Quality Assurance - Data Management
|
|
|
- Andrew Reed
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quality Assurance - Data Management Data Validation SIRFER makes extensive use of a LIMS system to control samples and process data. LIMS records information about the samples, stores the analytical raw results, corrects and normalizes the analytical results using standardized algorithms and templates and corrects the results to international scales. LIMS monitors instrument parameters and provides notification to the analyst of abnormalities. The LIMS database provides statistics on laboratory reference materials (long-term precision and reproducibility) plus a record of all correction factors. Validation of the data consists of a three-step process: Step 1 Analyst Review Step 2 LIMS Validation Step 3 QA Approval Analyst Review is the primary responsibility of the analyst. The analyst monitors instrument stability and is responsible for the initial examination of the IRMS data. The analyst assesses the quality of the work based on the following guidelines: The appropriate Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) has been followed. Sample preparation is correct and complete. Analytical results are correct and complete. QC samples are within established acceptable limits. LIMS Validation identifies data outliers, assesses instrument stability, notifies the analyst of non-conforming instrument parameters and verifies that the corrected/normalized data meet the criteria set forth in the SOP. QA Approval is the final assessment of the data before acceptance. QA Approval is an independent assessment of the final data by a researcher other than the analyst and must confirm the following: The reported results meet tolerances specified in the SOP. The results are traceable to internationally accepted standards. The results for a given sample are traceable throughout the entire analytical process. (This traceability is maintained through LIMS (which stores all of the pertinent data associated with the sample) and by the use of logbooks, instrument electronic files, and spreadsheets).
2 Quality Assurance Reference Materials δ 13 C, δ 15 N, δ 2 H, δ 18 O, δ 34 S, Solids, Continuous Flow Two different primary laboratory reference materials (PLRM) of known isotopic composition are included in every run for normalization purposes. In addition, quality control secondary laboratory reference materials (SLRM) are included in each analytical run. For δ 13 C, δ 15 N, δ 2 H, δ 18 O, and δ 34 S analysis there is at least one PLRM for every twelve unknowns. For δ 13 C, δ 15 N, and δ 34 S analysis of solid material, individual samples are analyzed once during an analytical run with the following exception: two unknown samples are run in duplicate during an analytical run. For δ 18 O and δ 2 H analysis of solid material, all samples are analyzed in duplicate during an analytical run. δ 13 C, Liquids, Continuous Flow Two different primary laboratory reference materials (PLRM) of known isotopic composition are included with the samples for normalization purposes. In addition, quality control secondary laboratory reference materials (SLRM) are included. Individual samples are analyzed in duplicate during an analytical run. δ 2 H and δ 18 O, Water, Continuous Flow Waters of known isotopic signatures are included in every run for normalization purposes, including PLRM and SLRM. These reference materials have been calibrated against accepted NIST and/or IAEA water reference materials. These PLRM and SLRM are analyzed after ten samples with the order of analysis reversed every set to allow LIMS to correct for memory effects and signal drift. All sample vials are analyzed in duplicate during an analytical run. δ 13 C, δ 15 N, δ 18 O, δ 2 H, Pure Gases, Dual Inlet Samples are compared to two PLRM gases of known isotopic composition using dual inlet methods. The PLRM gases are generated offline via in-tube combustion followed by cryogenic trapping and collection of the product gas. All gases (PLRM and unknown) are run against calibrated reference gases. The reference gases have been calibrated against accepted NIST and/or IAEA reference materials.
3 δ 13 C and δ 18 O, Atmospheric Gas Samples are analyzed for δ 13 C and δ 18 O using continuous flow methods and the samples are compared to multiple atmospheric PLRM of known isotopic signatures and CO 2 concentrations. The δ 13 C and δ 18 O isotopic composition of the PLRM is measured by extracting the CO 2 from the mixture and comparing this extracted CO 2 to pure gases of known isotopic composition using DI-IRMS. The CO 2 concentrations of the primary cylinders have been measured by the NOAA/CMDL/CCGG (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration / Climate Monitoring and Diagnostics Laboratory / Carbon Cycle Gases Group). This measurement by NOAA/CMDL places SIRFER on the WMO (World Meteorological Organization) CO 2 mole fraction scale. Note on N 2 O: Correcting atmospheric CO 2 for the presence of N 2 O is necessary if the δ 13 C and δ 18 O values of CO 2 need to be measured accurately because the raw CO 2 isotopic data contains a N 2 O contribution, which accounts for about 0.2% of the mass 44 signal. SIRFER employs the following method to eliminate N 2 O: Gas chromatography separation of N 2 O and CO 2. This method results in complete separation of N 2 O and CO 2 using a packed Porapak Q column. The method allows automated on-line applications and is invaluable for samples with high and/or variable N 2 O content.
4 Quality Assurance -Analytical Methods Carbon Isotope Ratio Analysis of Soils and Biological Materials Soils and biological samples submitted for carbon isotope ratio determination are analyzed using continuous flow isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is greater than 0.15, the unknowns are re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.3 ). The isotopic composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that USGS40 glutamic acid and USGS41 glutamic acid, respectively, are and Nitrogen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Soils and Biological Materials Soils and biological samples submitted for nitrogen isotope ratio determination are analyzed using continuous flow isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is greater than 0.2, the unknowns are re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.4 ). The isotopic composition is reported in per mil relative to nitrogen in AIR on a scale such that USGS40 glutamic acid and USGS41 glutamic acid, respectively, are and Sulfur Isotope Ratio Analysis of Soils and Biological Materials Samples submitted for sulfur isotope ratio determination are analyzed using continuous flow isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is greater than 0.4, the unknowns are re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.8 ). The isotopic composition is reported in per mil on a scale relative to VCDT such that IAEA-S-1 silver sulfide and IAEA-S-2 silver sulfide, respectfully, are, -0.3 and Hydrogen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Water The prepared samples are analyzed for δ 2 H using a High Temperature Conversion/Elemental Analyzer coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus XL Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Each water sample is analyzed in duplicate. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM of multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 2, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 4 ). The isotopic composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW water on a scale such that VSMOW and SLAP water, respectively, are 0 and -428.
