Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure
|
|
|
- Phebe Chandler
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist You may refer to pages 66-67, in your textbook for a general discussion of microscopes. Time required: 120 minutes Background Information Problem One of the most important tools of a life scientist is the microscope. The development of the microscope has made possible the identification of thousands of different organisms and parts of organisms that are invisible to the unaided eye. The microscope you will probably be using is a compound microscope. That is, it contains more than one lens. The lenses are the parts of the microscope that are responsible for magnifying the object being viewed. In this investigation you will learn how to correctly handle a microscope. The compound microscope that you are using may not look exactly like the one pictured in this investigation. However, the parts of most compound microscopes are the same and have the same names. What are the parts of a microscope? What are the functions of these parts? What is the correct method for handling a microscope? Materials (per group) microscope blank slides dropping pipette scissors prepared slide coverslips newspaper other printed materials Procedure Part A: Examining a Microscope 1. Become familiar with the names of the various parts of the microscope. Look at the labeled diagram of a microscope in Figure 1 and identify each part of the microscope.
2 7 th Life Science Lab The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist 2 2. Obtain a microscope. Keep in mind that a microscope is a very delicate instrument and should be handled with care. Always use two hands to pick up and carry a microscope. Hold the arm of the microscope in one hand, and place your other hand under the base for support. When using the microscope, be sure that the arm faces toward you. 3. Compare the microscope you are using to the one shown in Figure 1. Your microscope may not look exactly like the one shown. However, the basic parts of all microscopes are similar. Locate the parts on your microscope that correspond to the labeled parts in the diagram. 4. Following is a list of the parts of the microscope and their functions. Learn the name and function of each part so that you can properly use the microscope. a. The arm supports the body tube and is used for carrying the microscope. The base supports the microscope and is also used for carrying the microscope. Always carry the microscope by holding the arm with one hand and place your other hand under the base. Locate the arm and base of your microscope. b. The mirror collects light and directs it through the opening in the stage. By turning the mirror, you can control the amount of light being reflected through the stage opening. CAUTION: Never use direct sunlight as a source of light. Direct sunlight reflected off the mirror can damage the eye. Some microscopes have a built-in light source and therefore do not have a mirror. Locate the mirror on your microscope. Notice how it moves. c. The eyepiece (Ocular lens) is the part of the microscope that you look through to view an object placed on the stage. The eyepiece contains the ocular lens and usually has a magnification power of lox. This means that the lens enables you to see the object ten times larger than it actually is. Locate the eyepiece on your microscope. d. The body tube maintains the proper distance between the eyepiece and the objective lenses. It is the part of the microscope that allows light to pass upward and through to the eyepiece. Locate the body tube on your microscope. e. The stage supports the slide being viewed, and the stage clips hold the slide in place on the stage. In the middle of the stage is an opening that allows light from below to pass through the object being viewed. CAUTION: Never allow the clips to come in contact with the opening in the stage because they will scratch the glass and interfere with viewing objects. To place a microscope slide under the clips, gently lift the clips and move the slide under and across the clips. Never force the clips open with your fingers. Practice placing a microscope slide under the clips. f. The diaphragm is located under the stage and has several small openings of various sizes. By turning the diaphragm, you can increase or decrease the amount of light entering through the stage opening to see the object you are viewing more clearly. Look through the eyepiece and move the diaphragm settings to see the varying amounts of light that can enter the microscope. g. The revolving nosepiece holds the low- and high-power objective lenses and can be rotated to change magnification. Turn the revolving nosepiece on your microscope and listen closely for the click. If the objective lens is not in place, there will be no light visible through the nosepiece. h. The objective lenses, called the low- and high-power lenses, add to the magnification of the object you are viewing. The low-power objective lens usually has a magnification power of 10x. The highpower objective lens usually has a magnification power of 40X. To find the total magnification power of the microscope, multiply the magnification power of the eyepiece lens by the magnification power of the objective lens in use. For example: eyepiece (10X) X low-power lens (10X) = total magnification (100x). With the body tube in the uppermost position, turn the revolving nosepiece to the low-power objective. Notice how it clicks into place. Very slowly and carefully turn to the high-power objective. Notice how close it comes to the stage of the microscope. CAUTION: When turning to the high-power objective, you
3 7 th Life Science Lab The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist 3 should always look at the objective from the side of your microscope so that the objective does not hit or damage the slide. See Figure 2. i. The coarse adjustment knob moves the body tube up and down to bring the object into view. It is usually located on the top part of the arm. Turn the knob, and you should notice that the body tube moves up and down. Use the coarse adjustment knob when focusing with the low-power objective. CAUTION: Do not use the coarser adjustment knob when focusing the high-power objective lens. This could break your slide or damage the lens. Practice moving the coarse adjustment knob to see the movement that is allowed with each turn. j. The fine adjustment knob is usually located below the coarse adjustment knob. The fine adjustment knob is used to bring objects into clear, sharp focus. It moves the body tube very slightly. Use this knob when you are focusing with the high-power lens. Never use the fine adjustment knob for large adjustments. If the object is properly focused with the coarse adjustment knob, then it should take only one fourth of a turn of the fine adjustment knob to obtain a clear, sharp image. Part B: Handling a Microscope 1. Holding the prepared slide by its edges, place it on the stage of the microscope. 2. Turn the revolving nosepiece until the low-power objective lens clicks into place. 3. Looking through the eyepiece, adjust the diaphragm to permit sufficient light to enter the microscope. If your microscope has a mirror, adjust it for proper lighting. 4. Looking from the side of the microscope, turn the coarse adjustment knob so that the body tube is at its lowest position just over the opening in the stage. 5. Looking through the eyepiece, slowly raise the body tube with the coarse adjustment knob until the object on the slide comes into focus. 6. Looking from the side of the microscope again, slowly move the revolving nosepiece until the high-power objective lens clicks into place. Be careful not to touch the slide with the high-power objective lens. 7. Turn the fine adjustment knob no more than one fourth of a turn to bring the object on the slide into clear, sharp focus. 8. If the image of the object is not clear and sharp, do not continue to turn the fine adjustment knob. In this case, return to the low-power objective lens and refocus. Then try the high-power objective lens again, following the procedure in steps 6 and 7.
