliance, cost less and lead to a lower frequency of adverse reactions. However, in assessing the potential cost advantages of short-course regimens, one must also consider the potential added expense associated with treatment failure or recurrence arising from short-course therapy. One must also consider the potential psychological aspects of single-dose therapy: symptoms may not subside for 2 or 3 days, during which time the patient may doubt the efficacy of the treatment and so visit her physician again unnecessarily. A wide variety of drugs, doses, schedules and durations have been used to treat these common bacterial infections. Only a few of these regimens have been compared directly in adequately designed studies. In order to develop evidence-based guidelines for antimicrobial therapy of uncomplicated acute bacterial cystitis and pyelonephritis in women, a committee of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) reviewed systematically the literature published in English up to The recommendations were classified by the strength and quality of the evidence. These guidelines were reviewed by a number of infectious disease specialists and urologists worldwide and were endorsed by the American Urological Association (AUA) and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID). Of the several thousand titles and abstracts screened, only 75 studies met the inclusion criteria and only 32 were double-blinded. The following antimicrobial agents were considered: trimethoprim, co-trimoxazole, trimethoprim sulphadiazine, quinolones (ciprofloxacin, fleroxacin, lomefloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, pefloxacin, pipemidic acid and rufloxacin), nitrofurantoin, β-lactams (amoxycillin, ampicillin-like compounds, cefadroxil, pivmecillinam and ritipenem axetil) and fosfomycin trometamol. The guidelines 3 came to the following seven conclusions: (i) In otherwise healthy, non-pregnant adult women with acute uncomplicated cystitis, single-dose therapy is generally less effective than the same antibiotic used for longer. However, trimethoprim, co-trimoxazole and quinolones given for 3 days are as effective as treatment of longer duration. Longer duration of treatment usually causes higher rates of adverse events. (ii) Co-trimoxazole was the drug most frequently studied (30 studies). A 3 day regimen of co-trimoxazole, therefore, can be considered standard therapy. Trimethoprim alone was equivalent to co-trimoxazole in eradication and adverse effects. Considering the possible rare, but serious, adverse effects caused by sulphonamides, trimethoprim alone may be considered the preferred drug. However, trimethoprim (or co-trimoxazole) can be recommended as first-line empirical therapy only in communities where 10 20% of uropathogens are resistant to trimethoprim, because there is a close correlation between susceptibility and eradication of E. coli. 4 The risk of resistant uropathogens emerging and causing recurrences was also much higher when using trimethoprim as the first-line drug than with pivmecillinam and, especially, ciprofloxacin. 5 (iii) The fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, fleroxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin) are of similar efficacy to co-trimoxazole when given as a 3 day regimen. Pefloxacin and rufloxacin, given as 1 day therapies, are options and may be equivalent to co-trimoxazole in eradication of bacteriuria and prevention of recurrences; questions remain as to the possibility of a higher incidence of adverse effects than with other recommended therapies. Fluoroquinolones are more expensive than trimethoprim and co-trimoxazole and are thus not recommended as first-line drugs for empirical therapy, except in communities with rates of resistance to trimethoprim of 10 20% among uropathogens causing uncomplicated UTIs. With any of these agents, one should expect eradication of the bacteriuria in 90% of cases. 24
