Pakistan Real Time Interbank Settlement Mechanism: An Overview
|
|
|
- Rebecca Walker
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pakistan Real Time Interbank Settlement Mechanism: An Overview RTGS Project Management Office State Bank of Pakistan
2 The development of PRISM (Pakistan Real time Interbank Settlement Mechanism) system started as a response to the growing awareness of the need for sound risk management in settlement of large-value funds transfers in Pakistan. PRISM systems operated by State Bank of Pakistan offers a powerful mechanism for limiting settlement and systemic risks in the interbank settlement process by providing settlement on Gross Basis and in Real Time. In addition, PRISM also contributes to the reduction of settlement risk in securities transactions by providing a basis for deliveryversuspayment (DVP) mechanisms. PRISM Participation: Participation in PRISM System is based on SBP s approval which after assessing the institutions financial standing and based on a pre defined risk management criteria approves an institutions request for Participation in PRISM System. PRISM Components: PRISM System comprises of two major applications i.e. RTS/X and Depo/X. RTS/X is funds transfer application operated thorough software installed by SBP at Participant s premises. Depo/X is securities settlement web based application and is connected in Real Time with RTS/X applications to ensure transaction in DvP basis. Risks Handling in PRISM System: The payments of interbank financial transactions are prone to Settlement risk which refers to the risk that the completion or settlement of the interbank funds transfer system as a whole, will not take place as expected. Settlement risk comprises both credit and liquidity risks. Two major sources of these risks are (a) a time-lag between the execution of the transaction and its final completion and (b) a time-lag between the completion of the two legs of the transaction (i.e. any lag between payment leg and delivery leg). Within large-value funds transfer systems the first type of lag, which takes the form of a settlement lag between the initiation of payment messages and their final settlement, can be a major source of settlement risk. Settlement lags Page 2 of 5
3 create the possibility that sending banks could fail in the meantime or at least not be able to settle their obligations when due. PRISM System however offers the mechanism to settle transactions in Real Time throughout the day therefore significantly reducing the time lag unlike the settlement system where transactions are settled at the end of the day. The second type of lag, sometimes referred to as asynchronous settlement, is the largest source of principal risk in the settlement of securities transactions, or, more generally, in exchange-for-value systems. This is the risk that the seller of an asset could deliver but not receive payment or that the buyer of an asset could make payment but not receive delivery, which could entail a loss equal to the full principal value of the assets involved. PRISM System however offer settlement of securities transactions on DVP basis, which ensures that the delivery of securities occurs if and only if payment occurs, thus providing a mechanism for eliminating such principal risk. Main features of PRISM System: Real Time Gross Settlement PRISM System is gross settlement system in which both processing and final settlement of funds transfer instructions takes place continuously (i.e. in real time). As it is a gross settlement system, transfers are settled individually, that is, without netting debits against credits. As it is a real-time settlement system, the system effects final settlement continuously rather than periodically at pre-specified times provided that a sending bank has sufficient covering balances or credit. Moreover, this settlement process is based on the real-time transfer of central bank (i.e. State Bank of Pakistan) money. Payment processing: Main features of payment processing in PRISM System are as follows: Page 3 of 5
4 1. Queuing: PRISM System temporarily keeps the transfer orders in its central processor (centrally located queues) if the covering funds are not sufficient for settlement. In this case, the pending transfer s instructions are queued and are released for settlement when covering funds become available on the basis of FIFO plus Priority principal. The management of queues can be carried out by banks individually or /and State Bank. 2. Priority: Participant in PRISM system can assign different priorities to their payments based on criticality of the payment. Priorities ranging from 10 to 99 can be assigned to payments by the PRISM Participants. For details please see PRISM Operating Rules. 3. Gridlock: PRISM system is also equipped with the Gridlock resolutions mechanism which when activated by SBP can offset large number of transactions on individual basis by reprioritizing payments in queue using different algorithms. ILF (Intraday Liquidity Facility): ILF is an intraday liquidity facility offered to facilitate settlement. ILF is a fully collateralized liquidity facility extended against approved government securities. For details please see PRISM Operating Rules. Retail Clearing Settlement: Multilateral Net Settlement Batches (MNSB) for retail clearing prepared by NIFT is also settled in PRISM System. Currently PRISM System settles three clearing batches (Normal, Intercity, Same day) and one Return Batch (Same day Returns). Participants are required to ensure Clearing Settlement within time limits imposed by SBP from time to time. Intraday Finality: Payments once settled in PRISM System are final and final irrevocable. Finality of payments settle in PRISM System is protected under Payment Systems & Electronic Funds Transfer Act Page 4 of 5
5 Message flow structures: Arrangements for routing payment messages in the PRISM System is based on a so-called V-shaped message flow structure. In this structure the full message with all the information about the payment (including, for example, the details of the beneficiary) is initially passed to the State Bank and is sent to the receiving bank only after the transfer has been settled by the central bank. Connectivity: There are only two possible ways of connecting any number of participants in PRISM System i.e. wired and wireless. SBP is using both the medium of communication for connecting the participant banks with SBP i.e. the domestic private leased data circuit system and in parallel, radio frequency bridged links in a licensed frequency spectrum except for those banks whose treasuries are situated outside the metropolitan area of Karachi which have been connected to SBP through point-to-point links. In order to ensure operational and security management, monitoring as well as support to all PRISM participants, the topology has been selected as to be stab, and as a way forward this entire setup is managed through state-of-the-art technology tools to achieve optimum business availability targets complying with the adopted standards of IT management. Cryptography: The confidentiality and integrity of information in the PRISM system are ensured by securing transmission, delivery, and message storage by validating messages and using state of the art 128K cryptographic facilities. Disaster Recovery: To overcome operational availability risks, a disaster recovery site exclusively for the PRISM system has been made available which synchronizes in real time with the primary PRISM site. A service bureau also functions in SBP to facilitate as part of BCP. Page 5 of 5
