Risk Profiling Toolkit DEVELOPING A CORPORATE RISK PROFILE FOR YOUR ORGANIZATION
|
|
|
- Quentin Johnston
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Risk Profiling Toolkit DEVELOPING A CORPORATE RISK PROFILE FOR YOUR ORGANIZATION
2 I Background Under the TBS Risk Management Policy, departments and agencies must identify the potential perils, factors and types of risk to which their assets, program activities and interests are exposed. Similarly, in the Integrated Risk Management Framework, the first element is developing the Corporate Risk Profile whereby the organization's risks are identified through environmental scanning, the current status of risk management within the organization is assessed, and the organization s risk profile is identified. A. Departmental and agency requirements regarding risk profiling Departments and agencies are increasingly seeing the benefits of implementing an integrated risk management approach. A first step in pursuing integrated risk management is to develop an organization-wide risk profile (often referred to as a corporate risk profile). The risk profile should address the following elements: Key risk areas (e.g., strategic, operational, project) Strengths and weaknesses of the department/agency Major opportunities and threats Risk tolerance levels Capacity to manage risks Learning needs and tools The organization s risk tolerance, priority setting and ability to mitigate risks Linkages between different levels of risks (e.g., operational and overall departmental priorities, business and program risks, sector specific and department-wide) Linkages with management processes of the department A corporate risk profile can be prepared for a specific department, agency, or sector/branch, depending on the scope of its mandate and operations. The challenge is to ensure that risk management is aligned at the various levels of the organization. We present on the following pages some of the challenges in implementing integrated risk management and developing an organization-wide risk profile. We propose the use of workshops to develop the risk profile. Other long term approaches (e.g., environmental scanning) should also be pursued depending on the particular circumstances of the organization. However, the basic concepts would remain the same. 1
3 B. Issues and challenges of integrated risk management 1. Developments in integrated risk management Risk management is a very complex and wide sweeping subject matter area. Although the Integrated Risk Management Framework is relatively recent in the federal government as a management tool, departments and agencies have been carrying out risk management as a formal discipline for a number of years, for example, in the scientific assessment of food or product risks, IM/IT project planning, defence operational planning, threat and risk assessments. We have identified below some of the overall contextual factors that could have a bearing on the development of the organization-wide risk profile. Treasury Board Secretariat Integrated Risk Management Framework. Is intended to advance the use of a more corporate and systematic approach to risk management across government for longer term strategy and for dayto-day activities; to contribute to building a risk-smart workforce and environment that allows for innovation and responsible risk-taking while ensuring legitimate precautions are taken to protect the public interest, maintain public trust, and ensure due diligence; and to propose a set of risk management practices that departments can adopt, or adapt, to their specific circumstances and mandate. The Office of the Auditor General recently released the results of an audit of the application of integrated risk management in federal departments. It confirmed that departments are at the initial stages of developing their integrated risk management practices, and identified gaps in action plans to guide the process, risk profiling, and the need for more guidance toward integrating risk management in their management culture. Precautionary approach. Decisions must often be made in the presence of considerable uncertainty. The precautionary approach forces a conscious risk management decision to act, or to not act, more frequently, despite the lack of full scientific certainty. It emphasizes the need to take timely and appropriately preventative action, even in the absence of a full scientific demonstration of cause and effect. The precautionary principle/ approach are becoming a key issue in international relations, in terms of trade, health protection and environmental issues. Health Canada has played a leading role in the application of the precautionary approach. Modern Comptrollership/Modern Management. The Report on the Independent Review Panel on Modernization of Comptrollership in the Government of Canada highlighted risk management as one of the four key pillars of modern comptrollership. 2
4 Privy Council Office Risk Management for Canada and Canadians: Report of the ADM Working Group on Risk Management (2000). An objective of the Working Group was to identify common elements of approaches to risk management used in Departments and Agencies that are applicable across the Government of Canada, and to explore horizontal aspects of risk management in government. Emergence of threat management. With the increasing number of recent threats (e.g., terrorism, Nile Virus, SARS, Mad Cow), threat management is emerging as a management discipline which has close linkages with risk management. Key elements of threat management include collecting intelligence to identify threats, and then profiling and prioritizing these threats. Public perceptions of risks are changing. Changing public perceptions of risks impact the need for risk management, and more particularly, external risk communications. Specific considerations include: the loss of trust and confidence in government decisions (even where these are science-based); questions of transparency; and loss of confidence of the public in regulatory systems. Risk communications is becoming more and more important as a key element of risk 2. Challenges faced by departments in doing risk management We highlight below some of the specific challenges faced by federal departments in dong risk management, and need to be considered in developing the risk profiles. Federal departments must respond to unpredictable external emergencies that happen suddenly, are difficult to plan for, and vary considerably in scope. These emergencies happen over and above regular planned activities. Departments and agencies must often work within international and/or national collaborative frameworks. Partnerships with other countries, with the provinces and territories, or with other stakeholders, will set limits on the approach followed by federal departments and agencies in managing risks. Risk communication must appropriately balance the need for transparency with the need to be a responsible government. This is more difficult if there is a lack of understanding or trust between stakeholders. Increasing legal risks. Departments have been subject to an increasing level of litigation, and must increasingly consider the question of legal liabilities. Certain departments must also assume responsibility for contingent liabilities. The Department of Justice has been leading efforts to develop a sustainable approach to managing legal risks that protects the interest of the Crown and minimizes overall costs. 3
5 Need to better formalize the long term, organization-wide approach to risk management. Risks need to be assessed on both a short term and long term basis. The pressures facing departments have been changing at such a fast pace that they have inevitably been forced to take a more short term view of risk management. However, the mechanisms should be in place to help them focus on long term risks as well as short term ones. This means enhancing long range planning/ risk management capabilities at the organization-wide level, taking a more systematic approach to risk identification, and using scenario building and other techniques to help assess risks on a long term basis. Lack of quantitative data to support definition of risks. Most of risk management within the public sector has been qualitative. There is a lack of quantitative data on the level of hazards and exposure. Quantitative analysis is ideal but difficult to achieve. This has implications in developing the risk profiles in that there may not be a huge number of risks, but the description of the scope of each of the risks can be very challenging and complex. 3. Specific issues to be addressed in profiling organization-wide risks Need to consider the broad range of risks, including safety, economic, environmental, political, trade/ market access, and general business risks in addition to science-based risks. Linking the various types and levels of risks. Risks at the operational level, risks at the business line and program level, and risks at an organization-wide level, must all be linked as part of working toward an integrated risk management framework. Departmental capacity for risk profile is limited by its ability to do monitoring and surveillance for early identification and assessment of emerging risks. There is a need to strengthen intelligence gathering and early warning systems as these have a direct impact on the ability to identify and prioritize risks. With program review, a number of the programs in place to collect such intelligence were reduced as resources were retained for handling day to day crises. Need for close interface and communications between departments. A number of the risks are common to several departments, and require horizontal and collaborative arrangements. Public pressure and perceptions may result in existing resources or additional new resources being directed to areas of high concern in the public agenda. In some cases, the public may consider a risk to be of greater concern that it would otherwise be assessed from a strictly science-based or technical perspective. 4