3 Treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis (iv) β-lactams as a group are less effective than the abovementioned drugs. For second- or third-generation oral cephalosporins or aminopenicillins combined with a β-lactamase inhibitor, no large enough comparative studies of 3 day trimethoprim, co-trimoxazole or one of the above-mentioned fluoroquinolones were available for analysis. The only study of adequate size that assessed a β-lactam antimicrobial for 3 days compared with a longer duration was of pivmecillinam; 6 3 days of therapy was equivalent to 7 days of therapy in initial eradication of bacteriuria, although the shorter duration of treatment was associated with an increased incidence of recurrence. (v) Nitrofurantoin cannot, at present, be considered suitable for short-term therapy of acute uncomplicated cystitis. Further studies are needed. (vi) Fosfomycin trometamol used as single-dose therapy may be an alternative. However, published trials are still needed to demonstrate equivalence with standard agents, e.g. trimethoprim, co-trimoxazole or one of the fluoroquinolones administered for 3 days. (vii) Although no controlled trials have been undertaken, cystitis caused by S. saprophyticus may respond better to longer duration of therapy, e.g. 7 days. Urinary analgesics, such as phenazopyridine 200 mg tds, can be administered for 1 or 2 days to patients with severe dysuria. Women with cystitis, including those with severe dysuria and urgency, usually have resolution or marked improvement of symptoms within 2 3 days of initiating therapy. 1 This probable course of events should be explained to the patient. The need for and duration of analgesic therapy for women with UTI must be individualized. Although it is generally recommended that patients with UTI increase their fluid intake to promote micturition and elimination of uropathogens, it remains unclear whether this is beneficial or detrimental. 1 Urinalysis including a dipstick method is sufficient as routine. Routine post-treatment cultures in asymptomatic patients may not be indicated because the benefit of detecting and treating asymptomatic bacteriuria in healthy women has been demonstrated only in pregnancy and before urological instrumentation or surgery. In women whose symptoms do not resolve by the end of treatment and in those whose symptoms resolve but recur within 2 weeks, a urine culture and antimicrobial susceptibility testing must be performed. For therapy in this situation, one should assume that the infecting organism is not susceptible to the agent originally used and retreatment with a 7 day regimen of agent should be considered. 1 Prevention of recurrent uncomplicated cystitis One effective approach for the management of recurrent uncomplicated UTIs is to prevent infection by using longterm, low-dose prophylactic antimicrobials taken at bedtime. 7 A summary of different regimens is given in the Table. Generally, the occurrence of infection is decreased by 95% by the use of prophylaxis. The initial duration of prophylactic therapy is usually 6 months or 1 year. However, with co-trimoxazole, continuous prophylaxis for as long as 2 years 8 or 5 years 9 has remained efficacious. Prophylaxis does not modify the natural history of recurrent UTI. When discontinued, even after extended periods, approximately 60% of women will have another infection within 3 4 months. An alternative prophylactic approach is post-coital prophylaxis for women in whom episodes of infection are associated with sexual intercourse Alternative methods, such as acidification of urine, cranberry juice, 13 extract from the dried leaves of Arctostaphylos uva-ursi and vaginal application of lactobacilli 14,15 show variable effects. It has been claimed that immunostimulating extracts of E. coli reduce the frequency of recurrent infection 16 and even decrease the degree of bacteriuria in paraplegic patients. 17 These reports are difficult to explain in view of what is known about the immune response to UTI. 18 Water diuresis may be effective in some women with uncomplicated UTI, but its use often delays more effective management with antimicrobial drugs. The evidence is also too weak to recommend that women change their personal hygiene and menstrual practices or void after intercourse. 18 Acute uncomplicated cystitis during pregnancy UTIs are common during pregnancy. There is a debate about whether these infections can be classified as uncomplicated even in the absence of other risk factors. Most symptomatic UTIs in pregnant women represent acute cystitis as in their non-pregnant counterparts. Short-term therapy, Agent Table. Antimicrobial regimens of documented prophylactic efficacy for prevention of acute uncomplicated urinary infection in women (adapted from reference 28) Dose (mg/day) Standard regimens a co-trimoxazole 240 or three times weekly trimethoprim 100 nitrofurantoin 50 nitrofurantoin macrocrystals 100 Others cephalexin 125 or 250 norfloxacin 200 ciprofloxacin 125 a Taken at bedtime. 25