Real Time Gross Settlement Systems: An Overview
 Real Time Gross Settlement Systems: An Overview RTGS Project Management Office State Bank of Pakistan The development of RTGS systems started as a response to the growing awareness of the need for sound
Real Time Gross Settlement Systems: An Overview RTGS Project Management Office State Bank of Pakistan The development of RTGS systems started as a response to the growing awareness of the need for sound
8 PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEM
 8 PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEM A payments system is the set of instruments, procedures and rules used by financial institutions to transfer funds among themselves, either on their own behalf or that of
8 PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEM A payments system is the set of instruments, procedures and rules used by financial institutions to transfer funds among themselves, either on their own behalf or that of
CHAPS Technical Requirements
 CHAPS Technical Requirements 1. Technical Overview CHAPS provides a payment system between its Members settling in real time across sterling settlement accounts at the Bank of England. The key components
CHAPS Technical Requirements 1. Technical Overview CHAPS provides a payment system between its Members settling in real time across sterling settlement accounts at the Bank of England. The key components
Real-time Gross Settlement in Australia
 Real-time Gross Settlement in Australia Peter Gallagher, Jon Gauntlett and David Sunner* The introduction of real-time gross settlement (RTGS) in Australia in 1998 was a major reform to reduce risk in
Real-time Gross Settlement in Australia Peter Gallagher, Jon Gauntlett and David Sunner* The introduction of real-time gross settlement (RTGS) in Australia in 1998 was a major reform to reduce risk in
CLEARING AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS GENERAL ISSUES AND THE PHILIPPINE CASE. Mario B. Lamberte Philippine Institute for Development Studies
 CLEARING AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS GENERAL ISSUES AND THE PHILIPPINE CASE Mario B. Lamberte Philippine Institute for Development Studies ASEAN DEBT SECURITIES Figure 1 Outstanding Total Debt Securities in
CLEARING AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS GENERAL ISSUES AND THE PHILIPPINE CASE Mario B. Lamberte Philippine Institute for Development Studies ASEAN DEBT SECURITIES Figure 1 Outstanding Total Debt Securities in
Settlement Monitoring
 Monitoring Information Paper I have a Matched trade in the View Reported Trades. How will the system settle this trade? The system creates a set of 2 s for every Matched trade with a settle status of Accepted.
Monitoring Information Paper I have a Matched trade in the View Reported Trades. How will the system settle this trade? The system creates a set of 2 s for every Matched trade with a settle status of Accepted.
PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS IN SPAIN
 Francisco Linares Payment Settlement Systems Unit Manager Jesús Pérez Bonilla Securities Settlement Systems Unit Manager Payments Week 2005 Madrid 20 June 2005 PAYMENT SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT AGENDA PAYMENT
Francisco Linares Payment Settlement Systems Unit Manager Jesús Pérez Bonilla Securities Settlement Systems Unit Manager Payments Week 2005 Madrid 20 June 2005 PAYMENT SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT AGENDA PAYMENT
The Bank of Russia Payment System (BRPS)
 The Bank of Russia Payment System (BRPS) The BRPS is a systemically important payment system that plays a key role in the implementation of monetary and budgetary policy. It also plays a central part in
The Bank of Russia Payment System (BRPS) The BRPS is a systemically important payment system that plays a key role in the implementation of monetary and budgetary policy. It also plays a central part in
Payment and Settlement Systems of the CBRT
 Payment and Settlement Systems of the CBRT Elvan GÖÇMEN ERTEM Payment Systems Department Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey Experts Workshop on Payment Systems and Capacity Building in OIC Member Countries
Payment and Settlement Systems of the CBRT Elvan GÖÇMEN ERTEM Payment Systems Department Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey Experts Workshop on Payment Systems and Capacity Building in OIC Member Countries
A Guide to the Bank of England s Real Time Gross Settlement System
 A Guide to the Bank of England s Real Time Gross Settlement System October 2013 2 Contents Contents... 2 1. Introduction... 3 2. History and Main Functions of RTGS... 4 3. Settlement in RTGS... 5 4. Benefits
A Guide to the Bank of England s Real Time Gross Settlement System October 2013 2 Contents Contents... 2 1. Introduction... 3 2. History and Main Functions of RTGS... 4 3. Settlement in RTGS... 5 4. Benefits
VISION OF THE FUTURE NATIONAL PAYMENT SYSTEMS
 BANK OF JAMAICA (BOJ) VISION OF THE FUTURE NATIONAL PAYMENT SYSTEMS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY MARCH 2006 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. The Bank of Jamaica (BOJ) has embarked on a process of payment system reform to enhance
BANK OF JAMAICA (BOJ) VISION OF THE FUTURE NATIONAL PAYMENT SYSTEMS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY MARCH 2006 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. The Bank of Jamaica (BOJ) has embarked on a process of payment system reform to enhance
Payment flows of interbank payment and settlement systems in 2002
 Payment flows of interbank payment and settlement systems in 2002 1. Development and distribution of interbank turnover among payment systems The value of the interbank payment system in 2002 including
Payment flows of interbank payment and settlement systems in 2002 1. Development and distribution of interbank turnover among payment systems The value of the interbank payment system in 2002 including
Gridlock Resolution in Payment Systems
 67 Gridlock Resolution in Payment Systems Morten Linnemann Bech, Payment Systems, and Kimmo Soramäki, Bank of Finland. INTRODUCTION During the last few decades, most industrialised countries have introduced
67 Gridlock Resolution in Payment Systems Morten Linnemann Bech, Payment Systems, and Kimmo Soramäki, Bank of Finland. INTRODUCTION During the last few decades, most industrialised countries have introduced
OVERSIGHT OF THE PAYMENT SYSTEM IN LATVIA
 OVERSIGHT OF THE PAYMENT SYSTEM IN LATVIA Latvijas Banka, 2004 The source is to be indicated when reproduced. Riga 2004 LATVIJAS BANKA 2 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 1. OVERSIGHT OF SYSTEMICALLY IMPORTANT
OVERSIGHT OF THE PAYMENT SYSTEM IN LATVIA Latvijas Banka, 2004 The source is to be indicated when reproduced. Riga 2004 LATVIJAS BANKA 2 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 1. OVERSIGHT OF SYSTEMICALLY IMPORTANT
1. WHY WE NEED FOREIGN EXCHANGE 2. WHAT FOREIGN EXCHANGE MEANS 3. ROLE OF THE EXCHANGE RATE. 9 The Foreign Exchange Market in the United States
 CHAPTER 2 1. WHY WE NEED FOREIGN EXCHANGE Almost every nation has its own national currency or monetary unit its dollar, its peso, its rupee used for making and receiving payments within its own borders.
