Diagram of a Typical Plant
|
|
|
- Erica Higgins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
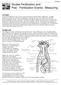
1 Grade: 9 to 12 Length: variable Subjects: life science Topics: weed identification Objectives Exercises in this lesson help students achieve the following objectives: Understand the basic parts of a plant Understand how the basic parts of a plant work together Follow the growth cycle of a plant from the seed stage to the production of a new seed Introduction Like most plants, weeds have four major parts: roots, stems, leaves, and flowers or seeds. Individual parts comprise each of the four major parts, and each part has a specific function. Students will learn about the parts of a plant and stages of plant development by planting bean seeds and observing the plants as they grow through all stages of development, until the plant produces seeds. Before teaching this lesson, read the entire lesson and make sure all materials are available. Diagram of a Typical Plant Invasives: Plants on the Move ~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 137
2 Background Roots Roots serve the following three major functions: Anchor the plant in the soil Absorb water and nutrients Store food Roots have a number of different components that help achieve these functions. Tiny root hairs absorb water and nutrients. Each root hair has a root cap to protect the root hair as it pushes through the soil. Behind the root cap is a zone of cell division. Behind the zone of cell division is the zone of cell elongation, where roots lengthen. Root growth takes place in these two zones. The meristematic zone includes the root cap and the zone of cell division. The xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the stem. Xylem tissue consists mainly of hollow tubes. The phloem carries food from the leaves to the roots. Cambium tissue is the living part of a stem. Cell division takes place in the cambium. The arrangement of the xylem and phloem and the location of the cambium are different in monocotyledons and dicotyledons. Cross-section of a monocot stem Cross-section of a dicot stem Cross-section of a stem Stems Stems serve the following three major functions: Transport water and minerals from the roots to the stem and food from the leaves to the roots Hold the plant erect so the leaves can reach the sunlight Store food Diagram of a Root Leaves Leaves serve the following three major functions: Produce food for the plant Store food Take in and let out various gases A plant produces food through a process called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, a plant uses sunlight to produce glucose or food. Specifically, a plant uses sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose. A plant produces oxygen as a waste product. Plants contain a chemical called chlorophyll, which makes photosynthesis possible. In most plants, chlorophyll is green in color, and tiny structures called chloroplasts contain the chlorophyll. 138 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Invasives: Plants on the Move
3 A plant must have energy to live. The plant obtains its energy by breaking down glucose through a process called respiration. Respiration is the reverse of photosynthesis. (See the illustration Respiration and Photosynthesis on page 122.) Plants continuously transport water to the leaves from the roots. Leaves release water vapor and other gases through openings called stomata. This process is called transpiration. Through transpiration, water comes into the plant, and transpiration keeps the plant cool during hot months. To carry out these complex functions, leaves have developed an amazing structure. coat disintegrates, a root hair emerges and begins to absorb water and nutrients, and seed leaves emerge and grow toward the sunlight. radicle (develops into a root) cotyledon plumule (develops into the stem and leaves) seed coat Bean Seed Cross-section Leaf Cross-section Flowers and seeds The major function of flowers is to help in sexual reproduction. Some parts of a flower, such as the petals, nectar, and perfume, attract bees and other insects. The male part of the flower is the stamen, which is comprised of the filament and anther. The anther holds pollen. The female part is the pistil, which is comprised of the stigma, style, and ovary. When insects land on flowers, they transfer pollen from the anther to the stigma. The pollen moves down the style and fertilizes the egg. Once fertilized, the egg becomes a seed, and the flower dies and drops off. The seed contains a living embryo. A seed coat encloses the embryo and protects the embryo until it is ready to germinate. The seed also contains seed leaves (cotyledons) and stored food (endosperm). The seed remains dormant until conditions are ideal for growth. Under ideal conditions, the seed Characteristics of plants Each weed has specific characteristics that help botanists identify the weed. Some characteristics are difficult to identify; others are obvious. The following characteristics are some of the more obvious characteristics botanists use to identify weeds: Flower color Flower arrangement on stem Vein arrangement in leaves Blade type Leaf arrangement on stem When identifying a weed, the color of the flower is one of the first characteristics botanists notice. However, many weeds have the same color of flower. Flower arrangement on the stem is the next characteristic botanists look for. Other identifying characteristics that botanists use include leaf shape, leaf margins, shape at the base of the blade, and shape of the blade tips. Preparation Materials bush bean seeds Have available 10 seeds for every two students. paper towels plastic sandwich bags Invasives: Plants on the Move ~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 139
4 Leaf Arrangements Flower Arrangements Leaf Venation Leaf Types 140 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Invasives: Plants on the Move
