Current mirrors are commonly used for current sources in integrated circuit design. This section covers other current sources that are often seen.
|
|
|
- Naomi Bennett
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 c Coyright W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Comuter Engineering. Current Sources Current mirrors are commonly used for current sources in integrated circuit design. This section covers other current sources that are often seen. FET Current Sources Figure 1(a) shows two FET current sources, one which uses an n-channel deletion mode MOSFET and the other which uses an n-channel JFET. The equivalent -channel sources are shown in Fig. 1(b). Remember that the JFET is a deletion mode device. The analysis for the two sources is the same with the excetion that the transconductance arameter is denoted by K for the MOSFET and by β for the JFET. Figure 1: MOSFET (deletion mode) and JFET current sources. (a) n-channel. (b) -channel. For the n-channel device, the MOSFET drain current and gate-source voltage are given by = K (V GS V TO ) 2 V GS = I S R S The object is to solve for R S for a desired drain current. When the equation for V GS is substituted into the equation for,weobtain ThiscanbesolvedforR S to obtain = K ( R S V TO ) 2 = K ( R S + V TO ) 2 ID /K V TO where V TO < 0. Note that K = K 0 (1 + λv DS ). If V DS is not secified, an often used aroximation is K ' K 0. For the n-channel JFET, the drain current is given by = β (V GS V TO ) 2 It follows that the MOSFET solution for R S canbeusedwiththesubstitutionofβ for K to obtain ID /β V TO 1
2 The outut resistance is a figure of merit for a current source. Ideally, it should be infinite. The outut resistance is the resistance seen looking into the drain of each source. It is given by r out = r id = r 0 1+ R S + R S r s = 1 r s g m r 0 = λ 1 + V DS where g m =2 K for the MOSFET and g m =2 β for the JFET. For the -channel devices, the subscrits for the voltages are reversed, e.g. V GS become V SG and V DS becomes V SD. Examle 1 A deletion mode MOSFET has the arameters K 0 = A/ V 2, λ =10 4 V 1,and V TO = 2V. Calculate the value of R S and r out if the transistor is to be used as a current source with a current =1.5mA. Assume V DS =8V. Solution. K = K 0 (1 + λv DS )= A/ V 2 ID /K V TO =2.47 kω r 0 = λ 1 + V DS =13.87 kω g m =2 K = S r s = 1 g m =566.1 Ω r out = r id = r 0 1+ R S kω r s Resistor R S causes r out to be greater than r 0 by more than a factor of 5. One-BJT Current Source Figure 2 shows nn and n BJT current sources. The object is to select the resistors in the circuit for a desired collector current. Figure 2: BJT current sources. 2
3 For the nn device, the stes can be summarized as follows: (a)chooseavalueforr E. It should be small but large enough for good bias stability. It is common to choose R E so that the voltage across it is some multile n of the base-emitter junction voltage V BE,where tyically 1 n 4. Thelargern, the better the current stability. It follows that I E R E = α R E = nv BE = R E = αnv BE (b)chooseavalueforr 2. It is usually chosen so that the current I 2 is some multile m of I B,where tyically m 9. It follows that I 2 R 2 = mi B R 2 = m β R 2 =(n +1)V BE = R 2 = β (n +1)V BE m If m is too small, the uncertainty in I B can cause errors if β is not known recisely or if β drifts with temerature. (c) Solve for R 1. I 1 R 1 = (m +1)I B R 1 =(m +1) β R 1 = V + V +(n +1)V BE = R 1 = β V + V (n +1)V BE (m +1) (d) Solve for r out. r out = r ic = r 0 + r 0 ekr E 1 αr E r 0 e + R E r 0 = V A + V CE r 0 e = R 1kR 2 + r x For the n device, the subscrits for the voltages are reversed, e.g. V BE become V EB and V CE becomes V EC. Examle 2 A BJT has the arameters β = 100, V A =75V,andr x =40Ω. The transistor is to be used asacurrentsourcewithacurrent =1.5mA, V + =15V,andV = 15 V. Calculate the values of R 1,,R 2,andr out if I 1 =10I B (n = 10) and I E R E =2V BE (m =2). Assume V BE =0.65 V and V CE =8V. + r e Solution. R E = αnv BE = βnv BE (1 + β) = 858 Ω R 1 = β V + V (n +1)V BE (m +1) = 170 kω R 2 = β (n +1)V BE m =13kΩ r 0 = V A + V CE =55.33 kω r 0 e = R 1kR 2 + r x + r e = R 1kR 2 + r x + αv T = Ω r out = r ic = r 0 + r 0 ekr E 1 αr E r 0 e + R E = 380.4kΩ Resistor R E causes rout to be greater than r 0 by almost a factor of 7. 3
