Interstitial Lung Disease
|
|
|
- Elvin Houston
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10 Interstitial lung disease is a term that broadly describes a diverse collection of more than 200 lung disorders. These diseases are classified together because they all affect the tissue and space around the alveoli (air sacs), called the interstitium. Depending on the specific disease, other compartments of the lung, including the alveoli themselves, the airways (trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles), the blood vessels, and the pleura (outside lining of the lung), may also be affected. In general, most interstitial lung disease is characterized by four manifestations: 1) respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath and cough, 2) specific chest radiographic abnormalities, 3) typical changes on pulmonary function tests in which the lung volume is decreased, and 4) characteristic microscopic patterns of inflammation and fibrosis. Whom does it affect? Epidemiology, prevalence, economic burden, vulnerable populations The lungs of patients with interstitial disease show varying degrees of fibrosis and inflammation. Fibrosis is characterized by an increased amount and abnormal structure of the connective tissue; inflammation is characterized by 99
2 Chapter 10 Prevalence of specific interstitial lung diseases in Bernalillo County, New Mexico, (1) Interstitial lung disease diagnosis Men (per 100,000) Women (per 100,000) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Pulmonary fibrosis Interstitial pneumonitis Occupational/environmental Sarcoidosis Connective tissue diseases Drug/radiation Pulmonary hemorrhage Other Total excessive inflammatory cells. Lung biopsies with a predominance of fibrosis typically indicate advanced disease and poor prognosis; whereas patients with a predominance of inflammation have a better prognosis and often respond to treatment. Although interstitial lung disease was once considered rare, epidemiologic investigations have found these diseases to be more common than previously recognized. One study reported that 80.9 per 100,000 men and 67.2 per 100,000 women suffer from interstitial disease in the United States, with 31.5 new cases diagnosed per 100,000 men per year and 26.1 new cases diagnosed per 100,000 women per year (1). In this study, the most prevalent interstitial diseases included pulmonary fibrosis, occupational- and environmental-associated disease, connective tissue disease associated interstitial disease, and sarcoidosis. Interstitial lung disease is predominantly a disease of adults, although it also occurs in children. Certain interstitial diseases such as sarcoidosis, pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis, and autoimmune-associated lung diseases, tend to develop in young adults, whereas idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) most often occurs between the ages of 40 and 70. In those with familial IPF 100
3 Chapter 10 (defined by its presence in two or more first-degree relatives), the onset of fibrosis appears to be earlier. Both incidence and mortality of interstitial disease increase with age (2,3). IPF has been reported to occur throughout the world in many different racial and ethnic groups. Studies in the United States have suggested that Caucasians are more likely to be diagnosed with IPF and have higher mortality rates from IPF than African Americans (3,4). It is unclear if these findings are due to real differences in racial characteristics or to an under-diagnosis of this condition in minority populations. The causes of interstitial lung disease can be classified into one of the following four categories: 1) diseases associated with a condition that affects other parts of the body (for example, autoimmune or collagen vascular disease), 2) diseases associated with a specific exposure to an agent known to damage the lungs (for example, medications such as bleomycin, occupational exposures such as asbestos, tobacco smoke, or agents in the environment that cause an immune reaction called hypersensitivity pneumonitis), 3) diseases associated with known genetic abnormalities (for example, Hermansky Pudlak syndrome), and 4) idiopathic diseases (diseases of an unknown cause). The most common interstitial lung diseases are idiopathic (5). Two recent studies found that both the number of new cases diagnosed per year and the mortality rates for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are rising in the United States (3,6). Investigators from the United Kingdom have reported similar trends: from 1990 to 2003, the incidence of this disease more than doubled (7). Of even greater concern, mortality rates from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are expected to increase because there is no established treatment that prolongs life for patients with these diseases (3). Persons with exposure to environmental hazards (for example, asbestos) have a higher incidence of interstitial lung disease, although less is known about most of the other forms of interstitial disease. Although not all patients who develop IPF have a history of cigarette smoking, smoking has been associated with the development of disease. Exposure to metal and wood dusts has also been associated with an increased likelihood of developing IPF. Although data are limited, other possible risk factors include exposure to certain prescription drugs and chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Genetics play a role in the development of the familial cases of IPF. About 8 percent of familial cases can be attributed to a single set of genes (8). 101
