ZERO-P VA. Variable angle zero-profile anterior cervical interbody fusion (ACIF) device SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
|
|
|
- Hillary Bryan
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ZERO-P VA Variable angle zero-profile anterior cervical interbody fusion (ACIF) device SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
2
3 Table of Contents Introduction Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants 2 AO Principles 4 Indications and Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning 6 Considerations for Use Adjacent to a Prior Fusion 7 Implant Insertion 8 Screw Fixation 14 Option A: Awl and Self-Drilling Screws 15 Option B: Drill Guide 20 Option C: Angled Instruments 25 Implant Removal 30 Product Information Implants 33 Instruments 34 Instrument Disassembly 37 Set Lists 39 Bibliography Bibliography 44 Image intensifier control Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes
4 Zero-P VA. Variable angle zero-profile anterior cervical interbody fusion (ACIF) device. The Zero-P VA implant is a stand-alone implant for use in cervical interbody fusion, 1 4 which combines the functionality of a cervical interbody spacer and the benefits of an anterior cervical plate. Zero-profile midline Designed to reduce the risk of contacting local anatomical structures The Zero-P VA implant does not extend beyond the confines of the intervertebral space midline, limiting risk of contact with vessels and adjacent soft tissues Designed to prevent contact with adjacent levels Cervical plates placed near the adjacent level discs may contribute to bone formation near or around the adjacent level, which may lead to future complications 5 Ease of use Variable angle screws, designed with a wide range of allowable screw trajectories, potentially facilitate screw insertion One-step screw securing mechanism features audible, tactile and visual cues to confirm screw is blocked upon insertion Because the interbody plate and stops assembly is preattached to the spacer, the interbody plate and stops assembly is automatically aligned upon implant insertion. This avoids the process of aligning and realigning an anterior cervical plate Zero-P VA may be used to facilitate surgeries where Zero-P VA is implanted adjacent to a prior fusion. 2 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
5 PEEK interbody spacer Includes a radiopaque marker for posterior visualization during imaging Spacer component is made of pure medical grade PEEK Optima (polyetheretherketone) Teeth on the superior and inferior implant surfaces provide initial stability range 29 Titanium alloy interbody plate and stops assembly Stresses in the interbody plate and stops assembly are decoupled from the spacer through an innovative interface Contralateral safety stops designed to reduce the risk of over-insertion and align with the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies 23 (nominal) Variable angle screws Can be inserted (17 range) in cranial-caudal direction and (14 range) in medial-lateral direction Variable angle and nominal angle insertion technique options Designed to resist graft expulsion Self-drilling and self-tapping options Screws are allowed to toggle post-operatively within vertebral bodies, which may potentially reduce or limit load shielding of the graft in the event of graft subsidence range 40 (nominal) 0.9 mm 0.9 mm 16.6 mm 13.6 mm 15 mm 17.5 mm 17.5 mm Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 3
6 AO Principles In 1958, the AO formulated four basic principles, which have become the guidelines for internal fixation. 6 They are: Anatomic reduction Stable fixation Preservation of blood supply Early, active mobilization The fundamental aims of fracture treatment in the limbs and the fusion of the spine are the same. A specific goal in the spine is returning as much function as possible to the neural elements. 7 4 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
7 Indications and Contraindications Indications The Synthes Zero-P VA implant is a stand-alone anterior cervical interbody fusion device indicated for use in skeletally mature patients with degenerative disc disease (DDD) with accompanying radicular symptoms at one level from C2 T1. DDD is defined as discogenic pain with degeneration of the disc confirmed by history and radiographic studies. These patients should have had six weeks of nonoperative treatment. The interior of the spacer component of the Zero-P VA implant should be packed with autogenous bone graft and implanted via an anterior approach. Contraindications 1. Use of the Synthes Zero-P is contraindicated when there is active systemic infection, infection localized to the site of the proposed implantation, or when the patient has demonstrated allergy or foreign body sensitivity to any of the implant materials. 2. Severe osteoporosis may prevent adequate fixation and thus preclude the use of this or any other orthopaedic implant. 3. Severe obesity or degenerative diseases, are relative contraindications. The decision whether to use these devices in such conditions must be made by the physician taking into account the risks versus the benefits to the patient. 4. Use of these implants is relatively contraindicated in patients whose activity, mental capacity, mental illness, alcoholism, drug abuse, occupation, or lifestyle may interfere with their ability to follow postoperative restrictions. These patients may place undue stresses on the implant during bony healing and may be at a higher risk of implant failure. 5. Prior fusion at the level to be treated. 6. Any condition not described in the Indications for Use. Please refer to product insert for complete system description, indications and warnings. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 5
8 Preoperative Planning Determine the surgical approach, and estimate the appropriate Zero-P VA implant size. Notes With the segment fully distracted, the Zero-P VA implant must fit firmly between the end plates before screws are inserted. When rocking the insertion device backward and forward in a cranial to caudal direction, no toggling of the implant should be evident. It is recommended to select the maximum implant size in order to optimize the stability of the segment through tension in the annulus fibrosis and longitudinal ligaments. 6 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
9 Considerations for Use Adjacent to a Prior Fusion When implanting Zero-P VA adjacent to a prior fusion, take care to avoid placing the Zero-P VA spacer and screws in direct contact with previously implanted hardware. As necessary, remove adjacent-level hardware that prevents Zero-P VA from being implanted using the correct technique. Caution: Placement of Zero-P VA adjacent to a previous, multi-level fusion could result in excessive loading. Supplemental fixation should be considered in cases where Zero-P VA is placed adjacent to a previous, multi-level fusion. Do not place Zero-P VA adjacent to previously placed hardware if the adjacent level cannot be confirmed to be fused or where fusion has not occurred. Important: Use radiographic imaging to verify final implant position relative to the vertebral bodies in the AP and lateral direction and remaining implanted hardware associated with the previously fused level. To accommodate previously-placed hardware, insert the Zero-P variable angle screws at a trajectory where they do not come in contact with adjacent hardware. Consider screw dimensions to determine desired orientation. Warnings: 1. If adjacent hardware prevents either Zero-P VA screw from being implanted, a different device should be used, as increased loading may be placed on the screws, leading to potential postoperative device failure and potentially increased harm to the patient. 2. If either screw cannot be inserted at the correct trajectory is or blocked by the blocking mechanism according to the recommended techniques as described in steps A1 C4, a different device should be used to avoid the risk of screw backout or screw failure. 3. Confirm that the Zero-P VA implant is not placed in direct contact with implanted hardware associated with the previously fused level. If the Zero-P VA implant remains in direct contact with hardware associated with the previously fused level, increased loading may be placed on the Zero-P VA implant leading to potential postoperative device failure and potential harm to the patient. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 7
10 Implant Insertion 1 Approach Using the standard surgical approach, expose the vertebral bodies to be fused. Prepare the fusion site following the appropriate technique for the given indication. 8 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
11 2 Determine appropriate implant Instruments Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, parallel, mm heights, purple Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, lordotic, mm heights, blue Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, convex, mm heights, gold Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, large.739 parallel, 5 12 mm heights, purple Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, large.769 lordotic, 5 12 mm heights, blue Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, large.799 convex, 5 12 mm heights, gold Optional instrument Slotted Mallet Choose a parallel, lordotic, or convex trial spacer of the appropriate height. Selection of the trial spacer depends on the height of the intervertebral space, the preparation technique, and patient anatomy. Position the trial spacer in the correct cranial/caudal alignment and carefully insert it into the disc space. The mallet can be used to help insert and/or remove the trial spacer. Trial spacers have depth stops corresponding to the depth stops of the Zero-P VA implant. Caution: Anterior osteophytes in the surgical site that prevent desired positioning of a trial spacer will likely prevent desired positioning of the Zero-P VA implant. It is recommended to remove interfering anterior osteophytes before implant insertion. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 9