CHAPTER 2 1. WHY WE NEED FOREIGN EXCHANGE Almost every nation has its own national currency or monetary unit its dollar, its peso, its rupee used for making and receiving payments within its own borders.
The Introduction of Same-day Settlement of Direct Entry Obligations in Australia
 The Introduction of Same-day Settlement of Direct Entry Obligations in Australia Sascha Fraser and Adriarne Gatty* In November 213, the Reserve Bank introduced changes to its Reserve Bank Information and
The Introduction of Same-day Settlement of Direct Entry Obligations in Australia Sascha Fraser and Adriarne Gatty* In November 213, the Reserve Bank introduced changes to its Reserve Bank Information and
INFORMATION PAPER RITS INFORMATION PAPER RITS REGULATIONS AND CONDITIONS OF OPERATION
 RITS REGULATIONS AND CONDITIONS OF OPERATION CONTENTS 1. OVERVIEW 1 2. OUTLINE OF REGULATIONS 2 3. KEY CONCEPTS 3.1 Types of Members 3.2 Branches 3.3 Cash Accounts 3.4 Cash Elements and Interbank Cash
RITS REGULATIONS AND CONDITIONS OF OPERATION CONTENTS 1. OVERVIEW 1 2. OUTLINE OF REGULATIONS 2 3. KEY CONCEPTS 3.1 Types of Members 3.2 Branches 3.3 Cash Accounts 3.4 Cash Elements and Interbank Cash
LankaSettle & LankaSecure. Participant
 P r e a m b l e In terms of Section 113 of the Monetary Law Act (MLA), Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) as the fiscal agent of the Government, is responsible for the management of Public Debt. Accordingly,
P r e a m b l e In terms of Section 113 of the Monetary Law Act (MLA), Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) as the fiscal agent of the Government, is responsible for the management of Public Debt. Accordingly,
The Payment and Settlement Systems in the Republic of China (Taiwan)
 The Payment and Settlement Systems in the Republic of China (Taiwan) October 2010 Central Bank of the Republic of China (Taiwan) 0 Preface Payment and settlement systems are a critical part of the financial
The Payment and Settlement Systems in the Republic of China (Taiwan) October 2010 Central Bank of the Republic of China (Taiwan) 0 Preface Payment and settlement systems are a critical part of the financial
Wholesale Payment Systems
 IT Examination Handbook Presentation Wholesale Payment Systems 1. Open music 2. 3. Retail vs. Wholesale Payments Wholesale Payment Examples The distinction between wholesale and retail payments, as discussed
IT Examination Handbook Presentation Wholesale Payment Systems 1. Open music 2. 3. Retail vs. Wholesale Payments Wholesale Payment Examples The distinction between wholesale and retail payments, as discussed
PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS
 4 PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS 4.1 Overview Payment and settlement systems are crucially important to the smooth functioning of the economy. It is the responsibility of a central bank to promote sound
4 PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS 4.1 Overview Payment and settlement systems are crucially important to the smooth functioning of the economy. It is the responsibility of a central bank to promote sound
GRAPH 13 ELECTRONIC TRANSFERS (Monthly average in billions of S/.) 49.6 2005 2006 2007 3.2 6.0 7.2 8.2
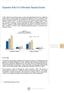 In 2007, the total value of the payments carried out through the Real Time Gross Settlement system (RTGS) 1 and the Cámara de Compensación Electrónica (CCE) increased by 25.9 percent compared to 2006.
In 2007, the total value of the payments carried out through the Real Time Gross Settlement system (RTGS) 1 and the Cámara de Compensación Electrónica (CCE) increased by 25.9 percent compared to 2006.
KINGDOM OF BAHRAIN FINANCIAL SECTOR ASSESSMENT PROGRAM
 IMF Country Report No. 16/170 June 2016 KINGDOM OF BAHRAIN FINANCIAL SECTOR ASSESSMENT PROGRAM DETAILED ASSESSMENT OF OBSERVANCE ASSESSMENT OF OBSERVANCE OF THE CPMI-IOSCO PRINCIPLES FOR FINANCIAL MARKET
IMF Country Report No. 16/170 June 2016 KINGDOM OF BAHRAIN FINANCIAL SECTOR ASSESSMENT PROGRAM DETAILED ASSESSMENT OF OBSERVANCE ASSESSMENT OF OBSERVANCE OF THE CPMI-IOSCO PRINCIPLES FOR FINANCIAL MARKET
PAYMENT SYSTEMS IN GHANA
 PAYMENT SYSTEMS IN GHANA OVERVIEW The payment system is the entire matrix of institutional infrastructure arrangements and processes in a country set up to enable economic agents (individuals, businesses,
PAYMENT SYSTEMS IN GHANA OVERVIEW The payment system is the entire matrix of institutional infrastructure arrangements and processes in a country set up to enable economic agents (individuals, businesses,
RTS/X. Scalable Solution for Payment Processing Systems. Guiding Principles of the system architecture. Overview
 RTS/X Scalable Solution for Payment Processing Systems Overview RTS/X is a full-functional RTGS solution with enhanced monitoring and liquidity management facilities, DvP/PvP support and built-in tools
RTS/X Scalable Solution for Payment Processing Systems Overview RTS/X is a full-functional RTGS solution with enhanced monitoring and liquidity management facilities, DvP/PvP support and built-in tools
Contagion in Payment and Settlement Systems
 Contagion in Payment and Settlement Systems Matti Hellqvist Financial Markets and Statistics Dept. - Bank of Finland Paper presented at the Expert Forum on Advanced Techniques on Stress Testing: Applications
Contagion in Payment and Settlement Systems Matti Hellqvist Financial Markets and Statistics Dept. - Bank of Finland Paper presented at the Expert Forum on Advanced Techniques on Stress Testing: Applications
1. Large-Value Payment System
 1. Large-Value Payment System 1.1 Outline The BOK has been running BOK-Wire as the only RTGS system for large-value funds since December 1994. It guarantees settlement finality for individual funds transfer
1. Large-Value Payment System 1.1 Outline The BOK has been running BOK-Wire as the only RTGS system for large-value funds since December 1994. It guarantees settlement finality for individual funds transfer
THE USE OF CENTRAL BANK MONEY FOR SETTLING SECURITIES TRANSACTIONS
 THE USE OF CENTRAL BANK MONEY FOR SETTLING SECURITIES TRANSACTIONS MAY 2004 CURRENT AND PRACTICES THE USE OF CENTRAL BANK MONEY FOR SETTLING SECURITIES TRANSACTIONS MAY 2004 CURRENT AND PRACTICES In 2004