4 Two-BJT Current Source Figure 3 shows nn and n two-transistor BJT current sources that are simler to design. The outut current in each is the collector current I O. For the circuit of Fig. 3(a), the following equations can be written V + V = I 1 R 1 + V BE2 + V BE1 + 1 IO I C1 R E2 = V BE1 + 1 α 2 β 1 1 = I 1 I O β 2 For the n circuit, the subscrits for the voltages are reversed, e.g. V BE become V EB. Figure 3: Two-BJT current sources. There is a ositive feedback effect in these circuits which increases the outut resistance seen looking into the collector of Q 1. To see this, consider the small-signal circuit with V + = V =0and the collector of Q 1 driven by a small-signal test current source i t.ifi t is ositive, it causes a current to flow through r 01 from its collector to its emitter. This forces the base voltage of Q 2 to increase. This is amlified by Q 2 to cause its collector voltage to decrease. This decrease is alied to the base of Q 1 to cause its collector voltage to increase. This feedback effect causes the collector voltage of Q 1 to be larger than it would be without the feedback. Because resistance is voltage divided by current, it follows that the resistance seen looking into the collector of Q 1 is increased. The circuit can be designed by secifying the currents I 1 and 1 and the resistor R E2. The current I 1 must be chosen so that it is much larger than the anticiated base current in Q 1. R E2 can be omitted, but it aids in reventing temerature drift of the currents. If it is too large, however, it reduces the gain around the ositive feedback loo, thus reducing the outut resistance. Tyically, R E2 mightbechosentohavea value such that V BE1 I E1 4V BE1.ResistorsR 1 and are then given by V + V (V BE1 + V BE2 ) I 1 I O RE1 β R 1 = 2 R E2 = I 1 V BE1 + 1 I O 1 α 2 β 1 4
5 Examle 3 For V + = 15V and V = 15 V, design the circuit in Fig. 3(a) for an outut current 1 =1.5mA. Solution. If we estimate β = 100, the base current in Q 1 is ma. LetuschooseI 1 =20I B2 =0.3mA. We estimate V BE1 = V BE2 =0.65 V. The current 1 is given by 1 = I 1 I O /β =0.285 ma. The current through is I E1 = 1 /α =0.288 ma. If we choose I E1 = V BE1, it follows that, R 1,andR E2 are given by = 0.65 =2.26 kω ma ma 2.26 kω R 1 = =91.2kΩ 0.3mA R E2 = mA = 867 Ω Current Sources Using an O Am Figure 4 shows two current sources that use an o am as an error amlifier. The emitter current in each transistor is I E = I O α This current divides between R F and R E go cause the voltage at the negative o-am inut to be V N = α R 1 R E + R F + R 1 R E Because the o am forces V N = V I, it follows that I O is given by I O = + R E + R F R 1 VI R E Figure 4: Current sources using an o am. 5
The BJT Differential Amplifier. Basic Circuit. DC Solution
 c Copyright 010. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The BJT Differential Amplifier Basic Circuit Figure 1 shows the circuit
c Copyright 010. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The BJT Differential Amplifier Basic Circuit Figure 1 shows the circuit
An FET Audio Peak Limiter
 1 An FET Audio Peak Limiter W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0250 USA email: [email protected] Copyright
1 An FET Audio Peak Limiter W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0250 USA email: [email protected] Copyright
COMMON-SOURCE JFET AMPLIFIER
 EXPERIMENT 04 Objectives: Theory: 1. To evaluate the common-source amplifier using the small signal equivalent model. 2. To learn what effects the voltage gain. A self-biased n-channel JFET with an AC
EXPERIMENT 04 Objectives: Theory: 1. To evaluate the common-source amplifier using the small signal equivalent model. 2. To learn what effects the voltage gain. A self-biased n-channel JFET with an AC
Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]
![Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57] Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]](/thumbs/40/21338705.jpg) Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
http://users.ece.gatech.edu/~mleach/ece3050/notes/feedback/fbexamples.pdf
 c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Feedback Amplifiers CollectionofSolvedProblems A collection of solved
c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Feedback Amplifiers CollectionofSolvedProblems A collection of solved
Lecture 21: Junction Field Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 21 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 21: Junction Fiel Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier As mentione in Lecture 16, there are two major families of transistors. We ve worke with BJTs
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 21 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 21: Junction Fiel Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier As mentione in Lecture 16, there are two major families of transistors. We ve worke with BJTs
Bob York. Transistor Basics - MOSFETs
 Bob York Transistor Basics - MOSFETs Transistors, Conceptually So far we have considered two-terminal devices that are described by a current-voltage relationship I=f(V Resistors: Capacitors: Inductors:
Bob York Transistor Basics - MOSFETs Transistors, Conceptually So far we have considered two-terminal devices that are described by a current-voltage relationship I=f(V Resistors: Capacitors: Inductors:
3.4 - BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS
 BJT Differential Amplifiers (6/4/00) Page 1 3.4 BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Define and characterize the differential amplifier.) Show the
BJT Differential Amplifiers (6/4/00) Page 1 3.4 BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Define and characterize the differential amplifier.) Show the
Figure 1: Common-base amplifier.
