MESOPOTAMIAN ARCHITECTURE The land between two rivers
|
|
|
- Diane Cook
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MESOPOTAMIAN ARCHITECTURE The land between two rivers (Gk mesos = middle + potamos = river) The Two (2) Rivers: 1. Euphrates 2. Tigris The river comprises the land of Sumer, Akkad and occupied successively by the Sumerians, Babylonians, Assyrians and Persians. The world's oldest civilization, Mesopotamia, was built by the Sumerians on the fertile land between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates, 5000 years ago. The Sumerians invented cuneiform characters, and built city states. This is the ancient city of Ur, built around 2000 BC, by Ur Nammu, the founder of the third Ur dynasty. Cuneiform - the oldest writing known to mankind; An ancient wedge-shaped script used in Mesopotamia and Persia Ur - An ancient city of Sumer located on a former channel of the Euphrates River (Birthplace of Abraham) Literally means very old The cult center of Nannar/Sin (moon god). The Ziggurat of Ur (c BCE) E. KISH. NU GAL ( House of Thirty, The Great Seed ) Dedicated to Nannar/Sin o Already very old, remodeled by Ur-Nammu (The Joy of Ur), first ruler of Dynasty III. FERTILE CRESENT An agricultural region arching from the Eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea in the west to Iraq and in: the location of humankind s earliest cultures. A. Massive architecture Mud brick construction set with clay mortar Heavy walls articulated by pilasters and recesses and faced with glazed bricks Columns were rare Small and infrequent windows
2 B. Actuated architecture system Doorways were spanned by double semi circular arches. C. Buildings were designed for both internal and external effects. D. Roofs were burnt brick vault. E. Mouldings were rare. F. Temples: Principal Building type Tripartite Plan o The standard and basic layout of Mesopotamian cult structures. o Originally employed in ziggurats of Sumer MESOPOTAMIAN ART AND ARCHITECTURE Mesopotamian art and architecture were produced by the diverse peoples who occupied the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers from about 3500 to 539 BC. The earliest civilization of MESOPOTAMIA was created by Sumerianspeaking people, and although their Sumerian language was preserved, the original inhabitants eventually either died out or were absorbed into the population of SEMITES who moved into this area at various periods in history. Elaboration of irrigation technology and cultivation of the date palm and barley made possible the growth of cities in the south. With changing patterns of land use and cultivation, the center of Mesopotamian civilization moved slowly north from Sumer in southernmost Babylonia to Akkad in northern Babylonia and finally to Assyria in the far north. Sumer - An ancient region in southern Mesopotamia, where a number of independent cities and city-states were established as early as 6000 BCE. Major cities and archaeological sites: o Eridu o Uruk o Ur o Lagash o Kish o Nippur The land was the first known and fully documented civilization sprang up after the Deluge As did the architecture, Mesopotamian art had two major preoccupations--man's relationship to the gods and conflict on either a real or mythological plane. Although art was primarily created for temple or king, a number of small objects were also produced, such as cylinder seals and clay plaques with mythological scenes. These objects were probably owned to a great extent by the population at large. Early Mesopotamian art was usually small in scale, because the south was poor in natural resources, and materials like stone and metals had to be imported. Later, Assyrian palaces were decorated with large stone-relief sculptures and immense gate guardian figures of animal or monstrous form.
3 PROTOLITERATE PERIOD (c BC) The first period of Mesopotamian civilization is the Protoliterate. This phase is most clearly seen at the southern city of URUK and indeed may have arisen there. However, Uruk's architecture is based on earlier forms at ERIDU, and during the Protoliterate period several southern cities--and even some cities in northern Mesopotamia and Syria--shared cultural traits with Uruk. Although there is little historical evidence, this cultural network was probably based on trade. FIRST PRE-DELUVIAL SETTLEMENTS/CITIES 1. E.RI.DU (House in a Faraway Built) 2. BAD.TIBIRA (Bright Place Where the Ores are Made Final) 3. LA.RA.AK (Seeing the Bright Glow) 4. SIPPAR (Bird City) 5. SHU.RUP.PAK (The Place of the Utmost Being) Uruk is the largest Sumerian cities. More than 9 km (6 miles) perimeter Archaeological findings o First colored pottery baked in a kiln. o Evidence of the first use of potter s wheel. o Oldest limestone pavement construction. o First inscribed texts. o First cylinder seals. o Other sites bear evidence of the emergence of the metal age. First ziggurat, on the top of which stood a white temple and red temple Southern Mesopotamian cities were built around temples, and the main temple in each city was dedicated to the chief god or goddess of that city. The White Temple on the Anu Ziggurat at Uruk is a characteristic example of Protoliterate temple architecture. The whitewashed outer walls of this small rectangular mudbrick structure are formed into the niches and buttresses that are a typical feature of all Mesopotamian temples. The temple stands on a ZIGGURAT, a tall artificial mountain formed from the remains of temples built and rebuilt on this site for centuries. The Protoliterate art at Uruk, largely religious in theme, exists principally in the form of temple furnishings. Typical objects of the period include the so-called cult vase of Uruk, a 1-m-high (3-ft) alabaster vessel decorated with scenes of offerings brought to the temple (Iraq Museum, Baghdad) and a beautiful stone head, 22 cm high (8.6 in), of a woman perhaps representing the fertility goddess Inanna (Iraq Museum). This image had probably been set into a temple wall as part of a cult relief made of various materials. The face is softly and realistically modeled; the white stone must have looked like flesh when surrounded by its original colorful inlays for the eyes, eyebrows, and headdress. EARLY DYNASTIC PERIOD (c BC) During the Early Dynastic period, independent city-states flourished in southern Mesopotamia, in MARI on the middle Euphrates River, and as far north as the city of Assur, as well as the Syrian city known today as Tell Khuera. The southern cities were the Sumerian heartland, while Semitic-speaking peoples inhabited the northern city-states. Trade networks united these distant places, and toward the end of the period kings began to conquer and rule over several city-states.
4 POST DELUVIAL CITIES ERIDU 3 principal temples 1. The E.EN.GUR.RA o Also known as the Temple of Anu. - No less than 18 strata or district phases were discovered. - Cones of baked clay were set in mud plaster over many of the wall faces. - Traditions maintained that the Great Gods (Anunnakis) themselves had fashioned its parts. - Built by the Annunakis for the celestial visit and for the honor of Anu. 2. The BIT-RESH ( Main Temple ), also a stage tower. 3. The IRIGAL temple dedicated to In.Anna/ Ishtar. A high pyramidal staged tower, of which the angles were oriented to cardinal points, which formed an important element in ancient Mesopotamian temple complexes. The number of stage rises from one to seven. The E.ANNA (House of Anu) Ziggurat the White Temple (4000 BCE) Believed to be the predecessor of the ziggurat. ZIGGURAT A high pyramidal staged tower, of which the angles were oriented to cardinal points, which formed an important element in ancient Mesopotamian temple complexes. The number of stage rises from one to seven. The E.ANNA (House of Anu) Ziggurat the White Temple (4000 BCE) Believed to be the predecessor of the ziggurat.