4 K. G. Naber however, is not established yet as suitable for non-pregnant women. Second- and third-generation oral cephalosporins, pivmecillinam or fosfomycin trometamol might be candidates for short-term therapy. Some smaller studies and expert opinion support this approach. 19 Otherwise, conventional courses of therapy with amoxycillin, cephalexin or nitrofurantoin are recommended. Quinolones, tetracyclines, trimethoprim (in the first trimester) and sulphonamides (in the last trimester) should not be used during pregnancy. Follow-up urine cultures should be obtained after therapy to demonstrate eradication of bacteriuria. There is no advantage in general in using long-term prophylaxis except for recurrent infections (as in non-pregnant women). Low-dose cephalexin ( mg) or nitrofurantoin (50 mg) taken at night up to and including the puerperium are recommended for prophylaxis if indicated. Post-coital prophylaxis 20,21 may be an alternative approach. Acute uncomplicated cystitis in postmenopausal women The vagina normally contains only low numbers of Gramnegative enteric bacilli because of competition from the resident microbial flora. Lactobacilli account for the low vaginal ph. They tend to be less abundant in postmenopausal women and after antimicrobial therapy. Oestrogens are presumed to protect against recurrent UTIs in postmenopausal women because they enhance the growth of lactobacilli and decrease vaginal ph. 22 Gramnegative enteric bacilli do not normally colonize the vagina in postmenopausal women, unless these women are prone to recurrent UTIs. 23 In postmenopausal women with recurrent UTIs, therapy with intravaginal oestriol 22 reduces the rate of recurrences significantly. For the remaining patients an antimicrobial prophylactic regimen (see Table) should be recommended. In cases of acute cystitis, antimicrobial treatment is similar to that in premenopausal women. Short-term therapy in postmenopausal women is, however, not as well documented as in younger women. Raz et al. 24 found that for postmenopausal women (mean age 65 years) with uncomplicated UTI, ofloxacin 200 mg od for 3 days was significantly more effective in both short- and long-term follow-up than a 7 day course of cephalexin 500 mg qds, even though all uropathogens were susceptible to the two agents. Acute uncomplicated cystitis in young men It has been conventional to consider all UTIs in men as complicated because most of them occur in newborns, infants or the elderly and are associated with urological abnormalities, bladder outlet obstruction or instrumentation. 18 UTIs in otherwise healthy adult men between the ages of 15 and 50 years are very uncommon. In Norway, a rate of six to eight cases of UTI/year/ men aged years was reported. 25 The large difference in prevalence between men and women is thought to be caused by a variety of factors, including the greater distance between the anus (the usual source of uropathogens) and the urethral meatus, the drier environment surrounding the male urethra, the greater length of the male urethra and the antibacterial activity of prostatic fluid. It has become clear, however, that a small number of year old men suffer acute uncomplicated UTIs. The reasons for such infections are not always clear, but risk factors include intercourse with an infected partner, anal intercourse and lack of circumcision. 26 The aetiological agents causing uncomplicated UTI in men are similar to those in women. Krieger et al. 27 noted that 37 (92.5%) of 40 uncomplicated UTIs in men were caused by E. coli. Symptoms of uncomplicated UTI in men are similar to those in women. Dysuria is common to UTI and urethritis. Urethritis must be ruled out in sexually active men by means of a Gram s stain of a urethral swab or examination of a first-voided urine wet mount to look for urethral leucocytosis. A urethral Gram s stain demonstrating leucocytes and a predominance of Gram-negative rods suggests E. coli urethritis, which may precede or accompany UTI. As a result of the infrequency with which UTIs occur in this group of men, there are no data from controlled treatment studies. Empirical use of the agents discussed previously for uncomplicated cystitis or pyelonephritis in women is recommended. Nitrofurantoin should probably not be used in men, since it does not achieve reliable tissue concentrations and would be ineffective for occult prostatitis or pyelonephritis. For acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis, the use of a fluoroquinolone as initial empirical oral treatment is recommended. Although it is possible that short-course treatment is effective in men with uncomplicated cystitis, there are no studies to support this practice. It is recommended, therefore, that such men receive a 7 day regimen, because the likelihood of an occult complicating factor is greater in men than in women, and because longer treatment may reduce the likelihood of persistent prostatic infection. The value of a urological evaluation in a man who has had a single uncomplicated UTI has not been determined. Urological evaluation should certainly be done routinely in adolescents and men with pyelonephritis, recurrent infections, or whenever a complicating factor is present. References 1. Hooton, T. M. & Stamm, W. C. (1997). Diagnosis and treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America 11, Naber, K. G. (1999). Short-term therapy of acute uncomplicated cystitis. Current Opinion in Urology 9,