THE USE OF CENTRAL BANK MONEY FOR SETTLING SECURITIES TRANSACTIONS MAY 2004 CURRENT AND PRACTICES THE USE OF CENTRAL BANK MONEY FOR SETTLING SECURITIES TRANSACTIONS MAY 2004 CURRENT AND PRACTICES In 2004
Assessment of Monte Titoli s observance of the ESCB-CESR Recommendations for Securities Settlement Systems
 Assessment of Monte Titoli s observance of the ESCB-CESR Recommendations for Securities Settlement Systems Premise Monte Titoli is Italy s central securities depository (CSD). It manages the securities
Assessment of Monte Titoli s observance of the ESCB-CESR Recommendations for Securities Settlement Systems Premise Monte Titoli is Italy s central securities depository (CSD). It manages the securities
Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems. Payment systems in Kazakhstan
 Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems Payment systems in Kazakhstan Prepared by the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems of the central
Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems Payment systems in Kazakhstan Prepared by the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems of the central
A Brief Description of the Bank of Russia Real Time Gross Settlement System (BESP System)
 A Brief Description of the Bank of Russia Real Time Gross Settlement System (BESP System) The Russian economy s rising demand for urgent payments, which require faster finality and the need for reliable
A Brief Description of the Bank of Russia Real Time Gross Settlement System (BESP System) The Russian economy s rising demand for urgent payments, which require faster finality and the need for reliable
Your Partner for European Payment Processing
 Your Partner for European Payment Processing A state-of-the-art platform built to support European diversity We believe that SEPA and domestic instruments will co-exist for some time, and both need to
Your Partner for European Payment Processing A state-of-the-art platform built to support European diversity We believe that SEPA and domestic instruments will co-exist for some time, and both need to
Swaziland Interbank Payment and Settlement System (SWIPSS)
 Adopted by RTGS Steering Committee May 2007 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 DEFINITIONS 3 SECTION 2 PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS 6 SECTION 3 PARTICIPATION REQUIREMENTS 7 SECTION 4 WITHDRAWAL AND SUSPENSION FROM
Adopted by RTGS Steering Committee May 2007 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 DEFINITIONS 3 SECTION 2 PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS 6 SECTION 3 PARTICIPATION REQUIREMENTS 7 SECTION 4 WITHDRAWAL AND SUSPENSION FROM
THE PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS 2007
 THE PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS 2007 1. INTRODUCTION The payment and settlement system was upgraded in 2007 with the introduction of a Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) system known in Israel as Zahav,
THE PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS 2007 1. INTRODUCTION The payment and settlement system was upgraded in 2007 with the introduction of a Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) system known in Israel as Zahav,
Fast Settlement Service Information Paper 3. Requirements Phase. April 2014. Fast Payments SPRINT Program
 Fast Settlement Service Information Paper 3 Requirements Phase April 2014 Fast Payments SPRINT Program Glossary Below is a list of selected terms used in this document. Relevant definitions have been adopted
Fast Settlement Service Information Paper 3 Requirements Phase April 2014 Fast Payments SPRINT Program Glossary Below is a list of selected terms used in this document. Relevant definitions have been adopted
Bank of Tanzania PAYMENT SYSTEMS IN THE SOUTHERN AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT COMMUNITY - TANZANIA CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Bank of Tanzania PAYMENT SYSTEMS IN THE SOUTHERN AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT COMMUNITY - TANZANIA CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INSTITUTIONAL ASPECTS 3 1.1 General Legal Aspects... 3 1.2 The Role of Financial Intermediaries
Bank of Tanzania PAYMENT SYSTEMS IN THE SOUTHERN AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT COMMUNITY - TANZANIA CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INSTITUTIONAL ASPECTS 3 1.1 General Legal Aspects... 3 1.2 The Role of Financial Intermediaries
Intra-day payment Frequently asked questions
 Intra-day payment Frequently asked questions Contents 1. THE MEANING, advantages and scope of intra-day payment... 3 1.1. What does the launch of intra-day payment mean?... 3 1.2. What advantages does
Intra-day payment Frequently asked questions Contents 1. THE MEANING, advantages and scope of intra-day payment... 3 1.1. What does the launch of intra-day payment mean?... 3 1.2. What advantages does
Bank of England Settlement Accounts
 Bank of England Settlement Accounts November 2014 Contents Foreword 3 1. Payment systems and the role of the central bank 4 Payment systems 4 Settlement in central bank money 4 Intraday liquidity 4 Use
Bank of England Settlement Accounts November 2014 Contents Foreword 3 1. Payment systems and the role of the central bank 4 Payment systems 4 Settlement in central bank money 4 Intraday liquidity 4 Use
Eesti Pank policy for the operation and oversight of payment systems and for facilitating the payment market
 Eesti Pank policy for the operation and oversight of payment systems and for facilitating the payment market Under the Eesti Pank strategy for 2014 2018, it is part of Eesti Pank's mission to promote a
Eesti Pank policy for the operation and oversight of payment systems and for facilitating the payment market Under the Eesti Pank strategy for 2014 2018, it is part of Eesti Pank's mission to promote a
Contents. List of abbreviations 146. Introduction 147
 latvia Contents List of abbreviations 146 Introduction 147 1 Institutional aspects 148 1.1 The general institutional framework 148 1.2 The role of Latvijas Banka 150 1.3 The role of other private and public