4 7 th Life Science Lab The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist 4 Rules for Using Microscopes Carry the microscope properly. Excessive jarring and bumping may bring the lenses out of adjustment. To avoid damaging the microscope, observe the following rules: 1. When taking a microscope out of the cabinet or cupboard, be careful not to bang the microscope against the sides of the cabinet. 2. Carry the instrument with one hand underneath the base and the other on the arm of the microscope. 3. Be sure to keep the microscope close to your body in an upright position so that the ocular does not slip out of the body tube. 4. Place the microscope gently on the table and position it about 10 centimeters (3 ½ in.) from the edge. Prepare the microscope properly. You may need to clean your microscope before you begin to use it. Observe these rules while you clean it. 1. Use lens paper to clean the lens surfaces and the mirror. Wipe the lenses in one direction across the diameter of each lens. 2. Consult your instructor if any material remains on your eyepiece or objectives. 3. Under no circumstances should you attempt to take your microscope apart. Return the microscope properly. When you have finished using a microscope, you should observe the following rules: 1. Make sure the microscope (including lenses) is clean. 2. Make sure the body tube is straight up and down. 3. Put the low-power objective directly under the body tube. 4. Adjust the body tube to its lowest position. 5. Carefully return the microscope to the place where you obtained it. Observations 1. Label the parts of the microscope in Figure 3.
5 7 th Life Science Lab The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist 5 2. What is the magnification power of each objective? Objective Lens Power Ocular Lens Power Total Magnification Objective 1 times equals Objective 2 times equals Objective 3 times equals Objective 4 times equals 3. What is the highest magnification power of the microscope? 4. How should you carry a microscope? 5. Give the function of each part of a microscope. a. Objective lenses: b. Eyepiece: c. Stage: d. Mirror: e. Diaphragm: f. Coarse adjustment knob: g. Fine adjustment knob: 6. What kind of light source do you have on your microscope? Prepare your microscope for viewing. Open the diaphragm on your microscope to its largest setting. If your microscope has an electric light, plug it in and turn it on. If your microscope has a mirror, adjust it until you are able to see a bright light through the ocular. You should try to use the brightest light source available, but you should not use direct sunlight. Prepare a microscope slide for viewing. Carefully clean and dry a glass slide and a coverslip. Once you have cleaned them, handle the slide and coverslip only by the edges. This will prevent your viewing fingerprints by mistake. Place a single drop of water on the center of your slide. Tear a letter e from a piece of newspaper and place it on the drop of water. Carefully lay the coverslip on top of the drop of water. If air bubbles appear near the piece of paper, tap the coverslip with a pencil. If too many bubbles remain, take the slide apart and start over.
6 7 th Life Science Lab The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist 6 Place the slide on the stage of your microscope and position it so that the newspaper is in the middle of the hole in the stage. Clip the slide in place. Focus the microscope on low power. Position the low-power objective so that it is directly under the body tube of your microscope. While looking at the side of your microscope, turn the coarse adjustment knob until the objective almost touches the coverslip. Look through the objective and SLOWLY turn the coarse adjustment knob so that the body tube goes UP until you are able to see the newspaper. NOTE: Never turn the coarse adjustment knob so that the body tube goes down while you are looking through the ocular! You could cause the objective to push into the slide and break it. If you have raised your objective more than an inch from the coverslip, you have raised it too far. Look at the side of your microscope and turn the coarse adjustment knob until the objective almost touches the coverslip. Then look through the ocular and start raising the body tube again. If you are still unable to see the newspaper, try the following: 1. Adjust the diaphragm to a slightly smaller setting and then try to focus the microscope again. 2. Check to make sure the newspaper is in the center of the hole in the stage and directly under the objective. If you still cannot see the newspaper, ask your teacher for help. Once you have found the newspaper by using the coarse adjustment knob, use the fine adjustment knob to obtain a clear image. You can adjust the fine adjustment knob either direction, but you should never have to turn it more than a full turn in either direction. Often you will need to readjust your fine adjustment knob while you are viewing something through the microscope. Note what happens when you move your slide. While looking through the objective, move your slide slightly to the left. What happens to the image that you are viewing? Move your slide slightly to the right. What happens to the image that you are viewing? Move your slide so that it goes away from you slightly. What happens to the image when you do this? Move your slide so that it comes toward you slightly. What happens to the image when you do this? Describe what the newspaper and the printed e look like under the low power of a microscope.
7 7 th Life Science Lab The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist 7 Focus your microscope on high power. Move your slide so that an edge of the newspaper crosses the center of the area you see through the microscope. Be sure this is in the very center! Carefully rotate the objectives so that the high-power objective is below the body tube. Adjust the fine adjustment knob. The image should be in focus when you turn the knob less than a full turn. If necessary, adjust the amount of light coming through the diaphragm. If you cannot see a good image through your microscope, return to low power and focus again. Make sure that your newspaper is in the center of the area you are viewing through the microscope. Try to focus on high power again. If you still have problems, ask your teacher for help. Move the slide around and observe the newspaper and the letter on high power. What is the difference between the image you see under low power and the image you see under high power? Make slides of printed letter e s from magazines and other sources. Typed letters are interesting. What differences do you notice between different kinds of paper and between different forms of printing? Analysis and Conclusions 1. Calculate the total magnification for each pair of lenses. Ocular Lens Objective Lens Total Magnification a. 5x 10x b. 10x 10x c. 10x 43x d. 20x 10x e. 20x 50x 2. Why must you be careful when you are focusing with the high-power lens? What precautions should you take?
8 7 th Life Science Lab The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist 8 3. Describe the procedure for focusing a microscope using the coarse and fine adjustment knobs. Critical Thinking and Application 1. Why is it a good idea to place your microscope at least 10 cm from the edge of the table? 2. Why should you always use the low-power objective lens to locate objects mounted on the slide first, even if you want to observe them with the high-power objective lens? 3. Why should a microscope slide be held by its edges? 4. When switching from the low-power objective to the high-power objective should you open or close the diaphragm? Explain your answer. Going Further Observe cells under the low- and high-power objective lenses of a microscope. Compare what you see under both objective lenses. Which objective lens allows you to see more detail? Which objective lens allows you to see more of the cell? Each person needs to draw and label two different cells. Be sure to include on each drawing the title of the slide, whether it was a cs or ls or wm, and the power used to make the drawing,?who Am I Riddles? Pick a cytoplasmic organelle to write a Who Am I riddle. The riddle must contain 5 lines the 5 th line must be Who Am I? Lines 2 and 4 must rhyme. The actual name of the organelle must not be in the riddle. Example: Found only in plant cells, I m green as can be. I make food for the plant Using the sun s energy Who Am I?
