Diagnosing ovarian cancer
|
|
|
- Hugh Watkins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the ovary. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 10. Diagnosis Contents Diagnosis Types of ovarian cancer Staging Grading Most women are diagnosed after going to see their GP when they notice symptoms. Your GP will ask about your symptoms and carry out an internal (vaginal) examination to check for any lumps or swellings. There is more information on this on the next page. They will arrange for you to have a blood test called a CA125 test (see page 2) and an ultrasound scan (see page 3) to look at your ovaries. If your GP suspects ovarian cancer, they will refer you to a gynaecologist (a specialist in women s health), or a gynaecology cancer team, within two weeks. Sometimes women are admitted directly to hospital if they have a symptom that is making them very unwell. At the hospital At the hospital, the gynaecologist will ask you about your general health, any previous health problems, and whether you have any history of cancer in your family. If you have not already had a CA125 blood test and ultrasound, they ll usually arrange for you to have these tests. They may also organise further tests, such as a CT scan (see page 4). You may be introduced to a clinical nurse specialist before or after you have your tests. They will give you information and support during and after treatment. Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan Page 1 of 10
2 Tests Your specialist doctor will explain the tests you need to have to diagnose ovarian cancer. Some tests may also be used to find the stage of the cancer. The stage of a cancer describes its size, position and if it has spread from where it started. Internal (vaginal) examination Your doctor will do an internal examination to check for any lumps or swelling in the ovaries or womb. It takes about five minutes and shouldn t be painful but may be uncomfortable. You can ask for a female doctor to examine you if you prefer. You lie on a couch, with your feet drawn up and knees apart. The doctor places one or two gloved fingers into your vagina and gently presses on your lower tummy with their other hand. They may put a speculum (which holds the vaginal walls apart) into the vagina to check that your cervix looks normal. CA125 blood test You ll have a blood test to check for raised levels of a protein called CA125. It s normal to have some CA125 in the blood but the level may be higher in women with ovarian cancer. The level of CA125 can also be raised by non-cancerous conditions and by other types of cancer. In early ovarian cancer, CA125 levels may be normal. Ultrasound scan An ultrasound scan uses sound waves to build up a picture of the organs inside the abdomen (tummy area) and the pelvis. A computer converts the sound waves into pictures that you can see on a screen. You have the scan in the hospital scanning department. The person doing the scan (ultrasonographer) will explain more about it and help you lie down comfortably on your back. There are two types that can be used: Pelvic ultrasound You ll be asked to drink plenty of fluids before this test so that your bladder is full. They spread a gel on to your abdomen and gently go over the area with a small hand held device, which produces the sound waves. Vaginal ultrasound They gently insert the tip of an ultrasound probe (tampon size) into your vagina. The probe produces sound waves. Although this scan may sound like it will be uncomfortable, you may find it easier than a pelvic ultrasound, as you don t need a full bladder. Page 2 of 10 Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan
3 Risk of malignancy index (RMI) Your gynaecologist may use a scoring system called the RMI to assess whether a lump or swelling on the ovary is likely to be a cancer. It takes into account: whether a woman has gone through the menopause the level of CA125 (see pages 2) in the blood the results of an ultrasound. Removing fluid from the abdomen Sometimes swelling or bloating in the tummy can be due to a build-up of fluid. This is called ascites and it can be caused by ovarian cancer or by other non-cancerous conditions. If you have ascites, your doctor may want to take a sample of this fluid to check for cancer cells. The doctor injects some local anaesthetic into the skin on your tummy (abdomen) to make it numb. They gently pass a small needle through the skin and withdraw a sample of the fluid into a syringe. The fluid is sent to the laboratory to be examined. If you have a lot of fluid in your abdomen, it can be uncomfortable so your doctor may remove it. You can have this done in the outpatient clinic or ward. The doctor puts a fine tube called a cannula through the skin. The tube attaches to a drainage bag that collects the fluid as it drains from your tummy. We can send you more information about ascites. CT (computerised tomography) scan A CT scan takes a series of x-rays, which build up a three dimensional picture of the inside of the body. The scan takes minutes and is painless. It uses a small amount of radiation, which is very unlikely to harm you and will not harm anyone you come into contact with. You may be given a drink or injection of a dye, which allows particular areas to be seen more clearly. This may make you feel hot all over for a few minutes. It s important to let your doctor know if you are allergic to iodine or have asthma, because you could have a more serious reaction to the injection. You ll probably be able to go home as soon as the scan is over. Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan Page 3 of 10
