Randomized Clinical Trials. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
|
|
|
- Chastity Patterson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this site. Copyright 2008, The Johns Hopkins University and Sukon Kanchanaraksa. All rights reserved. Use of these materials permitted only in accordance with license rights granted. Materials provided AS IS ; no representations or warranties provided. User assumes all responsibility for use, and all liability related thereto, and must independently review all materials for accuracy and efficacy. May contain materials owned by others. User is responsible for obtaining permissions for use from third parties as needed.
2 Randomized Clinical Trials Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
3 Section A Experimental Study
4 Objectives of Epidemiological Investigation Investigate the etiology of disease and modes of transmission Determine the extent of disease problems in the community Study the natural history of disease Evaluate new preventive and therapeutic measures and modes of health care delivery Provide a foundation for developing public policy and regulatory decisions 4
5 Epidemiological Studies Observational study The investigators use the data observed in the population to make inference on the relationship between the variables Experimental study The investigators intervene in the natural history by actively altering one of the variables and then making inference on the relationship between the variables based on the outcomes 5
6 Historical Example of an Experimental Study James Lind, Source: 6
7 Passages from A Treatise of the Scurvy Source: 7
8 Experimental Trial On the 20 th of May 1747, I took twelve patients in the scurvy, on board the Salisbury at sea. Their cases were as similar as I could have them. They all in general had putrid gums, the spots and lassitude, with weakness of their knees. They lay together in one place, being a proper apartment for the sick in the fore-hold; and had one diet common to all. Two of these were ordered each a quart of cider a day. Two others took twenty-five gutts of elixir vitriol three times a day, and so on. They continued but six days under this course. The consequence was that the most sudden and visible good effects were perceived from the use of oranges and lemons; one of those who had taken them, being at the end of six days fit for duty. James Lind,
9 Interventions that Can Be Evaluated New drugs and new treatment of diseases New medical and health care technology New methods of primary prevention New programs for screening New ways of organizing and delivering health services New community health programs New behavioral intervention programs 9
10 Comparison Groups in an Experimental Study Therapy vs. no therapy Therapy vs. placebo or sham Therapy A vs. Therapy B 10
11 Historical and Simultaneous Control Groups Historical controls Simultaneous controls Simultaneous non-randomized controls Simultaneous randomized controls 11
12 Results of a Trial of BCG Vaccination Vaccinations were selectively performed Cases Vaccinated 445 Controls 545 TB deaths Number Percent Levine MI, Sackett MF: Results of BCG immunization in New York City. Am Rev Tuberculosis 53: ,
13 Results of a Trial of BCG Vaccination Alternate children were vaccinated Cases Vaccinated 556 Controls 528 TB deaths Number Percent Levine MI, Sackett MF: Results of BCG immunization in New York City. Am Rev Tuberculosis 53: ,
14 Section B Randomized Clinical Trials
15 About Randomization Sir R.A. Fisher first developed the concept of experimental randomization in 1925 J.B. Amberson and B.T. McMahon (1931) randomized patients by using a coin flip to see who received treatment for tuberculosis Sir Austin Bradford Hill introduced the use of random numbers in the allocation of patients in the study of streptomycin and tuberculosis Amberson JB Jr, McMahon BT, Pinner M (1931). A clinical trial of sanocrysin in pulmonary tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc 24:
16 Experimental Trial The 24 (tuberculosis) patients were then divided into two approximately comparable groups of 12 each. The cases were individually matched, one with another, in making this division. Then by a flip of the coin, one group became identified as group I (treated group) and the other as group II (control). The members of the separate groups were known only to the nurse in charge of the ward and to two of us. The patients themselves were not aware of any distinctions in the treatment administered. Amberson, et al., 1931 Amberson JB Jr, McMahon BT, Pinner M (1931). A clinical trial of sanocrysin in pulmonary tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc 24:
17 Randomization Randomization is the process by which allocation of subjects to treatment groups is done by chance, without the ability to predict who is in what group 17
18 Randomized Clinical Trial A trial is an experiment A clinical trial is a controlled experiment having a clinical event as an outcome measure, done in a clinical setting, and involving persons having a specific disease or health condition A randomized clinical trial is a clinical trial in which participants are randomly assigned to separate groups that compare different treatments 18
19 Design of a Randomized Clinical Trial Defined Population R A N D O M I Z E D New Treatment Current Treatment Improved Not Improved Improved Not Improved 19
20 20 Table of Random Numbers Column Row
21 Allocation Scheme A simple example using a onedigit random number If two treatment groups are being studied: If digit is: assign to: 0 4 Treatment A 5 9 Treatment B If three treatment groups are being studied: If digit is: assign to: 1 3 Treatment A 4 6 Treatment B 7 9 Treatment C (0 ignore) Example (2 groups) Translated to B A A A B B B B A A Example (3 groups) Translated to B A A B C C C C A 21
22 Other Sources of Random Numbers Computers or calculators Pseudo-random numbers Based on a mathematical formula or a predetermined list Random number Web sites, such as True random numbers Based on true randomness (entropy) outside of the computer, such as time to radioactive decay or atmospheric noise from radio 22
23 Purpose of Randomization Primary purpose Prevent bias in allocating subjects to treatment groups (avoid predictability) Secondary purpose Achieve comparability between the groups (there is no guarantee) 23
24 Gold Standard of Study Designs Randomized trials are gold standard of study designs because the potential for bias (selection into treatment groups) is avoided 24
25 Non-Randomized Observational Study A comparative study of an intervention in two groups of patients with MI shows that the mortality between the two groups differs Intervention n = 1,000 No Intervention n = 1,000 Total deaths 180 Mortality 180/1,000 = 18% Conclusion? /1,000 = 30% 25