12 Implant Insertion Notes: Trial spacers are color-coded by shape. The height of the trial spacer is 0.8 mm less than that of the corresponding implant to account for penetration of the teeth into the vertebral end plate. Trial spacers are not for implantation and must be removed before insertion of the Zero-P VA implant. To minimize potential risk of injuring the patient, it is recommended to: trial with shorter height trial spacers before trialing with taller height trial spacers. trial with standard footprint size trial spacers before trialing with large footprint size trial spacers. Although the trial spacers have depth stops, use of an image intensifier is recommended to check the position during insertion. With the segment fully distracted, the trial spacer must fit tightly and accurately between the end plates. 10 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
13 3 Pack implant with autogenous bone graft Instruments Cancellous Bone Impactor Packing Block, for Zero-P VA Place the Zero-P VA implant into the packing block. Use the cancellous bone impactor to firmly pack the autogenous bone graft into the implant cavities. Note: To ensure optimal contact with the vertebral endplates, it is important to fill the implant until the autogenous bone graft protrudes from the perforations in the spacer. The bone impactor can only be used with the standard size footprints of Zero-P VA implants. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 11
14 Implant Insertion 4 Insert implant Instrument Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Optional instruments Impactor, flat Implant Holder for Zero-P VA Impactor, ball tip Slotted Mallet Use the insertion device or implant holder to introduce the implant into the disc space. Using the insertion device Attach the insertion device to the implant by aligning the recessed grooves located midline on the anterior face of the implant with the pronged tabs of the device tip. Squeeze the insertion device handles to secure the implant; the thumb nut on the insertion device may then be advanced clockwise to lock the implant to the insertion device. Carefully insert the implant into the distracted segment. Advance the implant until the implant stops rest on the anterior surface of the vertebral body. If necessary, the top of the insertion device can be tapped with a mallet to further advance the implant into the disc space. If distraction has been applied, release the distraction, leaving the insertion device attached to the implant. 12 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
15 Using the implant holder Alternatively, the implant can be carefully inserted into the disc space with the forceps-style implant holders. Attach the implant holder to the implant by aligning the recessed grooves located midline on the anterior face of the implant with the ends of the implant holder. Once the implant is partially introduced into the disc space, the implant can be advanced using the flat and/or ball tip impactors. Notes: The Zero-P VA interbody plate is marked with an arrow to indicate implant orientation. When inserting the Zero-P VA implant, the arrow should point to the cranial vertebral body upon insertion. Verify final implant position relative to the vertebral bodies in the AP and lateral directions with the help of an intraoperative x-ray. A posterior x-ray marker incorporated in the PEEK spacer enables accurate intraoperative radiographic assessment of implant position. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 13
16 Screw Fixation The Zero-P VA system is only intended to be implanted with two Zero-P VA screws, forming a stand-alone interbody fusion construct. By design, the Zero-P VA system enables insertion of the screws within a range of acceptable trajectories. Variable angle insertion range range 29 Nominal angle and variable angle instruments are available to prepare screw holes prior to screw insertion. Using an instrument to prepare screw holes is recommended; these instruments are designed to facilitate subsequent placement of screws at the desired trajectory. Variable angle instruments are designed for flexibility; both the variable angle awl and variable angle drill guide enable hole preparation within the full range of acceptable limits. Variable angle instruments are marked with a double green band at the tip. Nominal angle instruments are designed for repeatability; both the nominal angle awl and nominal angle drill guide enable hole preparation at the nominal trajectory. Nominal angle instruments are marked with a single green band at the tip. Nominal angle insertion 40 (nominal) 23 (nominal) The screw trajectory achieved during screw insertion will result in varied screw penetration into the vertebral bodies. Screw Penetration (mm) Screw AP Cranial/Caudal Length (mm) Min Nominal Max Min Nominal Max Min Nominal Max Cranial/ Caudal Caution: Depending on the selected screw length and instrumentation used, the screws may extend beyond the posterior edge of the implant. Min Nominal Max AP 14 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
17 Screw Fixation Option A: Awl and Self-drilling Screws A recommended screw fixation technique is to create pilot holes and then insert self-drilling screws range range (nominal) 23 (nominal) A1 Create first pilot hole Instruments Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA mm Awl with sleeve, variable angle Optional instruments Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA mm Awl with sleeve, nominal angle Determine the entry point and trajectory for the first screw. The correct angulations for the screws range between cranial/ caudal and medial/ lateral. Insert the awl into the first screw hole of the interbody plate. To ensure proper angle of pilot hole, fully seat the outer sleeve tip of the awl into the interbody plate. Push down on the ball handle of the awl while simultaneously twisting the handle to advance the awl. Remove the awl while maintaining alignment of the hole and implant. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 15
18 Screw Fixation Option A: Awl and Self-drilling Screws Important: Intraoperative imaging should be used to verify awl position. Notes: When using the awl, the insertion device and/or implant holder should be used to minimize implant movement. The tip of the awl fits into the screw hole of the interbody plate to produce the correct angle. The upper shaft of the awl, near the awl handle, is marked with two black rings. When advancing the awl, the appropriate depth has been reached when the end of the outer sleeve is flush with the first ring and only the second ring is still visible. Caution: Do not use the awl without the sleeve; use of the awl without the sleeve may cause injury to the patient. 16 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
19 A2 Insert first screw Instruments Screw Inserter, T8, self-retaining, quick coupling Handle with quick coupling, small Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Optional instruments Holding Sleeve, for StarDrive screw inserter, T Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA Select the appropriate screw length according to the preoperative plan and intraoperative findings. Attach the screw inserter to the handle then load the selected 3.7 mm self-drilling screw to the assembled driver. The screw will self-retain on the driver, but the holding sleeve may be used for additional screw retention. Advance the screw until the screwhead passes beyond the securing mechanism of the interbody plate. Visually verify screw is blocked by the securing mechanism. Note: When inserting screws, the insertion device and/or implant holder should be used to minimize implant movement. Important: Intraoperative imaging should be used to verify screw position and to verify the screw follows the trajectory of the pilot hole created by the awl. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 17
20 Screw Fixation Option A: Awl and Self-drilling Screws A3 Insert second screw Repeat Steps A1 and A2 for the second screw. 18 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
21 A4 Final tighten screws 1 Instruments Screw Inserter, T8, self-retaining, quick coupling Handle with quick coupling, small Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Optional instrument Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA To fully secure the implant, use the screw inserter to advance each screw another 1/4 1/2 turn. This final tightening step (1) lags the stops of the interbody plate to the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies and (2) increases the apposition of the implant to the vertebral body endplates. 2 Note: When tightening screws, the insertion device and/or implant holder should be used to minimize implant movement. Caution: Do not continue advancing any screw after the stops of the interbody plate are lagged to the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies and do not advance any screw more than 1/2 turn during final tightening. Over-tightening may strip bone and compromise fixation of the implant in vertebral bodies. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 19
22 Screw Fixation Option B: Drill Guide Alternatively, use a drill guide and drill to create a pilot hole. Then insert either self-drilling or self-tapping screws range range (nominal) 23 (nominal) B1 Drill first pilot hole Instruments mm Drill Bit with 12 mm stop, quick coupling mm Drill Bit with 14 mm stop, quick coupling mm Drill Bit with 16 mm stop, quick coupling Handle with quick coupling, small Drill Guide with handle, variable angle Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Optional instruments Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA Drill Guide with handle, Nominal Angle Determine the entry point and trajectory for the first screw. The correct angulations for the screws range between cranial/ caudal and medial/lateral. Insert the drill guide into the screw hole of the interbody plate. To ensure proper angle of pilot hole, fully seat the tip of the drill guide into the interbody plate. Insert the drill bit into the guide and drill until the stop of the drill contacts the guide. 20 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