5 Architecture HISTORY OF ARCHITECTURE 1.0 ANCIENT CITIES AND CIVILIZATIONS In the flourishing cities of this period, temples were numerous. The exact form might vary because of local traditions and the particular shape of the site, but most temples had a rectangular CELLA (the inner sacred chamber), with some sort of indirect access to the statue of the god that stood within it. For large and important temples of this period, an unusual form appeared which has so far been discovered at three cities--lagash, Khafaje, and Al 'Ubaid. This was the temple oval, an immense oval platform on which a temple was constructed, with a second outer oval wall surrounding the entire temple complex. Large palaces have been excavated at KISH and Mari, evidence of the rising power of local city rulers during the Early Dynastic period. Similarly, the city walls of Uruk testify to the growing need to fortify cities in this period of increasing warfare. The Palace of Sargon (Shuru-kin), Khorsabad The citadel: o Covered 23 acres Three main parts: o A group of 3 large and 3 small temples on the left. o Administrative offices and service quarters on the right. o Private and residential apartments and state chambers behind. The main portal: Flanked by great towers Guarded by LAMASSUS Approached from a broad ramp The Ziggurat of Khorsabad 7 stages Square in volume o 45 m (148 ft) both in height and base Ascended by winding ramp o 1.80 m (6 ft) wide Lamassu The monumental stone sculptures of human-headed, winged bulls, lions that guarded the entrances to Mesopotamian palaces and temples. Some refer these as stone demons. The kings of Ur continued to express a similar tone in their attitudes toward the gods. Much architecture of the city of Ur during the Neo-Sumerian period has been excavated, and it is apparent that although these rulers had great political power, their architectural efforts were largely devoted to religious expression. At the center of Ur was the religious precinct, which contained a large and elaborate ziggurat to the moon god Nannar (the chief deity of Ur), a smaller temple to Nannar's wife, and a still smaller royal palace. The ziggurat of Nannar was built in stages and was faced with a niched surface of baked
6 brick. A temple to the god, which could be reached by three ramps, was placed atop the ziggurat. A smaller temple was located at the ziggurat's base. Other such ziggurats were built in many cities throughout the empire. A characteristic form of temple used during this period was the so-called broad cella--a broad and shallow room approached through a series of entrance halls and courts. In this temple the statue of the god, or in some cases the deified ruler, could be glimpsed from afar. The statue was kept separate from the worshiper not by the layout of the temple as in earlier times, but by the many axially arranged spaces that separated the worshiper from his god. Compared to the architectural remains, Neo-Sumerian art is scarce. Those pieces which have been preserved are religious and conservative, yet exquisitely crafted, as is the art of Gudea. The designs of cylinder seals are rigidly composed, with a similar preponderance of religious themes. ISIN-LARSA AND OLD BABYLONIAN PERIODS (c.2006-c.1600 BC) In 2000 BC the rulers of Ur fell before invading AMORITES, a new wave of Semitic-speaking people who eventually were absorbed into the city-states of Babylonia. From then on, Semitic languages were to dominate Mesopotamian life. Early in the 2d millennium BC a number of independent city-states flourished, but an empire of small proportions was formed by King HAMMURABI of Babylon in the 18th century BC and was maintained by his successors. The architectural evidence of these two periods is not very extensive. Nothing is known of Babylon at this time, and the most impressive building yet excavated is the palace at Mari, a powerful trading center before it fell (c.1760 BC) to Hammurabi. The vast palace, with its complex ground plan, was an administrative, political, and religious center for the ruler of the city-state. Large wall paintings here of human figures and mythological animals are rare examples of the monumental art of this period. The best-known piece of art of the Old Babylonian period is the stone stele inscribed with the law code of Hammurabi (Louvre, Paris). At the top of this 2.3-m-high (90.5-in) stele Hammurabi is shown worshiping Shamash, the god of justice, who handed down the laws (inscribed beneath this relief sculpture) to the king who would enforce them. The images of the pious king and the powerful god are based on Neo-Sumerian prototypes, and the use of a picture to explain and justify the written law illustrates the close interrelationship between art and writing in ancient Mesopotamia. Cylinder seals of these periods show much the same themes as in the Neo-Sumerian period. NEO-ASSYRIAN PERIOD (c BC) little outstanding art or architecture was produced during the Middle Babylonian and Middle Assyrian periods of the second half of the 2d millennium BC. However, the succeeding Assyrian Empire, formed in the first half of the 1st millennium BC, became the most extensive Mesopotamian kingdom, and its material culture represents the crowning glory of Mesopotamian art and architecture. Warfare and trade were the two main concerns of Assyrian kings, and their art and architecture were cleverly designed to further these two concerns. Assyrian cities such as Calah (NIMRUD), Nineveh, and Dur Sharrukin (KHORSABAD) were military fortresses. The latter, built by King Sargon II (r BC), is a splendid example of Assyrian city architecture. The city was surrounded by heavy walls with powerful gates. Guarding the main gate was a small fortress built over the city wall, and the main citadel rose over the wall at the rear of the city. The inner area was perhaps filled with tents or
7 other light structures, because no architectural remains have been found there. The main citadel was itself a small walled city with palaces and temples. The most important building in the city was the huge royal palace, built at the very back of the inner citadel. Within the palace were public rooms and courtyards, private apartments for the king, and an entire temple complex with a freestanding ziggurat. Unlike southern cities, which were built around central temple areas, Assyrian cities had a peripheral emphasis, with the most important structure being the royal palace. Also unlike that of the south, Assyrian architecture could make use of local stone for orthostats, monumental vertical slabs that lined walls and gates. Notwithstanding these differences in architectural style and material, both northern and southern cities were planned to make it difficult for invaders to penetrate the main civic center, because warfare was a constant threat in Mesopotamian life. Assyrian art was largely architectural decoration in the form of relief sculptures on the walls of palaces and of huge guardian figures at gate entrances. This sculpture was meant to impress and intimidate people with the power and sanctity of the Assyrian king. The relief sculptures depict the endless battles of the Assyrian armies; inevitably, the king is shown triumphant over everyone who had dared to oppose the mighty empire. Sometimes the king is portrayed in a ritual stressing his religious powers, or else he is shown accepting the tribute brought him by the many peoples of the empire. The king might also be shown as a skillful hunter who could dispatch dangerous wild animals like lions and bulls as easily as he could conquer his enemies. A remarkable series of sculptures (now preserved in the British Museum, London) was discovered in the palace of King Ashurbanipal (r BC) at Nineveh. This king was particularly fond of sports, and the magnificent reliefs show many aspects of lion hunts as well as hunts of less dangerous animals. All Assyrian relief sculptures reveal a fascination with detail, with history, and with combat, an enduring theme throughout the history of Mesopotamian art. Cylinder seals of this period also frequently depict combat, often between a superhuman hero and a monster. NEO-BABYLONIAN PERIOD ( BC) In 609 BC the Assyrian Empire was conquered by an army of Medes and Babylonians, and the last Mesopotamian culture was that of the short-lived Neo-Babylonian Empire. The city of Babylon during this period displayed a combination of northern and southern architectural traditions. The city was built around a huge temple complex sacred to MARDUK, the chief Babylonian god; here stood the traditional temples as well as the ziggurat known in the Bible as the Tower of BABEL. The royal palace was built out over the city wall, perhaps in imitation of Assyrian palace architecture, although its rambling layout and hanging gardens, or planted terraces, were stylistically far more southern than northern. Also typically southern was the wall decoration used in the city. Instead of the grim and powerful themes of Assyrian relief sculptures, Babylon was adorned with colorful glazed bricks on the wall of the massive ISHTAR Gate on the main road or procession way, and on the facade of the throne room in the royal palace. These glazed brick panels, usually in the form of molded reliefs of lions, bulls, and strange monsters, gave an elegant and sophisticated air to the city. Proud of their millennia of historic tradition, the rulers of Babylon chose to emphasize beauty rather than power in their art.
