There are a number of other carcinogens (cancer causing agents) that are believed to be associated with lung cancer, and are reviewed elsewhere.
|
|
|
- Duane Greer
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lung Cancer What is cancer? First, some background on the way the body is built. Organs, like the heart, liver, and lung, are made up of tissues, such as blood vessels and muscle. Tissues, in turn, are made up of cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of tissue. Cancer results from the abnormal proliferation, or repeated divisions, of cells. The rapidly dividing cells of a cancer grow in number, developing into a tumor, or mass. A lung cancer develops when a group of cells in the lung begins dividing rapidly, and creates an enlarging mass within the lung. The size of the mass may double as quickly as every 30 days, or as slowly as every 400 days, depending upon the type of cells that are dividing, and on other factors. Different types of lung cancer originate from different types of cells. These different types of cells are identified by examining the cells under a microscope, and performing special tests on the cells. (1) If not treated early enough, most lung cancers have a tendency to eventually spread to other areas of the body. The cancers can spread through the lymphatic system to the regional lymph nodes (tiny filters in the lymphatics), or through the blood, usually to bones or to the brain. The location of distant spread is called a metastasis. (1) The degree of spread of the cancer is known as the Stage of the lung cancer. The stages of lung cancer will be discussed below. Risk factors for lung cancer The primary risk factor for lung cancer is cigarette smoking, and exposure to cigarette smoke.(2) 87% of patients with lung cancer have a history of tobacco exposure. The exposure can be either from smoking cigarettes, or from inhaling second hand smoke. The risk of lung cancer goes up with the number of cigarettes smoked per day, and the duration of use of tobacco. This is measured typically as pack-years, or the number of packs per day times the number of years of smoking. Other risk factors for lung cancer include exposure to environmental agents such as asbestos and radon, (3) and exposure to other industrial products. Asbestos exposure is linked to a tumor of the pleura called mesothelioma. However, the combination of smoking and asbestos exposure generates a risk factor for lung cancer that is greater than the simple sum of the relative risks. Asbestos was used in the past as an insulation material, and in automobile brake pads, and was frequently used in shipyards. Radon is a naturally occurring gas, a byproduct of the breakdown of uranium. Radon can be found in up to 6 per cent of homes in the US. It is most frequently found in unventilated basements, and in concrete buildings. Home tests for radon are commercially available. There are a number of other carcinogens (cancer causing agents) that are believed to be associated with lung cancer, and are reviewed elsewhere. (4) Incidence of lung cancer Lung cancer is the most frequent cause of death from cancer in both men and women.(3) Lung cancer is responsible for more cancer deaths in men than all other cancers combined.(ibid.) In the late 1980 s, the incidence of lung cancer in women surpassed the incidence of breast cancer due to the increasing use of tobacco by women.(ibid.) The incidence of lung cancer can be reduced in large populations by reducing the use of cigarettes. In England, the lung cancer rate in men from ages has dropped 50% in 30
2 years due to the development of non-smoking programs. (4) An individual can reduce his or her own risk by 50% by not smoking for 10 years.(5) Symptoms Most patients early in the course of lung cancer have no symptoms. The cancer grows silently when it is very small. However, some patients will develop symptoms of a persistent cough, hemoptysis (coughing up blood), recurrent pneumonia, weight loss, wheezing, fever, or pain. Sometimes a lump develops in the neck or armpit. A few lung cancers secrete hormones or proteins that cause signs or symptoms. By the time most lung cancers are discovered, 85% have spread beyond the ability of the surgeon to remove them.(3) Therefore, prevention, or early detection, when the cancer can still be removed, is important to obtain a cure. Categories of lung cancer There are two general categories of lung cancer: small cell and non-small cell. The categories are divided this way because they act differently and are treated differently. Small cell carcinoma One basic type Usually spreads early in the course Stages: limited or extensive Treated with chemotherapy Non-small cell carcinoma Three basic types o Adenocarcinoma o Squamous cell carcinoma o Large cell carcinoma Usually spreads later in the course Stages: I, II, III, IV Treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy, depending on the stage. Stages of Lung Cancer The amount of spread of a cancer in the lung is measured by its stage. The further that cancer cells have spread from the original mass, or the larger the cancer, then the higher the stage. The stage of a cancer determines the treatment that is selected for that particular cancer, and the prognosis. The higher the stage, the greater the spread. The greater the spread, the worse the prognosis. Non-small cell cancer is staged using the TNM staging system. TNM refers to T for tumor size, N for node status, and M for the presence or absence of metastases. In general, there are Stages I, II, III, and IV.
