Examination Approach. Case 1: Mental Status. Examination Approach. The Neurological Exam In the ICU: High Yield Techniques 5/30/2013
|
|
|
- Aubrie Warren
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Neurological Exam In the ICU: High Yield Techniques S. Andrew Josephson MD Carmen Castro-Franceschi and Gladyne K. Mitchell Neurohospitalist Distinguished Professor Vice Chairman, Parnassus Programs Director, Neurohospitalist Program Medical Director, Inpatient Neurology University of California, San Francisco The speaker has no disclosures Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests and techniques Examination Approach Case 1: Mental Status Organization 1. Mental Status 2. Cranial Nerves 3. Motor 4. Reflexes 5. Sensory 6. Coordination 7. Gait A 73 year-old woman comes to the ER with 2 days of feeling fatigued General physical examination is normal and there is no weakness on neurological examination Language testing is abnormal 1
2 Aphasia Testing Aphasia Anatomy Fluency: Use Naming and Conversation Comprehension: More difficult commands Repetition: Today is a sunny day Blumenfeld H. Neuroanatomy Through Clinical Cases Aphasia Chart Name Fluency Comp Rep Broca s Bad Good Bad Wernicke s Good Bad Bad Global Bad Bad Bad Conduction Good Good Bad Transcort Motor Bad Good Good Transcort Sens. Good Bad Good Transcort Mixed Bad Bad Good Evaluating Patients for Delirium Multiple screening tools have been examined for delirium, each with its own caveats Compared with DSM-IV criteria: likely insensitive Would like to design a tool that is short and easy to use by nurses as well as physicians ABCDE bundle 2
3 Confusion Assessment Method (CAM-ICU) Sensitivity and specificity > 90% Four elements (need 1 and 2 and 3 or 4) used to define delirium at the bedside 1. Acute Onset and Fluctuating Course 2. Inattention 3. Disorganized Thinking 4. Altered Level of Consciousness (RASS) Deficits of Attention Neuropsychologic hallmark of delirium Diffuse localization Diagnose during the history Tangential speech, fragmented ideas Test at bedside with digits forward task Four digits or less signifies lack of attention MMSE often not helpful icudelirium.org Cranial Nerve Testing II: Pupils, Acuity, Visual Fields III, IV, VI: Extraocular Movements V: Facial Sensation VII: Facial Strength VIII: Hearing IX, X: Palatal Elevation and Gag XI: SCM and Trapezius Power XII: Tongue Power Coma Definition: Not Awake Not Arousable Not Aware Test with cerebral motor response to pain centrally and in all four extremities (supraorbital and nail-bed pressure) 3
4 Structures involved in coma Two Localizations of Coma 1. Brainstem 2. Bilateral Hemispheres Use the CN exam to localize to brainstem or hemispheres Blumenfeld H. Neuroanatomy Through Clinical Cases Cranial Nerve Nuclei in the Brainstem Pupillary Reaction Midbrain: CN III Parasympathetics mediate Caveats Make sure light stimulus is adequate Assure no drug effects In many cases of brain death, the pupils are not blown and are midposition 4
5 Corneal Reflex Oculocephalic Reflex Pons: CN V and VII Test with a Q-tip or drops of saline Caveat: Make sure you are touching the cornea not the sclera Pons: CN III, VI, and VIII Vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) which we use on a moment-by-moment basis to foveate Testing procedure Doll s don t do this anymore Cold Calorics Cough and Gag Pons: CN III, VI, and VIII Stronger stimulus than oculocephalic 30cc of ice saline in each ear (1-3 min between); wait 1 minute for the response Correct response very misunderstood and poorly taught Medulla: CN IX and X Best to do both by suctioning through ET tube and touching each side of the palate with a tongue depressor Asymmetry is more interesting for us Remember percent have no gag normally 5
6 Respiratory Drive Lowest Part of the Medulla Technique Are they overbreathing? Consider apnea test in specific situations such as brain death determination Case 2: Motor A 75 yo male with HTN, DM and current tobacco use comes from the ED with mild problems walking and a complaint of my left arm is not working right. Case 2: Motor The ED physician tells you that he knows the patient has no weakness in his extremities as his own exam shows equal hand grasps, moving all fours, and stepping on the gas in the lower extremities. Upper Motor Neurons of the Pyramidal Tract Predictable Pattern of Weakness Distal Extensors of the UEs and Distal (Dorsi)Flexors of the LEs 6