6 4. Examples of risks faced by federal departments and agencies We have summarized below the types of risks that would typically need to be considered in profiling the risks of an organization. Risk Impact Type of Risk Examples of risks Health Incoming pathogens Emerging pathogens Unsafe products/ substances Trade/ market access International measures/ sanctions/ retaliatory External (affecting external public, action International standards clients and stakeholders) Socio-economic Internal (corporate business risks affecting the department) Environmental Public perception Security Consumer protection (on nonhealth matters) Service delivery (operational) Legal Technological Organizational/ human resources Asset Privacy Reaction from stakeholder groups Loss of quality of life Biotechnology crops Natural hazards Intensity of public reaction Timeliness of decisions Terrorism activities (e.g., contamination of the food supply) Fraud/ misleading labeling Tampering False claims Lack of resources/ increased costs Lack of capacity/ competencies Breakdowns Labour disruptions Implementation/ transition delays Claims/Liabilities Infrastructure problems Security of information Departure of staff over next 5-7 years Recruitment of staff with required expertise Retention of corporate knowledge Health, safety and security of staff Rust out of facilities and equipment Unauthorized access to information Misuse of information 5
7 5. Examples of opportunities for departments and agencies to improve risk profiling We have provided below examples of improvements that are typically required in the way risks are identified within departments and agencies: Develop an overall integrated risk profile that covers the full range of risks (program and internal business risks). This concept is not always readily accepted where business risks are seen as secondary to the program risks (e.g., human health, safety), and the relationships between business and program risks are not always evident in the short term. Maintain and update an overall profile of the internal/ external risks facing the organization (in the short and long term), and linkages with measures that are in place to mitigate these risks. The concept of maintaining/updating and prioritizing a list of risks is a straightforward one from a management perspective, but is often seen as being overly simplistic from a scientific, technical or operational perspective. Be more explicit about the acceptable level of risk tolerance in each program/ functional area, and review these with external stakeholders. Often, this information is available at the operational level, but is not well known at the senior management levels. Further, resources are typically not available to address those cases where risk levels are high, and resource allocation processes in departments must be made more flexible so that resources can be reallocated to the high risk areas. Establish more formal process for prioritizing risks and organizationwide priorities at the Senior Executive Committee. Senior management needs to become more actively engaged and play a leadership role in prioritizing the risks, and making management decisions (e.g., resource allocations) based on the prioritization of risks. Enhance communications of organization-wide risks to staff and external stakeholders. This has longer term implications in terms of training staff in risk management concepts, building risk profiling into strategic planning, monitoring risks as part of the performance measurement systems, and developing mechanisms to improve information sharing so that the information gets out to all staff. Continue to develop quantitative approaches to assess levels of hazards, risks and probabilities. This also means establishing a more dedicated focus on environmental scanning and intelligence gathering, improving information sharing between departments, and identifying and defining competencies required to do risk profiling. 6
8 II Approach and Technique Proposed A. The corporate risk profile Given that the concept of risk management is still relatively new to departments/agencies, our suggested approach would be to keep the risk profile as simple as possible at this particular time. In summary, the risk profile would include such elements as: Key risk areas (e.g., strategic, operational, project), including major opportunities and threats Categorization of risks (e.g., human health, environment, trade, legal, human resources) Description of the risks Probability of risk (low, med, high) Impact of risk Risk timeframe (e.g., short: 2 years or less, medium: 3-4 years, long term: 5 years or more) Relative priority of the risks Ways of measuring the risk (qualitative and quantitative) Risk tolerance levels (to the extent that these can be identified and/or measured) Mitigation measures that are currently in place, including strengths and weaknesses of the department Linkages between different levels of risks (e.g., operational and overall departmental priorities, business and program risks, sector specific and department-wide) Linkages with management processes of the organization Capacity of the organization to do risk management Learning needs and tools Our experience has been that it is not the process of identifying the risks that is difficult, but rather the challenge is to describe the risks in a meaningful way such that the information on the risks can be used for decision-making. For example, people are well aware that risks exist from new products, however determining the level of risk from these new products and establishing how much funding should be allocated to programs to control the introduction of new products is the much greater challenge. 7
9 Consequently, it is important not only to identify the risks, but to describe the scope of these risks in a way that the information can be meaningful for the organization in its future decision-making. This means prioritizing the risks, defining the risks at the right level, identifying ways of measuring the risks, and assessing the implications of these risks in terms of departmental decision-making. B. Key messages Although staff are often familiar with the concepts of risk assessment and risk management at the operational level, they are often less familiar with the concept of integrated risk management at the enterprise wide level that includes both business and program risks. In fact, there is typically a high level of scepticism. Consequently, key messages need to focus on the benefits of integrated risk management, for example: The close relationships that do exist between organization-wide business risks and program/commodity risks The benefits of collecting intelligence and sharing knowledge on risks at an organization wide level, and using this information to keep senior management informed of emerging risks The benefits of applying the same rigorous risk management approach that is used to assess operational risks to assess organization-wide business risks The merits of having an ongoing process to identify new emerging risks at an organization wide level, and continuously reviewing the relative priorities of these risks to help with resource allocation decisions How integrated risk management can help program managers in their day-today business decisions. How integrated risk management can help drive the planning and decisionmaking processes of the department. C. Proposed workshop program We have presented below a summary of the topics that could be covered during risk profiling workshops. A more detailed description is provided on the following pages. This workshop program is obviously preliminary and would need to be discussed and reviewed in greater detail at the time of a project engagement. 8
10 Preliminary workshop structure Day 1 A Overview of Integrated Risk Management concepts B Role playing exercise on risks faced by a fictitious department C Identification of corporate risks D Identification of criteria to prioritize risks E Prioritization of risks 2 hours 1 hour 1.5 hours 0.5 hour 1.0 hour Day 2 F Qualification of high priority risks G Responsibilities for risk management H Implementation plans I Biggest challenge for implementation J What does it mean for you as a manager? 2.0 hours 1.0 hour 1.0 hour 1.0 hour 0.5 hour Some overall themes regarding the overall approach proposed for the risk profiling workshops are: The workshops would be highly interactive to build on the knowledge of participants of risk management, as some participants will be highly knowledgeable of risk assessment and management in an operational context. Allowing sufficient time to qualify the risks in terms of significance, impact, ways of measuring the risk, and approach for measuring the level of risk tolerance. This recognizes that the major risks can be identified relatively easily (e.g., human health, trade, environment), however scoping and measuring these risks is the real challenge. Maintaining an appropriate balance between mixing staff from branches/units, and separating staff where appropriate. If there is a high similarity between certain risks between branches/units, then we will make an effort to combine staff from various areas of the organization. Flexibility in the approach used to develop the corporate risk profile. We would keep the overall approach sufficiently broad to allow participants to pursue different ways of profiling or describing the risks. We would also provide for time in the workshops to review the approach taken and obtain suggestions from workshop participants on potential improvements. Do the first workshop on a pilot basis. So as to enable changes to be made prior to the subsequent workshops. The proposed program for the workshops is described in greater detail below. 9