23 Select a drill bit of appropriate length and assemble the drill bit to the handle. Insert the drill bit into the drill guide and drill until the stop on the drill bit contacts the drill guide. Remove the drill bit and drill guide. Important: Intraoperative imaging should be used to verify drill bit position. Notes: The drill bits are marked with a colored ring corresponding to the color-coded screw lengths. When the ring is flush with the top of the drill guide, the appropriate depth has been reached. When drilling, the insertion device and/or implant holder should be used to minimize implant movement. Caution: When drilling, care should be taken to drill on-axis, in the same trajectory as the drill guide. Applying side loads and/or levering off-axis during drilling may result in broken or damaged instruments which may potentially cause harm to the patient. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 21
24 Screw Fixation Option B: Drill Guide B2 Insert first screw Instruments Screw Inserter, T8, self-retaining, quick coupling Handle with quick coupling, small Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Optional instruments Holding Sleeve, for StarDrive screw inserter, T Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA Select the appropriate screw length according to the preoperative plan and intraoperative findings. Attach the screw inserter to the handle, then load the selected 3.7 mm self-tapping screw to the assembled driver. The screw will self-retain to the driver, but the holding sleeve may be used for additional screw retention. Advance the screw until the screw head passes beyond the securing mechanism of the interbody plate. Visually verify screw is blocked by the securing mechanism. Note: When inserting screws, the insertion device and/or implant holder should be used to minimize implant movement. Important: Intraoperative imaging should be used to verify screw position and to verify the screw follows the trajectory of the pilot hole created by the drill. 22 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
25 B3 Insert second screw Repeat Steps B1 and B2 for the second screw. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 23
26 Screw Fixation Option B: Drill Guide B4 Final tighten screws 1 Instruments Screw Inserter, T8, self-retaining, quick coupling Handle with quick coupling, small Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Optional instrument Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA To fully secure the implant, use the screw inserter to advance each screw another 1/4 1/2 turn. This final tightening step (1) lags the stops of the interbody plate to the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies and (2) increases the apposition of the implant to the vertebral body endplates. 2 Note: When tightening screws, the insertion device and/or implant holder should be used to minimize implant movement. Caution: Do not continue advancing any screw after the stops of the interbody plate are lagged to the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies and do not advance any screw more than 1/2 turn during final tightening. Over-tightening may strip bone and compromise fixation of the implant in vertebral bodies. 24 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
27 Screw Fixation Option C: Angled Instruments When screws are difficult to drill or insert due to interfering anatomy, the angled awl and angled screwdriver may be used range range (nominal) 23 (nominal) C1 Create first pilot hole Instruments Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA mm Angled Awl Slotted Mallet Optional instrument Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA Determine the entry point and trajectory for the screw. The correct angulations for the screws range between cranial/ caudal and medial/ lateral. Insert the awl at the appropriate angle into the first screw hole of the interbody plate and tap with the slotted mallet until the awl is seated. Remove the awl while maintaining alignment of the hole and implant. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 25
28 Screw Fixation Option C: Angled Instruments Important: Intraoperative imaging should be used to verify awl position. Note: When using the angled awl, the insertion device and/or implant holder should be used to minimize implant movement. 26 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
29 C2 Insert first screw Instrument Angled StarDrive Screwdriver, T8, with sleeve, self-retaining Select the appropriate screw length according to the preoperative plan and intraoperative findings. Load the selected 3.7 mm self-drilling screw onto the angled screwdriver. Advance the screw until the screwhead passes beyond the securing mechanism of the interbody plate. Visually verify screw is blocked by the securing mechanism. Note: When inserting screws, the insertion device and/or implant holder should be used to minimize implant movement. Important: Intraoperative imaging should be used to verify screw position and to verify the screw follows the trajectory of the pilot hole created by the angled awl. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 27
30 Screw Fixation Option C: Angled Instruments C3 Insert second screw Repeat Steps C1 and C2 for the second screw. 28 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
31 C4 Final tighten screws 1 Instruments Angled StarDrive Screwdriver, T8, with sleeve, self-retaining Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Optional instrument Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA To fully secure the implant, use the screw inserter to advance each screw another 1/4 1/2 turn. This final tightening step (1) lags the stops of the interbody plate to the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies and (2) increases the apposition of the implant to the vertebral body endplates. 2 Note: When tightening screws, the insertion device and/or implant holder should be used to minimize implant movement. Caution: Do not continue advancing any screw after the stops of the interbody plate are lagged to the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies and do not advance any screw more than 1/2 turn during final tightening. Over-tightening may strip bone and compromise fixation of the implant in vertebral bodies. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 29
32 Implant Removal If a Zero-P VA implant must be removed, the following technique is recommended. 1 Remove screws Instruments Screw Inserter, T8, self-retaining, quick coupling Handle with quick coupling, small Screw Removal Blade Attach the handle to the screw inserter, then engage the assembled driver into the first screw to be removed. Engage a tip of the screw removal blade into the securing mechanism of the interbody plate corresponding to screw to be removed. While pressing the securing mechanism toward midline with the removal blade, turn the assembled driver counterclockwise to remove the screw. Repeat with the second screw. Note: If the securing mechanism is initially difficult to depress towards the midline, it may be binding on the head of the screw. In such cases, advance the screw 1/4 turn clockwise before continuing with screw removal. 30 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
33 Alternative technique: Using the removal screwdriver Instrument Removal Screwdriver Engage the tip of the removal screwdriver in the drive recess of the first screw to be removed. Turn the top knob of the removal driver (engraved 1 ) counterclockwise until the top knob is flush with the middle section ( engraved 3 ); this fully engages the inner shaft into the screw. Lower the outer sleeve of the removal driver (engraved 2 ) by turning clockwise until the sleeve retracts the securing mechanism in the interbody plate. Finally, turn the middle section (engraved 3 ) counterclockwise to remove the screw. Repeat with the second screw. Caution If the inner shaft is not fully engaged prior to attempting subsequent screw removal technique steps, breakage of the driver may occur and could potentially harm the patient. The removal screwdriver should only be used for screw removal; use of the removal screwdriver for screw insertion may lead to driver and/ or implant breakage. Note: If the securing mechanism is initially difficult to depress towards the midline, it may be binding on the head of the screw. In such cases, advance the screw 1 4 turn clockwise before continuing with screw removal. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 31
34 Implant Removal 2 Extract Implant Instrument Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Once the screws are removed, remove the Zero-P VA implant using the insertion device. Engage the insertion device to the implant by first aligning the recessed grooves located midline on the anterior face of the implant with the pronged tabs of the device tip. 32 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
35 Implants Zero-P VA Implants Supplied sterile and preassembled (spacer with interbody plate) Available in 3 different shapes: convex, lordotic, parallel Spacer component: PEEK Optima Interbody plate component: Titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-7Nb and Ti-6Al-4V) Blocking mechanism: Titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V, Elgiloy (40Co-20Cr-16FE-15Ni-7Mo) Standard Large Height (mm) Convex Lordotic Parallel Convex Lordotic Parallel S S S S* S* S* S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S* S* S* S S S S* S* S* S* S* S* Zero-P VA Titanium Cervical Spine Screws Self-tapping or self-drilling options Titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-7Nb) Color-coded by screw length Length (mm) Color Self-Drilling Self-Tapping Note: Screws are provided non-sterile unless otherwise indicated. For sterile screws, see additionally available implants. * Also available Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 33