4 Image-guided biopsy This test removes a sample of the tumour (biopsy) so that it can be tested to confirm the diagnosis of ovarian cancer. Your doctor may recommend this if other test results strongly suggest you have ovarian cancer and they think you should have chemotherapy before surgery. Your doctor numbs the skin over the ovary using a local anaesthetic injection. You may also be given a sedative to help you relax. The doctor passes a needle through the skin into the tumour using a CT or ultrasound scan to guide them to the right place. They remove a small sample of tissue (a biopsy) from the tumour. This is then sent to the laboratory for checking. You need to stay in hospital for a couple of hours after a biopsy, and possibly overnight because of the risk of bleeding afterwards. Surgery to diagnose the cancer Often the only way to be certain whether a lump on the ovary is cancer is to do an operation to look at the ovaries and the surrounding area. This is usually done with an operation called a laparoscopy (or keyhole surgery see below). Sometimes an operation called a laparotomy using one larger cut to open the abdomen and look inside is done instead. Doctors can take samples of tissue during surgery to check for ovarian cancer cells. Laparoscopy This operation allows the doctor to look at the ovaries the surrounding area and other organs and take small samples of tissue (biopsies). It s done under a general anaesthetic. You can usually go home the same day, but some women may have to stay in hospital overnight. The surgeon makes 3 4 small cuts (1cm long) in the skin and muscle of the lower abdomen. They pump some carbon dioxide gas into the abdomen to lift up the tummy wall, so the organs can be seen clearly. The doctor then puts a thin fibre-optic tube with a tiny camera on the end (called a laparoscope) into the abdomen. They examine the area and take biopsies that are checked for cancer cells. Page 4 of 10 Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan
5 You should be able to get up as soon as the effects of the anaesthetic have worn off. You may have discomfort in your neck and/or shoulder afterwards but this will go away after a day or two. Walking about can help relieve it. Some women have uncomfortable wind in the tummy after surgery. Taking sips of peppermint water and moving around can help. Laparotomy If a laparoscopy isn t suitable for you, your surgeon may carry out a laparotomy. You have this under a general anaesthetic. The surgeon makes a vertical ( up and down ) cut from your bikini line to your belly button or just above it. They examine your ovaries and the organs nearby and take small samples of tissue (biopsies). Sometimes if cancer is found, the surgeon may then operate to remove the cancer. This is only done if you and your doctor have discussed it and you have agreed (consented) to it before the operation. Waiting for test results Waiting for test results can be a difficult time. It may take from a few days to a couple of weeks for the results of your tests to be ready. You may find it helpful to talk with your partner, your family or a close friend. Your specialist nurse or organisations, such as Ovacome (visit ovacome.org.uk or call ), can also provide support. You can also talk things over with one of our cancer support specialists on As soon as I was diagnosed I was able to say I have ovarian cancer. I think you ve got to be able to admit it to yourself and not be afraid of it because it s just part of life. I think because I was able to talk about it I didn t feel shame or embarrassment or anything. It s just part of the journey. Clara Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan Page 5 of 10
6 Types of ovarian cancer Most ovarian cancers start in the cells that cover the surface of the ovary (the epithelium) and are called epithelial ovarian cancers. There are several types of epithelial ovarian cancer. They include: serous the most common type mucinous endometrioid clear cell undifferentiated or unclassifiable. It s now thought that high-grade serous ovarian cancer may start in the fallopian tube (page 7) and then spread to the ovary. But all epithelial ovarian cancers and cancers of the fallopian tube are treated in a similar way. Borderline tumours Borderline tumours are made up of abnormal epithelial cells, but they aren t true cancers. They can sometimes turn into cancer, but most don t. Borderline tumours usually grow slowly and are unlikely to spread. They are staged in the same way as ovarian cancers and are always stage 1. Non-epithelial ovarian cancers There are non-epithelial cancers that can affect the ovaries. We have separate information about germ cell ovarian tumours of the ovary. These non-epithelial tumours start in the ovarian cells that produce eggs. They usually affect young women. Page 6 of 10 Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan
7 Staging The stage of a cancer describes its size, position and if it has spread from where it started. Knowing the stage helps your doctors advise you on the best treatment for you. Your doctor will not usually be able tell the exact stage of the cancer until after it has been removed with surgery. If an operation isn t appropriate, they use the results of your tests to decide on the stage of the cancer. Doctors usually stage ovarian cancer using the FIGO staging system. It divides ovarian cancers into four number stages that are also subdivided. It may help to look at the diagrams below and on page 8 when reading this staging section. Organs close to the ovaries Kidney Ureter Lymph node Fallopian tube Omentum Lymphatic vessel Rectum Ovary Bladder Urethra Womb Vagina Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan Page 7 of 10
8 Side view of the body Liver Peritoneum Stomach Omentum Bowel Spine Peritoneal space Womb Ovary Bladder Rectum (back passage) Stage 1 This is early ovarian cancer. Stage 1a The cancer is only in one ovary. Stage 1b The cancer is in both ovaries. Stage 1c The cancer is in one or both ovaries with any of the following: The tissue surrounding the ovary (capsule) has broken during surgery, which could have let cancer cells leak into the abdomen or pelvis. There are cancer cells on the surface of one or both ovaries or the tissue surrounding the ovary (capsule) has broken before surgery, which could have let cancer cells leak into the abdomen or pelvis. There are cancer cells in the fluid taken from the abdomen during surgery. Page 8 of 10 Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan
9 Stage 2 The cancer has spread outside the ovary or ovaries to other areas inside the pelvis. Stage 2a The cancer has spread to the womb and/or fallopian tubes. Stage 2b The cancer has spread to other structures within the pelvis, such as the bowel or bladder. Stage 3 The cancer may have spread outside the pelvis to the peritoneum and/or to the lymph nodes at the back of the tummy (retroperitoneal lymph nodes). Stage 3a1 The cancer has spread but only to the retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Stage 3a2 The cancer has spread outside the pelvis but doctors can only see this under a microscope. The cancer may have spread to the retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Stage 3b The cancer has spread outside the pelvis but the tumour is less than 2cm in size. It may have spread to the retroperitoneal lymph nodes. There may be cancer cells on the surface of the liver and spleen but not inside these organs. Stage 3c The same as stage 3b but the tumour is 2cm or larger. Stage 4 The cancer has spread to organs outside the abdomen. Stage 4a The cancer has caused a build up of fluid in the lining of the lungs (called the pleura). This is called a pleural effusion. Stage 4b The cancer has spread to the inside of the liver or spleen, to lymph nodes in the groin or outside the abdomen and/or to other organs, such as the lungs. Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan Page 9 of 10
10 Grading Grading is about how the cancer cells look under the microscope compared with normal cells. Knowing the grade helps your doctor decide whether you need further treatment after surgery. This is how ovarian cancers are graded: Borderline tumours are made up of abnormal cells rather than cancer cells. Low-grade or well-differentiated (grade 1) The cancer cells look similar to normal cells and usually grow slowly and are less likely to spread. Moderate- or intermediate-grade (grade 2) The cancer cells look more abnormal and are slightly faster-growing. High-grade or poorly-differentiated (grade 3) The cancer cells look very different from normal cells and may grow more quickly. More information and support More than one in three of us will get cancer. For most of us it will be the toughest fight we ever face. And the feelings of isolation and loneliness that so many people experience make it even harder. But you don t have to go through it alone. The Macmillan team is with you every step of the way. To order a copy of Understanding cancer of the ovary, or any other cancer information, visit be.macmillan.org.uk or call We make every effort to ensure that the information we provide is accurate and up to date but it should not be relied upon as a substitute for specialist professional advice tailored to your situation. So far as is permitted by law, Macmillan does not accept liability in relation to the use of any information contained in this publication, or thirdparty information or websites included or referred to in it. Macmillan Cancer Support Registered charity in England and Wales (261017), Scotland (SC039907) and the Isle of Man (604). Registered office 89 Albert Embankment, London, SE1 7UQ REVISED IN MAY 2015 Planned review in 2017 Page 10 of 10 Questions about cancer? Ask Macmillan
Contents. Overview. Removing the womb (hysterectomy) Overview
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
Surgery for oesophageal cancer
 Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
Surgery and cancer of the pancreas
 Surgery and cancer of the pancreas This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the pancreas. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 8. Introduction
Surgery and cancer of the pancreas This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the pancreas. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 8. Introduction
More than 2,500 people are diagnosed with mesothelioma in the UK each year.