5 Oxygen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Water The prepared samples are analyzed for δ 18 O using a High Temperature Conversion/Elemental Analyzer coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus XL Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Every sample is analyzed in duplicate. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.15, the samples in the manifold are all re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.3 ). The isotopic composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW water on a scale such that VSMOW and SLAP water, respectively, are 0 and Hydrogen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Organic and Inorganic Materials (solid) The prepared samples are analyzed for δ 2 H using a High Temperature Conversion/Elemental Analyzer coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus XL Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 2.5, the samples in the manifold are all re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 4 ). The isotopic composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW water scale such that VSMOW and SLAP water, respectively, are 0 and Oxygen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Organic and Inorganic Materials (solid) The prepared samples are analyzed for δ 18 O using a High Temperature Conversion/Elemental Analyzer coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus XL Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.15, the samples in the manifold are all re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.3 ). The isotopic composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that L-SVEC LiCO 3 carbonate and NBS 19 CaCO 3, respectively, are and
6 Carbon, Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Pure Gases Gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C, δ 18 O and δ 2 H in dual inlet mode using a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus Advantage Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer. A minimum of two PLRM reference gases are generated from solid PLRM materials and analyzed along with the unknown gases. The standard uncertainty for δ 13 C in CO 2 is defined as +/- 0.05, δ 18 O in CO 2 is +/- 0.10, and δ 2 H in H 2 is +/ The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is The oxygen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is The hydrogen isotopic composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW water on a scale such that VSMOW water is 0. Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Atmospheric Gases Dual Inlet Method: Gas samples (CO 2 ) are analyzed for δ 13 C and δ 18 O in dual inlet mode using a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus Advantage Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer. The standard uncertainty for δ 13 C is defined as +/ and δ 18 O is +/ Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. For δ 13 C, if the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.05, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.1 ). For δ 18 O, if the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.1, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.2 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is The oxygen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is Continuous Flow Method: Gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C and δ 18 O using an flask autosampler coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus Advantage Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface.. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.15, the samples in the manifold are rejected. The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is The oxygen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is
7 Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Equilibration Gases Gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C and δ 18 O using a gas chromatograph coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus Advantage Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.15, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2- sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.3 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is The oxygen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is Carbon Isotope Ratio Analysis of DIC Samples Gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C and δ 18 O using gas chromatograph coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus Advantage Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.2, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2- sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.4 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Elevated [CO 2 ] Samples Elevated [CO 2 ] gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C and δ 18 O using gas chromatograph coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus Advantage Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.2, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.4 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is The oxygen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is Carbon Isotope Ratio Analysis of Pure CO 2 Samples Pure gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C using DI-IRMS methods Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.05, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.1 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is
8 Nitrogen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Pure N 2 Samples Pure gas samples are analyzed for δ 15 N using DI-IRMS methods. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.08, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.16 ). The nitrogen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to AIR on a scale such that IAEA-N1 is Hydrogen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Pure H 2 Samples Pure gas samples are analyzed for δ 2 H using DI-IRMS methods. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS.. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 2, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 4 ). The hydrogen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW on a scale such that VSMOW is +0. Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Carbonate Samples Pure gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C and δ 18 O using DI-IRMS methods. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS.. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.05, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.1 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is The oxygen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is Carbon Isotope Ratio Analysis of Gas Samples Gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C using a elemental analyzer coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus Advantage Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.4 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is
9 Carbon Isotope Ratio Analysis of Liquid Samples Liquid samples are analyzed for δ 13 C using an elemental analyzer coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta Plus Advantage Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.4 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Atmospheric CO 2 Samples Gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C and δ 18 O using a preconcentrator coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta S Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS.. If the standard standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.4 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is The oxygen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is Nitrogen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Atmospheric N 2 O Samples Gas samples are analyzed for δ 15 N using a preconcentrator coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta S Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.4 ). The nitrogen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to AIR on a scale such that IAEA-N1 is Carbon Isotope Ratio Analysis of Atmospheric CH 4 Samples Gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C using a preconcentrator coupled to a Thermo Finnigan Delta S Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.4 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is
10 Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Carbonate Samples Gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C using a common acid bath digestion autosampler coupled to a Thermo Finnigan MAT 252 Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard uncertainty is larger than 0.12, the sample is re-analyzed (until the 2-sigma expanded standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.24 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Ratio Analysis of Headspace CO 2 Samples Gas samples are analyzed for δ 13 C and δ 18 O using a headspace autosampler coupled to a Thermo Finnigan MAT 252 Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer through an open split interface. Quality assurance is based on the standard uncertainty of the known value of the SLRM calculated on multiple analyses of SLRM using LIMS. If the standard standard uncertainty of the result is better than 0.4 ). The carbon isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VPDB on a scale such that NBS 19 CaCO 3 is The oxygen isotope composition is reported in per mil relative to VSMOW on a scale such that NIST-19 CaCO 3 is
Good Practice Guide for Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry
 Good Practice Guide for Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry Good Practice Guide for Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry First Edition 2011 Editors Dr Jim Carter, UK Vicki Barwick, UK Acknowledgements This Guide
Good Practice Guide for Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry Good Practice Guide for Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry First Edition 2011 Editors Dr Jim Carter, UK Vicki Barwick, UK Acknowledgements This Guide
Thermo Scientific ConFlo IV Universal Interface
 m a s s s p e c t r o m e t r y Thermo Scientific ConFlo IV Universal Interface The Universal Interface Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific ConFlo IV Universal Interface The Universal Interface The development
m a s s s p e c t r o m e t r y Thermo Scientific ConFlo IV Universal Interface The Universal Interface Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific ConFlo IV Universal Interface The Universal Interface The development
AS1 MOLES. oxygen molecules have the formula O 2 the relative mass will be 2 x 16 = 32 so the molar mass will be 32g mol -1
 Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (L) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.023 x 10 23 mol -1. Example
Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (L) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.023 x 10 23 mol -1. Example
F321 MOLES. Example If 1 atom has a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g 1 mole of atoms will have a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g x 6.02 x 10 23 = 7.
 Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
1.1 This test method covers the qualitative and quantitative determination of the content of benzene and toluene in hydrocarbon wax.