7 Quick Screen for Upper Motor Neuron/Pyramidal Weakness UMN Pattern of Weakness Pyramidal Variable LMN Pronator Drift Fine Finger Movements/Toe Taps One muscle in each of four extremities Upper Extremities: 1 st DI or finger extensors Lower Extremities: Extensor of big toe Common ED screen VERY insensitive! Function/Dexterity Slow alternate motion rate Impairment of function is mostly due to weakness Tone Increased Decreased Tendon Reflex Increased Decreased, absent or normal Other signs Babinski sign, other CNS signs Atrophy (except with problem (e.g. aphasia, visual field cut) of neuromuscular junction) Weakness Pattern DTR Motor Neuron Disease Neuropathy NMJ Myopathy Variable Distal Diffuse Proximal Increased, Decreased or normal and/or absent decreased Normal or decreased Normal or decreased Atrophy Yes Yes No No Fasciculations Yes Sometimes No No Case 3: Sensory A 45 yo man presents with 2 days of progressive tingling and weakness of the lower extremities. He now is having trouble walking and rising from a chair. Sensory symptoms/ signs No Yes No No 7
8 Case 3: Sensory Case 4: Coordination Exam MS, CN normal Motor: normal tone throughout, normal power in upper ext., 4/5 throughout in the lower extremities Sensory: decreased PP/Vib/temp patchy in lower extremities A sensory level is found at T10 A 54 year-old woman presents with vertigo and gait difficulties On finger-nose-finger, she exhibits dysmetria with the right upper extremity, but not with the left Key Cerebellar Exam Tips Bilateral dysfunction is often benign and drug/medication related Unilateral dysfunction is a cerebellar lesion until proven otherwise CT insensitive in this region Cerebellar tracts run through the brainstem Cerebellar signs with cranial nerve deficits is a brainstem lesion until proven otherwise 8
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
Paediatric Bell s Palsy Paediatric Update November 2014
 Paediatric Bell s Palsy Paediatric Update November 2014 Richard Webster, Paediatric Neurologist Children s Hospital at Westmead Typical history Unilateral LMN facial weakness Acute onset over a day or
Paediatric Bell s Palsy Paediatric Update November 2014 Richard Webster, Paediatric Neurologist Children s Hospital at Westmead Typical history Unilateral LMN facial weakness Acute onset over a day or
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination
 Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Interval: [ ] Baseline [ ] 2 hours post treatment [ ] 24 hours post onset of symptoms ±20 minutes [ ] 7-10 days [ ] 3 months [ ] Other ( )
![Interval: [ ] Baseline [ ] 2 hours post treatment [ ] 24 hours post onset of symptoms ±20 minutes [ ] 7-10 days [ ] 3 months [ ] Other ( ) Interval: [ ] Baseline [ ] 2 hours post treatment [ ] 24 hours post onset of symptoms ±20 minutes [ ] 7-10 days [ ] 3 months [ ] Other ( )](/thumbs/29/13263233.jpg) Patient Identification. - - Pt. Date of Birth / / Hospital ( - ) Date of Exam / / Interval: [ ] Baseline [ ] 2 hours post treatment [ ] 24 hours post onset of symptoms ±20 minutes [ ] 7-10 days [ ] 3 months
Patient Identification. - - Pt. Date of Birth / / Hospital ( - ) Date of Exam / / Interval: [ ] Baseline [ ] 2 hours post treatment [ ] 24 hours post onset of symptoms ±20 minutes [ ] 7-10 days [ ] 3 months
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician
 EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
Update on Therapeutics in Neurology Evaluation Tabulation
 Update on Therapeutics in Neurology Evaluation Tabulation June 23, 2011 Georgetown, Washington, D.C. I am a: What was your overall rating of the faculty Jeffrey Frank, MD? The learning objectives designated
Update on Therapeutics in Neurology Evaluation Tabulation June 23, 2011 Georgetown, Washington, D.C. I am a: What was your overall rating of the faculty Jeffrey Frank, MD? The learning objectives designated
Functions of the Brain
 Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
REHABILITATION STANDARD: COMMUNICATION
 REHABILITATION STANDARD: COMMUNICATION Residents of Vancouver Island Health Authority (VIHA) will have reasonable access to consistent, integrated, measurable, evidence based rehabilitation services. This