11 Potential workshop program A Overview of Integrated Risk Management concepts Objective To review with managers the basic concepts of Integrated Risk Management. Format 45 minute presentation in plenary session by the consultant followed by general discussion and brief exercise Content Objectives of integrated risk management How risk management fits into government-wide/departmental initiatives Elements of risk management framework Identifying risks through intelligence gathering Risk profiling Risk assessment Concept of risk tolerance level Concept of threat management Gathering intelligence Communicating risks Risk monitoring/measurement Responsibilities for implementing risk management Responsibilities for developing risk profiles s Timeframe Tools Following the presentation, participants will be divided into teams (two people in each team). Using yellow post notes, each team (of two people) will be asked to identify the major issues and culture shifts that need to be made in their departments to make risk management a success. (About 30 minutes). Two hours in total for presentation, discussion and exercise ٱ Presentation on Integrated Risk Management ٱ Questions for exercise B Role playing exercise on risks faced by a fictitious department Objective To generate further thought on the major risks faced by the organization from the viewpoint of different stakeholders. Format Role playing exercise followed by open discussion in plenary. Content Identification of key risks Discussion on the significance of these risks Timeframe Tools Various roles (e.g., Minister, Deputy Minister, operational manager, employee, union, TBS, HR functional specialist) will be divided amongst participants. Each role player (in teams of 2 or 3) will be asked to provide their vision of the major risks faced by a department and whether these risks are being handled adequately by the department. We will then summarize in plenary the major risks, how they relate to departmental strategic objectives, and key measures of success. 60 minutes Descriptions of roles for role playing exercise 10
12 C Identification of corporate risks Objective To identify the organization-wide risks. Format Introduction by the consultant, followed by exercise in groups to identify corporate risks and presentation by each group. Content Identification of key risks Categorization of risks (e.g., human health, environment, trade, legal, human resources) Probability of risk (low, med, high) Impact of risk Risk timeframe Nil Timeframe 90 minutes Tools Questions for exercise Templates to identify risks D Identification of criteria to prioritize risks Objective To establish the criteria that should be used to prioritize the risks identified to date for each department. Format Introduction by the consultant, followed by exercise to brainstorm on criteria by individual groups and then a plenary discussion. Content Criteria to prioritize risks Approach for prioritizing risks Participants will be divided into groups. Each group will be asked to identify criteria to prioritize the risks (maximum of five or six criteria). For example, criteria could include impact on clients, impact on service delivery, and liability to the Crown, staff morale. Criteria could also be potential impact on strategic objectives of the department. During the plenary, we will develop a single list of prioritization criteria. Timeframe 30 minutes Tools Questions for exercise E Prioritization of risks Objective To assign a priority (high, medium, low) to each of the risks, using the prioritization criteria developed above. Format Introduction by the consultant, followed by exercise in groups and then a plenary discussion to agree on relative priorities. Content Prioritization process Participants will work in groups. Groups will be provided the same list of risks to prioritize. Each group will be asked to prioritize the risks using the criteria identified in the previous exercise. During the plenary, we will attempt to reach agreement on the relative priority of the risks. Timeframe 60 minutes Tools List of risks Prioritization worksheets Instructions for exercise 11
13 F Qualification of high priority risks Objective To describe for each of the high priority risks the significance of the risk, the potential impact, how the risk could be measured from a qualitative and quantitative perspective, how the level of risk tolerance could be established, and measures that are currently in place to mitigate the risk. Content Qualitative and quantitative description of risk Approach for measuring risk and risk tolerance level Mitigation measures in place (or that should be put in place) Format Timeframe Tools Introduction by the consultant, followed by exercises in groups and then a plenary discussion to share the results Each group will be asked to describe a specific risk based on a common template. 2 hours (including introduction by the consultant, work in group exercise, and plenary discussion of each risk) List of high priority risks Common template to describe each high priority risk G Responsibilities for risk management Objective Content Format Timeframe Tools To identify the responsibilities for implementing risk management in the department. ٱ Division of responsibilities for risk management ٱ Senior management commitment and sponsorship ٱ Champion for risk management Introduction by the consultant, followed by group exercises to identify key responsibilities for implementing risk management. Each group will be asked to identify key parties involved in implementing risk management and what their responsibilities should be 1 hour (including introduction by the consultant, work in group exercise, and plenary discussion) Questionnaire Draft list of responsibilities by key positions H Implementation plans Objective To determine the key tasks required to implement risk management in the organization (e.g., finalizing risk profile, communicating risk tolerance levels, learning programs, monitoring risks) Content Next steps, key implementation steps, sequencing and responsibilities Capacity of the department Major roadblocks Format Timeframe Tools Introduction by the consultant, followed by exercise in groups to develop implementation plans. Each group will be asked to identify the key deliverables, overall timeline, the overall approach, key steps, skills, and estimated level of effort. Each group will also be asked to identify critical issues in terms of the capacity of the department, and feasibility of being successful, and key risks or constraints. During the plenary, we will review the implementation plans, and discuss requirements in terms of the overall governance and leadership. 60 minutes (including health break) Instructions for exercise Implementation plan template 12
14 I Biggest challenge for implementation Objective To discuss the major culture change (or changes) that will be required by the department, and the implications of these changes for the organization at an operational level. Content Culture aspects Major roadblocks Major changes required Linkages with departmental processes Key communications messages Format Timeframe Tools Introduction by the consultant, followed by exercise all together to confirm the major cultural shifts required, and discuss adjustments required within the departments Discussion will be carried out around some key questions: what are the major cultural changes required to implement risk management? What adjustments will be required within departments to make this happen? How will we know if we have been successful? How will we monitor progress? 60 minutes Question set J What does it mean for you as a manager? Objective To think about the implications of risk management for each person as an individual manager, and what it means on a day-to-day basis. Content Impact on role of managers Impact on accountability agreements of managers Changes in orientation/outlook required by managers Key communication messages Format Timeframe Tools Individual exercise by each participant to identify the 1 to 3 changes that would need to be made in the next six months to better integrate risk management within their everyday operations. This will be followed by a plenary discussion. Participants will identify each change on a post note anonymously and stick it on a wall reserved for this purpose. We will then review the post notes as part of the plenary session, and note common trends or patterns. Participants would also be asked to evaluate the workshop by means of questionnaire. 30 minutes ٱ Question set 13
15 D. Proposed work plan The following work plan would need to be customized to the requirements of the organization. 1. Develop detailed work plan We will meet with the project authority, review the steps of the work plan, identify relevant documents and sources for the literature scan, and identify particular risks and issues that may arise during the project. Following this meeting, we will develop a detailed work plan for the project with an updated timeline. We will also update the proposed program structure for the workshop detailing the agenda, workshop outline, the scheduling, key messages to solicit participation at the workshops, and the roles of the facilitators and the participants. 2. Develop workshop materials We will develop an overall workbook for each participant, including detailed instructions for the workshop participants, exercise templates, and background documents (e.g., TBS Integrated Risk Management Framework, Guide to Getting Started: The Corporate Risk Profile). 3. Prepare for workshops The preparation for the workshops will include meetings with the project authority to review the workshop programme and documents, identification of key communications messages, strategies to maintain the interest of the participants, and logistical matters such as the scheduling of the workshops, and the translation, packaging and distribution of the documents. 4. Deliver workshops To ensure maximum flexibility, we have assumed that these workshops would be 2 days in length (this would need to be discussed further). Workshops would be held with a representative sample of participants, including DGs, Directors and middle managers. The organization would be responsible for soliciting participation from managers in their organization. 5. Agree on overall approach for preparing corporate risk profile We will develop a Corporate Risk Profile template to be used to identify the corporate risks and prepare the Corporate Risk Profile for the organization. This template would build on the findings of the workshops, and would be developed in close cooperation with the project authority. 14