36 Instruments Angled StarDrive Screwdriver, T8, with sleeve, self-retaining Screw Inserter, T8, self-retaining, quick coupling 2.0 mm Drill Bits, quick coupling with 12 mm stop with 14 mm stop with 16 mm stop Impactor, flat Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, parallel 5 12 mm heights Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, large parallel 5 12 mm heights Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, lordotic 5 12 mm heights Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, large lordotic 5 12 mm heights Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, convex 5 12 mm heights Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, convex 5 12 mm heights 34 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
37 Holding Sleeve, for StarDrive Screwdriver Shaft Handle with quick coupling, small Drill Guide with handle, variable angle Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Cancellous Bone Impactor Removal Screwdriver Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 35
38 Instruments Inner Shaft for Removal Screwdriver Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA Impactor, ball tip Packing Block, for Zero-P VA Screw Removal Blade mm Angled Awl mm Awl with sleeve, for variable angle insertion Slotted Mallet 36 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
39 Instrument Disassembly Angled Screwdriver, T8, with sleeve, self-retaining mm Awl with sleeve Lubricate with oil Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 37
40 Instrument Disassembly Holding Sleeve, for StarDrive Screwdriver Shaft Removal Screw Driver Lubricate with oil 38 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
41 Zero-P VA Instrument and Titanium Screw Set ( ) Graphic Case Graphic Case, for Zero-P VA Instrument and Implant Set Modules Module, for 3.7mm Titanium Zero-P VA Screws Module, for Trial Implants (These modules are included in ) Instruments Angled StarDrive Screwdriver, T8, with sleeve, self-retaining Screw Inserter, T8, self-retaining, quick coupling, 2 ea mm Drill Bit with 12 mm stop, quick coupling, 2 ea mm Drill Bit with 14 mm stop, quick coupling, 2 ea mm Drill Bit with 16 mm stop, quick coupling, 2 ea Impactor, flat Holding Sleeve, for StarDrive screw inserter, T8, 2 ea Handle with quick coupling, small, 2 ea Insertion Device, for Zero-P VA Drill Guide with handle, variable angle Cancellous Bone Impactor Removal Screwdriver Inner Shaft for Removal Screwdriver Implant Holder, for Zero-P VA Impactor, ball tip Packing Block, for Zero-P VA Screw Removal Blade Lower tray Middle tray Top tray For detailed cleaning and sterilization instructions, please refer to: In Canada, the cleaning and sterilization instructions will be provided with the Loaner shipments. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 39
42 Zero-P VA Instrument and Titanium Screw Set ( ) mm Angled Awl mm Awl with sleeve, for variable angle insertion Slotted Mallet Implants 3.7 mm Titanium Cervical Spine Screws, variable angle, 6 ea Self-drilling, 14 mm Self-drilling, 16 mm Self-tapping, 12 mm Self-tapping, 14 mm Self-tapping, 16 mm Self-tapping, 18 mm Carry case 40 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
43 Zero-P VA Trial Spacer and Implant Sets Zero-P VA Parallel Trial Spacer with Stops Set ( ) Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, parallel mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height Trial Spacer Tray Zero-P VA Parallel Implant Set ( ) Zero-P VA Implants, parallel, sterile S 5 mm height, 1 ea S 6 mm height, 2 ea S 7 mm height, 3 ea S 8 mm height, 3 ea S 9 mm height, 2 ea S 10 mm height, 1 ea Carry Case, for Zero-P Implants Zero-P VA Lordotic Trial Spacer with Stops Set ( ) Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, lordotic mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height Trial Spacer Tray Zero-P VA Lordotic Implant Set ( ) Zero-P VA Implants, lordotic, sterile S 5 mm height, 1 ea S 6 mm height, 2 ea S 7 mm height, 3 ea S 8 mm height, 3 ea S 9 mm height, 2 ea S 10 mm height, 1 ea Carry Case, for Zero-P Implants Zero-P VA Convex Trial Spacer with Stops Set ( ) Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, convex mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height Trial Spacer Tray Zero-P VA Convex Implant Set ( ) Zero-P VA Implants, convex, sterile S 5 mm height, 1 ea S 6 mm height, 2 ea S 7 mm height, 3 ea S 8 mm height, 3 ea S 9 mm height, 2 ea S 10 mm height, 1 ea Carry Case, for Zero-P Implants Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 41
44 Zero-P VA Trial Spacer and Implant Sets Zero-P VA Large Parallel Trial Spacer with Stops Set ( ) Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, large, parallel mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height Trial Spacer Tray Zero-P VA Large Lordotic Trial Spacer with Stops Set ( ) Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, large lordotic mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height Trial Spacer Tray Zero-P VA Large Convex Trial Spacer with Stops Set ( ) Zero-P VA Trial Spacers with stop, large, convex mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height mm height Trial Spacer Tray Zero-P VA Large Parallel Implant Set ( ), with sterile implants Zero-P VA Implants, large, parallel, sterile S 6 mm height, 2 ea S 7 mm height, 3 ea S 8 mm height, 3 ea S 9 mm height, 2 ea S 10 mm height, 1 ea S 11 mm height, 1 ea Carry Case, for Zero-P Implants Zero-P VA Large Lordotic Implant Set ( ), with sterile implants Zero-P VA Implants, large, lordotic, sterile S 6 mm height, 2 ea S 7 mm height, 3 ea S 8 mm height, 3 ea S 9 mm height, 2 ea S 10 mm height, 1 ea S 11 mm height, 1 ea Carry Case, for Zero-P Implants Zero-P VA Large Convex Implant Set ( ), with sterile implants Zero-P VA Implants, large, convex, sterile S 6 mm height, 2 ea S 7 mm height, 3 ea S 8 mm height, 3 ea S 9 mm height, 2 ea S 10 mm height, 1 ea S 11 mm height, 1 ea Carry Case, for Zero-P Implants 42 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
45 Also Available Instruments Ratcheting Screwdriver Handle StarDrive Screwdriver Shaft, T8, 105 mm StarDrive Screwdriver Shaft, T8, self-retaining Extension Shaft, 115 mm Handle, with large quick coupling Hex Adaptor, high strength, quick coupling S* Conical Extraction Screw Sleeve for Angled Stardrive Screwdriver, T8, locking S* 2.0 mm Drill Bit for Conical Extraction screw Drill Guide with handle, nominal angle mm Awl with sleeve, for nominal angle insertion Zero-P VA Trial Spacer with stop, parallel mm height mm height Zero-P VA Trial Spacer with stop, large, parallel mm height mm height Zero-P VA Trial Spacer with stop, lordotic mm height mm height Zero-P VA Trial Spacer with stop, large, lordotic mm height mm height Zero-P VA Trial Spacer with stop, convex mm height mm height Implants S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S S Zero-P VA Implants, parallel, sterile 11 mm height 12 mm height Zero-P VA Implants, lordotic, sterile 11 mm height 12 mm height Zero-P VA Implants, convex, sterile 11 mm height 12 mm height Zero-P VA Implants, large, parallel, sterile 5 mm height 12 mm height Zero-P VA Implants, large, lordotic, sterile 5 mm height 12 mm height Zero-P VA Implants, large, convex, sterile 5 mm height 12 mm height 3.7 mm Titanium Cervical Spine Screws, variable angle, sterile, (1/pkg) Self-drilling, 14 mm Self-drilling, 16 mm Self-tapping, 12 mm Self-tapping, 14 mm Self-tapping, 16 mm Self-tapping, 18 mm Cases and Label Sheets Label Sheet for Zero-P VA Trial Spacer Tray Graphic case for Zero-P VA Auxiliary Instrument Set Zero-P VA Trial Spacer with stop, large, convex mm height mm height *Refer to Zero-P Technique Guide (J8566) for instructions for use. Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide Synthes 43
46 Bibliography 1. Kaiser MG, RW Haid Jr., BR Suback, et al Anterior cervical plating enhances arthrodesis after discectomy and fusion with cortical allograft. Neurosurgery 50: Caspar W, FH Geisler, T Pitzen, et al Anterior Cervical plate stabilization in one and two level degenerative disease: overtreatment or benefit? J. Spinal Disord. 11: Mobbs RJ, P Rao and NK Chandran Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: analysis of surgical outcome with and without plating. J. Clin. Neurosci. 14: Moftakhar R and GR Trost Anterior cervical plates: a historical perspective. Neurosurg. Focus. 16:E8. 5. Park JB, YS Cho and KD Riew Development of adjacent-level ossification in patients with an anterior cervical plate. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 87: Müller ME, M Allgöwer, R Schneider, and H Willenegger. Manual of Internal Fixation, 3rd edition. Berlin: Springer- Verlag Ibid. 44 Synthes Zero-P VA Instruments and Implants Technique Guide
47
48 Limited Warranty and Disclaimer: DePuy Synthes Spine products are sold with a limited warranty to the original purchaser against defects in workmanship and materials. Any other express or implied warranties, including warranties of merchantability or fitness, are hereby disclaimed. WARNING: In the USA, this product has labeling limitations. See package insert for complete information. CAUTION: USA Law restricts these devices to sale by or on the order of a physician. Not all products are currently available in all markets. DePuy Synthes Spine 325 Paramount Drive Raynham, MA T. +1 (800) Synthes (Canada) Ltd Meadowpine Boulevard Mississauga, Ontario L5N 6P9 Telephone: (905) To order: (800) Fax: (905) DePuy Synthes Spine, a division of DOI All rights reserved. J9912-D 6/13 DS Studio
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF). Instrument set supports placement of ALIF spacers using anterior or anterolateral approach.
 Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF). Instrument set supports placement of ALIF spacers using anterior or anterolateral approach. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF). Instrument set supports placement of ALIF spacers using anterior or anterolateral approach. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
4052 Slimplicity Tech final_layout 1 6/29/15 3:29 PM Page 2 Surgical Technique
 Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Slimplicity Anterior Cervical Plate System Overview 2 Indications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 4 Surgical Technique 6 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 6 2. Plate Selection
Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Slimplicity Anterior Cervical Plate System Overview 2 Indications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 4 Surgical Technique 6 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 6 2. Plate Selection
Technique Guide. Screw Removal Set. Instruments for removing Synthes screws.
 Technique Guide Screw Removal Set. Instruments for removing Synthes screws. Table of Contents Introduction Screw Removal Set 2 Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning and Preparation 6 Removal of Intact
Technique Guide Screw Removal Set. Instruments for removing Synthes screws. Table of Contents Introduction Screw Removal Set 2 Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning and Preparation 6 Removal of Intact
MINI FRAGMENT SYSTEM. Instruments and implants for 1.5 mm, 2.0 mm, and 2.4 mm plate fixation PRODUCT OVERVIEW
 MINI FRAGMENT SYSTEM Instruments and implants for 1.5 mm, 2.0 mm, and 2.4 mm plate fixation PRODUCT OVERVIEW TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION Mini Fragment System 2 PRODUCT INFORMATION Plates 4 Screws 6
MINI FRAGMENT SYSTEM Instruments and implants for 1.5 mm, 2.0 mm, and 2.4 mm plate fixation PRODUCT OVERVIEW TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION Mini Fragment System 2 PRODUCT INFORMATION Plates 4 Screws 6
ANTERIOR LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION (ALIF) Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Lumbar Spine
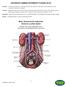 (ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
(ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Surgical Technique 2. Indications 4. Product Information 5. 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 2
 Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Surgical Technique 2 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 2 2. Intervertebral Device Implanted 2 3. Buttress Plate Selection 2 4. Awl Insertion 2 5. Screw Insertion
Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Surgical Technique 2 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 2 2. Intervertebral Device Implanted 2 3. Buttress Plate Selection 2 4. Awl Insertion 2 5. Screw Insertion
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System. Surgical Technique
 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Scout Vessel Guard. A cover for vessels during anterior lumbar spine surgery.
 Scout Vessel Guard. A cover for vessels during anterior lumbar spine surgery. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Scout Vessel Guard 2
Scout Vessel Guard. A cover for vessels during anterior lumbar spine surgery. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Scout Vessel Guard 2
CeSpace Titanium / PEEK
 Aesculap Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion System CeSpace Titanium / PEEK Aesculap Spine CeSpace Content A Foreword 3 B Implant Material 4 C Implant Features 6 D Surgical Technique 8 E Ordering Information
Aesculap Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion System CeSpace Titanium / PEEK Aesculap Spine CeSpace Content A Foreword 3 B Implant Material 4 C Implant Features 6 D Surgical Technique 8 E Ordering Information
AVS Anchor-C Cervical Cage System Surgical Technique. Large Graft Volume Self-Locking Screws Angled and Flexible Instrumentation
 AVS Anchor-C Cervical Cage System Large Graft Volume Self-Locking Screws Angled and Flexible Instrumentation Table of Contents Intended Use/Indications... 3 System Overview.... 6 Implantation Technique....
AVS Anchor-C Cervical Cage System Large Graft Volume Self-Locking Screws Angled and Flexible Instrumentation Table of Contents Intended Use/Indications... 3 System Overview.... 6 Implantation Technique....
Technique Guide. Orthopaedic Cable System. Cerclage solutions for general surgery.
 Technique Guide Orthopaedic Cable System. Cerclage solutions for general surgery. Table of Contents Introduction The Orthopaedic Cable System 2 Indications 4 Contraindications 4 Surgical Technique Cerclage
Technique Guide Orthopaedic Cable System. Cerclage solutions for general surgery. Table of Contents Introduction The Orthopaedic Cable System 2 Indications 4 Contraindications 4 Surgical Technique Cerclage
MatrixNEURO CMF Matrix
 MatrixNEURO CMF Matrix This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. MatrixNEURO Introduction The aim of surgical fracture treatment is to reconstruct the bony anatomy and restore its function.
MatrixNEURO CMF Matrix This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. MatrixNEURO Introduction The aim of surgical fracture treatment is to reconstruct the bony anatomy and restore its function.
Technique Guide. Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant Set. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant Set. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant Set
Technique Guide Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant Set. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction Large Fragment LCP Instrument and Implant Set
Modular Sternal Cable System. Flexibility and strength in sternal closure and repair.
 Modular Sternal Cable System. Flexibility and strength in sternal closure and repair. Multiple closure options Stable fixation in all configurations Improved strength and flexibility compared to wire Modular
Modular Sternal Cable System. Flexibility and strength in sternal closure and repair. Multiple closure options Stable fixation in all configurations Improved strength and flexibility compared to wire Modular
Posterior Referencing. Surgical Technique
 Posterior Referencing Surgical Technique Posterior Referencing Surgical Technique INTRO Introduction Instrumentation Successful total knee arthroplasty depends in part on re-establishment of normal lower
Posterior Referencing Surgical Technique Posterior Referencing Surgical Technique INTRO Introduction Instrumentation Successful total knee arthroplasty depends in part on re-establishment of normal lower
Degenerative Spine Solutions
 Degenerative Spine Solutions The Backbone for Your Surgical Needs Aesculap Spine Backbone for Your Degenerative Spine Needs Comprehensive operative solutions, unique product technology and world-class
Degenerative Spine Solutions The Backbone for Your Surgical Needs Aesculap Spine Backbone for Your Degenerative Spine Needs Comprehensive operative solutions, unique product technology and world-class
PERIPROSTHETIC IMPLANTS
 PERIPROSTHETIC IMPLANTS PRODUCT OVERVIEW CLINICAL SOLUTIONS Periprosthetic fractures present unique challenges, such as how to gain fixation when the medullary canal is occupied. Special techniques and
PERIPROSTHETIC IMPLANTS PRODUCT OVERVIEW CLINICAL SOLUTIONS Periprosthetic fractures present unique challenges, such as how to gain fixation when the medullary canal is occupied. Special techniques and
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion
 Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f screw Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f intact Primary Stability intact Primary Stability Extension Neutral Position Flexion Coflex
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f screw Biomechanical Evaluation (1) coflex-f intact Primary Stability intact Primary Stability Extension Neutral Position Flexion Coflex
NCB Distal Femur System. Surgical Technique
 NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique 3 Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Table of Contents Introduction 4 Indications 8 Preoperative Planning
NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique 3 Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Table of Contents Introduction 4 Indications 8 Preoperative Planning
Technique Guide. 4.5 mm LCP Proximal Femur Plates. Part of the Synthes Periarticular LCP Plating System.
 Technique Guide 4.5 mm LCP Proximal Femur Plates. Part of the Synthes Periarticular LCP Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm LCP Proximal Femur Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide 4.5 mm LCP Proximal Femur Plates. Part of the Synthes Periarticular LCP Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm LCP Proximal Femur Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Orthopedic Foot Instruments. Dedicated instruments for reconstructive foot surgery.
 Orthopedic Foot Instruments. Dedicated instruments for reconstructive foot surgery. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by
Orthopedic Foot Instruments. Dedicated instruments for reconstructive foot surgery. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by
Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Tibial Locking Plate
 Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Tibial Locking Plate 1 Table of Contents Introduction 2 Locking Screw Technology
Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Tibial Locking Plate 1 Table of Contents Introduction 2 Locking Screw Technology
Technique Guide. Reamer/Irrigator/Aspirator (RIA). For intramedullary reaming and bone harvesting.