 Standard Method for Analysis of Benzene and Toluene Content in Hydrocarbon Waxes by Headspace Gas Chromatography EWF METHOD 002/03 (Version 1 Reviewed 2015) 1 Scope 1.1 This test method covers the qualitative
Standard Method for Analysis of Benzene and Toluene Content in Hydrocarbon Waxes by Headspace Gas Chromatography EWF METHOD 002/03 (Version 1 Reviewed 2015) 1 Scope 1.1 This test method covers the qualitative
Fiscal Measurement Natural Gas
 White Paper FSG-WP-0012 February 2014 Fiscal Measurement Natural Gas Fiscal Measurement How much? Fiscal Measurement must not be confused with Custody Transfer; in fact, fiscal measurement is a more general
White Paper FSG-WP-0012 February 2014 Fiscal Measurement Natural Gas Fiscal Measurement How much? Fiscal Measurement must not be confused with Custody Transfer; in fact, fiscal measurement is a more general
An example: helium isotopes. An example: helium isotopes. Limits to Detection/Measurement. Lecture 14 Measurements II: Mass spectrometry
 Limits to Detection/Measurement Ionization is fundamentally a Probabilistic Process Just like radioactive decay So is transmission through the analyzer There is an intrinsic statistical uncertainty Proportional
Limits to Detection/Measurement Ionization is fundamentally a Probabilistic Process Just like radioactive decay So is transmission through the analyzer There is an intrinsic statistical uncertainty Proportional
1 Quality Assurance and Quality Control Project Plan
 1 Quality Assurance and Quality Control Project Plan The purpose of this section is to describe the quality assurance/quality control program that will be used during the system specific field testing
1 Quality Assurance and Quality Control Project Plan The purpose of this section is to describe the quality assurance/quality control program that will be used during the system specific field testing
DETERMINATION OF TOTAL CARBON, TOTAL ORGANIC CARBON AND INORGANIC CARBON IN SEDIMENTS
 DETERMINATION OF TOTAL CARBON, TOTAL ORGANIC CARBON AND INORGANIC CARBON IN SEDIMENTS Bernie B. Bernard, Heather Bernard, and James M. Brooks TDI-Brooks International/B&B Laboratories Inc. College Station,
DETERMINATION OF TOTAL CARBON, TOTAL ORGANIC CARBON AND INORGANIC CARBON IN SEDIMENTS Bernie B. Bernard, Heather Bernard, and James M. Brooks TDI-Brooks International/B&B Laboratories Inc. College Station,
Calculation of Molar Masses. Molar Mass. Solutions. Solutions
 Molar Mass Molar mass = Mass in grams of one mole of any element, numerically equal to its atomic weight Molar mass of molecules can be determined from the chemical formula and molar masses of elements
Molar Mass Molar mass = Mass in grams of one mole of any element, numerically equal to its atomic weight Molar mass of molecules can be determined from the chemical formula and molar masses of elements
Ecology Quality Assurance Glossary
 Ecology Quality Assurance Glossary Edited by William Kammin, Ecology Quality Assurance Officer Accreditation - A certification process for laboratories, designed to evaluate and document a lab s ability
Ecology Quality Assurance Glossary Edited by William Kammin, Ecology Quality Assurance Officer Accreditation - A certification process for laboratories, designed to evaluate and document a lab s ability
Pesticide Analysis by Mass Spectrometry
 Pesticide Analysis by Mass Spectrometry Purpose: The purpose of this assignment is to introduce concepts of mass spectrometry (MS) as they pertain to the qualitative and quantitative analysis of organochlorine
Pesticide Analysis by Mass Spectrometry Purpose: The purpose of this assignment is to introduce concepts of mass spectrometry (MS) as they pertain to the qualitative and quantitative analysis of organochlorine
CHEM 105 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99. = -163 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Ni(CO) 4 (g) = -260 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Cr(CO) 6 (g)
 CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 10 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A gas at a pressure of 10.0 Pa exerts a force of N on an area of 5.5 m2. A) 1.8 B) 0.55
Chapter 10 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A gas at a pressure of 10.0 Pa exerts a force of N on an area of 5.5 m2. A) 1.8 B) 0.55
USE OF REFERENCE MATERIALS IN THE LABORATORY
 USE OF REFERENCE MATERIALS IN THE LABORATORY What is a reference material? A general definition of a reference material is a material or substance one or more of whose property values are sufficiently
USE OF REFERENCE MATERIALS IN THE LABORATORY What is a reference material? A general definition of a reference material is a material or substance one or more of whose property values are sufficiently
4.2 Bias, Standards and Standardization
 4.2 Bias, Standards and Standardization bias and accuracy, estimation of bias origin of bias and the uncertainty in reference values quantifying by mass, chemical reactions, and physical methods standard
4.2 Bias, Standards and Standardization bias and accuracy, estimation of bias origin of bias and the uncertainty in reference values quantifying by mass, chemical reactions, and physical methods standard
Performance and advantages of qnmr measurements
 Return to Web Version This is the first of a series of articles related to the launch of new organic CRMs certified by quantitative NMR under double accreditation. In this issue, we focus on CRMs intended
Return to Web Version This is the first of a series of articles related to the launch of new organic CRMs certified by quantitative NMR under double accreditation. In this issue, we focus on CRMs intended
FP628. Nitrogen / Protein Determination by Combustion. Rev 1-6/8/11
 FP628 Nitrogen / Protein Determination by Combustion Rev 1-6/8/11 Presentation Outline LECO Background N Determination FP628 Theory of Operation Specifications Advantages Software Data LECO Background
FP628 Nitrogen / Protein Determination by Combustion Rev 1-6/8/11 Presentation Outline LECO Background N Determination FP628 Theory of Operation Specifications Advantages Software Data LECO Background
Chemistry 321, Experiment 8: Quantitation of caffeine from a beverage using gas chromatography
 Chemistry 321, Experiment 8: Quantitation of caffeine from a beverage using gas chromatography INTRODUCTION The analysis of soft drinks for caffeine was able to be performed using UV-Vis. The complex sample
Chemistry 321, Experiment 8: Quantitation of caffeine from a beverage using gas chromatography INTRODUCTION The analysis of soft drinks for caffeine was able to be performed using UV-Vis. The complex sample
Chapter 1 The Atomic Nature of Matter
 Chapter 1 The Atomic Nature of Matter 6. Substances that cannot be decomposed into two or more simpler substances by chemical means are called a. pure substances. b. compounds. c. molecules. d. elements.
Chapter 1 The Atomic Nature of Matter 6. Substances that cannot be decomposed into two or more simpler substances by chemical means are called a. pure substances. b. compounds. c. molecules. d. elements.
7. 1.00 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg = 101.325 kpa = 14.70 psi. = 0.446 atm. = 0.993 atm. = 107 kpa 760 torr 1 atm 760 mm Hg = 790.
 CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
MILESTONE H E L P I N G C H E M I S T S
 MILESTONE H E L P I N G C H E M I S T S 8 good reasons to choose the Milestone DMA-80 1. No sample preparation The DMA-80 does not require any sample preparation or other wet chemistry prior the analysis.
MILESTONE H E L P I N G C H E M I S T S 8 good reasons to choose the Milestone DMA-80 1. No sample preparation The DMA-80 does not require any sample preparation or other wet chemistry prior the analysis.