Care and Use of the Compound Microscope
 Revised Fall 2011 Care and Use of the Compound Microscope Objectives After completing this lab students should be able to 1. properly clean and carry a compound and dissecting microscope. 2. focus a specimen
Revised Fall 2011 Care and Use of the Compound Microscope Objectives After completing this lab students should be able to 1. properly clean and carry a compound and dissecting microscope. 2. focus a specimen
Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity
 Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity Wendy Kim 3B 24 Sep 2010 http://www.mainsgate.com/spacebio/modules/gs_resource/ CellDivisionMetaphase.jpeg 1 Introduction Microscope is a tool
Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity Wendy Kim 3B 24 Sep 2010 http://www.mainsgate.com/spacebio/modules/gs_resource/ CellDivisionMetaphase.jpeg 1 Introduction Microscope is a tool
MICROSCOPY. To demonstrate skill in the proper utilization of a light microscope.
 MICROSCOPY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate skill in the proper utilization of a light microscope. To demonstrate skill in the use of ocular and stage micrometers for measurements of cell size. To recognize
MICROSCOPY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate skill in the proper utilization of a light microscope. To demonstrate skill in the use of ocular and stage micrometers for measurements of cell size. To recognize
EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY
 EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY Brightfield Compound Light Microscope The light microscope is an important tool in the study of microorganisms. The compound light microscope uses visible light to directly illuminate
EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY Brightfield Compound Light Microscope The light microscope is an important tool in the study of microorganisms. The compound light microscope uses visible light to directly illuminate
Exercise 2. The Compound Light Microscope
 6 Exercise 2 The Compound Light Microscope INTRODUCTION: Student Learning Objectives: After completing this exercise students will: a. Demonstrate proficient use of the microscope using low, high dry,
6 Exercise 2 The Compound Light Microscope INTRODUCTION: Student Learning Objectives: After completing this exercise students will: a. Demonstrate proficient use of the microscope using low, high dry,
Compound microscope (Hund)
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Compound microscope (Hund) 15 16 17 18 19 20 1) Eyepieces (magnifies 10x), one with diopter adjustment, 2) Interp[upillary adjustment, 3) Head, 4) Revolving nosepiece,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Compound microscope (Hund) 15 16 17 18 19 20 1) Eyepieces (magnifies 10x), one with diopter adjustment, 2) Interp[upillary adjustment, 3) Head, 4) Revolving nosepiece,
MT-30 & MT-90 Series. Advanced Academic Microscopes/ Advanced Academic Polarizing Microscope INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Introduction With your purchase of an MT-30/MT-90 series type microscope you have chosen for a quality product. The MT-30/MT-90 series type microscopes are developed for use at schools and laboratories.
Introduction With your purchase of an MT-30/MT-90 series type microscope you have chosen for a quality product. The MT-30/MT-90 series type microscopes are developed for use at schools and laboratories.
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY
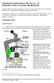 MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology
 Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
THE COMPOUND MICROSCOPE
 THE COMPOUND MICROSCOPE In microbiology, the microscope plays an important role in allowing us to see tiny objects that are normally invisible to the naked eye. It is essential for students to learn how
THE COMPOUND MICROSCOPE In microbiology, the microscope plays an important role in allowing us to see tiny objects that are normally invisible to the naked eye. It is essential for students to learn how
A Fishy Tale. Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope
 A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
Use of the Microscope and Cytology
 Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
National Optical & Scientific Instruments Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104
 National Optical & Scientific Instruments Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104 INSTRUCTIONS FOR MODELS 106, 106-L 107, 107-L 108, 108-L 109-L ELEMENTARY
National Optical & Scientific Instruments Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104 INSTRUCTIONS FOR MODELS 106, 106-L 107, 107-L 108, 108-L 109-L ELEMENTARY
BIO 10 Lab 1 Introduction Pre Lab Test
 BIO 10 Lab 1 Introduction Pre Lab Test 1. Why is the microscope in our lab called a compound microscope? 2. How do you calculate total magnification? 3. What is the lowest and the maximal magnification
BIO 10 Lab 1 Introduction Pre Lab Test 1. Why is the microscope in our lab called a compound microscope? 2. How do you calculate total magnification? 3. What is the lowest and the maximal magnification
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
 1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
CALIBRATION FOR LAL20X & LAL24X
 CALIBRATION AND FAULT FINDING FOR LAL20X & LAL24X DUMPY LEVELS MEASURING EXPERTS SINCE 1869 How The LAL20X & LAL24X Works The Automatic level is called Automatic because it requires only a simple basic
CALIBRATION AND FAULT FINDING FOR LAL20X & LAL24X DUMPY LEVELS MEASURING EXPERTS SINCE 1869 How The LAL20X & LAL24X Works The Automatic level is called Automatic because it requires only a simple basic
VISM CQB Scope Series
 1 VISM CQB Scope Series Congratulations on the purchase of your new VISM CQB Scope! The CQB Series of Scopes give you many great options so you can choose the scope that best fits your needs. Backed by
1 VISM CQB Scope Series Congratulations on the purchase of your new VISM CQB Scope! The CQB Series of Scopes give you many great options so you can choose the scope that best fits your needs. Backed by
The illustrations below reflect other scientists results in identifying and counting the stages of the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula.
 Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Pre-Lab Questions. 1. What is cell theory? 2. What do all cells contain? 3. What is a prokaryote? 4. What is a eukaryote? 5. What is an organelle?
