Vitamin D. Introduction
|
|
|
- Noreen Bond
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vitamin D Introduction Vitamin D is required in quantities smaller than any other fat-soluble vitamin. The major forms of vitamin D are vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). Vitamin D has been described as a pro-hormone or sunshine-dependent vitamin. Some dietary vitamin D2 comes from plants, but the largest contribution to dietary intake of vitamin D is the vitamin D3 in fish liver oils, eggs, milk, and liver. Milk is commonly fortified with 10 μg (400 IU) of vitamin D3 per quart. Extremely high potency (40,000 to 50,000 IU) products sold as prescription or sometimes over the counter often consist of vitamin D2. Most vitamin D dietary supplements contain vitamin D3. The conversion of international units to metric weights is extremely simple for both vitamin D2 and D3: 1 μg equals 40 IU; μg equals 1 IU. Vitamin D3 (or D2) from endogenous production, foods, or vitamin supplements is inert and must undergo two hydroxylation reactions in the body for activation. The first occurs in the liver and the second in the kidneys. The first hydroxylation produces 25-hydroxy vitamin D (25[OH] D) and the second produces the active hormone 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D (1,25-di[OH]D). Because the plasma half-life of the active form 1,25-di(OH)D is short (approximately 15 hours), the best indicator of vitamin D status is 25-(OH)D (plasma half-life of 15 days or so). Because of these pharmacokinetics, most vitamin D in plasma is present as 25(OH)D, also called calcidiol, and its concentration has become the standard index of vitamin D status. 1,25-di(OH)D (calcitriol), the activated vitamin, regulates intestinal absorption and plasma concentration of calcium. As calcitriol, vitamin D is fundamentally involved in the formation of bone, and so its deficiency can lead to rickets in children or osteoporotic changes in adults. Bioavailability Although it can be synthesized in the body with sufficient exposure to sunlight or another ultraviolet (UV) light source, most people are not exposed to such UV light in consistent and 1
2 sufficient quantities. No extra vitamin D is required when skin exposure to UV light is ample; but without such exposure, a person is completely dependent on ingested vitamin D. The UV component of sunlight converts internally produced 7-dehydrocholesterol naturally present in the skin to cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) (Life Sciences Research Office [LSRO] 1978; Holick 1999). Although adequate UV light exposure can provide sufficient vitamin D, many elderly persons have limited sunlight exposure, inadequate dietary sources, and a decreased ability to activate vitamin D, making them susceptible to vitamin D deficiency (Gloth et al. 1995; Holick 1999). Elderly people are likely to have substantially increased needs for dietary vitamin D because of their decreased mobility and exposure to sun and decreased activation in the liver and kidneys. Thus, the nutritional need for dietary vitamin D depends on the biosynthesis in the skin, which in turn is influenced by time of exposure to sunlight, season (sun intensity and clothing), latitude, skin pigmentation, and the use of sunscreens. Safety Considerations The formation of vitamin D in the skin is slowed once dietary vitamin D intakes are sufficient and blood levels of the activated forms are high. Therefore, excess exposure to sunlight does not lead to vitamin D toxicity (Holick 1999; Hathcock et al. 2007). Dietary vitamin D can, however, produce toxic effects when consumed in very large quantities, especially over an extended period of time. Studies have shown that subjects with abnormally high levels of vitamin D intake can suffer from a wide range of signs and symptoms, from dehydration to permanent mineral deposits in soft tissues, including muscle, heart, kidney, and cartilage. Continued intake of toxic levels can have severe and persistent adverse consequences. The widespread occurrence of vitamin D overdoses in British children just after World War II, caused by consumption of excessively fortified milk, led health professionals to be extremely conservative in estimating safe levels for vitamin D. 2
3 Prolonged intake of excess vitamin D may lead to predictable increases in plasma 25-hydroxy vitamin D concentrations (Institute of Medicine [IOM] 2011), and the increase is directly proportional to the vitamin D dose (Barger-Lux et al. 1998). Treatment with vitamin D or 25- hydroxy vitamin D does not generally increase the serum concentrations of the active metabolite (calcitriol, 1-alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, or 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D) (Barger-Lux et al. 1998). Nonetheless, excess vitamin D can have toxic effects, perhaps because of the increases in blood concentrations of 25-hydroxy vitamin D, a form that can overstimulate intestinal absorption of calcium and cause excessive calcium mobilization from bone and hypercalcemia (Norman 1996; Holick 1999). Although the IOM considers hypercalcemia to be the critical effect in vitamin D toxicity, no clinical trials have used levels sufficiently high to produce such high blood levels of calcium. All such evidence comes from reports of anecdotal cases of accidental massive overdoses. The amount of daily vitamin D ingestion needed to produce adverse effects varies widely. In most adults, daily intake in excess of 50,000 IU (1.25 mg) is needed to produce toxicity (Miller and Hayes 1982). Clinical trials in the last decade or so have found no hypercalcemia in subjects in subject taking 10,000 IU (250 µg) in long-term clinical trials. In certain disease conditions such as sarcoidosis, mycobacterium infections such as tuberculosis, or idiopathic hypercalcemia, toxicity can occur at levels of vitamin D intake lower than those in healthy persons. A causal relationship between excess vitamin D intake and hypercalcemia is unlikely, although people with idiopathic hypercalcemia may be subject to adverse effects of vitamin D at lower intakes than are comfortably tolerated by healthy individuals (Expert Group on Vitamins and Minerals [EVM] 2003). Body size matters. One study has found that in children of unspecified body weight (probably between 10 and 30 kg), the amount of dietary vitamin D causing adverse effects may be as low as 2,000 to 4,000 IU (50 to 100 µg) per day. In full-term infants, adverse effects are reported to occur with intakes as low as 1,800 IU (45 µg) per day (Chesney 1989), but no adverse effects occurred in a 6-month study of infants given 1,600 IU per day (Fomon et al. 1966). Numerous reports confirm a variety of adverse effects at very high intakes when vitamin D is used as a drug, whether administered parenterally or in activated forms (Nanji 1985; Goldman and 3
4 Wheeler 1987; Schwartzman and Franck 1987; Allen and Shah 1992; Boulard et al. 1994; Oymak et al. 1994; Matsukawa et al. 1995). These circumstances do not relate to the usual oral intakes of vitamin D from foods or dietary supplements, and such reports provide no useful information about the safety of dietary sources of vitamin D. Official Reviews Expert Group on Vitamins and Minerals (EVM 2003). The UK s EVM did not find the data sufficiently compelling to identify a NOAEL or a LOAEL. Instead, it set a guidance level of 25 μg, based on studies by Vieth et al. (2001) at 100 μg and Johnson et al. (1980) at 50 μg. The EVM concluded that long-term use of supplements of 25 μg is well tolerated, but did not establish a safe upper limit. IOM (2011). The IOM has established a UL of 100 μg (4,000 IU) vitamin D, based on downward extrapolation from the NOAEL of 250 μg (10,000 IU), as derived from multiple clinical trials in a risk assessment using UL methodology (Hathcock et al. 2007). To take into account uncertainties from emerging data regarding all-cause mortality, chronic disease risk, and falls at serum 25(OH)D levels of approximately 75 to 125 nmol per L, the IOM considered the findings of Heaney et al. (2003) in establishing a UL. In this study, intakes of 5,000 IU vitamin D per day for 160 days resulted in serum 25(OH)D levels that did not exceed 150 nmol per L and serum calcium levels within normal ranges. The UL was set at 20 percent below 5,000 IU (i.e. 4,000 IU) because of the uncertainties surrounding the data and the reliance on one study. The IOM intended not to determine that certain levels of intake definitively cause harm, but rather to decide whether the emerging data were sufficiently compelling to warrant caution relative to vitamin D intakes. The IOM approach, however, did not take into account the ample caution built into the NOAEL and the UL method in the peer-reviewed literature (Hathcock et al. 2007). In addition, the IOM examined the data related to several endpoints but based their UL of 4,000 IU on only one of several different adjustments of the data on all-cause mortality in several different age, gender, and disease groups (Visser et al. 2006). 4