UC Davis Analytical Laboratory Quality Manual
 1 of 18 Quality Manual Director: Dirk Holstege Laboratory Supervisor: Traci Francis Management Services Officer: Nikki Schwab Quality Assurance Officer: Kelly Gardner Date of Issue: October 7, 2010 224
1 of 18 Quality Manual Director: Dirk Holstege Laboratory Supervisor: Traci Francis Management Services Officer: Nikki Schwab Quality Assurance Officer: Kelly Gardner Date of Issue: October 7, 2010 224
Dissolved Gas Analysis Guide for Transformers Filled with Beta Fluid
 DSI Ventures, Inc. PHONE: (903) 526-7577 FAX: (903) 526-0021 www.dsiventures.com Dissolved Gas Analysis Guide for Transformers Filled with Beta Fluid Introduction Analysis of dissolved gases in transformer
DSI Ventures, Inc. PHONE: (903) 526-7577 FAX: (903) 526-0021 www.dsiventures.com Dissolved Gas Analysis Guide for Transformers Filled with Beta Fluid Introduction Analysis of dissolved gases in transformer
Lecture 35: Atmosphere in Furnaces
 Lecture 35: Atmosphere in Furnaces Contents: Selection of atmosphere: Gases and their behavior: Prepared atmospheres Protective atmospheres applications Atmosphere volume requirements Atmosphere sensors
Lecture 35: Atmosphere in Furnaces Contents: Selection of atmosphere: Gases and their behavior: Prepared atmospheres Protective atmospheres applications Atmosphere volume requirements Atmosphere sensors
Module 5: Combustion Technology. Lecture 33: Combustion air calculation
 1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 33: Combustion air calculation 2 P age Keywords: Heat of combustion, stoichiometric air, excess air, natural gas combustion Combustion air calculation The
1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 33: Combustion air calculation 2 P age Keywords: Heat of combustion, stoichiometric air, excess air, natural gas combustion Combustion air calculation The
METHOD 9075 TEST METHOD FOR TOTAL CHLORINE IN NEW AND USED PETROLEUM PRODUCTS BY X-RAY FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETRY (XRF)
 METHOD 9075 TEST METHOD FOR TOTAL CHLORINE IN NEW AND USED PETROLEUM PRODUCTS BY X-RAY FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETRY (XRF) 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 This test method covers the determination of total chlorine
METHOD 9075 TEST METHOD FOR TOTAL CHLORINE IN NEW AND USED PETROLEUM PRODUCTS BY X-RAY FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETRY (XRF) 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 This test method covers the determination of total chlorine
Unit 3 Notepack Chapter 7 Chemical Quantities Qualifier for Test
 Unit 3 Notepack Chapter 7 Chemical Quantities Qualifier for Test NAME Section 7.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter A. What is a mole? 1. Chemistry is a quantitative science. What does this term mean?
Unit 3 Notepack Chapter 7 Chemical Quantities Qualifier for Test NAME Section 7.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter A. What is a mole? 1. Chemistry is a quantitative science. What does this term mean?
BTU ANALYSIS USING A GAS CHROMATOGRAPH
 BTU ANALYSIS USING A GAS CHROMATOGRAPH By Joseph E. Landes Southern Petroleum Laboratories, Inc. Technical Director Hydrocarbon and Field Services 8820 Interchange Drive Houston, Texas 77054 Introduction
BTU ANALYSIS USING A GAS CHROMATOGRAPH By Joseph E. Landes Southern Petroleum Laboratories, Inc. Technical Director Hydrocarbon and Field Services 8820 Interchange Drive Houston, Texas 77054 Introduction
1. Standard conditions are 29.92 in. Hg (760 mm Hg, 14.696 psia) and 68 F (20 C).
 INTRODUCTION Emission Monitoring Inc. DETERMINING F-FACTORS FROM GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSES Roger T. Shigehara Emission Monitoring Incorporated Howard F. Schiff TRC Environmental Corporation EPA Method
INTRODUCTION Emission Monitoring Inc. DETERMINING F-FACTORS FROM GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSES Roger T. Shigehara Emission Monitoring Incorporated Howard F. Schiff TRC Environmental Corporation EPA Method
Stoichiometry. 1. The total number of moles represented by 20 grams of calcium carbonate is (1) 1; (2) 2; (3) 0.1; (4) 0.2.
 Stoichiometry 1 The total number of moles represented by 20 grams of calcium carbonate is (1) 1; (2) 2; (3) 01; (4) 02 2 A 44 gram sample of a hydrate was heated until the water of hydration was driven
Stoichiometry 1 The total number of moles represented by 20 grams of calcium carbonate is (1) 1; (2) 2; (3) 01; (4) 02 2 A 44 gram sample of a hydrate was heated until the water of hydration was driven
IB Chemistry 1 Mole. One atom of C-12 has a mass of 12 amu. One mole of C-12 has a mass of 12 g. Grams we can use more easily.
 The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Division of Remediation Management Response Site Remediation Program
 New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Division of Remediation Management Response Site Remediation Program NJDEP- SRP Low Level USEPA TO-15 Method (NJDEP-LLTO-15-3/2007) March 2007 March 2009
New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Division of Remediation Management Response Site Remediation Program NJDEP- SRP Low Level USEPA TO-15 Method (NJDEP-LLTO-15-3/2007) March 2007 March 2009
DMA-1 Direct Mercury Analyzer
 DMA-1 Direct Mercury Analyzer www.milestonesrl.com MILESTONE H E L P I N G C H E M I S T S 8 good reasons to choose the milestone DmA-1 1. no sample preparation 2. ease of use 3. lowest cost of analysis
DMA-1 Direct Mercury Analyzer www.milestonesrl.com MILESTONE H E L P I N G C H E M I S T S 8 good reasons to choose the milestone DmA-1 1. no sample preparation 2. ease of use 3. lowest cost of analysis
13C NMR Spectroscopy
 13 C NMR Spectroscopy Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for structural determination. A nucleus with an odd number of protons, an odd number
13 C NMR Spectroscopy Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for structural determination. A nucleus with an odd number of protons, an odd number
How To Test For Contamination In Large Volume Water
 Automated Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) of EPA Method 1694 for Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Large Volume Water Samples Keywords Application Note ENV0212 This collaboration study was performed
Automated Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) of EPA Method 1694 for Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Large Volume Water Samples Keywords Application Note ENV0212 This collaboration study was performed
The Empirical Formula of a Compound
 The Empirical Formula of a Compound Lab #5 Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant,
The Empirical Formula of a Compound Lab #5 Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant,
Chapter 1: Moles and equations. Learning outcomes. you should be able to:
 Chapter 1: Moles and equations 1 Learning outcomes you should be able to: define and use the terms: relative atomic mass, isotopic mass and formula mass based on the 12 C scale perform calculations, including
Chapter 1: Moles and equations 1 Learning outcomes you should be able to: define and use the terms: relative atomic mass, isotopic mass and formula mass based on the 12 C scale perform calculations, including
NANOCOMPOSIX'S GUIDE TO ICP-MS MEASUREMENT
 NANOCOMPOSIX'S GUIDE TO ICP-MS MEASUREMENT AND ANALYSIS SEPTEMBER 2012, V 1.1 4878 RONSON CT STE K SAN DIEGO, CA 92111 858-565 - 4227 NANOCOMPOSIX.COM Note to the Reader: We at nanocomposix have published
NANOCOMPOSIX'S GUIDE TO ICP-MS MEASUREMENT AND ANALYSIS SEPTEMBER 2012, V 1.1 4878 RONSON CT STE K SAN DIEGO, CA 92111 858-565 - 4227 NANOCOMPOSIX.COM Note to the Reader: We at nanocomposix have published
LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Docetaxel in Human Serum for Clinical Research
 LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Docetaxel in Human Serum for Clinical Research J. Jones, J. Denbigh, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Application Note 20581 Key Words SPE, SOLA,
LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Docetaxel in Human Serum for Clinical Research J. Jones, J. Denbigh, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Application Note 20581 Key Words SPE, SOLA,
STOICHIOMETRY OF COMBUSTION
 STOICHIOMETRY OF COMBUSTION FUNDAMENTALS: moles and kilomoles Atomic unit mass: 1/12 126 C ~ 1.66 10-27 kg Atoms and molecules mass is defined in atomic unit mass: which is defined in relation to the 1/12
STOICHIOMETRY OF COMBUSTION FUNDAMENTALS: moles and kilomoles Atomic unit mass: 1/12 126 C ~ 1.66 10-27 kg Atoms and molecules mass is defined in atomic unit mass: which is defined in relation to the 1/12
QUANTITATIVE INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY. Willard et. al. Instrumental Methods of Analysis, 7th edition, Wadsworth Publishing Co., Belmont, CA 1988, Ch 11.