5 1 potting soil with time-release fertilizer 4-inch pots Have available at least two pots for every two students. greenhouse, window, or other growing area dissecting microscope or hand-held lens copies of Life cycle of a Bean Plant, Plants and Their Parts, and From Seed to Shining Seed Weed Journal Entries worksheets Have available one copy for each student student Weed Journals Assemble all the materials listed above. Students will use these items during the Activity. Give each student a copy of each worksheet. Activity 1 Divide students into teams of two students per team. Discuss the Plants and Their Parts and Life cycle of a Bean Plant worksheets. 2 To observe the emergence of roots and determine seed viability: A. Instruct each team to place 10 bean seeds on a wet paper towel, and place the paper towel in a sandwich bag. B. Seal the bag and place it in a warm location. 3 C. As roots emerge, ask students to record their observations on the From Seed to Shining Seed Weed Journal Entries worksheet. D. After seeds have germinated, ask students to calculate the percentage of viable seeds. E. Discuss the germination process to ensure students understand the process. Have students carefully transplant at least two of the germinated seeds into 4-inch pots containing potting soil with slow-release fertilizer. 4 Instruct students to record emergence of the cotyledons and all stages of plant growth and development. 5 6 Remove one of the flowers and study it under a dissecting microscope. During the flowering stage, shake flowers to ensure cross-pollination. Conclusion and Evaluation Conclude the lesson when the plants produce beans and students have harvested the seeds. Evaluate students on their ability to identify weeds using the physical properties outlined earlier in this lesson. Or use the Weedy Crossword Puzzle as a quiz. Invasives: Plants on the Move ~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 141
6 Independent Practice and Related Activities Most commercial bean seeds are hybrids. Seeds from hybrids are not as viable as seeds from the parent plants, and hybrid plants are not as hardy as the parent plants. To demonstrate these characteristics, harvest the bean seeds, dry the seeds, and plant them. Calculate the percentage of viable seeds. Vocabulary alternate, anthers, blade, cambium, chlorophyll, chloroplasts, corymb, dicotyledon, dormancy, embryo, epidermal cells, glucose, guard cells, internode, meristem, monocotyledon, node, opposite, ovary, palmate compound, parallel, phloem, photosynthesis, pinnate, pinnate compound, pistil, plumule, pollen, pollination, raceme, radicle, respiration, root cap, root hairs, roots, rosulate, seed, sexual reproduction, simple, spike, stamen, stems, stigma, stoma, style, transpiration, umbel, venation, whorled, xylem, zone of cell division, zone of elongation Resources Peterson, Roger Tory and Margaret McKenny. A Field Guide to Wildflowers of Northeastern and North-central North America. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, National Science Education Standards As a result of their activities in grades 9 to 12, students should develop an understanding of and abilities in the following areas: Science as Inquiry Content Standard A: scientific inquiry, understandings about scientific inquiry Life Science - Content Standard C: matter, energy, and organization in living systems; behavior of organisms Solution to Weedy Crossword Across 1. Phloem 3. Spike 5. Embryo 7. Stoma 9. Respiration 11. Dicot 14. Photosynthesis 16. Corymb 17. Stem 18. Umbel 21. Germinate 22. Transpiration 23. Monocot 25. Raceme 26. Stigma 30. Pinnate 31. Cotyledon 33. Whorl 34. Alternate 35. Leaves 36. Palmate 37. Nodes Down 1. Petals 2. Meristematic 4. Stamen 5. Endosperm 6. Root cap 8. Anther 10. Roots 12. Xylem 13. Filament 15. Solitary 17. Seed 19. Elongation 20. Internode 24. Opposite 27. Stomata 28. Simple 29. Style 32. Ovary 142 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Invasives: Plants on the Move
7 Life Cycle of a Bean Plant Germination Germination occurs underground when sufficient water, oxygen, and heat are present. The seed coat swells and then starts to disintegrate. A tiny root (radicle) appears, followed by a tiny stem (plumule). Growth Approximately 5 to 7 days after planting, the first leaves two oblong seed leaves (cotyledons) emerge from the soil. As the plant continues to grow, true leaves begin to appear. radicle (develops into root) cotyledon plumule (develops into the stem and leaves) seed coat Reproduction After about 3 weeks, the first flowers appear. These flowers are white and solitary. If conditions are suitable for pollination, the flowers fade after 3 to 4 days. In the center of the flower, a small bean emerges. As the bean grows, the flower petals fall off. The bean pod continues to grow until it reaches a length of 3 to 4 inches. Seeds Once the pod is fully grown, it will contain 4 to 7 new bean seeds. Plant these seeds, and begin the whole process again. Invasives: Plants on the Move ~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 143
8 Plants and Their Parts Diagram of a root Diagram of a typical plant Cross-section of a monocot stem Cross-section of a dicot stem Leaf cross-section Cross-section of a stem 144 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Invasives: Plants on the Move
9 Weedy Definitions page 1 of 2 alternate leaf arrangement in which each leaf is attached at a different level on the stem anther the head at the top of the filament where pollen forms blade the flat part of a leaf; to physically scrape an area with a blade to remove weeds cambium tissue that forms the living part the stem; where cell division takes place in the stem chlorophyll a green-colored chemical that converts the sun s energy to food through the process of photosynthesis chloroplasts sacs in plant cells that contain chlorophyll corymb a flat flower head consisting of flowers whose stalks grow from different points on the flower stem but reach approximately the same height dicotyledon a flowering plant that produces two seed leaves when it germinates and whose subsequent leaves have a network of veins dormant in an inactive state, when growth and development slow or cease, in order to survive adverse environmental conditions embryo a plant in its earliest stages of development; in seed-bearing plants, the embryo is contained within the seed epidermal cells the outermost layer of cells glucose a sugar produced by plants through photosynthesis guard cells cells that surround the stoma internode the distance between nodes meristematic zone composed of the root cap and the zone of cell division monocotyledon a flowering plant