26 Non-Randomized Observational Study Proportions of patients with the arrhythmia X in the two groups differ Intervention n = 1,000 No Intervention n = 1,000 CFR Deaths Total deaths 800 X( ) 200 X(+) 500 X( ) 500 X(+) 10% 50% 10% 50% Mortality 180/1,000 = 18% 300/1,000 = 30% 26
27 Randomized Experimental Study Proportions of patients with the arrhythmia X in the two groups are likely to be similar Intervention n = 1,000 No Intervention n = 1, X( ) 350 X(+) 650 X( ) 350 X(+) 10% 50% 10% 50% Deaths Total deaths Mortality 240/1,000 = 24% 240/1,000 = 24% 27
28 Randomized Experimental Study Proportions of patients with the arrhythmia X in the two groups may differ (similarity is not guaranteed) Intervention n = 1,000 No Intervention n = 1,000 CFR Deaths Total deaths 800 X( ) 200 X(+) 500 X( ) 500 X(+) 10% 50% 10% 50% Mortality 180/1,000 = 18% 300/1,000 = 30% 28
29 Stratified Randomization Stratified randomization is random assignment within groups defined by participant characteristics, such as age or disease severity, intended to ensure good balance of these factors across intervention groups 29
30 Diagram of Stratified Randomization 1,000 patients Stratify by gender 600 males 400 females Stratify by age Randomize each sub-group 360 young 240 old 300 young 100 old = 500 New treatment = 500 Current treatment 30
31 Data Collection and Documentation Treatment Assigned and received Outcomes Including beneficial and adverse effects Prognostic profile at entry Randomization procedure Method used to generate the random allocation sequence Method used to implement the random allocation Personnel who generated the allocation sequence, enrolled participants, and assigned participants to groups 31
32 Masking or Blinding Masking or blinding is used to increase the objectivity of the persons dealing with the randomized study (to prevent prejudice) Subjects who can be masked/blinded Study participants Caregivers/treaters Data collectors/assessors of outcome Data analysts Investigators Level of masking/blinding Non-blinded (open) Single Double Triple 32
33 Placebo A placebo (from the Latin for I will please ) is a medical treatment (operation, therapy, chemical solution, pill, etc.), which is administered as if it were a therapy, but which has no therapeutic value other than the placebo effect A nocebo (from the Latin for I will harm ) is treatment like a placebo but which has a harmful result Notes Available 33
34 Placebo and Blinding Results of a questionnaire on a prophylactic drug ingested by each volunteer Suspected Drug Actual drug Vitamin C Placebo Unknown Total Vitamin C Placebo Total Note: p < Source: Karlowski et al. (1975). JAMA, 231(10),
35 Placebo and Side Effects Side effect results from the Women s Health study Side Effect Aspirin Placebo P-value GI bleeding 910 (4.6%) 751 (3.8%) <0.001 Peptic ulcer 542 (2.7%) 413 (2.1%) <0.001 Hematuria 3,039 (15.2%) 2,879 (14.4%) 0.02 Easy bruising 10,561 (53%) 8,494 (42.6%) <0.001 Any report of gastric upset 11,856 (59.5%) 11,915 (59.7%) 0.59 Ridker PM, et al. (2005). A randomized trial of low dose aspirin in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in women. NEJM 352(13):
36 Compliance Compliance is the willingness of the participants to carry out the procedures according to the established protocols (adherence) Drop-outs are the participants who do not adhere to the experimental regimen during follow-up Drop-ins are the participants who do not adhere to the control regimen during follow-up 36
37 Non-Adherence during Follow-Up Randomized NSAID Placebo Refuse or cannot tolerate NSAID Require NSAID or take on their own 37
38 Data Analysis Primary: intention to treat Analyze according to original allocation Net effect of non-compliance is to reduce the observed differences Secondary: actual treatment received Based on observed data No benefit of randomization 38
39 Example of Subgroup Analysis Number of Patients Five-Year Mortality Clofibrate 1, % Placebo 2, % Canner PL, et al. (1980). Influence of adherence to treatment and response of cholesterol on mortality in the coronary drug project. N Engl J Med 303:
40 Compliance Analysis Number of Patients Five-Year Mortality Clofibrate Poor complier % Good complier % Placebo 2, % Canner PL, et al. (1980). Influence of adherence to treatment and response of cholesterol on mortality in the coronary drug project. N Engl J Med 303:
41 Compliance Analysis Number of Patients Five-Year Mortality Clofibrate Poor complier % Good complier % Placebo Poor complier % Good complier 1, % Canner PL, et al. (1980). Influence of adherence to treatment and response of cholesterol on mortality in the coronary drug project. N Engl J Med 303:
42 Dealing with Non-Compliance Monitor compliance Observe treatment directly Count pills Conduct blood or urine tests to confirm compliance Use of run-in period 42
43 Example of Run-in from the Physicians Health Study The 33,223 willing and eligible physicians were enrolled in a run-in phase during which all received active aspirin and placebo beta-carotene. After 18 weeks, participants were sent a questionnaire asking about their health status, side effects, compliance, and willingness to continue in the trial. A total of 11,152 changed their minds, reported a reason for exclusion, or did not reliably take the study pills. The remaining 22,071 physicians were then randomly assigned. 43
44 Review Define Randomization Placebo Intention to treat Drop-in and drop-out Run-in period What is the primary purpose of randomization? 44
45 Section C Types of Clinical Trials
46 Randomized Trials: Study Designs Parallel treatment or simple, non-crossover Crossover Planned crossover Unplanned crossover Factorial 46
47 Parallel Treatment or Simple, Non-Crossover Trial A Outcome Study Population Randomized B Outcome 47
48 The Hypertension Detection and Follow-Up Program Eligible by elevated DBP 22,994 Successfully randomized 10,994 Stratified randomization Stepped care 5,485 Referred care 5,455 5 years Alive Dead Alive Dead 48
49 Mortality from All Causes During the HDFP Diastolic Blood pressure at entry (Mm hg) Stepped care (SC) Referred care (RC) 5-year death rate SC RC Percent mortality reduction in SC group ,903 3, , > Total 5,485 5, Source: HDFP Cooperative Group (1982), NEJM. 307:
50 Planned Crossover Trial Randomized New Treatment Current Treatment Group 1 Group 2 Observed Group 1 Group 2 Group 2 Observed Group 1 50
51 Unplanned Crossover Trial Cardiac Bypass Surgery Study Original Study Design Randomized Surgical Care Medical Care 51
52 Reality: Unplanned Crossover Randomized Surgical Care Medical Care Refuse Surgery Require Surgery Surgery No Surgery 52
53 Factorial Design Trial Treatment B + Treatment A + Both A and B B only A only Neither A nor B 53
