Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Children and Young Adults
|
|
|
- Alexia Lloyd
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in MSRHTC P.O. Box 6507 Aurora, CO (303) An Overview for Patients and Health Care Providers
2 2 15 GLOSSARY: venous thrombosis = a condition of developing a blood clot in a vein; this can occur in the superficial or deep veins of the arms or legs, the venous circulation of the brain (cerebral sinovenous thrombosis), kidneys (renal vein thrombosis), liver (hepatic vein thrombosis, portal vein thrombosis), a central vein of the body, or other locations deep venous thrombosis (DVT) = thrombosis of the deep veins; when this occurs in an arm or leg, it is categorized as extremity (meaning arm or leg) DVT; other examples of types of DVT are described above (under venous thrombosis) pulmonary embolism (PE) = a condition in which a blood clot has traveled from a vein into the lung circulation, often suspected when there is chest pain or difficulty breathing in a patient with DVT; sometimes PE occurs in patients in whom no DVT can be found thrombophilia = a condition of increased risk for developing blood clots in the veins or arteries due to increased blood clotting post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) = a chronic condition of poor venous blood circulation following DVT, often identified due to swelling of the arm/leg and pain in the arm/leg with activities; in severe cases of PTS, there may be skin breakdown as well as pain in the arm/leg at rest antiphospholipid antibody syndrome = a type of thrombophilia (see definition above) due to proteins, called antiphospholipid antibodies, that are consistently present in the blood over time following a stroke or blood clot in the vein, or in some women who have a history of miscarriage(s) rheumatologic condition = a broad category of medical disorders (including lupus, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, and others) in which the body s immune system is overactive, and sometimes found to be the cause of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome or inflammation of blood vessels in young patients with thrombosis AUTHOR: Neil A. Goldenberg, MD Department of Pediatrics, Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Oncology University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center The Children's Hospital, Denver, and The Mountain States Regional Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center, Aurora, CO Marilyn J. Manco-Johnson, MD Department of Pediatrics, Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center The Children's Hospital, Denver, and The Mountain States Regional Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center Denver/Aurora, CO ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: Review of manuscript: Stephan Moll, MD, Chapel Hill, NC Brenda Riske, MBA/MPA, Denver/Aurora, CO Ruth Ann Kirschman, RNC/NP, Denver/Aurora, CO Elizabeth Pounder, PA-C, Denver/Aurora, CO. anticoagulation = standard blood thinner therapy, such as unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparin, and warfarin (Coumadin ) thrombolysis = clot-buster therapies, including medicines such as tissue-type plasminogen activator (tpa) and the use of specialized catheter procedures to break up clots.
3 14 3 SELECTED REFERENCES WHAT ARE VENOUS THROMOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM? Antithrombotic therapy in children: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Monagle P et al. Chest 2004;126:645S-687S. Laboratory testing for thrombophilia in pediatric patients. On behalf of the Subcommittee for Perinatal and Pediatric Thrombosis of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH). Manco-Johnson J et al. Thromb Haemost 2003;89: Venous thrombosis is a condition of developing a blood clot in a vein, a blood vessel that returns blood from the body back to the heart. Venous thrombosis can occur in the superficial or deep veins of the arms or legs, the venous circulation of the brain (cerebral sinovenous thrombosis), kidneys (renal vein thrombosis), liver (hepatic vein or portal vein thrombosis), a central vein of the body (inferior or superior vena cava thrombosis), or other locations. Throughout most of this overview, venous thrombosis will refer to thrombosis of the deep veins (DVT). Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a condition in which a blood clot has traveled from a vein into the lung circulation, often suspected when there is chest pain or difficulty breathing in a patient with DVT; sometimes PE occurs in patients in whom no DVT can be found Long term outcomes of venous thrombosis in children. Goldenberg N. Curr Opin Hematol 2005;12: How I treat venous thrombosis in children. Manco-Johnson J. Blood 2006;107: WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF VENOUS THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM? DVT and PE in children and young adults can be caused by poor blood circulation (for example, during times of decreased mobility or vein constriction for a prolonged period), damage to the inner lining of veins (such as when a catheter is placed in a vein, or when certain drugs or toxins are circulating in the blood), and thrombophilia (excess clotting) states. In children and young adults, a combination of these risk factors is often present at the time of DVT or PE. Also, in young people, genetic causes of thrombophilia may be important contributing factors to DVT or PE. Sometimes, however, the cause of DVT or pulmonary embolism in children and young adults remains unclear. Research at some specialty centers in the U.S. is focusing on the discovery of new thrombophilia traits and other risk factors in these patients.