 Name: TOC# Background Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundred s of years of observations by many
Name: TOC# Background Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundred s of years of observations by many
VISM Evolution Scope Series
 1 VISM Evolution Scope Series Congratulations on the purchase of your New VISM Evolution (EVO) Series Scope! The EVO Series of Scopes give you many great high end features and various magnification ranges
1 VISM Evolution Scope Series Congratulations on the purchase of your New VISM Evolution (EVO) Series Scope! The EVO Series of Scopes give you many great high end features and various magnification ranges
Chapter 1 Parts C. Robert Bagnell, Jr., Ph.D., 2012
 Chapter 1 Parts C. Robert Bagnell, Jr., Ph.D., 2012 Figure 1.1 illustrates the parts of an upright compound microscope and indicates the terminology that I use in these notes. Figure 1.1. Parts of a Compound
Chapter 1 Parts C. Robert Bagnell, Jr., Ph.D., 2012 Figure 1.1 illustrates the parts of an upright compound microscope and indicates the terminology that I use in these notes. Figure 1.1. Parts of a Compound
FirstView 3 Reflector Telescope Owner s Manual
 FirstView 3 Reflector Telescope Owner s Manual 1. Horizontal Locking Auxiliary Screw 2. Main Mount 3. Pitching Auxiliary Knob 4. Pitching Shaft Screw 5. Rack and Pinion Focusing Knob 6. Thumb Nut for Finder
FirstView 3 Reflector Telescope Owner s Manual 1. Horizontal Locking Auxiliary Screw 2. Main Mount 3. Pitching Auxiliary Knob 4. Pitching Shaft Screw 5. Rack and Pinion Focusing Knob 6. Thumb Nut for Finder
Lenses and Telescopes
 A. Using single lenses to form images Lenses and Telescopes The simplest variety of telescope uses a single lens. The image is formed at the focus of the telescope, which is simply the focal plane of the
A. Using single lenses to form images Lenses and Telescopes The simplest variety of telescope uses a single lens. The image is formed at the focus of the telescope, which is simply the focal plane of the
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
 Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
PlaneWave CDK Telescope Instructions CDK12.5, 17, 20 and 24
 PlaneWave CDK Telescope Instructions CDK12.5, 17, 20 and 24 V112712 1 Collimation and Secondary Spacing Procedure The CDK optical design has four optical elements shown in Figure 1. The primary mirror
PlaneWave CDK Telescope Instructions CDK12.5, 17, 20 and 24 V112712 1 Collimation and Secondary Spacing Procedure The CDK optical design has four optical elements shown in Figure 1. The primary mirror
Measuring. User Manual
 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Measuring User Manual Accessories for measuring tasks Stage micrometer (1) for calibration Graticules with various measuring pitches (2) in mm and inches Graticule with mesh (3)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Measuring User Manual Accessories for measuring tasks Stage micrometer (1) for calibration Graticules with various measuring pitches (2) in mm and inches Graticule with mesh (3)
LIGHT SECTION 6-REFRACTION-BENDING LIGHT From Hands on Science by Linda Poore, 2003.
 LIGHT SECTION 6-REFRACTION-BENDING LIGHT From Hands on Science by Linda Poore, 2003. STANDARDS: Students know an object is seen when light traveling from an object enters our eye. Students will differentiate
LIGHT SECTION 6-REFRACTION-BENDING LIGHT From Hands on Science by Linda Poore, 2003. STANDARDS: Students know an object is seen when light traveling from an object enters our eye. Students will differentiate
Installation and use of Millett Tactical TRS-1 and TRS-2 scopes TRS-1 TRS-2. Before starting, make sure firearm is UNLOADED!!
 I N S T R U C T I O N a n d O P E R A T I O N TRS-1 TRS-2 Tactical Rifle scope Installation and use of Millett Tactical TRS-1 and TRS-2 scopes TRS-1 TRS-2 Before starting, make sure firearm is UNLOADED!!
I N S T R U C T I O N a n d O P E R A T I O N TRS-1 TRS-2 Tactical Rifle scope Installation and use of Millett Tactical TRS-1 and TRS-2 scopes TRS-1 TRS-2 Before starting, make sure firearm is UNLOADED!!
CrossFireII. 1-Inch Diameter Main Tube RIFLESCOPE MANUAL RIFLESCOPE RIFLESCOPE
 CrossFireII MANUAL 1-Inch Diameter Main Tube The Vortex Crossfire II Riflescopes Specifically designed for discriminating hunters and shooters, the Crossfire II series of riflescopes offer the highest
CrossFireII MANUAL 1-Inch Diameter Main Tube The Vortex Crossfire II Riflescopes Specifically designed for discriminating hunters and shooters, the Crossfire II series of riflescopes offer the highest
Using a Microscope to See Different Types of Cells
 Using a Microscope to See Different Types of Cells copyright 2003 by Dr. Vivianne Nachmias, University of Pennsylvania All organisms are made up of cells - a cell is the simplest collection of matter that
Using a Microscope to See Different Types of Cells copyright 2003 by Dr. Vivianne Nachmias, University of Pennsylvania All organisms are made up of cells - a cell is the simplest collection of matter that
RIFLESCOPE RIFLESCOPE MANUAL
 MANUAL The Vortex Diamondback Riflescopes The perfect match for hunters. Solid construction from a rugged singlepiece tube of aircraft-grade aluminum is the foundation for highly reliable performance features
MANUAL The Vortex Diamondback Riflescopes The perfect match for hunters. Solid construction from a rugged singlepiece tube of aircraft-grade aluminum is the foundation for highly reliable performance features
TS-E24mm f/3.5l TS-E45mm f/2.8 TS-E90mm f/2.8 Instructions
 TS-E24mm f/3.5l TS-E45mm f/2.8 TS-E90mm f/2.8 ENG Instructions Thank you for purchasing a Canon product. Canon s TS-E lenses are tilt-shift lenses designed for EOS cameras. The tilt-shift mechanism enables
TS-E24mm f/3.5l TS-E45mm f/2.8 TS-E90mm f/2.8 ENG Instructions Thank you for purchasing a Canon product. Canon s TS-E lenses are tilt-shift lenses designed for EOS cameras. The tilt-shift mechanism enables
National Optical & Scientific Instruments Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104
 National Optical & Scientific Instruments Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104 INSTRUCTIONS FOR MODELS 130, 131, 132, 138 & 139 COMPOUND MICROSCOPES
National Optical & Scientific Instruments Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104 INSTRUCTIONS FOR MODELS 130, 131, 132, 138 & 139 COMPOUND MICROSCOPES
MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES
 EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
Using a Pendulum to Measure Gravity s Acceleration Elizabeth B. Chesick
 SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 6.33-1 Using a Pendulum to Measure Gravity s Acceleration Elizabeth B. Chesick Topic Motion of a pendulum; gravity Time 1 2 hour! Safety Please click on the
SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 6.33-1 Using a Pendulum to Measure Gravity s Acceleration Elizabeth B. Chesick Topic Motion of a pendulum; gravity Time 1 2 hour! Safety Please click on the
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
 COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
Biology. STANDARD II: Objective 3. Osmosis Inquiry Labs
 Biology STANDARD II: Objective 3 Osmosis Inquiry Labs Background Knowledge: Students should have used a microscope before and be familiar with the parts. They should also know how to make a wet mount slide.
Biology STANDARD II: Objective 3 Osmosis Inquiry Labs Background Knowledge: Students should have used a microscope before and be familiar with the parts. They should also know how to make a wet mount slide.