54 Factorial Design Trial Study of treatment A Treatment B + Treatment A + Both A and B B only A only Neither A nor B 54
55 Factorial Design Trial Study of treatment B Treatment B + Treatment A + Both A and B B only A only Neither A nor B 55
56 Objectives of the Physicians Health Study Does aspirin prevent first myocardial infarction? Does beta carotene prevent cancer? 56
57 Physicians Health Study 22,071 physicians, years old Randomly assigned in 1982 to one of four groups 1. Aspirin only (beta-carotene placebo) 2. Beta carotene only (aspirin placebo) 3. Aspirin and beta carotene 4. Neither (both placebos) 57
58 Factorial Design Used in the Physicians' Health Study Aspirin + Beta carotene + Both aspirin and beta carotene Beta carotene only Aspirin only Neither aspirin nor beta carotene 58
59 Physicians Health Study Results Randomized aspirin component terminated early on January 25, 1988, with a positive effect (44% reduction in risk of MI) Randomized beta-carotene component continued as originally scheduled and terminated on December 31, 1995, and produced neither benefit nor harm for cancer 59
60 Physicians Health Study II Physicians Health Study II (PHS II) is a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial enrolling 15,000 willing and eligible physicians aged 55 years and older PHS II will utilize a 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 factorial design to test alternate day beta carotene, alternate day vitamin E, daily vitamin C, and a daily multivitamin in the prevention of total and prostate cancer, CVD, and the age-related eye diseases (cataract and macular degeneration) Randomization began in 1997 Study is scheduled to continue until 2007 Source: Ann Epidemiol Feb;10(2):
61 Results of Randomized Trials Efficacy = reduction in risk Efficacy = Rate in placebo Rate in treated Rate in placebo = 1 Rate in treated Rate in placebo 61
62 Example of Results of a Randomized Trial From the Physicians Health Study (unadjusted result), Rate of MI in the treated group = 139/54,560 = per 100,000 per year Rate of MI in the placebo group = 239/54,355.7 = per 100,000 per year Efficacy = = = = 42.05%
63 Internal and External Validity in a Randomized Trial Reference population Study population External validity (Generalizability) R a n d o m i z e d New treatment Current treatment Internal validity 63
64 External Validity (Generalizability) Physicians Health Study Aspirin reduced the risk of MI (reduction in risk = 44%) in men 50 years or older who did not have clinical evidence of coronary disease (primary prevention) Can the findings be generalized to women? From the Women s Health study Aspirin has no significant effect on the risk of MI in women 65 years or older who did not have history of cardiovascular disease Levin R. (2005.) The puzzle of aspirin and sex. N Engl J Med 352(13)
65 Phases in Testing of New Drugs Phase I studies (clinical pharmacologic studies) Test new drug or treatment in a small group of people (20 80) for the first time to evaluate its safety Determine levels of toxicity, metabolism, pharmacological effect, and safe dosage range Identify side effects Phase II studies (efficacy studies) The drug or treatment is given to a larger group of people ( ) for efficacy and to further evaluate its safety Source: 65
66 Phases in Testing of New Drugs (II) Phase III studies (effectiveness studies) The drug or treatment is given to a large group of people (1,000 3,000) to confirm its effectiveness, compare it to commonly used treatments, and monitor side effects Phase IV studies (post-marketing clinical trials) The drug or treatment is monitored to gather more information on risks, benefits, and optimal use 66
67 Some Ethical Issues in Randomized Clinical Trials Is randomization ethical? Can truly informed consent be obtained? When can placebo be used? Under what conditions should a randomized clinical trial be stopped earlier than originally planned? 67
Comparison/Control Groups. Mary Foulkes, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Cohort Studies. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Study Designs. Simon Day, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Measures of Prognosis. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Journal Club: Niacin in Patients with Low HDL Cholesterol Levels Receiving Intensive Statin Therapy by the AIM-HIGH Investigators
 Journal Club: Niacin in Patients with Low HDL Cholesterol Levels Receiving Intensive Statin Therapy by the AIM-HIGH Investigators Shaikha Al Naimi Doctor of Pharmacy Student College of Pharmacy Qatar University
Journal Club: Niacin in Patients with Low HDL Cholesterol Levels Receiving Intensive Statin Therapy by the AIM-HIGH Investigators Shaikha Al Naimi Doctor of Pharmacy Student College of Pharmacy Qatar University
Intervention and clinical epidemiological studies
 Intervention and clinical epidemiological studies Including slides from: Barrie M. Margetts Ian L. Rouse Mathew J. Reeves,PhD Dona Schneider Tage S. Kristensen Victor J. Schoenbach Experimental / intervention
Intervention and clinical epidemiological studies Including slides from: Barrie M. Margetts Ian L. Rouse Mathew J. Reeves,PhD Dona Schneider Tage S. Kristensen Victor J. Schoenbach Experimental / intervention
Case-Control Studies. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Biostatistics and Epidemiology within the Paradigm of Public Health. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Marie Diener-West, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
The VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL)
 The VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL) JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH Principal Investigator, VITAL Brigham and Women's Hospital Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women s Health
The VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL) JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH Principal Investigator, VITAL Brigham and Women's Hospital Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women s Health
Life Tables. Marie Diener-West, PhD Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
AVOIDING BIAS AND RANDOM ERROR IN DATA ANALYSIS
 AVOIDING BIAS AND RANDOM ERROR IN DATA ANALYSIS Susan Ellenberg, Ph.D. Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine FDA Clinical Investigator Course White Oak, MD November
AVOIDING BIAS AND RANDOM ERROR IN DATA ANALYSIS Susan Ellenberg, Ph.D. Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine FDA Clinical Investigator Course White Oak, MD November
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes
 ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
If several different trials are mentioned in one publication, the data of each should be extracted in a separate data extraction form.