5 For example, Figure 6-1 of the IOM report graphs the hazard ratio of all-cause mortality against serum 25(OH)D (nmol per L), with adjustments for various health and age factors. All risk curves are high when vitamin D status is low and progress downward to low points as vitamin D status increases. Although the two right side points are equal, there is no hint of a reverse J-shape to the curves and thus no indication that that vitamin D status up to 82 nmol per L causes any harm. Figure 6-2 plots relative risk of death in elderly people against baseline serum 25(OH)D, graphed with four different adjustments for factors that could influence health. Only Model 4 shows definite increases in risk as serum 25(OH)D reaches 75+ nmol per L. This model adjusts the data for gender, age, education, chronic disease, serum creatinine concentration, and lifestyle variables including smoking status, alcohol consumption, and physical activity; it adjusts for all these plus frailty indications including physical activity, low serum albumin concentration, and low serum total cholesterol concentration. Figure 6-3 displays the results of adjustment to the data similar to that in Figure 6-2 s Model 4, and there is no increase in risk with serum 25(OH)D concentrations up to There was no discussion of the likelihood of a random significant effect when more than 20 adjustments are made to the primary data. EFSA (2012). EFSA considered that a daily vitamin D dose of 250 µg per day reflects a NOAEL, based on two studies in which doses of 234 to 275 µg vitamin D3 per day for 8 weeks to approximately 5 months did not result in hypercalcemia in healthy young men (Barger-Lux et al. 1998; Heaney et al. 2003). A UF of 2.5 was applied to account for the variation in the sensitivity of the population to potential adverse effects of long-term vitamin D exposure, the short duration of the studies, as well as the small number and characteristics (healthy young men with minimal sun exposure) of the individuals studied. The UL was therefore estimated to be 100 µg per day. 5
6 CRN Recommendations The traditional but not data-based conservatism of vitamin D recommendations is rapidly being corrected to evidence-based assessments. These assessments indicate that larger amounts are now considered safe for most persons. The data by Heaney and coworkers (2003) indicate that the NOAEL for vitamin D is at least 250 μg (10,000 IU). Thus, from the available data, the LOAEL is greater than 250 µg per day in relation to its hypercalcemic effects. The IOM and EVM estimate vitamin D intakes from all nonsupplement sources to be in the range of 360 IU (9 μg) or less. Many dietary supplements that include vitamin D contain 10 μg (labeled in the U.S. as 400 IU) or less, although some recent formulations contain 600 to 800 IU. There are no reports of adverse effects at these levels of intake. It is noteworthy that hypercalcemia has never been observed in a causal relationship to vitamin D in a randomized clinical trial. All the evidence for vitamin D causing hypercalcemia comes from anecdotal reports of accidental or misinformed consumption of much higher amounts. With recent clinical trial data in mind, the CRN UL for supplements is identified as 250 µg (10,000 IU), based on the absence of adverse effects at this level of supplementation in clinical trials of sufficient size and duration and under a variety of conditions (Hathcock et al. 2007; IOM 2011). Having confidence in the safety of the 250 μg intake level, CRN does not consider this NOAEL μg to need adjustment by application of a UF (i.e., a UF of 1.0 is applied). Thus, CRN sets the UL for supplements at 250 μg (10,000 IU). Quantitative Summary for Vitamin D CRN UL, supplemental intake IOM UL, total intake EFSA UL, total intake EC supplement maximum EVM, guidance level, supplemental intake 250 μg (10,000 IU)/day 100 μg (4,000 IU)/day 100 μg (4,000 IU)/day Not determined 25 μg (1,000 IU)/day 6
7 References Allen SH, Shah JH Calcinosis and metastatic calcification due to vitamin D intoxication. Hormone Res. 37: Barger-Lux MJ, Heaney RP, Dowell S, Chen TC, Holick MF Vitamin D and its major metabolites: serum levels after graded oral dosing in healthy men. Osteoporosis Int. 8: Boulard JC, Hanslik T, Alterescu R, Baglin A Hypercalcémie symptomatique après association vitamine D diurétiques thiazidiques: 2 observations chez des femmes dosés [letter]. La Presse Medicale. 22:96. Chesney RW Vitamin D: can an upper limit be defined? J Nutr. 119: European Commission, Scientific Committee on Food (EC SCF) Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Vitamin E. European Commission, SCF/CS/NUT/UPPERLEV/31 Final Report. Brussels. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA); scientific opinion on the tolerable upper intake level of vitamin D. EFSA J. 10(7):2813. Expert Group on Vitamins and Minerals (EVM), Committee on Toxicity Safe Upper Levels for Vitamins and Minerals. London: Food Standards Agency Publications. Fomon SJ, Younoszal MK, Thomas LN Influence of vitamin D on linear growth of normal full-term infants. J Nutr. 88: Gloth FM, Gundberg CM, Hollis BW, Haddad JG, Tobin JD Vitamin D deficiency in homebound elderly persons. JAMA. 274:
8 Goldman JM, Wheeler MF Vitamin D-induced hypercalcemia [letter]. Am J Med. 82:1277. Hathcock JN, Shao A, Vieth R, Heaney R Risk assessment for vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr. 85:6 18. Heaney RP, Davies KM, Chen TC, et al Human serum 25-hydroxycholecalciferol response to extended oral dosing with cholecalciferol. Am J Clin Nutr. 77: Holick MF Vitamin D. In: Shils ME, Olson JA, Shike M, eds. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger; Institute of Medicine (IOM) Dietary Reference Intakes: Calcium, Vitamin D. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Johnson KR, Jobber J, Stonawski BJ Prophylactic vitamin D in the elderly. Age and Ageing. 9: Life Sciences Research Office (LSRO), SCOGS: Select Committee on GRAS Substances Evaluation of the Health Aspects of Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3 as Food Ingredients. Washington, DC: Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB). Matsukawa Y, Ikeda E, Hayama T, Nishinarita S, Sawada S, Horie T Ectopic calcinosis possibly due to lot (OH) vitamin D3 in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 13: Miller DR, Hayes KC Vitamin excess and toxicity. In: Hathcock JN, ed. Nutritional Toxicology. Vol. 1. New York: Academic Press; Nanji AA Symptomatic hypercalcaemia precipitated by magnesium therapy. Postgraduate Med J. 61:
9 Norman AW Vitamin D. In: Zeigler EE Jr, Filer LJ. Present Knowledge in Nutrition. 7th ed. Washington, DC: ILSI Press; Oymak O, Akpolat T, Arik N, Yasavul C, Turgan Q, Caglar S Hyperammonemic encephalopathy due to vitamin D induced hypercalcemia in a uremic patient [letter]. Nephron. 66:369. Schwartzman MS, Franck WA Vitamin D toxicity complicating the treatment of senile, postmenopausal, and glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Am J Med. 82: Vieth R, Chan P, MacFarlane GD Efficacy and safety of vitamin D3 intake exceeding the lowest observed adverse effect level. Am J Clin Nutr. 73: Visser M, Deeg DJH, Puts MTE, Seidell JC, Lips P Low serum concentrations of 25- hydroxyvitamin D in older persons and the risk of nursing home admission. Am J Clin Nutr. 84:
D. Vitamin D. 1. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3
 D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
Fluoride. Introduction
 Fluoride Introduction Most fluoride in the body is found in bones and teeth, due to its high affinity for calcium and calcium phosphate. Ingestion of and topical treatment with fluoride is effective in
Fluoride Introduction Most fluoride in the body is found in bones and teeth, due to its high affinity for calcium and calcium phosphate. Ingestion of and topical treatment with fluoride is effective in
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease. Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D.
 Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Press Information. Vitamin D deficiency
 DSM, Corporate Communications P.O. Box 6500, 6401 HJ Heerlen The Netherlands phone +31 (0) 45 578 2421 www.dsm.com Vitamin D is one of the essential nutrients for human health. Unlike other types of vitamins
DSM, Corporate Communications P.O. Box 6500, 6401 HJ Heerlen The Netherlands phone +31 (0) 45 578 2421 www.dsm.com Vitamin D is one of the essential nutrients for human health. Unlike other types of vitamins
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease. Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D.
 Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D. Frequently Asked Questions
 Vitamin D Frequently Asked Questions What is vitamin D? What is a vitamin? Why do we need vitamins? Is there more than one form of vitamin D? Where do I get vitamin D? How long should I be outdoors, and
Vitamin D Frequently Asked Questions What is vitamin D? What is a vitamin? Why do we need vitamins? Is there more than one form of vitamin D? Where do I get vitamin D? How long should I be outdoors, and
Key words: Vitamin D Production, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Vitamin D Treatment
 Title: Vitamin D Author: Kerry Lynn Kuffenkam Date: 4-29-09 Key words: Vitamin D Production, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Vitamin D Treatment Abstract: Since the term Vitamin D contains the word vitamin most
Title: Vitamin D Author: Kerry Lynn Kuffenkam Date: 4-29-09 Key words: Vitamin D Production, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Vitamin D Treatment Abstract: Since the term Vitamin D contains the word vitamin most
YOUR TRUSTED SOURCE - FOR ALL YOUR VITAMIN D 3 NEEDS
 Vitamin D YOUR TRUSTED SOURCE - FOR ALL YOUR VITAMIN D 3 NEEDS ü Natural form of vitamin D 3, cholecalciferol (from lanolin) ü Strengths from 400 iu to 10,000 iu ü Capsule and liquid forms available ü
Vitamin D YOUR TRUSTED SOURCE - FOR ALL YOUR VITAMIN D 3 NEEDS ü Natural form of vitamin D 3, cholecalciferol (from lanolin) ü Strengths from 400 iu to 10,000 iu ü Capsule and liquid forms available ü
DAILY MAXIMUM INTAKE LIMIT IN HEALTH FUNCTIONAL FOOD ACT
 Comment Number 1: By the Council for Responsible Nutrition, Washington, DC, USA DAILY MAXIMUM INTAKE LIMIT IN HEALTH FUNCTIONAL FOOD ACT The Republic of Korea (ROK) proposal is in agreement with the first
Comment Number 1: By the Council for Responsible Nutrition, Washington, DC, USA DAILY MAXIMUM INTAKE LIMIT IN HEALTH FUNCTIONAL FOOD ACT The Republic of Korea (ROK) proposal is in agreement with the first
Vitamin D. Why Vitamin D is important and how to get enough
 Vitamin D Why Vitamin D is important and how to get enough Why is vitamin D vital for health? Vitamin D is needed by the body for both physical and mental health, but is best known for making sure bones
Vitamin D Why Vitamin D is important and how to get enough Why is vitamin D vital for health? Vitamin D is needed by the body for both physical and mental health, but is best known for making sure bones
Vitamin D. Sources of vitamin D
 1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
Question I. A vitamin D deficient mother will give birth. A. True B. False. Answer A
 Vitamin D Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Question I A vitamin D deficient mother will give birth to an infant with Vit D deficiency A. True B. False Answer A Question II Human breast milk has adequate amounts
Vitamin D Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Question I A vitamin D deficient mother will give birth to an infant with Vit D deficiency A. True B. False Answer A Question II Human breast milk has adequate amounts
Risk assessment for vitamin D 1,2
 Review Article Risk assessment for vitamin D 1,2 John N Hathcock, Andrew Shao, Reinhold Vieth, and Robert Heaney ABSTRACT The objective of this review was to apply the risk assessment methodology used
Review Article Risk assessment for vitamin D 1,2 John N Hathcock, Andrew Shao, Reinhold Vieth, and Robert Heaney ABSTRACT The objective of this review was to apply the risk assessment methodology used
Selected Questions and Answers on Vitamin D
 Selected Questions and Answers on Vitamin D Joint FAQs to the BfR, German Nutrition Society (DGE) und Max Rubner-Institute (MRI) of 03 December 2014 1 Vitamin D promotes the intake of calcium from the
Selected Questions and Answers on Vitamin D Joint FAQs to the BfR, German Nutrition Society (DGE) und Max Rubner-Institute (MRI) of 03 December 2014 1 Vitamin D promotes the intake of calcium from the
25-hydroxyvitamin D: from bone and mineral to general health marker
 DIABETES 25 OH Vitamin D TOTAL Assay 25-hydroxyvitamin D: from bone and mineral to general health marker FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Vitamin D Receptors Brain Heart Breast Colon Pancreas Prostate
DIABETES 25 OH Vitamin D TOTAL Assay 25-hydroxyvitamin D: from bone and mineral to general health marker FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Vitamin D Receptors Brain Heart Breast Colon Pancreas Prostate
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM
 NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone Number:
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone Number:
Vitamin D (serum, plasma)
 Vitamin D (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Vitamin D 1.2 Alternative names The term vitamin D covers a group of closely related naturally occurring lipid soluble compounds
Vitamin D (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Vitamin D 1.2 Alternative names The term vitamin D covers a group of closely related naturally occurring lipid soluble compounds
DVITA PLUS Vitamin D 1000 IU Tablet INDICATED CLAIMS:
 DVITA PLUS Vitamin D 1000 IU Tablet INDICATED CLAIMS: Vitamin D is the principal regulator of calcium homeostasis in the body Vitamin D is particularly important in skeletal development and bone mineralization.