16 6. Prepare consolidated summary of workshop notes We will collect and prepare detailed notes on the participants input at the workshops and provide a typed summary of the notes to the project authority. These notes will be prepared in the format of a preliminary risk profile, with a summary highlighting overall findings and conclusions. 7. Develop draft of corporate risk profile We will develop a draft of the corporate risk profile for the organization based on the information gathered at the workshops, and other relevant information provided by the project authority. This risk profile will be prepared using the Corporate Risk Profile template, making appropriate adjustments to suit the particular circumstances of the organization. 8. Present corporate risk profile to senior managers of the organization We will meet with senior managers of the department to debrief them on the discussions and results of the workshops, to present and discuss with them the first draft of the risk profile, to review the proposed approach to the development of the corporate risk profile, and to seek their input and validation feedback. We have assumed that these meetings could be held on a group or individual basis. Group discussions would be preferable in terms of generating discussion, but may not always be possible in light of the availability of the managers. Based on these meetings, we will update the corporate risk profile for the department. 9. Present corporate risk profile to senior management We will prepare a presentation and present the corporate risk profile to senior management of the organization, including the key messages and findings from the workshops, and potential strategies to integrate the findings into the strategic decision-making processes of the organization, for example, the strategic planning and business planning processes. Based on feedback received during these presentations, we will update the corporate risk profile. 15
17 E. Definitions The following definitions have been taken from the TBS Integrated Risk Management Framework. Risk Risk management The uncertainty that surrounds future events and outcomes. It is the expression of the likelihood and impact of an event with the potential to influence the achievement of an organization's objectives. A systematic approach to setting the best course of action under uncertainty by identifying, assessing, understanding, acting on and communicating risk issues. Integrated management Risk tolerance risk A continuous, proactive and systematic process to understand, manage and communicate risk from an organization-wide perspective. It is about making strategic decisions that contribute to the achievement of an organization's overall corporate objectives. The degree of comfort of the stakeholders with various levels of risk Risk management capacity Risk maps Risk communication The organization s risk management culture, and risk management processes and practices. Summary charts and diagrams that help organizations identify, discuss, understand and address risks by portraying sources and types of risks and disciplines involved/needed Includes issue identification and assessment, analysis of the public environment (including stakeholder interests and concerns), development of consultation and communications strategies, message development, working with the media, monitoring and evaluating the public dialogue, and reporting to and communicating with Parliament. 16
Internal Audit Manual
 Internal Audit Manual Version 1.0 AUDIT AND EVALUATION SECTOR AUDIT AND ASSURANCE SERVICES BRANCH INDIAN AND NORTHERN AFFAIRS CANADA April 25, 2008 #933907 Acknowledgements The Institute of Internal Auditors
Internal Audit Manual Version 1.0 AUDIT AND EVALUATION SECTOR AUDIT AND ASSURANCE SERVICES BRANCH INDIAN AND NORTHERN AFFAIRS CANADA April 25, 2008 #933907 Acknowledgements The Institute of Internal Auditors
Policy 10.105: Enterprise Risk Management Policy
 Name: Responsibility: Complements: Enterprise Risk Management Framework Coordinator, Enterprise Risk Management Policy 10.105: Enterprise Risk Management Policy Date: November 2006 Revision Date(s): January
Name: Responsibility: Complements: Enterprise Risk Management Framework Coordinator, Enterprise Risk Management Policy 10.105: Enterprise Risk Management Policy Date: November 2006 Revision Date(s): January
Quality Assurance Checklist
 Internal Audit Foundations Standards 1000, 1010, 1100, 1110, 1111, 1120, 1130, 1300, 1310, 1320, 1321, 1322, 2000, 2040 There is an Internal Audit Charter in place Internal Audit Charter is in place The
Internal Audit Foundations Standards 1000, 1010, 1100, 1110, 1111, 1120, 1130, 1300, 1310, 1320, 1321, 1322, 2000, 2040 There is an Internal Audit Charter in place Internal Audit Charter is in place The
Manager, Corporate Planning & Reporting BC Oil & Gas Commission, Victoria Applied Leadership. Office of the Commissioner - Corporate Affairs
 Manager, Corporate Planning & Reporting BC Oil & Gas Commission, Victoria Applied Leadership Office of the Commissioner - Corporate Affairs The Manager, Corporate Planning & Reporting is responsible for
Manager, Corporate Planning & Reporting BC Oil & Gas Commission, Victoria Applied Leadership Office of the Commissioner - Corporate Affairs The Manager, Corporate Planning & Reporting is responsible for
ERM Program. Enterprise Risk Management Guideline
 ERM Program Enterprise Management Guideline Table of Contents PREAMBLE... 2 When should I refer to this Guideline?... 3 Why do we need a Guideline?... 4 How do I use this Guideline?... 4 Who is responsible
ERM Program Enterprise Management Guideline Table of Contents PREAMBLE... 2 When should I refer to this Guideline?... 3 Why do we need a Guideline?... 4 How do I use this Guideline?... 4 Who is responsible
OFFICE OF THE PRIVACY COMMISSIONER OF CANADA. Audit of Human Resource Management
 OFFICE OF THE PRIVACY COMMISSIONER OF CANADA Audit of Human Resource Management May 13, 2010 Prepared by the Centre for Public Management Inc. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Executive Summary... 2 2.0 Background...
OFFICE OF THE PRIVACY COMMISSIONER OF CANADA Audit of Human Resource Management May 13, 2010 Prepared by the Centre for Public Management Inc. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Executive Summary... 2 2.0 Background...
Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada. Internal Audit Report
 Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada Internal Audit Report Management Practices Audit of the Human Resources and Workplace Services Branch Prepared by: Audit and Assurance Services Branch
Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada Internal Audit Report Management Practices Audit of the Human Resources and Workplace Services Branch Prepared by: Audit and Assurance Services Branch
A Risk-based Approach to Performance Auditing
 CCAF-FCVI Fellow 2009/2010 A Risk-based Approach to Performance Auditing Strategic Paper by Levina Rusk Kishimba TANZANIA CANADA Table of Contents Page Acknowledgements Executive Summary v vii Introduction
CCAF-FCVI Fellow 2009/2010 A Risk-based Approach to Performance Auditing Strategic Paper by Levina Rusk Kishimba TANZANIA CANADA Table of Contents Page Acknowledgements Executive Summary v vii Introduction
Periodic risk assessment by internal audit
 Periodic risk assessment by internal audit I Introduction The Good Practice Internal Audit Manual Template, developed by the Internal Audit CoP of Pempal, defines the importance and the impact that an
Periodic risk assessment by internal audit I Introduction The Good Practice Internal Audit Manual Template, developed by the Internal Audit CoP of Pempal, defines the importance and the impact that an
RISK BASED AUDITING: A VALUE ADD PROPOSITION. Participant Guide
 RISK BASED AUDITING: A VALUE ADD PROPOSITION Participant Guide About This Course About This Course Adding Value for Risk-based Auditing Seminar Description In this seminar, we will focus on: The foundation
RISK BASED AUDITING: A VALUE ADD PROPOSITION Participant Guide About This Course About This Course Adding Value for Risk-based Auditing Seminar Description In this seminar, we will focus on: The foundation
Corporate Risk Management Policy
 Corporate Risk Management Policy Managing the Risk and Realising the Opportunity www.reading.gov.uk Risk Management is Good Management Page 1 of 19 Contents 1. Our Risk Management Vision 3 2. Introduction
Corporate Risk Management Policy Managing the Risk and Realising the Opportunity www.reading.gov.uk Risk Management is Good Management Page 1 of 19 Contents 1. Our Risk Management Vision 3 2. Introduction
Organizational Design Toolkit
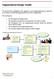 Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Appendix B: Sample Interview Assessment Booklet
 Appendix B: Sample Interview Assessment Booklet This template, designed for the position of Assistant Deputy Minister, may be adapted to suit any occupational group or level and the specific assessment
Appendix B: Sample Interview Assessment Booklet This template, designed for the position of Assistant Deputy Minister, may be adapted to suit any occupational group or level and the specific assessment
Risk Management Primer
 Risk Management Primer Purpose: To obtain strong project outcomes by implementing an appropriate risk management process Audience: Project managers, project sponsors, team members and other key stakeholders
Risk Management Primer Purpose: To obtain strong project outcomes by implementing an appropriate risk management process Audience: Project managers, project sponsors, team members and other key stakeholders
How To Write A Listing Policy For A Species At Risk Act
 Fisheries and Oceans Canada Species at Risk Act Listing Policy and Directive for Do Not List Advice DFO SARA Listing Policy Preamble The Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) Species at Risk Act (SARA) Listing
Fisheries and Oceans Canada Species at Risk Act Listing Policy and Directive for Do Not List Advice DFO SARA Listing Policy Preamble The Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) Species at Risk Act (SARA) Listing
Audit of the Test of Design of Entity-Level Controls
 Audit of the Test of Design of Entity-Level Controls Canadian Grain Commission Audit & Evaluation Services Final Report March 2012 Canadian Grain Commission 0 Entity Level Controls 2011 Table of Contents
Audit of the Test of Design of Entity-Level Controls Canadian Grain Commission Audit & Evaluation Services Final Report March 2012 Canadian Grain Commission 0 Entity Level Controls 2011 Table of Contents
Office of the Auditor General AUDIT OF IT GOVERNANCE. Tabled at Audit Committee March 12, 2015
 Office of the Auditor General AUDIT OF IT GOVERNANCE Tabled at Audit Committee March 12, 2015 This page has intentionally been left blank Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 1 Background...
Office of the Auditor General AUDIT OF IT GOVERNANCE Tabled at Audit Committee March 12, 2015 This page has intentionally been left blank Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 1 Background...