4 4 13 WHY ARE VENOUS THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IMPORTANT IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG ADULTS? DVT and PE in young people can occur at any age, but the first month of life (especially in premature and other hospitalized infants) and the teenage years appear to be times of increased risk for blood clots. Although DVT and PE in children and young adults occur less commonly than in elderly adults, their consequences can be equally devastating. In particular, issues of evaluation for causes and risk factors, short-term treatments, and long-term prevention of future DVT and PE all play a very prominent role in the care of children and young adults with these disorders. Young people with DVT or PE appear to have single or multiple genetic thrombophilia traits more frequently than older adults, and this can affect the risk of a future blood clot in both the young patients and their family members. In addition, children and young adults appear to be at least as likely as older adults to develop a chronic condition of poor venous blood circulation called the postthrombotic syndrome (PTS) following DVT. PTS is often diagnosed when swelling of the arm/leg and pain in the arm/leg with activities develops or persists over a period of months to years following the diagnosis of DVT. In severe cases of PTS, there may be skin breakdown as well as pain in the arm/leg at rest. Although medical guidelines exist for the evaluation and treatment of DVT and PE in children and young adults, the medical evidence for the optimal treatment of these disorders in young people comes mostly from studies in older adults. In addition, the particular circumstances of each patient are important to consider when making longtreatment decisions. This highlights the importance of expertise in thrombosis care for young people, and is also important to keep in mind when reading this general overview. KEY SUMMARY POINTS Venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in children and young adults occur less commonly than in elderly adults, but their consequences can be equally devastating. Evaluation for causes and risk factors, short-term treatments, and long-term prevention of future blood clots and their complications all play a very prominent role in DVT and PE care for young people. Optimal DVT and PE treatment and prevention in children and young adults requires specialized care, particularly involving Hematologists with expertise in blood clotting disorders in young people. Thrombophilia testing is an important part of the evaluation of causes and risk factors for DVT and PE in children and young adults, and is best guided by experts in blood clotting. Thrombophilia affects decision-making for both short-term treatment and long-term prevention of future DVT and PE. Patients taking blood thinners should exercise appropriate bleeding precautions and seek prompt medical attention for bleeding concerns. Long-term management of DVT and PE is focused primarily upon safely preventing further blood clotting, as well as optimizing the child s/young adult s level of function in school, work, family, and/or society. This includes efforts to prevent and treat the post-thrombotic syndrome, a chronic condition of poor venous blood circulation following DVT.
5 12 5 Coumadin dose may be required. Coumadin educational brochures and dietary instructions are available through most anticoagulation clinics and treatment centers that specialize in thrombosis and thrombophilia. In order to help assure the proper medical treatment during medical emergencies, patients who are on anticoagulation should wear a medical bracelet showing the blood thinner they take aspirin and carry a list of their medications in their wallet or purse at all times. Patients taking anticoagulation should also be sure to advise their physician/surgeon of their blood thinner use prior to undergoing surgery or other invasive medical procedures; typically, Coumadin is discontinued one week prior to these procedures, while low molecular weight heparin medications like Lovenox and Fragmin are stopped 24 hours before surgery. In addition, other medications that increase the risk for bleeding (e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, certain herbal products) should be avoided while on anticoagulation therapy, unless prescribed and monitored by a physician. HOW ARE VENOUS THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM DIAGNOSED IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG ADULTS? Signs and symptoms DVT in young people may occur with a variety of signs and symptoms, depending mainly on the area of the body that is affected and the degree of blockage of the vein(s) involved. The typical signs and symptoms of DVT in arm or leg are unexplained pain and swelling, sometimes also with redness of the skin. When a clot completely blocks blood flow in a central vein of the lower body, swelling of both legs can occur, and when a clot blocks a central vein the upper body, there can be swelling of both arms as well as swelling of the head and neck. For clots in the venous circulation of the brain, signs and symptoms can include unusually severe or persistent headache or unexplained change in vision. Clots affecting venous drainage of the kidney can cause signs and symptoms that include high blood pressure and blood in the urine. Because Coumadin can cause birth defects when used early in pregnancy, all female patients who have reached puberty should be counseled on taking