DVITA PLUS Vitamin D 1000 IU Tablet INDICATED CLAIMS: Vitamin D is the principal regulator of calcium homeostasis in the body Vitamin D is particularly important in skeletal development and bone mineralization.
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only OR for Specialist Use only
 For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only OR for Specialist Use only Cholecalciferol Granules VITOMIN D3 COMPOSITION Each sachet of 1 g contains: Cholecalciferol
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only OR for Specialist Use only Cholecalciferol Granules VITOMIN D3 COMPOSITION Each sachet of 1 g contains: Cholecalciferol
Calcium. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nuf40101 Last reviewed: 02/19/2013 1
 Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Importance of zinc in human body. Overview of terminology. Rationale for upper intake level for zinc as recommended by the US Institute of
 Sonja Y. Hess, PhD University of California, Davis Importance of zinc in human body Overview of terminology Rationale for upper intake level for zinc as recommended by the US Institute of Medicine (2001)
Sonja Y. Hess, PhD University of California, Davis Importance of zinc in human body Overview of terminology Rationale for upper intake level for zinc as recommended by the US Institute of Medicine (2001)
GUIDE FOR VITAMIN D IN CHILDHOOD
 GUIDE FOR VITAMIN D IN CHILDHOOD October 2013 Introduction There are many different recommendations for the prevention, detection and treatment of Vitamin D deficiency in the UK. The following is a practical
GUIDE FOR VITAMIN D IN CHILDHOOD October 2013 Introduction There are many different recommendations for the prevention, detection and treatment of Vitamin D deficiency in the UK. The following is a practical
Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age
 Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Vitamin D deficiency: the cause of everything?
 Health problems linked to vitamin D deficiency: Vitamin D deficiency: the cause of everything? Louise Gagné M.D. Family Physician Saskatoon Community Clinic Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Community
Health problems linked to vitamin D deficiency: Vitamin D deficiency: the cause of everything? Louise Gagné M.D. Family Physician Saskatoon Community Clinic Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Community
Overview. Nutritional Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. How does the liver affect nutritional status?
 Overview Nutritional Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Tracy Burch, RD, CNSD Kovler Organ Transplant Center Northwestern Memorial Hospital Importance of nutrition therapy in PBC Incidence and pertinence
Overview Nutritional Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Tracy Burch, RD, CNSD Kovler Organ Transplant Center Northwestern Memorial Hospital Importance of nutrition therapy in PBC Incidence and pertinence
Nutritional risk analysis approaches for establishing maximum levels of vitamins and minerals in food (dietary) supplements
 Nutritional risk analysis approaches for establishing maximum levels of vitamins and minerals in food (dietary) supplements The International Alliance of Dietary/Food Supplement Associations (IADSA) brings
Nutritional risk analysis approaches for establishing maximum levels of vitamins and minerals in food (dietary) supplements The International Alliance of Dietary/Food Supplement Associations (IADSA) brings
The Association of Vitamin D Dietary Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Among African Americans in Central Ohio
 The Association of Vitamin D Dietary Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Among African Americans in Central Ohio Presenter: Sin Nee Ng Advisors: Dr. Julie Kennel, Dr. Tonya Orchard Copyright 2014 Sin Nee Ng. All
The Association of Vitamin D Dietary Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Among African Americans in Central Ohio Presenter: Sin Nee Ng Advisors: Dr. Julie Kennel, Dr. Tonya Orchard Copyright 2014 Sin Nee Ng. All
FOR HEALTH. Huldschinsky 1919. Rickets THE D-LIGHTFUL VITAMIN. Solar UV Radiation. Treated VITAMIN D TOXIC OH FROM SUN EXPOSURE. with Mercury Arc Lamp
 THE D-LIGHTFUL VITAMIN W DO YOU MAKE VITAMIN D???? FOR HEALTH Michael F. Holick Boston University Medical Center Solar UV Radiation 7-DHC UV PreD 3 UV UV Tachysterol 3 7-DHC CH2 Vitamin D 3 ΔH PreD 3 Vitamin
THE D-LIGHTFUL VITAMIN W DO YOU MAKE VITAMIN D???? FOR HEALTH Michael F. Holick Boston University Medical Center Solar UV Radiation 7-DHC UV PreD 3 UV UV Tachysterol 3 7-DHC CH2 Vitamin D 3 ΔH PreD 3 Vitamin
Shining a light on the Sunshine Vitamin Lin A. Brown,MD Dartmouth and DHMC
 Shining a light on the Sunshine Vitamin Lin A. Brown,MD Dartmouth and DHMC Vitamin D What do surfers have in abundance and maybe most of the rest of us lack? Vit D - a vitamin primarily obtained by man
Shining a light on the Sunshine Vitamin Lin A. Brown,MD Dartmouth and DHMC Vitamin D What do surfers have in abundance and maybe most of the rest of us lack? Vit D - a vitamin primarily obtained by man
A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels. Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD
 A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD The sunshine vitamin Existed over 500 million years. Prehormone, not only a vitamin. Two major sources:
A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD The sunshine vitamin Existed over 500 million years. Prehormone, not only a vitamin. Two major sources:
A product of living cells that circulates in body fluids. Webinar broadcast at live.oregonstate.edu (only on day and time of the event).
 Vitamin D: Bone Up For Winter The "Vitamin D Winter" is coming. In this webinar we will learn about this important molecule and how you can get the you need to help maintain more than just healthy bones.
Vitamin D: Bone Up For Winter The "Vitamin D Winter" is coming. In this webinar we will learn about this important molecule and how you can get the you need to help maintain more than just healthy bones.