 The Common-Base Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of a single stage common-base amplifier. The object is to solve for the small-signal voltage gain, input resistance, and output
The Common-Base Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of a single stage common-base amplifier. The object is to solve for the small-signal voltage gain, input resistance, and output
BJT Ebers-Moll Model and SPICE MOSFET model
 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
Lecture 12: DC Analysis of BJT Circuits.
 Whites, 320 Lecture 12 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 12: D Analysis of JT ircuits. n this lecture we will consider a number of JT circuits and perform the D circuit analysis. For those circuits with an active mode
Whites, 320 Lecture 12 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 12: D Analysis of JT ircuits. n this lecture we will consider a number of JT circuits and perform the D circuit analysis. For those circuits with an active mode
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers
 BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler [email protected] EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler [email protected] EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
W04 Transistors and Applications. Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören
 W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS IN ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
Superposition Examples
 Superposition Examples The following examples illustrate the proper use of superposition of dependent sources. All superposition equations are written by inspection using voltage division, current division,
Superposition Examples The following examples illustrate the proper use of superposition of dependent sources. All superposition equations are written by inspection using voltage division, current division,
Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors.
 Whites, EE 320 Lecture 30 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors. There are two different environments in which MOSFET amplifiers are found, (1) discrete circuits and
Whites, EE 320 Lecture 30 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors. There are two different environments in which MOSFET amplifiers are found, (1) discrete circuits and
Lecture 060 Push-Pull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 060-1. ECE 6412 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems II P.E. Allen - 2002
 Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Transistors. NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor
 Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
EDC Lesson 12: Transistor and FET Characteristics. 2008 EDCLesson12- ", Raj Kamal, 1
 EDC Lesson 12: Transistor and FET Characteristics Lesson-12: MOSFET (enhancement and depletion mode) Characteristics and Symbols 2008 EDCLesson12- ", Raj Kamal, 1 1. Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect
EDC Lesson 12: Transistor and FET Characteristics Lesson-12: MOSFET (enhancement and depletion mode) Characteristics and Symbols 2008 EDCLesson12- ", Raj Kamal, 1 1. Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect
Field Effect Transistors and Noise
 Physics 3330 Experiment #8 Fall 2005 Field Effect Transistors and Noise Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors. We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct
Physics 3330 Experiment #8 Fall 2005 Field Effect Transistors and Noise Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors. We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct
Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems
 c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems This document contains
c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems This document contains
5.11 THE JUNCTION FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTOR (JFET)
 This material is from a previous edition of Microelectronic Circuits. These sections provide valuable information, but please note that the references do not correspond to the 6th or 7th edition of the
This material is from a previous edition of Microelectronic Circuits. These sections provide valuable information, but please note that the references do not correspond to the 6th or 7th edition of the
Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Bipolar Junction Transistors
 Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
Field Effect Transistors
 506 19 Principles of Electronics Field Effect Transistors 191 Types of Field Effect Transistors 193 Principle and Working of JFET 195 Importance of JFET 197 JFET as an Amplifier 199 Salient Features of
506 19 Principles of Electronics Field Effect Transistors 191 Types of Field Effect Transistors 193 Principle and Working of JFET 195 Importance of JFET 197 JFET as an Amplifier 199 Salient Features of
CO2005: Electronics I (FET) Electronics I, Neamen 3th Ed. 1
 CO2005: Electronics I The Field-Effect Transistor (FET) Electronics I, Neamen 3th Ed. 1 MOSFET The metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) becomes a practical reality in the 1970s. The
CO2005: Electronics I The Field-Effect Transistor (FET) Electronics I, Neamen 3th Ed. 1 MOSFET The metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) becomes a practical reality in the 1970s. The
The basic cascode amplifier consists of an input common-emitter (CE) configuration driving an output common-base (CB), as shown above.
 Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Bipolar Junction Transistor Basics
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
Field-Effect (FET) transistors
 Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
3 The TTL NAND Gate. Fig. 3.1 Multiple Input Emitter Structure of TTL
 3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
Lecture-7 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) Part-I Continued
 1 Lecture-7 ipolar Junction Transistors (JT) Part-I ontinued 1. ommon-emitter (E) onfiguration: Most JT circuits employ the common-emitter configuration shown in Fig.1. This is due mainly to the fact that
1 Lecture-7 ipolar Junction Transistors (JT) Part-I ontinued 1. ommon-emitter (E) onfiguration: Most JT circuits employ the common-emitter configuration shown in Fig.1. This is due mainly to the fact that
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
Objectives The purpose of this lab is build and analyze Differential amplifiers based on NPN transistors (or NMOS transistors).
 1 Lab 03: Differential Amplifiers (BJT) (20 points) NOTE: 1) Please use the basic current mirror from Lab01 for the second part of the lab (Fig. 3). 2) You can use the same chip as the basic current mirror;
1 Lab 03: Differential Amplifiers (BJT) (20 points) NOTE: 1) Please use the basic current mirror from Lab01 for the second part of the lab (Fig. 3). 2) You can use the same chip as the basic current mirror;
Transistor Biasing. The basic function of transistor is to do amplification. Principles of Electronics
 192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
Notes about Small Signal Model. for EE 40 Intro to Microelectronic Circuits
 Notes about Small Signal Model for EE 40 Intro to Microelectronic Circuits 1. Model the MOSFET Transistor For a MOSFET transistor, there are NMOS and PMOS. The examples shown here would be for NMOS. Figure
Notes about Small Signal Model for EE 40 Intro to Microelectronic Circuits 1. Model the MOSFET Transistor For a MOSFET transistor, there are NMOS and PMOS. The examples shown here would be for NMOS. Figure
MOS Transistors as Switches
 MOS Transistors as Switches G (gate) nmos transistor: Closed (conducting) when Gate = 1 (V DD ) D (drain) S (source) Oen (non-conducting) when Gate = 0 (ground, 0V) G MOS transistor: Closed (conducting)
MOS Transistors as Switches G (gate) nmos transistor: Closed (conducting) when Gate = 1 (V DD ) D (drain) S (source) Oen (non-conducting) when Gate = 0 (ground, 0V) G MOS transistor: Closed (conducting)
Basic FET Ampli ers 6.0 PREVIEW 6.1 THE MOSFET AMPLIFIER
 C H A P T E R 6 Basic FET Ampli ers 6.0 PREVIEW In the last chapter, we described the operation of the FET, in particular the MOSFET, and analyzed and designed the dc response of circuits containing these
C H A P T E R 6 Basic FET Ampli ers 6.0 PREVIEW In the last chapter, we described the operation of the FET, in particular the MOSFET, and analyzed and designed the dc response of circuits containing these
BJT Amplifier Circuits
 JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
BJT Amplifier Circuits
 JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
AN105. Introduction: The Nature of VCRs. Resistance Properties of FETs
 Introduction: The Nature of s A voltage-controlled resistor () may be defined as a three-terminal variable resistor where the resistance value between two of the terminals is controlled by a voltage potential
Introduction: The Nature of s A voltage-controlled resistor () may be defined as a three-terminal variable resistor where the resistance value between two of the terminals is controlled by a voltage potential
BJT AC Analysis. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
Transconductance. (Saturated) MOSFET Small-Signal Model. The small-signal drain current due to v gs is therefore given by
 11 (Saturated) MOSFET Small-Signal Model Transconductance Concept: find an equivalent circuit which interrelates the incremental changes in i D v GS v DS etc. for the MOSFET in saturation The small-signal
11 (Saturated) MOSFET Small-Signal Model Transconductance Concept: find an equivalent circuit which interrelates the incremental changes in i D v GS v DS etc. for the MOSFET in saturation The small-signal
Biasing in MOSFET Amplifiers
 Biasing in MOSFET Amplifiers Biasing: Creating the circuit to establish the desired DC oltages and currents for the operation of the amplifier Four common ways:. Biasing by fixing GS. Biasing by fixing
Biasing in MOSFET Amplifiers Biasing: Creating the circuit to establish the desired DC oltages and currents for the operation of the amplifier Four common ways:. Biasing by fixing GS. Biasing by fixing
Small Signal Analysis of a PMOS transistor Consider the following PMOS transistor to be in saturation. Then, 1 2
 Small Signal Analysis of a PMOS transistor Consider the following PMOS transistor to be in saturation. Then, 1 I SD = µ pcox( VSG Vtp)^2(1 + VSDλ) 2 From this equation it is evident that I SD is a function
Small Signal Analysis of a PMOS transistor Consider the following PMOS transistor to be in saturation. Then, 1 I SD = µ pcox( VSG Vtp)^2(1 + VSDλ) 2 From this equation it is evident that I SD is a function