 Technique Guide Reamer/Irrigator/Aspirator (RIA). For intramedullary reaming and bone harvesting. Table of Contents Introduction Reamer/ Irrigator/ Aspirator (RIA) 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Preparation
Technique Guide Reamer/Irrigator/Aspirator (RIA). For intramedullary reaming and bone harvesting. Table of Contents Introduction Reamer/ Irrigator/ Aspirator (RIA) 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Preparation
V-TEK IVP System 2.7 System 4.0
 V-TEK IVP System Ankle 2.7 Fix System 4.0 Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Titanium osteosynthesis system for tibio-talar and tibio-talo-calcaneal fusion SECTION 1 Ankle Fix System 4.0 Titanium osteosynthesis
V-TEK IVP System Ankle 2.7 Fix System 4.0 Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Titanium osteosynthesis system for tibio-talar and tibio-talo-calcaneal fusion SECTION 1 Ankle Fix System 4.0 Titanium osteosynthesis
LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle.
 LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution
LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm Curved Locking Compression Plates (LCP). For minimally invasive osteosynthesis.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm Curved Locking Compression Plates (LCP). For minimally invasive osteosynthesis. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm Curved Locking Compression 2 Plates (LCP)
Technique Guide 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm Curved Locking Compression Plates (LCP). For minimally invasive osteosynthesis. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm Curved Locking Compression 2 Plates (LCP)
Zimmer Periarticular Elbow Locking Plate System
 Zimmer Periarticular Elbow Locking Plate System Surgical Technique The Right Solutions for Fractures Around the Elbow Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for physicians and is not intended
Zimmer Periarticular Elbow Locking Plate System Surgical Technique The Right Solutions for Fractures Around the Elbow Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for physicians and is not intended
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DISCECTOMY AND FUSION. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Cervical Spine
 Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Expert LFN. Lateral Femoral Nail.
 Expert LFN. Lateral Femoral Nail. Surgical Technique EXPERT Nailing System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier
Expert LFN. Lateral Femoral Nail. Surgical Technique EXPERT Nailing System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Dall-Miles Cabling System Dall-Miles Recon and Trauma Cable System Trochanteric Reattachment Using the Trochanteric
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Dall-Miles Cabling System Dall-Miles Recon and Trauma Cable System Trochanteric Reattachment Using the Trochanteric
Technique Guide. DHS/DCS Dynamic Hip and Condylar Screw System. Designed to provide stable internal fixation.
 Technique Guide DHS/DCS Dynamic Hip and Condylar Screw System. Designed to provide stable internal fixation. Table of Contents Introduction Dynamic Hip Screw (DHS) 2 Dynamic Condylar Screw (DCS) 3 Indications
Technique Guide DHS/DCS Dynamic Hip and Condylar Screw System. Designed to provide stable internal fixation. Table of Contents Introduction Dynamic Hip Screw (DHS) 2 Dynamic Condylar Screw (DCS) 3 Indications
Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique
 *smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique Prepared in Consultation with: C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative
*smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique Prepared in Consultation with: C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative
How To Use A Phoenix Retrograde Femoral Nail
 Phoenix Retrograde Femoral Nail System Featuring CoreLock Technology Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 Indications... Page 2 Design Features... Page 3 Surgical Technique... Page 6 Product
Phoenix Retrograde Femoral Nail System Featuring CoreLock Technology Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 Indications... Page 2 Design Features... Page 3 Surgical Technique... Page 6 Product
TwinFix Cannulated Compression Screw
 TwinFix Cannulated Compression Screw Leibinger Solutions for Hand Surgery Procedural Guide TwinFix Sterilization, Organization, Storage 29-12020 Profyle MODULAR Sterilizing Container 29-40162 TwinFix Implant
TwinFix Cannulated Compression Screw Leibinger Solutions for Hand Surgery Procedural Guide TwinFix Sterilization, Organization, Storage 29-12020 Profyle MODULAR Sterilizing Container 29-40162 TwinFix Implant
Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. For canthal tendon procedures.
 Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. For canthal tendon procedures. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle
Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. For canthal tendon procedures. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle
Technique Guide. 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System. Part of the Synthes variable angle locking compression plate (VA-LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System. Part of the Synthes variable angle locking compression plate (VA-LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable
Technique Guide 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System. Part of the Synthes variable angle locking compression plate (VA-LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Indications and Contraindications 3. Features and Benefits 4. Ease of connection 4 Stable fixation concept 5
 Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Indications and Contraindications 3 Features and Benefits 4 Ease of connection 4 Stable fixation concept 5 Surgical Technique Steps 6 Identification and preparation
Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Indications and Contraindications 3 Features and Benefits 4 Ease of connection 4 Stable fixation concept 5 Surgical Technique Steps 6 Identification and preparation
Technique Guide. Titanium Trochanteric Fixation Nail System. For intramedullary fixation of proximal femur fractures.
 Technique Guide Titanium Trochanteric Fixation Nail System. For intramedullary fixation of proximal femur fractures. Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Trochanteric Fixation Nail System 2 Biomechanical
Technique Guide Titanium Trochanteric Fixation Nail System. For intramedullary fixation of proximal femur fractures. Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Trochanteric Fixation Nail System 2 Biomechanical
Zimmer Natural Nail System. Cephalomedullary Nail Surgical Technique STANDARD
 Zimmer Natural Nail System Cephalomedullary Nail Surgical Technique STANDARD Zimmer Natural Nail System Cephalomedullary Nail Surgical Technique - Standard 1 Zimmer Natural Nail System Cephalomedullary
Zimmer Natural Nail System Cephalomedullary Nail Surgical Technique STANDARD Zimmer Natural Nail System Cephalomedullary Nail Surgical Technique - Standard 1 Zimmer Natural Nail System Cephalomedullary
(English) NEXUS SPINE SPACER SYSTEM
 (English) NEXUS SPINE SPACER SYSTEM INDICATIONS FOR USE NEXUS Spine Spacer System, a GEO Structure is indicated for use in the thoraco-lumbar spine (i.e., T1 to L5) to replace a diseased vertebral body
(English) NEXUS SPINE SPACER SYSTEM INDICATIONS FOR USE NEXUS Spine Spacer System, a GEO Structure is indicated for use in the thoraco-lumbar spine (i.e., T1 to L5) to replace a diseased vertebral body
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF).
 Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra,
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra,
DRAFT. Triathlon TS Knee System. Surgical Protocol. Version 1
 DRAFT Version 1 Triathlon TS Knee System Table of Contents Acknowledgments..........................................................2 Tibial Canal Preparation....................................................4
DRAFT Version 1 Triathlon TS Knee System Table of Contents Acknowledgments..........................................................2 Tibial Canal Preparation....................................................4
visualized. The correct level is then identified again. With the use of a microscope and
 SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion
 Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
CLAW II. Polyaxial Compression Plating System SURGIC A L T ECHNIQUE
 CLAW II Polyaxial Compression Plating System SURGIC A L T ECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 2 3 3 3 Chapter 2 4 4 7 Chapter 3 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 9 11 11 11 Chapter 4 12 Introduction Intended Use Indications Contraindications
CLAW II Polyaxial Compression Plating System SURGIC A L T ECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 2 3 3 3 Chapter 2 4 4 7 Chapter 3 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 9 11 11 11 Chapter 4 12 Introduction Intended Use Indications Contraindications
How To Fix A Radial Head Plate
 Mayo Clinic CoNGRUENT RADIAL HEAD PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
Mayo Clinic CoNGRUENT RADIAL HEAD PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF).
 Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Lentur Cable System. Surgical Technique
 Lentur Cable System Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 System Design Features And Benefits... Page 2 Implants... Page 3 Instrumentation... Page 4 Surgical Technique... Page 5 Single Cable...