Nutrition and Parkinson s Disease: Can food have an impact? Sarah Zangerle, RD, CD Registered Dietitian Froedtert Memorial Lutheran Hospital
 Nutrition and Parkinson s Disease: Can food have an impact? Sarah Zangerle, RD, CD Registered Dietitian Froedtert Memorial Lutheran Hospital Importance of Nutrition & Parkinson s Disease Good nutrition
Nutrition and Parkinson s Disease: Can food have an impact? Sarah Zangerle, RD, CD Registered Dietitian Froedtert Memorial Lutheran Hospital Importance of Nutrition & Parkinson s Disease Good nutrition
Vitamin D und seine Bedeutung im Immunsystem und bei der Infektabwehr
 Vitamin D und seine Bedeutung im Immunsystem und bei der Infektabwehr Stefan Pilz Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Medical University of Graz, Austria Department
Vitamin D und seine Bedeutung im Immunsystem und bei der Infektabwehr Stefan Pilz Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Medical University of Graz, Austria Department
Towards an adequate intake of vitamin D
 Towards an adequate intake of vitamin D Gezondheidsraad Health Council of the Netherlands To the Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport Subject : Presentation of advisory report Towards an adequate intake
Towards an adequate intake of vitamin D Gezondheidsraad Health Council of the Netherlands To the Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport Subject : Presentation of advisory report Towards an adequate intake
Fact Sheet on Vitamin D
 Fact Sheet on Vitamin D DISCLAIMER: This Fact Sheet Does Not Constitute Medical Advice. This sheet is a compilation of recommendations by top researchers. These recommendations may or may not apply to
Fact Sheet on Vitamin D DISCLAIMER: This Fact Sheet Does Not Constitute Medical Advice. This sheet is a compilation of recommendations by top researchers. These recommendations may or may not apply to
Safety of Vitamin and Mineral Supplements
 Safety of Vitamin and Mineral Supplements Safe Levels Identified by Risk Assessment John N Hathcock, Ph.D. The International Alliance of Dietary/Food Supplement Associations (IADSA) brings together over
Safety of Vitamin and Mineral Supplements Safe Levels Identified by Risk Assessment John N Hathcock, Ph.D. The International Alliance of Dietary/Food Supplement Associations (IADSA) brings together over
The evidencebehindthe increased NordicNutritionRecommendations for vitamind. Christel Lamberg-Allardt University of Helsinki
 The evidencebehindthe increased NordicNutritionRecommendations for vitamind Christel Lamberg-Allardt University of Helsinki Aimsfor NutritionRecommendations Aimsfor vitamind The overall aim was to review
The evidencebehindthe increased NordicNutritionRecommendations for vitamind Christel Lamberg-Allardt University of Helsinki Aimsfor NutritionRecommendations Aimsfor vitamind The overall aim was to review
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand
 Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
Vitamin D and You. By Dr. Sherri Tenpenny www.drtenpenny.com www.osteomed2.com
 Vitamin D and You By Dr. Sherri Tenpenny www.drtenpenny.com www.osteomed2.com What is Vitamin D? Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin produced in the body when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin.
Vitamin D and You By Dr. Sherri Tenpenny www.drtenpenny.com www.osteomed2.com What is Vitamin D? Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin produced in the body when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin.
Considerations With Calcium And Vitamin D Supplementation
 Considerations With Calcium And Vitamin D Supplementation Activity Preview Calcium is an electrolyte involved in many systems in the body including bone health, nerve signaling pathways, muscle contractions,
Considerations With Calcium And Vitamin D Supplementation Activity Preview Calcium is an electrolyte involved in many systems in the body including bone health, nerve signaling pathways, muscle contractions,
Earth at Night View from the Space Shuttle. Vitamin D: All You Need to Know
 Earth at Night View from the Space Shuttle Vitamin D: All You Need to Know Sunil Wimalawansa, MD, PhD, MBA 11/12/2011 Vitamin D: All You Need to Know Sunil J. Wimalawansa, MD, PhD, MBA, FACE, FACP Professor
Earth at Night View from the Space Shuttle Vitamin D: All You Need to Know Sunil Wimalawansa, MD, PhD, MBA 11/12/2011 Vitamin D: All You Need to Know Sunil J. Wimalawansa, MD, PhD, MBA, FACE, FACP Professor
Symposium: Vitamin D Insufficiency: A Significant Risk Factor in Chronic Diseases and Potential Disease-Specific Biomarkers of Vitamin D Sufficiency
 Symposium: Vitamin D Insufficiency: A Significant Risk Factor in Chronic Diseases and Potential Disease-Specific Biomarkers of Vitamin D Sufficiency Dietary Recommendations for Vitamin D: a Critical Need
Symposium: Vitamin D Insufficiency: A Significant Risk Factor in Chronic Diseases and Potential Disease-Specific Biomarkers of Vitamin D Sufficiency Dietary Recommendations for Vitamin D: a Critical Need
Hold the Sunscreen: Your Body Needs that Vitamin D
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hold-the-sunscreen-your-body-needs-that-vitamind/4149/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hold-the-sunscreen-your-body-needs-that-vitamind/4149/
Vitamin D and Calcium Guideline
 Vitamin D and Calcium Guideline Vitamin D Functions of Vitamin D 2 Serum Levels 2 Deficiency 2 Toxicity 2 Dietary Reference Intakes 3 Sources of Vitamin D 3 Therapeutic Options 4 Adults 4 Children (0 18
Vitamin D and Calcium Guideline Vitamin D Functions of Vitamin D 2 Serum Levels 2 Deficiency 2 Toxicity 2 Dietary Reference Intakes 3 Sources of Vitamin D 3 Therapeutic Options 4 Adults 4 Children (0 18
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. Vitamin D
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Vitamin D Purpose of guideline Provide clear advice on when to measure vitamin D and identify patients with insufficiency and deficiency. To provide
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Vitamin D Purpose of guideline Provide clear advice on when to measure vitamin D and identify patients with insufficiency and deficiency. To provide
Vitamin D and MS: Implications for Clinical Practice
 733 Third Avenue New York, NY 10017-3288 Clinical Bulletin Information for Health Professionals Vitamin D and MS: Implications for Clinical Practice Allen C. Bowling, MD, PhD Introduction Recent studies
733 Third Avenue New York, NY 10017-3288 Clinical Bulletin Information for Health Professionals Vitamin D and MS: Implications for Clinical Practice Allen C. Bowling, MD, PhD Introduction Recent studies
Vitamin D: Are higher doses needed? Dan Milosevich, C.N.
 Vitamin D: Are higher doses needed? Dan Milosevich, C.N. Startling new information shows that the recommendations for Vitamin D may have been set too low. See the following review of what we now know.
Vitamin D: Are higher doses needed? Dan Milosevich, C.N. Startling new information shows that the recommendations for Vitamin D may have been set too low. See the following review of what we now know.
Ca : methods for determining DRIs. Adults. 4average requirement, meta-analyzed balance studies by FAO/WHO :
 Minerals Categories of Ds for Minerals - Ca, P, Na, Cl, K, Mg - Mineral Ca RDA P Ca ; 서울대학교 이연숙 Na P ; 국민대학교 김선희 Na, Cl ; 동의대학교 임화재 K ; 국민대학교 장문정 Mg ; 인하대학교 천종희 Cl K Mg Indicators for Estimating Ds Ca
Minerals Categories of Ds for Minerals - Ca, P, Na, Cl, K, Mg - Mineral Ca RDA P Ca ; 서울대학교 이연숙 Na P ; 국민대학교 김선희 Na, Cl ; 동의대학교 임화재 K ; 국민대학교 장문정 Mg ; 인하대학교 천종희 Cl K Mg Indicators for Estimating Ds Ca
Vitamin D in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence
 Vitamin D in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Christopher Kovacs, MD, FRCPC, FACP Professor of Medicine (Endocrinology) Memorial University of Newfoundland ckovacs@mun.ca Disclosure I am currently serving
Vitamin D in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Christopher Kovacs, MD, FRCPC, FACP Professor of Medicine (Endocrinology) Memorial University of Newfoundland ckovacs@mun.ca Disclosure I am currently serving
Public Assessment Report. UK National Procedure. (colecalciferol) PL 16508/0047 PL 16508/0048. ProStrakan Ltd.