Final Report. Audit of the Project Management Framework. December 2014
 Final Report Audit of the Project Management Framework December 2014 Audit of the Project Management Framework Table of Contents Executive summary... i A - Introduction... 1 1. Background... 1 2. Audit
Final Report Audit of the Project Management Framework December 2014 Audit of the Project Management Framework Table of Contents Executive summary... i A - Introduction... 1 1. Background... 1 2. Audit
Status Report of the Auditor General of Canada to the House of Commons
 2011 Status Report of the Auditor General of Canada to the House of Commons Chapter 1 Financial Management and Control and Risk Management Office of the Auditor General of Canada The 2011 Status Report
2011 Status Report of the Auditor General of Canada to the House of Commons Chapter 1 Financial Management and Control and Risk Management Office of the Auditor General of Canada The 2011 Status Report
Final Report. 2013-709 Audit of Vendor Performance and Corrective Measures. September 18, 2014. Office of Audit and Evaluation
 2013-709 Audit of Vendor Performance and Corrective Measures September 18, 2014 Office of Audit and Evaluation TABLE OF CONTENTS MAIN POINTS... i INTRODUCTION... 1 FOCUS OF THE AUDIT... 7 STATEMENT OF
2013-709 Audit of Vendor Performance and Corrective Measures September 18, 2014 Office of Audit and Evaluation TABLE OF CONTENTS MAIN POINTS... i INTRODUCTION... 1 FOCUS OF THE AUDIT... 7 STATEMENT OF
Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada. Internal Audit Report. Audit of Economic Development Programs. Prepared by:
 Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada Internal Audit Report Audit of Economic Development Programs Prepared by: Audit and Assurance Services Branch Project No. 13-44 February 2014 TABLE OF
Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada Internal Audit Report Audit of Economic Development Programs Prepared by: Audit and Assurance Services Branch Project No. 13-44 February 2014 TABLE OF
Audit of the Management of Projects within Employment and Social Development Canada
 Unclassified Internal Audit Services Branch Audit of the Management of Projects within Employment and Social Development Canada February 2014 SP-607-03-14E Internal Audit Services Branch (IASB) You can
Unclassified Internal Audit Services Branch Audit of the Management of Projects within Employment and Social Development Canada February 2014 SP-607-03-14E Internal Audit Services Branch (IASB) You can
Computing Services Network Project Methodology
 Computing Services Network Project Prepared By: Todd Brindley, CSN Project Version # 1.0 Updated on 09/15/2008 Version 1.0 Page 1 MANAGEMENT PLANNING Project : Version Control Version Date Author Change
Computing Services Network Project Prepared By: Todd Brindley, CSN Project Version # 1.0 Updated on 09/15/2008 Version 1.0 Page 1 MANAGEMENT PLANNING Project : Version Control Version Date Author Change
Regulatory Risk Analysis in the European Union, United States, and Canada
 Regulatory Risk Analysis in the European Union, United States, and Canada A Joint Presentation by: Takis Daskaleros, European Commission Nancy Beck, United States, Office of the Management of the Budget
Regulatory Risk Analysis in the European Union, United States, and Canada A Joint Presentation by: Takis Daskaleros, European Commission Nancy Beck, United States, Office of the Management of the Budget
GOVERNMENT RESPONSE TO THE CHILD INTERVENTION SYSTEM REVIEW
 GOVERNMENT RESPONSE TO THE CHILD INTERVENTION SYSTEM REVIEW October 2010 Closing the Gap Between Vision and Reality: Strengthening Accountability, Adaptability and Continuous Improvement in Alberta s Child
GOVERNMENT RESPONSE TO THE CHILD INTERVENTION SYSTEM REVIEW October 2010 Closing the Gap Between Vision and Reality: Strengthening Accountability, Adaptability and Continuous Improvement in Alberta s Child
Introduction to Enterprise Risk Management at UVM DRAFT
 Introduction to Enterprise Management at UVM 1 Enterprise What is Enterprise Management? Enterprise risk management is a structured, consistent, and continuous process across the whole organization for
Introduction to Enterprise Management at UVM 1 Enterprise What is Enterprise Management? Enterprise risk management is a structured, consistent, and continuous process across the whole organization for
IFAD Policy on Enterprise Risk Management
 Document: EB 2008/94/R.4 Agenda: 5 Date: 6 August 2008 Distribution: Public Original: English E IFAD Policy on Enterprise Risk Management Executive Board Ninety-fourth Session Rome, 10-11 September 2008
Document: EB 2008/94/R.4 Agenda: 5 Date: 6 August 2008 Distribution: Public Original: English E IFAD Policy on Enterprise Risk Management Executive Board Ninety-fourth Session Rome, 10-11 September 2008
Process Guide TALENT MANAGEMENT. This document is protected by copyright. The consent of the copyright owner must be obtained for reproduction.
 TALENT MANAGEMENT Process Guide This document is protected by copyright. The consent of the copyright owner must be obtained for reproduction. Innovation & Growth Nova Scotia Public Service Commission
TALENT MANAGEMENT Process Guide This document is protected by copyright. The consent of the copyright owner must be obtained for reproduction. Innovation & Growth Nova Scotia Public Service Commission
2007 Follow-Up Report on the Audit of Information Technology January 2005
 2007 Follow-Up Report on the Audit of Information Technology January 2005 Natural Sciences & Engineering Research Council of Canada & Social Sciences & Humanities Research Council of Canada October 2007
2007 Follow-Up Report on the Audit of Information Technology January 2005 Natural Sciences & Engineering Research Council of Canada & Social Sciences & Humanities Research Council of Canada October 2007
ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT. A Resource Guide for Departmental Managers and HR Professionals
 ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT A Resource Guide for Departmental Managers and HR Professionals Public Service Secretariat Revised, September, 2009 Government of Newfoundland and Labrador P.O. Box 8700 St.
ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT A Resource Guide for Departmental Managers and HR Professionals Public Service Secretariat Revised, September, 2009 Government of Newfoundland and Labrador P.O. Box 8700 St.
Executive summary. Climate change assessments Review of the processes and procedures of the IPCC
 Executive summary Climate change is a long-term challenge that will require every nation to make decisions about how to respond. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was established by
Executive summary Climate change is a long-term challenge that will require every nation to make decisions about how to respond. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was established by
the Defence Leadership framework
 the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
Capacity Assessment Tool
 Capacity Assessment Tool 2013 Government of Yukon all rights reserved All materials, content and forms contained in this document/website are property of Yukon Government and may not be copied, reproduced,
Capacity Assessment Tool 2013 Government of Yukon all rights reserved All materials, content and forms contained in this document/website are property of Yukon Government and may not be copied, reproduced,
The College of New Jersey Enterprise Risk Management and Higher Education For Discussion Purposes Only January 2012
 The College of New Jersey Enterprise Risk Management and Higher Education For Discussion Purposes Only Agenda Introduction Basic program components Recent trends in higher education risk management Why
The College of New Jersey Enterprise Risk Management and Higher Education For Discussion Purposes Only Agenda Introduction Basic program components Recent trends in higher education risk management Why
Guide for the Development of Results-based Management and Accountability Frameworks
 Guide for the Development of Results-based Management and Accountability Frameworks August, 2001 Treasury Board Secretariat TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1. Introduction to the Results-based Management and
Guide for the Development of Results-based Management and Accountability Frameworks August, 2001 Treasury Board Secretariat TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1. Introduction to the Results-based Management and
Risk Management Strategy and Policy. The policy provides the framework for the management and control of risk within the GOC
 Annex 1 TITLE VERSION Version 2 Risk Management Strategy and Policy SUMMARY The policy provides the framework for the management and control of risk within the GOC DATE CREATED January 2013 REVIEW DATE
Annex 1 TITLE VERSION Version 2 Risk Management Strategy and Policy SUMMARY The policy provides the framework for the management and control of risk within the GOC DATE CREATED January 2013 REVIEW DATE
UNITED NATIONS OFFICE FOR PROJECT SERVICES. ORGANIZATIONAL DIRECTIVE No. 33. UNOPS Strategic Risk Management Planning Framework
 UNOPS UNITED NATIONS OFFICE FOR PROJECT SERVICES Headquarters, Copenhagen O.D. No. 33 16 April 2010 ORGANIZATIONAL DIRECTIVE No. 33 UNOPS Strategic Risk Management Planning Framework 1. Introduction 1.1.
UNOPS UNITED NATIONS OFFICE FOR PROJECT SERVICES Headquarters, Copenhagen O.D. No. 33 16 April 2010 ORGANIZATIONAL DIRECTIVE No. 33 UNOPS Strategic Risk Management Planning Framework 1. Introduction 1.1.