CHAPTER 10 OPERATIONAL-AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 10 OPERATIONAL-AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 10.1 The Two-Stage CMOS Op Amp 10.2 The Folded-Cascode CMOS Op Amp 10.3 The 741 Op-Amp Circuit 10.4 DC Analysis of the 741 10.5 Small-Signal Analysis
CHAPTER 10 OPERATIONAL-AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 10.1 The Two-Stage CMOS Op Amp 10.2 The Folded-Cascode CMOS Op Amp 10.3 The 741 Op-Amp Circuit 10.4 DC Analysis of the 741 10.5 Small-Signal Analysis
HALF-WAVE & FULL-WAVE RECTIFICATION
 HALF-WAE & FULL-WAE RECTIFICATION Objectives: HALF-WAE & FULL-WAE RECTIFICATION To recognize a half-wave rectified sinusoidal voltage. To understand the term mean value as alied to a rectified waveform.
HALF-WAE & FULL-WAE RECTIFICATION Objectives: HALF-WAE & FULL-WAE RECTIFICATION To recognize a half-wave rectified sinusoidal voltage. To understand the term mean value as alied to a rectified waveform.
Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads.
 Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
BJT Circuit Configurations
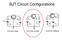 BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
Transistor amplifiers: Biasing and Small Signal Model
 Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FT are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly. Then, similar FT
Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FT are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly. Then, similar FT
Peak Atlas DCA. Semiconductor Component Analyser Model DCA55. User Guide
 GB55-7 Peak Atlas DCA Semiconductor Component Analyser Model DCA55 User Guide Peak Electronic Design Limited 2000/2007 In the interests of development, information in this guide is subject to change without
GB55-7 Peak Atlas DCA Semiconductor Component Analyser Model DCA55 User Guide Peak Electronic Design Limited 2000/2007 In the interests of development, information in this guide is subject to change without
Chapter 10 Advanced CMOS Circuits
 Transmission Gates Chapter 10 Advanced CMOS Circuits NMOS Transmission Gate The active pull-up inverter circuit leads one to thinking about alternate uses of NMOS devices. Consider the circuit shown in
Transmission Gates Chapter 10 Advanced CMOS Circuits NMOS Transmission Gate The active pull-up inverter circuit leads one to thinking about alternate uses of NMOS devices. Consider the circuit shown in
Constant Voltage and Constant Current Controller for Adaptors and Battery Chargers
 TECHNICAL DATA Constant Voltage and Constant Current Controller for Adaptors and Battery Chargers IK3051 Description IK3051 is a highly integrated solution for SMPS applications requiring constant voltage
TECHNICAL DATA Constant Voltage and Constant Current Controller for Adaptors and Battery Chargers IK3051 Description IK3051 is a highly integrated solution for SMPS applications requiring constant voltage
High Voltage Current Shunt Monitor AD8212
 High Voltage Current Shunt Monitor AD822 FEATURES Adjustable gain High common-mode voltage range 7 V to 65 V typical 7 V to >500 V with external pass transistor Current output Integrated 5 V series regulator
High Voltage Current Shunt Monitor AD822 FEATURES Adjustable gain High common-mode voltage range 7 V to 65 V typical 7 V to >500 V with external pass transistor Current output Integrated 5 V series regulator
BJT AC Analysis 1 of 38. The r e Transistor model. Remind Q-poiint re = 26mv/IE
 BJT AC Analysis 1 of 38 The r e Transistor model Remind Q-poiint re = 26mv/IE BJT AC Analysis 2 of 38 Three amplifier configurations, Common Emitter Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Common Base BJT
BJT AC Analysis 1 of 38 The r e Transistor model Remind Q-poiint re = 26mv/IE BJT AC Analysis 2 of 38 Three amplifier configurations, Common Emitter Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Common Base BJT
BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS
 CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
 LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS
 LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS Objective In this experiment you will study the i-v characteristics of an MOS transistor. You will use the MOSFET as a variable resistor and as a switch. BACKGROUND
LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS Objective In this experiment you will study the i-v characteristics of an MOS transistor. You will use the MOSFET as a variable resistor and as a switch. BACKGROUND
SPI-8001TW. Switching Regulators. Dual 1.5 A, DC/DC Step-Down Converter. SANKEN ELECTRIC CO., LTD. http://www.sanken-ele.co.jp/en/
 Data Sheet 27469.301.1 Designed to meet high-current requirements at high efficiency in industrial and consumer applications; embedded core, memory, or logic supplies; TVs, VCRs, and office equipment,
Data Sheet 27469.301.1 Designed to meet high-current requirements at high efficiency in industrial and consumer applications; embedded core, memory, or logic supplies; TVs, VCRs, and office equipment,
CIRCUITS LABORATORY. In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low
 CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
VI. Transistor amplifiers: Biasing and Small Signal Model
 VI. Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model 6.1 Introduction Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FET are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly.
VI. Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model 6.1 Introduction Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FET are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly.
g fs R D A V D g os g os
 AN12 JFET Biasing Techniques Introduction Engineers who are not familiar with proper biasing methods often design FET amplifiers that are unnecessarily sensitive to device characteristics. One way to obtain
AN12 JFET Biasing Techniques Introduction Engineers who are not familiar with proper biasing methods often design FET amplifiers that are unnecessarily sensitive to device characteristics. One way to obtain
05 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) basics
 The first bipolar transistor was realized in 1947 by Brattain, Bardeen and Shockley. The three of them received the Nobel prize in 1956 for their invention. The bipolar transistor is composed of two PN
The first bipolar transistor was realized in 1947 by Brattain, Bardeen and Shockley. The three of them received the Nobel prize in 1956 for their invention. The bipolar transistor is composed of two PN
Physics 120 Lab 6: Field Effect Transistors - Ohmic region
 Physics 120 Lab 6: Field Effect Transistors - Ohmic region The FET can be used in two extreme ways. One is as a voltage controlled resistance, in the so called "Ohmic" region, for which V DS < V GS - V
Physics 120 Lab 6: Field Effect Transistors - Ohmic region The FET can be used in two extreme ways. One is as a voltage controlled resistance, in the so called "Ohmic" region, for which V DS < V GS - V
One-Chip Linear Control IPS, F5106H
 One-Chi Linear Control IPS, F5106H NAKAGAWA Sho OE Takatoshi IWAMOTO Motomitsu ABSTRACT In the fi eld of vehicle electrical comonents, the increasing demands for miniaturization, reliability imrovement
One-Chi Linear Control IPS, F5106H NAKAGAWA Sho OE Takatoshi IWAMOTO Motomitsu ABSTRACT In the fi eld of vehicle electrical comonents, the increasing demands for miniaturization, reliability imrovement
V out. Figure 1: A voltage divider on the left, and potentiometer on the right.
 Living with the Lab Fall 202 Voltage Dividers and Potentiometers Gerald Recktenwald v: November 26, 202 [email protected] Introduction Voltage dividers and potentiometers are passive circuit components
Living with the Lab Fall 202 Voltage Dividers and Potentiometers Gerald Recktenwald v: November 26, 202 [email protected] Introduction Voltage dividers and potentiometers are passive circuit components
Bob York. Transistor Basics - BJTs
 ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier
 Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Configuration Common Base Configuration Small Signal Analysis Design Example Amplifier Input and Output Impedances
Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Configuration Common Base Configuration Small Signal Analysis Design Example Amplifier Input and Output Impedances
Lecture 17. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.
 Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
AMPLIFIERS BJT BJT TRANSISTOR. Types of BJT BJT. devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level
 AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
Design of a TL431-Based Controller for a Flyback Converter
 Design of a TL431-Based Controller for a Flyback Converter Dr. John Schönberger Plexim GmbH Technoparkstrasse 1 8005 Zürich 1 Introduction The TL431 is a reference voltage source that is commonly used
Design of a TL431-Based Controller for a Flyback Converter Dr. John Schönberger Plexim GmbH Technoparkstrasse 1 8005 Zürich 1 Introduction The TL431 is a reference voltage source that is commonly used
Power MOSFET Basics Abdus Sattar, IXYS Corporation
 Power MOSFET Basics Abdus Sattar, IXYS Corporation Power MOSFETs have become the standard choice for the main switching devices in a broad range of power conversion applications. They are majority carrier
Power MOSFET Basics Abdus Sattar, IXYS Corporation Power MOSFETs have become the standard choice for the main switching devices in a broad range of power conversion applications. They are majority carrier
Chapter 8 Differential and Multistage Amplifiers. EE 3120 Microelectronics II
 1 Chapter 8 Differential and Multistage Amplifiers Operational Amplifier Circuit Components 2 1. Ch 7: Current Mirrors and Biasing 2. Ch 9: Frequency Response 3. Ch 8: Active-Loaded Differential Pair 4.
1 Chapter 8 Differential and Multistage Amplifiers Operational Amplifier Circuit Components 2 1. Ch 7: Current Mirrors and Biasing 2. Ch 9: Frequency Response 3. Ch 8: Active-Loaded Differential Pair 4.
Low Noise, Matched Dual PNP Transistor MAT03
 a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime
 Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Application Report SLVA072
 Application Report August 1999 Mixed Signal Products SLVA72 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue any product
Application Report August 1999 Mixed Signal Products SLVA72 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue any product
ST SiC MOSFET Evolution in Power Electronics
 ST SiC MOSFET Evolution in Power Electronics Simone Buonomo Market & Application Development Manager Power Transistor Division [email protected] Power Transistor Division Agenda 2 SiC MOSFET Time Speaker
ST SiC MOSFET Evolution in Power Electronics Simone Buonomo Market & Application Development Manager Power Transistor Division [email protected] Power Transistor Division Agenda 2 SiC MOSFET Time Speaker
IRLR8743PbF IRLU8743PbF HEXFET Power MOSFET
 Applications l High Frequency Synchronous Buck Converters for Computer Processor Power l High Frequency Isolated DC-DC Converters with Synchronous Rectification for Telecom and Industrial Use l Lead-Free
Applications l High Frequency Synchronous Buck Converters for Computer Processor Power l High Frequency Isolated DC-DC Converters with Synchronous Rectification for Telecom and Industrial Use l Lead-Free
ENEE 307 Electronic Circuit Design Laboratory Spring 2012. A. Iliadis Electrical Engineering Department University of Maryland College Park MD 20742
 1.1. Differential Amplifiers ENEE 307 Electronic Circuit Design Laboratory Spring 2012 A. Iliadis Electrical Engineering Department University of Maryland College Park MD 20742 Differential Amplifiers
1.1. Differential Amplifiers ENEE 307 Electronic Circuit Design Laboratory Spring 2012 A. Iliadis Electrical Engineering Department University of Maryland College Park MD 20742 Differential Amplifiers
Common-Emitter Amplifier
 Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
Transistor Models. ampel
 Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Understanding Low Drop Out (LDO) Regulators
 Understanding Low Drop Out (LDO) Regulators Michael Day, Texas Instruments ABSTRACT This paper provides a basic understanding of the dropout performance of a low dropout linear regulator (LDO). It shows
Understanding Low Drop Out (LDO) Regulators Michael Day, Texas Instruments ABSTRACT This paper provides a basic understanding of the dropout performance of a low dropout linear regulator (LDO). It shows
An Introduction to the EKV Model and a Comparison of EKV to BSIM
 An Introduction to the EKV Model and a Comparison of EKV to BSIM Stephen C. Terry 2. 3.2005 Integrated Circuits & Systems Laboratory 1 Overview Characterizing MOSFET operating regions EKV model fundamentals
An Introduction to the EKV Model and a Comparison of EKV to BSIM Stephen C. Terry 2. 3.2005 Integrated Circuits & Systems Laboratory 1 Overview Characterizing MOSFET operating regions EKV model fundamentals
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor
 The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
MOSFET N-channel enhancement switching transistor IMPORTANT NOTICE. http://www.philips.semiconductors.com use http://www.nxp.com
 Rev. 3 21 November 27 Product data sheet Dear customer, IMPORTANT NOTICE As from October 1st, 26 Philips Semiconductors has a new trade name - NXP Semiconductors, which will be used in future data sheets
Rev. 3 21 November 27 Product data sheet Dear customer, IMPORTANT NOTICE As from October 1st, 26 Philips Semiconductors has a new trade name - NXP Semiconductors, which will be used in future data sheets
Features. Symbol JEDEC TO-220AB
 Data Sheet June 1999 File Number 2253.2 3A, 5V,.4 Ohm, N-Channel Power MOSFET This is an N-Channel enhancement mode silicon gate power field effect transistor designed for applications such as switching
Data Sheet June 1999 File Number 2253.2 3A, 5V,.4 Ohm, N-Channel Power MOSFET This is an N-Channel enhancement mode silicon gate power field effect transistor designed for applications such as switching
Bi-directional level shifter for I²C-bus and other systems.