4 Chapter 10 CASE STUDY An otherwise healthy 59-year-old physical therapist sought medical attention for increasing shortness of breath and a dry cough over a year. He had no other symptom, no exposure to an environmental cause of interstitial lung disease, no medication associated with interstitial lung disease, no family history of lung disease, and no history of smoking. The physical examination revealed abnormal breath sounds at the bases of his lungs (crackles), but was otherwise normal. Crackles are subtle sounds made by the opening of the smallest air spaces with inspiration, which indicate that they close on expiration, an abnormality. Pulmonary function tests showed decreased lung volume (a restrictive pattern) and low blood oxygenation (hypoxemia) on exertion. A computed tomography scan showed the characteristic pattern of IPF. As there was no proven effective medical therapy for IPF, the patient elected to participate in a clinical trial. He was referred for lung transplant evaluation, started on supplemental oxygen, and enrolled in a pulmonary physical rehabilitation program. Comment As in this case, IPF typically develops insidiously, with a gradual onset of shortness of breath and a nonproductive cough. The symptoms often progress to become debilitating and all consuming. Although not necessary in this patient, a tissue biopsy is often needed to reach a conclusive diagnosis. Interstitial diseases are generally difficult to treat because established fibrosis causes permanent structural changes of the lungs. What are we learning about this disease? Pathophysiology, causes, genetic, environment, microbes Inflammation is a characteristic cellular and molecular response to injury, noxious exposure, or infectious agents. Fibrosis, or scarring, can be part of the healing response to injury, but fibrosis as a disease process occurs when restoration to normal tissue does not occur. Many of the cells and chemical mediators involved in inflammation are also involved in fibrosis. Fibrosis occurs when the laying down of collagen and other connective tissue does not stop and allow a return to the normal structure. This activity could result from ongoing inflammation, 102
5 Chapter 10 possibly because the injurious events continue, or because of defects in the inflammatory or repair processes. When the injurious agent is known, the extent of the injury and time of exposure to the injurious agent are important determinants in disease outcome. More is known about the interstitial diseases with known causes, such as the occupational exposures. For example, it appears that minerals (for example, asbestos and silica) that cause interstitial lung disease directly injure the lung and cannot be easily eliminated. Thus, ongoing inflammatory and fibrotic reactions occur. In patients with farmer s lung, recurrent exposure to the offending particles (antigens) stimulates the immune system recurrently, which results in fibrosis. A similar recurrent immune stimulation probably occurs with the autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis. For most of the interstitial lung diseases of unknown cause, the mechanisms of lung injury and fibrosis are also unknown. In several interstitial diseases, viral infection has been postulated to be the inciting cause, but this association has not yet been proven. How is it prevented, treated, and managed? Prevention, treatment, staying healthy, prognosis When the cause of the disease is known, the injurious agent should be avoided. For example, with hypersensitivity pneumonitis, one should avoid dust and mold. With idiopathic disorders, because the cause is unknown, there is no known way to prevent them. However, a number of possible risk factors for disease have been reported, and abstaining from cigarette smoking and treating gastroesophageal reflux disease are recommended. As it has been long thought that inflammation precedes fibrosis, therapeutic regimens for interstitial lung disease have included corticosteroids (for example, prednisone) and immunosuppressive agents (for example, azathioprine and cyclophosphamide). These drugs are helpful in cases of connective tissue related lung disease and certain other interstitial lung diseases. In patients with severe fibrosis, treatments targeting inflammation, however, have not been shown to improve survival or quality of life. One study did find that patients with IPF treated with high-dose N-acetyl cysteine, an antioxidant, in addition to a standard regimen of corticosteroids and azathioprine had better lung function compared to those on the standard regimen alone (9). Other drugs are being studied. 103
6 Chapter 10 Lung transplantation is the only option shown to prolong survival in cases of advanced interstitial lung disease, especially IPF, and is possible for patients younger than 65 without other significant medical conditions. However, lung transplantation outcomes remain unsatisfactory, as the five-year survival rate is approximately 40 percent and the median survival is 3.9 years in post-transplant patients with IPF (10). Of those patients with IPF who are waiting to receive a transplant, more than 30 percent die before receiving one. In 2007, IPF surpassed chronic obstructive pulmonary disease as the most common diagnostic group to receive a lung transplant (11), further highlighting the urgent need for effective medical therapies for this and related progressive lung diseases. Interstitial lung diseases have varying prognoses. Sarcoidosis usually has a good prognosis, with reversal of disease in most cases. On the other hand, IPF, one of the most common interstitial lung diseases, has the worst prognosis, with a median survival of two to three years (2). Are we making a difference? Research past, present, and future An understanding of the mechanisms of the idiopathic forms of interstitial lung disease is only now emerging. Studies of cells in culture and in animals have revealed a number of molecules and molecular pathways (such as transforming growth factor-beta) that promote