LGMA Qld Governance and Corporate Planning Village Forum
 www.pwc.com.au Fraud Risk Management Fraud Risk Assessments LGMA Qld Governance and Corporate Planning Village Forum March 2015 Agenda Introductions Fraud Risk Management Fraud Statistics s Global Economic
www.pwc.com.au Fraud Risk Management Fraud Risk Assessments LGMA Qld Governance and Corporate Planning Village Forum March 2015 Agenda Introductions Fraud Risk Management Fraud Statistics s Global Economic
COSO Internal Control Integrated Framework (2013)
 COSO Internal Control Integrated Framework (2013) The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) released its updated Internal Control Integrated Framework (2013 Framework)
COSO Internal Control Integrated Framework (2013) The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) released its updated Internal Control Integrated Framework (2013 Framework)
Good Practice Guide: the internal audit role in information assurance
 Good Practice Guide: the internal audit role in information assurance Janaury 2010 Good Practice Guide: the internal audit role in information assurance January 2010 Official versions of this document
Good Practice Guide: the internal audit role in information assurance Janaury 2010 Good Practice Guide: the internal audit role in information assurance January 2010 Official versions of this document
Process Management: Creating Supply Chain Value
 Process Management: Creating Supply Chain Value Carol L. Marks, C.P.M., Director of Purchasing and Business Management Systems Industrial Distribution Group, Southern Division 704/398-5666; [email protected]
Process Management: Creating Supply Chain Value Carol L. Marks, C.P.M., Director of Purchasing and Business Management Systems Industrial Distribution Group, Southern Division 704/398-5666; [email protected]
Implementing an Integrated City-wide Risk Management Framework
 AUDITOR GENERAL S REPORT ACTION REQUIRED Implementing an Integrated City-wide Risk Management Framework Date: June 11, 2015 To: From: Wards: Audit Committee Auditor General All Reference Number: SUMMARY
AUDITOR GENERAL S REPORT ACTION REQUIRED Implementing an Integrated City-wide Risk Management Framework Date: June 11, 2015 To: From: Wards: Audit Committee Auditor General All Reference Number: SUMMARY
GUIDE ON DEVELOPING SERVICE STANDARDS
 GUIDE ON DEVELOPING SERVICE STANDARDS Contents 1. Background... 3 2. Why the Guide/ Toolkit?... 4 3. Service Delivery Planning Value Chain Components... 4 4. Definition and types of Service Standards...
GUIDE ON DEVELOPING SERVICE STANDARDS Contents 1. Background... 3 2. Why the Guide/ Toolkit?... 4 3. Service Delivery Planning Value Chain Components... 4 4. Definition and types of Service Standards...
Finding the Right People for Your Program Evaluation Team: Evaluator and Planning Team Job Descriptions
 : Evaluator and Planning Team Job Descriptions I. Overview II. Sample Evaluator Job Description III. Evaluator Competencies IV. Recruiting members of your strategic evaluation planning team V. Recruiting
: Evaluator and Planning Team Job Descriptions I. Overview II. Sample Evaluator Job Description III. Evaluator Competencies IV. Recruiting members of your strategic evaluation planning team V. Recruiting
Internal Audit of the Sport Canada Hosting Program
 Internal Audit of the Sport Canada Hosting Program Office of the Chief Audit and Evaluation Executive November 2009 Table of Contents Executive Summary...i 1. Introduction and Context...1 1.1 Authority
Internal Audit of the Sport Canada Hosting Program Office of the Chief Audit and Evaluation Executive November 2009 Table of Contents Executive Summary...i 1. Introduction and Context...1 1.1 Authority
The Insightlink 4Cs. Employee Survey Feedback and Action Planning Workbook
 Insightlink Communications 80 South Lake Ave. Suite 680 Pasadena, CA 91101 USA w w w.insightlink.com - Tel: 866.802.8095 - Email: [email protected] This guide is designed as a workbook to enable HR
Insightlink Communications 80 South Lake Ave. Suite 680 Pasadena, CA 91101 USA w w w.insightlink.com - Tel: 866.802.8095 - Email: [email protected] This guide is designed as a workbook to enable HR
Developing a Public-Private Partnership Framework: Policies and PPP Units
 Note 4 May 2012 Developing a Public-Private Partnership Framework: Policies and PPP Units This note is the fourth in a series of notes on developing a comprehensive policy, legal, and institution framework
Note 4 May 2012 Developing a Public-Private Partnership Framework: Policies and PPP Units This note is the fourth in a series of notes on developing a comprehensive policy, legal, and institution framework
A Risk Management Standard
 A Risk Management Standard Introduction This Risk Management Standard is the result of work by a team drawn from the major risk management organisations in the UK, including the Institute of Risk management
A Risk Management Standard Introduction This Risk Management Standard is the result of work by a team drawn from the major risk management organisations in the UK, including the Institute of Risk management
RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY (Revised October 2015)
 UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY (Revised October 2015) 1. This risk management policy ( the policy ) forms part of the University s internal control and corporate governance arrangements.
UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY (Revised October 2015) 1. This risk management policy ( the policy ) forms part of the University s internal control and corporate governance arrangements.
A&CS Assurance Review. Accounting Policy Division Rule Making Participation in Standard Setting. Report
 A&CS Assurance Review Accounting Policy Division Rule Making Participation in Standard Setting Report April 2010 Table of Contents Background... 1 Engagement Objectives, Scope and Approach... 1 Overall
A&CS Assurance Review Accounting Policy Division Rule Making Participation in Standard Setting Report April 2010 Table of Contents Background... 1 Engagement Objectives, Scope and Approach... 1 Overall
Henkel s Compliance Management System (CMS)
 Henkel s Compliance Management System (CMS) As a company that operates in an ethically and legally correct manner, Henkel s image and reputation is inseparable from the appropriate conduct of each of its
Henkel s Compliance Management System (CMS) As a company that operates in an ethically and legally correct manner, Henkel s image and reputation is inseparable from the appropriate conduct of each of its
A FRAMEWORK FOR THE APPLICATION OF PRECAUTION IN SCIENCE-BASED DECISION MAKING ABOUT RISK
 Government of Canada Gouvernement du Canada A FRAMEWORK FOR THE APPLICATION OF PRECAUTION IN SCIENCE-BASED DECISION MAKING ABOUT RISK National Library of Canada cataloguing in publication data Main entry
Government of Canada Gouvernement du Canada A FRAMEWORK FOR THE APPLICATION OF PRECAUTION IN SCIENCE-BASED DECISION MAKING ABOUT RISK National Library of Canada cataloguing in publication data Main entry
RISK MANAGEMENT GUIDANCE FOR GOVERNMENT DEPARTMENTS AND OFFICES
 RISK MANAGEMENT GUIDANCE FOR GOVERNMENT DEPARTMENTS AND OFFICES GOVERNMENT ACCOUNTING SECTION DEPARTMENT OF FINANCE MARCH 2004 Risk Management Guidance CONTENTS Pages List of guidelines on risk management
RISK MANAGEMENT GUIDANCE FOR GOVERNMENT DEPARTMENTS AND OFFICES GOVERNMENT ACCOUNTING SECTION DEPARTMENT OF FINANCE MARCH 2004 Risk Management Guidance CONTENTS Pages List of guidelines on risk management
Corporate risk register
 EXECUTIVE BOARD EB133/10 133rd Session 17 May 2013 Provisional agenda item 7.3 Corporate risk register Organization-wide strategic risk management in WHO Report by the Secretariat 1. This report is submitted
EXECUTIVE BOARD EB133/10 133rd Session 17 May 2013 Provisional agenda item 7.3 Corporate risk register Organization-wide strategic risk management in WHO Report by the Secretariat 1. This report is submitted
Re. Request for feedback on Assurance on <IR> Introduction & Exploration of Issues
 Chartered Professional Accountants of Canada 277 Wellington Street West Toronto ON CANADA M5V 3H2 T. 416 977.3222 F. 416 977.8585 www.cpacanada.ca Comptables professionnels agréés du Canada 277, rue Wellington