Lentur Cable System Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 System Design Features And Benefits... Page 2 Implants... Page 3 Instrumentation... Page 4 Surgical Technique... Page 5 Single Cable...
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
chronos BOne VOid Filler Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (b-tcp) bone graft substitute
 chronos BOne VOid Filler Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (b-tcp) bone graft substitute chronos Bone Void Filler Osteoconductive Resorbable Synthetic chronos Granules and Preforms are synthetic, porous, osteoconductive,
chronos BOne VOid Filler Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (b-tcp) bone graft substitute chronos Bone Void Filler Osteoconductive Resorbable Synthetic chronos Granules and Preforms are synthetic, porous, osteoconductive,
LCP Olecranon Plate. The anatomical fixation system with angular stability for olecranon and proximal ulnar fractures.
 LCP Olecranon Plate. The anatomical fixation system with angular stability for olecranon and proximal ulnar fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Olecranon Plate. The anatomical fixation system with angular stability for olecranon and proximal ulnar fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
BONE PRESERVATION STEM
 TRI-LOCK BONE PRESERVATION STEM Featuring GRIPTION Technology SURGICAL TECHNIQUE IMPLANT GEOMETRY Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK BONE PRESERVATION STEM Featuring GRIPTION Technology SURGICAL TECHNIQUE IMPLANT GEOMETRY Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
MatrixNEURO. The next generation cranial plating system.
 MatrixNEURO. The next generation cranial plating system. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table
MatrixNEURO. The next generation cranial plating system. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table
Expert HAN. Expert Hindfoot Arthrodesis Nail.
 Expert HAN. Expert Hindfoot Arthrodesis Nail. Surgical Technique Expert Nailing System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
Expert HAN. Expert Hindfoot Arthrodesis Nail. Surgical Technique Expert Nailing System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
TFN Titanium Trochanteric Fixation Nail System. For intramedullary fixation of proximal femur fractures.
 TFN Titanium Trochanteric Fixation Nail System. For intramedullary fixation of proximal femur fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and
TFN Titanium Trochanteric Fixation Nail System. For intramedullary fixation of proximal femur fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and
Surgical technique. End Cap for TEN. For axial stabilization and simultaneous protection of soft tissue.
 Surgical technique End Cap for TEN. For axial stabilization and simultaneous protection of soft tissue. Table of contents Indications and contraindications 3 Implants 4 Instruments 4 Preoperative planning
Surgical technique End Cap for TEN. For axial stabilization and simultaneous protection of soft tissue. Table of contents Indications and contraindications 3 Implants 4 Instruments 4 Preoperative planning
CORNERSTONE TISSUE PARALLEL TISSUE OFFERINGS
 CORNERSTONE TISSUE PARALLEL TISSUE OFFERINGS Precision Machined Tissue Medtronic Sofamor Danek established itself as a leader in the machined allograft tissue market with the introduction of the CORNERSTONE-SR
CORNERSTONE TISSUE PARALLEL TISSUE OFFERINGS Precision Machined Tissue Medtronic Sofamor Danek established itself as a leader in the machined allograft tissue market with the introduction of the CORNERSTONE-SR
Aesculap Spine activ L
 Aesculap Spine activ L Lumbar intervertebral disc prosthesis Operating technique 2 activ L Contents A) Pre-operative planning A.1 Size estimation 4 A.2 Patient positioning 4 B) Approach B.1 Marking the
Aesculap Spine activ L Lumbar intervertebral disc prosthesis Operating technique 2 activ L Contents A) Pre-operative planning A.1 Size estimation 4 A.2 Patient positioning 4 B) Approach B.1 Marking the
LCP Compact Foot/Compact Hand.
 LCP Compact Foot/Compact Hand. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table of contents Indications 2
LCP Compact Foot/Compact Hand. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table of contents Indications 2
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
 Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Expert ALFN. Adolescent Lateral Femoral Nail.
 Expert ALFN. Adolescent Lateral Femoral Nail. Surgical Technique EXPERT Nailing System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
Expert ALFN. Adolescent Lateral Femoral Nail. Surgical Technique EXPERT Nailing System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
SPINAL FUSION. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 SPINAL FUSION North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS SPINAL FUSION? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
SPINAL FUSION North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS SPINAL FUSION? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Knotilus TM. Anchor Instability Repair. Technique Guide
 Knotilus TM Anchor Instability Repair Technique Guide Instability Repair Using the Knotilus TM Anchor Introduction While the shoulder has more mobility than any other joint in the body, it is also the
Knotilus TM Anchor Instability Repair Technique Guide Instability Repair Using the Knotilus TM Anchor Introduction While the shoulder has more mobility than any other joint in the body, it is also the
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances?
 Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
VENTURE. Anterior Cervical Plate System Surgical Technique
 VENTURE Anterior Cervical Plate System Surgical Technique as described by: Regis Haid, MD Atlanta Brain and Spine Care Atlanta, Georgia Iain Kalfas, MD Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio Steve
VENTURE Anterior Cervical Plate System Surgical Technique as described by: Regis Haid, MD Atlanta Brain and Spine Care Atlanta, Georgia Iain Kalfas, MD Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio Steve
Aesculap Spine activ C
 Aesculap Spine activ C Cervical Disc Prosthesis Retain Mobility activ C Back to life enjoyed to the full I N N O V A Natural mobility Safety during surgery and in everyday life Stability in every situation
Aesculap Spine activ C Cervical Disc Prosthesis Retain Mobility activ C Back to life enjoyed to the full I N N O V A Natural mobility Safety during surgery and in everyday life Stability in every situation
Aesculap Veterinary Orthopaedics. Targon VET Interlocking Nail
 Aesculap Veterinary Orthopaedics Targon VET Interlocking Nail Flexibility Stability Dynamics The Targon VET is based on new, technology which reverses the known principles of interlocking nails. The rotation-stabilising
Aesculap Veterinary Orthopaedics Targon VET Interlocking Nail Flexibility Stability Dynamics The Targon VET is based on new, technology which reverses the known principles of interlocking nails. The rotation-stabilising
Small Battery Drive. For orthopaedic trauma applications.
 Small Battery Drive. For orthopaedic trauma applications. Ergonomic, lightweight design Compatible with a wide variety of attachments Variable speed trigger with instant reverse and oscillation Small
Small Battery Drive. For orthopaedic trauma applications. Ergonomic, lightweight design Compatible with a wide variety of attachments Variable speed trigger with instant reverse and oscillation Small
Technique Guide. Norian SRS Fast Set Putty. Calcium phosphate bone void filler.
 Technique Guide Norian SRS Fast Set Putty. Calcium phosphate bone void filler. TableofContents Introduction Norian SRS Fast Set Putty 2 Indications and Contraindications 3 Basic Science 4 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide Norian SRS Fast Set Putty. Calcium phosphate bone void filler. TableofContents Introduction Norian SRS Fast Set Putty 2 Indications and Contraindications 3 Basic Science 4 Surgical Technique
Value Analysis Brief MIS Lateral Approach to Interbody Fusion
 Value Analysis Brief MIS Lateral Approach to Interbody Fusion Methods This value analysis brief presents information on the clinical and economic benefits of the minimally invasive lateral approach to
Value Analysis Brief MIS Lateral Approach to Interbody Fusion Methods This value analysis brief presents information on the clinical and economic benefits of the minimally invasive lateral approach to
Cable System. For Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery.
 Cable System. For Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier
Cable System. For Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C. clinical study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C clinical study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C clinical study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause
Expert TN. Tibial Nail.
 Expert TN. Tibial Nail. Surgical Technique Expert Nailing System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier
Expert TN. Tibial Nail. Surgical Technique Expert Nailing System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier
Shoulder Restoration System
 Shoulder Restoration System PopLok Knotless Suture Anchor Simple, Secure, Versatile all-peek knotless anchor system for rotator cuff and instability repairs CO M M I T T ED TO I N N OVATI O N SURGICAL
Shoulder Restoration System PopLok Knotless Suture Anchor Simple, Secure, Versatile all-peek knotless anchor system for rotator cuff and instability repairs CO M M I T T ED TO I N N OVATI O N SURGICAL
Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Enhancing Stability and Increasing Range of Motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique
Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Enhancing Stability and Increasing Range of Motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique
COMPACT ELITE MAT CUTTER
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL MODEL 350-1 COMPACT ELITE MAT CUTTER INSTRUCTIONS AND OPERATION MANUAL 32in (81cm) mat cutting system with bevel & straight cutters, production stops and 20 in (51 cm) squaring bar.