that has a single leaf in the seed and floral parts in multiples of three node composed of the leaf axil and bud opposite leaf arrangement in which two leaves are attached at one level but on different sides of the stem ovary where seeds develop at the base of a flower palmately compound leaflets attached at the end of a stalk, spreading like fingers on a hand parallel veining veins that run alongside each other and never intersect phloem a tube that carries food from the leaves to the roots photosynthesis process through which plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make glucose and oxygen pinnately compound leaflets arranged around a central stalk pistil the female reproductive part of a flower, composed of the ovary, style, and stigma plumule the rudimentary primary shoot of a plant embryo pollination the process of transferring pollen from the anther to the stigma to fertilize a plant raceme a flower cluster in which the flowers are borne on short stalks along a long main stem radicle the part of a plant embryo that forms the root of the young plant respiration the process through which plants break down glucose to make energy; the reverse of photosynthesis root cap protects the root hair Invasives: Plants on the Move ~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 145
10 Weedy Definitions page 2 of 2 root hairs absorb water an nutrients roots function to anchor a plant, absorb water and nutrients, and store food rosulate leaf arrangement in which leaves are attached around the base of the stem seed the body produced by reproduction in most plants that contains the embryo and produces a new individual sexual reproduction natural process by which some plants and animals produce offspring as a result of fertilization of the egg from another plant or animal simple a leaf that is not divided, either totally or partially, into separate segments spike a long cluster of flowers attached directly to a stem, with the newest flowers at the tip stamen the male reproductive organ of a flower, composed of the anther and the filament that holds the anther stem the main trunk of a plant stigma the sticky top of the style that collects pollen stomata ventilation holes in a leaf that take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen style stem-like extension of the ovary through which a pollen tube grows down into the ovary carrying the pollen necessary for fertilization transpiration the process of evaporation from a plant s leaves umbel a flower cluster that has a number of branches all attached at one point venation the pattern of veins whorl a leaf arrangement in which three or more leaves are attached in a ring at one level xylem a tube which transports water and minerals zone of cell division the place in the root where cells divide zone of cell elongation the place in the root where cells become larger Respiration and photosynthesis 146 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Invasives: Plants on the Move
11 From Seed to Shining Seed Weed Journal Entries Event Date Observations Number of seeds planted First radicle appears First seed leaves appear Last seeds germinate number of seeds germinated % viability Seedlings transplanted First flowers appear First bean pods appear Bean pods appear Bean pods appear Bean pods appear Bean pods appear Bean seeds harvested Invasives: Plants on the Move ~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 147
12 Weedy Crossword Puzzle Across 1. Carries food from the leaves to the roots 3. Long cluster of flowers attached directly to a stem, with the newest flowers at the tip 5. Plant in its earliest stages of development 7. Leaves release gases through this opening 9. Process through which plants break down glucose to make energy 11. Flowering plant that produces two seed leaves when it germinates 14. Process through which plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make glucose and oxygen 16. Flat flower head consisting of flowers whose stalks grow from different points on the flower stem but reach about the same height 17. Transports minerals and water from the roots to the stem and food from the leaves to the roots 18. Flower cluster with branches all attached at one point 21. To grow from a seed into a new plant 22. Process through which plants bring water to the leaves from the roots and release gases from the leaves 23. Flowering plant that has a single leaf in the seed 25. Flower cluster in which flowers are on short stalks along a long main stem 26. Sticky top of the style that collects pollen 30. Arranged along a central stalk or stem 31. Seed leaves within a seed 33. Leaf arrangement in which three or more leaves are attached at different levels on the stem 34. Usual leaf arrangement where leaves are attached at different levels on the stem 35. Produce food for the plant and take in or let out gases 36. Leaves or veins which spread like fingers on a hand 37. Consist of leaf axils and buds Down 1. Showy colored parts that form the outer part of a flower 2. This zone is made of the root cap and the zone of cell division 4. Composed of an anther and filament 5. Stored food within a seed 6. Protects root hairs as they push through soil 8. Head where pollen forms at the top of the filament 10. Anchor plants in soil and absorb water and nutrients 12. Part of the stem that transports water and minerals 13. Stalk-like part of the stamen 15. Flower that grows singly rather than as a cluster 17. Body produced by reproduction in most plants that contains the embryo and produces a new individual 19. In this zone, cells become larger 20. Distance between nodes 24. Leaf arrangement where leaves are attached at one level on different sides of the stem 27. Plural of 7 Across 28. Leaf that is not divided, either totally or partially, into separate segments 29. Stem-like extension of the ovary through which a pollen tube grows down into the ovary carrying the pollen necessary for fertilization 32. Seeds develop here 148 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Weed Identification ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Invasives: Plants on the Move
Plant Parts. Background Information
 Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions. Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9. Chapter 6 Plant structure and function