How to make a Galileian Telescope
 How to make a Galileian Telescope I. THE BASICS THE PRINCIPLES OF OPTICS A Galileian telescope uses just two lenses. The objective lens is convergent (plano-convex), the ocular lens is divergent (plano-concave).
How to make a Galileian Telescope I. THE BASICS THE PRINCIPLES OF OPTICS A Galileian telescope uses just two lenses. The objective lens is convergent (plano-convex), the ocular lens is divergent (plano-concave).
Conservation of Momentum Greg Kifer
 SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 6.7-1 Conservation of Momentum Greg Kifer Topic Conservation of momentum Time 1 hour! Safety Please click on the safety icon to view the safety precautions.
SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 6.7-1 Conservation of Momentum Greg Kifer Topic Conservation of momentum Time 1 hour! Safety Please click on the safety icon to view the safety precautions.
30 mm Diameter Main Tube 1-4x24 Models
 CrossFire RIFLESCOPE RIFLESCOPE MANUAL 30 mm Diameter Main Tube 1-4x24 Models The Vortex Crossfire Riflescopes Specifically designed for discriminating hunters and shooters, the Crossfire series of riflescopes
CrossFire RIFLESCOPE RIFLESCOPE MANUAL 30 mm Diameter Main Tube 1-4x24 Models The Vortex Crossfire Riflescopes Specifically designed for discriminating hunters and shooters, the Crossfire series of riflescopes
MACRO PHOTO LENS. MP-E 65mm f/2.8 1-5 ENG. Instruction
 MACRO PHOTO LENS MP-E 65mm f/2.8 1-5 ENG Instruction Thank you for purchasing a Canon product. Canon Macro Photo Lens MP-E 65mm f/2.8 1-5 is a high-magnification macro lens that can magnify the subject
MACRO PHOTO LENS MP-E 65mm f/2.8 1-5 ENG Instruction Thank you for purchasing a Canon product. Canon Macro Photo Lens MP-E 65mm f/2.8 1-5 is a high-magnification macro lens that can magnify the subject
9/16 Optics 1 /11 GEOMETRIC OPTICS
 9/6 Optics / GEOMETRIC OPTICS PURPOSE: To review the basics of geometric optics and to observe the function of some simple and compound optical devices. APPARATUS: Optical bench, lenses, mirror, target
9/6 Optics / GEOMETRIC OPTICS PURPOSE: To review the basics of geometric optics and to observe the function of some simple and compound optical devices. APPARATUS: Optical bench, lenses, mirror, target
EXPERIMENT 6 OPTICS: FOCAL LENGTH OF A LENS
 EXPERIMENT 6 OPTICS: FOCAL LENGTH OF A LENS The following website should be accessed before coming to class. Text reference: pp189-196 Optics Bench a) For convenience of discussion we assume that the light
EXPERIMENT 6 OPTICS: FOCAL LENGTH OF A LENS The following website should be accessed before coming to class. Text reference: pp189-196 Optics Bench a) For convenience of discussion we assume that the light
Protocol for Microscope Calibration
 Protocol for Microscope Calibration A properly calibrated system is essential for successful and efficient software use. The following are step by step instructions on how to calibrate the hardware using
Protocol for Microscope Calibration A properly calibrated system is essential for successful and efficient software use. The following are step by step instructions on how to calibrate the hardware using
National Optical & Scientific Instruments Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104
 National Optical & Scientific Instruments Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104 INSTRUCTIONS FOR MODELS 156, 156-S, 157 COMPOUND BIOLOGICAL MICROSCOPES
National Optical & Scientific Instruments Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104 INSTRUCTIONS FOR MODELS 156, 156-S, 157 COMPOUND BIOLOGICAL MICROSCOPES
Students will identify these animal cell structures: Students should properly answer the pre-activity cell membrane, nucleus. questions.
 WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
Figure 1. Basic structure of the leaf, with a close up of the leaf surface showing Stomata and Guard cells.
 BIOL100 Laboratory Assignment 3: Analysis of Stomata Name: Stomata (singular=stoma) are the respiratory control structures in plants (see Figure 1 below). They are essentially small holes in the surface
BIOL100 Laboratory Assignment 3: Analysis of Stomata Name: Stomata (singular=stoma) are the respiratory control structures in plants (see Figure 1 below). They are essentially small holes in the surface
Features: Mounting the Optic
 MICRO GREEN DOT with INTEGRATED RED LASER The Patented Micro Green Dot with Integrated Red Laser is a compact optical system packed with many features. The Green Dot is designed as the primary targeting
MICRO GREEN DOT with INTEGRATED RED LASER The Patented Micro Green Dot with Integrated Red Laser is a compact optical system packed with many features. The Green Dot is designed as the primary targeting
Osmosis Demonstration Lab
 Osmosis Demonstration Lab Objectives The student will: 1) Observe the effects of different concentrations of salt solutions on potato cores. 2) Infer the relationship between weight loss and rate of osmosis.
Osmosis Demonstration Lab Objectives The student will: 1) Observe the effects of different concentrations of salt solutions on potato cores. 2) Infer the relationship between weight loss and rate of osmosis.
Instructions for Using the Watch Works Tool Kit to Change a Watch Battery
 Instructions for Using the Watch Works Tool Kit to Change a Watch Battery Click on this link http://www.allamericanwatches.com/site/626101/product/e2306-a to purchase the Watch Battery Replacement Tool
Instructions for Using the Watch Works Tool Kit to Change a Watch Battery Click on this link http://www.allamericanwatches.com/site/626101/product/e2306-a to purchase the Watch Battery Replacement Tool
Solution Derivations for Capa #14
 Solution Derivations for Capa #4 ) An image of the moon is focused onto a screen using a converging lens of focal length (f = 34.8 cm). The diameter of the moon is 3.48 0 6 m, and its mean distance from
Solution Derivations for Capa #4 ) An image of the moon is focused onto a screen using a converging lens of focal length (f = 34.8 cm). The diameter of the moon is 3.48 0 6 m, and its mean distance from
DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY. To demonstrate bacterial motility by microscopic and macroscopic techniques.
 DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate bacterial motility by microscopic and macroscopic techniques. To observe flagella in prepared slides stained by specific flagellar stains. II.
DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate bacterial motility by microscopic and macroscopic techniques. To observe flagella in prepared slides stained by specific flagellar stains. II.