8 The Babylonian Empire fell to the Persians in 539 BC, and thus the final Mesopotamian kingdom was supplanted as the center of Near Eastern civilization. However, the traditions of Mesopotamian art and architecture were so rich and enduring that they enhanced the cultures of surrounding peoples, left their imprint in the Bible, and inspired many aspects of Greek art and architecture ASSYRIAN ARCHITECTURE Information provided by: Assyria (Gen.10:11) Mesopotamian architecture developed by Assyrian king emperors. Cities: o Fortified with crenellated and battlemented towers. Palaces: o Large and emphasizing the central role of the monarchy. o Took precedence over religious buildings. Externals: o Ornamented in carved relief or polychrome glazed bricks (originated by the Assyrians). o Use of high plinths or dadoes of great stone slabs placed on edged and usually carved with relief sculpture. Employment of the brick barrel-vaulting. Columns: o Filled the interior courts. o Slender with high molded bases, fluted shafts, and capital of recurring vertical scroll. o Widely spaced to support timber and clay roofs. Openings: o Doorways: - With semicircular arches - With glazed bricks around the circumference Windows: o Square-headed and high up in the wall. THE CITY OF NINEVEH Capital of Assyrian empire, built by Sargon s son Sennacherib ( BC). Contained the following structures: o o The Palace of Sennacherib (The South-West Palace) The Palace Without a Rival - Undergone a massive labor in securing the foundation. - Platform on the mound formed by successive levels of earlier occupation Further developed by successors (Esarhaddon and Ashurbanipal) Finally fell in 612 BC after a prolonged assault by the Medes and the Babylonians, and was never to rise again. THE CITY OF ASHUR The ancient and religious center of the Assyrian state Dedicated to Ashur, Assyrian s national god Always important wherever the administrative capital might be built on high rocky headland above the Tigris. Surrounded by a strong defensive wall (2 nd mil. BCE) Contained: o The temple of In.Anna/ Ishtar - First shrine (early dynastic period)
9 o o HISTORY OF ARCHITECTURE 1.0 ANCIENT CITIES AND CIVILIZATIONS The ziggurat temple of Ashur The double temple of Anu and Adad - With twin ziggurats THE CITY OF NIMRUD Modern Calah Restored and enlarged as capital by Ashurnasirpal II (c BCE). The city layout with ziggurat complex, throne room, administrative block and residential wing, all enclosing large public court, became standard. The Temple of Nabu (Ezida, The God of Writing), Nimrud Built toward the end of 9C BCE. A double sanctuary in the main wing for the deity in his consort. A well located in front of the sanctuary o A source of water in mixing the finest clay used for the tablets for writing by the scribes in cuneiform. A double sanctuary in the north wing o Used for the New Year festival each spring. BABYLONIAN ARCHITECTURE ( BCE) Characterized by: o Mud brick walls articulated by pilasters and faced with glazed brick. THE CITY OF BABYLON Contained the Tower of Babel (the famed Hanging Garden of Semiramis) and the Ishtar Gate. o Dominated the region in 6 BC and was heavily fortified.
10 The Ishtar Gate This strong gatehouse is adorned with colored bricks showing animal symbols of Babylonian gods on a blue background. Reliefs of bulls and dragons Glazed bricks HITTITE ARCHITECTURE ( BCE) Found in northern Syria and Asia Minor o Centered in Lake Van Characterized by: o Fortifications constructed with stone masonry and gateways ornamented with a sculpture. o Massive fortifications Lion s Gate, Boghazkoy: Outer Side (c.1360 BCE) Yazilikaya Rock Cut chamber, Hattusha Map of Hatussas PERSIAN ARCHITECTURE ( BCE) Developed under the kings who ruled ancient Persia during the Achaemenid Dynasty. Characterized by: o A synthesis of architectural elements from surrounding countries such as Assyria, Egypt, and Greece. The Palace of Persepolis Begun in 518 BCE by Darius Mostly executed by Xerxes ( BCE) Finished by Artaxerxes
Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and
 Mesopotamia Review Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. This curving strip
Mesopotamia Review Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. This curving strip
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia
 Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period of almost 1800 years. This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period of almost 1800 years. This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period
CUNEIFORM INSCRIPTIONS IN THE LOOTED IRAQ MUSEUM
 Originally Printed in: Iraq Double Issue: Volume 6, Nos. 1 & 2 Art Loss In Iraq CUNEIFORM INSCRIPTIONS IN THE LOOTED IRAQ MUSEUM by ROBERT BIGGS Robert Biggs, Ph. D., is Professor of Assyriology at the
Originally Printed in: Iraq Double Issue: Volume 6, Nos. 1 & 2 Art Loss In Iraq CUNEIFORM INSCRIPTIONS IN THE LOOTED IRAQ MUSEUM by ROBERT BIGGS Robert Biggs, Ph. D., is Professor of Assyriology at the
7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR?
 7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR? In this three-part video David Christian explains how the rise of agriculture led to the formation of the world s first large-scale civilizations. Fueled by
7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR? In this three-part video David Christian explains how the rise of agriculture led to the formation of the world s first large-scale civilizations. Fueled by
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L
 7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the soil was rich and easy to farm. It is there that the world
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the soil was rich and easy to farm. It is there that the world
Mesopotamia. The 'Ram in a Thicket' From Ur, southern Iraq, 2600-2400 BC. Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2
 The 'Ram in a Thicket' From Ur, southern Iraq, 2600-2400 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities
The 'Ram in a Thicket' From Ur, southern Iraq, 2600-2400 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities
Lecture 9 Ancient Near East Cultures: Sumeria, Babylonia, Judea
 1 Lecture 9 Ancient Near East Cultures: Sumeria, Babylonia, Judea The ancient Near East cultures, known as Mesopotamian civilization are largely based on Semitic populations that existed between the Tigris
1 Lecture 9 Ancient Near East Cultures: Sumeria, Babylonia, Judea The ancient Near East cultures, known as Mesopotamian civilization are largely based on Semitic populations that existed between the Tigris
Eleanor Guralnick. oi.uchicago.edu. khorsabad Relief fragment project. Figure 2. Falling warrior. Room 13 or 14. OIM A70605
 KHORSABAD Relief Fragment PROJECT Eleanor Guralnick For more than three summers progress has been made on uncrating, cleaning, conserving, photographing, registering, and cataloging the hundreds of fragment
KHORSABAD Relief Fragment PROJECT Eleanor Guralnick For more than three summers progress has been made on uncrating, cleaning, conserving, photographing, registering, and cataloging the hundreds of fragment
Ancient Greek Arts and Architecture
 Ancient Greek Arts and Architecture Ancient Greek Architecture The earliest buildings built in Greece in the New Stone Age are small houses or huts with wooden walls around them for protection. Later bigger
Ancient Greek Arts and Architecture Ancient Greek Architecture The earliest buildings built in Greece in the New Stone Age are small houses or huts with wooden walls around them for protection. Later bigger
The Rise of Civilizations
 Page 1 of 6 The Rise of Civilizations Thousands of years ago, several societies in different parts of the world changed from hunting and gathering to farming. Some began to produce surpluses of food. Those
Page 1 of 6 The Rise of Civilizations Thousands of years ago, several societies in different parts of the world changed from hunting and gathering to farming. Some began to produce surpluses of food. Those
AP World History Class Notes, Bentley Brief Edition Ch 1 The Foundations of Complex Societies September 14, 2010
 This first chapter of Traditions and Encounters sets the stage for the drama of world history by tracing the development of humans from their earliest appearance on earth through the rise of important