fibrosis. It appears that an unidentified, probably inhaled, agent may injure the lung and activate cells, such as macrophages and airway lining epithelial cells. The activated cells then produce factors that recruit immune cells into the lung. The immune cells produce or activate sets of molecules that, in turn, activate other molecules to stimulate other cells called fibroblasts to produce and deposit collagen and other connective tissue components, which constitute lung fibrosis. Studies of the genetic background of patients show that alterations in specific genes (for example, surfactant protein genes and telomerase) may predispose individuals to IPF. Further evidence for the role of genetics in interstitial lung disease comes from studies in patients with other disorders (for example, sarcoidosis and Hermansky Pudlak syndrome) where mutations in specific genes are associated with a higher incidence of lung fibrosis (12). Further research on these rare diseases caused by a single gene defect may shed light on disease processes that are also important in interstitial lung disease. 104
7 Chapter 10 Dean E. Schraufnagel The end result of interstitial lung disease is fibrosis, in which scar tissue accumulates and air spaces break down into large cysts, a process sometimes called honeycombing. What do we need to do to cure or eliminate interstitial lung disease? Although considerable progress has been made in understanding these conditions, curing and eliminating interstitial lung disease is still a distant goal. A clearer understanding of how the cells fail to adequately repair the lung is still needed. Understanding basic mechanisms should lead to better markers to diagnose and follow patients. With these much-needed markers, therapeutic trials will be easier and more cost effective to conduct. Current clinical trials are studying agents that reduce the fibrotic signaling within the lung, reduce pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease, and alleviate oxidative stress. These clinical studies are usually coupled with basic science studies to learn more about the mechanisms of disease and to develop biological 105 Whitebook_breathing_Ch10.indd 105 6/25/10 12:48:26 PM
8 Chapter 10 Hulton Archive/Getty Images Hulton Archive/Getty Images Darren McCollester/Getty Images Steve Zusy/Getty Images Michael Ochs Archives/Getty Images ILD has affected many notable A mericans Interstitial lung disease is killing more Americans each year. Former Utah Governor Olene Smith Walker (top left) is living with the disease. Others, unfortunately, have died of the disease, including folk singer and human rights advocate Odetta, writer Peter Benchley (bottom left) and actors Marlon Brando and James Doohan. arkers. To date, trials testing new drugs for the treatment of interstitial lung m disease have not been successful or have slowed the progression of disease only modestly, but it is hoped as more is learned about the cells and molecules that are altered in these conditions, the better the chance for success. Both academic centers and pharmaceutical companies are conducting clinical trials to test the safety and effectiveness of several drugs. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s clinical research network (IPFnet) conducts therapeutic trials in the United States. Recently, stem cells have been considered for therapy, but more needs to be learned before these and other potential therapeutic strategies can be used. 106 Whitebook_breathing_Ch10.indd 106 6/25/10 12:49:09 PM
9 Chapter 10 References 1. Coultas DB, Zumwalt RE, Black WC, Sobonya RE. The epidemiology of interstitial lung diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994;150: American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161: Olson AL, Swigris JJ, Lezotte DC, Norris JM, Wilson CG, Brown KK. Mortality from pulmonary fibrosis increased in the United States from 1992 to Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007;176: Mannino DM, Etzel RA, Parrish RG. Pulmonary fibrosis deaths in the United States, An analysis of multiple-cause mortality data. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996;153: American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/ European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165: Raghu G, Weycker D, Edelsberg J, Bradford WZ, Oster G. Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006;174: Gribbin J, Hubbard RB, Le Jeune I, Smith CJ, West J, Tata LJ. Incidence and morality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis in the UK. Thorax 2006;61: Armanios MY, Chen JJ, Cogan JD, Alder JK, Ingersoll RG, Markin C, Lawson WE, Xie M, Vulto I, Phillips JA 3rd, et al. Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 2007;356: Demedts M, Behr J, Buhl R, Costabel U, Dekhuijzen R, Jansen HM, MacNee W, Thomeer M, Wallaert B, Laurent F, et al. High-dose acetylcysteine in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 2005;353: Trulock EP, Christie JD, Edwards LB, Boucek MM, Aurora P, Taylor DO, Dobbels F, Rahmel AO, Keck BM, Hertz MI. Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: twenty-fourth official adult lung and heart-lung transplantation report J Heart Lung Transplant 2007;26: McCurry KR, Shearon TH, Edwards LB, et al. Lung transplantation in the United States, Am J Transplant 2009;9: Steele MP, Brown KK. Genetic predisposition to respiratory diseases: infiltrative lung diseases. Respiration 2007;74:
10 Chapter 10 Web sites of interest ATS/ERS Consensus Statement on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis NIH Clinical trials Coalition of Pulmonary Fibrosis Children s Foundation, Inc. Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation 108
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis What is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a condition that causes persistent and progressive scarring of the tiny air sacs (alveoli) in