adequate measures to prevent pregnancy while on Coumadin. For non-urgent concerns relating to bleeding or blood thinners, patients should contact their Hematologist or primary care physician. A description of on of these trials can be found at OTHER PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS It is important to work with a knowledgeable team of health care providers, including blood clotting specialists from Hematology, in the care of the child or young adult with DVT or PE. Thorough evaluation of DVT and PE is often challenging, and both short-term and long-term treatment decisions can be difficult. The identification of thrombophilia is an important component of this care, and is best guided by experts in blood clotting. Family testing should be considered for young DVT or PE patients in whom genetically-determined thrombophilia traits are identified, so that appropriate measures to prevent DVT and PE in family members can be taken. A list of centers specialized in clotting disorders can be found at The signs and symptoms of PE in young people include unexplained shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, and chest pain that usually is worse when taking a deep breath. When PE affects a large part of the circulation to the lung, it is often a medical emergency due to the body s inability to provide enough oxygen to vital organs. Unfortunately, in some cases of DVT and PE, signs and symptoms can be absent. When DVT or PE are found on scans in a patient who does not have (or does not recall) any signs or symptoms, it is often difficult to know whether the clot is new or old, and this can affect treatment decisions. Radiologic imaging tests (scans) Suspected DVT or PE in children and young adults is confirmed by scans. For DVT in an arm or leg, ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) is typically used. For DVT in a central vein of the body, or in a vein draining organs like the kidneys or liver, CT is usually necessary. In some cases, a dye scan of the veins (venogram) may be required in order to be sure about the diagnosis of DVT. To diagnose clots in the venous circulation of the brain, CT or magnetic
6 6 11 resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is typically used. Suspected PE is confirmed by specialized CT scans or by a nuclear medicine scan called a V/Q scan. Laboratory tests Another critical step in the evaluation includes laboratory testing for thrombophilia. In addition, because young people who develop DVT or PE often have an underlying illness, other laboratory testing relating to the underlying illness may be performed in order to monitor its course. For example, blood markers of inflammation and cultures of blood and other body fluids may be closely monitored closely in children and young adults who are being evaluated or treated for infections as well as blood clots. In addition, patients who have other signs and symptoms that could suggest an underlying rheumatologic condition (broad category of medical disorders -- including lupus, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, and others -- in which the body s immune system is overactive) may have specialized testing to evaluate for these disorders. WHAT THROMBOPHILIA TESTING SHOULD BE PERFORMED IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG ADULTS WITH VENOUS THROMBOSIS OR PULMONARY EMBOLISM? Thrombophilia testing is an important part of the evaluation of causes and risk factors for DVT and PE in children and young adults, and is best guided by experts in blood clotting. Thrombophilia affects decision-making for both shortterm treatment and long-term prevention of future DVT and PE. Thrombophilia testing for blood clotting risk factors can vary across treatment centers. However, in young people with newly-diagnosed DVT or PE, comprehensive thrombophilia testing is recommended by a group of blood clotting experts, the Scientific Subcommittee on Perinatal and Pediatric Thrombosis of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis, and is routinely performed at many specialty centers. This includes testing for: anticoagulant deficiencies (protein C activity, free protein S antigen, antithrombin activity); antiphospholipid antibodies (lupus anticoagulant, anti-beta-2-glycoprotein-i antibody, anticardiolipin antibody); elevated homocysteine concentration; factor V Leiden HOW DO COUMADIN AND HEPARINS WORK, WHAT ARE THEIR SIDE EFFECTS, AND WHAT PRECAUTIONS SHOULD BE TAKEN WHILE ON BLOOD THINNERS? By blocking the effects of vitamin K, Coumadin interferes with the function of several blood clotting proteins ( factors ) that require vitamin K in order to allow proper blood clotting. In this way, Coumadin makes the blood less clottable ( thins the blood). Heparins (including unfractionated and low molecular weight heparins) work somewhat differently then coumadin. These medicines make the blood less clottable by increasing the function of a natural blood thinner in the blood, called antithrombin. Whether the anticoagulation medication being used is Coumadin, a type of heparin, or other medications, due to the blood thinning effects, anticoagulation increases the risk for bleeding, especially after injury. For this reason, patients taking anticoagulation who develop significant bleeding or become significantly injured should seek medical evaluation. Patients on blood thinners should always use proper safety restraints (e.g., seatbelt) in a motor vehicle and wear a helmet when on a bicycle, skateboard, rollerskates, etc. High-impact