SP AF 90mm F/2.8 Di Macro 1:1 (Model 272E)
 SP AF 90mm F/2.8 Di Macro 1:1 (Model 272E) Thank you for purchasing this Tamron lens as the latest addition to your photographic equipment. Before using your new lens, please read the contents of this
SP AF 90mm F/2.8 Di Macro 1:1 (Model 272E) Thank you for purchasing this Tamron lens as the latest addition to your photographic equipment. Before using your new lens, please read the contents of this
PENNY IN A CUP: DEMONSTRATING THE LAW OF INERTIA
 PENNY IN A CUP: DEMONSTRATING THE LAW OF INERTIA Introduction Newton s (Sir Isaac Newton, English physicist, 1642 1727) First Law of Motion states that: An object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an
PENNY IN A CUP: DEMONSTRATING THE LAW OF INERTIA Introduction Newton s (Sir Isaac Newton, English physicist, 1642 1727) First Law of Motion states that: An object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an
Making a reflector telescope
 Making a reflector telescope telescope built by Sir Isaac Newton Replica of the first reflector Nowadays, professional astronomers use another type of telescope that is different to the first telescope
Making a reflector telescope telescope built by Sir Isaac Newton Replica of the first reflector Nowadays, professional astronomers use another type of telescope that is different to the first telescope
EXPERIMENT O-6. Michelson Interferometer. Abstract. References. Pre-Lab
 EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
Fig. 1. Background. Name: Class: Date:
 Background Bubbles make a great stand in for cell membranes. They re fluid, flexible, and can self-repair. Bubbles and cell membranes are alike because their parts are so similar. If you could zoom down
Background Bubbles make a great stand in for cell membranes. They re fluid, flexible, and can self-repair. Bubbles and cell membranes are alike because their parts are so similar. If you could zoom down
7.2. Focusing devices: Unit 7.2. context. Lenses and curved mirrors. Lenses. The language of optics
 context 7.2 Unit 7.2 ocusing devices: Lenses and curved mirrors Light rays often need to be controlled and ed to produce s in optical instruments such as microscopes, cameras and binoculars, and to change
context 7.2 Unit 7.2 ocusing devices: Lenses and curved mirrors Light rays often need to be controlled and ed to produce s in optical instruments such as microscopes, cameras and binoculars, and to change
To measure an object length, note the number of divisions spanned by the object then multiply by the conversion factor for the magnification used.
 STAGE MICROMETERS Introduction Whenever there is a need to make measurements with an eyepiece graticule, there is also a need to ensure that the microscope is calibrated. The use of a stage micrometer
STAGE MICROMETERS Introduction Whenever there is a need to make measurements with an eyepiece graticule, there is also a need to ensure that the microscope is calibrated. The use of a stage micrometer
STAAR Science Tutorial 30 TEK 8.8C: Electromagnetic Waves
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 30 TEK 8.8C: Electromagnetic Waves TEK 8.8C: Explore how different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum such as light and radio waves are used to
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 30 TEK 8.8C: Electromagnetic Waves TEK 8.8C: Explore how different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum such as light and radio waves are used to
3.1 Cells and cell function
 BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
STEADYfast Stabilizer Installation Notes Fifth Wheel and Travel Trailers 11/23/13
 STEADYfast Stabilizer Installation Notes Fifth Wheel and Travel Trailers 11/23/13 (See Supplemental Instructions for trailers with heavy duty round footplates and/or Power Leveling Systems) PHONE SUPPORT
STEADYfast Stabilizer Installation Notes Fifth Wheel and Travel Trailers 11/23/13 (See Supplemental Instructions for trailers with heavy duty round footplates and/or Power Leveling Systems) PHONE SUPPORT
Be careful not to scratch or hit front edge of the side viewing micro prisms onto hard objects!
 Instructions Manual Flexia BGA Inspection Systems This manual describes how to use Flexia BGA Inspection System Optilia Instruments 1 AB Contents 1. Safety and maintenance Instructions 3 2. About Flexia
Instructions Manual Flexia BGA Inspection Systems This manual describes how to use Flexia BGA Inspection System Optilia Instruments 1 AB Contents 1. Safety and maintenance Instructions 3 2. About Flexia
Animal & Plant Cell Slides
 Animal & Plant Cell Slides Category: Biology Type: Class Experiment, 60 min class Materials: 2 Glass Slides 2 Cover Slips 1 Bottle of methylene blue (optional) 1 Plastic tray 1 Bottle of iodine 1 Plastic
Animal & Plant Cell Slides Category: Biology Type: Class Experiment, 60 min class Materials: 2 Glass Slides 2 Cover Slips 1 Bottle of methylene blue (optional) 1 Plastic tray 1 Bottle of iodine 1 Plastic
waves rays Consider rays of light from an object being reflected by a plane mirror (the rays are diverging): mirror object
 PHYS1000 Optics 1 Optics Light and its interaction with lenses and mirrors. We assume that we can ignore the wave properties of light. waves rays We represent the light as rays, and ignore diffraction.
PHYS1000 Optics 1 Optics Light and its interaction with lenses and mirrors. We assume that we can ignore the wave properties of light. waves rays We represent the light as rays, and ignore diffraction.