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis What is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a condition that causes persistent and progressive scarring of the tiny air sacs (alveoli) in
Interstitial Lung Disease (Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease) Focusing on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Interstitial Lung Disease (Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease) Focusing on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis J. D Urbano, RCP, RRT Founder / CEO: BreathSounds, LLC E-Mail: [email protected] Mobile: (480)
Interstitial Lung Disease (Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease) Focusing on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis J. D Urbano, RCP, RRT Founder / CEO: BreathSounds, LLC E-Mail: [email protected] Mobile: (480)
Pulmonary interstitium. Interstitial Lung Disease. Interstitial lung disease. Interstitial lung disease. Causes.
 Pulmonary interstitium Interstitial Lung Disease Alveolar lining cells (types 1 and 2) Thin elastin-rich connective component containing capillary blood vessels Interstitial lung disease Increase in interstitial
Pulmonary interstitium Interstitial Lung Disease Alveolar lining cells (types 1 and 2) Thin elastin-rich connective component containing capillary blood vessels Interstitial lung disease Increase in interstitial
Defending the Rest Basics on Lung Cancer, Other Cancers and Asbestosis: Review of the B-Read and Pulmonary Function Testing
 Defending the Rest Basics on Lung Cancer, Other Cancers and Asbestosis: Review of the B-Read and Pulmonary Function Testing ASBESTOSIS November 2013 Bruce T. Bishop Lucy L. Brandon Willcox & Savage 440
Defending the Rest Basics on Lung Cancer, Other Cancers and Asbestosis: Review of the B-Read and Pulmonary Function Testing ASBESTOSIS November 2013 Bruce T. Bishop Lucy L. Brandon Willcox & Savage 440
Pulmonary Disorders. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Pulmonary Disorders Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Characterized by decreased expiratory airflow Reduction in expiratory
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Pulmonary Disorders Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Characterized by decreased expiratory airflow Reduction in expiratory
SARCOIDOSIS. Signs and symptoms associated with specific organ involvement can include the following:
 SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
Emphysema. Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Exploring the Role of Vitamins in Achieving a Healthy Heart
 Exploring the Role of Vitamins in Achieving a Healthy Heart There are many avenues you can take to keep your heart healthy. The first step you should take is to have a medical professional evaluate the
Exploring the Role of Vitamins in Achieving a Healthy Heart There are many avenues you can take to keep your heart healthy. The first step you should take is to have a medical professional evaluate the
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids
 Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
HEALTH EFFECTS. Inhalation
 Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Position Statement from the Irish Thoracic Society on the treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 BACKGROUND Position Statement from the Irish Thoracic Society on the treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a rare, chronic and fatal disease characterised by
BACKGROUND Position Statement from the Irish Thoracic Society on the treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a rare, chronic and fatal disease characterised by
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Restrictive vs. Obstructive Disease (Dedicated to my good friend Joe Walsh)
 Restrictive vs. Obstructive Disease (Dedicated to my good friend Joe Walsh) The field of medicine has a long history of describing or classifying disease. Pulmonary disease is no different. Although there
Restrictive vs. Obstructive Disease (Dedicated to my good friend Joe Walsh) The field of medicine has a long history of describing or classifying disease. Pulmonary disease is no different. Although there
Collagen Vascular Lung Disease
 6 Collagen Vascular Lung Disease Collagen vascular or connective tissue disorders are a group of autoimmune diseases in which antibodies attack the body s own organs and systems. Among the many targets
6 Collagen Vascular Lung Disease Collagen vascular or connective tissue disorders are a group of autoimmune diseases in which antibodies attack the body s own organs and systems. Among the many targets
TREATING AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES WITH HOMEOPATHY. Dr. Stephen A. Messer, MSEd, ND, DHANP Professor and Chair of Homeopathic Medicine
 TREATING AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES WITH HOMEOPATHY Dr. Stephen A. Messer, MSEd, ND, DHANP Professor and Chair of Homeopathic Medicine AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body s immune
TREATING AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES WITH HOMEOPATHY Dr. Stephen A. Messer, MSEd, ND, DHANP Professor and Chair of Homeopathic Medicine AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body s immune
Restrictive lung diseases
 Restrictive lung diseases Characterized by reduced compliance of the lung. Prominent changes in the interstitium (interstitial lung disease). Important signs and symptoms: - Dyspnea. - Hypoxia. - With
Restrictive lung diseases Characterized by reduced compliance of the lung. Prominent changes in the interstitium (interstitial lung disease). Important signs and symptoms: - Dyspnea. - Hypoxia. - With
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Paul F. Simonelli, MD, Ph.D.