INSTRUCTION MANUAL MODEL 350-1 COMPACT ELITE MAT CUTTER INSTRUCTIONS AND OPERATION MANUAL 32in (81cm) mat cutting system with bevel & straight cutters, production stops and 20 in (51 cm) squaring bar.
ZEPHIR Anterior Cervical Plate System
 SOFAMOR DANEK ZEPHIR Anterior Cervical Plate System Surgical Technique as described by: Richard Assaker, M.D. Lille University Hospital Lille, France Paul McCormick, M.D. Columbia Presbyterian Hospital
SOFAMOR DANEK ZEPHIR Anterior Cervical Plate System Surgical Technique as described by: Richard Assaker, M.D. Lille University Hospital Lille, France Paul McCormick, M.D. Columbia Presbyterian Hospital
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique
 TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External Fixation
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External Fixation
Trabecular Metal Femoral Component. Surgical Technique
 Trabecular Metal Femoral Component Surgical Technique INTRO Trabecular Metal Femoral Component Surgical Technique Introduction The Persona Trabecular Metal Femoral Component is designed to unite stable
Trabecular Metal Femoral Component Surgical Technique INTRO Trabecular Metal Femoral Component Surgical Technique Introduction The Persona Trabecular Metal Femoral Component is designed to unite stable
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Zimmer FuZion Instruments. Surgical Technique (Beta Version)
 Zimmer FuZion Surgical Technique (Beta Version) INTRO Surgical Technique Introduction Surgical goals during total knee arthroplasty (TKA) include establishment of normal leg alignment, secure implant fixation,
Zimmer FuZion Surgical Technique (Beta Version) INTRO Surgical Technique Introduction Surgical goals during total knee arthroplasty (TKA) include establishment of normal leg alignment, secure implant fixation,
INSTALLATION MANUAL. Installation Instructions
 INSTALLATION MANUAL Power-Pole Signature Series Shallow Water Anchor Installation Instructions CAUTION: Read this instruction manual carefully. Become familiar with the controls and know how to operate
INSTALLATION MANUAL Power-Pole Signature Series Shallow Water Anchor Installation Instructions CAUTION: Read this instruction manual carefully. Become familiar with the controls and know how to operate
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System. A comprehensive plating system to address a variety of fracture patterns.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System. A comprehensive plating system to address a variety of fracture patterns. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System. A comprehensive plating system to address a variety of fracture patterns. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System 2 AO Principles
DARCO MRS. Locked Plating System for Reconstructive Rearfoot Surgery
 DARCO MRS Locked Plating System for Reconstructive Rearfoot Surgery DARCO MRS Locked plating system for reconstructive rearfoot surgery System Basics The DARCO MRS plating system for the rearfoot has been
DARCO MRS Locked Plating System for Reconstructive Rearfoot Surgery DARCO MRS Locked plating system for reconstructive rearfoot surgery System Basics The DARCO MRS plating system for the rearfoot has been
Battery Power Line. Battery-driven power tool system for orthopaedics and traumatology.
 Battery Power Line. Battery-driven power tool system for orthopaedics and traumatology. High performance Excellent torque for drilling and reaming Precise cutting with Synthes saw blades Battery Power
Battery Power Line. Battery-driven power tool system for orthopaedics and traumatology. High performance Excellent torque for drilling and reaming Precise cutting with Synthes saw blades Battery Power
MEDACTA UNCONSTRAINED SCREW TECHNOLOGY. Surgical Technique. Hip Knee Spine Navigation
 .U.S.T. MEDACTA UNCONSTRAINED SCREW TECHNOLOGY Hip Knee Spine Navigation M.U.S.T. Hip Knee Spine Navigation CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale distrribution and use by or on the order
.U.S.T. MEDACTA UNCONSTRAINED SCREW TECHNOLOGY Hip Knee Spine Navigation M.U.S.T. Hip Knee Spine Navigation CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale distrribution and use by or on the order
Patient Guide to Neck Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
Speed-Mat Rectangle Cutter
 Speed-Mat Rectangle Cutter 1 Honeycomb baseboard. 2 Left hold down. 14 3 Bottom hold down. 4 4 Left / right rule. 8 5 8 5 Left / right rule pointer. 1 6 Top / bottom rule. 7 Top / bottom rule pointer.
Speed-Mat Rectangle Cutter 1 Honeycomb baseboard. 2 Left hold down. 14 3 Bottom hold down. 4 4 Left / right rule. 8 5 8 5 Left / right rule pointer. 1 6 Top / bottom rule. 7 Top / bottom rule pointer.
Navico-Northstar 2kW JRC Radar Package, Scanner Cable Removal and Replacement
 Navico-Northstar 2kW JRC Radar Package, Scanner Cable Removal and Replacement This work instruction describes the methods and means for which to remove and reinstall optional scanner cable configurations
Navico-Northstar 2kW JRC Radar Package, Scanner Cable Removal and Replacement This work instruction describes the methods and means for which to remove and reinstall optional scanner cable configurations
Cable Drum Installation
 20 Cable Drum Installation COUNTERBALANCE None Shake the TorqueMaster spring tube gently to extend the winding shafts out about 5" on each side. For single spring applications, there will be no left hand
20 Cable Drum Installation COUNTERBALANCE None Shake the TorqueMaster spring tube gently to extend the winding shafts out about 5" on each side. For single spring applications, there will be no left hand
Integra. Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
A Patient s Guide to the Disorders of the Cervical and Upper Thoracic Spine
 A Patient s Guide to the Disorders of the Cervical and Upper Thoracic Spine General Anatomy of the Spine The spine can be divided into four regions based on vertebral shape and sagittal plane curve.» CERVICAL:
A Patient s Guide to the Disorders of the Cervical and Upper Thoracic Spine General Anatomy of the Spine The spine can be divided into four regions based on vertebral shape and sagittal plane curve.» CERVICAL:
SALVATION. Fusion Bolts and Beams SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 SALVATION Fusion Bolts and Beams SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 4 Introduction Chapter 2 4 Intended Use Chapter 3 4 Device Description 4 Fusion Beams 5 Fusion Bolts Chapter 4 5 Preoperative Planning
SALVATION Fusion Bolts and Beams SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 4 Introduction Chapter 2 4 Intended Use Chapter 3 4 Device Description 4 Fusion Beams 5 Fusion Bolts Chapter 4 5 Preoperative Planning
Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
coligne treatment technology
 coligne treatment technology coligne a strategy in spine Leadership begins before the patient enters the surgical theater, among the spine care professionals forming the coalliance. This may be a small
coligne treatment technology coligne a strategy in spine Leadership begins before the patient enters the surgical theater, among the spine care professionals forming the coalliance. This may be a small
Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion A Minimally Invasive Approach to Spinal Stabilization
 APPROVED IRN10389-1.1-04 Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion A Minimally Invasive Approach to Spinal Stabilization Because it involves accessing the spine through the patient s side, the Direct Lateral approach
APPROVED IRN10389-1.1-04 Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion A Minimally Invasive Approach to Spinal Stabilization Because it involves accessing the spine through the patient s side, the Direct Lateral approach
Wrist and Hand. Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Carpal bones
 Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Implants in your Laboratory: Abutment Design
 1/2 point CDT documented scientific credit. See Page 41. Implants in your Laboratory: Abutment Design By Leon Hermanides, CDT A patient s anatomical limitations have the greatest predictive value for successful
1/2 point CDT documented scientific credit. See Page 41. Implants in your Laboratory: Abutment Design By Leon Hermanides, CDT A patient s anatomical limitations have the greatest predictive value for successful