Chartered Professional Accountants of Canada 277 Wellington Street West Toronto ON CANADA M5V 3H2 T. 416 977.3222 F. 416 977.8585 www.cpacanada.ca Comptables professionnels agréés du Canada 277, rue Wellington
The Role of Internal Audit in Risk Governance
 The Role of Internal Audit in Risk Governance How Organizations Are Positioning the Internal Audit Function to Support Their Approach to Risk Management Executive summary Risk is inherent in running any
The Role of Internal Audit in Risk Governance How Organizations Are Positioning the Internal Audit Function to Support Their Approach to Risk Management Executive summary Risk is inherent in running any
How to stay competitive in a converging healthcare system kpmg.com
 Managing risk in a transforming healthcare organization How to stay competitive in a converging healthcare system kpmg.com 2 Healthcare Risk Management Managing the risk of healthcare transformation Healthcare
Managing risk in a transforming healthcare organization How to stay competitive in a converging healthcare system kpmg.com 2 Healthcare Risk Management Managing the risk of healthcare transformation Healthcare
Review of Staffing Modernization and Delegation
 Review of Staffing Modernization and Delegation June 2005 7055-55 (CRS) NOTICE OF CAVEAT TO THE READER This review was conducted as part of the approved Branch Work Plan. The review conclusions do not
Review of Staffing Modernization and Delegation June 2005 7055-55 (CRS) NOTICE OF CAVEAT TO THE READER This review was conducted as part of the approved Branch Work Plan. The review conclusions do not
Framework for Cooperative Market Conduct Supervision in Canada
 Framework for Cooperative Market Conduct Supervision in Canada November 2015 1 Purpose The Framework for Cooperative Market Conduct Supervision in Canada ( Cooperative Framework ) is intended to provide
Framework for Cooperative Market Conduct Supervision in Canada November 2015 1 Purpose The Framework for Cooperative Market Conduct Supervision in Canada ( Cooperative Framework ) is intended to provide
PRIORITIZING CYBERSECURITY
 April 2016 PRIORITIZING CYBERSECURITY Five Investor Questions for Portfolio Company Boards Foreword As the frequency and severity of cyber attacks against global businesses continue to escalate, both companies
April 2016 PRIORITIZING CYBERSECURITY Five Investor Questions for Portfolio Company Boards Foreword As the frequency and severity of cyber attacks against global businesses continue to escalate, both companies
Information Management
 G i Information Management Information Management Planning March 2005 Produced by Information Management Branch Open Government Service Alberta 3 rd Floor, Commerce Place 10155 102 Street Edmonton, Alberta,
G i Information Management Information Management Planning March 2005 Produced by Information Management Branch Open Government Service Alberta 3 rd Floor, Commerce Place 10155 102 Street Edmonton, Alberta,
Government Communication Professional Competency Framework
 Government Communication Professional Competency Framework April 2013 Introduction Every day, government communicators deliver great work which supports communities and helps citizens understand their
Government Communication Professional Competency Framework April 2013 Introduction Every day, government communicators deliver great work which supports communities and helps citizens understand their
Integrated Risk Management:
 Integrated Risk Management: A Framework for Fraser Health For further information contact: Integrated Risk Management Fraser Health Corporate Office 300, 10334 152A Street Surrey, BC V3R 8T4 Phone: (604)
Integrated Risk Management: A Framework for Fraser Health For further information contact: Integrated Risk Management Fraser Health Corporate Office 300, 10334 152A Street Surrey, BC V3R 8T4 Phone: (604)
IT strategy. What is an IT strategy? 3. Why do you need an IT strategy? 5. How do you write an IT strategy? 6. Conclusion 12. Further information 13
 IT strategy made simple What is an IT strategy? 3 Why do you need an IT strategy? 5 How do you write an IT strategy? 6 step 1 Planning and preparation 7 step 2 Understanding your organisation s IT needs
IT strategy made simple What is an IT strategy? 3 Why do you need an IT strategy? 5 How do you write an IT strategy? 6 step 1 Planning and preparation 7 step 2 Understanding your organisation s IT needs
11/12/2013. Role of the Board. Risk Appetite. Strategy, Planning and Performance. Risk Governance Framework. Assembling an effective team
 Role of the Board Risk Appetite Strategy, Planning and Performance Risk Governance Framework Assembling an effective team Role of the CEO Accountability and Disclosure 1 Board members should act on a fully
Role of the Board Risk Appetite Strategy, Planning and Performance Risk Governance Framework Assembling an effective team Role of the CEO Accountability and Disclosure 1 Board members should act on a fully
MoP Glossary of Terms - English
 English Term aggregated risk English Definition The overall level of risk to the portfolio when all the risks are viewed as a totality rather than individually. This could include the outputs of particular
English Term aggregated risk English Definition The overall level of risk to the portfolio when all the risks are viewed as a totality rather than individually. This could include the outputs of particular
ISO 31000:2009 - ISO/IEC 31010 & ISO Guide 73:2009 - New Standards for the Management of Risk
 Kevin W Knight AM CPRM; Hon FRMIA; FIRM (UK); LMRMIA: ANZIIF (Mem) ISO 31000:2009 - ISO/IEC 31010 & ISO Guide 73:2009 - New Standards for the Management of Risk History of the ISO and Risk Management Over
Kevin W Knight AM CPRM; Hon FRMIA; FIRM (UK); LMRMIA: ANZIIF (Mem) ISO 31000:2009 - ISO/IEC 31010 & ISO Guide 73:2009 - New Standards for the Management of Risk History of the ISO and Risk Management Over
Guidance Note: Corporate Governance - Board of Directors. March 2015. Ce document est aussi disponible en français.
 Guidance Note: Corporate Governance - Board of Directors March 2015 Ce document est aussi disponible en français. Applicability The Guidance Note: Corporate Governance - Board of Directors (the Guidance
Guidance Note: Corporate Governance - Board of Directors March 2015 Ce document est aussi disponible en français. Applicability The Guidance Note: Corporate Governance - Board of Directors (the Guidance
IT Professional Standards. Information Security Discipline. Sub-discipline 605 Information Security Testing and Information Assurance Methodologies
 IT Professional Standards Information Security Discipline Sub-discipline 605 Information Security Testing and Information Assurance Methodologies December 2012 Draft Version 0.6 DOCUMENT REVIEW Document
IT Professional Standards Information Security Discipline Sub-discipline 605 Information Security Testing and Information Assurance Methodologies December 2012 Draft Version 0.6 DOCUMENT REVIEW Document
Leading Experts in Employment Law, Industrial Relations and best practice Human Resource Management in Ireland
 Leading Experts in Employment Law, Industrial Relations and best practice Human Resource Management in Ireland Who We Are Established in 2003, we are one of Ireland s best-known and respected providers
Leading Experts in Employment Law, Industrial Relations and best practice Human Resource Management in Ireland Who We Are Established in 2003, we are one of Ireland s best-known and respected providers
STRATEGIC PLANNING Guide for Managers
 STRATEGIC PLANNING Guide for Managers 1 Strategic Planning Basics for Managers In all UN offices, departments and missions, it is critical that managers utilize the most effective approach toward developing
STRATEGIC PLANNING Guide for Managers 1 Strategic Planning Basics for Managers In all UN offices, departments and missions, it is critical that managers utilize the most effective approach toward developing
How to achieve excellent enterprise risk management Why risk assessments fail
 How to achieve excellent enterprise risk management Why risk assessments fail Overview Risk assessments are a common tool for understanding business issues and potential consequences from uncertainties.
How to achieve excellent enterprise risk management Why risk assessments fail Overview Risk assessments are a common tool for understanding business issues and potential consequences from uncertainties.