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Paul F. Simonelli, MD, Ph.D. Definition: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a broad range of conditions that have common clinical, physiological, and radiological features.
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Paul F. Simonelli, MD, Ph.D. Definition: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a broad range of conditions that have common clinical, physiological, and radiological features.
Asbestos Related Diseases. Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease. connecting raising awareness supporting advocating
 Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease connecting raising awareness supporting advocating 1800 017 758 www.asbestosassociation.com.au Asbestos lagging was widely
Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease connecting raising awareness supporting advocating 1800 017 758 www.asbestosassociation.com.au Asbestos lagging was widely
BACKGROUND MEDIA INFORMATION Fast facts about liver disease
 BACKGROUND MEDIA INFORMATION Fast facts about liver disease Liver, or hepatic, disease comprises a wide range of complex conditions that affect the liver. Liver diseases are extremely costly in terms of
BACKGROUND MEDIA INFORMATION Fast facts about liver disease Liver, or hepatic, disease comprises a wide range of complex conditions that affect the liver. Liver diseases are extremely costly in terms of
Asbestos Related Diseases
 Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease Asbestosis and Mesothelioma (LUNG CANCER) Support Group 1800 017 758 www.amsg.com.au ii Helping you and your family through
Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease Asbestosis and Mesothelioma (LUNG CANCER) Support Group 1800 017 758 www.amsg.com.au ii Helping you and your family through
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Research
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): Why Early Referral is Critical Even if Your Patient is Not Eligible for a Clinical Trial Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Research Management of IPF requires a confident
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): Why Early Referral is Critical Even if Your Patient is Not Eligible for a Clinical Trial Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Research Management of IPF requires a confident
1 ALPHA-1. What is Alpha-1? A family history... of lung disease? of liver disease? FOUNDATION
 What is Alpha-1? A family history... of lung disease? of liver disease? What you need to know about Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What is Alpha-1? Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1)
What is Alpha-1? A family history... of lung disease? of liver disease? What you need to know about Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What is Alpha-1? Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1)
Asbestos and your lungs
 This information describes what asbestos is and the lung conditions that are caused by exposure to it. It also includes information about what to do if you have been exposed to asbestos, and the benefits
This information describes what asbestos is and the lung conditions that are caused by exposure to it. It also includes information about what to do if you have been exposed to asbestos, and the benefits
The Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases
 The Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases Pulmonary hypertension Dr Marc Humbert What is the burden of pulmonary hypertension? The true burden of pulmonary hypertension is currently unknown
The Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases Pulmonary hypertension Dr Marc Humbert What is the burden of pulmonary hypertension? The true burden of pulmonary hypertension is currently unknown
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
Respiratory Concerns in Children with Down Syndrome
 Respiratory Concerns in Children with Down Syndrome Paul E. Moore, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Pharmacology Director, Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonary Medicine Vanderbilt University
Respiratory Concerns in Children with Down Syndrome Paul E. Moore, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Pharmacology Director, Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonary Medicine Vanderbilt University
An Overview of Asthma - Diagnosis and Treatment
 An Overview of Asthma - Diagnosis and Treatment Asthma is a common chronic disorder of the airways that is complex and characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness,
An Overview of Asthma - Diagnosis and Treatment Asthma is a common chronic disorder of the airways that is complex and characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness,
These factors increase your chance of developing emphysema. Tell your doctor if you have any of these risk factors:
 Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis
 COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
Lung cancer is not just one disease. There are two main types of lung cancer:
 1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
1 ALPHA-1. The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) FOUNDATION FOUNDATION. A patient s guide to Alpha-1 liver disease
 The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people
The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
About lung cancer. Contents. The lungs
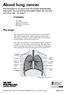 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Treatment Guide Interstitial Lung Disease
 Treatment Guide Interstitial Lung Disease Since interstitial lung disease (ILD) is not a single disease but a group of more than 200 different pulmonary disorders, it can be confusing to understand exactly