 1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice
 10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS
 PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
8. Study the cladogram underline the derived characteristics and circle the organisms that developed from them.
 Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
What's in a Flower. Ages: 8 to 12. Contributor: Susan Jaquette, Cornell Plantations volunteer
 Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Germination is the process in which a
 The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions Sepals Anther Stamens (male) Filament Stigma Pistil Style (female) Ovary Petals sepals petals stamens pistil
 Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development. Chapter 35
 Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones
 Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit
 Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Biology 213 Angiosperms. Introduction
 Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN VASCULAR AND NON- VASCULAR PLANTS?
 WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN VASCULAR AND NON- VASCULAR PLANTS? Let s take a closer look. What makes them different on the outside and inside? Learning Intentions To understand how vascular plant cells
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN VASCULAR AND NON- VASCULAR PLANTS? Let s take a closer look. What makes them different on the outside and inside? Learning Intentions To understand how vascular plant cells
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview Objectives bold Part I Floral Anatomy . calyx sepals corolla, petals, stamens, filament
 Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function. I. Background
 Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Parts of a Flower and Pollination
 Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Leaf Structure and Transpiration
 10 LESSON Leaf Structure and Transpiration INTRODUCTION Have you wondered what happens to all that water that disappears from the reservoir of your growing system? Although some might have evaporated from
10 LESSON Leaf Structure and Transpiration INTRODUCTION Have you wondered what happens to all that water that disappears from the reservoir of your growing system? Although some might have evaporated from
Laboratory. Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs
 Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to
 Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types
 Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Plant Reproduction. 2. Evolutionarily, floral parts are modified A. stems B. leaves C. roots D. stolons E. suberins
 Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Look at the back of this paper
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Look at the back of this paper
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents?
 2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
The Seed Challenge How Many Seeds Can You Get from a Single Seed?
 The Seed Challenge How Many Seeds Can You Get from a Single Seed? Grade Level: K-4 Catalog Number: 15-8973 Time to pollinate the flowers Time to harvest the seeds True leaves grow Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 Day
The Seed Challenge How Many Seeds Can You Get from a Single Seed? Grade Level: K-4 Catalog Number: 15-8973 Time to pollinate the flowers Time to harvest the seeds True leaves grow Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 Day
PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY
 PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY David W. Lockwood Department of Plant Sciences & Landscape Systems University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996 D. C. Coston Agricultural Experiment Station Oklahoma State University
PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY David W. Lockwood Department of Plant Sciences & Landscape Systems University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996 D. C. Coston Agricultural Experiment Station Oklahoma State University
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education. April, 2006
 Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones
 Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Phototropism - plant growth response to light shoots bend toward light - positive
Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Phototropism - plant growth response to light shoots bend toward light - positive
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Dissect a Flower. Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring
 WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort
 The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Things Plants Need There are certain things that every living thing needs in order to live and grow. Just like you, plants need
The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Things Plants Need There are certain things that every living thing needs in order to live and grow. Just like you, plants need
Plants, like all other living organisms have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food),
 LEARNING FROM LEAVES: A LOOK AT LEAF SIZE Grades 3 6 I. Introduction Plants, like all other living organisms have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food), water, space in which to live, air, and optimal
LEARNING FROM LEAVES: A LOOK AT LEAF SIZE Grades 3 6 I. Introduction Plants, like all other living organisms have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food), water, space in which to live, air, and optimal
Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth?
 1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All. Evolution of Plants
 And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
Anatomy and Physiology of Leaves
 I. Leaf Structure and Anatomy Anatomy and Physiology of Leaves A. Structural Features of the Leaf Question: How do plants respire? Plants must take in CO 2 from the atmosphere in order to photosynthesize.
I. Leaf Structure and Anatomy Anatomy and Physiology of Leaves A. Structural Features of the Leaf Question: How do plants respire? Plants must take in CO 2 from the atmosphere in order to photosynthesize.