Chapter 17: Light and Image Formation
 Chapter 17: Light and Image Formation 1. When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it is A. absorbed. B. bent away from the normal. C. bent towards from the normal. D. continues in the
Chapter 17: Light and Image Formation 1. When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it is A. absorbed. B. bent away from the normal. C. bent towards from the normal. D. continues in the
Parts List. The HyperStar Lens Assembly includes three pieces: HyperStar Lens Secondary Mirror Holder Counterweight
 The HyperStar Lens allows CCD imaging at f/2.3 with compatible Celestron 9.25 Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes and compatible CCD cameras. These instructions show the proper methods for installing the HyperStar
The HyperStar Lens allows CCD imaging at f/2.3 with compatible Celestron 9.25 Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes and compatible CCD cameras. These instructions show the proper methods for installing the HyperStar
how to change a watch battery
 how to change a watch battery contents STEP 1 Determine your case back. SNAP BACK If the watch looks similar to this, follow the step-bystep instructions contained in the first section labeled snap back
how to change a watch battery contents STEP 1 Determine your case back. SNAP BACK If the watch looks similar to this, follow the step-bystep instructions contained in the first section labeled snap back
KNITTING MACHINE Quick Tips for Knitting Success
 Visit our website: www.nsiinnovations.com KNITTING MACHINE Quick Tips for Knitting Success Intended for Adult Use No. 7590-08 Addendum BEFORE YOU START: Before you start knitting, wind your yarn into an
Visit our website: www.nsiinnovations.com KNITTING MACHINE Quick Tips for Knitting Success Intended for Adult Use No. 7590-08 Addendum BEFORE YOU START: Before you start knitting, wind your yarn into an
Parallel Circuits Charles Lang
 SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 6.20-1 Parallel Circuits Charles Lang Topic Parallel circuits Time 1 1 2 hours! Safety Adult supervision is required. Please click on the safety icon to view
SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 6.20-1 Parallel Circuits Charles Lang Topic Parallel circuits Time 1 1 2 hours! Safety Adult supervision is required. Please click on the safety icon to view
Physics 41, Winter 1998 Lab 1 - The Current Balance. Theory
 Physics 41, Winter 1998 Lab 1 - The Current Balance Theory Consider a point at a perpendicular distance d from a long straight wire carrying a current I as shown in figure 1. If the wire is very long compared
Physics 41, Winter 1998 Lab 1 - The Current Balance Theory Consider a point at a perpendicular distance d from a long straight wire carrying a current I as shown in figure 1. If the wire is very long compared
ST-80 MICROSCOPE With Electronic Eyepiece #6810. User Guide
 ST-80 MICROSCOPE With Electronic Eyepiece #6810 User Guide The ST-80 Microscope Thank you for purchasing your student microscope from ioptron. The ST-80 Microscope is both versatile and easy to use with
ST-80 MICROSCOPE With Electronic Eyepiece #6810 User Guide The ST-80 Microscope Thank you for purchasing your student microscope from ioptron. The ST-80 Microscope is both versatile and easy to use with
Lab Activity on Air Pressure, Wind and Air Circulation Caused by Heating of the Atmosphere
 Lab Activity on Air Pressure, Wind and Air Circulation Caused by Heating of the Atmosphere 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico *
Lab Activity on Air Pressure, Wind and Air Circulation Caused by Heating of the Atmosphere 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico *
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
Contents Contents Contents Overview Charging your headset Wearing the headset Powering on the headset Connecting your headset for dictation
 1 Contents Contents Contents 2 Overview 3 Charging your headset 4 Wearing the headset 4 Powering on the headset 4 Connecting your headset for dictation 5 The adapter 5 Adjusting your computer's audio settings
1 Contents Contents Contents 2 Overview 3 Charging your headset 4 Wearing the headset 4 Powering on the headset 4 Connecting your headset for dictation 5 The adapter 5 Adjusting your computer's audio settings
OLYMPUS STUDENT MICROSCOPES INSTRUCTIONS ST. HS&HSC MODELS OLYMPUS
 OLYMPUS STUDENT MICROSCOPES INSTRUCTIONS MODELS ST. HS&HSC OLYMPUS OLYMPUS MICROSCOPES MODELS ST, HS, HSB, HSC This booklet describes the common features and functions of Models ST, HS. HSB and HSC of
OLYMPUS STUDENT MICROSCOPES INSTRUCTIONS MODELS ST. HS&HSC OLYMPUS OLYMPUS MICROSCOPES MODELS ST, HS, HSB, HSC This booklet describes the common features and functions of Models ST, HS. HSB and HSC of
Manual for GlobePharma Mini-Press II Rotary Tablet Press
 1 of 13 Preparing the Rotary Press 1. Make sure the rotary press is unplugged. 2. Open the bottom cabinet of the rotary press and take out the grey tool kit, and the beige box of punches and dies. 3. Take
1 of 13 Preparing the Rotary Press 1. Make sure the rotary press is unplugged. 2. Open the bottom cabinet of the rotary press and take out the grey tool kit, and the beige box of punches and dies. 3. Take
GRADE 7: Life science 1. UNIT 7L.1 7 hours. Specialised cells. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Key vocabulary and technical terms
 GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
OWNER S MANUAL Table Tennis Table Patent Pending
 OWNER S MANUAL Table Tennis Table Patent Pending Be sure to write your model number and serial number here for future reference. You can find these numbers printed on the bottom of the table. MODEL # T8179
OWNER S MANUAL Table Tennis Table Patent Pending Be sure to write your model number and serial number here for future reference. You can find these numbers printed on the bottom of the table. MODEL # T8179
The Krasnogorsk-3. Operating Instructions. Sold by NCS Products, New York
 The Krasnogorsk-3 Operating Instructions Sold by NCS Products, New York [6] Viewfinder [7] Light Meter FPS Dial [8] Light Meter Power Switch [9] Light Meter ASA/ISO Knob [10] Pistol Grip [11] Lens Focus
The Krasnogorsk-3 Operating Instructions Sold by NCS Products, New York [6] Viewfinder [7] Light Meter FPS Dial [8] Light Meter Power Switch [9] Light Meter ASA/ISO Knob [10] Pistol Grip [11] Lens Focus
Air Hockey Training Camp Care and repair of your Air Hockey Playfield
 The playfield is the single most expensive part of your Dynamo Air Hockey table. Proper care will keep your table attractive and functional for your players, and bring them back for more games. CLEAN YOUR
The playfield is the single most expensive part of your Dynamo Air Hockey table. Proper care will keep your table attractive and functional for your players, and bring them back for more games. CLEAN YOUR
Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays.
 Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays. Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview...
Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays. Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview...
8.9 - Flash Column Chromatography Guide
 8.9 - Flash Column Chromatography Guide Overview: Flash column chromatography is a quick and (usually) easy way to separate complex mixtures of compounds. We will be performing relatively large scale separations
8.9 - Flash Column Chromatography Guide Overview: Flash column chromatography is a quick and (usually) easy way to separate complex mixtures of compounds. We will be performing relatively large scale separations
2) A convex lens is known as a diverging lens and a concave lens is known as a converging lens. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Var: 1 Page Ref: Sec.
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 4e (Giancoli) Chapter 33 Lenses and Optical Instruments 33.1 Conceptual Questions 1) State how to draw the three rays for finding the image position due to a thin
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 4e (Giancoli) Chapter 33 Lenses and Optical Instruments 33.1 Conceptual Questions 1) State how to draw the three rays for finding the image position due to a thin
Operator s Maintenance Manual STEINER BINOCULARS. Military ruggedness and precision 07/03
 Operator s Maintenance Manual STEINER BINOCULARS Military ruggedness and precision 07/03 W arning! When using the binocular, never point it directly at the sun. The heat generated by the focused rays of
Operator s Maintenance Manual STEINER BINOCULARS Military ruggedness and precision 07/03 W arning! When using the binocular, never point it directly at the sun. The heat generated by the focused rays of
Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV
 Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
Router. A. Identify the major parts of the router. B. Complete a written test on safety and operating procedures of the router with 100% accuracy.
