Key words: CRM, Systems Implementation, Relationship Marketing
|
|
|
- Carmella Randall
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IS 470 Literature Review Customer Relationship Management Systems Implementation 1. Introduction Systems implementation, in general, is one of the most widely discussed topics in IS academic literature and could be easily named one of the core areas of interests from both academic and practical perspectives. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system, however, is relatively new type of business process automation that deserves a closer look at arising issues and risks related to the implementation of the system. Current review is conducted to answer the following main question of What are the main issues and concerns discussed in academic articles in relation to CRM systems implementation? In this paper first, attempt was made to distinguish the CRM systems from other information systems. A broader view of issues and risks that can be related to the CRM implementation are presented afterwards, without concentrating on any of three major perspectives of CRM implementation. These perspectives are discussed separately later. Starting with economic perspective, where CRM is presented as a tool to measure and increase customer profitability and life time value, we further move towards social and organizational side of CRM implementation bringing social exchange theory and resistance factors, and then follow to technological aspects of CRM implementation that is discussed in the literature. Finally, for more visible and practical discussion of CRM systems implementation the paper concludes with review of industry specific articles. Key words: CRM, Systems Implementation, Relationship Marketing 1
2 2. Challenging CRM: from relationship marketing, through data mining and towards calculating profits IS CRM ANY DIFFERENT FROM OTHER IS? Most of the academics discussing CRM Systems Implementation were inspired with several researches that prove low percentage of successful CRM implementation cases. Bygstad, for example, draws on Tafti, (2002) research that revealed 70% failure rate of CRM projects, as did Bull 2003 citing Giga,(2001) research. On the other hand statistics show growing expenditures on corporate CRM and big growth rate of CRM software sales (Bull 2003, Rigby, 2004). It should be noted however that CRM implementation has certain specifics and differences compared to other IS implementation. Parties and Politics Citing Marble (2000) paper that suggests an implied dynamic between user function and IS function as two main parties engaged in IS implementation, Corner and Hinton (2002) argue that, at least, in CRM system implementation dynamic is much more complex and engage other parties, such as extra-company contributors and project managers. These extra parties, in tandem with higher sensitivity of organizational politics surrounding sales and marketing or customerservice systems, require consideration of new risks, resulting from this complexity. (Corner and Hinton, 2002) Non Standard Activities Gefen (2002) add to this complexity by comparing CRM to ERP systems and arguing that customer relationship activities are not as standardized as other business activities, such as accounting or procurement. Hence CRM implementation calls for much more complex and flexible approach. (Gefen, 2002). Privacy Another specifics of CRM that is brought forward by Rygielski, Wang and Yen (2002), calls for increased responsibility by CRM implementers in terms of privacy rights. The authors urge 2
3 implementers to balance between respect towards the privacy of consumers and economic gains from using CRM and establish privacy policy to make sure the CRM doesn t gain opposite results. (Rygielski, Wang and Yen, 2002) Diversity of Users The diversity of users in CRM systems implementation is also emphasized by Fjermestad and Romano (2003), who claim that compared to homogeneous users of other traditional information systems, users of CRM may include all levels of management, permanent and temporary field customer service representatives and customers themselves. Hence the CRM should be designed to cross much more organizational boundaries and contain broader functionalities that would be used by both known and unknown users. (Fjermestad and Romano, 2003) CRM IMLEMENTATION RISKS In a hope to help practitioners to adopt better implementation procedures, Corner and Hinton build their idea by examining eight sets of CRM specific implementation risks asserted by Hewson and McAlpine (1999), differing them from other IS implementations. Hewson and McAlpine (1999) present 25 risks grouped in eight sets that cover quite wide range of aspects of IS implementation including users, processes, speed of change, politics, need for mobility and need for change, funding and reliance on methodology. The case study that Corner and Hinton (2002) used to examine the theoretical risks is based on a software developer company that adopted and used CRM. The paper however concludes that most of the risks mentioned by Hewson and McAlpine were not viable and that other areas need to be examined that can undermine the CRM implementation process as well as, need to discover how various risk categories may impact each other. (Corner, Hinton 2002) The paper also provides with quite valuable insight into technological, economic and organizational risks to be considered while implementing a CRM system, however its controversial conclusion leaves little hope for usage by practitioners as most of the risks 3
4 appeared to be not viable and specific for only CRM systems and risk categories listed are claimed to be inexhaustible BUSINESS BEFORE TECHNOLOGY Quite simple approach is presented by Rigby (2004), who emphasizes various aspects of CRM implementation through offering the management of CRM adopting companies to answer four basic questions: 1. Is it strategic? Claiming that only the processes that are key to ensure the competitiveness of an organization need to be addressed through CRM implementation. 2. Where does it hurt? Offering to look closer at customer relationship cycle and choose from many phases, the ones that mostly harm the entire cycle. 3. Do we need a perfect data? Arguing that only areas that require highly perfect data should be considered first of all, as perfect data generation and dissemination is an expensive process. 4. Were do we go from here? Bringing practitioners attention to how the data generated by the CRM can be consequently used to extend the capacity and ''power'' of technology to improve other business areas and processes. By suggesting to put business thinking before technological issues and based on the notion of customer relationship cycle Rigby (2004) provides a good material for thought to CRM adopters. Customer Profitability This ''business before technology'' (Rigby, 2004) approach is also explicit in Bull's (2003) discussion of ''CRM Implementation Strategic Issues'', where the author clearly distinguishes between transaction customers and relationship customers and calls the CRM to be an important tool for identification of right customer groups, based on their profitability. Bull's (2004) paper also uses a case study to demonstrate how miscommunication among management, IT and marketing staff, lack of engagement and empowerment of certain employees, led to 4
5 failure in addressing issues related to targeting the customer as the most important problem the new CRM was intended to solve. Customer Lifetime Value Business composite of CRM implementation proved to be useful also in papers, where the authors came up with a model of classifying customers based on their value and loyalty. For example Gurau, Ranchhold and Hackney, (2003) argue that technology can be used to define detailed customer profile based on their value and loyalty. However, proper advantage needs to be taken of the data insight that may require significant changes in organizational processes. The Gurau s (2003) paper uses Conway and Fitzpatrick (1999) relationship equity matrix presented in Figure 1, to categorize the customer groups based on their value and loyalty and to demonstrate where the technology can be useful to transform customers from one group to another to increase the profitability of the business and decrease costs where possible. Thus, Gurau, Ranchhold and Hackney (2003), being more concerned with strategic planning and customer-centric approach that organizations need to follow for success in CRM implementation, ground most of their arguments for evaluating CRM efficiency from economic perspective. According to them effective CRM should give precise understanding of customer cost and revenue generation and one of the overarching aims of technology enabled CRM should be customer segmentation based on their lifetime value. (Gurau, Ranchhold and Hackney, 2003) High Value Disloyal Customer A At risk Customer C Marginal Value Customer B Profitable Loyal Customer D Over Service Low Value FIGURE 1. Relationship equity matrix Conway and Fitzpatrick (1999) 5