 QUANTITATIVE INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY Objective: The objectives of this experiment are: (1) to learn proper sample handling procedures for acquiring infrared spectra. (2) to determine the percentage composition
QUANTITATIVE INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY Objective: The objectives of this experiment are: (1) to learn proper sample handling procedures for acquiring infrared spectra. (2) to determine the percentage composition
MATHESON REFINERY PROGRAM for Specialty Gas Supply. Experience the MATHESON Commitment to Supply Chain Excellence
 MATHESON REFINERY PROGRAM for Specialty Gas Supply MATHESON REFINERY PROGRAM for Specialty Gas Supply MATHESON is a single source for industrial, medical, specialty, and electronics gases as well as gas
MATHESON REFINERY PROGRAM for Specialty Gas Supply MATHESON REFINERY PROGRAM for Specialty Gas Supply MATHESON is a single source for industrial, medical, specialty, and electronics gases as well as gas
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
 Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
Element of same atomic number, but different atomic mass o Example: Hydrogen
 Atomic mass: p + = protons; e - = electrons; n 0 = neutrons p + + n 0 = atomic mass o For carbon-12, 6p + + 6n 0 = atomic mass of 12.0 o For chlorine-35, 17p + + 18n 0 = atomic mass of 35.0 atomic mass
Atomic mass: p + = protons; e - = electrons; n 0 = neutrons p + + n 0 = atomic mass o For carbon-12, 6p + + 6n 0 = atomic mass of 12.0 o For chlorine-35, 17p + + 18n 0 = atomic mass of 35.0 atomic mass
Analysis of the Vitamin B Complex in Infant Formula Samples by LC-MS/MS
 Analysis of the Vitamin B Complex in Infant Formula Samples by LC-MS/MS Stephen Lock 1 and Matthew Noestheden 2 1 AB SCIEX Warrington, Cheshire (UK), 2 AB SCIEX Concord, Ontario (Canada) Overview A rapid,
Analysis of the Vitamin B Complex in Infant Formula Samples by LC-MS/MS Stephen Lock 1 and Matthew Noestheden 2 1 AB SCIEX Warrington, Cheshire (UK), 2 AB SCIEX Concord, Ontario (Canada) Overview A rapid,
MATHESON STACK EMISSION CALIBRATION PROGRAM. Experience the MATHESON Commitment to Supply Chain Excellence
 MATHESON STACK EMISSION CALIBRATION PROGRAM MATHESON STACK EMISSION CALIBRATION PROGRAM MATHESON is a single source for industrial, medical, specialty, and electronics gases as well as gas handling equipment,
MATHESON STACK EMISSION CALIBRATION PROGRAM MATHESON STACK EMISSION CALIBRATION PROGRAM MATHESON is a single source for industrial, medical, specialty, and electronics gases as well as gas handling equipment,
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM (ICE METHOD)
 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM (ICE METHOD) Introduction Chemical equilibrium occurs when opposing reactions are proceeding at equal rates. The rate at which the products are formed from the reactants equals the
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM (ICE METHOD) Introduction Chemical equilibrium occurs when opposing reactions are proceeding at equal rates. The rate at which the products are formed from the reactants equals the
23 The Thermal Conductivity Detector
 23 The Thermal Conductivity Detector General Information TCD pneumatics Conditions that prevent the detector from operating Filament passivation Carrier, reference, and makeup gas Negative polarity Analyzing
23 The Thermal Conductivity Detector General Information TCD pneumatics Conditions that prevent the detector from operating Filament passivation Carrier, reference, and makeup gas Negative polarity Analyzing
Name Date Class CHEMICAL QUANTITIES. SECTION 10.1 THE MOLE: A MEASUREMENT OF MATTER (pages 287 296)
 Name Date Class 10 CHEMICAL QUANTITIES SECTION 10.1 THE MOLE: A MEASUREMENT OF MATTER (pages 287 296) This section defines the mole and explains how the mole is used to measure matter. It also teaches
Name Date Class 10 CHEMICAL QUANTITIES SECTION 10.1 THE MOLE: A MEASUREMENT OF MATTER (pages 287 296) This section defines the mole and explains how the mole is used to measure matter. It also teaches
MOLES AND MOLE CALCULATIONS
 35 MOLES ND MOLE CLCULTIONS INTRODUCTION The purpose of this section is to present some methods for calculating both how much of each reactant is used in a chemical reaction, and how much of each product
35 MOLES ND MOLE CLCULTIONS INTRODUCTION The purpose of this section is to present some methods for calculating both how much of each reactant is used in a chemical reaction, and how much of each product
Atomic Mass/Molar Mass, Percent Composition, & Empirical and Molecular Formula
 Name AP Chemistry Atomic Mass/Molar Mass, Percent Composition, & Empirical and Molecular Formula Atomic Mass/Molar Mass The mass for an element reported on the Periodic Table is the average mass of all
Name AP Chemistry Atomic Mass/Molar Mass, Percent Composition, & Empirical and Molecular Formula Atomic Mass/Molar Mass The mass for an element reported on the Periodic Table is the average mass of all
 Quality Assurance Program Quality Assurance Plan Periodic Audits Standard Operating Procedures Preventive Maintenance Outline Quality Assurance Plan (QAP) What is a QAP Why is a QAP required? What does
Quality Assurance Program Quality Assurance Plan Periodic Audits Standard Operating Procedures Preventive Maintenance Outline Quality Assurance Plan (QAP) What is a QAP Why is a QAP required? What does
CONFIRMATION OF ZOLPIDEM BY LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY MASS SPECTROMETRY
 CONFIRMATION OF ZOLPIDEM BY LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY MASS SPECTROMETRY 9.1 POLICY This test method may be used to confirm the presence of zolpidem (ZOL), with diazepam-d 5 (DZP-d 5 ) internal standard, in
CONFIRMATION OF ZOLPIDEM BY LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY MASS SPECTROMETRY 9.1 POLICY This test method may be used to confirm the presence of zolpidem (ZOL), with diazepam-d 5 (DZP-d 5 ) internal standard, in
Appendix 5 Overview of requirements in English
 Appendix 5 Overview of requirements in English This document is a translation of Appendix 4 (Bilag 4) section 2. This translation is meant as a service for the bidder and in case of any differences between
Appendix 5 Overview of requirements in English This document is a translation of Appendix 4 (Bilag 4) section 2. This translation is meant as a service for the bidder and in case of any differences between
NMR and other Instrumental Techniques in Chemistry and the proposed National Curriculum.