physical activities and contact sports should generally be avoided while on treatment doses of anticoagulation, given the risk of bleeding from injury. The risk for life-threatening bleeding in the brain in association with head injury is of particular concern while on blood thinners. The blood thinning effects of Coumadin, as measured by INR levels in the blood, can be affected by other medications, including many antibiotics. The INR is also affected by the amount of vitamin K consumed in the diet. Patients should inform the physician or pharmacy doctor managing their Coumadin treatment about any new medications or herbal supplements being taken, as well as any major changes in diet (particularly, the amount of green leafy vegetables being consumed that may contain vitamin K); in many instances, more frequent INR checks will initially be necessary following these changes, and adjustments in
7 10 7 DVT or PE during times of increased risk for thrombosis, such as during hospitalization for severe infection, periods of decreased mobility (for example, after a major surgical procedure or casting of a fractured upper arm or leg). To prevent a first or subsequent DVT or PE, all patients and at-risk family members should also take care to avoid dehydration and smoking, and should adopt a regular aerobic exercise program. Some research suggests that aerobic exercise stimulates our veins to release small amounts of the stored natural clot buster tpa, and in this way helps to keep our veins healthy and prevent blood clots. Prevention and treatment of post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) Enabling the child/young adult to function as best as possible in school, work, family, and/or society involves prevention and treatment of PTS. PTS is a chronic condition of poor venous blood circulation called the post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) following DVT. PTS is often diagnosed when swelling of the arm/leg and pain in the arm/leg with activities develops or persists over a period of months to years following the diagnosis of DVT. In severe cases of PTS, there may be skin breakdown as well as pain in the arm/leg at rest. Clinical research studies in older adults have shown that daily continuous use of compression stockings on an affected leg or arm for a period of at least 1 year following the diagnosis of DVT can reduce the risk of developing PTS. Based on this knowledge, routine use of compression stockings should also be strongly encouraged for all young patients with DVT. In children and young adults with DVT, if PTS is severe and does not adequately improve with the use of compression stockings, or if chronic SVC syndrome is present (a syndrome of swelling of the head and neck due to blockage of a central vein in the upper body, called the superior vena cava), other options may be available. For example, in some patients, procedures to restore or improve venous drainage may be possible. These procedures (including stenting, venous bypass grafting, and other techniques) are typically evaluated and performed by specialists in interventional radiology or vascular surgery. mutation; prothrombin mutation; elevated factor VIII activity; and elevated lipoprotein(a) concentration. Testing for methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) mutations may also be considered. For nearly all of the above-mentioned factors, clinical studies have suggested an increased association with blood clots or vascular disease in young people. HOW ARE VENOUS THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM INITIALLY TREATED IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG ADULTS? The initial treatments thrombosis of the deep veins and PE in young people are complex, and can differ somewhat for patients with different circumstances. The initial treatment involves attention to blood pressure, fluid levels, and blood levels of oxygen, sugar, salts, acid, etc. Additional important treatment decisions involve consideration of the identified causes and risk factors for DVT or PE, the amount of blood clot and degree of blockage of blood flow, the area(s) of the body affected, and the medical status of the patient. When risk factors for DVT or PE are identified, they should be treated or removed if possible. For example, adolescent girls who develop DVT or PE while taking the birth control pill should stop the pill, especially if their thrombophilia testing shows that they have the factor V Leiden mutation. In a child or young adult with newly-diagnosed DVT, the standard treatment is anticoagulation (blood thinner therapy). Blood thinners typically used include unfractionated heparin given intravenously (I.V.) as a continuous infusion, low molecular weight heparin given under the skin as twice-daily injections, and warfarin (Coumadin ) taken as a daily pill. The dose of Coumadin initially chosen for treatment of DVT or PE in young people is approximately 0.1 mg per kg of body weight. For unfractionated heparin, depending on the age of the young patient, the dose used may be between 15 and 25 Units per hour per kg of body weight, often after an initial loading dose of Units per kg of body weight. For the low molecular weight heparin enoxaparin (Lovenox ), depending on the age of the young patient, between 1.0 and 1.5 Units per kg of body weight is often used for each treatment dose (for the low molecular weight heparin dalteparin (Fragmin ), a