6 Relational Economic Benefits Relational benefits to services industries through effective relationship management suggested by Panda (2003) span from predictable sales and hence, profits, to generation of new business through sharing positive opinions and recommendations. On the other hand, customers should also feel benefits from entering a relationship with a company. In addition to security and comfort the customers would also seek economic benefits expressed in special discounts, rewarding for their loyalty, as well as time savings, and special treatment by company front line staff. And these customer expectations that are very difficult to manage, should be properly studied and reflected in company s approach towards service delivery and product quality. Panda (2002) suggests that many organizations fail to do so only because of technology involvement the CRM implementation is perceived mainly as a technological exercise rather than a strategic goal. (Panda, 2002) 2.4. ORGANIZATION AND PEOPLE AROUND CRM An interesting organizational and social perspective of CRM systems implementation is discussed by Gefen (2002) where he attempts to extend finding of his previous research of Enterprise Resource Planning, to CRM systems implementation. As with ERP, here the author again examines the CRM system adoption against perceived responsiveness, cooperative intentions and configuration correctness. (Gefen, 2002) By grounding his arguments on the Social Exchange Theory, Gefen (2002) describes the implementation process as an exchange of intangible values. Because there are no specific rules and regulations, against which the success of the CRM implementation can be assessed, as in case with economic exchange, social exchange heavily relies on cooperation and perception of responsiveness of the CRM implementing team. In other words, the users are more likely to willingly adopt and appreciate the value of a system if the process of development of CRM application was a harmonic cooperation and the software developer demonstrated increased responsiveness both in term of configuring the software and helping the users to overcome general problems and bugs during system introduction. (Gefen, 2002) 6
7 The practical implications discussed by Gefen (2002) contain mainly controlling elements that managers of software companies may use to increase acceptance and adoption of the CRM by users. (Gefen, 2002). Usability and Resistance Another set of issues in organizational dimension are related to resistance and usability of the systems presented by Fjermestad and Romano (2003). The authors revisit three basic theories of resistance, introduced by Markus (1983), to apply them to CRM systems. These theories are People determined theory, System determined theory and Interaction theory. While people determined theory is putting forward people s general resistance to change, systems resistance theory mainly develops on the idea of the features of the system or certain application. The third, Interaction theory tries to balance the previous two technological and human polarities of resistance by acknowledging the possibility of both the social context and design features to be the reason for resistance. (Fjermestad and Romano, 2003). Usability issues of the ecrm system implementation suggested by Fjermestad and Romano (2003), are based on Nielsen s (1992) usability engineering life cycle that discusses various ways and issues the designers and system implementation managers should consider during predesign, design and post-design stages. User involvement and their assumption of the role of stakeholder, prototyping, pilot project implementation and investigation of needs and what outcome is desired are few among many tools and ideas the CRM implementers should make use of throughout introduction of the system and considering increased user diversity of CRM systems. After analyzing 13 case studies based on the resistance/usability and three design stages framework Fjermestad and Romano (2003) conclude that resistance and usability of e-crm system should be always taken together throughout the pre-design, design and post-design stages of system implementation. 7
8 2.5. HOW CRM TECHNOLOGY WORKS? To better answer the question How CRM works? one should study the implementation issues from the technological perspective. US and Taiwan IS academicians, Rygielski, Wang and Yen (2002), claim that development of relationship marketing in industries with extremely large number of customers and huge amount of data related to them was maid possible only through advancement in technology of data warehousing, mining and campaign management. Rygielski, Wang and Yen (2002), introduce two techniques of data mining: CHAID-chi-square automated interaction detection and neural networks. (Rygielski, Wang and Yen, 2002) By defining data mining as a sophisticated capability to search data, and tracing through evolutionary stages of Data Collection, Data Access and Data Navigation the authors arrive at a state where Finally, on-line analytic tools provided real-time feedback and information exchange with collaborating business units as a current evolutionary phase of Data Mining (Rygielski, Wang and Yen, 2002, p. 485). However the most useful insight that article provides from practitioners perspective, would be how three general categories of data mining activities of 1) discovery, 2) predictive modeling and 3) forensic analysis process can be used to solve various problems in retail, banking, telecommunications and other industries. Applications such as sales forecasting, database marketing, fraud detection and customer loyalty are described with overall concluding advice to practitioners to pay more attention to the technology of data mining while choosing an appropriate software from many CRM applications INDUSTRY SPECIFIC DISCUSSION OF CRM IMPLEMENTATION ISSUES CRM implementation issues are widely discussed in sector specific literature, such as CRM in financial and telecommunications, retail and IT industries. These discussions however provide also general, non-industry specific frameworks that can be used across various sectors. CRM in Services Industries 8
9 Efficient CRM systems are more important and can produce more tangible benefits in service industries, such as telecommunications, banking and insurance. Panda (2003) in a discussion of CRM in financial services brings three main reasons why the CRM is critical in service industries in general. First, services such as banking and insurance have more often membership nature, which implies a long term relationship. Second, even without membership, customers feel secure when establishing relationship. Third, it is more likely to establish relationship with service provider, be it a person or organization, than a product manufacturer. Financial Services CRM and Adoption Framework The most advanced user of CRM in UK, according to Ryals and Payne (2001), is financial sector and a lot can be learned by other sectors from CRM implementation experience in financial companies (Ryals and Payne, 2001). The authors try to use financial sector experience to theorize approaches of CRM implementation and present a framework to its adoption. Before doing so, an attempt is made to describe the essential technological notions of information enabled CRM systems including: data warehouse, data marts, data mining and tools, such as clustering techniques, conjoint analysis, regression analysis and neural networks. These techniques are best presented in relation to marketing objectives that they need to serve. Segmentation of customers based on their behavior or finding what patterns the relationships between customers follow, helps the companies to better profile the customer and model their needs. Mining tools provide the company with intelligence as opposed to a memory, which Ryals and Payne (2001) consider to be the data warehousing only. (Ryals and Payne, 2001, p 9). The framework of CRM adoption that Ryals and Payne (2001) propose is built around the philosophy of Relationship Marketing, which the authors argue should be recognized by company leaders along with the role that IT can play in achieving customer oriented organizational thinking. Once leadership agrees that relationship marketing is the right way to go forward, other elements of the framework, covering economic measurability (Data Utilization for Customer Management), organizational flexibility (Appropriate Organizational Structure) and technological empowerment (Leveraging of Data Warehouse) are presented to demonstrate the 9