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Impressions of a Stoma
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Impressions of a Stoma Overview Students use two different methods to view stomata on the underside of leaves. Introduction Plants exchange the
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Impressions of a Stoma Overview Students use two different methods to view stomata on the underside of leaves. Introduction Plants exchange the
2. Fill in the blank. The of a cell is like a leader, directing and telling the different parts of the cell what to do.
 1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
The Tiny Seed Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9
 Teacher s Guide to Third and Fourth Grade Reading and Writing Exercises for Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9 Developed by Jennifer A. Seitz For Florida
Teacher s Guide to Third and Fourth Grade Reading and Writing Exercises for Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9 Developed by Jennifer A. Seitz For Florida
Figure 1. Basic structure of the leaf, with a close up of the leaf surface showing Stomata and Guard cells.
 BIOL100 Laboratory Assignment 3: Analysis of Stomata Name: Stomata (singular=stoma) are the respiratory control structures in plants (see Figure 1 below). They are essentially small holes in the surface
BIOL100 Laboratory Assignment 3: Analysis of Stomata Name: Stomata (singular=stoma) are the respiratory control structures in plants (see Figure 1 below). They are essentially small holes in the surface
Making a Terrarium. fairchild tropical botanic garden 1
 Making a Terrarium What is a Terrarium? A terrarium is a collection of small plants growing in a transparent, sealed container. A terrarium is a closed environment, and can actually be used to illustrate
Making a Terrarium What is a Terrarium? A terrarium is a collection of small plants growing in a transparent, sealed container. A terrarium is a closed environment, and can actually be used to illustrate
Plants, like all living organisms have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food), water,
 WHAT PLANTS NEED IN ORDER TO SURVIVE AND GROW: LIGHT Grades 3 6 I. Introduction Plants, like all living organisms have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food), water, space in which to live, air, and
WHAT PLANTS NEED IN ORDER TO SURVIVE AND GROW: LIGHT Grades 3 6 I. Introduction Plants, like all living organisms have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food), water, space in which to live, air, and
How do living things get their energy?
 KEY TERMS How do living things get their energy? 26 Lesson - photosynthesis: food-making process in plants respiration: process by which organisms release energy from food 175 LESSON How ci? living things
KEY TERMS How do living things get their energy? 26 Lesson - photosynthesis: food-making process in plants respiration: process by which organisms release energy from food 175 LESSON How ci? living things
Introduction to Plant Propagation. Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM
 Introduction to Plant Propagation Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM Purposes for Plant Propagation Multiply the number of a species Perpetuate a species Maintain the youthfulness
Introduction to Plant Propagation Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM Purposes for Plant Propagation Multiply the number of a species Perpetuate a species Maintain the youthfulness
Photosynthesis. Chemical Energy (e.g. glucose) - They are the ultimate source of chemical energy for all living organisms: directly or indirectly.
 Photosynthesis Light Energy transduction Chemical Energy (e.g. glucose) - Only photosynthetic organisms can do this (e.g. plants) - They are the ultimate source of chemical energy for all living organisms:
Photosynthesis Light Energy transduction Chemical Energy (e.g. glucose) - Only photosynthetic organisms can do this (e.g. plants) - They are the ultimate source of chemical energy for all living organisms:
3MNN Behavioral Outcomes Eat fruits and veggies, etc. SNAP-Education Nutrition Messages Eat fruits and veggies as healthy snacks, MyPyramid servings
 DRAFT 1 Lesson Plan Title: Phenomenal Plant Parts Grade Level: 3 Content Area: Science Setting: School garden, or classroom Instructional Time: 60 to 90 minutes Grade Level Expectations: Life Science L.OL.E3:
DRAFT 1 Lesson Plan Title: Phenomenal Plant Parts Grade Level: 3 Content Area: Science Setting: School garden, or classroom Instructional Time: 60 to 90 minutes Grade Level Expectations: Life Science L.OL.E3:
Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY
 Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My!
 Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My! Objectives 1. The student will be able to identify parts of a plant. 2. The student will understand the function of plant parts. Grade Level 1-3 4-6 TEKS: 1.6B, 2.6C;
Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My! Objectives 1. The student will be able to identify parts of a plant. 2. The student will understand the function of plant parts. Grade Level 1-3 4-6 TEKS: 1.6B, 2.6C;
What is a Terrarium? Supplies Choosing your container Choosing your plants Building Your Terrarium
 What is a Terrarium? A terrarium is a collection of small plants growing in a transparent, sealed container. A terrarium is a closed environment, and can actually be used to illustrate how an ecosystem
What is a Terrarium? A terrarium is a collection of small plants growing in a transparent, sealed container. A terrarium is a closed environment, and can actually be used to illustrate how an ecosystem
Introducing the parts of a flower
 Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination
 Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
GERMINATION WORKSHEET 1: WHAT DO SEEDS NEED IN ORDER TO GROW?