3 Stage I is a tumor that is localized to the lung, and has no lymph node involvement. Stage II is a tumor that has lymph node involvement inside the lung only, or a tumor which has grown directly into another nearby structure, such as the chest wall. Stage III is a tumor that has spread to the lymph nodes in the mediastinum (the center of the chest between the lungs.) Stage IV is a tumor that has spread anywhere outside the confines of the chest. That is, tumor which has spread to the adrenal glands, bones, ribs, brain, or elsewhere.(6) Diagnostic Studies The true diagnosis of lung cancer can only be made by looking at cells from a mass or lymph node under a microscope. There are a number of diagnostic tests that are performed in preparation or in pursuit of making a tissue diagnosis. Chest X-ray The chest x-ray, also known as a chest radiograph or CXR, is a screening test for lung cancer. Many cancers are initially detected on a routine chest radiograph that is taken for an annual physical or in the process of evaluating another medical problem. CT scan of the chest The CT scan is also known as a CAT scan, or computerized axial tomography. This scan takes only a few minutes to perform, and gives a very detailed image of the anatomy of the chest and lungs. It is used to evaluate the location and size of tumors in the chest, and is used to evaluate the size and location of lymph nodes in the chest. In addition, the adrenal glands are usually evaluated with this test, because the adrenal glands are an area where lung cancer can spread early in its course. PET scan A PET scan is a test using injectable radioactive material which is detected by a special camera. The most frequent PET scan used for the lung measures the relative metabolism of glucose by tissues in the body. Infections, inflammation, and cancers use more glucose than surrounding tissues. This area of increased utilization of glucose appears to the camera as more intense radioactivity than surrounding areas on the scan (a hot spot. ). The PET scan is not perfect at predicting cancer. It only creates significant suspicion of cancer. In contrast, a PET scan that does not show increased activity in a lung tumor is very reliable. The chance of the nodule being a cancer in such a scan is very, very low. Bone Scan A bone scan is a test using injectable radioactive material that is detected by a speical camera. The bone scan is used to detect abnormal areas in the bones of the body. Sometimes these areas are abnormal due to arthritis or other changes, and sometimes due to spread of cancer to the bone. If an abnormality is detected by bone scan, then further investigation into the abnormal area may be necessary. Bronchoscopy Bronchoscopy is a procedure done by Pulmonologists and Thoracic Surgeons. This procedure is done under sedation in a special area of the hospital or outpatient procedure suite. While the patient is sedated, a small, flexible tube is advanced through the nose or mouth into the windpipe (trachea). All of the visible branches of the windpipe (airways, or bronchi) are examined,
4 and biopsies of any abnormalities are performed. Sometimes biopsies of lung tumors are performed, and occasionally lymph node biopsies are done. The patient may return home on the same day of the procedure. Coughing up small amounts of blood for a few days after the procedure is not unusual. CT directed needle biopsy When a lung tumor is located far away from the airways, and cannot be reached by bronchoscopy and biopsy, another test may be performed. This test is performed by a Radiologist with the use of a CT scanner. The tumor is precisely located by using a CT scan. With the patient still in the CT scanner, local anesthesia (numbing medicine) is injected into the patient s skin. Then, a small needle is advanced directly into the lung tumor, and tumor cells are aspirated into a syringe, then examined under a microscope. In the vast majority of cases, there are no complications from a CT directed needle biopsy. Occasionally a small amount of air leaks from the lung into the chest, and the air must be removed by placing a small drain into the chest for several hours or a for a day. Mediastinoscopy/Mediastinotomy/Chamberlain Procedure Mediastinoscopy is an operation performed by a Thoracic Surgeon in a surgical suite with the patient under general anesthesia. Mediastinoscopy and the related procedures are used to evaluate the lymph nodes in the mediastinum, the center of the chest (media is derived from the Latin medius meaning the middle, or center.) For more detailed information, please see the related article on Mediastinoscopy. The lymphatic vessels of the mediastinum carry lymphatic fluid from the lungs, returning the fluid to the venous system of the blood. This lymphatic fluid contains fluid and cells from the lung and pleura. The lymph nodes in the mediastinum serve as filters for lymph that leaves the lung. These filters act somewhat as a line of defense against the spread of cancer, trapping cancer cells, and preventing them from spreading