latvia Contents List of abbreviations 146 Introduction 147 1 Institutional aspects 148 1.1 The general institutional framework 148 1.2 The role of Latvijas Banka 150 1.3 The role of other private and public
Payment & Settlement Systems in Sri Lanka and the Future Expectations. Ranjani Weerasinghe Director Payments and Settlements
 Payment & Settlement Systems in Sri Lanka and the Future Expectations Ranjani Weerasinghe Director Payments and Settlements Outline Payments and Settlement Systems in the country Recent Developments Future
Payment & Settlement Systems in Sri Lanka and the Future Expectations Ranjani Weerasinghe Director Payments and Settlements Outline Payments and Settlement Systems in the country Recent Developments Future
REAL TIME GROSS SETTLEMENT (RTGS) SYSTEM AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR CENTRAL BANKING
 REAL TIME GROSS SETTLEMENT (RTGS) SYSTEM AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR CENTRAL BANKING Wilhelmina C. Mañalac, Agnes M. Yap and Magno Torreja, Jr. Introduction A payments system comprises the cultural, political,
REAL TIME GROSS SETTLEMENT (RTGS) SYSTEM AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR CENTRAL BANKING Wilhelmina C. Mañalac, Agnes M. Yap and Magno Torreja, Jr. Introduction A payments system comprises the cultural, political,
How To Settle A Transaction In Japanese Bank Of Japanesia
 Chapter IV Payment and Settlement and the Roles of the Bank of Japan The Bank of Japan provides Bank of Japan notes and current account deposits at the Bank (hereafter, BOJ account deposits ) as payment
Chapter IV Payment and Settlement and the Roles of the Bank of Japan The Bank of Japan provides Bank of Japan notes and current account deposits at the Bank (hereafter, BOJ account deposits ) as payment
Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council FFIEC. Wholesale Payment Systems WPS JULY 2004 IT EXAMINATION HANDBOOK
 Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council FFIEC Wholesale Payment Systems JULY 2004 WPS IT EXAMINATION HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 INTERBANK PAYMENT AND MESSAGING SYSTEMS... 3
Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council FFIEC Wholesale Payment Systems JULY 2004 WPS IT EXAMINATION HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 INTERBANK PAYMENT AND MESSAGING SYSTEMS... 3
RESERVE BANK INFORMATION AND TRANSFER SYSTEM. Same-day Settlement of Low-value Payments in RITS. Industry Consultation Paper
 RESERVE BANK INFORMATION AND TRANSFER SYSTEM Same-day Settlement of Low-value Payments in RITS Industry Consultation Paper May 2008 1. INTRODUCTION...2 2. ALTERNATIVES FOR SAME-DAY SETTLEMENT OF BULK LOW-VALUE
RESERVE BANK INFORMATION AND TRANSFER SYSTEM Same-day Settlement of Low-value Payments in RITS Industry Consultation Paper May 2008 1. INTRODUCTION...2 2. ALTERNATIVES FOR SAME-DAY SETTLEMENT OF BULK LOW-VALUE
The Role of Exchange Settlement Accounts
 Reserve Bank of Australia Bulletin March 1999 The Role of Exchange Settlement Accounts Introduction Exchange Settlement (ES) Accounts provided by the Reserve Bank play an important role in the Australian
Reserve Bank of Australia Bulletin March 1999 The Role of Exchange Settlement Accounts Introduction Exchange Settlement (ES) Accounts provided by the Reserve Bank play an important role in the Australian
DECISION on the Croatian Large Value Payment System and on the Settlement in Bank Accounts Held with the Croatian National Bank.
 Pursuant to Article 38 paragraph 3 under m) of the Croatian National Bank Act (official gazette Narodne novine, No. 36/2001) and Article 44 paragraph 1 items 7 and 8 of the National Payment System Act
Pursuant to Article 38 paragraph 3 under m) of the Croatian National Bank Act (official gazette Narodne novine, No. 36/2001) and Article 44 paragraph 1 items 7 and 8 of the National Payment System Act
PAYMENT SYSTEM OVERSIGHT ACCESS POLICY JAMCLEAR RTGS
 ACCESS POLICY JAMCLEAR RTGS July 2012 Table of Contents 1.0 Purpose... 3 2.0 Background... 3 3.0 Criteria for Access... 4 July 2012 2 1.0 Purpose 1.1 JamClear RTGS is owned and operated by the Bank of
ACCESS POLICY JAMCLEAR RTGS July 2012 Table of Contents 1.0 Purpose... 3 2.0 Background... 3 3.0 Criteria for Access... 4 July 2012 2 1.0 Purpose 1.1 JamClear RTGS is owned and operated by the Bank of
2 Basic Concepts. Contents
 2. Basic Concepts Contents 2 Basic Concepts a. Link configuration b. Topology c. Transmission mode d. Classes of networks 1 a. Link Configuration Data links A direct data link is one that establishes a
2. Basic Concepts Contents 2 Basic Concepts a. Link configuration b. Topology c. Transmission mode d. Classes of networks 1 a. Link Configuration Data links A direct data link is one that establishes a
TARGET2 a single Europe for individual payments. Department Payments and Settlement Systems
 a single Europe for individual payments Department Payments and Settlement Systems Page 2 TARGET2 single technical platform for processing urgent euro payments TARGET2 is the real-time gross settlement
a single Europe for individual payments Department Payments and Settlement Systems Page 2 TARGET2 single technical platform for processing urgent euro payments TARGET2 is the real-time gross settlement
Sayan Pariwat Rungsun Hataiseree Bank of Thailand
 Working Paper 2003-02 Payment Systems Group September, 2003 Managing Payment and Settlement System Reform: A Thai Perspective Prepared by Sayan Pariwat and Rungsun Hataiseree * ABSTRACT This paper deals
Working Paper 2003-02 Payment Systems Group September, 2003 Managing Payment and Settlement System Reform: A Thai Perspective Prepared by Sayan Pariwat and Rungsun Hataiseree * ABSTRACT This paper deals
A Study Looking the Electronic Funds Transfer
 92 A Study Looking the Electronic Funds Transfer Codruţa POENAR Department of Economics Informatics Faculty of Economics and Business Administration Babeş-Bolyai University, Cluj-Napoca, România [email protected]
92 A Study Looking the Electronic Funds Transfer Codruţa POENAR Department of Economics Informatics Faculty of Economics and Business Administration Babeş-Bolyai University, Cluj-Napoca, România [email protected]
DISCLOSURE FRAMEWORK FOR SECURITIES SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS SITEME. Markets and Reserve Management Department