This first chapter of Traditions and Encounters sets the stage for the drama of world history by tracing the development of humans from their earliest appearance on earth through the rise of important
ARCHAEO-PRO SAMPLE QUESTION SHEET
 ARCHAEO-PRO SAMPLE QUESTION SHEET 1. Case 11 The Royal Graves of Ur What animal is mounted on the top of the rein ring? How old are the Royal Cemetery burials? Why do you think the excavator believed these
ARCHAEO-PRO SAMPLE QUESTION SHEET 1. Case 11 The Royal Graves of Ur What animal is mounted on the top of the rein ring? How old are the Royal Cemetery burials? Why do you think the excavator believed these
Ancient Greece: the Nereid Tomb
 Ancient Greece: the Nereid Tomb Relief from the Nereid Tomb showing warriors storming a city Lycia, Turkey 390-380 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information
Ancient Greece: the Nereid Tomb Relief from the Nereid Tomb showing warriors storming a city Lycia, Turkey 390-380 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information
The Greeks 500 300 BC. Greek City States Early Greek sates called polis Usually built around a market or fortified hill top called an acropolis
 The Greeks 500 300 BC Greek City States Early Greek sates called polis Usually built around a market or fortified hill top called an acropolis Greek City-State Political Monarch - ruled by a single person
The Greeks 500 300 BC Greek City States Early Greek sates called polis Usually built around a market or fortified hill top called an acropolis Greek City-State Political Monarch - ruled by a single person
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao
 Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
CH10 Practice Test 2015
 Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
 Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet
 Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet Your group will research Ancient Egyptian culture focusing on the Government of Ancient Egypt. Assign jobs to group members. Everyone must have a job. Research
Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet Your group will research Ancient Egyptian culture focusing on the Government of Ancient Egypt. Assign jobs to group members. Everyone must have a job. Research
Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Lighthouse of Alexandria. The Colossus of Rhodes. Hanging Gardens of Babylon. www.montessoriforeveryone.
 Seven Wonders of the Ancient World Lighthouse of Alexandria The Colossus of Rhodes Hanging Gardens of Babylon Please note: this PDF is copyrighted by Montessori for Everyone and is free for personal use
Seven Wonders of the Ancient World Lighthouse of Alexandria The Colossus of Rhodes Hanging Gardens of Babylon Please note: this PDF is copyrighted by Montessori for Everyone and is free for personal use
KINGS AND EVENTS OF THE BABYLONIAN, PERSIAN, AND GREEK DYNASTIES
 KINGS AND EVENTS OF THE BABYLONIAN, PERSIAN, AND GREEK DYNASTIES 612 B.C. Nineveh falls to neo-babylonian army (Nebuchadnezzar) 608 Pharaoh Necho II marched to Carchemesh to halt expansion of neo-babylonian
KINGS AND EVENTS OF THE BABYLONIAN, PERSIAN, AND GREEK DYNASTIES 612 B.C. Nineveh falls to neo-babylonian army (Nebuchadnezzar) 608 Pharaoh Necho II marched to Carchemesh to halt expansion of neo-babylonian
Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK #
 Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK # H0MEWORK # I THE RIVER NILE The river Nile is one of the world's great rivers. It begins its long journey in Africa, as two
Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK # H0MEWORK # I THE RIVER NILE The river Nile is one of the world's great rivers. It begins its long journey in Africa, as two
Ancient India Lesson 2
 Name: Date: Ancient India Lesson 2 Early Indian Civilization Over 1,000 miles separate the Indus River valley from Iraq, the region once known as Mesopotamia. This distance did not keep people from traveling
Name: Date: Ancient India Lesson 2 Early Indian Civilization Over 1,000 miles separate the Indus River valley from Iraq, the region once known as Mesopotamia. This distance did not keep people from traveling
PERSIAN WARRIORS DEFEATED
 PERSIAN WARRIORS DEFEATED Questions to ask before reading the story: What is a counter offensive move? How is it different from a defensive move? What is the meaning of the statement The surest defense
PERSIAN WARRIORS DEFEATED Questions to ask before reading the story: What is a counter offensive move? How is it different from a defensive move? What is the meaning of the statement The surest defense
Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack
 Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack This pack includes the following lessons: Locating Egypt The River Nile Archeology Hieroglyphics Pharaohs Every effort has been made to seek permission for the
Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack This pack includes the following lessons: Locating Egypt The River Nile Archeology Hieroglyphics Pharaohs Every effort has been made to seek permission for the
Ancient Greece: Teacher s Guide
 Ancient Greece: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Curriculum Focus: Ancient History Lesson Duration: 2 or 3 class periods Program Description Warring city-states flourished into centers of culture 2,500
Ancient Greece: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Curriculum Focus: Ancient History Lesson Duration: 2 or 3 class periods Program Description Warring city-states flourished into centers of culture 2,500
Figure 10.1 Totally collapsed mosque at Kavakl district of Gölcük
 10 DAMAGE TO DOMES, MINARETS AND HISTORICAL STRUCTURES Most of historical structures existing in the earthquake-affected area are in Istanbul. Istanbul is situated on two continents; Asia and Europe. Istanbul
10 DAMAGE TO DOMES, MINARETS AND HISTORICAL STRUCTURES Most of historical structures existing in the earthquake-affected area are in Istanbul. Istanbul is situated on two continents; Asia and Europe. Istanbul
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties
 Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Kingship in the Hebrew Bible By Cian Power
 Kingship in the Hebrew Bible By Cian Power Understanding kingship is essential when reading the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament. Most of its authors knew no other political system and it influenced their work
Kingship in the Hebrew Bible By Cian Power Understanding kingship is essential when reading the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament. Most of its authors knew no other political system and it influenced their work
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Lesson title: Reflections of Ancient Greece Grade level: 5-6, with an adaptation for older students Subject area: Ancient History Duration: Two or three class periods Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
Lesson title: Reflections of Ancient Greece Grade level: 5-6, with an adaptation for older students Subject area: Ancient History Duration: Two or three class periods Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
a. farmers b. merchants c. priests d. warriors a. the Maya b. the Moche c. the Nazca a. making pottery b. making textiles c.
 Ancient America Chapter 9 Test Form A Part 1: Multiple Choice Choose the letter of the best answer. (4 points each) 1. What geographic feature is common in Mesoamerica s tropical lowlands? a. jungles b.
Ancient America Chapter 9 Test Form A Part 1: Multiple Choice Choose the letter of the best answer. (4 points each) 1. What geographic feature is common in Mesoamerica s tropical lowlands? a. jungles b.
Egypt. The Old Kingdom
 Egypt The Old Kingdom Vocabulary: Narmer (Menes)- King that united Upper and Lower Egypt Old Kingdom Began around 2600BC, rise of Egyptian cities as centers for religion and government Artisans- someone
Egypt The Old Kingdom Vocabulary: Narmer (Menes)- King that united Upper and Lower Egypt Old Kingdom Began around 2600BC, rise of Egyptian cities as centers for religion and government Artisans- someone
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE.
 SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 17 Egypt: Naqada III and Early Dynastic Copyright Bruce Owen 2009
 Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 17 Egypt: Naqada III and Early Dynastic Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Naqada III (roughly 3200-3050 BC): the last century of the Predynastic period Contemporary
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 17 Egypt: Naqada III and Early Dynastic Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Naqada III (roughly 3200-3050 BC): the last century of the Predynastic period Contemporary
Subject Ceramics II Calendar: 1 st 9 weeks Timeframe: Level: Secondary
 Subject Ceramics II Calendar: 1 st 9 weeks Timeframe: Level: Secondary Identify basic properties of clay Experiment with different styles of wedging and kneading. Discuss how ancient potters found, formed,
Subject Ceramics II Calendar: 1 st 9 weeks Timeframe: Level: Secondary Identify basic properties of clay Experiment with different styles of wedging and kneading. Discuss how ancient potters found, formed,
Lions and Warriors: Mycenaean Greece Lecture 12
 Lions and Warriors: Mycenaean Greece Lecture 12 Greece Anatolia (Turkey) CYCLADES ISLANDS CRETE Europa and the Bull. According to the Greek myth, Zeus, disguised as a bull, kidnapped the beautiful young
Lions and Warriors: Mycenaean Greece Lecture 12 Greece Anatolia (Turkey) CYCLADES ISLANDS CRETE Europa and the Bull. According to the Greek myth, Zeus, disguised as a bull, kidnapped the beautiful young
Pre-reading class discussion about Islamic Culture and Islamic Art 1
 Contents: PRE-VISIT ACTIVITIES Pre-reading class discussion about Islamic Culture and Islamic Art 1 Reading Islamic Art in Egypt / Arabic Calligraphy 2 Arabesques / Geometrical designs 3 VISIT ACTIVITIES
Contents: PRE-VISIT ACTIVITIES Pre-reading class discussion about Islamic Culture and Islamic Art 1 Reading Islamic Art in Egypt / Arabic Calligraphy 2 Arabesques / Geometrical designs 3 VISIT ACTIVITIES
Lesson 6: The Great City of Babylon Today
 Lesson 6: The Great City of Babylon Today Frightened by the torture that she experiences, they will stand far away and cry out, "How terrible, how terrible it is for that great city, the powerful city
Lesson 6: The Great City of Babylon Today Frightened by the torture that she experiences, they will stand far away and cry out, "How terrible, how terrible it is for that great city, the powerful city
KS2: Baghdad AD 900 (6 lessons)
 KS2: Baghdad AD 900 (6 lessons) Contents Include: An Introduction to Mesopotamia Building Baghdad The House of Wisdom The Mongol Attack on Baghdad in 1258 This pack of lessons has been designed for Key
KS2: Baghdad AD 900 (6 lessons) Contents Include: An Introduction to Mesopotamia Building Baghdad The House of Wisdom The Mongol Attack on Baghdad in 1258 This pack of lessons has been designed for Key
Teacher s Guide For. Ancient History: The Greek City-State and Democracy
 Teacher s Guide For Ancient History: The Greek City-State and Democracy For grade 7 - College Programs produced by Centre Communications, Inc. for Ambrose Video Publishing, Inc. Executive Producer William
Teacher s Guide For Ancient History: The Greek City-State and Democracy For grade 7 - College Programs produced by Centre Communications, Inc. for Ambrose Video Publishing, Inc. Executive Producer William
What the Ancients Knew The Egyptians Teacher s Guide
 What the Ancients Knew The Egyptians Grade Level: 6 8 Curriculum Focus: Social Studies Lesson Duration: 5 class periods Program Description What the Ancients Knew: The Egyptians The earliest Egyptians
What the Ancients Knew The Egyptians Grade Level: 6 8 Curriculum Focus: Social Studies Lesson Duration: 5 class periods Program Description What the Ancients Knew: The Egyptians The earliest Egyptians
Ancient Greece: The Parthenon
 Ancient Greece: The Parthenon Figure of a river-god from the Parthenon Greece, 438-432 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information
Ancient Greece: The Parthenon Figure of a river-god from the Parthenon Greece, 438-432 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information
Ancient China. Vocabulary. 15. Terracotta Army collection of seven thousand life-sized sculptures made from pottery in the tomb of Shi Huangdi
 Ancient China 1. Analects the collected sayings and teachings of Confucius 2. Bronze Age (3300 1200 B.C.) time when people made weapons and tools from bronze 3. calligraphy artistic form of ancient Chinese
Ancient China 1. Analects the collected sayings and teachings of Confucius 2. Bronze Age (3300 1200 B.C.) time when people made weapons and tools from bronze 3. calligraphy artistic form of ancient Chinese
Reading: The Diverse Cultures of Ancient Egypt / Mummy Portrait 1
 Contents PRE-VISIT ACTIVITIES Reading: The Diverse Cultures of Ancient Egypt / Mummy Portrait 1 Portrait Mask 2 Dionysos 3 Questions from the Reading Passage 4 VISIT ACTIVITIES Worksheet 1 5 Worksheet
Contents PRE-VISIT ACTIVITIES Reading: The Diverse Cultures of Ancient Egypt / Mummy Portrait 1 Portrait Mask 2 Dionysos 3 Questions from the Reading Passage 4 VISIT ACTIVITIES Worksheet 1 5 Worksheet
STUDY GUIDE AND STUDY QUESTIONS FOR EZRA
 STUDY GUIDE AND STUDY QUESTIONS FOR EZRA Historical Time and Background for Ezra This historical book of Ezra covers the beginning of what is called the Post-Exillic period of Israel s history. It is also
STUDY GUIDE AND STUDY QUESTIONS FOR EZRA Historical Time and Background for Ezra This historical book of Ezra covers the beginning of what is called the Post-Exillic period of Israel s history. It is also
Timeline of Egyptian History. Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script)
 Timeline of Egyptian History 1 Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script) Timeline of Egyptian History 2 Early Dynastic Period 3100 2686 BCE 1 st & 2 nd Dynasty Narmer
Timeline of Egyptian History 1 Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script) Timeline of Egyptian History 2 Early Dynastic Period 3100 2686 BCE 1 st & 2 nd Dynasty Narmer
The Neolithic Revolution
 The Neolithic Revolution The archaeologist took out his small brush and carefully removed the remaining dirt from the fragment of human skull. To help him reconstruct the life of the ancient human, he
The Neolithic Revolution The archaeologist took out his small brush and carefully removed the remaining dirt from the fragment of human skull. To help him reconstruct the life of the ancient human, he
The Origins and Impacts of the Persian Empire
 The Origins and Impacts of the Persian Empire The origin of the Persian Empire can be attributed to the leadership of one man Cyrus the Great. A brilliant and powerful Persian king, Cyrus strategy for
The Origins and Impacts of the Persian Empire The origin of the Persian Empire can be attributed to the leadership of one man Cyrus the Great. A brilliant and powerful Persian king, Cyrus strategy for
Natural Advantages 2/21/2012. Lecture 9: Pre-Dynastic Egypt
 Lecture 9: Pre-Dynastic Egypt HIST 213 Spring 2012 750 miles long Natural Advantages Transportation (both ways) rich soil (450/sq. mi.) annual flooding (silt) simple irrigation systems relatively unified
Lecture 9: Pre-Dynastic Egypt HIST 213 Spring 2012 750 miles long Natural Advantages Transportation (both ways) rich soil (450/sq. mi.) annual flooding (silt) simple irrigation systems relatively unified
The history of Egypt is divided into dynasties of rulers. What is a dynasty? A succession of rulers from the same family or line is called a Dynasty.