5 Treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis 3. Warren, J. W., Abrutyn, E., Hebel, J. R., Johnson, J. R., Schaeffer, A. J. & Stamm, W. E. (1999). Guidelines for antimicrobial treatment of uncomplicated acute bacterial cystitis and acute pyelonephritis in women. Clinical Infectious Diseases 29, Minassian, M. A., Lewis, D. A., Chattopadhyay, D., Bovill, B., Duckworth, G. J. & Williams, J. D. (1998). A comparison between single-dose fosfomycin trometamol (Monuril) and a 5-day course of trimethoprim in the treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infection in women. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 10, Henning, C. & Bengtsson, L. (1997). Treatment of acute urinary disorders. Simple tests and questions make the diagnosis and therapeutic choices easier. Läkartidningen 94, Pitkajarvi, T., Pyykonen, M. L., Kannisto, K., Piippo, T. & Viita, P. (1990). Pivmecillinam treatment in acute cystitis. Three versus seven days study. Arzneimittel Forschung 40, Nicolle, L. E. & Ronald, A. R. (1987). Recurrent urinary tract infection in adult women: diagnosis and treatment. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America 1, Harding, G. K., Ronald, A. R., Nicolle, L. E., Thomson, M. J. & Gray, G. J. (1982). Long-term antimicrobial prophylaxis for recurrent urinary tract infection in women. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 4, Nicolle, L. E., Harding, G. K., Thomson, M., Kennedy, J., Urias, B. & Ronald, A. R. (1988). Efficacy of five years of continuous low dose trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis for urinary tract infection. Journal of Infectious Diseases 157, Vosti, K. L. (1975). Recurrent urinary tract infections: prevention by prophylactic antibiotics after sexual intercourse. Journal of the American Medical Association 231, Stapleton, A., Latham, R. H., Johnson, C. & Stamm, W. E. (1990). Post-coital antimicrobial prophylaxis for recurrent urinary infection. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Journal of the American Medical Association 264, Melekos, M. D., Asbach, H. W., Gerharz, E., Zarakovitis, I. E., Weingaertner, K. & Naber, K. G. (1997). Post-intercourse versus daily ciprofloxacin prophylaxis for recurrent urinary tract infections in premenopausal women. Journal of Urology 157, Avorn, J., Monane, M., Gurwitz, J. H., Glynn, R. J., Choodnovskiy, I. & Lipsitz, L. A. (1994). Reduction of bacteriuria and pyuria after ingestion of cranberry juice. Journal of the American Medical Association 271, Reid, G., Bruce, A. W. & Taylor, M. (1992). Influence of threeday antimicrobial therapy and lactobacillus vaginal suppositories on recurrence of urinary tract infections. Clinical Therapeutics 14, Baerheim, A., Larsen, E. & Digranes, A. (1994). Vaginal application of lactobacilli in the prophylaxis of recurrent lower urinary tract infection in women. Scandinavian Journal of Primary Health Care 12, Schulman, C. C., Corbusier, A., Michiels, H. & Taenzer, H. J. (1993). Oral immunotherapy of recurrent urinary tract infections: a double-blind placebo-controlled multicentre study. Journal of Urology 150, Hachen, H. J. (1990). Oral immunotherapy in paraplegic patients with chronic urinary tract infections: a double-blind placebocontrolled trial. Journal of Urology 143, Kunin, C. M. (1997). Urinary Tract Infections. Detection, Prevention, and Management, 5th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD. 19. Bailey, R. R. (1994). Single-dose/short-term therapy in children and in pregnant women. Infection 22, Suppl. 1, S Pfau, A. & Sacks, T. G. (1992). Effective prophylaxis for recurrent urinary tract infections during pregnancy. Clinical Infectious Diseases 14, Pfau, A. (1994). Recurrent UTI in pregnancy. Infection 22, Suppl. 1, S Raz, R. & Stamm, W. E. (1993). A controlled trial of intravaginal estriol in postmenopausal women with recurrent urinary tract infections. New England Journal of Medicine 329, Pfau, A. & Sacks, T. (1977). The bacterial flora of the vaginal vestibule, urethra and vagina in the normal premenopausal woman. Journal of Urology 118, Raz, R. & Rosenfeld, S. (1996). 