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. Contents Introduction Pleural mesothelioma Peritoneal
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. Contents Introduction Pleural mesothelioma Peritoneal
Surgery for breast cancer in men
 Surgery for breast cancer in men This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer in men. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
Surgery for breast cancer in men This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer in men. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
What is DCIS? Contents. The breasts
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding ductal carinoma in situ (DCIS). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 6. Contents The breasts What is
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding ductal carinoma in situ (DCIS). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 6. Contents The breasts What is
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Controlling symptoms of mesothelioma
 Controlling symptoms of mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
Controlling symptoms of mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
The main surgical options for treating early stage cervical cancer are:
 INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT
 OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre National Cancer Plan May 2015 Contents About this booklet 1 The Ovaries
OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre National Cancer Plan May 2015 Contents About this booklet 1 The Ovaries
About the kidneys and kidney cancer
 About the kidneys and kidney cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding kidney cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. The kidneys
About the kidneys and kidney cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding kidney cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. The kidneys
After pelvic radiotherapy
 After pelvic radiotherapy in women 1 After pelvic radiotherapy in women This information is from the booklet Pelvic radiotherapy in women managing side effects during treatment. You may find the full booklet
After pelvic radiotherapy in women 1 After pelvic radiotherapy in women This information is from the booklet Pelvic radiotherapy in women managing side effects during treatment. You may find the full booklet
Radiotherapy for vulval cancer
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the vulva. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents External radiotherapy Internal
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the vulva. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents External radiotherapy Internal
Chemotherapy for head and neck cancers
 Chemotherapy for head and neck cancers This information is from the booklet Understanding head and neck cancers. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
Chemotherapy for head and neck cancers This information is from the booklet Understanding head and neck cancers. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide
 NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
Ovarian Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Ovarian cancer. Patient information from the BMJ Group. What is ovarian cancer? What are the symptoms?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
Hysterectomy for womb cancer
 Gynaecology Oncology Service Hysterectomy for womb cancer April 2014 Great Staff Great Care Great Future INTRODUCTION This leaflet has been produced to provide you with general information about your operation.
Gynaecology Oncology Service Hysterectomy for womb cancer April 2014 Great Staff Great Care Great Future INTRODUCTION This leaflet has been produced to provide you with general information about your operation.