 1 The history of Egypt is divided into dynasties of rulers What is a dynasty? A succession of rulers from the same family or line is called a Dynasty. 2 3 Predynasty: c.3100 2649 BC Major Events: Unification
1 The history of Egypt is divided into dynasties of rulers What is a dynasty? A succession of rulers from the same family or line is called a Dynasty. 2 3 Predynasty: c.3100 2649 BC Major Events: Unification
Field Report: Caere Project 2015
 Bryn Critz Schockmel Boston University History of Art and Architecture Field Report: Caere Project 2015 This summer I had the pleasure of participating in the Caere Project, led by Professor Fabio Colivicchi
Bryn Critz Schockmel Boston University History of Art and Architecture Field Report: Caere Project 2015 This summer I had the pleasure of participating in the Caere Project, led by Professor Fabio Colivicchi
Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks
 Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
AP ART HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP ART HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 Left slide: Right slide: Maison Carrée, Nîmes, France. ca. 1 10 CE Blank 2. Analyze how this Roman temple is similar to and different from a Greek temple.
AP ART HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 Left slide: Right slide: Maison Carrée, Nîmes, France. ca. 1 10 CE Blank 2. Analyze how this Roman temple is similar to and different from a Greek temple.
Africa Before the Slave Trade
 Africa Before the Slave Trade Overview of African Kingdoms Ghana and Songhai Ghana (Wagadu) is the earliest known empire of the western Sudan, came into the history books around the eighth century but
Africa Before the Slave Trade Overview of African Kingdoms Ghana and Songhai Ghana (Wagadu) is the earliest known empire of the western Sudan, came into the history books around the eighth century but
Sumerian Civilization
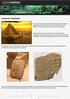 Sumerian Civilization In the south eastern region of Mesopotamia between the mighty Euphrates and Tigris Rivers lay the ruins of the Sumerian City- States. The history of the Sumerians is shrouded in mystery.
Sumerian Civilization In the south eastern region of Mesopotamia between the mighty Euphrates and Tigris Rivers lay the ruins of the Sumerian City- States. The history of the Sumerians is shrouded in mystery.
HANWORTH PARK Boundary: Date of Designation: Date of alteration and extension: Additional protection to the area:
 HANWORTH PARK Boundary: See Map 8 Date of Designation: 06 March 1984 Date of alteration and extension: None Additional protection to the area: Listed buildings, Archaeological Priority Area; Scheduled
HANWORTH PARK Boundary: See Map 8 Date of Designation: 06 March 1984 Date of alteration and extension: None Additional protection to the area: Listed buildings, Archaeological Priority Area; Scheduled
Cy8, the second register, inscription 美 國 紐 約 大 都 會 博 物 館
 20140904 回 目 錄 Cy8, the second register, inscription 美 國 紐 約 大 都 會 博 物 館 收 藏 Cy3, Cy6, Cy7, Cy8, Cy9, Cy10, Cy11, Cy12, Cy13, Cy16, Cy17, Cy18 參 考 Phoenician Bronze and Silver Bowls from Cyprus and the
20140904 回 目 錄 Cy8, the second register, inscription 美 國 紐 約 大 都 會 博 物 館 收 藏 Cy3, Cy6, Cy7, Cy8, Cy9, Cy10, Cy11, Cy12, Cy13, Cy16, Cy17, Cy18 參 考 Phoenician Bronze and Silver Bowls from Cyprus and the
In this chapter, you will visit ancient Egypt. You will meet four leaders, called pharaohs.
 Name: Date: Period: Lesson 8 - The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will visit ancient Egypt. You will meet four leaders, called pharaohs. In 1922, archaeologists
Name: Date: Period: Lesson 8 - The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will visit ancient Egypt. You will meet four leaders, called pharaohs. In 1922, archaeologists
Hieroglyphs and Community By Grant
 Hieroglyphs and Community By Grant Hieroglyphs were hard to understand in the ancient times and are still hard to understand today. Hieroglyphs are carvings of an object or creature that Egyptians used
Hieroglyphs and Community By Grant Hieroglyphs were hard to understand in the ancient times and are still hard to understand today. Hieroglyphs are carvings of an object or creature that Egyptians used
Devotion NT347 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Hall of Faith. THEME: God wants us to trust Him. SCRIPTURE: Hebrews 11:1-40
 Devotion NT347 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Hall of Faith THEME: God wants us to trust Him. SCRIPTURE: Hebrews 11:1-40 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids! This is a
Devotion NT347 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Hall of Faith THEME: God wants us to trust Him. SCRIPTURE: Hebrews 11:1-40 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids! This is a
Hieroglyphic Questions
 Name: Hieroglyphic Questions Class: 1. Why did the ancient Egyptians need to develop a system of writing? 2. What was the name of the system of writing the Egyptians developed? 3. How did the development
Name: Hieroglyphic Questions Class: 1. Why did the ancient Egyptians need to develop a system of writing? 2. What was the name of the system of writing the Egyptians developed? 3. How did the development
Garden design and restoration - rebuilding hystorical places Yvoire France
 Volume 17(3), 118-122, 2013 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Garden design and restoration - rebuilding hystorical places Yvoire France Szekely G. 1 * 1 Banat
Volume 17(3), 118-122, 2013 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Garden design and restoration - rebuilding hystorical places Yvoire France Szekely G. 1 * 1 Banat
Ancient Egypt: Symbols of the pharaoh
 Ancient Egypt: Symbols of the pharaoh Colossal bust of Ramesses II Thebes, Egypt 1250 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information
Ancient Egypt: Symbols of the pharaoh Colossal bust of Ramesses II Thebes, Egypt 1250 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information
Four Early River Valley Civilizations. Egyptian Civilization - Nile River
 Four Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River I. GEOGRAPHY A. The Nile Egypt on the Nile 1. Egypt s settlements
Four Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River I. GEOGRAPHY A. The Nile Egypt on the Nile 1. Egypt s settlements
Ancient Rome Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guide, Activities, and Crafts
 A J T L Any Age Ancient Rome Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guide, Activities, and Crafts A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors-Paula
A J T L Any Age Ancient Rome Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guide, Activities, and Crafts A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors-Paula
Carlo Scarpa and the Brioni family cemetery
 Carlo Scarpa was asked by the industrialist Giuseppe Brion to design the Brion cemetery and the tombs for him and his wife. The site was an L- shaped plot of land wrapped around the north-east corner of
Carlo Scarpa was asked by the industrialist Giuseppe Brion to design the Brion cemetery and the tombs for him and his wife. The site was an L- shaped plot of land wrapped around the north-east corner of
ROSKILDE CATHEDRAL DISCOVER UNESCO WORLD HERITAGE AND ROYAL TOMBS IN...
 DISCOVER UNESCO WORLD HERITAGE AND ROYAL TOMBS IN... ROSKILDE CATHEDRAL Roskilde Cathedral has been inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List since 1995 a list including the most spectacular monuments
DISCOVER UNESCO WORLD HERITAGE AND ROYAL TOMBS IN... ROSKILDE CATHEDRAL Roskilde Cathedral has been inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List since 1995 a list including the most spectacular monuments
AFRICAN KINGDOMS. Ghana. Around AD 800 the rulers of many farming villages united to create the kingdom of Ghana.