 GERMINATION WORKSHEET 1: WHAT DO SEEDS NEED IN ORDER TO GROW? The Experiment Under controlled conditions, students will learn what happens to seedlings when they are deprived of their basic needs and what
GERMINATION WORKSHEET 1: WHAT DO SEEDS NEED IN ORDER TO GROW? The Experiment Under controlled conditions, students will learn what happens to seedlings when they are deprived of their basic needs and what
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers
 Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
nucleus cytoplasm membrane wall A cell is the smallest unit that makes up living and nonliving things.
 1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
Plant Growth & Development. Growth Stages. Differences in the Developmental Mechanisms of Plants and Animals. Development
 Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort
 The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Seeds What Is a Seed? A seed is a very young plant that is in the dormant, or resting stage. It is very much alive. There are three
The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Seeds What Is a Seed? A seed is a very young plant that is in the dormant, or resting stage. It is very much alive. There are three
Vascular Plants Bryophytes. Seedless Plants
 plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
Our American Trees by Robert C. Birkby
 North arolina Testing Program Our merican Trees by Robert. irkby The largest and oldest living things on earth are trees. Over a thousand kinds grow in the United States, and thousands more flourish in
North arolina Testing Program Our merican Trees by Robert. irkby The largest and oldest living things on earth are trees. Over a thousand kinds grow in the United States, and thousands more flourish in
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator
 Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Question. Which of the following are necessary in order for photosynthesis to occur? A. water B. light energy C. carbon dioxide D.
 Photosynthesis is the process through which plants convert light energy to chemical energy in order to produce food The energy involved in photosynthesis is eventually stored in the chemical bonds of molecules
Photosynthesis is the process through which plants convert light energy to chemical energy in order to produce food The energy involved in photosynthesis is eventually stored in the chemical bonds of molecules
Light in the Greenhouse: How Much is Enough?
 Light in the Greenhouse: How Much is Enough? by: James W. Brown http://www.cropking.com/articlelghe Most of us know that green plants need light for photosynthesis, growth, and development. As important
Light in the Greenhouse: How Much is Enough? by: James W. Brown http://www.cropking.com/articlelghe Most of us know that green plants need light for photosynthesis, growth, and development. As important
Plant Structure and Function Notes
 For plants, when they made the transition from water to land, they had to make adaptations for obtaining water and prevent loss by desiccation (drying out) -water also needed for fertilization of eggs
For plants, when they made the transition from water to land, they had to make adaptations for obtaining water and prevent loss by desiccation (drying out) -water also needed for fertilization of eggs
Exploring Seed Germination by Brad Williamson
 Exploring Seed Germination by Brad Williamson Background: Seeds are very remarkable. Laying dormant inside the seed is an embryo plant. Packed with the embryo is enough stored chemical energy to power
Exploring Seed Germination by Brad Williamson Background: Seeds are very remarkable. Laying dormant inside the seed is an embryo plant. Packed with the embryo is enough stored chemical energy to power
5 E Lesson Plan. Title: Modeling Photosynthesis Grade Level and Course: 7 th grade, Life Science 10 th grade, Biology
 5 E Lesson Plan Title: Modeling Photosynthesis Grade Level and Course: 7 th grade, Life Science 10 th grade, Biology Materials: a. aluminum tray b. waxed paper c. 6 green marshmallows d. 12 pink marshmallows
5 E Lesson Plan Title: Modeling Photosynthesis Grade Level and Course: 7 th grade, Life Science 10 th grade, Biology Materials: a. aluminum tray b. waxed paper c. 6 green marshmallows d. 12 pink marshmallows
Organic Gardening Certificate Program Quiz Week 3 Answer Key
 Q uiz for week 3 readings: 1. The database on the Organic Weed management Website contains the following sections except: A. Picture B. Ecology C. Management D. Description 2. The weed quackgrass can reproduce
Q uiz for week 3 readings: 1. The database on the Organic Weed management Website contains the following sections except: A. Picture B. Ecology C. Management D. Description 2. The weed quackgrass can reproduce
Transpiration. C should equal D.BUT SOMETIMES. 1. Loss in mass is greater than volume of water added.
 Transpiration Transpiration is the loss of water by evaporation from the leaves through the stomata. The source of water for the plants is soil water. It is taken up by root hair cells by osmosis. Once
Transpiration Transpiration is the loss of water by evaporation from the leaves through the stomata. The source of water for the plants is soil water. It is taken up by root hair cells by osmosis. Once
Plant Growth - Light and Shade
 Science Unit: Lesson 5: Plants Plant Growth - Light and Shade School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School
Science Unit: Lesson 5: Plants Plant Growth - Light and Shade School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School
2- The Top and bottom of the leaf is covered by thin layer of cells called epidermis that allow sunlight to easily pass into the middle of the leaf.