 Public Assessment Report UK National Procedure STEXEROL-D 3 1,000 IU FILM-COATED TABLETS STEXEROL-D 3 25,000 IU FILM-COATED TABLETS (colecalciferol) PL 16508/0047 PL 16508/0048 ProStrakan Ltd. 1 LAY SUMMARY
Public Assessment Report UK National Procedure STEXEROL-D 3 1,000 IU FILM-COATED TABLETS STEXEROL-D 3 25,000 IU FILM-COATED TABLETS (colecalciferol) PL 16508/0047 PL 16508/0048 ProStrakan Ltd. 1 LAY SUMMARY
3 Food Standards Agency, London, UK
 Chapter six From Hazard to Risk e Assessing the Risk Charlotte Bernhard Madsen 1, Geert Houben 2, Sue Hattersley 3, Rene W.R. Crevel 4, Ben C. Remington 5, Joseph L. Baumert 5 1 DVM Research Leader Division
Chapter six From Hazard to Risk e Assessing the Risk Charlotte Bernhard Madsen 1, Geert Houben 2, Sue Hattersley 3, Rene W.R. Crevel 4, Ben C. Remington 5, Joseph L. Baumert 5 1 DVM Research Leader Division
Micronutrient. Functio. Vitamin A
 EHPM Leaflet UK 25/4/00 14:50 Page 1 (1,1) Vitamin and mineral intake We cannot, however, afford to be complacent about our intake of vitamins and minerals. Poor diets with low quantities of fruit and
EHPM Leaflet UK 25/4/00 14:50 Page 1 (1,1) Vitamin and mineral intake We cannot, however, afford to be complacent about our intake of vitamins and minerals. Poor diets with low quantities of fruit and
EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet
 BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health
 What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
VITAMIN D PRODUCTS -WHAT AND WHEN TO PRESCRIBE. Claudette Allerdyce Principal Pharmacist Croydon CCG Pharmacy Team
 VITAMIN D PRODUCTS -WHAT AND WHEN TO PRESCRIBE Claudette Allerdyce Principal Pharmacist Croydon CCG Pharmacy Team WHAT ARE THE ISSUES? A lack of suitable licensed vitamin D products in the UK for treating
VITAMIN D PRODUCTS -WHAT AND WHEN TO PRESCRIBE Claudette Allerdyce Principal Pharmacist Croydon CCG Pharmacy Team WHAT ARE THE ISSUES? A lack of suitable licensed vitamin D products in the UK for treating
Bruce W Hollis and Carol L Wagner 1752S
 Vitamin D requirements during lactation: high-dose maternal supplementation as therapy to prevent hypovitaminosis D for both the mother and the nursing infant 1 4 Bruce W Hollis and Carol L Wagner ABSTRACT
Vitamin D requirements during lactation: high-dose maternal supplementation as therapy to prevent hypovitaminosis D for both the mother and the nursing infant 1 4 Bruce W Hollis and Carol L Wagner ABSTRACT
Vitamin D & Iron Dosing Guidelines
 Vitamin D & Iron Dosing Guidelines Ayman Khmour, MD I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program. Objectives Review Ca metabolism Review Recent AAP Guidelines Review CMH
Vitamin D & Iron Dosing Guidelines Ayman Khmour, MD I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program. Objectives Review Ca metabolism Review Recent AAP Guidelines Review CMH
Nutrition for Family Living
 Susan Nitzke, Nutrition Specialist; susan.nitzke@ces.uwex.edu Sherry Tanumihardjo, Nutrition Specialist; sherry.tan@ces.uwex.edu Amy Rettammel, Outreach Specialist; arettamm@facstaff.wisc.edu Betsy Kelley,
Susan Nitzke, Nutrition Specialist; susan.nitzke@ces.uwex.edu Sherry Tanumihardjo, Nutrition Specialist; sherry.tan@ces.uwex.edu Amy Rettammel, Outreach Specialist; arettamm@facstaff.wisc.edu Betsy Kelley,
Vitamin D. Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353
 Vitamin D Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Vitamin D Date of issue: February 2010 Review date: February 2011 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2.
Vitamin D Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Vitamin D Date of issue: February 2010 Review date: February 2011 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2.
Vitamin A 10,000 IU Softgels
 Vitamin A 10,000 IU Softgels Product Summary: Vitamins are required nutrients that must be obtained by diet or supplementation. Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps in the maintenance of eyesight,
Vitamin A 10,000 IU Softgels Product Summary: Vitamins are required nutrients that must be obtained by diet or supplementation. Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps in the maintenance of eyesight,
Vitamin D Supplement Doses and Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in the Range Associated with Cancer Prevention
 Vitamin D Supplement Doses and Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in the Range Associated with Cancer Prevention CEDRIC F. GARLAND 1, CHRISTINE B. FRENCH 2, LEO L. BAGGERLY 2 and ROBERT P. HEANEY 3 1 University
Vitamin D Supplement Doses and Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in the Range Associated with Cancer Prevention CEDRIC F. GARLAND 1, CHRISTINE B. FRENCH 2, LEO L. BAGGERLY 2 and ROBERT P. HEANEY 3 1 University
Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults: Primary Care Guideline
 Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults: Primary Care Guideline The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the UK is 16% and around 50% of the UK adult population have vitamin D insufficiency in winter and spring.
Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults: Primary Care Guideline The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the UK is 16% and around 50% of the UK adult population have vitamin D insufficiency in winter and spring.
Vitamin D Deficiency in Older Patients
 Fourth Year Medical Students Required Written Patient Care Assignments Reflecting Awareness of Use of Vitamin D in Older Patients at Risk for Falling John Agens, M.D. Associate Professor in Geriatrics
Fourth Year Medical Students Required Written Patient Care Assignments Reflecting Awareness of Use of Vitamin D in Older Patients at Risk for Falling John Agens, M.D. Associate Professor in Geriatrics
The Science of Chemical Safety Essential Toxicology - 4. Hazard and Risk. John Duffus & Howard Worth. IUPAC Educators Resource Material IUPAC
 The Science of Chemical Safety Essential Toxicology - 4 Hazard and Risk John Duffus & Howard Worth IUPAC Educators Resource Material IUPAC Hazard and Risk - 1 Hazard is the potential of a substance to
The Science of Chemical Safety Essential Toxicology - 4 Hazard and Risk John Duffus & Howard Worth IUPAC Educators Resource Material IUPAC Hazard and Risk - 1 Hazard is the potential of a substance to
Protecting and improving the nation s health. Vitamin D. Information for healthcare professionals
 Protecting and improving the nation s health Vitamin D Information for healthcare professionals 1 Vitamin D: Information for healthcare professionals Why is vitamin D important? Some of the UK population
Protecting and improving the nation s health Vitamin D Information for healthcare professionals 1 Vitamin D: Information for healthcare professionals Why is vitamin D important? Some of the UK population
PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement)
 1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
Fat-Soluble Vitamins. Quick Facts... Vitamin A. by J. Anderson and L. Young 1 (8/08)
 Fat-Soluble s by J. Anderson and L. Young 1 (8/08) Quick Facts... Small amounts of vitamins A, D, E and K are needed to maintain good health. Foods that contain these vitamins will not lose them when cooked.