3-day course of ofloxacin versus cefalexin in the treatment of urinary tract infections in postmenopausal women. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 40, Vorland, L. H., Carlson, K. & Aalen, O. D. (1985). An epidemiological survey of urinary tract infections among outpatients in Northern Norway. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 17, Stamm, W. E. (1997). Urinary tract infections in young men. In Urinary Tract Infections, (Bergan, T., Ed.), Vol. 1: Infectiology, pp Karger, Basel. 27. Krieger, J. N., Ross, S. O. & Simonsen, J. M. (1993). Urinary tract infections in healthy university men. Journal of Urology 149, Nicolle, L. E. (1992). Prophylaxis: recurrent urinary tract infection in women. Infection 20, Suppl. 3, S
6
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2014) M. Grabe (chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2014) M. Grabe (chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
IDSA GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD
 82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults. A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013)
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Urinary Tract Infection
 Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department. 24/06/2013 Beryl Navti, Clinical Pharmacist, SEPT
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1. Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs
 Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases Boston University School of Medicine
 2010 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department
2010 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Kalpana Gupta, M.D. Associate Professor Department
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
COMPASS Therapeutic Notes on the Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Primary Care
 COMPASS Therapeutic Notes on the Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Primary Care In this issue: Page Introduction, Background & Diagnostic Tests 1 UTI in non-pregnant women 3 UTI in pregnant
COMPASS Therapeutic Notes on the Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Primary Care In this issue: Page Introduction, Background & Diagnostic Tests 1 UTI in non-pregnant women 3 UTI in pregnant
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
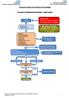 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
Therapeutic protocoles for adults concerning ESBL Enterobacteria infections in health care institutions
 Therapeutic protocoles for adults concerning ESBL Enterobacteria infections in health care institutions CYSTITIS The growing importance of resistance to quinolones, their environmental impact and reduced
Therapeutic protocoles for adults concerning ESBL Enterobacteria infections in health care institutions CYSTITIS The growing importance of resistance to quinolones, their environmental impact and reduced
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
How To Find Out If A Diabetic Woman Has A Urinary Tract Infection
 Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D.
 ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women
 Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Frequently Asked Questions
 Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Managing the E coli UTI
 C o n s u l t a n t o n C a l l I N F E C T I O U S / Z O O N O T I C D I S E A S E Peer Reviewed Kate S. KuKanich, DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACVIM Kansas State University Managing the E coli UTI PROFILE Definition
C o n s u l t a n t o n C a l l I N F E C T I O U S / Z O O N O T I C D I S E A S E Peer Reviewed Kate S. KuKanich, DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACVIM Kansas State University Managing the E coli UTI PROFILE Definition
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2015) M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2015) M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance
 Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
Guidelines on Urological Infections
 Guidelines on Urological Infections M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, T. Cai (Guidelines Associate), M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
Guidelines on Urological Infections M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, T. Cai (Guidelines Associate), M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis for Transrectal Prostate Biopsy: Organizational Recommendations. J. Stuart Wolf, Jr., M.D.