 General Remarks This template of a data extraction form is intended to help you to start developing your own data extraction form, it certainly has to be adapted to your specific question. Delete unnecessary
General Remarks This template of a data extraction form is intended to help you to start developing your own data extraction form, it certainly has to be adapted to your specific question. Delete unnecessary
Evaluation of Diagnostic and Screening Tests: Validity and Reliability. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Intent-to-treat Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
 Intent-to-treat Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials Michael P. LaValley Boston University http://people.bu.edu/mlava/ ACR/ARHP Annual Scientific Meeting Orlando 10/27/2003 Outline Origin of Randomization
Intent-to-treat Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials Michael P. LaValley Boston University http://people.bu.edu/mlava/ ACR/ARHP Annual Scientific Meeting Orlando 10/27/2003 Outline Origin of Randomization
Glossary of Clinical Trial Terms
 Glossary of Clinical Trial Terms ADVERSE REACTION: (Adverse Event): Also known as side effects, adverse reactions include any undesired actions or effects of the experimental drug or treatment. Experimental
Glossary of Clinical Trial Terms ADVERSE REACTION: (Adverse Event): Also known as side effects, adverse reactions include any undesired actions or effects of the experimental drug or treatment. Experimental
Ask Us About Clinical Trials
 Ask Us About Clinical Trials Clinical Trials and You. Our specialists and researchers are at the forefront of their fields and are leading the way in developing new therapies and procedures for diagnosing
Ask Us About Clinical Trials Clinical Trials and You. Our specialists and researchers are at the forefront of their fields and are leading the way in developing new therapies and procedures for diagnosing
Cost-Benefit and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Kevin Frick, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results
 Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Not All Clinical Trials Are Created Equal Understanding the Different Phases
 Not All Clinical Trials Are Created Equal Understanding the Different Phases This chapter will help you understand the differences between the various clinical trial phases and how these differences impact
Not All Clinical Trials Are Created Equal Understanding the Different Phases This chapter will help you understand the differences between the various clinical trial phases and how these differences impact
Apixaban Plus Mono vs. Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndromes: Insights from the APPRAISE-2 Trial
 Apixaban Plus Mono vs. Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndromes: Insights from the APPRAISE-2 Trial Connie N. Hess, MD, MHS, Stefan James, MD, PhD, Renato D. Lopes, MD, PhD, Daniel M. Wojdyla,
Apixaban Plus Mono vs. Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndromes: Insights from the APPRAISE-2 Trial Connie N. Hess, MD, MHS, Stefan James, MD, PhD, Renato D. Lopes, MD, PhD, Daniel M. Wojdyla,
Clinical Study Design and Methods Terminology
 Home College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University WSU Faculty &Staff Page Page 1 of 5 John Gay, DVM PhD DACVPM AAHP FDIU VCS Clinical Epidemiology & Evidence-Based Medicine Glossary: Clinical
Home College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University WSU Faculty &Staff Page Page 1 of 5 John Gay, DVM PhD DACVPM AAHP FDIU VCS Clinical Epidemiology & Evidence-Based Medicine Glossary: Clinical
Articles Presented. Journal Presentation. Dr Albert Lo. Dr Albert Lo
 * This presentation is prepared by the author in one s personal capacity for the purpose of academic exchange and does not represent the views of his/her organisations on the topic discussed. Journal Presentation
* This presentation is prepared by the author in one s personal capacity for the purpose of academic exchange and does not represent the views of his/her organisations on the topic discussed. Journal Presentation
Introduction to study design
 Introduction to study design Doug Altman EQUATOR Network, Centre for Statistics in Medicine, NDORMS, University of Oxford EQUATOR OUCAGS training course 4 October 2014 Objectives of the day To understand
Introduction to study design Doug Altman EQUATOR Network, Centre for Statistics in Medicine, NDORMS, University of Oxford EQUATOR OUCAGS training course 4 October 2014 Objectives of the day To understand
University of Hawai i Human Studies Program. Guidelines for Developing a Clinical Research Protocol
 University of Hawai i Human Studies Program Guidelines for Developing a Clinical Research Protocol Following are guidelines for writing a clinical research protocol for submission to the University of
University of Hawai i Human Studies Program Guidelines for Developing a Clinical Research Protocol Following are guidelines for writing a clinical research protocol for submission to the University of
Participating in Alzheimer s Disease Clinical Trials and Studies
 Participating in Alzheimer s Disease Clinical Trials and Studies FACT SHEET When Margaret was diagnosed with earlystage Alzheimer s disease at age 68, she wanted to do everything possible to combat the
Participating in Alzheimer s Disease Clinical Trials and Studies FACT SHEET When Margaret was diagnosed with earlystage Alzheimer s disease at age 68, she wanted to do everything possible to combat the
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #317: Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for High Blood Pressure and Follow-Up Documented National Quality Strategy Domain: Community / Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #317: Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for High Blood Pressure and Follow-Up Documented National Quality Strategy Domain: Community / Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Research on Research: Learning about Phase 1 Trials
 CLINICAL CASE STUDY SERIES Research on Research: Learning about Phase 1 Trials Phases of clinical trial investigation are described in some detail in the Code of Federal Regulations. Phase 1 is described
CLINICAL CASE STUDY SERIES Research on Research: Learning about Phase 1 Trials Phases of clinical trial investigation are described in some detail in the Code of Federal Regulations. Phase 1 is described
Efficacy, safety and preference study of a insulin pen PDS290 vs. a Novo Nordisk marketed insulin pen in diabetics
 Efficacy, safety and preference study of a insulin pen PDS290 vs. a Novo Nordisk marketed insulin pen in diabetics This trial is conducted in the United States of America (USA). The aim of this clinical
Efficacy, safety and preference study of a insulin pen PDS290 vs. a Novo Nordisk marketed insulin pen in diabetics This trial is conducted in the United States of America (USA). The aim of this clinical
Sponsor. Novartis Generic Drug Name. Vildagliptin. Therapeutic Area of Trial. Type 2 diabetes. Approved Indication. Investigational.
 Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Vildagliptin Therapeutic Area of Trial Type 2 diabetes Approved Indication Investigational Study Number CLAF237A2386 Title A single-center,
Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Vildagliptin Therapeutic Area of Trial Type 2 diabetes Approved Indication Investigational Study Number CLAF237A2386 Title A single-center,
Rapid Critical Appraisal of Controlled Trials
 Rapid Critical Appraisal of Controlled Trials Carl Heneghan Dept of Primary Health Care University of Oxford November 23rd 2009 Five steps in EBM 1. Formulate an answerable question 2. Track down the best
Rapid Critical Appraisal of Controlled Trials Carl Heneghan Dept of Primary Health Care University of Oxford November 23rd 2009 Five steps in EBM 1. Formulate an answerable question 2. Track down the best
Aspirin to Prevent Heart Attack and Stroke: What s the Right Dose?