further throughout the body. The lymph nodes will actually try to kill the cancer cells in some cases. If cancer is present in the lymph nodes of the mediastinum, it means that the cancer has spread outside of the lung itself. The presence of cancer in the mediastinal lymph nodes makes the lung cancer a Stage III. Stage III lung cancers are usually treated with chemotherapy rather than surgery, with a few exceptions. Thoracoscopy Thoracoscopy is a surgical procedure done by a Thoracic Surgeon. The operation is performed under general anesthesia using a tiny endoscope, or fiberoptic camera, to look inside the chest. The surgeons of Thoracic Surgery Associates, PC, use a 5 mm endoscope, slimmer than a drinking straw, for this operation. With the use of special instruments, a biopsy of the lung, of the chest wall, or the mediastinal lymph nodes can be performed. Thoracoscopy can be used to help determine the stage of a cancer, and to treat some conditions associated with cancer, such as effusions, or pneumothorax. For more detailed information, please see the article on Thoracoscopy elsewhere in this site. Thoracotomy Thoracotomy is a surgical procedure done under general anestheria by a Thoracic Surgeon. At Thoracic Surgery Associates, PC, we utilize an incision approximately six inches long, beneath the armpit, to go between the ribs and into the chest. This incision allows complete access to the chest to perform biopsies of the lung, the lymph nodes, or the chest wall. In addition, if necessary, a large section of the lung can be removed (a lobectomy.) For more detailed information, please see the article on Thoracotomy elsewhere in the site.
5 Treatment of Lung Cancer Decision making The decision regarding how a specific lung cancer is treated in a specific patient depends upon the cell type, the location, and the stage of the cancer. The collaboration of a medical oncologist, radiation oncologist, and thoracic surgeon gives the patient every possible option for treatment. Non surgical treatment Stage III B and Stage IV cancers are almost always treated with chemotherapy, with or without radiation therapy. Surgery is not usually used for lung cancers that have spread outside the chest. Surgical treatment Surgical removal of lung cancer is usually reserved for non-small cell lung cancer that is Stage I or II. There are a few Stage IIIA patients that will benefit from surgery. Stage IV patients with non-small cell lung cancer with a singe brain metastasis in the presence of a single primary lung cancer may be candidates for surgery. Surgical techniques Risks of surgery Operations used for staging Staging operations done by a Thoracic Surgeon. Such operations include: Bronchoscopy Mediastinoscopy Chamberlain Procedure Thoracoscopy Thoracotomy These procedures are explained in detail elsewhere in the site. Operations used for removal of a lung cancer The removal of a lung cancer is done by a Thoracic Surgeon. The operation is called a thoracotomy and lobectomy. A six inch incision is made on the side or back of the chest, the large muscles of the chest wall are moved out of the way, and a space is developed between the ribs to gain access to the inside of the chest. The tumor mass is located in the appropriate lobe of the lung. The blood vessels leading to, and rising from, that particular lobe are ligated and divided. Then, the bronchus (airway, or breathing tube) to the lobe is divided, and the lobe, with the cancer and surrounding lymph nodes in it, is removed. For a more detailed description, please see the article elsewhere on the site. The immediate risks of surgery of the chest include bleeding (which could require blood transfusion), infection (which could require antibiotics or re-operation), and pneumonia. The risk of surgery increases with worsening lung function, worsening oxygen diffusion capacity, and age. In the immediate post-operative period, the patient is at risk for pneumonia (made worse by smoking, COPD, and chronic bronchitis), bronchitis, wheezing, and irregular heart beats. Patients
6 with chronic lung disease, heart disease, or kidney disease are at increased risk of surgery, or of worsening those conditions in the immediate post-operative period. Some rarer risks include the risk of hoarseness, development of a pulmonary hernia, and fluid collection under the skin (seroma.) Recovery from surgery In hospital At home Most patients that have staging procedures go home on the day of surgery. Most patients that have thoracotomy lung resections stay in the ICU the night of surgery. If recovering well, the patient will be transferred to a surgical floor for the remainder of their stay. Most patients will have a heart monitor for most of their stay. Pain is controlled for the first few days with an epidural, and later with a patient-controlled analgesia pump. The usual length of stay after a thoracotomy is 5 to 7 days. The rate of recovery is directly related to lung function and other related medical problems. Usually, the patient will get out of bed on the first post-operative