 Antimicrobial Prophylaxis for Transrectal Prostate Biopsy: Organizational Recommendations J. Stuart Wolf, Jr., M.D. Department of Urology University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Official Recommendations for
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis for Transrectal Prostate Biopsy: Organizational Recommendations J. Stuart Wolf, Jr., M.D. Department of Urology University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Official Recommendations for
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection
 SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE No. 250, November 2010 Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection This Clinical Practice Guideline has been prepared by the Urogynaecology Committee, reviewed by the Family Physicians
SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE No. 250, November 2010 Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection This Clinical Practice Guideline has been prepared by the Urogynaecology Committee, reviewed by the Family Physicians
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011
 The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
Age in years Females (% prevalence) Males (% prevalence) 6-15 Vesicoureteral reflux (4.4%) Vesicoureteral reflux (0.5%)
 Magdalena E. Sobieszczyk Urinary Tract Infections AIMS: 1. Understand epidemiology and microbiology of urinary tract infections 2. Understand pathogenesis of lower and upper urinary tract infections 3.
Magdalena E. Sobieszczyk Urinary Tract Infections AIMS: 1. Understand epidemiology and microbiology of urinary tract infections 2. Understand pathogenesis of lower and upper urinary tract infections 3.
Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use.
 Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
Guidelines on Urological Infections
 Guidelines on Urological Infections M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt European Association of Urology 2013 TABLE
Guidelines on Urological Infections M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt European Association of Urology 2013 TABLE
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
signs suggesting chlamydia:
 Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
Urinary tract infections
 Facts Behind the Fact Card Pharmacist CPE Urinary tract infections by Lynn Gould Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are very common, affecting about 250,000 people in Australia each year. 1 Many people go
Facts Behind the Fact Card Pharmacist CPE Urinary tract infections by Lynn Gould Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are very common, affecting about 250,000 people in Australia each year. 1 Many people go
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
 PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN ADULTS
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN ADULTS Urinary tract infection in adults is common and may be complicated or uncomplicated. Infection of the urinary tract (UTI) is frequently encountered in clinical practice
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN ADULTS Urinary tract infection in adults is common and may be complicated or uncomplicated. Infection of the urinary tract (UTI) is frequently encountered in clinical practice
Common Questions About Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in Women
 Common Questions About Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in Women JAMES J. ARNOLD, DO; LAURA E. HEHN, MD; and DAVID A. KLEIN, MD, MPH, National Capital Consortium Family Medicine Residency, Fort Belvoir,
Common Questions About Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in Women JAMES J. ARNOLD, DO; LAURA E. HEHN, MD; and DAVID A. KLEIN, MD, MPH, National Capital Consortium Family Medicine Residency, Fort Belvoir,
Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults
 IDSA GUIDELINES Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults Lindsay E. Nicolle, 1 Suzanne Bradley, 2 Richard Colgan, 3 James
IDSA GUIDELINES Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults Lindsay E. Nicolle, 1 Suzanne Bradley, 2 Richard Colgan, 3 James
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence
 Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
Urinary Tract Infections - How to Identify, Treat and Prevent Them
 1 of 12 4/29/2016 1:49 PM Library Home Find A Physician Find A Practice Request An Appointment Search Clinical Studies Classes and Support Groups Ask A Health Librarian Subscribe to enewsletters Bone and
1 of 12 4/29/2016 1:49 PM Library Home Find A Physician Find A Practice Request An Appointment Search Clinical Studies Classes and Support Groups Ask A Health Librarian Subscribe to enewsletters Bone and
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings
 Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
GONORRHOEA. Use of lidocaine as a diluent when using ceftriaxone (see Appendix 1)
 Key practice notes: 1 st line therapy GONORRHOEA Decreasing sensitivity of gonorrhoea to cephalosporins is now a real threat: CEFTRIAXONE 500mg IM stat first-line for all gonococcal infections AZITHROMYCIN
Key practice notes: 1 st line therapy GONORRHOEA Decreasing sensitivity of gonorrhoea to cephalosporins is now a real threat: CEFTRIAXONE 500mg IM stat first-line for all gonococcal infections AZITHROMYCIN