 Final exam summary sheet Topic 5, lesson 2 How leaf is adapted to carry on photosynthesis? 1- Waxy layer called the cuticle cover the leaf slow the water loss. 2- The Top and bottom of the leaf is covered
Final exam summary sheet Topic 5, lesson 2 How leaf is adapted to carry on photosynthesis? 1- Waxy layer called the cuticle cover the leaf slow the water loss. 2- The Top and bottom of the leaf is covered
(K-5) A scientist keeps a notebook to record his/her process (experiences, observations, and thinking).
 FIFTH GRADE Science Curriculum Framework 1 Investigations will be integrated with social studies and mathematics where appropriate. 2 Investigations will be integrated with language arts non-fiction reading,
FIFTH GRADE Science Curriculum Framework 1 Investigations will be integrated with social studies and mathematics where appropriate. 2 Investigations will be integrated with language arts non-fiction reading,
Soybean Physiology: How Well Do You Know Soybeans?
 Soybean Physiology: How Well Do You Know Soybeans? Shaun Casteel, Purdue University Soybean Extension Specialist www.soybeanstation.org 2010-11, Purdue University - 1 Vegetative Growth Stages Reproductive
Soybean Physiology: How Well Do You Know Soybeans? Shaun Casteel, Purdue University Soybean Extension Specialist www.soybeanstation.org 2010-11, Purdue University - 1 Vegetative Growth Stages Reproductive
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP. KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy.
 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy. 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP Molecules in food store chemical energy in their bonds. Starch molecule Glucose molecule The chemical
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy. 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP Molecules in food store chemical energy in their bonds. Starch molecule Glucose molecule The chemical
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard. Biology Level 2
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Biology for Achievement Standard 91160 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Biology for Achievement Standard 91160 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land,
 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
Dry Bean Types and Development Stages
 Dry Bean Types and Development Stages Two basic plant growth habits are found in dry edible bean: determinate (bush) or indeterminate (vining or trailing). Cultivars may be classified according to plant
Dry Bean Types and Development Stages Two basic plant growth habits are found in dry edible bean: determinate (bush) or indeterminate (vining or trailing). Cultivars may be classified according to plant
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout
 PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
Growing seedlings Activity 1: Growing seedlings in the classroom (1)
 Parts of a plant Teacher Guidance Growing seedlings Activity 1: Growing seedlings in the classroom (1) Resources Water t Film pots (film cans) with wick (e.g. from capillary matting or J-cloth) Seed compost
Parts of a plant Teacher Guidance Growing seedlings Activity 1: Growing seedlings in the classroom (1) Resources Water t Film pots (film cans) with wick (e.g. from capillary matting or J-cloth) Seed compost
Fungi and plants practice
 Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Kindergarten Science Unit B: Life Science Chapter 4: Plant and Animal Parts Lesson 1: What do plant parts do?
 Insert Photo or Graphic for Unit or Lesson Theme Kindergarten Science Unit B: Life Science Chapter 4: Plant and Animal Parts Lesson 1: What do plant parts do? Insert Photo/Graphic parts Insert Photo/Graphic
Insert Photo or Graphic for Unit or Lesson Theme Kindergarten Science Unit B: Life Science Chapter 4: Plant and Animal Parts Lesson 1: What do plant parts do? Insert Photo/Graphic parts Insert Photo/Graphic
Life Science. A curriculum and activity guide for Carlsbad Caverns National Park. Middle School Biology
 Life Science A curriculum and activity guide for Carlsbad Caverns National Park Middle School Biology Life Science Biology Curriculum I. Introduction... 1 II. Curriculum unit overview and activities A.
Life Science A curriculum and activity guide for Carlsbad Caverns National Park Middle School Biology Life Science Biology Curriculum I. Introduction... 1 II. Curriculum unit overview and activities A.