day, and walk in their room the second day. By the third day, most patients should be able to walk in the halls. Drains, called chest tubes, are left in place for 3 to 5 days to remove excess air and fluid from the chest after surgery. These drains are removed at the bedside when the drainage is sufficiently diminished, usually around the third to fifth day after surgery. We encourage our patients to remain active at home after discharge. If the patient remains sedentary, they are at increased risk for pneumonia and for development of blood clots in the legs. Both of these conditions can require readmission to the hospital for a prolonged period of time. The first week at home, we encourage the patient to walk around the house and the yard several times a day. The second week, the patient should walk around the block, or its equivalent, about a quarter of a mile a day. The third week, the patient should walk up to a mile a day, in parts, or at one time. We restrict driving for three weeks, or later, until narcotic pain medicine is no longer needed.
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer About Your Lungs and Lung Cancer How do your lungs work? To understand lung cancer it is helpful to understand your lungs. Your lungs put oxygen into the blood, which the heart
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer About Your Lungs and Lung Cancer How do your lungs work? To understand lung cancer it is helpful to understand your lungs. Your lungs put oxygen into the blood, which the heart
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide
 What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
How To Treat Lung Cancer At Cleveland Clinic
 Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
 Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of information
Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of information
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma
 Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Lung Cancer small cell
 Lung Cancer small cell Overview Lung cancer is a cancer starts in the lungs. In order to understand lung cancer, it helps to know about the normal structure and function of the lungs. Most lung cancer
Lung Cancer small cell Overview Lung cancer is a cancer starts in the lungs. In order to understand lung cancer, it helps to know about the normal structure and function of the lungs. Most lung cancer
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
SMALL. 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org
 Understanding series SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient I TABLE OF CONTENTS ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS The following image shows different parts that make up
Understanding series SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient I TABLE OF CONTENTS ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS The following image shows different parts that make up
The lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Risks & symptoms Diagnosis & treatment options
 Why We re Here The lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Risks & symptoms Diagnosis & treatment options What Are Lungs? What Do They Do? 1 Located in the chest Allow you to breathe Provide oxygen
Why We re Here The lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Risks & symptoms Diagnosis & treatment options What Are Lungs? What Do They Do? 1 Located in the chest Allow you to breathe Provide oxygen
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Department of Surgery
 Thoracic Surgery After Your Lung Surgery Patient Education Discharge Information You have just had lung surgery. The following are definitions of terms you may hear in connection with your surgery: THORACOTOMY
Thoracic Surgery After Your Lung Surgery Patient Education Discharge Information You have just had lung surgery. The following are definitions of terms you may hear in connection with your surgery: THORACOTOMY
Lung Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Asbestos and your lungs
 This information describes what asbestos is and the lung conditions that are caused by exposure to it. It also includes information about what to do if you have been exposed to asbestos, and the benefits
This information describes what asbestos is and the lung conditions that are caused by exposure to it. It also includes information about what to do if you have been exposed to asbestos, and the benefits
SARCOIDOSIS. Signs and symptoms associated with specific organ involvement can include the following:
 SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY
 INFORMED CONSENT INFORMATION ADDRESSOGRAPH DATA CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY You have decided to have an important procedure and we appreciate your selection of UCLA Healthcare to meet your needs.
INFORMED CONSENT INFORMATION ADDRESSOGRAPH DATA CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY You have decided to have an important procedure and we appreciate your selection of UCLA Healthcare to meet your needs.