CEFA-DROPS AND CEFA-TABS
 Page 1 of 5 FORT DODGE ANIMAL HEALTH Division of Wyeth 800-5TH STREET N.W., P.O. BOX 518 FORT DODGE IA 50501 USA Telephone: 515-955-4600 Fax: 515-955-3730 Order Desk Telephone: 800-685-5656 Order Desk
Page 1 of 5 FORT DODGE ANIMAL HEALTH Division of Wyeth 800-5TH STREET N.W., P.O. BOX 518 FORT DODGE IA 50501 USA Telephone: 515-955-4600 Fax: 515-955-3730 Order Desk Telephone: 800-685-5656 Order Desk
Drug Sensitivity Pattern ofe. coli Causing Urinary Tract Infection in Diabetic and Non-diabetic Patients
 The Journal of International Medical Research 1996; 24: 296-301 in Diabetic and Non-diabetic Patients F JINNAH\ M S ISLAM\ M A K RUMI\ M G MORSHED 2 AND F H UQ3 'Department of Microbiology and Immunology,
The Journal of International Medical Research 1996; 24: 296-301 in Diabetic and Non-diabetic Patients F JINNAH\ M S ISLAM\ M A K RUMI\ M G MORSHED 2 AND F H UQ3 'Department of Microbiology and Immunology,
Case Studies in Urinary Tract Infections
 Case Studies in Urinary Tract Infections Robert L. Holley, MSc, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Case Studies in Urinary Tract Infections Robert L. Holley, MSc, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
RECOMMENDATIONS. MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION Clinical Practice Guideline November 2013 PRACTICE POINT
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION Clinical Practice Guideline November 2013 GOALS Urgent primary care assessment and management of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION Clinical Practice Guideline November 2013 GOALS Urgent primary care assessment and management of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View.
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View. Samir K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Microbiology Dhaka Shishu Hospital Bangladesh Typhoid Fever:Salmonella
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View. Samir K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Microbiology Dhaka Shishu Hospital Bangladesh Typhoid Fever:Salmonella
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Patients with Urinary Catheters
 Clinical Review Article Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Patients with Urinary Catheters Maria L. Alcaide, MD Daniel M. Lichtstein, MD Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients with urinary
Clinical Review Article Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Patients with Urinary Catheters Maria L. Alcaide, MD Daniel M. Lichtstein, MD Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients with urinary
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
MODULE 2: ADULT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 MODULE 2: ADULT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS KEYWORDS: Urinary tract infection (UTI); cystitis; pyelonephritis; uropathogens; antibiotics LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will
MODULE 2: ADULT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS KEYWORDS: Urinary tract infection (UTI); cystitis; pyelonephritis; uropathogens; antibiotics LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will
Urinary Tract Infections in Adults
 Urinary Tract Infections in Adults National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a urinary tract infection
Urinary Tract Infections in Adults National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a urinary tract infection
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative treatment
 STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
Examination Content Blueprint
 Examination Content Blueprint Overview The material on NCCPA s certification and recertification exams can be organized in two dimensions: (1) organ systems and the diseases, disorders and medical assessments
Examination Content Blueprint Overview The material on NCCPA s certification and recertification exams can be organized in two dimensions: (1) organ systems and the diseases, disorders and medical assessments
Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE
 PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER VII-E-5 PAGE 1 OF 7 APPROVED BY: CATEGORY: Tri-site Nursing Policy and Procedures Review Committee Body Systems; Genitourinary 1.0 GOALS To influence patient care providers
PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER VII-E-5 PAGE 1 OF 7 APPROVED BY: CATEGORY: Tri-site Nursing Policy and Procedures Review Committee Body Systems; Genitourinary 1.0 GOALS To influence patient care providers
William Atkinson, MD, MPH Hepatitis B Vaccine Issues June 16, 2016
 William Atkinson, MD, MPH Hepatitis B Vaccine Issues June 16, 2016 Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) The recommendations to be discussed are primarily those of the ACIP composed of 15
William Atkinson, MD, MPH Hepatitis B Vaccine Issues June 16, 2016 Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) The recommendations to be discussed are primarily those of the ACIP composed of 15
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Testing for Gonorrhea Q1: What test should be completed for accurately diagnosing gonorrhea? A1: Testing is done with either a culture or a NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test).