 NMR and other Instrumental Techniques in Chemistry and the proposed National Curriculum. Dr. John Jackowski Chair of Science, Head of Chemistry Scotch College Melbourne john.jackowski@scotch.vic.edu.au
NMR and other Instrumental Techniques in Chemistry and the proposed National Curriculum. Dr. John Jackowski Chair of Science, Head of Chemistry Scotch College Melbourne john.jackowski@scotch.vic.edu.au
How To Run A Gas Plant
 MATHESON Petrochemical Industry Program for Specialty Gas Supply MATHESON Petrochemical Industry Program for Specialty Gas Supply MATHESON is a single source for industrial, medical, specialty, and electronics
MATHESON Petrochemical Industry Program for Specialty Gas Supply MATHESON Petrochemical Industry Program for Specialty Gas Supply MATHESON is a single source for industrial, medical, specialty, and electronics
Chemical Proportions in Compounds
 Chapter 6 Chemical Proportions in Compounds Solutions for Practice Problems Student Textbook page 201 1. Problem A sample of a compound is analyzed and found to contain 0.90 g of calcium and 1.60 g of
Chapter 6 Chemical Proportions in Compounds Solutions for Practice Problems Student Textbook page 201 1. Problem A sample of a compound is analyzed and found to contain 0.90 g of calcium and 1.60 g of
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry)
 Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry
 Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Bomb Calorimetry. Electrical leads. Stirrer
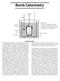 Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
CHE334 Identification of an Unknown Compound By NMR/IR/MS
 CHE334 Identification of an Unknown Compound By NMR/IR/MS Purpose The object of this experiment is to determine the structure of an unknown compound using IR, 1 H-NMR, 13 C-NMR and Mass spectroscopy. Infrared
CHE334 Identification of an Unknown Compound By NMR/IR/MS Purpose The object of this experiment is to determine the structure of an unknown compound using IR, 1 H-NMR, 13 C-NMR and Mass spectroscopy. Infrared
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology November 1996 ICH Guidance for Industry Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology Additional copies are available from:
Guidance for Industry Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology November 1996 ICH Guidance for Industry Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology Additional copies are available from:
A Laboratory Information Management System for Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes in Water Samples by Laser Absorption Spectroscopy
 A Laboratory Information Management System for Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes in Water Samples by Laser Absorption Spectroscopy User Manual & Tutorial Revision v 1.0 2012/11/05 1 Foreword The routine
A Laboratory Information Management System for Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes in Water Samples by Laser Absorption Spectroscopy User Manual & Tutorial Revision v 1.0 2012/11/05 1 Foreword The routine
BASIC UNDERSTANDING OF FLOW CALCULATIONS AND ESTIMATES MAKES SIZING VALVES SIMPLER
 BASIC UNDERSTANDING OF FLOW CALCULATIONS AND ESTIMATES MAKES SIZING VALVES SIMPLER Valve size often is described by the nominal size of the end connections but a more important measure is the flow that
BASIC UNDERSTANDING OF FLOW CALCULATIONS AND ESTIMATES MAKES SIZING VALVES SIMPLER Valve size often is described by the nominal size of the end connections but a more important measure is the flow that
Unit 2: Quantities in Chemistry
 Mass, Moles, & Molar Mass Relative quantities of isotopes in a natural occurring element (%) E.g. Carbon has 2 isotopes C-12 and C-13. Of Carbon s two isotopes, there is 98.9% C-12 and 11.1% C-13. Find
Mass, Moles, & Molar Mass Relative quantities of isotopes in a natural occurring element (%) E.g. Carbon has 2 isotopes C-12 and C-13. Of Carbon s two isotopes, there is 98.9% C-12 and 11.1% C-13. Find
CH3 Stoichiometry. The violent chemical reaction of bromine and phosphorus. P.76
 CH3 Stoichiometry The violent chemical reaction of bromine and phosphorus. P.76 Contents 3.1 Counting by Weighing 3.2 Atomic Masses 3.3 The Mole 3.4 Molar Mass 3.5 Percent Composition of Compounds 3.6
CH3 Stoichiometry The violent chemical reaction of bromine and phosphorus. P.76 Contents 3.1 Counting by Weighing 3.2 Atomic Masses 3.3 The Mole 3.4 Molar Mass 3.5 Percent Composition of Compounds 3.6
Chapter 3. Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions This chapter uses the concepts of conservation of mass to assist the student in gaining an understanding of chemical changes. Upon completion of Chapter
Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions This chapter uses the concepts of conservation of mass to assist the student in gaining an understanding of chemical changes. Upon completion of Chapter
CHAPTER 8: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
 CHAPTER 8: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION Active Learning: 1-4, 6-8, 12, 18-25; End-of-Chapter Problems: 3-4, 9-82, 84-85, 87-92, 94-104, 107-109, 111, 113, 119, 125-126 8.2 ATOMIC MASSES: COUNTING ATOMS BY WEIGHING
CHAPTER 8: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION Active Learning: 1-4, 6-8, 12, 18-25; End-of-Chapter Problems: 3-4, 9-82, 84-85, 87-92, 94-104, 107-109, 111, 113, 119, 125-126 8.2 ATOMIC MASSES: COUNTING ATOMS BY WEIGHING
Effects of Temperature, Pressure and Water Vapor on Gas Phase Infrared Absorption by CO 2
 Effects of Temperature, Pressure and Water Vapor on Gas Phase Infrared Absorption by CO 2 D. K. McDermitt, J. M. Welles, and R. D. Eckles - LI-COR, inc. Lincoln, NE 68504 USA Introduction Infrared analysis
Effects of Temperature, Pressure and Water Vapor on Gas Phase Infrared Absorption by CO 2 D. K. McDermitt, J. M. Welles, and R. D. Eckles - LI-COR, inc. Lincoln, NE 68504 USA Introduction Infrared analysis
A MANUAL FOR A LABORATORY INFORMATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (LIMS) FOR LIGHT STABLE ISOTOPES VERSION 7.0
 A MANUAL FOR A LABORATORY INFORMATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (LIMS) FOR LIGHT STABLE ISOTOPES VERSION 7.0 U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Open-File Report 98-284 Revision of Open-File Report 97-812 A MANUAL FOR A LABORATORY
A MANUAL FOR A LABORATORY INFORMATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (LIMS) FOR LIGHT STABLE ISOTOPES VERSION 7.0 U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Open-File Report 98-284 Revision of Open-File Report 97-812 A MANUAL FOR A LABORATORY
The art of elemental analysis
 vario MACRO CUBE The art of elemental analysis 100 years ago, in the center of Germany, near Frankfurt, the advanced technology company Heraeus developed and manufactured the world s first elemental analyzer
vario MACRO CUBE The art of elemental analysis 100 years ago, in the center of Germany, near Frankfurt, the advanced technology company Heraeus developed and manufactured the world s first elemental analyzer
Chapter Test B. Chapter: Measurements and Calculations
 Assessment Chapter Test B Chapter: Measurements and Calculations PART I In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1.