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
Lung Carcinoid Tumor
 Lung Carcinoid Tumor What are lung carcinoid tumors? Lung carcinoid tumors (also known as lung carcinoids) are a type of lung cancer, which is a cancer that starts in the lungs. Cancer starts when cells
Lung Carcinoid Tumor What are lung carcinoid tumors? Lung carcinoid tumors (also known as lung carcinoids) are a type of lung cancer, which is a cancer that starts in the lungs. Cancer starts when cells
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Lung Carcinoid Tumor
 Lung Carcinoid Tumor What are lung carcinoid tumors? Lung carcinoid tumors (also known as lung carcinoids) are a type of lung cancer, which is a cancer that starts in the lungs. Cancer starts when cells
Lung Carcinoid Tumor What are lung carcinoid tumors? Lung carcinoid tumors (also known as lung carcinoids) are a type of lung cancer, which is a cancer that starts in the lungs. Cancer starts when cells
Lung Cancer (Small Cell) Overview
 Lung Cancer (Small Cell) Overview The information that follows is an overview of this type of cancer. It is based on the more detailed information in our document Lung Cancer (Small Cell). This document
Lung Cancer (Small Cell) Overview The information that follows is an overview of this type of cancer. It is based on the more detailed information in our document Lung Cancer (Small Cell). This document
SMALL. 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org
 UNDERSTANDING Non- SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient I ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS The following image shows different parts that make up the lungs. Please use
UNDERSTANDING Non- SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient I ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS The following image shows different parts that make up the lungs. Please use
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
What is Mesothelioma?
 What is Mesothelioma? Mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that develops in the mesothelial cells found in one s body. These cells form membranous linings that surround and protect the body s organs and
What is Mesothelioma? Mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that develops in the mesothelial cells found in one s body. These cells form membranous linings that surround and protect the body s organs and
Lung Cancer. Know how to stay strong
 Lung Cancer Know how to stay strong What is cancer? 2 Cancer is a disease when some cells in the body grow out of control Normal cells Your body has many tiny cells and keeps making new cells to keep you
Lung Cancer Know how to stay strong What is cancer? 2 Cancer is a disease when some cells in the body grow out of control Normal cells Your body has many tiny cells and keeps making new cells to keep you
People Living with Cancer
 Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer John delcharco, MD (Statistics based on CVMC data 2009-2013) Statistics Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer John delcharco, MD (Statistics based on CVMC data 2009-2013) Statistics Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates
SPOTS AND DOTS. What Is That In My Lung? Elsira M. Pina, DO FCCP University of Cincinnati Medical Center Pulmonary-Critical Care Medicine
 SPOTS AND DOTS What Is That In My Lung? Elsira M. Pina, DO FCCP University of Cincinnati Medical Center Pulmonary-Critical Care Medicine DISCLOSURE ANTI-TOBACCO PRO-LUNG FORCE TODAY S PRESENTATION Discuss
SPOTS AND DOTS What Is That In My Lung? Elsira M. Pina, DO FCCP University of Cincinnati Medical Center Pulmonary-Critical Care Medicine DISCLOSURE ANTI-TOBACCO PRO-LUNG FORCE TODAY S PRESENTATION Discuss
Lung cancer. Lung cancer: English
 Lung cancer: English Lung cancer This fact sheet is about how lung cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side effects of
Lung cancer: English Lung cancer This fact sheet is about how lung cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side effects of
Understanding Your Surgical Options for Lung Cancer
 Information Booklet for Patients Understanding Your Surgical Options for Lung Cancer Understanding Lung Cancer If you have just been diagnosed with lung cancer, this booklet will serve as an informational
Information Booklet for Patients Understanding Your Surgical Options for Lung Cancer Understanding Lung Cancer If you have just been diagnosed with lung cancer, this booklet will serve as an informational
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) Overview
 Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) Overview The information that follows is an overview of this type of cancer. It is based on the more detailed information in our document Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell). This
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) Overview The information that follows is an overview of this type of cancer. It is based on the more detailed information in our document Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell). This
Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer
 Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Removal of Lymph Nodes Why are the Lymph Nodes so important when I have penile cancer? Lymph nodes are small bean shaped
Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Removal of Lymph Nodes Why are the Lymph Nodes so important when I have penile cancer? Lymph nodes are small bean shaped
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Lung cancer (non-small-cell)
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
Understanding Lung Cancer
 Lung Understanding Lung Cancer Information for individuals with lung cancer and their families Your Primary Team at the JCC Medical Oncologist Primary Nurse Radiation Oncologist Primary Nurse Other Oncology
Lung Understanding Lung Cancer Information for individuals with lung cancer and their families Your Primary Team at the JCC Medical Oncologist Primary Nurse Radiation Oncologist Primary Nurse Other Oncology
Lung surgery. Patient Information. Introduction
 Lung surgery Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about surgery to remove all or part of your lung. It includes the different types of surgery and so not all of it will apply to you.