Plant and Soil Science I
 Plant and Soil Science I Levels: Grades 9-12 Units of Credit: 1.00 CIP Code: 02.0411 Core Code: 30-02-00-00-080 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: # 140 COURSE DESCRIPTION Students will develop knowledge and
Plant and Soil Science I Levels: Grades 9-12 Units of Credit: 1.00 CIP Code: 02.0411 Core Code: 30-02-00-00-080 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: # 140 COURSE DESCRIPTION Students will develop knowledge and
Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification
 1 Tips for Identifying Broadleaf Weeds Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification The cotyledon is an important identifying characteristic for broadleaf weeds. Shape and position of leaves, presence of pubescence
1 Tips for Identifying Broadleaf Weeds Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification The cotyledon is an important identifying characteristic for broadleaf weeds. Shape and position of leaves, presence of pubescence
Photosynthesis. Grade-Level Expectations The exercises in these instructional tasks address content related to the following grade-level expectations:
 GRADE 5 SCIENCE INSTRUCTIONAL TASKS Photosynthesis Grade-Level Expectations The exercises in these instructional tasks address content related to the following grade-level expectations: SI-M-A5 Use evidence
GRADE 5 SCIENCE INSTRUCTIONAL TASKS Photosynthesis Grade-Level Expectations The exercises in these instructional tasks address content related to the following grade-level expectations: SI-M-A5 Use evidence
TREE STRUCTURE AND BIOLOGY
 TREE STRUCTURE AND BIOLOGY Introduction. Sarasota County lies along a transient tension zone line. In this region, climate cycles cause periods of warmer weather, when normally tropical trees find their
TREE STRUCTURE AND BIOLOGY Introduction. Sarasota County lies along a transient tension zone line. In this region, climate cycles cause periods of warmer weather, when normally tropical trees find their
Unit 3 Lesson 5: People Need Plants
 Focus Areas: Characteristics of Plants; Science Focus Skills: observing, identifying, drawing conclusions Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objectives To identify parts of a plant To recognize the importance
Focus Areas: Characteristics of Plants; Science Focus Skills: observing, identifying, drawing conclusions Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objectives To identify parts of a plant To recognize the importance
Phenology. Phenology and Growth of Grapevines. Vine Performance
 Phenology and Growth of Grapevines Ker 2007 1 Soil Depth Texture Water and nutrient supply Climate Radiation Temperature Humidity Windspeed Rainfall Evaporation Cultural decisions Vine density Scion and
Phenology and Growth of Grapevines Ker 2007 1 Soil Depth Texture Water and nutrient supply Climate Radiation Temperature Humidity Windspeed Rainfall Evaporation Cultural decisions Vine density Scion and
3) Transpiration creates a force that pulls water upward in. xylem. 2) Water and minerals transported upward form roots to shoots in.
 3) Transpiration creates a force that pulls water upward in xylem Figure 36.1 An overview of transport in whole plants (Layer 1) Transport in plants 2) Water and minerals transported upward form roots
3) Transpiration creates a force that pulls water upward in xylem Figure 36.1 An overview of transport in whole plants (Layer 1) Transport in plants 2) Water and minerals transported upward form roots
2. Which type of macromolecule contains high-energy bonds and is used for long-term energy storage?
 Energy Transport Study Island 1. During the process of photosynthesis, plants use energy from the Sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. These products are, in turn, used by the
Energy Transport Study Island 1. During the process of photosynthesis, plants use energy from the Sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. These products are, in turn, used by the
Mighty Oaks From Little Acorns
 Science Process: Observe and Measure / Life Science / Math: Measurement (Length), data Analysis (graphing) / reading: Sequencing / Listening / Writing / Visual Arts expression Background Buds are on the
Science Process: Observe and Measure / Life Science / Math: Measurement (Length), data Analysis (graphing) / reading: Sequencing / Listening / Writing / Visual Arts expression Background Buds are on the
Seed Respiration. Biology Individual or teams of 2. Grade 10-12 DESCRIPTION LEARNING OUTCOMES MATERIALS READINESS ACTIVITIES.
 Seed Respiration Science Grade 10-12 Lab Individual or teams of 2 DESCRIPTION Plants generate Oxygen, which is essential for humans to survive. However, plants also consume Oxygen during respiration. It
Seed Respiration Science Grade 10-12 Lab Individual or teams of 2 DESCRIPTION Plants generate Oxygen, which is essential for humans to survive. However, plants also consume Oxygen during respiration. It
B2 1 Cells, Tissues and Organs
 B2 Cells, Tissues and Organs 5 minutes 5 marks Page of 7 Q. The diagram shows a bacterium. On the drawing, name the structures labelled A, B, C and D. (Total 4 marks) Q2. (a) The diagrams show cells containing
B2 Cells, Tissues and Organs 5 minutes 5 marks Page of 7 Q. The diagram shows a bacterium. On the drawing, name the structures labelled A, B, C and D. (Total 4 marks) Q2. (a) The diagrams show cells containing
Cellular Energy. 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following?
 Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
Plant Parts and Their Function
 Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Get It Right. Answers. Chapter 1: The Science of Life. A biologist studies all living things.
 Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
Laboratory. Plant Structure
 Laboratory 4 Plant Structure 2 Laboratory 4: Plant Structure OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Differentiate between dicots and monocots within the following categories: a. root
Laboratory 4 Plant Structure 2 Laboratory 4: Plant Structure OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Differentiate between dicots and monocots within the following categories: a. root
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1
 Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
What Do Plants Need to Grow?
 Lesson #401 What Do Plants Need to Grow? Grades 2-4 Editors Mandi Bottoms Shaney Emerson Robin Satnick 2300 River Plaza Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 (916) 561-5625 (800) 700-2482 www.learnaboutag.org California
Lesson #401 What Do Plants Need to Grow? Grades 2-4 Editors Mandi Bottoms Shaney Emerson Robin Satnick 2300 River Plaza Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 (916) 561-5625 (800) 700-2482 www.learnaboutag.org California