Treatment Guide Interstitial Lung Disease Since interstitial lung disease (ILD) is not a single disease but a group of more than 200 different pulmonary disorders, it can be confusing to understand exactly
COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system
 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
Lymphomas after organ transplantation
 Produced 21.03.2011 Revision due 21.03.2011 Lymphomas after organ transplantation People who have undergone an organ transplant are more at risk of developing lymphoma known as post-transplant lymphoproliferative
Produced 21.03.2011 Revision due 21.03.2011 Lymphomas after organ transplantation People who have undergone an organ transplant are more at risk of developing lymphoma known as post-transplant lymphoproliferative
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
LECTURES IN OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES
 LECTURES IN OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES الدكتورة سجال فاضل فرھود الجبوري M.B.Ch.B.(Babylon University) M.Sc.(Community Medicine-Al Nahrain) Asbestosis Asbestosis is a chronic inflammatory medical condition affecting
LECTURES IN OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES الدكتورة سجال فاضل فرھود الجبوري M.B.Ch.B.(Babylon University) M.Sc.(Community Medicine-Al Nahrain) Asbestosis Asbestosis is a chronic inflammatory medical condition affecting
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Orkambi (lumacaftor and ivacaftor)
 EMA/662624/2015 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Orkambi (lumacaftor and ivacaftor) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Orkambi, which details the measures to be taken
EMA/662624/2015 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Orkambi (lumacaftor and ivacaftor) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Orkambi, which details the measures to be taken
Individualizing Your Lung Cancer Care: Informing Decisions Through Biomarker Testing
 Individualizing Your Lung Cancer Care: Informing Decisions Through Biomarker Testing These Are Hopeful Times for Lung Cancer Survivors When people first learn they have cancer, they are often afraid. But
Individualizing Your Lung Cancer Care: Informing Decisions Through Biomarker Testing These Are Hopeful Times for Lung Cancer Survivors When people first learn they have cancer, they are often afraid. But
Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis By Kerry V. Cooke
 Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev (nintedanib)
 EMA/738120/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev (nintedanib) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure that
EMA/738120/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev (nintedanib) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure that
ASK A DOC. Clinical Trial Update May 28, 2014. Welcome!
 ASK A DOC Clinical Trial Update May 28, 2014 Welcome! ASK A DOC CLINICAL TRIAL UPDATE Dr. Gregory Cosgrove PFF Chief Medical Officer Dr. Kevin Flaherty Chairman Steering Committee PFF CCN and PFF Registry
ASK A DOC Clinical Trial Update May 28, 2014 Welcome! ASK A DOC CLINICAL TRIAL UPDATE Dr. Gregory Cosgrove PFF Chief Medical Officer Dr. Kevin Flaherty Chairman Steering Committee PFF CCN and PFF Registry
Francine Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario 2003
 ASBESTOS Francine Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario 2003 Asbestosis Asbestosis is a model for other dust diseases as well as
ASBESTOS Francine Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario 2003 Asbestosis Asbestosis is a model for other dust diseases as well as
National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry
 National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry Instructions: This consent statement is to be signed and dated by the patient in the presence of a certified study staff
National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry Instructions: This consent statement is to be signed and dated by the patient in the presence of a certified study staff
Autoimmune Diseases More common than you think Randall Stevens, MD
 Autoimmune Diseases More common than you think Randall Stevens, MD picture placeholder Autoimmune Diseases More than 60 different disorders Autoimmune disorders (AID) diseases caused by the immune system
Autoimmune Diseases More common than you think Randall Stevens, MD picture placeholder Autoimmune Diseases More than 60 different disorders Autoimmune disorders (AID) diseases caused by the immune system
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS about asbestos related diseases
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS about asbestos related diseases 1. What are the main types of asbestos lung disease? In the human body, asbestos affects the lungs most of all. It can affect both the spongy
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS about asbestos related diseases 1. What are the main types of asbestos lung disease? In the human body, asbestos affects the lungs most of all. It can affect both the spongy
The Liver and Alpha-1. Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION
 The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What Is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency? Alpha-1 is a condition that may result in serious lung disease in adults and/or liver
The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What Is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency? Alpha-1 is a condition that may result in serious lung disease in adults and/or liver
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.021: Musculoskeletal Pathophysiology, IAP 2006 Course Director: Dr. Dwight R. Robinson Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A multi-system autoimmune
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.021: Musculoskeletal Pathophysiology, IAP 2006 Course Director: Dr. Dwight R. Robinson Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A multi-system autoimmune