Fat-Soluble s by J. Anderson and L. Young 1 (8/08) Quick Facts... Small amounts of vitamins A, D, E and K are needed to maintain good health. Foods that contain these vitamins will not lose them when cooked.
Four Vitamins You Should NEVER Take
 Four Vitamins You Should NEVER Take If you think that all vitamins are safe, you re dead wrong. Here at the Health Sciences Institute (HSI), we talk a lot about vitamins and minerals being essential for
Four Vitamins You Should NEVER Take If you think that all vitamins are safe, you re dead wrong. Here at the Health Sciences Institute (HSI), we talk a lot about vitamins and minerals being essential for
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs): Estimated Average Requirements Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine, National Academies
 Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs): Estimated Average Requirements Life Stage Group Calcium CHO Protein (g/kg/d) Vit A a Vit C Vit D Vit E b Thiamin Riboflavin Niacin c Vit B 6 0 to 6 mo 6 to 12 mo 1.0 6.9
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs): Estimated Average Requirements Life Stage Group Calcium CHO Protein (g/kg/d) Vit A a Vit C Vit D Vit E b Thiamin Riboflavin Niacin c Vit B 6 0 to 6 mo 6 to 12 mo 1.0 6.9
Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of vitamin D 1
 EFSA Journal 2012;10(7):2813 SCIENTIFIC OPINION Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of vitamin D 1 EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) 2, 3 European Food Safety
EFSA Journal 2012;10(7):2813 SCIENTIFIC OPINION Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of vitamin D 1 EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) 2, 3 European Food Safety
Vitamin A. Introduction
 Vitamin A Introduction Vitamin A has essential actions in areas of health that include vision, cellular differentiation, organ development during embryonic and fetal growth, and membrane structure and
Vitamin A Introduction Vitamin A has essential actions in areas of health that include vision, cellular differentiation, organ development during embryonic and fetal growth, and membrane structure and
Guideline on Diagnosis & Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults for Non-Specialists
 Guideline on Diagnosis & Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults for Non-Specialists January 2014 (Review date: Jan 2016) Contents Summary Flowchart... 2 Introduction... 3 Structure and mechanism
Guideline on Diagnosis & Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults for Non-Specialists January 2014 (Review date: Jan 2016) Contents Summary Flowchart... 2 Introduction... 3 Structure and mechanism
FACT SHEET TESTETROL, A NOVEL ORALLY BIOACTIVE ANDROGEN
 FACT SHEET TESTETROL, A NOVEL ORALLY BIOACTIVE ANDROGEN General Pantarhei Bioscience B.V. is an emerging specialty pharmaceutical company with a creative approach towards drug development. The Company
FACT SHEET TESTETROL, A NOVEL ORALLY BIOACTIVE ANDROGEN General Pantarhei Bioscience B.V. is an emerging specialty pharmaceutical company with a creative approach towards drug development. The Company
NHS GGC Vitamin D Supplementation Frequently asked Questions
 Pharmacy & Prescribing Support Unit NHS GGC Vitamin D Supplementation Frequently asked Questions In February 2012 the Scottish Government issued advice on supplements for groups at risk of vitamin D deficiency.
Pharmacy & Prescribing Support Unit NHS GGC Vitamin D Supplementation Frequently asked Questions In February 2012 the Scottish Government issued advice on supplements for groups at risk of vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D Status: United States, 2001 2006
 Vitamin D Status: United States, 2001 2006 Anne C. Looker, Ph.D.; Clifford L. Johnson, M.P.H.; David A. Lacher, M.D.; Christine M. Pfeiffer, Ph.D.; Rosemary L. Schleicher, Ph.D.; and Christopher T. Sempos,
Vitamin D Status: United States, 2001 2006 Anne C. Looker, Ph.D.; Clifford L. Johnson, M.P.H.; David A. Lacher, M.D.; Christine M. Pfeiffer, Ph.D.; Rosemary L. Schleicher, Ph.D.; and Christopher T. Sempos,
Package leaflet: Information for the patient. Cholecalciferol mibe 500 IE, tabletten Cholecalciferol. For use in infants, children and adults
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient Cholecalciferol mibe 500 IE, tabletten Cholecalciferol For use in infants, children and adults Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this
Package leaflet: Information for the patient Cholecalciferol mibe 500 IE, tabletten Cholecalciferol For use in infants, children and adults Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model
 Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Our main source of vitamin D is that made by our own bodies. 90% of our vitamin D is made in the skin with the help of sunlight.
 Vitamin D Deficiency Vitamin D deficiency is a very common problem - more than half of the UK population has insufficient levels of vitamin D Vitamin D is mostly made in the skin by exposure to sunlight
Vitamin D Deficiency Vitamin D deficiency is a very common problem - more than half of the UK population has insufficient levels of vitamin D Vitamin D is mostly made in the skin by exposure to sunlight
Vitamin D and Cardiometabolic risk
 Vitamin D and Cardiometabolic risk 서울의대, 분당서울대병원 내과 최 성 희 2013년 대한당뇨병학회 춘계학술대회 Metabolism Of Vitamin D Risk factors for vitamin D deficiency - Aging decreased concentrations of 7-dehydro-cholesterol in
Vitamin D and Cardiometabolic risk 서울의대, 분당서울대병원 내과 최 성 희 2013년 대한당뇨병학회 춘계학술대회 Metabolism Of Vitamin D Risk factors for vitamin D deficiency - Aging decreased concentrations of 7-dehydro-cholesterol in
Re: GRAS Notice No. AGRN 000-009
 May 4, 2012 Dr. Hardy Edwards III Vitamin Derivatives, Inc. 625 Lem Edwards Road Winterville, Georgia 30683 Re: GRAS Notice No. AGRN 000-009 Dear Dr. Edwards: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is
May 4, 2012 Dr. Hardy Edwards III Vitamin Derivatives, Inc. 625 Lem Edwards Road Winterville, Georgia 30683 Re: GRAS Notice No. AGRN 000-009 Dear Dr. Edwards: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is
Nursing 113. Pharmacology Principles
 Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Testosterone Replacement Informed Consent. Patient Name: Date:
 Testosterone Replacement Informed Consent Patient Name: Date: This form is designed to document that you understand the information regarding Testosterone Replacement Therapy, so that you can make an informed
Testosterone Replacement Informed Consent Patient Name: Date: This form is designed to document that you understand the information regarding Testosterone Replacement Therapy, so that you can make an informed
Bone Appétit: New Information on Calcium & Vitamin D QUESTION & ANSWER
 Bone Appétit: New Information on Calcium & Vitamin D QUESTION & ANSWER Wednesday, November 17, 2010 1:30 p.m. to 3:00 p.m. ET 1. I like to drink warm milk, but I have heard that heating some vitamins can