8 8 9 treatment dose of Units per kg of body weight has been suggested in young patients). The blood-thinning effect of these anticoagulation treatments is measured by blood tests in order to keep the level of blood thinning in a safe and effective range. For Coumadin, a standardized test call the international normalized ratio (INR) is used for monitoring. For unfractionated and low molecular weight heparins, a test called the anti-factor Xa activity test is preferred, although the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) test is sometimes used when anti-factor Xa testing is not available. In cases of acute DVT where a clot has occurred at the site of a central venous catheter, and where the clot is confined to the tip of a central venous catheter and is completely removed along with the catheter, sometimes no anticoagulation is felt necessary, and in other instances a short course of anticoagulation treatment is given. The best approach in this circumstance is not clear. In cases of acute DVT that is large and completely blocks venous drainage from an arm or leg, special medicines or techniques to remove or break up the clot (thrombolysis) may be considered early in the initial treatment instead of routine anticoagulation (although later followed by anticoagulation). Thrombolysis can include medicines such as tissue-type plasminogen activator (tpa) and/or the use of specialized catheter procedures to break up clots. Based on clinical trials in older adults, many experts also consider thrombolysis to be the best option for treatment in young patients with acute PE in whom a large part of the circulation to the lung is affected and/or there is evidence of strain on the heart by heart ultrasound (echocardiogram). Because tpa has a higher risk of bleeding complications than standard anticoagulants, patients are monitored especially closely for signs and symptoms of bleeding during tpa treatment. In addition, monitoring of tpa involves blood markers of clot breakdown as well as blood levels of proteins involved in the clot breakdown process. While monitoring for bleeding and blood markers are essential, follow-up scans currently remain the best measures of effectiveness of thrombolysis, showing the response of the clot to this therapy by changes in clot size and degree of blockage of blood flow. Clinical trials designed to determine the optimal treatment for DVT specifically in children have recently been proposed or are currently underway. HOW ARE VENOUS THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATED OVER THE LONG-TERM IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG ADULTS? Long-term management of DVT and PE is focused primarily upon: (1) safely preventing further blood clots; and (2) enabling the child/young adult to function as best as possible in school, work, family, and/or society. Prevention of further DVT or PE In an effort to prevent further blood clotting (including the worsening of an existing blood clot and the development of a new DVT or PE), most children and young adults with acute DVT or PE are treated with anticoagulation for at least 3-6 months. Some patients, such as those with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (i.e., whose thrombophilia testing showed lasting antiphospholipid antibodies in the blood since the time of stroke) or other very strong thrombophilia traits, patients with other risk factors for the development further blood clots (for example, abnormalities of blood vessel anatomy that can cause decrease blood flow, and certain strong thrombophilia traits), and individuals who have had further blood clots while on adequate anticoagulation treatment, may also be prescribed long-term blood thinners, such as Coumadin. In patients with certain underlying medical conditions, other treatments aimed at improving the underlying disorder may also decrease the risk of further blood clotting. For example, in patients with severe infections, antibiotic treatment is also given, and in patients with rheumatologic conditions, drugs to control the overactive immune system may also be used. In families where several members have had DVT or PE (especially before the age of 55 years), patients and family members who test positive for milder genetic thrombophilia traits, such as single factor V Leiden or prothrombin mutations, should strongly consider using a short course of low-dose blood thinners to prevent a first or subsequent
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
 Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
What Does Pregnancy Have to Do With Blood Clots in a Woman s Legs?
 Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients. Information For Patients
 Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 3 CLOTTING DISORDERS Original authors: Edith A. Nutescu, Jessica B. Michaud, Joseph A. Caprini, Louis W. Biegler, and Robert R. McCormick Abstracted by Kellie R. Brown Introduction The normal balance
CHAPTER 3 CLOTTING DISORDERS Original authors: Edith A. Nutescu, Jessica B. Michaud, Joseph A. Caprini, Louis W. Biegler, and Robert R. McCormick Abstracted by Kellie R. Brown Introduction The normal balance
Warfarin. (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely
 Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely Welcome This booklet is designed to provide you with important information about warfarin to help you take this medication safely and effectively.
Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely Welcome This booklet is designed to provide you with important information about warfarin to help you take this medication safely and effectively.