THINGS TO BE AWARE OF ABOUT PROSTATE AND LUNG CANCER. Lawrence Lackey Jr., M.D. Internal Medicine 6001 W. Outer Dr. Ste 114
 THINGS TO BE AWARE OF ABOUT PROSTATE AND LUNG CANCER Lawrence Lackey Jr., M.D. Internal Medicine 6001 W. Outer Dr. Ste 114 WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal
THINGS TO BE AWARE OF ABOUT PROSTATE AND LUNG CANCER Lawrence Lackey Jr., M.D. Internal Medicine 6001 W. Outer Dr. Ste 114 WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal
Staging of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: past, present and future
 REVIEW IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS Staging of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: past, present and future Martin Kolb 1 and Harold R. Collard 2 Affiliations: 1 Dept of Medicine, Firestone Institute for Respiratory
REVIEW IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS Staging of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: past, present and future Martin Kolb 1 and Harold R. Collard 2 Affiliations: 1 Dept of Medicine, Firestone Institute for Respiratory
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
How To Treat Lung Cancer At Cleveland Clinic
 Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program
 Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Measures of Prognosis. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
ELEMENTS FOR A PUBLIC SUMMARY. Overview of disease epidemiology. Summary of treatment benefits
 VI: 2 ELEMENTS FOR A PUBLIC SUMMARY Bicalutamide (CASODEX 1 ) is a hormonal therapy anticancer agent, used for the treatment of prostate cancer. Hormones are chemical messengers that help to control the
VI: 2 ELEMENTS FOR A PUBLIC SUMMARY Bicalutamide (CASODEX 1 ) is a hormonal therapy anticancer agent, used for the treatment of prostate cancer. Hormones are chemical messengers that help to control the
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
Your Go-to COPD Guide
 Your Go-to COPD Guide Learning how to live with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Inside, you ll learn: COPD facts COPD symptoms and triggers How to talk with your doctor Different treatment
Your Go-to COPD Guide Learning how to live with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Inside, you ll learn: COPD facts COPD symptoms and triggers How to talk with your doctor Different treatment
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim)
 EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
RADIATION THERAPY FOR LYMPHOMA. Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels extending
RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels extending
Objectives COPD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 4/19/2011
 Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
Likelihood of Cancer
 Suggested Grade Levels: 9 and up Likelihood of Cancer Possible Subject Area(s): Social Studies, Health, and Science Math Skills: reading and interpreting pie charts; calculating and understanding percentages
Suggested Grade Levels: 9 and up Likelihood of Cancer Possible Subject Area(s): Social Studies, Health, and Science Math Skills: reading and interpreting pie charts; calculating and understanding percentages
Gene Therapy. The use of DNA as a drug. Edited by Gavin Brooks. BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press
 Gene Therapy The use of DNA as a drug Edited by Gavin Brooks BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press Contents Preface xiii Acknowledgements xv About the editor xvi Contributors xvii An introduction
Gene Therapy The use of DNA as a drug Edited by Gavin Brooks BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press Contents Preface xiii Acknowledgements xv About the editor xvi Contributors xvii An introduction
2011 Pulmonary Pathology Society Biennial Meeting Program
 2011 Pulmonary Pathology Society Biennial Meeting Program Thursday, August 18, 2011 7:00 AM Registration and Continental Breakfast 7:45 AM Welcome: Donald Guinee / Elisabeth Brambilla 8:00 AM Interstitial
2011 Pulmonary Pathology Society Biennial Meeting Program Thursday, August 18, 2011 7:00 AM Registration and Continental Breakfast 7:45 AM Welcome: Donald Guinee / Elisabeth Brambilla 8:00 AM Interstitial
ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML),
 1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
F r e q u e n t l y A s k e d Q u e s t i o n s
 Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
Test Your Breast Cancer Knowledge
 Test Your Breast Cancer Knowledge Regular exams and a good understanding can help defend against breast cancer, yet many women hold outdated ideas about their own breast cancer risk. Take this quiz to
Test Your Breast Cancer Knowledge Regular exams and a good understanding can help defend against breast cancer, yet many women hold outdated ideas about their own breast cancer risk. Take this quiz to
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Male. Female. Death rates from lung cancer in USA
 Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Leanne M Poulos Patricia K Correll Brett G Toelle Helen K Reddel Guy B Marks Woolcock Institute of Medical Research, University of Sydney, NSW
 Lung disease in Australia Leanne M Poulos Patricia K Correll Brett G Toelle Helen K Reddel Guy B Marks Woolcock Institute of Medical Research, University of Sydney, NSW Prepared for Lung Foundation Australia
Lung disease in Australia Leanne M Poulos Patricia K Correll Brett G Toelle Helen K Reddel Guy B Marks Woolcock Institute of Medical Research, University of Sydney, NSW Prepared for Lung Foundation Australia
Presented by: Donna M. Ringo, CIH. DMR & Associates, Inc., Louisville, Kentucky
 New Considerations for: If It s Silica It s Not Just Dust Presented by: Donna M. Ringo, CIH DMR & Associates, Inc., Louisville, Kentucky Honorable Mention OSHA / NIOSH updates Disclaimer : I am not a toxicologist.