Assessment Chapter Test B Chapter: Measurements and Calculations PART I In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1.
Daniel M. Mueller, Katharina M. Rentsch Institut für Klinische Chemie, Universitätsspital Zürich, CH-8091 Zürich, Schweiz
 Toxichem Krimtech 211;78(Special Issue):324 Online extraction LC-MS n method for the detection of drugs in urine, serum and heparinized plasma Daniel M. Mueller, Katharina M. Rentsch Institut für Klinische
Toxichem Krimtech 211;78(Special Issue):324 Online extraction LC-MS n method for the detection of drugs in urine, serum and heparinized plasma Daniel M. Mueller, Katharina M. Rentsch Institut für Klinische
5. Which temperature is equal to +20 K? 1) 253ºC 2) 293ºC 3) 253 C 4) 293 C
 1. The average kinetic energy of water molecules increases when 1) H 2 O(s) changes to H 2 O( ) at 0ºC 3) H 2 O( ) at 10ºC changes to H 2 O( ) at 20ºC 2) H 2 O( ) changes to H 2 O(s) at 0ºC 4) H 2 O( )
1. The average kinetic energy of water molecules increases when 1) H 2 O(s) changes to H 2 O( ) at 0ºC 3) H 2 O( ) at 10ºC changes to H 2 O( ) at 20ºC 2) H 2 O( ) changes to H 2 O(s) at 0ºC 4) H 2 O( )
IB Chemistry. DP Chemistry Review
 DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
ACID-BASE TITRATIONS: DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE BY TITRATION WITH HYDROCHLORIC ACID BACKGROUND
 #3. Acid - Base Titrations 27 EXPERIMENT 3. ACID-BASE TITRATIONS: DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE BY TITRATION WITH HYDROCHLORIC ACID BACKGROUND Carbonate Equilibria In this experiment a solution of hydrochloric
#3. Acid - Base Titrations 27 EXPERIMENT 3. ACID-BASE TITRATIONS: DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE BY TITRATION WITH HYDROCHLORIC ACID BACKGROUND Carbonate Equilibria In this experiment a solution of hydrochloric
NSW Air Quality Monitoring Network: Quality Assurance Procedures
 NSW Air Quality Monitoring Network: Quality Assurance Procedures Copyright State of NSW and Office of Environment and Heritage With the exception of photographs, the State of NSW and Office of Environment
NSW Air Quality Monitoring Network: Quality Assurance Procedures Copyright State of NSW and Office of Environment and Heritage With the exception of photographs, the State of NSW and Office of Environment
1- Monitoring of Industrial Pollution
 $541 &I*\ ib3 - '+dl +I\ + Office of Research - Central Laboratories Unit m -4 Details on the Courses Offered 1. Lecturers: Professors, experts and technicians in the CLU 2. Language: English 3. Applied
$541 &I*\ ib3 - '+dl +I\ + Office of Research - Central Laboratories Unit m -4 Details on the Courses Offered 1. Lecturers: Professors, experts and technicians in the CLU 2. Language: English 3. Applied
Evaluating Laboratory Data. Tom Frick Environmental Assessment Section Bureau of Laboratories
 Evaluating Laboratory Data Tom Frick Environmental Assessment Section Bureau of Laboratories Overview of Presentation Lab operations review QA requirements MDLs/ PQLs Why do we sample? Protect physical,
Evaluating Laboratory Data Tom Frick Environmental Assessment Section Bureau of Laboratories Overview of Presentation Lab operations review QA requirements MDLs/ PQLs Why do we sample? Protect physical,
Inspection, Measuring and Test Equipment (IMTE) Calibration
 Inspection, Measuring and Test Equipment (IMTE) Calibration Purpose and Scope 2 Responsibilities 2 About IMTE 3 Master IMTE Log 4 Identification of IMTE Calibration Status 5 Handling and Storage of IMTE
Inspection, Measuring and Test Equipment (IMTE) Calibration Purpose and Scope 2 Responsibilities 2 About IMTE 3 Master IMTE Log 4 Identification of IMTE Calibration Status 5 Handling and Storage of IMTE
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid
 Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid Introduction Many metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas. In this experiment, you will use the reactions
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid Introduction Many metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas. In this experiment, you will use the reactions
Additional Lecture: TITRATION BASICS
 Additional Lecture: TITRATION BASICS 1 Definition and Applications Titration is the incremental addition of a reagent solution (called titrant) to the analyte until the reaction is complete Common applications:
Additional Lecture: TITRATION BASICS 1 Definition and Applications Titration is the incremental addition of a reagent solution (called titrant) to the analyte until the reaction is complete Common applications:
MultiQuant Software 2.0 for Targeted Protein / Peptide Quantification
 MultiQuant Software 2.0 for Targeted Protein / Peptide Quantification Gold Standard for Quantitative Data Processing Because of the sensitivity, selectivity, speed and throughput at which MRM assays can
MultiQuant Software 2.0 for Targeted Protein / Peptide Quantification Gold Standard for Quantitative Data Processing Because of the sensitivity, selectivity, speed and throughput at which MRM assays can
Calibration & Preventative Maintenance. Sally Wolfgang Manager, Quality Operations Merck & Co., Inc.