 APPLICATION NOTE Bi-directional level shifter for I²C-bus and other Abstract With a single MOS-FET a bi-directional level shifter circuit can be realised to connect devices with different supply voltages
APPLICATION NOTE Bi-directional level shifter for I²C-bus and other Abstract With a single MOS-FET a bi-directional level shifter circuit can be realised to connect devices with different supply voltages
Electronics. Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit. LD Physics Leaflets P4.2.1.1
 Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
Operational Amplifier - IC 741
 Operational Amplifier - IC 741 Tabish December 2005 Aim: To study the working of an 741 operational amplifier by conducting the following experiments: (a) Input bias current measurement (b) Input offset
Operational Amplifier - IC 741 Tabish December 2005 Aim: To study the working of an 741 operational amplifier by conducting the following experiments: (a) Input bias current measurement (b) Input offset
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
AC Transport constant current vs. low impedance modes
 Application Note 184-42 AC Transport constant current vs. low impedance modes The AC Transport option offers the user the ability to put the current source in a low output impedance mode. This mode is
Application Note 184-42 AC Transport constant current vs. low impedance modes The AC Transport option offers the user the ability to put the current source in a low output impedance mode. This mode is
IRF740 N-CHANNEL 400V - 0.46Ω - 10A TO-220 PowerMESH II MOSFET
 N-CHANNEL 400V - 0.46Ω - 10A TO-220 PowerMESH II MOSFET TYPE V DSS R DS(on) I D IRF740 400 V < 0.55 Ω 10 A TYPICAL R DS (on) = 0.46Ω EXCEPTIONAL dv/dt CAPABILITY 100% AVALANCHE TESTED LOW GATE CHARGE VERY
N-CHANNEL 400V - 0.46Ω - 10A TO-220 PowerMESH II MOSFET TYPE V DSS R DS(on) I D IRF740 400 V < 0.55 Ω 10 A TYPICAL R DS (on) = 0.46Ω EXCEPTIONAL dv/dt CAPABILITY 100% AVALANCHE TESTED LOW GATE CHARGE VERY
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
BUZ11. 30A, 50V, 0.040 Ohm, N-Channel Power MOSFET. Features. [ /Title (BUZ1 1) /Subject. (30A, 50V, 0.040 Ohm, N- Channel. Ordering Information
 Data Sheet June 1999 File Number 2253.2 [ /Title (BUZ1 1) /Subject (3A, 5V,.4 Ohm, N- Channel Power MOS- FET) /Autho r () /Keywords (Intersil Corporation, N- Channel Power MOS- FET, TO- 22AB ) /Creator
Data Sheet June 1999 File Number 2253.2 [ /Title (BUZ1 1) /Subject (3A, 5V,.4 Ohm, N- Channel Power MOS- FET) /Autho r () /Keywords (Intersil Corporation, N- Channel Power MOS- FET, TO- 22AB ) /Creator
Features. Description. Table 1. Device summary. Order code Marking Package Packing. STP110N8F6 110N8F6 TO-220 Tube
 N-channel 80 V, 0.0056 Ω typ.,110 A, STripFET F6 Power MOSFET in a TO-220 package Features Datasheet - production data Order code V DS R DS(on)max I D P TOT TAB STP110N8F6 80 V 0.0065 Ω 110 A 200 W TO-220
N-channel 80 V, 0.0056 Ω typ.,110 A, STripFET F6 Power MOSFET in a TO-220 package Features Datasheet - production data Order code V DS R DS(on)max I D P TOT TAB STP110N8F6 80 V 0.0065 Ω 110 A 200 W TO-220
TO-92 SOT-23 Mark: 3G. TA = 25 C unless otherwise noted. Symbol Parameter Value Units
 MPSH MMBTH MPSH / MMBTH E B TO-92 SOT-2 Mark: G B E This device is designed for common-emitter low noise amplifier and mixer applications with collector currents in the µa to ma range to MHz, and low frequency
MPSH MMBTH MPSH / MMBTH E B TO-92 SOT-2 Mark: G B E This device is designed for common-emitter low noise amplifier and mixer applications with collector currents in the µa to ma range to MHz, and low frequency