New Considerations for: If It s Silica It s Not Just Dust Presented by: Donna M. Ringo, CIH DMR & Associates, Inc., Louisville, Kentucky Honorable Mention OSHA / NIOSH updates Disclaimer : I am not a toxicologist.
Transcript for Asbestos Information for the Community
 Welcome to the lecture on asbestos and its health effects for the community. My name is Dr. Vik Kapil and I come to you from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Agency for Toxic Substances
Welcome to the lecture on asbestos and its health effects for the community. My name is Dr. Vik Kapil and I come to you from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Agency for Toxic Substances
DISCLOSURES RISK ASSESSMENT. Stroke and Heart Disease -Is there a Link Beyond Risk Factors? Daniel Lackland, MD
 STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
Cystic Lung Diseases. Melissa Price Gillian Lieberman, MD Advanced Radiology Clerkship Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center November, 2008
 Cystic Lung Diseases Melissa Price Gillian Lieberman, MD Advanced Radiology Clerkship Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center November, 2008 How do we define a cyst of the lung? Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon
Cystic Lung Diseases Melissa Price Gillian Lieberman, MD Advanced Radiology Clerkship Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center November, 2008 How do we define a cyst of the lung? Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
An overview of CLL care and treatment. Dr Dean Smith Haematology Consultant City Hospital Nottingham
 An overview of CLL care and treatment Dr Dean Smith Haematology Consultant City Hospital Nottingham What is CLL? CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too
An overview of CLL care and treatment Dr Dean Smith Haematology Consultant City Hospital Nottingham What is CLL? CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
1 ALPHA-1. Am I an Alpha-1 Carrier? FOUNDATION FOUNDATION. Learn how being an Alpha-1 carrier can affect you and your family
 Am I an Alpha-1 Carrier? 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people affected by Alpha-1 worldwide.
Am I an Alpha-1 Carrier? 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people affected by Alpha-1 worldwide.
Maria Dalbey RN. BSN, MA, MBA March 17 th, 2015
 Maria Dalbey RN. BSN, MA, MBA March 17 th, 2015 2 Objectives Participants will be able to : Understand the Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis (TB) Identify the Goals of Public Health for TB Identify Hierarchy
Maria Dalbey RN. BSN, MA, MBA March 17 th, 2015 2 Objectives Participants will be able to : Understand the Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis (TB) Identify the Goals of Public Health for TB Identify Hierarchy
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
PARTICLE SIZE AND CHEMISTRY:
 Pneumoconioses LW/Please note: This information is additional to Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medicine. /Hierdie inligting is aanvullend tot Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medicine. Pneumoconioses
Pneumoconioses LW/Please note: This information is additional to Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medicine. /Hierdie inligting is aanvullend tot Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medicine. Pneumoconioses
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide
 What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
Chapter 3 Type 1 Diabetes
 Chapter 3 Type 1 Diabetes Type 1 diabetes is one of the most common chronic disorders of childhood. Unfortunately, it is increasing in incidence, particularly in young children. The reason for this is
Chapter 3 Type 1 Diabetes Type 1 diabetes is one of the most common chronic disorders of childhood. Unfortunately, it is increasing in incidence, particularly in young children. The reason for this is