Frequently Asked Questions Testing for Gonorrhea Q1: What test should be completed for accurately diagnosing gonorrhea? A1: Testing is done with either a culture or a NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test).
Study of bacteria isolated from urinary tract infections and determination of their susceptibility to antibiotics
 Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology (2009); 2(3): 118-123 118 Original article Study of bacteria isolated from urinary tract infections and determination of their susceptibility to antibiotics Mansour
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology (2009); 2(3): 118-123 118 Original article Study of bacteria isolated from urinary tract infections and determination of their susceptibility to antibiotics Mansour
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
 Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL
 PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product)
 PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H.
 CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection
 BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
TREATMENT OF STI CONTACTS
 This decision support tool is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca TREATMENT OF STI CONTACTS
This decision support tool is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca TREATMENT OF STI CONTACTS
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Long-term urinary catheter-associated urinary tract infection (UTI)
 Peer reviewed article Long-term urinary catheter-associated urinary tract infection (UTI) Abstract This paper reviews the literature on the current management of symptomatic urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Peer reviewed article Long-term urinary catheter-associated urinary tract infection (UTI) Abstract This paper reviews the literature on the current management of symptomatic urinary tract infections (UTIs)
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients.
 Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
PROCEEDINGS INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT
 INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model
 Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Three Versus Seven-Day Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women: A Pilot Investigation
 94 The Open Infectious Diseases Journal, 2009, 3, 94-98 Open Access Three Versus Seven-Day Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women: A Pilot Investigation Pooja Mittal, Vivien Pan and Deborah
94 The Open Infectious Diseases Journal, 2009, 3, 94-98 Open Access Three Versus Seven-Day Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women: A Pilot Investigation Pooja Mittal, Vivien Pan and Deborah
TRANSVAGINAL MESH IN PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE REPAIR.
 TRANSVAGINAL MESH IN PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE REPAIR. Spanish full text SUMMARY Introduction: Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterised by the descent or herniation of the uterus, vaginal vault, bladder
TRANSVAGINAL MESH IN PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE REPAIR. Spanish full text SUMMARY Introduction: Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterised by the descent or herniation of the uterus, vaginal vault, bladder
Urinary Incontinence. Patient Information Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom
 British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
Laboratory confirmation requires isolation of Bordetella pertussis or detection of B. pertussis nucleic acid, preferably from a nasopharyngeal swab.
 Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
TREATMENT OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS (PD) RELATED PERITONITIS. General Principles
 WA HOME DIALYSIS PROGRAM (WAHDIP) GUIDELINES General Principles 1. PD related peritonitis is an EMERGENCY early empiric treatment followed by close review is essential 2. When culture results and sensitivities
WA HOME DIALYSIS PROGRAM (WAHDIP) GUIDELINES General Principles 1. PD related peritonitis is an EMERGENCY early empiric treatment followed by close review is essential 2. When culture results and sensitivities
Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections
 Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections Craig Umscheid, MD, MSCE Carolyn Gould, MD, MSCR and David A. Pegues, MD HICPAC Meeting November 13, 2008 Washington, DC Outline Progress
Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections Craig Umscheid, MD, MSCE Carolyn Gould, MD, MSCR and David A. Pegues, MD HICPAC Meeting November 13, 2008 Washington, DC Outline Progress