10 comprehensiveness and complexity of "information-enabled CRM systems. (Ryals and Payne, 2001) Software Development - Organizational Transformation Change CRM systems are very popular in knowledge intensive industries, such as software development. Many practitioners and academics recognize the documentation of knowledge and it s accessibility for various levels of organization and through different communication channels with customers, to be one of the biggest values of any CRM system. It is very interesting to see how the companies structures and values are reshaped by the shared knowledge and its wide accessibility. An organizational transformation enabled by a CRM system is discussed by Orlikowski (1996). Her study of a software company that introduced an Incident Tracking Support System is a valuable piece to refer to while implementing a CRM in IT business. The five metamorphosis of organizational change associated with the introduction of new electronic system to capture, document and reuse the knowledge of incidents and their responses can broaden our understanding of how technology can impact people and business processes and more importantly what people can do and what values can be set to get the most of technology. The author suggests three types of outcomes that can be expected from the new technology: Deliberate and Emerging changes in both managers and specialist practices and an Unanticipated outcome. Orlikowski (2001) underlines many areas of changes such as nature and texture of work; patterns of interaction; distribution of work; evaluation of performance; forms of accountability; nature of knowledge and mechanisms of coordination (Orlikowski, 2001, p 89). The value that practitioners can get from this example is getting prepared to any type of change, not only on the front line, where CRM considered to be operating most intensively, but also in back office business processes. 10
11 3. Conclusion CRM is recognized to be relatively new approach in managing sales and marketing activities of an organization. One of the reasons of its emergence is businesses understanding of benefits of building efficient relationships with customers to increase profitability and stability. Although the subject of CRM implementation may seem quite specific and narrow the approaches various authors followed are quite different and diverse. However, most of the discussions reveal commonalities such as, discussion of certain theory based on empirical study and focusing on one of the aspects of system implementation while appreciating equal importance of other perspectives as well. A broader question of how these articles address practical needs and answer commonly raised questions of CRM implementers in field was also discussed but still leaves place for broader and more in-depth research. Further research might also be directed at finding out which perspective of CRM implementation is of greater concern to a certain party involved in implementation, be it software company, front-line users, strategic management or project manager. 11
12 4. References Bull C., (2003). ''Strategic issues in customer relationship management (CRM) implementation''. Business Process Management Journal Bygstad, Bendik. (2003), ''The Implementation Puzzle of CRM Systems in Knowledge Based Organizations''. Information Resources Management Journal Conway, D. K., Fitzpatrick J.M. (1999). The Customer Relationship Revolution A methodology for creating golden customers. CRM Forum. Corner I., Hinton M., (2002). ''Customer relationship management systems: implementation risks and relationship dynamics''. Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal. Fjermestad J., Romano N., (2003). Electronic customer relationship management. Revisiting the general principles of usability and resistance an integrative implementation framework. Business Process Management Journa.l GEFEN, D (2002). "Implementation Team Responsiveness and User Evaluation of Customer Relationship Management: A Quasi-Experimental Design Study of Social Exchange Theory". Journal of management information systems ( ), 19 (1), p. 47. Giga (2001), "Seven out of ten CRM projects fail", Computing, No.16. Gurău, Călin (2003). "Customer-Centric Strategic Planning: Integrating CRM in Online Business Systems". Information technology and management Hewson, W., McAlpine, G. (1999), The CRM Systems Handbook, Hewson Consulting Group, Cambridge. Marble, R. (2000), "Operationalising the implementation puzzle: an argument for eclecticism in research and practice". European Journal of Information Systems. Markus, M.L. (1983). "Power, politics, and MIS implementation", Communications of the ACM, Vol. 26 No.6, pp Nielsen, J. (1992), "The usability engineering life cycle", IEEE Computer, No.March, pp Orlikowski W., (1996). Improvising Organizational Transformation Over Time: A Situated Change Perspective. Information Systems Research. Panda T. K., (2002). Creating Customer Life Time Value Through Effective CRM in Financial Services Industry. Journal of Services Research. Payne, A., Christopher, M., Clark, M., Peck, H. (1999). ''Relationship Marketing for Competitive Advantage'', Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford. Reichheld, F.F. (1996). ''The Loyalty Effect''. Harvard Business School Press, Boston, MA. Rigby, DK (2004). "CRM Done Right". Harvard business review Ryals, L., Payne, A., (2001). Customer Relationship Management in Financial Services: Towards Information Enabled Relationship Marketing. Journal of Strategic Management. Rygielski, C., Wang, J.-C., Yen, D. C. (2002). Data mining techniques for customer relationship management, Technology in Society. Tafti M. H. A. (2002). ''Analysis of Factors Affecting Implementation of Customer Relationship Management Systems. IRMA, Seattle, Idea Group Publishing 12
Customer Relationship Management: A Case Study of Religare Securities Maraimalai Nagar
 65 Customer Relationship Management: A Case Study of Religare Securities Maraimalai Nagar Josephine Lalrindiki, Research Scholar, Department of Management, Mizoram University, Aizawl Dr Amit Kumar Singh,
65 Customer Relationship Management: A Case Study of Religare Securities Maraimalai Nagar Josephine Lalrindiki, Research Scholar, Department of Management, Mizoram University, Aizawl Dr Amit Kumar Singh,
A STUDY ON CRM IMPLEMENTATION IN THE INDIAN BANKS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO COIMBATORE CITY
 IJER Serials Publications 12(2), 2015: 477-485 ISSN: 0972-9380 A STUDY ON CRM IMPLEMENTATION IN THE INDIAN BANKS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO COIMBATORE CITY Abstract: Purpose - To understand the critical
IJER Serials Publications 12(2), 2015: 477-485 ISSN: 0972-9380 A STUDY ON CRM IMPLEMENTATION IN THE INDIAN BANKS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO COIMBATORE CITY Abstract: Purpose - To understand the critical
IMPLEMENTING ELECTRONIC CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
 SWEDISH SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION RESEARCH METHODOLOGY IMPLEMENTING ELECTRONIC CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT SYSTEM TERM PAPER 14.5.2007 SARI MERINEN 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...3
SWEDISH SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION RESEARCH METHODOLOGY IMPLEMENTING ELECTRONIC CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT SYSTEM TERM PAPER 14.5.2007 SARI MERINEN 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...3
SYLLABUS. B.B.A. V SEM Subject Customer Relationship Management
 SYLLABUS B.B.A. V SEM Subject Customer Relationship Management UNIT I Introduction to CRM: Definition and concepts of CRM, Components of CRM, Understanding the goal of CRM and Customer Touch Points. UNIT
SYLLABUS B.B.A. V SEM Subject Customer Relationship Management UNIT I Introduction to CRM: Definition and concepts of CRM, Components of CRM, Understanding the goal of CRM and Customer Touch Points. UNIT
How To Use Data Mining For Knowledge Management In Technology Enhanced Learning
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Applications of Electrical Engineering, Istanbul, Turkey, May 27-29, 2007 115 Data Mining for Knowledge Management in Technology Enhanced Learning