Ischaemic stroke 85% (85 in every 100 strokes)
 UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
what is warfarin? Treatment with Warfarin (Coumadin ) What is warfarin?
 What is warfarin? Warfarin sodium (Coumadin ) is a medication that works as an anti-coagulant. Anti means against and coagulant refers to blood clotting. An anticoagulant helps to prevent clots from forming
What is warfarin? Warfarin sodium (Coumadin ) is a medication that works as an anti-coagulant. Anti means against and coagulant refers to blood clotting. An anticoagulant helps to prevent clots from forming
To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation
 Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Using Blood-Thinning (Anticoagulant) Drugs
 A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
Thrombophilia. Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003
 Thrombophilia Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003 Thrombophilia Hereditary and acquired risk factors for thrombosis Venous thromboembolism Arterial thromboembolism
Thrombophilia Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003 Thrombophilia Hereditary and acquired risk factors for thrombosis Venous thromboembolism Arterial thromboembolism
FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin )
 FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin ) What is warfarin? Warfarin is the most commonly used anticoagulant in the US. An anticoagulant is a drug used to prevent unwanted and harmful blood clots. Although
FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin ) What is warfarin? Warfarin is the most commonly used anticoagulant in the US. An anticoagulant is a drug used to prevent unwanted and harmful blood clots. Although
Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Remain free of unusual bleeding Maintain effective tissue perfusion Implementation
 Obtain complete heath history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Assess baseline coagulation studies and CBC Assess for history of bleeding disorders, GI bleeding, cerebral bleed, recent
Obtain complete heath history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Assess baseline coagulation studies and CBC Assess for history of bleeding disorders, GI bleeding, cerebral bleed, recent
Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism
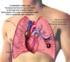 What You Need to Know After Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease,
What You Need to Know After Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease,
MEDICATION GUIDE COUMADIN (COU-ma-din) (warfarin sodium)
 MEDICATION GUIDE COUMADIN (COU-ma-din) (warfarin sodium) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking COUMADIN (warfarin sodium) and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
MEDICATION GUIDE COUMADIN (COU-ma-din) (warfarin sodium) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking COUMADIN (warfarin sodium) and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
How To Take Xarelto
 A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE)
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for people with a blood clot (thrombus) What is this
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for people with a blood clot (thrombus) What is this
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients
 Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight heparins to patients.
 UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
Sudden dizziness, trouble walking, loss of balance or coordination
 rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Patient Education Information Sheet Veterans Health System Pharmacy Service 119 What is rivaroxaban (Xarelto)? A new anticoagulant ( blood thinner ) that reduces the risk of stroke
rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Patient Education Information Sheet Veterans Health System Pharmacy Service 119 What is rivaroxaban (Xarelto)? A new anticoagulant ( blood thinner ) that reduces the risk of stroke
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines
 Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Anticoagulants. Anticoagulants Definition. When are blood clots GOOD? Where and why do blood clots occur? 6/12/2014
 Anticoagulants Steven R. Kayser, PharmD Professor Emeritus Department of Clinical Pharmacy UCSF Anticoagulants Definition A substance that hinders the clotting of blood Sometimes referred to as blood thinners
Anticoagulants Steven R. Kayser, PharmD Professor Emeritus Department of Clinical Pharmacy UCSF Anticoagulants Definition A substance that hinders the clotting of blood Sometimes referred to as blood thinners
ADVICE ON TRAVEL-RELATED DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS
 ADVICE ON TRAVEL-RELATED DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS Introduction 1. A possible link between deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and long haul air travel was first suggested by reports in medical journals in the 1950s.
ADVICE ON TRAVEL-RELATED DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS Introduction 1. A possible link between deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and long haul air travel was first suggested by reports in medical journals in the 1950s.