 DISCLOSURE FRAMEWORK FOR SECURITIES SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS SITEME Markets and Reserve Management Department SEPTEMBER 2004 DISCLAIMER This document comprises the answers given by Banco de Portugal (the Portuguese
DISCLOSURE FRAMEWORK FOR SECURITIES SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS SITEME Markets and Reserve Management Department SEPTEMBER 2004 DISCLAIMER This document comprises the answers given by Banco de Portugal (the Portuguese
DISCLOSURE FRAMEWORK FOR SECURITIES SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS. Central Register of Short-term Securities maintained by the National Bank of Slovakia
 DISCLOSURE FRAMEWORK FOR SECURITIES SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS Central Register of Short-term Securities maintained by the National Bank of Slovakia Introduction The following document comprises the answers formulated
DISCLOSURE FRAMEWORK FOR SECURITIES SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS Central Register of Short-term Securities maintained by the National Bank of Slovakia Introduction The following document comprises the answers formulated
RISK MANAGEMENT IN NETTING SCHEMES FOR SETTLEMENT OF SECURITIES TRANSACTIONS
 RISK MANAGEMENT IN NETTING SCHEMES FOR SETTLEMENT OF SECURITIES TRANSACTIONS A background paper for the 4th OECD/World Bank Bond Market Workshop 7-8 March 02 by Jan Woltjer 1 1 Introduction Settlement
RISK MANAGEMENT IN NETTING SCHEMES FOR SETTLEMENT OF SECURITIES TRANSACTIONS A background paper for the 4th OECD/World Bank Bond Market Workshop 7-8 March 02 by Jan Woltjer 1 1 Introduction Settlement
Monetary Authority of Singapore MEPS+ PRINCIPLES FOR FINANCIAL MARKET INFRASTRUCTURES DISCLOSURE
 Monetary Authority of Singapore MEPS+ PRINCIPLES FOR FINANCIAL MARKET INFRASTRUCTURES DISCLOSURE Table of Contents I. Executive Summary... 4 II. General Background on the FMI... 6 III. Principle-By-Principle
Monetary Authority of Singapore MEPS+ PRINCIPLES FOR FINANCIAL MARKET INFRASTRUCTURES DISCLOSURE Table of Contents I. Executive Summary... 4 II. General Background on the FMI... 6 III. Principle-By-Principle
COMMITTEE ON PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS
 COMMITTEE ON PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS SECRETARIAT January 2001 The Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems (CPSS) A. Introduction: the role and purpose of the CPSS. B. Areas of work: 1. Core
COMMITTEE ON PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS SECRETARIAT January 2001 The Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems (CPSS) A. Introduction: the role and purpose of the CPSS. B. Areas of work: 1. Core
SETTLEMENT FAILS REPORT ON SECURITIES SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS (SSS) MEASURES TO ENSURE TIMELY SETTLEMENT
 SETTLEMENT FAILS REPORT ON SECURITIES SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS (SSS) MEASURES TO ENSURE TIMELY SETTLEMENT INTRODUCTION Understanding settlement fails serves the interest of central banks with respect to their
SETTLEMENT FAILS REPORT ON SECURITIES SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS (SSS) MEASURES TO ENSURE TIMELY SETTLEMENT INTRODUCTION Understanding settlement fails serves the interest of central banks with respect to their
Federal Reserve Policy on Payments System Risk
 Federal Reserve Policy on Payments System Risk As amended effective January 11, 2007 INTRODUCTION RISKS IN PAYMENTS AND SETTLEMENT SYTEMS I. RISK MANAGEMENT IN PAYMENTS AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS A. Scope
Federal Reserve Policy on Payments System Risk As amended effective January 11, 2007 INTRODUCTION RISKS IN PAYMENTS AND SETTLEMENT SYTEMS I. RISK MANAGEMENT IN PAYMENTS AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS A. Scope
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN INFORMATION ASSURANCE PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE HAMPTON UNIVERSITY
 MASTER OF SCIENCE IN INFORMATION ASSURANCE PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE HAMPTON UNIVERSITY HTTP://SCIENCE.HAMPTONU.EDU/COMPSCI/ The Master of Science in Information Assurance focuses on providing
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN INFORMATION ASSURANCE PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE HAMPTON UNIVERSITY HTTP://SCIENCE.HAMPTONU.EDU/COMPSCI/ The Master of Science in Information Assurance focuses on providing
Operating rules for Settlement Systems (EXPRESS II) and related activities
 Monte Titoli Operating rules for Settlement Systems (EXPRESS II) and related activities 9 S e p t e m b e r 2 0 1 3 T h e I t a l i a n t e x t s h a l l p r e v a i l o v e r t h e E n g l i s h v e r
Monte Titoli Operating rules for Settlement Systems (EXPRESS II) and related activities 9 S e p t e m b e r 2 0 1 3 T h e I t a l i a n t e x t s h a l l p r e v a i l o v e r t h e E n g l i s h v e r
Section 4 E-SETTLEMENT COST/BENEFIT ANALYSIS
 Section 4, page 7 Section 4 E-SETTLEMENT COST/BENEFIT ANALYSIS The views expressed here are those of the project. They are at the moment preliminary and open for all comments. The views do not necessarily
Section 4, page 7 Section 4 E-SETTLEMENT COST/BENEFIT ANALYSIS The views expressed here are those of the project. They are at the moment preliminary and open for all comments. The views do not necessarily
OVERSIGHT STANDARDS FOR EURO RETAIL PAYMENT SYSTEMS
 OVERSIGHT STANDARDS FOR EURO RETAIL PAYMENT SYSTEMS 1 Introduction The oversight of payment systems is an essential function of central banks and aims to ensure the smooth functioning of payment systems
OVERSIGHT STANDARDS FOR EURO RETAIL PAYMENT SYSTEMS 1 Introduction The oversight of payment systems is an essential function of central banks and aims to ensure the smooth functioning of payment systems
Innovations in International Payment Systems and Their Implications for Banks. (August 2007)
 Innovations in International Payment Systems and Their Implications for Banks (August 2007) Yoon S. Park Professor of International Finance George Washington University School of Business Washington, D.C.