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Applications of Electrical Engineering, Istanbul, Turkey, May 27-29, 2007 115 Data Mining for Knowledge Management in Technology Enhanced Learning
A study of application of information technology using e-crm in bank in rural area with special reference to SBI Bank, Sangamner
 Feb., 2012 Marketing management A study of application of information technology using e-crm in bank in rural area with special reference to SBI Bank, Sangamner Dr. Kirti Gulati (Ass Prof) Institute of
Feb., 2012 Marketing management A study of application of information technology using e-crm in bank in rural area with special reference to SBI Bank, Sangamner Dr. Kirti Gulati (Ass Prof) Institute of
Appendix B Data Quality Dimensions
 Appendix B Data Quality Dimensions Purpose Dimensions of data quality are fundamental to understanding how to improve data. This appendix summarizes, in chronological order of publication, three foundational
Appendix B Data Quality Dimensions Purpose Dimensions of data quality are fundamental to understanding how to improve data. This appendix summarizes, in chronological order of publication, three foundational
Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects
 Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects Abstract: Build a model to investigate system and discovering relations that connect variables in a database
Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects Abstract: Build a model to investigate system and discovering relations that connect variables in a database
73. Human Processes in Customer Relationship Management
 73. Human Processes in Customer Relationship Management Shari S. C. Shang National Chengchi University, Taiwan [email protected] Chih-Hsiang Chen National Chengchi University, Taiwan [email protected]
73. Human Processes in Customer Relationship Management Shari S. C. Shang National Chengchi University, Taiwan [email protected] Chih-Hsiang Chen National Chengchi University, Taiwan [email protected]
Part VIII: ecrm (Customer Relationship Management)
 Part VIII: ecrm (Customer Relationship Management) Learning Targets What are the objectives of CRM? How can we achieve customer acquisition and loyalty? What is the customer buying cycle? How does the
Part VIII: ecrm (Customer Relationship Management) Learning Targets What are the objectives of CRM? How can we achieve customer acquisition and loyalty? What is the customer buying cycle? How does the
Healthcare Measurement Analysis Using Data mining Techniques
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 03 Issue 07 July, 2014 Page No. 7058-7064 Healthcare Measurement Analysis Using Data mining Techniques 1 Dr.A.Shaik
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 03 Issue 07 July, 2014 Page No. 7058-7064 Healthcare Measurement Analysis Using Data mining Techniques 1 Dr.A.Shaik
The Impact of Knowledge Management on Customer Relationship Management
 The Impact of Knowledge Management on Customer Relationship Management Hadi Nejatian Khalilabad*, Omid Nasrollah Mazandarani*, Ilham Sentosa*, Shishi Kumar Piaralal* The business environment is transforming
The Impact of Knowledge Management on Customer Relationship Management Hadi Nejatian Khalilabad*, Omid Nasrollah Mazandarani*, Ilham Sentosa*, Shishi Kumar Piaralal* The business environment is transforming
E-Customer Relationship Management in the Clothing Retail Shops in Zimbabwe
 IJMBS Vo l. 3, Is s u e 1, Ja n - Ma r c h 2013 ISSN : 2230-9519 (Online) ISSN : 2230-2463 (Print) E-Customer Relationship Management in the Clothing Retail Shops in Zimbabwe 1 Muchaneta Enipha Muruko,
IJMBS Vo l. 3, Is s u e 1, Ja n - Ma r c h 2013 ISSN : 2230-9519 (Online) ISSN : 2230-2463 (Print) E-Customer Relationship Management in the Clothing Retail Shops in Zimbabwe 1 Muchaneta Enipha Muruko,
Critical Success Factors for Implementing CRM Using Data Mining*
 Interscience Management Review, Vol.I/1, 2008 Critical Success Factors for Implementing CRM Using Data Mining* Jayanti Ranjan 1 Abstract: Vishal Bhatnagar 2 The paper presents the Critical success factors
Interscience Management Review, Vol.I/1, 2008 Critical Success Factors for Implementing CRM Using Data Mining* Jayanti Ranjan 1 Abstract: Vishal Bhatnagar 2 The paper presents the Critical success factors
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT WITHIN TAIWANESE BANKS
 THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT WITHIN TAIWANESE BANKS Dr. Ying-Yueh Su, Chinese Culture University, Taiwan R.O.C. [email protected] Dr. Yen-Ku Kuo*, Chinese Culture University,
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT WITHIN TAIWANESE BANKS Dr. Ying-Yueh Su, Chinese Culture University, Taiwan R.O.C. [email protected] Dr. Yen-Ku Kuo*, Chinese Culture University,
ETPL Extract, Transform, Predict and Load
 ETPL Extract, Transform, Predict and Load An Oracle White Paper March 2006 ETPL Extract, Transform, Predict and Load. Executive summary... 2 Why Extract, transform, predict and load?... 4 Basic requirements
ETPL Extract, Transform, Predict and Load An Oracle White Paper March 2006 ETPL Extract, Transform, Predict and Load. Executive summary... 2 Why Extract, transform, predict and load?... 4 Basic requirements
Relationship Marketing: Is It a Paradigm Shift?
 Introduction Relationship marketing emerged as a contestant to traditional marketing theories since the early 1990s. Proponents of relationship marketing as a paradigm shift to traditional marketing theories
Introduction Relationship marketing emerged as a contestant to traditional marketing theories since the early 1990s. Proponents of relationship marketing as a paradigm shift to traditional marketing theories
E-Commerce & CRM Building Relationships, Satisfaction, and Loyalty
 Lecture 8 E-Commerce & CRM Building Relationships, Satisfaction, and Loyalty CRM Defined a combination of business process & technology that seeks to understand a company s customers from the perspective
Lecture 8 E-Commerce & CRM Building Relationships, Satisfaction, and Loyalty CRM Defined a combination of business process & technology that seeks to understand a company s customers from the perspective
Digging for Gold: Business Usage for Data Mining Kim Foster, CoreTech Consulting Group, Inc., King of Prussia, PA
 Digging for Gold: Business Usage for Data Mining Kim Foster, CoreTech Consulting Group, Inc., King of Prussia, PA ABSTRACT Current trends in data mining allow the business community to take advantage of
Digging for Gold: Business Usage for Data Mining Kim Foster, CoreTech Consulting Group, Inc., King of Prussia, PA ABSTRACT Current trends in data mining allow the business community to take advantage of
Applying CRM in Information Product Pricing
 Applying CRM in Information Product Pricing Wenjing Shang, Hong Wu and Zhimin Ji School of Economics and Management, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing100876, P.R. China [email protected]
Applying CRM in Information Product Pricing Wenjing Shang, Hong Wu and Zhimin Ji School of Economics and Management, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing100876, P.R. China [email protected]
The Impact of Market Orientation and IT Management Orientation on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Technology Adoption
 The Impact of Market Orientation and IT Management Orientation on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Technology Adoption James E. Richard, Peter C. Thirkell and Sid L. Huff, Victoria University of
The Impact of Market Orientation and IT Management Orientation on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Technology Adoption James E. Richard, Peter C. Thirkell and Sid L. Huff, Victoria University of
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com
 Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENTS AND MODELS Predictive Analytics and ROI: Lessons from IDC's Financial Impact
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENTS AND MODELS Predictive Analytics and ROI: Lessons from IDC's Financial Impact
The Benefits of the Electronic Customer Relationship Management to the Banks and their Customers
 The Benefits of the Electronic Customer Relationship Management to the Banks and their Customers Zlatko Bezhovski 1* Fida Hussain 2 1. Goce Delchev University, Krste Misirkov No.10-A, Stip, Macedonia 2.
The Benefits of the Electronic Customer Relationship Management to the Banks and their Customers Zlatko Bezhovski 1* Fida Hussain 2 1. Goce Delchev University, Krste Misirkov No.10-A, Stip, Macedonia 2.
Barriers to the implementation of Integrated Marketing Communications: The client perspective.