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: MOBILITY WITH A DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Page 1 of 10
 Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine
 What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
Through Thick and Thin
 Through Thick and Thin Learning to Live with Warfarin South Denver Cardiology Associates PC What is Anticoagulation? Anti = against Coagulation = blood clotting An anticoagulant is a medication that reduces
Through Thick and Thin Learning to Live with Warfarin South Denver Cardiology Associates PC What is Anticoagulation? Anti = against Coagulation = blood clotting An anticoagulant is a medication that reduces
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 19 VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Original authors: David H. Deaton, Byung Boong Lee, James Loredo, Richard F. Neville, William H. Pearce, and Heron E. Rodriguez Abstracted by Raghu Motaganahalli Introduction
CHAPTER 19 VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Original authors: David H. Deaton, Byung Boong Lee, James Loredo, Richard F. Neville, William H. Pearce, and Heron E. Rodriguez Abstracted by Raghu Motaganahalli Introduction
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update
 UC SF Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update Jeffrey Tabas, MD Professor UCSF School of Medicine Emergency Department San Francisco General Hospital sf g h Disclosure No Financial Relationships to Disclose
UC SF Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update Jeffrey Tabas, MD Professor UCSF School of Medicine Emergency Department San Francisco General Hospital sf g h Disclosure No Financial Relationships to Disclose
Paul G. Lee. 2 ND YEAR RESEARCH ELECTIVE RESIDENT S JOURNAL Volume III, 1998-1999. A. Objective
 A comparison of six months of anticoagulation with extended anticoagulation for a first episode of venous thromboembolism in patients with thrombophilia Paul G. Lee A. Objective a. To evaluate the risk
A comparison of six months of anticoagulation with extended anticoagulation for a first episode of venous thromboembolism in patients with thrombophilia Paul G. Lee A. Objective a. To evaluate the risk
Your Guide to Preventing and Treating Blood Clots
 Your Guide to Preventing and Treating Blood Clots U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 540 Gaither Road Rockville, MD 20850 AHRQ Pub. No. 09 0067 C May
Your Guide to Preventing and Treating Blood Clots U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 540 Gaither Road Rockville, MD 20850 AHRQ Pub. No. 09 0067 C May
Registered Charity No: 326679 Caring for those with a rare, complex and lifelong disease www.behcets.org.uk
 Registered Charity No: 326679 Caring for those with a rare, complex and lifelong disease www.behcets.org.uk Behçet s Disease and the Kidneys How are the kidneys affected by Behçet s disease? Kidney disease
Registered Charity No: 326679 Caring for those with a rare, complex and lifelong disease www.behcets.org.uk Behçet s Disease and the Kidneys How are the kidneys affected by Behçet s disease? Kidney disease
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
XARELTO (rivaroxaban tablets) in Knee and Hip Replacement Surgery
 XARELTO (rivaroxaban tablets) in Knee and Hip Replacement Surgery Fast Facts: XARELTO is a novel, once-daily, oral anticoagulant recently approved in the United States for the prevention (prophylaxis)
XARELTO (rivaroxaban tablets) in Knee and Hip Replacement Surgery Fast Facts: XARELTO is a novel, once-daily, oral anticoagulant recently approved in the United States for the prevention (prophylaxis)
Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
Human Normal Immunoglobulin Solution for Intravenous Infusion.
 CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION (CMI) OCTAGAM Human Normal Immunoglobulin Solution for Intravenous Infusion. OCTAGAM is available in single use bottles of 20 ml, 50 ml, 100 ml and 200 ml. OCTAGAM contains
CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION (CMI) OCTAGAM Human Normal Immunoglobulin Solution for Intravenous Infusion. OCTAGAM is available in single use bottles of 20 ml, 50 ml, 100 ml and 200 ml. OCTAGAM contains
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
CHAPTER 15 SCLEROTHERAPY FOR VENOUS DISEASE
 Introduction CHAPTER 15 SCLEROTHERAPY FOR VENOUS DISEASE Original authors: Niren Angle, John J. Bergan, Joshua I. Greenberg, and J. Leonel Villavicencio Abstracted by Teresa L. Carman New technology has
Introduction CHAPTER 15 SCLEROTHERAPY FOR VENOUS DISEASE Original authors: Niren Angle, John J. Bergan, Joshua I. Greenberg, and J. Leonel Villavicencio Abstracted by Teresa L. Carman New technology has
Atrial Fibrillation. Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends. Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group
 Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast. Information for patients Pharmacy
 Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF) with one or more risk factors
 News Release For use outside the US and UK only Bayer Pharma AG 13342 Berlin Germany Tel. +49 30 468-1111 www.bayerpharma.com Bayer s Xarelto Approved in the EU for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients
News Release For use outside the US and UK only Bayer Pharma AG 13342 Berlin Germany Tel. +49 30 468-1111 www.bayerpharma.com Bayer s Xarelto Approved in the EU for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 P A T I E N T I N F O R M A T I O N G U I D E Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Information for Newly Diagnosed Patients CONTENTS A. Blood clot basics a. What is a blood clot? b. What causes
P A T I E N T I N F O R M A T I O N G U I D E Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Information for Newly Diagnosed Patients CONTENTS A. Blood clot basics a. What is a blood clot? b. What causes