Innovations in International Payment Systems and Their Implications for Banks (August 2007) Yoon S. Park Professor of International Finance George Washington University School of Business Washington, D.C.
10.1 ASX SETTLEMENT ENTITLED TO ASSUME RULES COMPLIED WITH...6 10.1.1 ASX Settlement entitled to assume without inquiry... 6
 SECTION 10 BATCH SETTLEMENT 10.1 ASX SETTLEMENT ENTITLED TO ASSUME RULES COMPLIED WITH...6 10.1.1 ASX Settlement entitled to assume without inquiry... 6 10.2 PARTICIPATION IN BATCH SETTLEMENT...6 10.2.1
SECTION 10 BATCH SETTLEMENT 10.1 ASX SETTLEMENT ENTITLED TO ASSUME RULES COMPLIED WITH...6 10.1.1 ASX Settlement entitled to assume without inquiry... 6 10.2 PARTICIPATION IN BATCH SETTLEMENT...6 10.2.1
PAYMENT SYSTEMS REVIEW (FISCAL YEAR 2014-15)
 PAYMENT SYSTEMS REVIEW (FISCAL YEAR 214-15) PAYMENT SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT STATE BANK OF PAKISTAN Payment Systems Review Fiscal Year 214-15 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. OVERVIEW OF COUNTRY S PAYMENT SYSTEMS... 4 2.
PAYMENT SYSTEMS REVIEW (FISCAL YEAR 214-15) PAYMENT SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT STATE BANK OF PAKISTAN Payment Systems Review Fiscal Year 214-15 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. OVERVIEW OF COUNTRY S PAYMENT SYSTEMS... 4 2.
Intraday credit transfer: Frequently Asked Questions and Definitions. Bank customers enjoy significant advantages
 Intraday credit transfer: Frequently Asked Questions and Definitions Bank customers enjoy significant advantages Following 1 July 2012 the execution time of domestic HUF credit transfers will be one business
Intraday credit transfer: Frequently Asked Questions and Definitions Bank customers enjoy significant advantages Following 1 July 2012 the execution time of domestic HUF credit transfers will be one business
GLOSSARY OF TERMS RELATED TO PAYMENT, CLEARING AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS 1
 GLOSSARY OF TERMS RELATED TO PAYMENT, CLEARING AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS 1 Acceptance: this term has two meanings: 1) in the field of transfer systems, it refers to the inclusion of a transfer order for funds
GLOSSARY OF TERMS RELATED TO PAYMENT, CLEARING AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEMS 1 Acceptance: this term has two meanings: 1) in the field of transfer systems, it refers to the inclusion of a transfer order for funds
OVERSIGHT OF THE PAYMENT SYSTEM IN LATVIA
 RIGA 2002 Latvijas Banka, 2002 The source is to be indicated when reproduced. ISBN 9984 676 47 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 5 NATIONAL PAYMENT SYSTEM 7 Payment System Risks 8 THE BANK OF LATVIA'S PAYMENT SYSTEM
RIGA 2002 Latvijas Banka, 2002 The source is to be indicated when reproduced. ISBN 9984 676 47 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 5 NATIONAL PAYMENT SYSTEM 7 Payment System Risks 8 THE BANK OF LATVIA'S PAYMENT SYSTEM
Settlement risk in foreign exchange markets and CLS Bank 1
 Gabriele Galati +41 61 280 8923 [email protected] Settlement risk in foreign exchange markets and CLS Bank 1 Introduction In September 2002, CLS Bank, a new financial institution set up to reduce
Gabriele Galati +41 61 280 8923 [email protected] Settlement risk in foreign exchange markets and CLS Bank 1 Introduction In September 2002, CLS Bank, a new financial institution set up to reduce
SWIFT for high-value payment market infrastructures. End-to-end solutions for payment clearing and settlement
 SWIFT for high-value payment market infrastructures End-to-end solutions for payment clearing and settlement 1 Table of contents Introduction 03 03 Executive Summary 04 04 Evolving demand 05 05 SWIFT s
SWIFT for high-value payment market infrastructures End-to-end solutions for payment clearing and settlement 1 Table of contents Introduction 03 03 Executive Summary 04 04 Evolving demand 05 05 SWIFT s
Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems. CPSS Payment, clearing and settlement systems in Macedonia, FYR, 2013
 Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems CPSS Payment, clearing and settlement systems in Macedonia, FYR, 2013 Prepared by the National Bank of the Republic of Macedonia and the Committee on Payment
Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems CPSS Payment, clearing and settlement systems in Macedonia, FYR, 2013 Prepared by the National Bank of the Republic of Macedonia and the Committee on Payment
How To Settle In Asx
 SECTION 9. SETTLEMENT... 9-1 9.1 Settlement Principles... 9-1 9.1.1 Delivery versus Payment (DvP) Settlement...9-1 9.1.2 Free of Payment (FOP) Delivery... 9-2 9.1.3 Settlement of Market Trades... 9-2 9.1.4
SECTION 9. SETTLEMENT... 9-1 9.1 Settlement Principles... 9-1 9.1.1 Delivery versus Payment (DvP) Settlement...9-1 9.1.2 Free of Payment (FOP) Delivery... 9-2 9.1.3 Settlement of Market Trades... 9-2 9.1.4
Interlinkages between Payment and Securities. Settlement Systems
 Interlinkages between Payment and Securities Settlement Systems David C. Mills, Jr. y Federal Reserve Board Samia Y. Husain Washington University in Saint Louis September 4, 2009 Abstract Payments systems
Interlinkages between Payment and Securities Settlement Systems David C. Mills, Jr. y Federal Reserve Board Samia Y. Husain Washington University in Saint Louis September 4, 2009 Abstract Payments systems