 Barriers to the implementation of Integrated Marketing Communications: The client perspective. Discussions on Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) in the academic and practitioner journals are gradually
Barriers to the implementation of Integrated Marketing Communications: The client perspective. Discussions on Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) in the academic and practitioner journals are gradually
6/10/2015. Chapter Nine Overview. Learning Outcomes. Opening Case: Twitter: A Social CRM Tool
 Opening Case: Twitter: A Social CRM Tool McGraw-Hill-Ryerson 2015 The McGraw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved Chapter Nine Overview SECTION 9.1 CRM FUNDAMENTALS Introduction Using Information to Drive
Opening Case: Twitter: A Social CRM Tool McGraw-Hill-Ryerson 2015 The McGraw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved Chapter Nine Overview SECTION 9.1 CRM FUNDAMENTALS Introduction Using Information to Drive
Customer relationship management MB-104. By Mayank Kumar Pandey Assistant Professor at Noida Institute of Engineering and Technology
 Customer relationship management MB-104 By Mayank Kumar Pandey Assistant Professor at Noida Institute of Engineering and Technology University Syllabus UNIT-1 Customer Relationship Management- Introduction
Customer relationship management MB-104 By Mayank Kumar Pandey Assistant Professor at Noida Institute of Engineering and Technology University Syllabus UNIT-1 Customer Relationship Management- Introduction
CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
 CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM) 3.1 INTRODUCTION The most important purpose of any service orientated organisation is to retain customers. It is critical for any organization to keep
CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM) 3.1 INTRODUCTION The most important purpose of any service orientated organisation is to retain customers. It is critical for any organization to keep
FFIEC Cybersecurity Assessment Tool
 Overview In light of the increasing volume and sophistication of cyber threats, the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council 1 (FFIEC) developed the Cybersecurity Tool (), on behalf of its members,
Overview In light of the increasing volume and sophistication of cyber threats, the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council 1 (FFIEC) developed the Cybersecurity Tool (), on behalf of its members,
Customer Relationship Management: an Organizational Survival Approach to Perceive Customer Loyalty
 Customer Relationship Management: an Organizational Survival Approach to Perceive Customer Loyalty Dr. Mehran Molavi1, Ayub Nahardah2 1-Department of Public Administration, College of Human Sciences, Mahabad
Customer Relationship Management: an Organizational Survival Approach to Perceive Customer Loyalty Dr. Mehran Molavi1, Ayub Nahardah2 1-Department of Public Administration, College of Human Sciences, Mahabad
20 Best Practices for Customer Feedback Programs Building a Customer-Centric Company
 Business growth through customer insight 20 Best Practices for Customer Feedback Programs Building a Customer-Centric Company The content of this paper is based on the book, Beyond the Ultimate Question,
Business growth through customer insight 20 Best Practices for Customer Feedback Programs Building a Customer-Centric Company The content of this paper is based on the book, Beyond the Ultimate Question,
Master of Science in Marketing Analytics (MSMA)
 Master of Science in Marketing Analytics (MSMA) COURSE DESCRIPTION The Master of Science in Marketing Analytics program teaches students how to become more engaged with consumers, how to design and deliver
Master of Science in Marketing Analytics (MSMA) COURSE DESCRIPTION The Master of Science in Marketing Analytics program teaches students how to become more engaged with consumers, how to design and deliver
Data Mining is sometimes referred to as KDD and DM and KDD tend to be used as synonyms
 Data Mining Techniques forcrm Data Mining The non-trivial extraction of novel, implicit, and actionable knowledge from large datasets. Extremely large datasets Discovery of the non-obvious Useful knowledge
Data Mining Techniques forcrm Data Mining The non-trivial extraction of novel, implicit, and actionable knowledge from large datasets. Extremely large datasets Discovery of the non-obvious Useful knowledge
Module description Customer Relationship Management
 Module description Customer Relationship Management 17/11/2014 page 1/6 Module code Central theme W.MSCBA_CRM01.08 This module discusses CRM as a strategic approach that is concerned with creating improved
Module description Customer Relationship Management 17/11/2014 page 1/6 Module code Central theme W.MSCBA_CRM01.08 This module discusses CRM as a strategic approach that is concerned with creating improved
The Critical Success Factors for Implementation of Customer Relationship Management in the Banking Sector of Saudi Arabia
 The Critical Success Factors for Implementation of Customer Relationship Management in the Banking Sector of Saudi Arabia Dr. Sulaiman A. Al-Hudhaif, Associate Dean for Quality and Development, College
The Critical Success Factors for Implementation of Customer Relationship Management in the Banking Sector of Saudi Arabia Dr. Sulaiman A. Al-Hudhaif, Associate Dean for Quality and Development, College
Chapter 4: Implementing the CRM Strategy
 Chapter 4: Implementing the CRM Strategy Overview Topics discussed: Elements of a CRM System Customer Interphase / Touch Points CRM Applications Return on Investment (ROI) of CRM CRM Costs Why is ROI of
Chapter 4: Implementing the CRM Strategy Overview Topics discussed: Elements of a CRM System Customer Interphase / Touch Points CRM Applications Return on Investment (ROI) of CRM CRM Costs Why is ROI of
PANORATIO. Big data : Benefits of a strategic vision. White Paper June 2013. Executive Summary
 PANORATIO Big data : Benefits of a strategic vision White Paper June 2013 Executive Summary Following the massive deployment of new mobile technologies and social media, sources of data regarding organizations
PANORATIO Big data : Benefits of a strategic vision White Paper June 2013 Executive Summary Following the massive deployment of new mobile technologies and social media, sources of data regarding organizations
Managing the Next Best Activity Decision
 Managing the Next Best Activity Decision James Taylor CEO, Decision Management Solutions Treating customers right, every time More information at: www.decisionmanagementsolutions.com No matter what the
Managing the Next Best Activity Decision James Taylor CEO, Decision Management Solutions Treating customers right, every time More information at: www.decisionmanagementsolutions.com No matter what the
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies
 ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
Becoming Data Driven 101: Planning for Success
 Becoming Data Driven 101: Planning for Success Tom Davenport, Babson College Bill Franks, Teradata August 5, 2015 SPONSORED BY Featured Speakers Tom Davenport is the President s Distinguished Professor
Becoming Data Driven 101: Planning for Success Tom Davenport, Babson College Bill Franks, Teradata August 5, 2015 SPONSORED BY Featured Speakers Tom Davenport is the President s Distinguished Professor
TEXT ANALYTICS INTEGRATION
 TEXT ANALYTICS INTEGRATION A TELECOMMUNICATIONS BEST PRACTICES CASE STUDY VISION COMMON ANALYTICAL ENVIRONMENT Structured Unstructured Analytical Mining Text Discovery Text Categorization Text Sentiment
TEXT ANALYTICS INTEGRATION A TELECOMMUNICATIONS BEST PRACTICES CASE STUDY VISION COMMON ANALYTICAL ENVIRONMENT Structured Unstructured Analytical Mining Text Discovery Text Categorization Text Sentiment
Customer Relationship Strategies: The Study on Customer Perspectives
 International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 3 No. 15; August 2012 Customer Relationship Strategies: The Study on Customer Perspectives ML. Saviga Unhanandana Associate Professor Chulalongkorn
International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 3 No. 15; August 2012 Customer Relationship Strategies: The Study on Customer Perspectives ML. Saviga Unhanandana Associate Professor Chulalongkorn
A Knowledge Management Framework Using Business Intelligence Solutions
 www.ijcsi.org 102 A Knowledge Management Framework Using Business Intelligence Solutions Marwa Gadu 1 and Prof. Dr. Nashaat El-Khameesy 2 1 Computer and Information Systems Department, Sadat Academy For
www.ijcsi.org 102 A Knowledge Management Framework Using Business Intelligence Solutions Marwa Gadu 1 and Prof. Dr. Nashaat El-Khameesy 2 1 Computer and Information Systems Department, Sadat Academy For
How To Understand And Understand The Concept Of Customer Relationship Management
 ROLE AND IMPORTANCE OF BUSINESS PROCESSES IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CRM SYSTEMS Luis H. Bibiano, Enric Mayol, Joan A. Pastor Facultat d Infomàtica de Barcelona Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya {lbibiano,
ROLE AND IMPORTANCE OF BUSINESS PROCESSES IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CRM SYSTEMS Luis H. Bibiano, Enric Mayol, Joan A. Pastor Facultat d Infomàtica de Barcelona Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya {lbibiano,
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENT IN MARKETING: TRENDS AND CHALLENGES
 EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENT IN MARKETING: TRENDS AND CHALLENGES Georgine Fogel, Salem International University INTRODUCTION Measurement, evaluation, and effectiveness have become increasingly important
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENT IN MARKETING: TRENDS AND CHALLENGES Georgine Fogel, Salem International University INTRODUCTION Measurement, evaluation, and effectiveness have become increasingly important
Hello, Goodbye. The New Spin on Customer Loyalty. From Customer Acquisition to Customer Loyalty. Definition of CRM.