Lung surgery Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about surgery to remove all or part of your lung. It includes the different types of surgery and so not all of it will apply to you.
Facing Lung Cancer? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for lung cancer.
 Facing Lung Cancer? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for lung cancer. The Condition: Lung Cancer The lung is the organ that moves oxygen through your body. You have two lungs
Facing Lung Cancer? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for lung cancer. The Condition: Lung Cancer The lung is the organ that moves oxygen through your body. You have two lungs
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma
 Produced 28.02.2011 Revision due 28.02.2013 Symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer of cells called lymphocytes. These cells are part of our immune system, which helps us to fight off infections.
Produced 28.02.2011 Revision due 28.02.2013 Symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer of cells called lymphocytes. These cells are part of our immune system, which helps us to fight off infections.
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
How To Understand How Cancer Works
 Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Surgeons Role in Symptom Management. A/Prof Cliff K. C. Choong Consultant Thoracic Surgeon Latrobe Regional Hospital GIPPSLAND
 Surgeons Role in Symptom Management A/Prof Cliff K. C. Choong Consultant Thoracic Surgeon Latrobe Regional Hospital GIPPSLAND Conditions PLEURAL Pleural effusion Pneumothorax ENDOBRONCHIAL Haemoptysis
Surgeons Role in Symptom Management A/Prof Cliff K. C. Choong Consultant Thoracic Surgeon Latrobe Regional Hospital GIPPSLAND Conditions PLEURAL Pleural effusion Pneumothorax ENDOBRONCHIAL Haemoptysis
Thyroid Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital Frequently Asked Questions
 Thyroid Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital Frequently Asked Questions Q: What is the thyroid gland? A: The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. It is one of the
Thyroid Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital Frequently Asked Questions Q: What is the thyroid gland? A: The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. It is one of the
Lung Cancer Kit. Introduction. Understanding Lung Cancer. Small Cell and Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
 Lung Cancer Kit Introduction We created the Lung Cancer Kit to highlight the key principles for you as you manage the cancer decision-making process. In it, you will find tools designed to present you
Lung Cancer Kit Introduction We created the Lung Cancer Kit to highlight the key principles for you as you manage the cancer decision-making process. In it, you will find tools designed to present you
Lung Cancer. Public Outcomes Report. Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD
 Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
Mesothelioma and Asbestos
 CANCER INFORMATION FACTSHEET Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
CANCER INFORMATION FACTSHEET Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Surgery for oesophageal cancer
 Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
Lung cancer is not just one disease. There are two main types of lung cancer:
 1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC
 A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC Robert J. Korst, M.D. Director, Thoracic Surgery Medical Director, The Blumenthal Cancer Center The Valley Hospital Objectives Revised staging
A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC Robert J. Korst, M.D. Director, Thoracic Surgery Medical Director, The Blumenthal Cancer Center The Valley Hospital Objectives Revised staging
Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary
 TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) Overview
 Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) Overview The information that follows is an overview of this type of cancer. It is based on the more detailed information in our document Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell). This
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) Overview The information that follows is an overview of this type of cancer. It is based on the more detailed information in our document Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell). This
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
This factsheet aims to outline the characteristics of some rare lung cancers, and highlight where each type of lung cancer may be different.