The assessment report on the kdpw_stream s compliance with the ESCB-CESR recommendations for securities settlement systems
 The assessment report on the kdpw_stream s compliance with the ESCB-CESR recommendations for securities settlement systems 1 I. Introduction General Presented assessment of securities settlement system
The assessment report on the kdpw_stream s compliance with the ESCB-CESR recommendations for securities settlement systems 1 I. Introduction General Presented assessment of securities settlement system
T2S Special Series I Issue No 1 I April 2012 I T2S benefits: much more than fee reductions
 T2S Special Series I Issue No 1 I April 2012 I T2S benefits: much more than fee reductions T2S Special Series Issue No 2 October 2012 T2S Auto-collateralisation Author: Mehdi Manaa, T2S Programme Office,
T2S Special Series I Issue No 1 I April 2012 I T2S benefits: much more than fee reductions T2S Special Series Issue No 2 October 2012 T2S Auto-collateralisation Author: Mehdi Manaa, T2S Programme Office,
Performance and resilience to liquidity disruptions in interdependent RTGS payment systems
 Sandia National Laboratories Performance and resilience to liquidity disruptions in interdependent RTGS payment systems Fabien Renault 1 Morten L. Bech 2 Walt Beyeler 3 Robert J. Glass 3 Kimmo Soramäki
Sandia National Laboratories Performance and resilience to liquidity disruptions in interdependent RTGS payment systems Fabien Renault 1 Morten L. Bech 2 Walt Beyeler 3 Robert J. Glass 3 Kimmo Soramäki
Protection of deferred net payment and securities settlement systems: the examples of SIT and Relit
 Protection of deferred net payment and securities settlement systems: the examples of SIT and Relit CHRISTINE SAMPIC, FRÉDÉRIC HERVO Directorate General Operations Payment Systems Directorate Payment and
Protection of deferred net payment and securities settlement systems: the examples of SIT and Relit CHRISTINE SAMPIC, FRÉDÉRIC HERVO Directorate General Operations Payment Systems Directorate Payment and
Payment Systems Roadmap 2012-2016
 November 2011 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Background... 4 Summary of Thailand s payment systems assessment... 5 1) Needs of Key Stakeholders... 6 2) Assessment of payment systems environment...
November 2011 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Background... 4 Summary of Thailand s payment systems assessment... 5 1) Needs of Key Stakeholders... 6 2) Assessment of payment systems environment...
MSc in FINANCE. FINANCIAL ENGINEERING May 2012. Settlement Risk. Giacomo Marchetti Massimiliano Morelli Vincenzo Raimondi
 MSc in FINANCE FINANCIAL ENGINEERING May 2012 Settlement Risk Giacomo Marchetti Massimiliano Morelli Vincenzo Raimondi 1 - Definition of 'Settlement Risk'. A key source of risk is the possibility that
MSc in FINANCE FINANCIAL ENGINEERING May 2012 Settlement Risk Giacomo Marchetti Massimiliano Morelli Vincenzo Raimondi 1 - Definition of 'Settlement Risk'. A key source of risk is the possibility that
How To Pay A Bank Transfer At The University Of Central Florida
 ELECTRONIC FUNDS TRANSFER PROCEDURE MANUAL Effective Date: 7/1/2012 Updated: July 25, 2012 Contents Introduction... 1 Incoming EFTs:... 3 ACH/Wire Transfers received... 3 Outgoing EFTs... 3 Student Direct
ELECTRONIC FUNDS TRANSFER PROCEDURE MANUAL Effective Date: 7/1/2012 Updated: July 25, 2012 Contents Introduction... 1 Incoming EFTs:... 3 ACH/Wire Transfers received... 3 Outgoing EFTs... 3 Student Direct
Assessment of the USD Payment System in Hong Kong Against the Ten Core Principles for Systemically Important Payment Systems
 Assessment of the USD Payment System in Hong Kong Against the Ten Core Principles for Systemically Important Payment Systems Introduction The US Dollar Clearing House Automated Transfer System ( USD CHATS
Assessment of the USD Payment System in Hong Kong Against the Ten Core Principles for Systemically Important Payment Systems Introduction The US Dollar Clearing House Automated Transfer System ( USD CHATS
Liquidity, risks and speed in payment and settlement systems a simulation approach Bank of Finland Studies E:31 2005. Harry Leinonen (ed.
 Liquidity, risks and speed in payment and settlement systems a simulation approach Bank of Finland Studies E:31 2005 Harry Leinonen (ed.) Liquidity, risks and speed in payment and settlement systems a
Liquidity, risks and speed in payment and settlement systems a simulation approach Bank of Finland Studies E:31 2005 Harry Leinonen (ed.) Liquidity, risks and speed in payment and settlement systems a
Federal Reserve Banks Operating Circular No. 4 AUTOMATED CLEARING HOUSE ITEMS
 Federal Reserve Banks AUTOMATED CLEARING HOUSE ITEMS Effective November 4, 2013 FEDERAL RESERVE BANKS OPERATING CIRCULAR NO. 4 Effective November 4, 2013 AUTOMATED CLEARING HOUSE ITEMS (Click CTRL + section
Federal Reserve Banks AUTOMATED CLEARING HOUSE ITEMS Effective November 4, 2013 FEDERAL RESERVE BANKS OPERATING CIRCULAR NO. 4 Effective November 4, 2013 AUTOMATED CLEARING HOUSE ITEMS (Click CTRL + section
Fundamentals of Payment Systems
 Fundamentals of Payment Systems www.treasuryalliance.com Contents Introduction 1 I. Payment Systems 2 II. Payment Channels 5 1. Paper-Based Payments 5 2. High-Value Transfers 7 3. Batch Systems 9 4. Card
Fundamentals of Payment Systems www.treasuryalliance.com Contents Introduction 1 I. Payment Systems 2 II. Payment Channels 5 1. Paper-Based Payments 5 2. High-Value Transfers 7 3. Batch Systems 9 4. Card