 Hello, Goodbye. The New Spin on Customer Loyalty The so-called typical customer no longer exists. Companies were focused on selling as many products as possible, without regard to who was buying them.
Hello, Goodbye. The New Spin on Customer Loyalty The so-called typical customer no longer exists. Companies were focused on selling as many products as possible, without regard to who was buying them.
How to Measure a Loyalty Programme s Return on Investment. Managing information and transactions securely
 How to Measure a Loyalty Programme s Return on Investment Managing information and transactions securely Introduction Successful programmes have longevity because the overall benefits clearly justify the
How to Measure a Loyalty Programme s Return on Investment Managing information and transactions securely Introduction Successful programmes have longevity because the overall benefits clearly justify the
THE PLANNING OF A CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT PROJECT: REQUIREMENTS AND OPPORTUNITIES
 THE PLANNING OF A CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT PROJECT: REQUIREMENTS AND OPPORTUNITIES Professor PhD Adriana OLARU Lecturer Alexandru CAPATINA Dunărea de Jos University of Galati, Romania Abstract:
THE PLANNING OF A CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT PROJECT: REQUIREMENTS AND OPPORTUNITIES Professor PhD Adriana OLARU Lecturer Alexandru CAPATINA Dunărea de Jos University of Galati, Romania Abstract:
Analysis of the Readiness of Thai SME for Applying CRM
 Analysis of the Readiness of Thai SME for Applying CRM Anongnart Srivihok Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Thailand Email: [email protected] Dentcho Batanov
Analysis of the Readiness of Thai SME for Applying CRM Anongnart Srivihok Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Thailand Email: [email protected] Dentcho Batanov
Small business CRM examined
 Small business CRM examined Ing. Štefan Vantroba MSc. University of Technology in Brno, Faculty of Business and Management, Kolejní 2, 61200 Brno Abstract CRM practices can help small businesses to step
Small business CRM examined Ing. Štefan Vantroba MSc. University of Technology in Brno, Faculty of Business and Management, Kolejní 2, 61200 Brno Abstract CRM practices can help small businesses to step
INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING SAS ENTERPRISE MINER
 INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING SAS ENTERPRISE MINER Mary-Elizabeth ( M-E ) Eddlestone Principal Systems Engineer, Analytics SAS Customer Loyalty, SAS Institute, Inc. AGENDA Overview/Introduction to Data Mining
INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING SAS ENTERPRISE MINER Mary-Elizabeth ( M-E ) Eddlestone Principal Systems Engineer, Analytics SAS Customer Loyalty, SAS Institute, Inc. AGENDA Overview/Introduction to Data Mining
Exploring, selecting, implementing and using a customer relationship management system. A case study of theory applied in practice.
 Exploring, selecting, implementing and using a customer relationship management system. A case study of theory applied in practice. V. Sparks, ECCO Oxford/Oxford Brookes University, KTP associate. [email protected]
Exploring, selecting, implementing and using a customer relationship management system. A case study of theory applied in practice. V. Sparks, ECCO Oxford/Oxford Brookes University, KTP associate. [email protected]
Aon Case Study: Creating a Global Leadership Culture
 Aon Case Study: Creating a Global Leadership Culture Aon Corporation provides risk management services, insurance and reinsurance brokerage, human capital and management consulting. Aon has approximately
Aon Case Study: Creating a Global Leadership Culture Aon Corporation provides risk management services, insurance and reinsurance brokerage, human capital and management consulting. Aon has approximately
Consulting Performance, Rewards & Talent. Measuring the Business Impact of Employee Selection Systems
 Consulting Performance, Rewards & Talent Measuring the Business Impact of Employee Selection Systems Measuring the Business Impact of Employee Selection Systems Many, if not all, business leaders readily
Consulting Performance, Rewards & Talent Measuring the Business Impact of Employee Selection Systems Measuring the Business Impact of Employee Selection Systems Many, if not all, business leaders readily
Technology-Driven Demand and e- Customer Relationship Management e-crm
 E-Banking and Payment System Technology-Driven Demand and e- Customer Relationship Management e-crm Sittikorn Direksoonthorn Assumption University 1/2004 E-Banking and Payment System Quick Win Agenda Data
E-Banking and Payment System Technology-Driven Demand and e- Customer Relationship Management e-crm Sittikorn Direksoonthorn Assumption University 1/2004 E-Banking and Payment System Quick Win Agenda Data
e-crm: Latest Paradigm in the world of CRM
 e-crm: Latest Paradigm in the world of CRM Leny Michael (Research Scholar, Bharathiyar University, Coimbatore) Assistnat Professor Caarmel Engineering College Koonamkara Post, Perunad ranni-689711 Mobile
e-crm: Latest Paradigm in the world of CRM Leny Michael (Research Scholar, Bharathiyar University, Coimbatore) Assistnat Professor Caarmel Engineering College Koonamkara Post, Perunad ranni-689711 Mobile
5 PRACTICES. That Improve the Business Impact of Research EFFECTIVE DSTAKEHOLDERS
 5 PRACTICES That Improve the Business Impact of Research 1. ALIGN DIRECTLY WITH KEY STAKEHOLDERS 2. LINK THE WHYS TO THE WHATS OF BIG DATA 3. FOCUS ON METRICS THAT MATTER 4. PROVE RESEARCH ROI 5. GET TO
5 PRACTICES That Improve the Business Impact of Research 1. ALIGN DIRECTLY WITH KEY STAKEHOLDERS 2. LINK THE WHYS TO THE WHATS OF BIG DATA 3. FOCUS ON METRICS THAT MATTER 4. PROVE RESEARCH ROI 5. GET TO
CRM Adoption Framework and Its Success Measurement
 CRM Adoption Framework and Its Success Measurement Leo Willyanto Santoso Faculty of Industrial Technology, Petra Christian University Jl. Siwalankerto 121-131, Surabaya 60236 Tel. 031-2983455, Fax. 031-8417658,
CRM Adoption Framework and Its Success Measurement Leo Willyanto Santoso Faculty of Industrial Technology, Petra Christian University Jl. Siwalankerto 121-131, Surabaya 60236 Tel. 031-2983455, Fax. 031-8417658,
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT - A NEW METHOD OF TARGETING THE 21 ST CENTURY CONSUMERS
 Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 9(3), 2009, 255-260 255 CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT - A NEW METHOD OF TARGETING THE 21 ST CENTURY CONSUMERS LUIGI DUMITRESCU, MIRCEA FUCIU * ABSTRACT:
Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 9(3), 2009, 255-260 255 CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT - A NEW METHOD OF TARGETING THE 21 ST CENTURY CONSUMERS LUIGI DUMITRESCU, MIRCEA FUCIU * ABSTRACT:
Using Data Mining Techniques to Increase Efficiency of Customer Relationship Management Process
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 4(23): 5010-5015, 2012 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: February 22, 2012 Accepted: July 02, 2012 Published:
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 4(23): 5010-5015, 2012 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: February 22, 2012 Accepted: July 02, 2012 Published:
Amon Mutyasira. CRM Implementation: Not for profit organisations and profitmaking CRM compared (Case Study)
 Amon Mutyasira CRM Implementation: Not for profit organisations and profitmaking CRM compared (Case Study) 0 Title CRM Implementation: Not for profit organisations and profit-making CRM compared (Case