 The American Journal of Medicine (2006) 119, 198-202 REVIEW Aspirin to Prevent Heart Attack and Stroke: What s the Right Dose? James E. Dalen, MD, MPH Professor Emeritus, University of Arizona, Tucson
The American Journal of Medicine (2006) 119, 198-202 REVIEW Aspirin to Prevent Heart Attack and Stroke: What s the Right Dose? James E. Dalen, MD, MPH Professor Emeritus, University of Arizona, Tucson
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
 Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Research Rationale 1. What does PrEP stand for? There is scientific evidence that antiretroviral (anti-hiv) medications may be able to play an important role in reducing
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Research Rationale 1. What does PrEP stand for? There is scientific evidence that antiretroviral (anti-hiv) medications may be able to play an important role in reducing
Biostat Methods STAT 5820/6910 Handout #6: Intro. to Clinical Trials (Matthews text)
 Biostat Methods STAT 5820/6910 Handout #6: Intro. to Clinical Trials (Matthews text) Key features of RCT (randomized controlled trial) One group (treatment) receives its treatment at the same time another
Biostat Methods STAT 5820/6910 Handout #6: Intro. to Clinical Trials (Matthews text) Key features of RCT (randomized controlled trial) One group (treatment) receives its treatment at the same time another
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, MD 21244
 March 7, 2014 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, MD 21244 Re: Dear Sir or Madam: On behalf of the American Heart Association (AHA), including the American Stroke
March 7, 2014 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, MD 21244 Re: Dear Sir or Madam: On behalf of the American Heart Association (AHA), including the American Stroke
"Statistical methods are objective methods by which group trends are abstracted from observations on many separate individuals." 1
 BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY / 3 CHAPTER ONE BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY "Statistical methods are objective methods by which group trends are abstracted from observations on many separate individuals." 1 Medicine
BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY / 3 CHAPTER ONE BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY "Statistical methods are objective methods by which group trends are abstracted from observations on many separate individuals." 1 Medicine
Atrial Fibrillation, Chronic - Antithrombotic Treatment - OBSOLETE
 Atrial Fibrillation, Chronic - Antithrombotic Treatment - OBSOLETE Clinical practice guidelines serve as an educational reference, and do not supersede the clinical judgment of the treating physician with
Atrial Fibrillation, Chronic - Antithrombotic Treatment - OBSOLETE Clinical practice guidelines serve as an educational reference, and do not supersede the clinical judgment of the treating physician with
Analysis Issues II. Mary Foulkes, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
An Introduction to Medication Adherence
 An Introduction to Medication Adherence Medication Adherence Project (MAP) A project of the Cardiovascular Prevention & Control Program and the Fund for Public Health in New York Drugs don t work in patients
An Introduction to Medication Adherence Medication Adherence Project (MAP) A project of the Cardiovascular Prevention & Control Program and the Fund for Public Health in New York Drugs don t work in patients
The Clinical Trials Process an educated patient s guide
 The Clinical Trials Process an educated patient s guide Gwen L. Nichols, MD Site Head, Oncology Roche TCRC, Translational and Clinical Research Center New York DISCLAIMER I am an employee of Hoffmann-
The Clinical Trials Process an educated patient s guide Gwen L. Nichols, MD Site Head, Oncology Roche TCRC, Translational and Clinical Research Center New York DISCLAIMER I am an employee of Hoffmann-
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain
 P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
Laurie Shaker-Irwin, Ph.D., M.S. Co-Leader, Regulatory Knowledge and Research Ethics UCLA Clinical and Translational Science Institute
 Laurie Shaker-Irwin, Ph.D., M.S. Co-Leader, Regulatory Knowledge and Research Ethics UCLA Clinical and Translational Science Institute Understand the protocol completely Recognize institutional polices
Laurie Shaker-Irwin, Ph.D., M.S. Co-Leader, Regulatory Knowledge and Research Ethics UCLA Clinical and Translational Science Institute Understand the protocol completely Recognize institutional polices
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CLINICAL TRIALS E8
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CLINICAL TRIALS E8 Current
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CLINICAL TRIALS E8 Current
CHOICE OF CONTROL GROUP AND RELATED ISSUES IN CLINICAL TRIALS E10
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE CHOICE OF CONTROL GROUP AND RELATED ISSUES IN CLINICAL
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE CHOICE OF CONTROL GROUP AND RELATED ISSUES IN CLINICAL
Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial Marcus R. Pereira A. Study Purpose Hepatic encephalopathy is a common complication
Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial Marcus R. Pereira A. Study Purpose Hepatic encephalopathy is a common complication
Novel Trial Designs in T2D to Satisfy Regulatory Requirements for CV Safety
 Novel Trial Designs in T2D to Satisfy Regulatory Requirements for CV Safety Anders Svensson MD, PhD Head of Global Clinical Development Metabolism, F Hoffmann LaRoche Ltd. Basel, Switzerland Overview of
Novel Trial Designs in T2D to Satisfy Regulatory Requirements for CV Safety Anders Svensson MD, PhD Head of Global Clinical Development Metabolism, F Hoffmann LaRoche Ltd. Basel, Switzerland Overview of
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
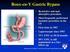 Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
The largest clinical study of Bayer's Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Wednesday, 14 November 2012 07:38
 Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
TAKING PART IN CANCER TREATMENT RESEARCH STUDIES
 For more infomation about Cancer Clinical Trials at Upstate Cancer Center please call Upstate Connect 1.800.464.8668 TAKING PART IN CANCER TREATMENT RESEARCH STUDIES Information provided by: National Cancer