 Calibration & Preventative Maintenance Sally Wolfgang Manager, Quality Operations Merck & Co., Inc. Calibration: A comparison of two instruments or measuring devices one of which is a standard of known
Calibration & Preventative Maintenance Sally Wolfgang Manager, Quality Operations Merck & Co., Inc. Calibration: A comparison of two instruments or measuring devices one of which is a standard of known
Chapter 3. Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry. Lecture Presentation. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY
 GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY Higher Tier Paper 4: Chemistry 2H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed)
GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY Higher Tier Paper 4: Chemistry 2H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed)
Name Date Class STOICHIOMETRY. SECTION 12.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358)
 Name Date Class 1 STOICHIOMETRY SECTION 1.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358) This section explains how to calculate the amount of reactants required or product formed in a nonchemical process.
Name Date Class 1 STOICHIOMETRY SECTION 1.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358) This section explains how to calculate the amount of reactants required or product formed in a nonchemical process.
LIST OF EQUIPMENT IN CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
 LIST OF EQUIPMENT IN CHEMISTRY LABORATORY 1 Adana Science and Technology University-Bioengineering Department INSTRUMENTS: Analytical Balance (RADWAG AS220 C/2) 3 Analytical Balance (Denver Instrument)...4
LIST OF EQUIPMENT IN CHEMISTRY LABORATORY 1 Adana Science and Technology University-Bioengineering Department INSTRUMENTS: Analytical Balance (RADWAG AS220 C/2) 3 Analytical Balance (Denver Instrument)...4
Problem Solving. Empirical Formulas
 Skills Worksheet Problem Solving Empirical Formulas Suppose you analyze an unknown compound that is a white powder and find that it is composed of 36.5% sodium, 38.1% oxygen, and 25.4% sulfur. You can
Skills Worksheet Problem Solving Empirical Formulas Suppose you analyze an unknown compound that is a white powder and find that it is composed of 36.5% sodium, 38.1% oxygen, and 25.4% sulfur. You can
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES
 PAGE: 1 of 33 CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING, AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS 6.0 REAGENTS
PAGE: 1 of 33 CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING, AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS 6.0 REAGENTS
Atomic Masses. Chapter 3. Stoichiometry. Chemical Stoichiometry. Mass and Moles of a Substance. Average Atomic Mass
 Atomic Masses Chapter 3 Stoichiometry 1 atomic mass unit (amu) = 1/12 of the mass of a 12 C atom so one 12 C atom has a mass of 12 amu (exact number). From mass spectrometry: 13 C/ 12 C = 1.0836129 amu
Atomic Masses Chapter 3 Stoichiometry 1 atomic mass unit (amu) = 1/12 of the mass of a 12 C atom so one 12 C atom has a mass of 12 amu (exact number). From mass spectrometry: 13 C/ 12 C = 1.0836129 amu
Name Date Class CHEMICAL QUANTITIES. SECTION 10.1 THE MOLE: A MEASUREMENT OF MATTER (pages 287 296)
 10 CHEMICAL QUANTITIES SECTION 10.1 THE MOLE: A MEASUREMENT OF MATTER (pages 287 296) This section defines the mole and explains how the mole is used to measure matter. It also teaches you how to calculate
10 CHEMICAL QUANTITIES SECTION 10.1 THE MOLE: A MEASUREMENT OF MATTER (pages 287 296) This section defines the mole and explains how the mole is used to measure matter. It also teaches you how to calculate
Stoichiometry. What is the atomic mass for carbon? For zinc?
 Stoichiometry Atomic Mass (atomic weight) Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams We use atomic mass units an atomic mass unit (AMU) is one twelfth the mass of the catbon-12
Stoichiometry Atomic Mass (atomic weight) Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams We use atomic mass units an atomic mass unit (AMU) is one twelfth the mass of the catbon-12
CHEM 101/105 Numbers and mass / Counting and weighing Lect-03
 CHEM 101/105 Numbers and mass / Counting and weighing Lect-03 Interpretation of Elemental Chemical Symbols, Chemical Formulas, and Chemical Equations Interpretation of an element's chemical symbol depends
CHEM 101/105 Numbers and mass / Counting and weighing Lect-03 Interpretation of Elemental Chemical Symbols, Chemical Formulas, and Chemical Equations Interpretation of an element's chemical symbol depends
Chemistry Diagnostic Questions
 Chemistry Diagnostic Questions Answer these 40 multiple choice questions and then check your answers, located at the end of this document. If you correctly answered less than 25 questions, you need to
Chemistry Diagnostic Questions Answer these 40 multiple choice questions and then check your answers, located at the end of this document. If you correctly answered less than 25 questions, you need to
Technical Guidance Manual for the Implementation of the Hawai`i State Contingency Plan. Interim Final SECTION 10
 Technical Guidance Manual for the Implementation of the Hawai`i State Contingency Plan SECTION 10 DATA QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL (QA/QC) Hawai`i HEER TGM 10-1 December 31, 2008 CONTENTS Acronyms
Technical Guidance Manual for the Implementation of the Hawai`i State Contingency Plan SECTION 10 DATA QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL (QA/QC) Hawai`i HEER TGM 10-1 December 31, 2008 CONTENTS Acronyms
General Chemistry I (FC, 09-10) Lab #3: The Empirical Formula of a Compound. Introduction
 General Chemistry I (FC, 09-10) Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant, does not
General Chemistry I (FC, 09-10) Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant, does not
Application Note # LCMS-62 Walk-Up Ion Trap Mass Spectrometer System in a Multi-User Environment Using Compass OpenAccess Software
 Application Note # LCMS-62 Walk-Up Ion Trap Mass Spectrometer System in a Multi-User Environment Using Compass OpenAccess Software Abstract Presented here is a case study of a walk-up liquid chromatography
Application Note # LCMS-62 Walk-Up Ion Trap Mass Spectrometer System in a Multi-User Environment Using Compass OpenAccess Software Abstract Presented here is a case study of a walk-up liquid chromatography
Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) Code
 GUIDELINE PAPER Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) Code for Stationary Source Air Emissions Version: Final March 2016 DER2016/000490 1 Produced and published by Department of Environment Regulation
GUIDELINE PAPER Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) Code for Stationary Source Air Emissions Version: Final March 2016 DER2016/000490 1 Produced and published by Department of Environment Regulation