Amon Mutyasira CRM Implementation: Not for profit organisations and profitmaking CRM compared (Case Study) 0 Title CRM Implementation: Not for profit organisations and profit-making CRM compared (Case
Status of Customer Relationship Management in India
 Status of Customer Relationship Management in India by Dr. G. Shainesh & Ramneesh Mohan Management Development Institute Gurgaon, India Introduction Relationship marketing is emerging as the core marketing
Status of Customer Relationship Management in India by Dr. G. Shainesh & Ramneesh Mohan Management Development Institute Gurgaon, India Introduction Relationship marketing is emerging as the core marketing
DATA WAREHOUSE AND DATA MINING NECCESSITY OR USELESS INVESTMENT
 Scientific Bulletin Economic Sciences, Vol. 9 (15) - Information technology - DATA WAREHOUSE AND DATA MINING NECCESSITY OR USELESS INVESTMENT Associate Professor, Ph.D. Emil BURTESCU University of Pitesti,
Scientific Bulletin Economic Sciences, Vol. 9 (15) - Information technology - DATA WAREHOUSE AND DATA MINING NECCESSITY OR USELESS INVESTMENT Associate Professor, Ph.D. Emil BURTESCU University of Pitesti,
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies
 ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
IS PLANNING IN NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS: AN EXPLORATORY STUDY
 IS PLANNING IN NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS: AN EXPLORATORY STUDY Janice Klemz, The University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Gerry Simon, The University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Anil Kumar, Central Michigan University,
IS PLANNING IN NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS: AN EXPLORATORY STUDY Janice Klemz, The University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Gerry Simon, The University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Anil Kumar, Central Michigan University,
CRM Solutions. Banking Sector
 CRM Solutions Banking Sector BY COMMUNICATION PROGRESS Agenda Changing Sales/Marketing Trends Distinct Markets Banks Strategic Goals Introduction to CRM CRM as a Business Strategy Design an effective segmentation
CRM Solutions Banking Sector BY COMMUNICATION PROGRESS Agenda Changing Sales/Marketing Trends Distinct Markets Banks Strategic Goals Introduction to CRM CRM as a Business Strategy Design an effective segmentation
1 Annex 11: Market failure in broadcasting
 1 Annex 11: Market failure in broadcasting 1.1 This annex builds on work done by Ofcom regarding market failure in a number of previous projects. In particular, we discussed the types of market failure
1 Annex 11: Market failure in broadcasting 1.1 This annex builds on work done by Ofcom regarding market failure in a number of previous projects. In particular, we discussed the types of market failure
Chapter 2: Relationship Marketing and the Concept of Customer Value
 Chapter 2: Relationship Marketing and the Concept of Customer Value Overview Topics discussed: The Link between CRM and Database Marketing, and the Importance of Customer Value Satisfaction-Loyalty-Profit
Chapter 2: Relationship Marketing and the Concept of Customer Value Overview Topics discussed: The Link between CRM and Database Marketing, and the Importance of Customer Value Satisfaction-Loyalty-Profit
Indian Institute of Management Bangalore. Customer Relationship Management
 Faculty: Prof. G. Shainesh Indian Institute of Management Bangalore Customer Relationship Management Term VI PGP (2011-12) 3 Credit Course Background The primary purpose of any business is to win and keep
Faculty: Prof. G. Shainesh Indian Institute of Management Bangalore Customer Relationship Management Term VI PGP (2011-12) 3 Credit Course Background The primary purpose of any business is to win and keep
10 Steps for Setting up a Customer Loyalty Program By Kim Skaaning Jørgensen
 10 Steps for Setting up a Customer Loyalty Program By Kim Skaaning Jørgensen Step 1: Evaluate the Product The first step is always to answer the following questions honestly: Is my product good enough?
10 Steps for Setting up a Customer Loyalty Program By Kim Skaaning Jørgensen Step 1: Evaluate the Product The first step is always to answer the following questions honestly: Is my product good enough?
THE ALIGNMENT BETWEEN CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT AND IT STRATEGY: A PROPOSED RESEARCH MODEL
 THE ALIGNMENT BETWEEN CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT AND IT STRATEGY: A PROPOSED RESEARCH MODEL Durand Aurelie The University of Lyon 3 [email protected] Bouzidi Laïd The University of Lyon
THE ALIGNMENT BETWEEN CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT AND IT STRATEGY: A PROPOSED RESEARCH MODEL Durand Aurelie The University of Lyon 3 [email protected] Bouzidi Laïd The University of Lyon
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT
 3-02-70 INFORMATION MANAGEMENT: STRATEGY, SYSTEMS, AND TECHNOLOGIES CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT Ken Liang and Houston H. Carr INSIDE Customer Relationship Management; Information Technology and CRM;
3-02-70 INFORMATION MANAGEMENT: STRATEGY, SYSTEMS, AND TECHNOLOGIES CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT Ken Liang and Houston H. Carr INSIDE Customer Relationship Management; Information Technology and CRM;
Examining the role of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) on Attracting Customers in Internet Marketing
 Examining the role of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) on Attracting Customers in Internet Marketing Vajihe Mogharabi M.A. Student of Information Technology Management, Shahid beheshti
Examining the role of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) on Attracting Customers in Internet Marketing Vajihe Mogharabi M.A. Student of Information Technology Management, Shahid beheshti
Worldwide Advanced and Predictive Analytics Software Market Shares, 2014: The Rise of the Long Tail
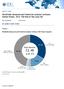 MARKET SHARE Worldwide Advanced and Predictive Analytics Software Market Shares, 2014: The Rise of the Long Tail Alys Woodward Dan Vesset IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide Advanced and Predictive
MARKET SHARE Worldwide Advanced and Predictive Analytics Software Market Shares, 2014: The Rise of the Long Tail Alys Woodward Dan Vesset IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide Advanced and Predictive
PIVOTAL CRM RETAIL INDUSTRY
 PIVOTAL CRM RETAIL INDUSTRY PROVIDING RETAIL ORGANIZATIONS WITH A COMPETITIVE EDGE Pivotal CRM for Retail delivers 36O o business insight to stay ahead of competition COMMITTED TO MEETING INDIVIDUAL NEEDS
PIVOTAL CRM RETAIL INDUSTRY PROVIDING RETAIL ORGANIZATIONS WITH A COMPETITIVE EDGE Pivotal CRM for Retail delivers 36O o business insight to stay ahead of competition COMMITTED TO MEETING INDIVIDUAL NEEDS
4) CRM provides support for front-end customer facing functionality. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 334
 Enterprise Systems for Management, 2e (Motiwalla/Thompson) Chapter 12 Customer Relationship Management 1) CRM implementations should be technology driven. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 333 2) CRM stands for "Customer
Enterprise Systems for Management, 2e (Motiwalla/Thompson) Chapter 12 Customer Relationship Management 1) CRM implementations should be technology driven. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 333 2) CRM stands for "Customer
Investors in People First Assessment Report
 Investors in People First Assessment Report K.H.Construction Cambridge Assessor: Lesley E Ling On-site Date/s: 3 rd September 2008. Recognition Date: Contents 1. Introduction Page 2 2. Assessment and Client