For more infomation about Cancer Clinical Trials at Upstate Cancer Center please call Upstate Connect 1.800.464.8668 TAKING PART IN CANCER TREATMENT RESEARCH STUDIES Information provided by: National Cancer
Measure #257 (NQF 1519): Statin Therapy at Discharge after Lower Extremity Bypass (LEB) National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #257 (NQF 1519): Statin Therapy at Discharge after Lower Extremity Bypass (LEB) National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
Measure #257 (NQF 1519): Statin Therapy at Discharge after Lower Extremity Bypass (LEB) National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
MANAGEMENT OF LIPID DISORDERS: IMPLICATIONS OF THE NEW GUIDELINES
 MANAGEMENT OF LIPID DISORDERS: IMPLICATIONS OF THE NEW GUIDELINES Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and Associate Dean UCSF School of Medicine Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of interest EXPLAINING
MANAGEMENT OF LIPID DISORDERS: IMPLICATIONS OF THE NEW GUIDELINES Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and Associate Dean UCSF School of Medicine Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of interest EXPLAINING
DUAL ANTIPLATELET THERAPY. Dr Robert S Mvungi, MD(Dar), Mmed (Wits) FCP(SA), Cert.Cardio(SA) Phy Tanzania Cardiac Society Dar es Salaam Tanzania
 DUAL ANTIPLATELET THERAPY Dr Robert S Mvungi, MD(Dar), Mmed (Wits) FCP(SA), Cert.Cardio(SA) Phy Tanzania Cardiac Society Dar es Salaam Tanzania DUAL ANTIPLATELET THERAPY (DAPT) Dual antiplatelet regimen
DUAL ANTIPLATELET THERAPY Dr Robert S Mvungi, MD(Dar), Mmed (Wits) FCP(SA), Cert.Cardio(SA) Phy Tanzania Cardiac Society Dar es Salaam Tanzania DUAL ANTIPLATELET THERAPY (DAPT) Dual antiplatelet regimen
CLINICAL RESEARCH PROTOCOL CHECKLIST
 CLINICAL RESEARCH PROTOCOL CHECKLIST [taken from ICH GCP : Guidance for Industry, Good Clinical Practice: Consolidated Guidance, Revision 1 (R1) June 1996] ICH GCP, Section 6. CLINICAL TRIAL PROTOCOL AND
CLINICAL RESEARCH PROTOCOL CHECKLIST [taken from ICH GCP : Guidance for Industry, Good Clinical Practice: Consolidated Guidance, Revision 1 (R1) June 1996] ICH GCP, Section 6. CLINICAL TRIAL PROTOCOL AND
Glossary of Methodologic Terms
 Glossary of Methodologic Terms Before-After Trial: Investigation of therapeutic alternatives in which individuals of 1 period and under a single treatment are compared with individuals at a subsequent
Glossary of Methodologic Terms Before-After Trial: Investigation of therapeutic alternatives in which individuals of 1 period and under a single treatment are compared with individuals at a subsequent
Diabetes Complications
 Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
Sponsor Novartis Pharmaceuticals
 Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Pharmaceuticals Generic Drug Name Indacaterol Therapeutic Area of Trial Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Indication studied: COPD Study
Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Pharmaceuticals Generic Drug Name Indacaterol Therapeutic Area of Trial Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Indication studied: COPD Study
Bios 6648: Design & conduct of clinical research
 Bios 6648: Design & conduct of clinical research Section 1 - Specifying the study setting and objectives 1. Specifying the study setting and objectives 1.0 Background Where will we end up?: (a) The treatment
Bios 6648: Design & conduct of clinical research Section 1 - Specifying the study setting and objectives 1. Specifying the study setting and objectives 1.0 Background Where will we end up?: (a) The treatment
THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT
 THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Gregory Albers, M.D. Director Stanford Stroke Center Professor of Neurology and Neurological
THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Gregory Albers, M.D. Director Stanford Stroke Center Professor of Neurology and Neurological
AP Stats- Mrs. Daniel Chapter 4 MC Practice
 AP Stats- Mrs. Daniel Chapter 4 MC Practice Name: 1. Archaeologists plan to examine a sample of 2-meter-square plots near an ancient Greek city for artifacts visible in the ground. They choose separate
AP Stats- Mrs. Daniel Chapter 4 MC Practice Name: 1. Archaeologists plan to examine a sample of 2-meter-square plots near an ancient Greek city for artifacts visible in the ground. They choose separate
What is a P-value? Ronald A. Thisted, PhD Departments of Statistics and Health Studies The University of Chicago
 What is a P-value? Ronald A. Thisted, PhD Departments of Statistics and Health Studies The University of Chicago 8 June 1998, Corrections 14 February 2010 Abstract Results favoring one treatment over another
What is a P-value? Ronald A. Thisted, PhD Departments of Statistics and Health Studies The University of Chicago 8 June 1998, Corrections 14 February 2010 Abstract Results favoring one treatment over another
ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES
 ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES FAST FACTS Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a novel, oral direct Factor Xa inhibitor. On September 30, 2008, the European Commission granted marketing approval for Xarelto for the
ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES FAST FACTS Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a novel, oral direct Factor Xa inhibitor. On September 30, 2008, the European Commission granted marketing approval for Xarelto for the
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication. Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South
 Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Measure #236 (NQF 0018): Controlling High Blood Pressure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #236 (NQF 0018): Controlling High Blood Pressure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage of patients
Measure #236 (NQF 0018): Controlling High Blood Pressure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage of patients
Paper PO06. Randomization in Clinical Trial Studies
 Paper PO06 Randomization in Clinical Trial Studies David Shen, WCI, Inc. Zaizai Lu, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals ABSTRACT Randomization is of central importance in clinical trials. It prevents selection
Paper PO06 Randomization in Clinical Trial Studies David Shen, WCI, Inc. Zaizai Lu, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals ABSTRACT Randomization is of central importance in clinical trials. It prevents selection
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D.
 Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center on behalf of the REAL-LATE and the ZEST-LATE trial
 Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Drug-Eluting Stent Implantation A Pooled Analysis of the REAL-LATE and the ZEST-LATE Trial Seung-Jung Park MD PhD Seung-Jung Park, MD, PhD, University of Ulsan
Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Drug-Eluting Stent Implantation A Pooled Analysis of the REAL-LATE and the ZEST-LATE Trial Seung-Jung Park MD PhD Seung-Jung Park, MD, PhD, University of Ulsan
Long term anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation at high risk of stroke: a new scenario after RE-LY trial
 Long term anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation at high risk of stroke: a new scenario after RE-LY trial Camillo Autore Università di Roma Sapienza II Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia
Long term anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation at high risk of stroke: a new scenario after RE-LY trial Camillo Autore Università di Roma Sapienza II Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia
Randomized trials versus observational studies
 Randomized trials versus observational studies The case of postmenopausal hormone therapy and heart disease Miguel Hernán Harvard School of Public Health www.hsph.harvard.edu/causal Joint work with James
Randomized trials versus observational studies The case of postmenopausal hormone therapy and heart disease Miguel Hernán Harvard School of Public Health www.hsph.harvard.edu/causal Joint work with James
Achieving Quality and Value in Chronic Care Management
 The Burden of Chronic Disease One of the greatest burdens on the US healthcare system is the rapidly growing rate of chronic disease. These statistics illustrate the scope of the problem: Nearly half of
The Burden of Chronic Disease One of the greatest burdens on the US healthcare system is the rapidly growing rate of chronic disease. These statistics illustrate the scope of the problem: Nearly half of
ThinkTwice! Treating Alcohol Dependence with Topiramate: A Critical Appraisal Learning Activity JOURNAL ARTICLE TEI PLAIN LANGUAGE ANTHOLOGY
 JOURNAL ARTICLE Transformed into part of a plain language anthology Treating Alcohol Dependence with Topiramate: A Critical Appraisal Learning Activity Abstract: This study set out to test a drug, topiramate,
JOURNAL ARTICLE Transformed into part of a plain language anthology Treating Alcohol Dependence with Topiramate: A Critical Appraisal Learning Activity Abstract: This study set out to test a drug, topiramate,
Clinical Trial Design. Sponsored by Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute
 Clinical Trial Design Sponsored by Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute Overview Clinical research is research conducted on human beings (or on material of human origin such as tissues,
Clinical Trial Design Sponsored by Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute Overview Clinical research is research conducted on human beings (or on material of human origin such as tissues,
Priority Program Translational Oncology Applicants' Guidelines
 Stiftung Deutsche Krebshilfe Dr. h.c. Fritz Pleitgen Präsident Spendenkonto Kreissparkasse Köln IBAN DE65 3705 0299 0000 9191 91 BIC COKSDE33XXX Priority Program Translational Oncology Applicants' Guidelines
Stiftung Deutsche Krebshilfe Dr. h.c. Fritz Pleitgen Präsident Spendenkonto Kreissparkasse Köln IBAN DE65 3705 0299 0000 9191 91 BIC COKSDE33XXX Priority Program Translational Oncology Applicants' Guidelines
chapter 1 Chapter 2 chapter 3
 SUMMARY summary Theaimofthisthesiswastodescribethedevelopmentandevaluationofanindividual basedlifestyleinterventionamongworkersintheconstructionindustrywithanelevated risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
SUMMARY summary Theaimofthisthesiswastodescribethedevelopmentandevaluationofanindividual basedlifestyleinterventionamongworkersintheconstructionindustrywithanelevated risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Chapter 3. Sampling. Sampling Methods
 Oxford University Press Chapter 3 40 Sampling Resources are always limited. It is usually not possible nor necessary for the researcher to study an entire target population of subjects. Most medical research
Oxford University Press Chapter 3 40 Sampling Resources are always limited. It is usually not possible nor necessary for the researcher to study an entire target population of subjects. Most medical research
Study Design and Statistical Analysis
 Study Design and Statistical Analysis Anny H Xiang, PhD Department of Preventive Medicine University of Southern California Outline Designing Clinical Research Studies Statistical Data Analysis Designing
Study Design and Statistical Analysis Anny H Xiang, PhD Department of Preventive Medicine University of Southern California Outline Designing Clinical Research Studies Statistical Data Analysis Designing
National Cancer Institute
 National Cancer Institute Taking Part in Cancer Treatment Research Studies U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Taking Part in Cancer Treatment Research Studies If
National Cancer Institute Taking Part in Cancer Treatment Research Studies U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Taking Part in Cancer Treatment Research Studies If
Design and Analysis of Phase III Clinical Trials
 Cancer Biostatistics Center, Biostatistics Shared Resource, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine June 19, 2008 Outline 1 Phases of Clinical Trials 2 3 4 5 6 Phase I Trials: Safety, Dosage Range, and
Cancer Biostatistics Center, Biostatistics Shared Resource, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine June 19, 2008 Outline 1 Phases of Clinical Trials 2 3 4 5 6 Phase I Trials: Safety, Dosage Range, and
Clinical Trials: The Crux of Cancer Innovation
 Clinical Trials: The Crux of Cancer Innovation Even as medical science is transforming cancer care, major deficiencies in the way cancer clinical trials are designed, carried out, regulated and funded
Clinical Trials: The Crux of Cancer Innovation Even as medical science is transforming cancer care, major deficiencies in the way cancer clinical trials are designed, carried out, regulated and funded
Series 1 Case Studies Adverse Events that Represent Unanticipated Problems: Reporting Required
 Welcome! This document contains three (3) series of Case Study examples that will demonstrate all four OHSU reporting categories (#1 4) as well as examples of events that are considered not reportable.
Welcome! This document contains three (3) series of Case Study examples that will demonstrate all four OHSU reporting categories (#1 4) as well as examples of events that are considered not reportable.