How to Improve Bladder After Bowler Cancer
 Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide
 Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Types of surgery for kidney cancer
 Useful information for cancer patients Contents This information is about the different operations that you may have for kidney cancer. Surgery can be used to treat almost any stage of kidney cancer. There
Useful information for cancer patients Contents This information is about the different operations that you may have for kidney cancer. Surgery can be used to treat almost any stage of kidney cancer. There
Mesothelioma and Asbestos
 CANCER INFORMATION FACTSHEET Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
CANCER INFORMATION FACTSHEET Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Cervical Cancer. Cervical smear test. The cervix. Dysplasia. Cervical cancer. The female reproductive system
 INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
How treatment is planned Giving your consent The benefits and disadvantages of treatment Second opinion
 Treatment overview for lung cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. Contents How
Treatment overview for lung cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. Contents How
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma
 Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Total laparoscopic hysterectomy bilateral salpingooophorectomy
 Total laparoscopic hysterectomy bilateral salpingooophorectomy We dedicate this book to all of the women who have entrusted their care to us. By allowing us to take part in their surgery and after care,
Total laparoscopic hysterectomy bilateral salpingooophorectomy We dedicate this book to all of the women who have entrusted their care to us. By allowing us to take part in their surgery and after care,
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Radiotherapy for breast cancer
 Radiotherapy for breast cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy for breast cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents Radiotherapy
Vesico-Vaginal Fistula
 Saint Mary s Hospital The Warrell Unit Vesico-Vaginal Fistula Information For Patients Contents Page What is a vesico-vaginal fistula? 3 How does a fistula develop? 3 What tests will I need? 3 How can
Saint Mary s Hospital The Warrell Unit Vesico-Vaginal Fistula Information For Patients Contents Page What is a vesico-vaginal fistula? 3 How does a fistula develop? 3 What tests will I need? 3 How can
About lung cancer. Contents. The lungs
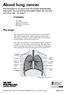 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
Chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer
 Chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 3. Contents
Chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 3. Contents
Treatment for pleural mesothelioma
 Treatment for pleural mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents Treatment
Treatment for pleural mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents Treatment
How To Understand How Cancer Works
 Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Surgery for rectal cancer
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding rectal cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 12. Contents Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) Before
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding rectal cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 12. Contents Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) Before
Mesothelioma and Asbestos
 Cancer information factsheet Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Cancer information factsheet Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Treatment of colon cancer
 Treatment of colon cancer This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding colon cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents How treatment
Treatment of colon cancer This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding colon cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents How treatment
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet
 U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet 1. Invitation You are being invited to take part in a research study. Before you decide it is important for you
U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet 1. Invitation You are being invited to take part in a research study. Before you decide it is important for you
A practical guide to understanding cancer. Understanding. cervical. CAnCER
 A practical guide to understanding cancer Understanding cervical CAnCER Contents Contents About Understanding cervical cancer 4 What is cancer? 5 The lymphatic system 7 The cervix 9 How cervical cancer
A practical guide to understanding cancer Understanding cervical CAnCER Contents Contents About Understanding cervical cancer 4 What is cancer? 5 The lymphatic system 7 The cervix 9 How cervical cancer
Keyhole (Laparoscopic) Surgery
 Patient Information leaflet Keyhole (Laparoscopic) Surgery Produced by: Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology December 2002 Reviewed April 2010 1 What is keyhole (laparoscopic) surgery? Laparoscopic surgery
Patient Information leaflet Keyhole (Laparoscopic) Surgery Produced by: Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology December 2002 Reviewed April 2010 1 What is keyhole (laparoscopic) surgery? Laparoscopic surgery
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
How To Plan A Staging Investigation For Cancer Of The Oesophagus Or Stomach
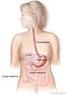 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Upper Gastrointestinal Centre Staging of cancers of the oesophagus and stomach Information for patients Introduction This leaflet gives you information about
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Upper Gastrointestinal Centre Staging of cancers of the oesophagus and stomach Information for patients Introduction This leaflet gives you information about
Questions about your pain medicines
 Questions about your pain medicines This information is an extract from the booklet Controlling cancer pain. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 6. Contents Common
Questions about your pain medicines This information is an extract from the booklet Controlling cancer pain. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 6. Contents Common
The ovaries are part of a woman s reproductive system. There are two ovaries, the size and shape of almonds, one on either side of the womb.