Cardioversion for. Atrial Fibrillation. Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Resurfacing hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Procedure Information Guide Resurfacing hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
MEDICATION GUIDE. PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
Renovascular Disease. Renal Artery and Arteriosclerosis
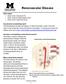 Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013
 Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS
 NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
Why your weight matters during pregnancy and after birth
 Information for you Published in November 2011 (next review date: 2015) Why your weight matters during pregnancy and after birth Most women who are overweight have a straightforward pregnancy and birth
Information for you Published in November 2011 (next review date: 2015) Why your weight matters during pregnancy and after birth Most women who are overweight have a straightforward pregnancy and birth
Low Molecular Weight Heparin. All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice
 Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Warfarin therapy for stroke patients with atrial fibrillation
 Warfarin therapy for stroke patients with atrial fibrillation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Warfarin therapy for stroke patients with atrial fibrillation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery
 medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This Medicine Update is for people who have been prescribed
medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This Medicine Update is for people who have been prescribed
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE)
 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) This leaflet aims to answer your questions about rivaroxaban that may be prescribed for you when you are diagnosed
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) This leaflet aims to answer your questions about rivaroxaban that may be prescribed for you when you are diagnosed
Investor News. Not intended for U.S. and UK media
 Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Approved for the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Approved for the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
PROTOCOL TITLE: Ambulatory Initiation and Management of Warfarin for Adults
 PROTOCOL NUMBER: 7 PROTOCOL TITLE: Ambulatory Initiation and Management of Warfarin for Adults THIS PROTOCOL APPLIES TO: UW Health Clinics: all adult outpatients with an active order for warfarin TARGET
PROTOCOL NUMBER: 7 PROTOCOL TITLE: Ambulatory Initiation and Management of Warfarin for Adults THIS PROTOCOL APPLIES TO: UW Health Clinics: all adult outpatients with an active order for warfarin TARGET
Goiter. This reference summary explains goiters. It covers symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
The largest clinical study of Bayer's Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Wednesday, 14 November 2012 07:38
 Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
Living with a Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC)
 Living with a Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC) dabigatran (Pradaxa ) rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) apixaban (Eliquis ) Information for patients Produced and made available by the Western Australian
Living with a Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC) dabigatran (Pradaxa ) rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) apixaban (Eliquis ) Information for patients Produced and made available by the Western Australian
Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org
 OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTOPLUS MET (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
11 Serious and life-threatening side effects can occur while taking EVISTA. These include 12 blood clots and dying from stroke:
 1 1 BNL 3123 AMP 2 Medication Guide 3 EVISTA (E-VISS-tah) 4 (raloxifene hydrochloride) 5 Tablets for Oral Use 6 Read the Medication Guide that comes with EVISTA before you start taking it and each time
1 1 BNL 3123 AMP 2 Medication Guide 3 EVISTA (E-VISS-tah) 4 (raloxifene hydrochloride) 5 Tablets for Oral Use 6 Read the Medication Guide that comes with EVISTA before you start taking it and each time
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS
 GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
MANAGING ANEMIA. When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure. www.kidney.org
 MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Anticoagulant therapy
 Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Guide to Warfarin Therapy
 Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013. Anticoagulants
 MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide
 Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
The Liver and Alpha-1. Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION
 The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What Is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency? Alpha-1 is a condition that may result in serious lung disease in adults and/or liver
The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What Is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency? Alpha-1 is a condition that may result in serious lung disease in adults and/or liver
Guide to Warfarin Therapy
 Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
Objective of This Lecture
 Component 2: The Culture of Health Care Unit 3: Health Care Settings The Places Where Care Is Delivered Lecture 5 This material was developed by Oregon Health & Science University, funded by the Department
Component 2: The Culture of Health Care Unit 3: Health Care Settings The Places Where Care Is Delivered Lecture 5 This material was developed by Oregon Health & Science University, funded by the Department
What to Know About. Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis By Kerry V. Cooke
 Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