REHABILITATION STANDARD: COMMUNICATION Residents of Vancouver Island Health Authority (VIHA) will have reasonable access to consistent, integrated, measurable, evidence based rehabilitation services. This
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Coding and Documentation in Practice
 Coding and Documentation in Practice Great Exam Documentation By: Kathy Mills Chang Kathy Mills Chang is a Certified Medical Compliance Expert, Reimbursement Consultant, Medicare Specialist, and a Documentation
Coding and Documentation in Practice Great Exam Documentation By: Kathy Mills Chang Kathy Mills Chang is a Certified Medical Compliance Expert, Reimbursement Consultant, Medicare Specialist, and a Documentation
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives
 Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Role of Electrodiagnostic Tests in Neuromuscular Disease
 Role of Electrodiagnostic Tests in Neuromuscular Disease Electrodiagnostic tests Electroencephalogram (EEG) Electromyography (NCV, EMG) Cerebral evoked potentials (CEP) Motor evoked potentials (MEP) Electronystagmogram
Role of Electrodiagnostic Tests in Neuromuscular Disease Electrodiagnostic tests Electroencephalogram (EEG) Electromyography (NCV, EMG) Cerebral evoked potentials (CEP) Motor evoked potentials (MEP) Electronystagmogram
Global Objectives. Use of the NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) in Emergency Department Patients with Acute Stroke. Why Do This Exercise? Session Objectives
 1 Use of the NIH Scale (NIHSS) in Emergency Department Patients with Acute Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois College of Medicine Chicago, IL Global Objectives Improve pt
1 Use of the NIH Scale (NIHSS) in Emergency Department Patients with Acute Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois College of Medicine Chicago, IL Global Objectives Improve pt
Primary Motor Pathway
 Understanding Eye Movements Abdullah Moh. El-Menaisy, MD, FRCS Chief, Neuro-ophthalmology ophthalmology & Investigation Units, Dhahran Eye Specialist Hospital, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Primary Motor Pathway
Understanding Eye Movements Abdullah Moh. El-Menaisy, MD, FRCS Chief, Neuro-ophthalmology ophthalmology & Investigation Units, Dhahran Eye Specialist Hospital, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Primary Motor Pathway
How to Do the EDSS EDSS
 How to Do the EDSS Stephen S. Kamin, MD New Jersey Medical School EDSS Expanded Disability Status Scale Devised by John Kurtzke in the 1960s and modified in the 1980s 1 EDSS Advantages Widely used Provides
How to Do the EDSS Stephen S. Kamin, MD New Jersey Medical School EDSS Expanded Disability Status Scale Devised by John Kurtzke in the 1960s and modified in the 1980s 1 EDSS Advantages Widely used Provides
The Normal Neurological Examination
 Normal Neurological Examination 1 of 10 The Normal Neurological Examination Introduction One of the most daunting aspects of the medical examination for the Emergency Physician and the primary care provider
Normal Neurological Examination 1 of 10 The Normal Neurological Examination Introduction One of the most daunting aspects of the medical examination for the Emergency Physician and the primary care provider
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy
 Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Neurological Assessment of the School Age Child
 O U T R E A C H E D U C A T I O N Neurological Assessment of the School Age Child April 3, 2008 Program Handouts This information is provided as a courtesy by Children's Health Care System and its related
O U T R E A C H E D U C A T I O N Neurological Assessment of the School Age Child April 3, 2008 Program Handouts This information is provided as a courtesy by Children's Health Care System and its related
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Neurogenic Disorders of Speech in Children and Adults
 Neurogenic Disorders of Speech in Children and Adults Complexity of Speech Speech is one of the most complex activities regulated by the nervous system It involves the coordinated contraction of a large
Neurogenic Disorders of Speech in Children and Adults Complexity of Speech Speech is one of the most complex activities regulated by the nervous system It involves the coordinated contraction of a large
Dizziness and Vertigo
 Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
The Basic Neurologic Examination
 The Basic Neurologic Examination Sally De Castro Tilsen, P.A.-C, MSCS Hoag Neuroscience Center and MS Center of Southern California Newport Beach, California OBJECTIVES: Understanding the importance of
The Basic Neurologic Examination Sally De Castro Tilsen, P.A.-C, MSCS Hoag Neuroscience Center and MS Center of Southern California Newport Beach, California OBJECTIVES: Understanding the importance of
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD
 Multifocal Motor Neuropathy Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD What is Multifocal Motor Neuropathy? Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) is a rare condition in which multiple motor nerves are attacked by
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD What is Multifocal Motor Neuropathy? Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) is a rare condition in which multiple motor nerves are attacked by
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease.
 Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Stuart B Black MD, FAAN Chief of Neurology Co-Medical Director: Neuroscience Center Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas
 Billing and Coding in Neurology and Headache Stuart B Black MD, FAAN Chief of Neurology Co-Medical Director: Neuroscience Center Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas CPT Codes vs. ICD Codes Category
Billing and Coding in Neurology and Headache Stuart B Black MD, FAAN Chief of Neurology Co-Medical Director: Neuroscience Center Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas CPT Codes vs. ICD Codes Category
Pseudoabducens palsy: When a VI nerve palsy is not a VI nerve palsy
 Pseudoabducens palsy: When a VI nerve palsy is not a VI nerve palsy Emily S. Birkholz, MD, and Michael Wall, MD December 30, 2009 CC: 44 year old male with diplopia HPI: This 44 year old man with a history
Pseudoabducens palsy: When a VI nerve palsy is not a VI nerve palsy Emily S. Birkholz, MD, and Michael Wall, MD December 30, 2009 CC: 44 year old male with diplopia HPI: This 44 year old man with a history
Multiple Sclerosis Jeffrey M. Gelfand, MD
 Multiple Sclerosis Jeffrey M. Gelfand, MD UCSF Multiple Sclerosis Center SFGH Neuroimmunology Clinic UCSF and SFGH Departments of Neurology Goals To review the fundamentals of neurological localization
Multiple Sclerosis Jeffrey M. Gelfand, MD UCSF Multiple Sclerosis Center SFGH Neuroimmunology Clinic UCSF and SFGH Departments of Neurology Goals To review the fundamentals of neurological localization
Evaluating muscle injuries and residuals of shell fragment and gunshot wounds
 Evaluating muscle injuries and residuals of shell fragment and gunshot wounds Training conducted by: Michael Fishman and Sandrine Fisher 1 Objectives To become familiar with the application of the rating
Evaluating muscle injuries and residuals of shell fragment and gunshot wounds Training conducted by: Michael Fishman and Sandrine Fisher 1 Objectives To become familiar with the application of the rating
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab. Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
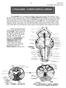 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
F r e q u e n t l y A s k e d Q u e s t i o n s
 Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs
 6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs As a Maxillofacial SHO you are not required to manage established head injury, however an awareness of the process is essential when dealing with
6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs As a Maxillofacial SHO you are not required to manage established head injury, however an awareness of the process is essential when dealing with
SPECIMEN. Interactive Training DVD-ROM for a standardised, quantified neurological examination and assessment of Kurtzke s Functional Systems and
 Definitions for a standardised, quantified neurological examination and assessment of Kurtzke s Functional Systems and Expanded Disability Status Scale in Multiple Sclerosis Independent Internet Platform
Definitions for a standardised, quantified neurological examination and assessment of Kurtzke s Functional Systems and Expanded Disability Status Scale in Multiple Sclerosis Independent Internet Platform
Delirium. The signs of delirium are managed by treating the underlying cause of the medical condition causing the delirium.
 Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Barry S. Oken, MD, Carter D. Wray MD Objectives: 1. Know the role of EMG/NCS in evaluating nerve and muscle function 2. Recognize common EEG findings and their significance 3.
CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Barry S. Oken, MD, Carter D. Wray MD Objectives: 1. Know the role of EMG/NCS in evaluating nerve and muscle function 2. Recognize common EEG findings and their significance 3.
Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario
 Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
PHYSICAL CAPACITIES EVALUATION FORM/RESIDUAL FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY ASSESSMENT FORM
 PHYSICAL CAPACITIES EVALUATION FORM/RESIDUAL FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY ASSESSMENT FORM ACTUAL SAMPLE (Note: This is an example of the specificity with which this form should be completed to be useful for the
PHYSICAL CAPACITIES EVALUATION FORM/RESIDUAL FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY ASSESSMENT FORM ACTUAL SAMPLE (Note: This is an example of the specificity with which this form should be completed to be useful for the
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing
 3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing Peter D. Donofrio, M.D. Professor of Neurology Vanderbilt University Medical Center
3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing Peter D. Donofrio, M.D. Professor of Neurology Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Cranial Nerves. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve
 Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY?
 WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd.
 About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Occupational Therapy in Cognitive Rehabilitation
 Occupational Therapy in Cognitive Rehabilitation Connie MS Lee Occupational therapist Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong Cognition Cognition refers to mental processes that include the abilities to concentrate,
Occupational Therapy in Cognitive Rehabilitation Connie MS Lee Occupational therapist Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong Cognition Cognition refers to mental processes that include the abilities to concentrate,
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy. Adam P. Smith, MD
 Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
HEAD INJURY Discharge Instructions
 Hospital Copy NEUROSURGICAL CONSULTANTS, INC. www.neurosurgical-consult.com MICHAEL GIEGER, ABNS MICHAEL H. FREED, M.D., FACS, ABNS MARC H. FRIEDBERG, M.D., Ph.D., FACS, ABNS LINDEN BUILDING FIRST FLOOR
Hospital Copy NEUROSURGICAL CONSULTANTS, INC. www.neurosurgical-consult.com MICHAEL GIEGER, ABNS MICHAEL H. FREED, M.D., FACS, ABNS MARC H. FRIEDBERG, M.D., Ph.D., FACS, ABNS LINDEN BUILDING FIRST FLOOR
Angela Wilkin May 2013
 Angela Wilkin May 2013 Upper Motor Neuron v Lower Motor Neuron Lesions UMN Lesion LMN Lesion Forehead usually unaffected (bilateral innervation) Forehead affected Contralateral side Ipsilateral side Often
Angela Wilkin May 2013 Upper Motor Neuron v Lower Motor Neuron Lesions UMN Lesion LMN Lesion Forehead usually unaffected (bilateral innervation) Forehead affected Contralateral side Ipsilateral side Often
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration. Objectives. Traumatic Brain Injury. Which came first, the injury or the behavior?
 Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Guideline for the Management of Acute Peripheral Facial nerve palsy. Bells Palsy in Children
 Guideline for the Management of Acute Peripheral Facial nerve palsy Definition Bells Palsy in Children Bell palsy is an acute, idiopathic unilateral lower motor neurone facial nerve palsy that is not associated
Guideline for the Management of Acute Peripheral Facial nerve palsy Definition Bells Palsy in Children Bell palsy is an acute, idiopathic unilateral lower motor neurone facial nerve palsy that is not associated
BLOOD ALCOHOL CONCENTRATION
 BLOOD ALCOHOL CONCENTRATION Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) is the amount of alcohol in the bloodstream. It is measured in percentages. For instance, having a BAC of 0.10 percent means that a person
BLOOD ALCOHOL CONCENTRATION Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) is the amount of alcohol in the bloodstream. It is measured in percentages. For instance, having a BAC of 0.10 percent means that a person
Overview. Neuropsychological Assessment in Stroke. Why a Neuropsychologist. How to make a referral. Referral Questions 11/6/2013
 Overview Neuropsychological Assessment in Stroke Brandon Ally, PhD Department of Neurology What is Neuropsychology Stroke Specific Neuropsychology Neuropsychological Domains Case Study What is Neuropsychology?
Overview Neuropsychological Assessment in Stroke Brandon Ally, PhD Department of Neurology What is Neuropsychology Stroke Specific Neuropsychology Neuropsychological Domains Case Study What is Neuropsychology?
Post-Concussion Syndrome
 Post-Concussion Syndrome Anatomy of the injury: The brain is a soft delicate structure encased in our skull, which protects it from external damage. It is suspended within the skull in a liquid called
Post-Concussion Syndrome Anatomy of the injury: The brain is a soft delicate structure encased in our skull, which protects it from external damage. It is suspended within the skull in a liquid called
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis. Disclosures: None
 Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
Managing the Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis. Yolanda Harris, MSN, CRNP-AC CPODD Nurse Practitioner
 Managing the Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis Yolanda Harris, MSN, CRNP-AC CPODD Nurse Practitioner What is Multiple Sclerosis An autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS) The immune
Managing the Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis Yolanda Harris, MSN, CRNP-AC CPODD Nurse Practitioner What is Multiple Sclerosis An autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS) The immune
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS
 DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
When it s time to apply for Social Security Disability Insurance: Making a stressful and complicated process easier for you and your family!
 When it s time to apply for Social Security Disability Insurance: Making a stressful and complicated process easier for you and your family! Presenter Disclosures Art Spencer The following personal financial
When it s time to apply for Social Security Disability Insurance: Making a stressful and complicated process easier for you and your family! Presenter Disclosures Art Spencer The following personal financial
Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis. ultimately lead to the crippling of the muscular system, there are many differences between these
 Battles 1 Becky Battles Instructor s Name English 1013 21 November 2006 Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis Although muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis are both progressive diseases that ultimately
Battles 1 Becky Battles Instructor s Name English 1013 21 November 2006 Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis Although muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis are both progressive diseases that ultimately
Providence Brain Institute Providence Portland Medical Center
 NIH Stroke Scale In Plain English Sandy Dancer, RN, MSN, ANP-C Sandy Dancer, RN, MSN, ANP C Providence Brain Institute Providence Portland Medical Center I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Preferred
NIH Stroke Scale In Plain English Sandy Dancer, RN, MSN, ANP-C Sandy Dancer, RN, MSN, ANP C Providence Brain Institute Providence Portland Medical Center I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Preferred
Cerebral Palsy. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nr200105 Last reviewed: 06/17/2014 1
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral palsy can be classified according to the type of abnormal muscle tone or movement, and the distribution of these motor impairments.
 The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION
 CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
IF ANY ITEM IS LEFT UNTESTED, A DETAILED EXPLANATION MUST BE CLEARLY WRITTEN ON THE FORM.
 NIH Stroke Scale The NINDS tpa Stroke Trial No. - - Pt. Date of Birth / / Hospital ( - ) Date of Exam / / Interval: 1 Baseline 2 2 hours post treatment 3 24 hours post onset of symptoms 6 minutes 4 7 10
NIH Stroke Scale The NINDS tpa Stroke Trial No. - - Pt. Date of Birth / / Hospital ( - ) Date of Exam / / Interval: 1 Baseline 2 2 hours post treatment 3 24 hours post onset of symptoms 6 minutes 4 7 10
Doctor I can t walk properly - a guided walk around some gait problems
 Doctor I can t walk properly - a guided walk around some gait problems Dr Jeremy Rees Consultant Neurologist National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Queen Square www.london-neurology.co.uk Walking
Doctor I can t walk properly - a guided walk around some gait problems Dr Jeremy Rees Consultant Neurologist National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Queen Square www.london-neurology.co.uk Walking
Revised 10-4-10 Bethel Park s Sports Concussion and Closed Head Injury Protocol and Procedures for Student-Athletes
 Bethel Park s Sports Concussion and Closed Head Injury Protocol and Procedures for Student-Athletes If the Certified Athletic Trainer of Bethel Park School District has a concern that a student-athlete
Bethel Park s Sports Concussion and Closed Head Injury Protocol and Procedures for Student-Athletes If the Certified Athletic Trainer of Bethel Park School District has a concern that a student-athlete
Cerebral Palsy. In order to function, the brain needs a continuous supply of oxygen.
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Purpose/Goal: Care partners will have an understanding of Multiple Sclerosis and will demonstrate safety and promote independence while providing care to the client with MS. Introduction
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Purpose/Goal: Care partners will have an understanding of Multiple Sclerosis and will demonstrate safety and promote independence while providing care to the client with MS. Introduction
NIH Stroke Scale. Upon completion of this course, the nurse will understand the following principles:
 NIHSS 1 NIH Stroke Scale Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the United States and cause more serious long-term disabilities than any other disease. Forty-five percent of all Medicare dollars
NIHSS 1 NIH Stroke Scale Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the United States and cause more serious long-term disabilities than any other disease. Forty-five percent of all Medicare dollars
STROKE CARE NOW NETWORK CONFERENCE MAY 22, 2014
 STROKE CARE NOW NETWORK CONFERENCE MAY 22, 2014 Rehabilitation Innovations in Post- Stroke Recovery Madhav Bhat, MD Fort Wayne Neurological Center DISCLOSURE Paid speaker for TEVA Neuroscience Program.
STROKE CARE NOW NETWORK CONFERENCE MAY 22, 2014 Rehabilitation Innovations in Post- Stroke Recovery Madhav Bhat, MD Fort Wayne Neurological Center DISCLOSURE Paid speaker for TEVA Neuroscience Program.
The CAM-S Score for Delirium Severity Training Manual and Coding Guide
 The CAM-S Score for Delirium Severity Training Manual and Coding Guide Please address questions to: Sharon K. Inouye, M.D., MPH Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Milton and Shirley F. Levy
The CAM-S Score for Delirium Severity Training Manual and Coding Guide Please address questions to: Sharon K. Inouye, M.D., MPH Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Milton and Shirley F. Levy
Supporting MS-Related Disability Claims to Private Insurers: The Physician s Role
 Supporting MS-Related Disability Claims to Private Insurers: The Physician s Role What Is This Guide? This guide was compiled by the National Multiple Sclerosis Society as an aid to health care professionals
Supporting MS-Related Disability Claims to Private Insurers: The Physician s Role What Is This Guide? This guide was compiled by the National Multiple Sclerosis Society as an aid to health care professionals
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report
 Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
NEUROLOGICAL ASSESSMENT
 Components of a Neurological Assessment: 1. Interview 2. Level of Consciousness 3. Pupillary Assessment 4. Cranial Nerve Testing 5. Vital signs 6. Motor Function 7. Sensory Function 8. Tone 9. Cerebral
Components of a Neurological Assessment: 1. Interview 2. Level of Consciousness 3. Pupillary Assessment 4. Cranial Nerve Testing 5. Vital signs 6. Motor Function 7. Sensory Function 8. Tone 9. Cerebral
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Patient Sticker Multiple Sclerosis Ambulatory Emergency Care Pathway
 Multiple Sclerosis Ambulatory Emergency Care Pathway 1 Consultant: Dr M Oldfield Consultant: Dr D Harris Lead Nurse: Catie Paterson Ambulatory Emergency Care (AEC) Unit Patient From ED (Emergency Department)
Multiple Sclerosis Ambulatory Emergency Care Pathway 1 Consultant: Dr M Oldfield Consultant: Dr D Harris Lead Nurse: Catie Paterson Ambulatory Emergency Care (AEC) Unit Patient From ED (Emergency Department)
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D]
![SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D] SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D]](/thumbs/27/9667060.jpg) SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D] I. Definitions: Detoxification is the process of interrupting the momentum of compulsive drug and/or alcohol use in an individual
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D] I. Definitions: Detoxification is the process of interrupting the momentum of compulsive drug and/or alcohol use in an individual
PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS
 PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS De Anna Looper, RN CHPN Corporate Clinical Consultant / Legal Nurse Consultant Carrefour Associates L.L.C. PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS
PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS De Anna Looper, RN CHPN Corporate Clinical Consultant / Legal Nurse Consultant Carrefour Associates L.L.C. PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS
Organ Donation: A Call for Greater Palliative Care Involvement
 Organ Donation: A Call for Greater Palliative Care Involvement Heather A. Harris, M.D. Associate Medical Director, Supportive & Palliative Care Service San Francisco General Hospital & Trauma Center Associate
Organ Donation: A Call for Greater Palliative Care Involvement Heather A. Harris, M.D. Associate Medical Director, Supportive & Palliative Care Service San Francisco General Hospital & Trauma Center Associate
AUGMENTATIVE COMMUNICATION EVALUATION
 AUGMENTATIVE COMMUNICATION EVALUATION Date: Name: Age: Date of Birth: Address: Telephone: Referral Source: Diagnosis: Participants: Social History and Current Services: lives with his in a private home
AUGMENTATIVE COMMUNICATION EVALUATION Date: Name: Age: Date of Birth: Address: Telephone: Referral Source: Diagnosis: Participants: Social History and Current Services: lives with his in a private home
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Conversion Commonly Used Neurologic Diagnosis
 ICD-9 to ICD-10 Conversion Commonly Used Neurologic Diagnosis 327.20 Organic sleep apnea, unspecified... 1 331.0 Alzheimer s disease...3 333.1 Essential and other specified forms of tremor...4 340 Multiple
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Conversion Commonly Used Neurologic Diagnosis 327.20 Organic sleep apnea, unspecified... 1 331.0 Alzheimer s disease...3 333.1 Essential and other specified forms of tremor...4 340 Multiple
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Return to same game if sx s resolve within 15 minutes. Return to next game if sx s resolve within one week Return to Competition
 Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Interdisciplinary Case Conference II
 Interdisciplinary Case Conference II Pacific University College of Health Professions John White- Occupational Therapy Katie Farrell- Physical Therapy Latha Reddy- Physician Assistant In-patient Rehab
Interdisciplinary Case Conference II Pacific University College of Health Professions John White- Occupational Therapy Katie Farrell- Physical Therapy Latha Reddy- Physician Assistant In-patient Rehab
Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Speech and Language Therapy
 Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Speech and Language Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Speech and Language Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
OVERVIEW. NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. WHAT IS THE MOST IMPORTANT PART OF THE PHYSICAL EXAM?
 NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. Neurological Surgery Bluegrass Orthopaedics and Hand Care OVERVIEW SCOPE OF THE PROBLEM PREVALENCE PATHOLOGY ANATOMIC CONSIDERATIONS ASSESSMENT
NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. Neurological Surgery Bluegrass Orthopaedics and Hand Care OVERVIEW SCOPE OF THE PROBLEM PREVALENCE PATHOLOGY ANATOMIC CONSIDERATIONS ASSESSMENT