 There are several different kinds of lung cancer, often referred to as lung cancer subtypes. Some of these occur more often than others. In this factsheet we will specifically look at the subtypes of cancers
There are several different kinds of lung cancer, often referred to as lung cancer subtypes. Some of these occur more often than others. In this factsheet we will specifically look at the subtypes of cancers
Goiter. This reference summary explains goiters. It covers symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
Malignant Mesothelioma
 Malignant Mesothelioma What is malignant mesothelioma? Malignant mesothelioma is a cancer that starts in cells in the linings of certain parts of the body, especially in the linings of the chest or abdomen.
Malignant Mesothelioma What is malignant mesothelioma? Malignant mesothelioma is a cancer that starts in cells in the linings of certain parts of the body, especially in the linings of the chest or abdomen.
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Malignant Mesothelioma
 Malignant Mesothelioma What is malignant mesothelioma? Malignant mesothelioma is a cancer that starts in cells in the linings of certain parts of the body, especially in the linings of the chest or abdomen.
Malignant Mesothelioma What is malignant mesothelioma? Malignant mesothelioma is a cancer that starts in cells in the linings of certain parts of the body, especially in the linings of the chest or abdomen.
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer?
 Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Mesothelioma and Asbestos
 Cancer information factsheet Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Cancer information factsheet Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
About lung cancer. Contents. The lungs
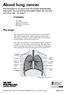 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners
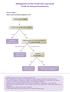 Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
TREATING LUNG CANCER AT VA PITTSBURGH HEALTHCARE SYSTEM A HERO S GUIDE
 Providing the best in cancer care for Veterans TREATING LUNG CANCER AT VA PITTSBURGH HEALTHCARE SYSTEM A HERO S GUIDE VA Pittsburgh s state-of-the-art TomoTherapy machine, which delivers radiation to patients.
Providing the best in cancer care for Veterans TREATING LUNG CANCER AT VA PITTSBURGH HEALTHCARE SYSTEM A HERO S GUIDE VA Pittsburgh s state-of-the-art TomoTherapy machine, which delivers radiation to patients.
CHAPTER 4: LUNG CANCER DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING
 CHAPTER 4: LUNG CANCER DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING INTRODUCTION The lungs are vital organs. Working with the heart and circulatory system, they provide lifesustaining oxygen and rid the body of carbon dioxide.
CHAPTER 4: LUNG CANCER DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING INTRODUCTION The lungs are vital organs. Working with the heart and circulatory system, they provide lifesustaining oxygen and rid the body of carbon dioxide.
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid.
 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Laparoscopic Adrenal Gland Removal (Adrenalectomy) Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Adrenal Gland Removal (Adrenalectomy) Patient Information from SAGES What are the Adrenal Glands? The adrenal glands are two small organs, one located above each kidney. They are triangular
Laparoscopic Adrenal Gland Removal (Adrenalectomy) Patient Information from SAGES What are the Adrenal Glands? The adrenal glands are two small organs, one located above each kidney. They are triangular
Lung cancer. A guide for journalists on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and its treatment
 Lung cancer A guide for journalists on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Lung Cancer 4 i. Types of lung cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms
Lung cancer A guide for journalists on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Lung Cancer 4 i. Types of lung cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms
Lung Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide
 Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Asbestos Related Diseases
 Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease Asbestosis and Mesothelioma (LUNG CANCER) Support Group 1800 017 758 www.amsg.com.au ii Helping you and your family through
Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease Asbestosis and Mesothelioma (LUNG CANCER) Support Group 1800 017 758 www.amsg.com.au ii Helping you and your family through
National Cancer Institute
 National Cancer Institute What You Need To Know About Lung Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only one of many
National Cancer Institute What You Need To Know About Lung Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only one of many
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer?
 Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a
.org. Metastatic Bone Disease. Description
 Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA
 Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
The TV Series. www.healthybodyhealthymind.com INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK
 The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Lung Cancer Prevention and Early Detection
 Lung Cancer Prevention and Early Detection Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women (not counting skin cancer), and is by far the leading cause of cancer death among both men
Lung Cancer Prevention and Early Detection Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women (not counting skin cancer), and is by far the leading cause of cancer death among both men
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