 Surgery for Suspicious Ovarian Cysts Patient Information sheet The Ovaries The ovaries are part of a woman s reproductive system. There are two ovaries, the size and shape of almonds, one on either side
Surgery for Suspicious Ovarian Cysts Patient Information sheet The Ovaries The ovaries are part of a woman s reproductive system. There are two ovaries, the size and shape of almonds, one on either side
Uterine Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
NHS Cervical Screening Having a colposcopy
 NHS Cervical Screening Having a colposcopy What is a colposcopy? 1 Why do I need a colposcopy? 1 What does a colposcopy involve? 2 Colposcopy results 4 Treatment to remove abnormal cells in the cervix
NHS Cervical Screening Having a colposcopy What is a colposcopy? 1 Why do I need a colposcopy? 1 What does a colposcopy involve? 2 Colposcopy results 4 Treatment to remove abnormal cells in the cervix
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Chemotherapy for lung cancer
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 8. Contents Chemoradiation Small cell lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 8. Contents Chemoradiation Small cell lung cancer
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant
 Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder)
 Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
 Any further questions? Please contact the matron for Women s Health on 020 7288 5161 (answerphone) Monday - Thursday 9am - 5pm. For more information: Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Recovering
Any further questions? Please contact the matron for Women s Health on 020 7288 5161 (answerphone) Monday - Thursday 9am - 5pm. For more information: Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Recovering
Name of procedure: Laparoscopic (key-hole) ovarian surgery. Left/ Right unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy* (removal of one fallopian tube and ovary)
 For staff use only: Patient Details: Surname: First names: Date of birth: Hospital no: Female: (Use hospital identification label) Gynaecology Patient agreement to treatment Name of procedure: Laparoscopic
For staff use only: Patient Details: Surname: First names: Date of birth: Hospital no: Female: (Use hospital identification label) Gynaecology Patient agreement to treatment Name of procedure: Laparoscopic
Radical Hysterectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection
 Radical Hysterectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's
Radical Hysterectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD)
 Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding donor stem cell (allogeneic) transplants. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding donor stem cell (allogeneic) transplants. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients What is an image-guided abdominal drain insertion? A drain is a thin plastic tube which is inserted
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients What is an image-guided abdominal drain insertion? A drain is a thin plastic tube which is inserted
Cervical Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Cervical Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Cervical Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Cervical Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Cervical Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
CT scan. Useful information. Contents. This information is about CT scans. There are sections on
 CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
Lung cancer. Lung cancer: English
 Lung cancer: English Lung cancer This fact sheet is about how lung cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side effects of
Lung cancer: English Lung cancer This fact sheet is about how lung cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side effects of
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
Finding travel insurance cover
 This information is an extract from the booklet Getting travel insurance. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 11. Contents Finding travel insurance Contacting insurance
This information is an extract from the booklet Getting travel insurance. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 11. Contents Finding travel insurance Contacting insurance
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Breast reconstruction using an implant after risk-reducing surgery
 Breast reconstruction using an implant after risk-reducing surgery This information is from the booklet Understanding riskreducing breast surgery. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you
Breast reconstruction using an implant after risk-reducing surgery This information is from the booklet Understanding riskreducing breast surgery. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you
Chemotherapy for pancreatic
 Chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer 1 Chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer This information is from the booklet Understanding pancreatic cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free
Chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer 1 Chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer This information is from the booklet Understanding pancreatic cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free
Large bowel cancer. Large bowel cancer: English
 Large bowel cancer: English Large bowel cancer This fact sheet is about how cancer of the large bowel is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy,
Large bowel cancer: English Large bowel cancer This fact sheet is about how cancer of the large bowel is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy,
Massage therapy and energy-based therapies
 Massage therapy and energy-based therapies This information is an extract from the booklet Complementary therapies and cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page
Massage therapy and energy-based therapies This information is an extract from the booklet Complementary therapies and cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed In this fact sheet: How is prostate cancer diagnosed? What tests are done by my GP? What tests will I have at the hospital? What do my biopsy results mean? Will I need
How prostate cancer is diagnosed In this fact sheet: How is prostate cancer diagnosed? What tests are done by my GP? What tests will I have at the hospital? What do my biopsy results mean? Will I need
Radioactive iodine treatment for thyroid cancer
 Radioactive iodine treatment for thyroid cancer This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding thyroid cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page
Radioactive iodine treatment for thyroid cancer This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding thyroid cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page
Fact sheet 10. Borderline ovarian tumours. The difficult cases. What is borderline ovarian cancer (BOC)?