 AFRICAN KINGDOMS In Africa, towns soon became part of an important trade network. Gold and salt were the most important products traded. People needed salt in their diets to prevent dehydration. There
AFRICAN KINGDOMS In Africa, towns soon became part of an important trade network. Gold and salt were the most important products traded. People needed salt in their diets to prevent dehydration. There
download instant at http://testbankinstant.com TEST ITEM FILE Amy Millicent Morris University of Nebraska at Omaha ART HISTORY 5 th EDITION
 TEST ITEM FILE Amy Millicent Morris University of Nebraska at Omaha ART HISTORY 5 th EDITION Marilyn Stokstad Judith Harris Murphy Distinguished Professor of Art History Emerita The University of Kansas
TEST ITEM FILE Amy Millicent Morris University of Nebraska at Omaha ART HISTORY 5 th EDITION Marilyn Stokstad Judith Harris Murphy Distinguished Professor of Art History Emerita The University of Kansas
EARLIEST CIVILIZATIONS. Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush
 PART I Chapter 2 EARLIEST CIVILIZATIONS Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush I. The First and Second Dynasties (3100 2686 B.C.) II. 1. The natural barriers of deserts and sea insulated Egypt from invading armies
PART I Chapter 2 EARLIEST CIVILIZATIONS Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush I. The First and Second Dynasties (3100 2686 B.C.) II. 1. The natural barriers of deserts and sea insulated Egypt from invading armies
Nebamun goes hunting
 Nebamun goes hunting Cross-curricular literacy activities Key Stage 2 classroom resource Nebamun goes hunting Introduction Introduction This resource pack contains instructions and resources for five cross-curricular
Nebamun goes hunting Cross-curricular literacy activities Key Stage 2 classroom resource Nebamun goes hunting Introduction Introduction This resource pack contains instructions and resources for five cross-curricular
Period #1: Technological and Environmental Transformations, c. 8,000 B.C.E. - 600 B.C.E. Study Guide by Key Concepts
 Note: the question numbers are my own customization, and do NOT reflect official College Board designation. Ask yourself the question in the left column. Your answer should come close to the middle column.
Note: the question numbers are my own customization, and do NOT reflect official College Board designation. Ask yourself the question in the left column. Your answer should come close to the middle column.
ART OF THE AMERICAS AFTER 1300
 ART OF THE AMERICAS AFTER 1300 AZTECS Tenochtitlan and the Codex Mendoza The Great Pyramid Religious Sculpture: iconography and style Featherwork INCAS Masonry techniques Machu Picchu: city-sanctuary Textiles:
ART OF THE AMERICAS AFTER 1300 AZTECS Tenochtitlan and the Codex Mendoza The Great Pyramid Religious Sculpture: iconography and style Featherwork INCAS Masonry techniques Machu Picchu: city-sanctuary Textiles:
The World of. Mythology. Middle Eastern. By Jim Ollhoff
 The World of Mythology: Middle Eastern Mythology By Jim Ollhoff VISIT US AT WWW.ABDOPUBLISHING.COM Published by ABDO Publishing Company, 8000 West 78th Street, Suite 310, Edina, MN 55439. Copyright 2012
The World of Mythology: Middle Eastern Mythology By Jim Ollhoff VISIT US AT WWW.ABDOPUBLISHING.COM Published by ABDO Publishing Company, 8000 West 78th Street, Suite 310, Edina, MN 55439. Copyright 2012
The Revelation of Jesus Christ: A commentary by John F. Walvoord The Victory of the Lamb and His Followers Chapter 14
 The Revelation of Jesus Christ: A commentary by John F. Walvoord The Victory of the Lamb and His Followers Chapter 14 Vs. 1 We are seeing, through John s eyes, the end of the Tribulation period. The 144,000
The Revelation of Jesus Christ: A commentary by John F. Walvoord The Victory of the Lamb and His Followers Chapter 14 Vs. 1 We are seeing, through John s eyes, the end of the Tribulation period. The 144,000
West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society
 West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society Bantu Migration Around 1500 BCE farmers of the Niger and Benue River valleys in West Africa began migrating south and east, bringing with them their
West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society Bantu Migration Around 1500 BCE farmers of the Niger and Benue River valleys in West Africa began migrating south and east, bringing with them their
Jainism Jainism also began in India; religion teaches ahimsa nonviolence - Jains believe all living things have souls and should not be hurt
 Lesson 3 Buddhism and India s Golden Age MAIN IDEAS Belief System A teacher called the Buddha developed a new religion that focused on helping people to escape suffering. Government The Maurya rulers united
Lesson 3 Buddhism and India s Golden Age MAIN IDEAS Belief System A teacher called the Buddha developed a new religion that focused on helping people to escape suffering. Government The Maurya rulers united
Name Period. The Indus Valley Civilization
 Name Period The Indus Valley Civilization Indus Valley Civilization Daily Life 3000BCE 1500BCE We know very little about the Indus Valley civilization, but what we do know is fascinating! Over 4,000 years
Name Period The Indus Valley Civilization Indus Valley Civilization Daily Life 3000BCE 1500BCE We know very little about the Indus Valley civilization, but what we do know is fascinating! Over 4,000 years
Thermopylae Lesson Plan. Central Historical Question: How many Persians were at the Battle of Thermopylae?
 Thermopylae Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: How many Persians were at the Battle of Thermopylae? Materials: Copies of Documents A-D Copies of Graphic Organizer Battle of Thermopylae PowerPoint
Thermopylae Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: How many Persians were at the Battle of Thermopylae? Materials: Copies of Documents A-D Copies of Graphic Organizer Battle of Thermopylae PowerPoint
Keywords for the study of Junior Cert art
 able abstract acrylic activity aesthetic/aesthetics analyze ancient animation applied arch arches architect architectural architecture art art process artist artistic artists arts artwork artworks assemble
able abstract acrylic activity aesthetic/aesthetics analyze ancient animation applied arch arches architect architectural architecture art art process artist artistic artists arts artwork artworks assemble
PUSD High Frequency Word List
 PUSD High Frequency Word List For Reading and Spelling Grades K-5 High Frequency or instant words are important because: 1. You can t read a sentence or a paragraph without knowing at least the most common.
PUSD High Frequency Word List For Reading and Spelling Grades K-5 High Frequency or instant words are important because: 1. You can t read a sentence or a paragraph without knowing at least the most common.
Ninth Grade History & Social Science World History I
 SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
History of the Rule of Law
 History of the Rule of Law CONTEMPORARY FINE ART COLLECTION Since it opened in 1933, the Thomas J. Moyer Ohio Judicial Center has been home to numerous soaring and spectacular murals, and neoclassical,
History of the Rule of Law CONTEMPORARY FINE ART COLLECTION Since it opened in 1933, the Thomas J. Moyer Ohio Judicial Center has been home to numerous soaring and spectacular murals, and neoclassical,
HERITAGE STATEMENT: For MILTON HALL, MILTON, CAMBRIDGESHIRE THE WORKSPACE CONSULTANTS LLP
 HERITAGE STATEMENT: For MILTON HALL, MILTON, CAMBRIDGESHIRE Supporting documentation for Listed Building application January 2013. 1 Kingston Barns Bourn Road Kingston CB23 2NP Tel: 01223 696111 CONTENTS:
HERITAGE STATEMENT: For MILTON HALL, MILTON, CAMBRIDGESHIRE Supporting documentation for Listed Building application January 2013. 1 Kingston Barns Bourn Road Kingston CB23 2NP Tel: 01223 696111 CONTENTS:
Could Babylon be the Revived Head of the Beast?