 Router I. Competencies Given a properly adjusted router, instruction and demonstration of use, each student will be able to: A. Identify the major parts of the router. B. Complete a written test on safety
Router I. Competencies Given a properly adjusted router, instruction and demonstration of use, each student will be able to: A. Identify the major parts of the router. B. Complete a written test on safety
Impressions of a Stoma
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Impressions of a Stoma Overview Students use two different methods to view stomata on the underside of leaves. Introduction Plants exchange the
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Impressions of a Stoma Overview Students use two different methods to view stomata on the underside of leaves. Introduction Plants exchange the
Build Your Own Solar Car Teach build learn renewable Energy! Page 1 of 1
 Solar Car Teach build learn renewable Energy! Page 1 of 1 Background Not only is the sun a source of heat and light, it s a source of electricity too! Solar cells, also called photovoltaic cells, are used
Solar Car Teach build learn renewable Energy! Page 1 of 1 Background Not only is the sun a source of heat and light, it s a source of electricity too! Solar cells, also called photovoltaic cells, are used
National Optical & Scientific Instrument Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104
 National Optical & Scientific Instrument Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104 INSTRUCTIONS FOR STEREOSCOPIC MICROSCOPES MODEL NUMBERS 400 400TL
National Optical & Scientific Instrument Inc. 11113 Landmark 35 Drive San Antonio, Texas 78233 Phone (210) 590-9010 Fax (210) 590-1104 INSTRUCTIONS FOR STEREOSCOPIC MICROSCOPES MODEL NUMBERS 400 400TL
Buying Your First Telescope By Mike Usher
 Buying Your First Telescope By Mike Usher The first thing to understand is that a telescope is a high quality optical device and high quality optical devices are not inexpensive. Second mortgages are not
Buying Your First Telescope By Mike Usher The first thing to understand is that a telescope is a high quality optical device and high quality optical devices are not inexpensive. Second mortgages are not
600 Series Camera. User Guide
 600 Series Camera User Guide IMPORTANT SAFEGUARDS Note: This product is listed by Underwriters Laboratories, Inc. (UL). As a condition of listing, UL requires that basic safety information be provided.
600 Series Camera User Guide IMPORTANT SAFEGUARDS Note: This product is listed by Underwriters Laboratories, Inc. (UL). As a condition of listing, UL requires that basic safety information be provided.
Instruction Manual Genesis 200 EQ
 Instruction Manual Genesis 200 EQ English version 8.2014 Rev A 1 The Zoomion Genesis 200 EQ Congratulations on the purchase of the new Zoomion Genesis 200 EQ. This advanced telescope will give you hours
Instruction Manual Genesis 200 EQ English version 8.2014 Rev A 1 The Zoomion Genesis 200 EQ Congratulations on the purchase of the new Zoomion Genesis 200 EQ. This advanced telescope will give you hours
EF70-300mm f/4-5.6 IS USM
 EF70-300mm f/4-5.6 IS USM ENG Instruction Thank you for purchasing a Canon product. Dedicated to EOS cameras, the Canon EF70-300mm f/4-5.6 IS USM lens is a highperformance telephoto zoom lens equipped
EF70-300mm f/4-5.6 IS USM ENG Instruction Thank you for purchasing a Canon product. Dedicated to EOS cameras, the Canon EF70-300mm f/4-5.6 IS USM lens is a highperformance telephoto zoom lens equipped
SAFETY & OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
 SAFETY & OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS EDLUND TOMATO LASER, Models ETL -316, -140 & -380 READ AND UNDERSTAND THIS MANUAL AND ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE OPERATING THIS SLICER. 159 Industrial Parkway, Burlington,
SAFETY & OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS EDLUND TOMATO LASER, Models ETL -316, -140 & -380 READ AND UNDERSTAND THIS MANUAL AND ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE OPERATING THIS SLICER. 159 Industrial Parkway, Burlington,
5.3 Cleaning the Printer
 5.3 Cleaning the Printer As discussed earlier, the following parts must be cleaned each time the toner container and waste toner box are replaced: Main charger wire Main charger grid Registration roller
5.3 Cleaning the Printer As discussed earlier, the following parts must be cleaned each time the toner container and waste toner box are replaced: Main charger wire Main charger grid Registration roller
EF-S18-55mm f/3.5-5.6 IS II COPY ENG. Instruction
 EF-S18-55mm f/3.5-5.6 IS II ENG Instruction Thank you for purchasing a Canon product. The Canon EF-S18-55mm f/3.5-5.6 IS II lens is a high-performance standard zoom lens developed for digital SLRs compatible
EF-S18-55mm f/3.5-5.6 IS II ENG Instruction Thank you for purchasing a Canon product. The Canon EF-S18-55mm f/3.5-5.6 IS II lens is a high-performance standard zoom lens developed for digital SLRs compatible
Inclined Plane: Distance vs. Force
 1a Inclined Plane: Distance vs. Force Look at the inclined plane model you built for Card 2. It s a ramp, so it s easy to slide or roll things up and down it. As you noticed, it is a little more difficult
1a Inclined Plane: Distance vs. Force Look at the inclined plane model you built for Card 2. It s a ramp, so it s easy to slide or roll things up and down it. As you noticed, it is a little more difficult
The Vortex Spitfire 1x Prism Scope
 REPLACE image The Vortex Spitfire 1x Prism Scope Perfect for the AR platform, the Vortex Spitfire 1x prism scope combines a compact, prism-based design with the intuitive, glass-etched DRT (Dual Ring Tactical)
REPLACE image The Vortex Spitfire 1x Prism Scope Perfect for the AR platform, the Vortex Spitfire 1x prism scope combines a compact, prism-based design with the intuitive, glass-etched DRT (Dual Ring Tactical)
HS-T RIFLESCOPE. riflescope manual. Second Focal Plane MOA
 riflescope manual Second Focal Plane MOA The Vortex Viper HS-T tm Riflescope Specifically designed for the tactical, law enforcement and committed precision shooting communities, the Vortex Viper HS-T
riflescope manual Second Focal Plane MOA The Vortex Viper HS-T tm Riflescope Specifically designed for the tactical, law enforcement and committed precision shooting communities, the Vortex Viper HS-T