 For this reason, some doctors prefer the term borderline ovarian tumour rather than borderline ovarian cancer. Fact sheet 10 Borderline ovarian tumours We, Ovacome, are a support network for people affected
For this reason, some doctors prefer the term borderline ovarian tumour rather than borderline ovarian cancer. Fact sheet 10 Borderline ovarian tumours We, Ovacome, are a support network for people affected
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Breathing techniques to help breathlessness 1
 Breathing techniques to help breathlessness 1 Breathing techniques to help breathlessness This information is from the booklet Managing breathlessness. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send
Breathing techniques to help breathlessness 1 Breathing techniques to help breathlessness This information is from the booklet Managing breathlessness. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
How insurance works How cancer can affect buying insurance Unfair discrimination
 This information is an extract from the booklet Insurance, which is part of the financial guidance series. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. Contents What is
This information is an extract from the booklet Insurance, which is part of the financial guidance series. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. Contents What is
How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
 Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
Radiotherapy: English. Radiotherapy
 Radiotherapy: English Radiotherapy This fact sheet is about radiotherapy. Radiotherapy is used to treat some cancers. It can also be used to control the symptoms of cancer. Many people with cancer will
Radiotherapy: English Radiotherapy This fact sheet is about radiotherapy. Radiotherapy is used to treat some cancers. It can also be used to control the symptoms of cancer. Many people with cancer will
Effect of breast cancer treatment
 Effect of breast cancer treatment on the bones 1 Effect of breast cancer treatment on the bones This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of breast cancer treatment. You may find the
Effect of breast cancer treatment on the bones 1 Effect of breast cancer treatment on the bones This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of breast cancer treatment. You may find the
A practical guide to understanding cancer. signs and symptoms. of cancer. what to be aware of
 A practical guide to understanding cancer signs and symptoms of cancer what to be aware of More than a quarter of a million people are diagnosed with cancer in the UK each year. The earlier a cancer is
A practical guide to understanding cancer signs and symptoms of cancer what to be aware of More than a quarter of a million people are diagnosed with cancer in the UK each year. The earlier a cancer is
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Understanding your pathology report
 Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
Information for patients having Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH)
 1 TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC HYSTERECTOMY LEAFLET (For patients, relatives and hospital personnel) Information for patients having Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH) You have been given this information sheet
1 TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC HYSTERECTOMY LEAFLET (For patients, relatives and hospital personnel) Information for patients having Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH) You have been given this information sheet
Are you worried about prostate cancer? 1
 Are you worried about prostate cancer? 1 Are you worried about prostate cancer? This information is from the leaflet Are you worried about prostate cancer? You may find the full leaflet helpful. We can
Are you worried about prostate cancer? 1 Are you worried about prostate cancer? This information is from the leaflet Are you worried about prostate cancer? You may find the full leaflet helpful. We can
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (T.U.R.B.T)
 Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (T.U.R.B.T) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to help you understand the surgery you are about to undergo. It will give you information
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (T.U.R.B.T) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to help you understand the surgery you are about to undergo. It will give you information
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Leukaemia and lymphoma what s the difference?
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk Leukaemia and lymphoma what s the difference? This is a difficult question to answer simply but it is one that is often
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk Leukaemia and lymphoma what s the difference? This is a difficult question to answer simply but it is one that is often
OUTPATIENT HYSTEROSCOPY SERVICES JASMINE SUITE
 OUTPATIENT HYSTEROSCOPY SERVICES JASMINE SUITE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 This information is for patients having a hysteroscopy (diagnostic or operative). It explains what
OUTPATIENT HYSTEROSCOPY SERVICES JASMINE SUITE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 This information is for patients having a hysteroscopy (diagnostic or operative). It explains what
Cervical Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Cervical Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Cervical Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Cervical Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Cervical Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Ovarian cancer. A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment
 Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
A practical guide to understanding cancer
 A practical guide to understanding cancer About this booklet 1 About this booklet This booklet is about a type of cancer called mesothelioma. It is about the diagnosis and treatment of the two main types
A practical guide to understanding cancer About this booklet 1 About this booklet This booklet is about a type of cancer called mesothelioma. It is about the diagnosis and treatment of the two main types