 Could Babylon be the Revived Head of the Beast? by Rodrigo Silva 12/20/2008 www.beastfromtheeast.org In Revelation 17 we read one of the most mysterious passages in the entire Bible. It goes as follows:
Could Babylon be the Revived Head of the Beast? by Rodrigo Silva 12/20/2008 www.beastfromtheeast.org In Revelation 17 we read one of the most mysterious passages in the entire Bible. It goes as follows:
eb.com/>. eastern Africa, history of. Encyclopaedia Britannica Online. May 27,
 Daily Life in Aksum Aksum was a powerful and wealthy ancient kingdom. Located in East Africa, it was very influential between A.D. 50 and 600. During this time, goods from all over the ancient world were
Daily Life in Aksum Aksum was a powerful and wealthy ancient kingdom. Located in East Africa, it was very influential between A.D. 50 and 600. During this time, goods from all over the ancient world were
Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt
 Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt MAIN IDEAS Economics Egyptians developed a complex society with many different jobs and social roles. Science and Technology Egyptians made advances in calendars, geometry,
Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt MAIN IDEAS Economics Egyptians developed a complex society with many different jobs and social roles. Science and Technology Egyptians made advances in calendars, geometry,
Monetary History of the World
 Monetary History of the World 700-550BC by Martin A. Armstrong Electrum Stater of Asia Minor circa 650 BC Only since about 700 B.C. do we find a consistent record of the monetary system of the world. The
Monetary History of the World 700-550BC by Martin A. Armstrong Electrum Stater of Asia Minor circa 650 BC Only since about 700 B.C. do we find a consistent record of the monetary system of the world. The
Thе subject of our thesis are the semiotic aspects of the architectural graphics' history.
 SEMIOTIC ASPECTS OF ARCHITECTURAL GRAPHICS' HISTORY Arch. Stela Borisova Tasheva 1 Abstract Thе subject of our thesis are the semiotic aspects of the architectural graphics' history. It is suggested that
SEMIOTIC ASPECTS OF ARCHITECTURAL GRAPHICS' HISTORY Arch. Stela Borisova Tasheva 1 Abstract Thе subject of our thesis are the semiotic aspects of the architectural graphics' history. It is suggested that
OMC Study Group MEETING 3: NOTES. Section 1: Building Design Page 2 Section 2: Site Layout Page 9 Section 3: Summary Page 16
 OMC Study Group MEETING 3: NOTES Section 1: Building Design Page 2 Section 2: Site Layout Page 9 Section 3: Summary Page 16 Section 1 Building Design Page 2 of 16 General Comments during Building Design
OMC Study Group MEETING 3: NOTES Section 1: Building Design Page 2 Section 2: Site Layout Page 9 Section 3: Summary Page 16 Section 1 Building Design Page 2 of 16 General Comments during Building Design
Shapes & Symbols. Shape is an element of art. There are two kinds of shapes, geometric and organic.
 Notes 10/6 Name: Period: Date: Shapes & Symbols Shape is an element of art. There are two kinds of shapes, geometric and organic. Geometric Shapes Geometric shapes are shapes that have names. These are
Notes 10/6 Name: Period: Date: Shapes & Symbols Shape is an element of art. There are two kinds of shapes, geometric and organic. Geometric Shapes Geometric shapes are shapes that have names. These are
Chapel Flat Woollas Hall Eckington Pershore Worcestershire WR10 3DN
 14 Broad Street, Pershore, Worcestershire WR10 1AY Telephone: 01386 555368 residential@bomfordandcoffey.co.uk Chapel Flat Woollas Hall Eckington Pershore Worcestershire WR10 3DN For Sale By Private Treaty
14 Broad Street, Pershore, Worcestershire WR10 1AY Telephone: 01386 555368 residential@bomfordandcoffey.co.uk Chapel Flat Woollas Hall Eckington Pershore Worcestershire WR10 3DN For Sale By Private Treaty
Ancient Greece: Pots. Black-figured lip cup Greek, around 540 BC. Visit resource for teachers Key stage 2
 Ancient Greece: Pots Black-figured lip cup Greek, around 540 BC Visit resource for teachers Key stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities
Ancient Greece: Pots Black-figured lip cup Greek, around 540 BC Visit resource for teachers Key stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities
PYRAMID CFE 3284V. OPEN CAPTIONED PBS VIDEO 1988 Grade Levels: 9-13+ 57 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed
 PYRAMID CFE 3284V OPEN CAPTIONED PBS VIDEO 1988 Grade Levels: 9-13+ 57 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed DESCRIPTION Burial practices and beliefs, such as the building of pyramids, mummification,
PYRAMID CFE 3284V OPEN CAPTIONED PBS VIDEO 1988 Grade Levels: 9-13+ 57 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed DESCRIPTION Burial practices and beliefs, such as the building of pyramids, mummification,
Note Taking Study Guide CIVILIZATIONS OF MESOAMERICA
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide CIVILIZATIONS OF MESOAMERICA Focus Question: What factors encouraged the rise of powerful civilizations in Mesoamerica? A. As you read People Settle in the Americas, complete
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide CIVILIZATIONS OF MESOAMERICA Focus Question: What factors encouraged the rise of powerful civilizations in Mesoamerica? A. As you read People Settle in the Americas, complete
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE
 SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE In sixth grade, students are ready to deepen their understanding of the Earth and its peoples through the study of history, geography, politics, culture, and
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE In sixth grade, students are ready to deepen their understanding of the Earth and its peoples through the study of history, geography, politics, culture, and
Webquest: The Dog of Pompeii by Louis Untermeyer
 Name Date Webquest: The Dog of Pompeii by Louis Untermeyer http://www.history.com/topics/ancient history/pompeii Watch the 2 minute video. Pay special attention to where Pompeii is and where Vesuvius is
Name Date Webquest: The Dog of Pompeii by Louis Untermeyer http://www.history.com/topics/ancient history/pompeii Watch the 2 minute video. Pay special attention to where Pompeii is and where Vesuvius is
The Xenophile Historian
 The Xenophile Historian Map Gallery Map 1: The spread of civilization in thousand-year steps. The purple areas became civilized by 3000 B.C. Civilization spread to the green areas by 2000 B.C., yellow
The Xenophile Historian Map Gallery Map 1: The spread of civilization in thousand-year steps. The purple areas became civilized by 3000 B.C. Civilization spread to the green areas by 2000 B.C., yellow
Wall of China Project
 Target Age: K-3 rd Grades Wall of China Project Skills Used Following directions, introduction to fractions, measuring with a ruler using half-inches, 2-D to 3-D concept transfer, creative interpretation,
Target Age: K-3 rd Grades Wall of China Project Skills Used Following directions, introduction to fractions, measuring with a ruler using half-inches, 2-D to 3-D concept transfer, creative interpretation,
I ve always had a great passion. Double-Walled Vessels. Studio Ceramics. by Hiroe Hanazono
 Double-Walled Vessels by Hiroe Hanazono Double-walled vessels cast from original molds, sprayed glazes, fired to cone 6. I ve always had a great passion for food cooking, eating, setting the table, and
Double-Walled Vessels by Hiroe Hanazono Double-walled vessels cast from original molds, sprayed glazes, fired to cone 6. I ve always had a great passion for food cooking, eating, setting the table, and