Bone Appétit: New Information on Calcium & Vitamin D QUESTION & ANSWER Wednesday, November 17, 2010 1:30 p.m. to 3:00 p.m. ET 1. I like to drink warm milk, but I have heard that heating some vitamins can
BULLETIN. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health
 BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial Marcus R. Pereira A. Study Purpose Hepatic encephalopathy is a common complication
Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial Marcus R. Pereira A. Study Purpose Hepatic encephalopathy is a common complication
UPDATE ON RESEARCH FOR RP TREATMENT: VITAMIN A PALMITATE, OMEGA-3-RICH FISH AND LUTEIN
 UPDATE ON RESEARCH FOR RP TREATMENT: VITAMIN A PALMITATE, OMEGA-3-RICH FISH AND LUTEIN VITAMIN A PALMITATE / OMEGA-3-RICH FISH / LUTEIN Table of Contents Introduction 3 Important Guidelines from Dr. Berson
UPDATE ON RESEARCH FOR RP TREATMENT: VITAMIN A PALMITATE, OMEGA-3-RICH FISH AND LUTEIN VITAMIN A PALMITATE / OMEGA-3-RICH FISH / LUTEIN Table of Contents Introduction 3 Important Guidelines from Dr. Berson
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis
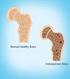 Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Public Assessment Report. Scientific discussion. Calcium and Vitamine D3 Alpex 1000 mg/880 IE, effervescent granules
 Public Assessment Report Scientific discussion Calcium and Vitamine D3 Alpex 1000 mg/880 IE, effervescent granules (calcium carbonate and cholecalciferol) NL License RVG: 111783 Date: 12 March 2015 This
Public Assessment Report Scientific discussion Calcium and Vitamine D3 Alpex 1000 mg/880 IE, effervescent granules (calcium carbonate and cholecalciferol) NL License RVG: 111783 Date: 12 March 2015 This
Refresher Course Vitamin D - Post Graduate Level
 Refresher Course Vitamin D - Post Graduate Level Reproduced below is an extract taken from: (with my parenthetical commentary in italics where the need is found to amplify and clarify) James M. Orten,
Refresher Course Vitamin D - Post Graduate Level Reproduced below is an extract taken from: (with my parenthetical commentary in italics where the need is found to amplify and clarify) James M. Orten,
Medication Utilization. Understanding Potential Medication Problems of the Elderly
 Medication Utilization Understanding Potential Medication Problems of the Elderly NICE - National Initiative for the Care of the Elderly WHAT ARE MEDICATION UTILIZATION PROBLEMS AMONG THE ELDERLY? A useful
Medication Utilization Understanding Potential Medication Problems of the Elderly NICE - National Initiative for the Care of the Elderly WHAT ARE MEDICATION UTILIZATION PROBLEMS AMONG THE ELDERLY? A useful
Vitamin and Mineral Safety 3 rd Edition
 Vitamin and Mineral Safety 3 rd Edition by John N. Hathcock, Ph.D. with a foreword by James C. Griffiths, Ph.D. edited by Douglas MacKay, N.D. Andrea Wong, Ph.D. Haiuyen Nguyen Vitamin and Mineral Safety
Vitamin and Mineral Safety 3 rd Edition by John N. Hathcock, Ph.D. with a foreword by James C. Griffiths, Ph.D. edited by Douglas MacKay, N.D. Andrea Wong, Ph.D. Haiuyen Nguyen Vitamin and Mineral Safety
Not All Clinical Trials Are Created Equal Understanding the Different Phases
 Not All Clinical Trials Are Created Equal Understanding the Different Phases This chapter will help you understand the differences between the various clinical trial phases and how these differences impact
Not All Clinical Trials Are Created Equal Understanding the Different Phases This chapter will help you understand the differences between the various clinical trial phases and how these differences impact
Regulatory Risk Assessment
 Regulatory Risk Assessment Richard B. Belzer PhD Regulatory Checkbook Mt. Vernon, VA Belzer@RegulatoryCheckbook.Org What is the Purpose of Risk Assessment? For regulatory analysis [A] risk assessment should
Regulatory Risk Assessment Richard B. Belzer PhD Regulatory Checkbook Mt. Vernon, VA Belzer@RegulatoryCheckbook.Org What is the Purpose of Risk Assessment? For regulatory analysis [A] risk assessment should
Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D
 Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D Contents Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D 1. Introduction. 3 2. Product Data Sheet..... 5 3. Product Performances...... 6 4. Product Analysis....... 9 5.
Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D Contents Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D 1. Introduction. 3 2. Product Data Sheet..... 5 3. Product Performances...... 6 4. Product Analysis....... 9 5.
Low Vitamin D Status: Time to Recognize and Correct a Wisconsin Epidemic
 Low Vitamin D Status: Time to Recognize and Correct a Wisconsin Epidemic Neil Binkley, MD; Diane Krueger, BS, CCRC, CDT; Marc K. Drezner, MD Abstract As a result of low dietary intake and sun avoidance,
Low Vitamin D Status: Time to Recognize and Correct a Wisconsin Epidemic Neil Binkley, MD; Diane Krueger, BS, CCRC, CDT; Marc K. Drezner, MD Abstract As a result of low dietary intake and sun avoidance,
Workshop 1. How to use Moringa leaves and other highly nutritious plants in a medical or nutritional context
 Workshop 1. How to use Moringa leaves and other highly nutritious plants in a medical or nutritional context Summary of discussions 1 Expected Results Product standards with acceptable range of variation
Workshop 1. How to use Moringa leaves and other highly nutritious plants in a medical or nutritional context Summary of discussions 1 Expected Results Product standards with acceptable range of variation
(NON-PRESCRIPTION) LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION. CALTRATE VITAMIN D3 600mg/400 IU, film-coated tablet Calcium and Cholecalciferol
 (NON-PRESCRIPTION) LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION CALTRATE VITAMIN D3 600mg/400 IU, film-coated tablet Calcium and Cholecalciferol Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information
(NON-PRESCRIPTION) LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION CALTRATE VITAMIN D3 600mg/400 IU, film-coated tablet Calcium and Cholecalciferol Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information
Calcium (serum, plasma, blood)
 Calcium (serum, plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Calcium (total in serum, plasma, ionised in blood (see 2.1 (2)). 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description
Calcium (serum, plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Calcium (total in serum, plasma, ionised in blood (see 2.1 (2)). 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description
Vitamin D for Prevention of Falls and their Consequences in Older Adults
 AMERICAN GERIATRICS SOCIETY CONSENSUS STATEMENT Vitamin D for Prevention of Falls and their Consequences in Older Adults Developed by the Workgroup of the Consensus Conference on Vitamin D for the Prevention
AMERICAN GERIATRICS SOCIETY CONSENSUS STATEMENT Vitamin D for Prevention of Falls and their Consequences in Older Adults Developed by the Workgroup of the Consensus Conference on Vitamin D for the Prevention