Investors in People First Assessment Report K.H.Construction Cambridge Assessor: Lesley E Ling On-site Date/s: 3 rd September 2008. Recognition Date: Contents 1. Introduction Page 2 2. Assessment and Client
Major Trends in the Insurance Industry
 To survive in today s volatile marketplace? Information or more precisely, Actionable Information is the key factor. For no other industry is it as important as for the Insurance Industry, which is almost
To survive in today s volatile marketplace? Information or more precisely, Actionable Information is the key factor. For no other industry is it as important as for the Insurance Industry, which is almost
IMPORTANCE OF QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES IN MANAGERIAL DECISIONS
 IMPORTANCE OF QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES IN MANAGERIAL DECISIONS Abstract The term Quantitative techniques refers to the methods used to quantify the variables in any discipline. It means the application
IMPORTANCE OF QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES IN MANAGERIAL DECISIONS Abstract The term Quantitative techniques refers to the methods used to quantify the variables in any discipline. It means the application
Customer Relationship Management
 Customer Relationship Management The philosophy of CRM is the recognition of the fact that a long-term relationship with customers can be one of the most important assets of an organization, providing
Customer Relationship Management The philosophy of CRM is the recognition of the fact that a long-term relationship with customers can be one of the most important assets of an organization, providing
PERCEPTION OF BASIS OF SHE AND SHE RISK MANAGEMENT
 PERCEPTION OF BASIS OF SHE AND SHE RISK MANAGEMENT Per Berg and Roger Preston Safety Section, Global SHE, AstraZeneca INTRODUCTION After the merger between the two pharmaceutical companies Astra and Zeneca
PERCEPTION OF BASIS OF SHE AND SHE RISK MANAGEMENT Per Berg and Roger Preston Safety Section, Global SHE, AstraZeneca INTRODUCTION After the merger between the two pharmaceutical companies Astra and Zeneca
The Role of Controlled Experiments in Software Engineering Research
 The Role of Controlled Experiments in Software Engineering Research Victor R. Basili 1 The Experimental Discipline in Software Engineering Empirical studies play an important role in the evolution of the
The Role of Controlled Experiments in Software Engineering Research Victor R. Basili 1 The Experimental Discipline in Software Engineering Empirical studies play an important role in the evolution of the
CHAPTER - 5 CONCLUSIONS / IMP. FINDINGS
 CHAPTER - 5 CONCLUSIONS / IMP. FINDINGS In today's scenario data warehouse plays a crucial role in order to perform important operations. Different indexing techniques has been used and analyzed using
CHAPTER - 5 CONCLUSIONS / IMP. FINDINGS In today's scenario data warehouse plays a crucial role in order to perform important operations. Different indexing techniques has been used and analyzed using
The role of Data Mining in Customer Relationship Management
 The role of Data Mining in Customer Relationship Management Mohlabeng M.R1 ISACA Faculty of ICT: Computer Science, Tshwane University of Technology, South Africa, [email protected] Prof Van der Walt
The role of Data Mining in Customer Relationship Management Mohlabeng M.R1 ISACA Faculty of ICT: Computer Science, Tshwane University of Technology, South Africa, [email protected] Prof Van der Walt
Building Loyalty in a Web 2.0 World
 Building Loyalty in a Web 2.0 World A Consona CRM White Paper By Nitin Badjatia, Enterprise Solutions Architect Over the last decade, a radical shift has occurred in the way customers interact with the
Building Loyalty in a Web 2.0 World A Consona CRM White Paper By Nitin Badjatia, Enterprise Solutions Architect Over the last decade, a radical shift has occurred in the way customers interact with the
Mapping Hospital Growth Through Strategic Service Promotion Management
 World Journal of Social Sciences Vol. 2. No. 6. September 2012 Issue. Pp. 101 112 Mapping Hospital Growth Through Strategic Service Promotion Management 1. Introduction Sanjay Bhalerao* and Rajendra Singh**
World Journal of Social Sciences Vol. 2. No. 6. September 2012 Issue. Pp. 101 112 Mapping Hospital Growth Through Strategic Service Promotion Management 1. Introduction Sanjay Bhalerao* and Rajendra Singh**
2. CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW
 2. CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1. Introduction This literature review is an attempt to understand CRM Systems and its contribution towards improving organizational competitiveness, customer satisfaction
2. CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1. Introduction This literature review is an attempt to understand CRM Systems and its contribution towards improving organizational competitiveness, customer satisfaction
REFLECTIONS ON THE USE OF BIG DATA FOR STATISTICAL PRODUCTION
 REFLECTIONS ON THE USE OF BIG DATA FOR STATISTICAL PRODUCTION Pilar Rey del Castillo May 2013 Introduction The exploitation of the vast amount of data originated from ICT tools and referring to a big variety
REFLECTIONS ON THE USE OF BIG DATA FOR STATISTICAL PRODUCTION Pilar Rey del Castillo May 2013 Introduction The exploitation of the vast amount of data originated from ICT tools and referring to a big variety
Data analytics Delivering intelligence in the moment
 www.pwc.co.uk Data analytics Delivering intelligence in the moment January 2014 Our point of view Extracting insight from an organisation s data and applying it to business decisions has long been a necessary
www.pwc.co.uk Data analytics Delivering intelligence in the moment January 2014 Our point of view Extracting insight from an organisation s data and applying it to business decisions has long been a necessary
TRADITIONAL ERP ERP FOR ECOMMERCE?
 TRADITIONAL ERP < OR > ERP FOR ECOMMERCE? How to evaluate your options to choose the right direction for your retail business. SALESWARP.COM TRADITIONAL ERP OR ERP FOR ECOMMERCE? The retail industry is
TRADITIONAL ERP < OR > ERP FOR ECOMMERCE? How to evaluate your options to choose the right direction for your retail business. SALESWARP.COM TRADITIONAL ERP OR ERP FOR ECOMMERCE? The retail industry is
How to achieve excellent enterprise risk management Why risk assessments fail
 How to achieve excellent enterprise risk management Why risk assessments fail Overview Risk assessments are a common tool for understanding business issues and potential consequences from uncertainties.
How to achieve excellent enterprise risk management Why risk assessments fail Overview Risk assessments are a common tool for understanding business issues and potential consequences from uncertainties.
SUSTAINING COMPETITIVE DIFFERENTIATION
 SUSTAINING COMPETITIVE DIFFERENTIATION Maintaining a competitive edge in customer experience requires proactive vigilance and the ability to take quick, effective, and unified action E M C P e r s pec
SUSTAINING COMPETITIVE DIFFERENTIATION Maintaining a competitive edge in customer experience requires proactive vigilance and the ability to take quick, effective, and unified action E M C P e r s pec
Data Mining Algorithms and Techniques Research in CRM Systems
 Data Mining Algorithms and Techniques Research in CRM Systems ADELA TUDOR, ADELA BARA, IULIANA BOTHA The Bucharest Academy of Economic Studies Bucharest ROMANIA {Adela_Lungu}@yahoo.com {Bara.Adela, Iuliana.Botha}@ie.ase.ro
Data Mining Algorithms and Techniques Research in CRM Systems ADELA TUDOR, ADELA BARA, IULIANA BOTHA The Bucharest Academy of Economic Studies Bucharest ROMANIA {Adela_Lungu}@yahoo.com {Bara.Adela, Iuliana.Botha}@ie.ase.ro