Making Strategic Planning Work
 Making Strategic Planning Work Strategic Planning: A Basic Framework By Brent Stockwell The Importance of Stakeholder Trust and Engagement in Strategic Planning By Joseph P. Casey Strategic Planning: A
Making Strategic Planning Work Strategic Planning: A Basic Framework By Brent Stockwell The Importance of Stakeholder Trust and Engagement in Strategic Planning By Joseph P. Casey Strategic Planning: A
The Child at the Centre. Overview
 The Child at the Centre Overview Giving our children the best start in life Twin aims of early education and childcare: Free part-time quality pre-school education place for all three and four year olds;
The Child at the Centre Overview Giving our children the best start in life Twin aims of early education and childcare: Free part-time quality pre-school education place for all three and four year olds;
Linking Risk Management to Business Strategy, Processes, Operations and Reporting
 Linking Risk Management to Business Strategy, Processes, Operations and Reporting Financial Management Institute of Canada February 17 th, 2010 KPMG LLP Agenda 1. Leading Practice Risk Management Principles
Linking Risk Management to Business Strategy, Processes, Operations and Reporting Financial Management Institute of Canada February 17 th, 2010 KPMG LLP Agenda 1. Leading Practice Risk Management Principles
Australia leads water reporting initiative 1
 1 Australia leads water reporting initiative 1 Professor Jayne M Godfrey Professor of Financial Accounting, Monash University Member, Water Accounting Standards Board Disclaimer: The views expressed in
1 Australia leads water reporting initiative 1 Professor Jayne M Godfrey Professor of Financial Accounting, Monash University Member, Water Accounting Standards Board Disclaimer: The views expressed in
RISK AND OPPORTUNITY MANAGEMENT STRATEGY 2013-2014
 RISK AND OPPORTUNITY MANAGEMENT STRATEGY 2013-2014 Version 1.0 October 2013 Not protectively marked INDEX PAGE NO TITLE 3 Executive Summary 4 Our Shared Vision and Priorities 5 Outline of the Risk and
RISK AND OPPORTUNITY MANAGEMENT STRATEGY 2013-2014 Version 1.0 October 2013 Not protectively marked INDEX PAGE NO TITLE 3 Executive Summary 4 Our Shared Vision and Priorities 5 Outline of the Risk and
Unit Standard 116339: Apply risk management in South African municipalities Karel van der Molen
 Unit Standard 116339: Apply risk management in South African municipalities Karel van der Molen Group 2: Municipal accounting and risk management: Module 4: Risk management, internal control framework
Unit Standard 116339: Apply risk management in South African municipalities Karel van der Molen Group 2: Municipal accounting and risk management: Module 4: Risk management, internal control framework
How To Maintain An Effective System Of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
 Internal control over financial reporting Statement, assessment summary and action plan For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2012 Summary of the assessment of effectiveness of the system of internal control
Internal control over financial reporting Statement, assessment summary and action plan For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2012 Summary of the assessment of effectiveness of the system of internal control
Sustainable Development Strategy 2011-2014 Responsibility. Innovation. Commitment.
 Canada Revenue Agency Sustainable Development Strategy 2011-2014 Responsibility. Innovation. Commitment. RC4087(E) Rev. 11 xxxx Message from the Commissioner The Government of Canada tabled its first Federal
Canada Revenue Agency Sustainable Development Strategy 2011-2014 Responsibility. Innovation. Commitment. RC4087(E) Rev. 11 xxxx Message from the Commissioner The Government of Canada tabled its first Federal
Engaging Community FACULTY AND STAFF PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT TASK FORCE
 Engaging Community FACULTY AND STAFF PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT TASK FORCE Content Process... 1 Scope... 1 Definition... 1 Vision... 2 Identified Goals... 2 Prioritized Recommendations... 2 Proposed Tasks
Engaging Community FACULTY AND STAFF PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT TASK FORCE Content Process... 1 Scope... 1 Definition... 1 Vision... 2 Identified Goals... 2 Prioritized Recommendations... 2 Proposed Tasks
CHANGE MANAGEMENT PLAN
 Appendix 10 Blaby District Council Housing Stock Transfer CHANGE MANAGEMENT PLAN 1 Change Management Plan Introduction As part of the decision making process to pursue transfer, the Blaby District Council
Appendix 10 Blaby District Council Housing Stock Transfer CHANGE MANAGEMENT PLAN 1 Change Management Plan Introduction As part of the decision making process to pursue transfer, the Blaby District Council
QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY
 QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY ACADEMIC DEVELOPMENT & QUALITY ASSURANCE OFFICE ALPHA UNIVERSITY COLLEGE 1. BACKGROUND The Strategic Plan of 2003-2005 E.C of Alpha University s defines the direction Alpha University
QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY ACADEMIC DEVELOPMENT & QUALITY ASSURANCE OFFICE ALPHA UNIVERSITY COLLEGE 1. BACKGROUND The Strategic Plan of 2003-2005 E.C of Alpha University s defines the direction Alpha University
Audit of Project Management Governance. Audit Report
 Audit of Project Management Governance Audit Report March 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary... 3 What we examined... 3 Why it is important... 3 What we found... 3 Background... 5 Objective... 6
Audit of Project Management Governance Audit Report March 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary... 3 What we examined... 3 Why it is important... 3 What we found... 3 Background... 5 Objective... 6
Governance Guideline SEPTEMBER 2013 BC CREDIT UNIONS. www.fic.gov.bc.ca
 Governance Guideline SEPTEMBER 2013 BC CREDIT UNIONS www.fic.gov.bc.ca INTRODUCTION The Financial Institutions Commission 1 (FICOM) holds the Board of Directors 2 (board) accountable for the stewardship
Governance Guideline SEPTEMBER 2013 BC CREDIT UNIONS www.fic.gov.bc.ca INTRODUCTION The Financial Institutions Commission 1 (FICOM) holds the Board of Directors 2 (board) accountable for the stewardship
Saldanha Bay Municipality. Risk Management Strategy. Inclusive of, framework, procedures and methodology
 Inclusive of, framework, procedures and methodology Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Legislative Framework and best practice 1 1.2 Purpose of Enterprise Risk Management 2 1.3 Scope and Applicability 3 1.4
Inclusive of, framework, procedures and methodology Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Legislative Framework and best practice 1 1.2 Purpose of Enterprise Risk Management 2 1.3 Scope and Applicability 3 1.4
Avondale College Limited Enterprise Risk Management Framework 2014 2017
 Avondale College Limited Enterprise Risk Management Framework 2014 2017 President s message Risk management is part of our daily life, something we do regularly; often without realising we are doing it.
Avondale College Limited Enterprise Risk Management Framework 2014 2017 President s message Risk management is part of our daily life, something we do regularly; often without realising we are doing it.
CSR / Sustainability Governance and Management Assessment By Coro Strandberg Principal, Strandberg Consulting www.corostrandberg.
 Introduction CSR / Sustainability Governance and Management Assessment By Coro Strandberg Principal, Strandberg Consulting www.corostrandberg.com June 2015 Companies which adopt CSR or sustainability 1
Introduction CSR / Sustainability Governance and Management Assessment By Coro Strandberg Principal, Strandberg Consulting www.corostrandberg.com June 2015 Companies which adopt CSR or sustainability 1
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PLAN CHECKLIST
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT PLAN CHECKLIST The project management plan is a comprehensive document that defines each area of your project. The final document will contain all the required plans you need to manage,
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PLAN CHECKLIST The project management plan is a comprehensive document that defines each area of your project. The final document will contain all the required plans you need to manage,
Practical Experience Requirements Initial Professional Development for Professional Accountants
 International Accounting Education Standards Board AGENDA ITEM 2-3 Revised Draft of IEPS(Clean Version) Proposed International Education Practice Statement Practical Experience Requirements Initial Professional
International Accounting Education Standards Board AGENDA ITEM 2-3 Revised Draft of IEPS(Clean Version) Proposed International Education Practice Statement Practical Experience Requirements Initial Professional
Evaluation Division Office of Strategic Planning and Performance Management
 LEGAL RISK MANAGEMENT IN THE DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE FORMATIVE EVALUATION Final Report October 2008 Evaluation Division Office of Strategic Planning and Performance Management Legal Risk Management in the
LEGAL RISK MANAGEMENT IN THE DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE FORMATIVE EVALUATION Final Report October 2008 Evaluation Division Office of Strategic Planning and Performance Management Legal Risk Management in the
Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada. Internal Audit Report. Audit of Management of Negotiation Loans. Prepared by:
 Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada Internal Audit Report Audit of Management of Negotiation Loans Prepared by: Audit and Assurance Services Branch Project No. 12-11 February 2013 TABLE
Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada Internal Audit Report Audit of Management of Negotiation Loans Prepared by: Audit and Assurance Services Branch Project No. 12-11 February 2013 TABLE
Team Dynamics in Process Simplification. Introduction to Process Improvement Slide 1
 Team Dynamics in Process Simplification Understanding the Basics of Team Development Slide 1 Teams are all around us Slide 2 Each team should: Define their principles in alignment with organizational vision
Team Dynamics in Process Simplification Understanding the Basics of Team Development Slide 1 Teams are all around us Slide 2 Each team should: Define their principles in alignment with organizational vision