ICH Topic E 8 General Considerations for Clinical Trials. Step 5 NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CLINICAL TRIALS (CPMP/ICH/291/95)
 European Medicines Agency March 1998 CPMP/ICH/291/95 ICH Topic E 8 General Considerations for Clinical Trials Step 5 NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CLINICAL TRIALS (CPMP/ICH/291/95) TRANSMISSION
European Medicines Agency March 1998 CPMP/ICH/291/95 ICH Topic E 8 General Considerations for Clinical Trials Step 5 NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CLINICAL TRIALS (CPMP/ICH/291/95) TRANSMISSION
Sponsor Novartis. Generic Drug Name Secukinumab. Therapeutic Area of Trial Psoriasis. Approved Indication investigational
 Clinical Trial Results Database Page 2 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Secukinumab Therapeutic Area of Trial Psoriasis Approved Indication investigational Clinical Trial Results Database Page 3 Study
Clinical Trial Results Database Page 2 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Secukinumab Therapeutic Area of Trial Psoriasis Approved Indication investigational Clinical Trial Results Database Page 3 Study
4/4/2013. Mike Rizo, Pharm D, MBA, ABAAHP THE PHARMACIST OF THE FUTURE? METABOLIC SYNDROME AN INTEGRATIVE APPROACH
 METABOLIC SYNDROME AN INTEGRATIVE APPROACH AN OPPORTUNITY FOR PHARMACISTS TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE Mike Rizo, Pharm D, MBA, ABAAHP THE EVOLUTION OF THE PHARMACIST 1920s 1960s 2000s THE PHARMACIST OF THE FUTURE?
METABOLIC SYNDROME AN INTEGRATIVE APPROACH AN OPPORTUNITY FOR PHARMACISTS TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE Mike Rizo, Pharm D, MBA, ABAAHP THE EVOLUTION OF THE PHARMACIST 1920s 1960s 2000s THE PHARMACIST OF THE FUTURE?
Survey Research: Choice of Instrument, Sample. Lynda Burton, ScD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
FULL COVERAGE FOR PREVENTIVE MEDICATIONS AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IMPACT ON RACIAL AND ETHNIC DISPARITIES
 FULL COVERAGE FOR PREVENTIVE MEDICATIONS AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IMPACT ON RACIAL AND ETHNIC DISPARITIES Niteesh K. Choudhry, MD, PhD Harvard Medical School Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics
FULL COVERAGE FOR PREVENTIVE MEDICATIONS AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IMPACT ON RACIAL AND ETHNIC DISPARITIES Niteesh K. Choudhry, MD, PhD Harvard Medical School Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Stenting
 Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Stenting C. DEAN KATSAMAKIS, DO, FACC, FSCAI INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGIST ADVOCATE LUTHERAN GENERAL HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION Coronary artery stents are
Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Stenting C. DEAN KATSAMAKIS, DO, FACC, FSCAI INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGIST ADVOCATE LUTHERAN GENERAL HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION Coronary artery stents are
Preventive Care Guideline for Asymptomatic Elderly Patients Age 65 and Over
 Preventive Care Guideline for Asymptomatic Elderly Patients Age 65 and Over 1. BMI - Documented in patients medical record on an annual basis up to age 74. Screen for obesity and offer counseling to encourage
Preventive Care Guideline for Asymptomatic Elderly Patients Age 65 and Over 1. BMI - Documented in patients medical record on an annual basis up to age 74. Screen for obesity and offer counseling to encourage
PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR BIOSTATISTICS
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR BIOSTATISTICS BIOSTATISTICS DESCRIBING DATA, THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION 1. The duration of time from first exposure to HIV infection to AIDS diagnosis is called the incubation period.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR BIOSTATISTICS BIOSTATISTICS DESCRIBING DATA, THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION 1. The duration of time from first exposure to HIV infection to AIDS diagnosis is called the incubation period.
The Women s Health Initiative: The Role of Hormonal Therapy in Disease Prevention
 The Women s Health Initiative: The Role of Hormonal Therapy in Disease Prevention Robert B. Wallace, MD, MSc Departments of Epidemiology and Internal Medicine University of Iowa College of Public Health
The Women s Health Initiative: The Role of Hormonal Therapy in Disease Prevention Robert B. Wallace, MD, MSc Departments of Epidemiology and Internal Medicine University of Iowa College of Public Health
Dual Antiplatelet Therapy. Stephen Monroe, MD FACC Chattanooga Heart Institute
 Dual Antiplatelet Therapy Stephen Monroe, MD FACC Chattanooga Heart Institute Scope of Talk Identify the antiplatelet drugs and their mechanisms of action Review dual antiplatelet therapy in: The medical
Dual Antiplatelet Therapy Stephen Monroe, MD FACC Chattanooga Heart Institute Scope of Talk Identify the antiplatelet drugs and their mechanisms of action Review dual antiplatelet therapy in: The medical
Chapter 6. Examples (details given in class) Who is Measured: Units, Subjects, Participants. Research Studies to Detect Relationships
 Announcements: Midterm Friday. Bring calculator and one sheet of notes. Can t use the calculator on your cell phone. Assigned seats, random ID check. Review Wed. Review sheet posted on website. Fri discussion
Announcements: Midterm Friday. Bring calculator and one sheet of notes. Can t use the calculator on your cell phone. Assigned seats, random ID check. Review Wed. Review sheet posted on website. Fri discussion
Critical Appraisal of Article on Therapy
 Critical Appraisal of Article on Therapy What question did the study ask? Guide Are the results Valid 1. Was the assignment of patients to treatments randomized? And was the randomization list concealed?
Critical Appraisal of Article on Therapy What question did the study ask? Guide Are the results Valid 1. Was the assignment of patients to treatments randomized? And was the randomization list concealed?
Summary HTA. HTA-Report Summary. Introduction
 Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Antioxidative vitamines for prevention of cardiovascular disease for patients after renal transplantation and patients with chronic renal failure Schnell-Inderst P, Kossmann
Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Antioxidative vitamines for prevention of cardiovascular disease for patients after renal transplantation and patients with chronic renal failure Schnell-Inderst P, Kossmann
AVAILABILITY AND ACCESSIBILITY OF CARDIAC REHABILITATION SERVICES IN LOW- AND MIDDLE-INCOME COUNTRIES QUESTIONNAIRE
 AVAILABILITY AND ACCESSIBILITY OF CARDIAC REHABILITATION SERVICES IN LOW- AND MIDDLE-INCOME COUNTRIES QUESTIONNAIRE To be completed by Staff Cardiologists at an adult cardiac institute/department. INSTRUCTIONS:
AVAILABILITY AND ACCESSIBILITY OF CARDIAC REHABILITATION SERVICES IN LOW- AND MIDDLE-INCOME COUNTRIES QUESTIONNAIRE To be completed by Staff Cardiologists at an adult cardiac institute/department. INSTRUCTIONS:
