BEHAVIOR OF WELDED T-STUBS SUBJECTED TO TENSILE LOADS
|
|
|
- Nancy Cook
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BEHAVIOR OF WELDED T-STUBS SUBJECTED TO TENSILE LOADS R.A. Herrera 1, G. Desjouis 2, G. Gomez 2, M. Sarrazin 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Chile, Santiago, Chile 2 Civil Engineer, Former Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Chile, Santiago, Chile ABSTRACT : 3 Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Chile, Santiago, Chile [email protected] T-stub moment connections are an alternative to welded steel beam-to-column moment connections. Significant research has been conducted on the behavior of the connection and the T-stub, resulting in models and design procedures. However, most research has been conducted on hot-rolled T stubs. Welded T stubs are a promising alternative to hot-rolled T-stubs, considering the freedom of sizing, and the absence of hot-rolled sections in several countries. Analytical and experimental studies on the behavior of welded T-stubs subjected to tensile loading were conducted. The objectives of these studies included determining the controlling limit states for welded T-stubs, increasing the database of tests for these components, and evaluating applicability of current design recommendations to welded T-stub moment connections. A finite element model of a welded T-stub was created and subjected to monotonic tensile loads to study the effects of stem-to-flange thickness ratio and bolt arrangement. Fillet welds between stem and flange were modeled. The analysis results indicate that yielding of the T stem may not be the controlling limit state because of the presence of the weld, and that allowing for a controlled prying of the T flange may be more appropriate. A series of T-stubs with configurations similar to those studied analytically, scaled to one-half the original sizes, were tested under monotonically increasing tensile loads. The test results show that the strength of the T stub is above that predicted by current strength models and the dominating failure mode is bolt fracture due to prying action. KEYWORDS: Connections, Steel structures, Testing, Modeling, T-stub
2 1. INTRODUCTION One of the main goals of seismic resistant design is to achieve ductile structural behavior, which enables the structure to sustain considerable damage during a severe earthquake without collapsing, and provides it with a large source of energy dissipation through hysteretic behavior. Strong column-weak beam design is one of the established means to achieve ductile structural behavior. In this type of design, the plastic collapse mechanism plastic hinges develop in the beams at every floor and at the base of the first story columns. To ensure that plastic hinges can form in the beams, the connections must be designed with enough capacity to transfer the largest forces and moments that will develop in the beams. In the 1970s, several research programs were conducted (Popov and Stephen, 1970; Krawinkler and Bertero, 1971) to verify the most used connections for moment resisting frames at the time. One of the most extended was the welded unreinforced flange (WUF) connection, shown in Figure 1(a). In this connection, the flanges were welded using complete joint penetration welds to the column flange and the beam web was connected through a plate to the column flange. The studies determined that if the welds were properly executed, these connections were adequate. Column flange Beam web Continuity plate Access hole weld Backing bar Beam flange (a) Overview (b) Fracture detail Figure 1 Pre-Northridge WUF connection Following the damage observed on this type of connections after the Northridge, 1994 earthquake, a large research effort was carried out to study the behavior of moment connections between steel beams and columns. The main objectives of such efforts were to investigate the causes of the damage observed and to elaborate improved design procedures and recommendations for new steel moment resisting frames. The conclusions of the research conducted were summarized in the FEMA 350 report (FEMA, 2000) and they formed the basis for the new AISC Seismic Provisions (AISC, 2005). One innovation introduced by FEMA 350 was a list of prequalified connections, complete with design procedures and modeling recommendations. These connections had been extensively studied experimentally and analytically, such that their use for seismic resistant construction was approved, without further testing required. Among these connections was the Double Split Tee (DST) connection, shown in Figure 2. In this connection, the beam and column flanges are connected through a pair of bolted T stubs, while the beam web is connected through a shear tab to the column. Figure 2 DST connection
3 The advantages of this connection are that it moves the plastic hinge in the beam away from the column flange and it can be easily installed on the field. However, all the research conducted to prequalify this connection was done using hot-rolled T stubs obtained from wide flange sections, which provide limited flexibility in the choice of flanges and stem dimensions, and are not readily available in all countries. Therefore, further studies on welded T stubs are needed to overcome these limitations. This paper presents the results of analytical and experimental studies on the behavior of welded T stubs subjected to monotonic tensile loading. The objectives of these studies were to determine the parameters that control the behavior of these elements when used in DST connections. 2. PREVIOUS RELATED RESEARCH A number of studies have been carried out using hot-rolled T stubs. Only the most relevant to the research reported are presented here. Swanson and Leon (2000) conducted tests on 48 T stubs under monotonic and cyclic loading. They found that most of the specimens failed by shear fracture of the T stem and fracture of the tension bolts due to the increased tension and bending caused on them by the prying of the T flanges, and that the energy was dissipated through bending of the T flanges due to prying effect and slippage of the T stem with respect to the T flange. Following the T stub tests, Swanson and Leon (2000) tested six full scale beam-column connections, where similar failure modes were observed, but only after significant plastic hinging had developed in the beams. Tests on back-to-back T stubs loaded through the stems, performed by Piluso et al. (2001a), confirmed these conclusions. Regarding welded T stubs, Coelho et al. (2004) tested 32 specimens, where the parameters studied included the thickness and type of weld, the type of steel, and the bolt properties. Again, the most common failure mode was fracture of the tension bolts due to prying of the T flange; however, some specimens developed fractures in the heat affected zone in the stem of the T. These fractures were attributed by the authors to defects in the fabrication process of the T stubs. Several models have been developed to reproduce the stiffness and strength of a DST connection. The multiple failure modes involved and possible interaction between them make the analytical formulation complex, but they can be readily implemented numerically. Piluso et al. (2001b) developed a model based on the failure modes observed in their tests: T flange bending due to prying effect, T flange bending combined with fracture of the tension bolts, and fracture of the tension bolts alone. The model adequately reproduced the test results of the same authors. However, it neglects the influence of the stem of the T, which can control the strength of the T stub (Swanson and Leon, 2000). Swanson and Leon (2001) extended this model to include the effects of the deformations developed in the T stub in a DST connection, namely tension bolt elongation, T flange flexure, T stem deformation, slip between T stem and beam flange, and bearing of the bolts on the T stem and beam flange. The model, known as the component model, was a combination of springs acting in series and in parallel, which represented the different deformation components previously indicated. They validated the component model with their own experimental data. Due to the difficulties involved in testing, finite element (FE) models have been developed to conduct parametric studies on the behavior of DST connections. Most of them are 2-dimensional models, with all the limitations associated with trying to represent a 3-dimensional problem with a planar model. Sherbourne and Bahaari (1996) developed a detailed FE model which included the interaction between T stub and columns and beams, and the nonlinear friction between the stem of the T and the beam flange. The main conclusion of this study was the need to use 3D models to include the biaxial flexure developed in the T flanges. More recently, Coelho et al. (2006) developed a 3D FE model to reproduce their experimental results. The model included only one quarter of the connection and the model of the T did not consider the discontinuity in material properties and geometry induced by the fillet welds. 3. ANALYTICAL STUDIES Considering all the limitations in previous analytical studies, a FE model of a T stub in a DST connection was constructed using the finite element package ANSYS multiphysics (ANSYS, 2005). This model was used to conduct parametric studies on the behavior of welded T stubs. The parameters considered were: distance
4 between tension bolts, layout of tension bolts, and flange-to-stem thickness ratio. The basic T stub dimensions were obtained from the design of a DST connection for a IN30x45.8 beam. The beam was made of A42-27 steel, according to NCh 203 (INN, 1977), which has a yield strength F y of 270 MPa and a tensile strength F u of 420 MPa. The T stub was made of ASTM A572 Gr. 50 steel, which has nominal F y and F u values of 350 MPa and 450 MPa, respectively. A490 bolts, 7/8 diameter were assumed, in order to be able to compare with the results of Swanson and Leon (2000). The dimensions of the beam and the resulting T stub dimensions are shown in Figure 3, where all dimensions are in millimeters. The bending strength of the connection associated to each failure mode is shown in Table 3.1. (a) Beam (b) T stub Figure 3 DST connection design Table 3.1 Connection moment capacity according to FEMA 350 (FEMA 2000) Failure Mode Moment capacity [kn-m] Shear bolts fracture 726 T stem tension fracture 687 T flange plastification 309 Tension bolts fracture 553 T stem block shear 399 This basic T stub was modified in order to conduct the parametric studies. Table 3.2 shows the parameters for the configurations analyzed under monotonic loading. (a) TSDD1 (b) TSDD2 Figure 4 Configurations to study the effect of the tension bolts layout To generate the analysis matrix, the flange thickness was maintained, while the stem thickness and distance between tension bolts were varied. The last two configurations correspond to the outer tension bolts spaced
5 closer and farther than the interior bolts, respectively, as shown in Figure 4. Table 3.2 Analysis matrix Name Stem thickness [mm] Tension bolt gage spacing [mm] TSD TSD TSD TSD TSD TSE TSE TSE TSE TSDD TSDD Model description The finite element model developed is shown in Figure 5. To simplify the model, only one half of the T stub was modeled considering symmetry conditions, the beam flange was modeled as a rigid element, and the column was replaced by a rigid surface with compression-only supports. The steel properties for the T stub and the A490 bolts proposed by Swanson and Leon (2001), shown in Figure 5, were used. (a) Mesh (b) T stub properties (c) Bolt properties (d) Weld properties Figure 5 Finite element model of the T stub The weld region was modeled with material properties recommended by an electrode provider, considering an
6 E7010A1 electrode and data from tests performed according to AWS 5.5 specifications (AWS, 1996). A space was provided between the flange and the stem, to simulate the situation of incomplete penetration through the thickness of the stem of the fillet welds. Solid rectangular 20-node and tetrahedral 10-node elements were used to mesh the T stub and bolts. The load was applied in two stages; first, the bolts were subjected to a pretension, followed by the application of monotonic loading through the beam flange. The analysis was stopped when the fracture strain ε u was reached on any of the elements of the model (8% for the A490 bolts, 23% for the A572 Gr.50 and 29% for the weld material) Analytical results The total force-deformation behavior of the tees for different tension bolt distances is shown in Figure 6(a). All the configurations failed due to fracture of the tension bolts. It can be seen that the strength and ductility of the T stub decrease with an increase in the distance between tension bolts. The decrease in strength is consistent with that predicted by FEMA 350 (FEMA, 2000), as illustrated in Figure 6(b). The reduced ductility is explained by the increase in the bolt force due to prying action. Force (kn) TS140 TS150 TS TS170 TS Total deformation (mm) Force (kn) FEMA350 FE Model Distance between tension bolts (mm) (a) T stub force-deformation results (b) Comparison with FEMA 350 (FEMA, 2000) Figure 6 Effect of tension bolt spacing It was also observed that, for the configurations with more closely spaced tension bolts (TD140 and TD150), the strains in the welds approached the fracture strains. This may explain in part the fractures observed by Coelho et al. (2004) in their experiments. The results of the variation in T stem thickness are shown in Figure 7. For the thinner stem configurations (TSE8 and TSE10) the failure occurred due to tension fracture in the net section of the stem, while for the others, minor inelastic deformations were observed in the stem and the failure occurred by fracture of the tension bolts Force (kn) TSE08 TSE TSE14 TSE Total deformation (mm) Figure 7 Effect of stem-to-flange thickness ratio
7 It can be seen that the configurations with thinner stems developed less capacity, but more ductility than the others. However, the large inelastic deformations in the stem affect the weld and the resulting design is inefficient with respect the use of the available bolt strength. No significant effects on the behavior and strength of the T stub were observed when the layout of the tension bolts was modified (TSDD1 and TSDD2 configurations). 4. EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES In order to validate the analytical conclusions, 2 series of 11 T stub configurations were tested under monotonically increasing tension. The specimens were one-half scale models of the configurations studied analytically. The specimens were tested under load control using a 600 kn universal testing machine. The instrumentation used included strain gages to measure strains in the T stem; LVDTs to measure total deformation, T flange prying, and uplift in the line of tension bolts; and a pressure gage to determine the applied load. The test setup is shown in Figure 8(a), and the results for different tension bolt spacing in Figure 8(b). These results confirm the conclusions of the analytical studies about the relationship between bolt spacing and strength Force [kn] TSD 170 TSD Deformation [mm] (a) Experimental setup (b) Effect of tension bolt spacing Figure 8 Experimental studies TSD 140 TSD 150 TSD 160 The results for different stem thicknesses also confirm the analytical results: specimens TSE8 and TSE10 failed by tensile fracture of the T stem and had significantly lower strength than specimens TSE14 and TSE16. No significant damage was observed on the welds. 5. CONCLUSIONS Analytical and experimental studies on the behavior of welded T stubs under tension were conducted. The objective of these studies was to evaluate the behavior of welded T stubs for use in DST connections. The analytical studies involved the development of a finite element model of the T stub in the connection, which included material nonlinearities and geometric discontinuities. The analytical results showed the potential for weld fracture when thin stems are used, or when the tension bolts to one side of the stem are spaced close to the tension bolts on the opposite side of the stem. The experimental studies verified some of the conclusions of the analyses. Tension bolt fracture was the main failure mode for all specimens, with the exception of the specimens with thinner stems. The strength was larger than the strength predicted by current design recommendations and the analytical model. The analytical and experimental results will be used to revise and improve model for strength and stiffness of DST connections, when using welded T stubs.
8 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The studies reported herein were possible thanks to the support of the University of Chile, Grant Nº INI 06/05-2. REFERENCES AISC (2005). Seismic Provisions for Structural Steel Buildings, ANSI/AISC , American Institute of Steel Construction, Chicago, Illinois, USA. ANSYS (2005). ANSYS. Theory Reference, ANSYS Inc., Canonsburg, PA, USA. AWS (1996). ANSI/AWS A5.5-96, Specification For Low-Alloy Steel Electrodes For Shielded Metal Arc Welding, American Welding Society, Miami, Florida, USA. Coelho A., Biljaard F. Gresnigt N., and Simoes Da Silva L. (2004). Experimental assessment of the behaviour of bolted T-stub connections made up of welded plates. Journal of Constructional Steel Research 60, Coelho A., Biljaard F., and Simoes Da Silva L. (2006). Characterization of the Nonlinear Behaviour of Single Bolted T-Stub Connections. Journal of Structural Engineering 132:6, FEMA (2000). FEMA 350 Recommended Seismic Design Criteria for New Steel Moment-Frame Buildings, Federal Emergency Management Agency, Washington DC, USA. Krawinkler, H., and Bertero, V.V. (1971). Inelastic behaviour of steel beam-to-column subassemblies, EERC - University of California, Berkeley, California, USA. INN (1977), NCh203. Of77. Aceros para Uso Estructural. Requisitos, Instituto Nacional de Normalización, Santiago, Chile. Piluso V., Faella C. and Rizzano G. (2001a). Ultimate Behaviour of Bolted T-Stubs. II: Model Validation. Journal of Structural Engineering 127:6, Piluso V., Faella C. and Rizzano G. (2001b).Ultimate Behaviour of Bolted T-Stubs. I: Theoretical Model, Journal of Structural Engineering 127:6, Popov, E. P., and Stephen, R. M. (1970). Cyclic loading of full-size steel connections, EERC - University of California, Berkeley, California, USA. Sherbourne A.N., and Bahaari M.R. (1996). 3D Simulation of Bolted Connections to Unstiffened Columns-I. T-stub Connections. Journal of Constructional Steel Research 40, Swanson, J.A., and Leon, R.T. (2000). Bolted Steel Connections: Tests On T-Stub Components. Journal of Structural Engineering 126:1, Swanson, J.A., and Leon, R.T. (2001). Stiffness modelling of bolted t-stub connection components. Journal of Structural Engineering 127:5,
CE591 Fall 2013 Lecture 26: Moment Connections
 CE591 Fall 2013 Lecture 26: Moment Connections Explain basic design procedure for moment (FR) connections Explain considerations for connections in momentresisting frames for seismic demands Describe problems
CE591 Fall 2013 Lecture 26: Moment Connections Explain basic design procedure for moment (FR) connections Explain considerations for connections in momentresisting frames for seismic demands Describe problems
Design Parameters for Steel Special Moment Frame Connections
 SEAOC 2011 CONVENTION PROCEEDINGS Design Parameters for Steel Special Moment Frame Connections Scott M. Adan, Ph.D., S.E., SECB, Chair SEAONC Structural Steel Subcommittee Principal Adan Engineering Oakland,
SEAOC 2011 CONVENTION PROCEEDINGS Design Parameters for Steel Special Moment Frame Connections Scott M. Adan, Ph.D., S.E., SECB, Chair SEAONC Structural Steel Subcommittee Principal Adan Engineering Oakland,
A DESIGN PROCEDURE FOR BOLTED TOP-AND-SEAT ANGLE CONNECTIONS FOR USE IN SEISMIC APPLICATIONS
 A DESIGN PROCEDURE FOR BOLTED TOP-AND-SEAT ANGLE CONNECTIONS FOR USE IN SEISMIC APPLICATIONS Jared D. Schippers, Daniel J. Ruffley, Dr. Gian A. Rassati, and Dr. James A. Swanson School of Advanced Structures,
A DESIGN PROCEDURE FOR BOLTED TOP-AND-SEAT ANGLE CONNECTIONS FOR USE IN SEISMIC APPLICATIONS Jared D. Schippers, Daniel J. Ruffley, Dr. Gian A. Rassati, and Dr. James A. Swanson School of Advanced Structures,
! # # % % & () +, & +,,. / 0 % 1 + + 0 % 1 + + 2) () 3
 ! # # % % & () +, & +,,. / 0 % 1 + + 0 % 1 + + 2) () 3 4 SEISMIC EVALUATION OF REDUCED WEB SECTION(RWS) MOMENT CONNECTIONS Konstantinos Daniel Tsavdaridis Assistant Professor of Structural Engineering
! # # % % & () +, & +,,. / 0 % 1 + + 0 % 1 + + 2) () 3 4 SEISMIC EVALUATION OF REDUCED WEB SECTION(RWS) MOMENT CONNECTIONS Konstantinos Daniel Tsavdaridis Assistant Professor of Structural Engineering
ANALYSIS OF A LAP JOINT FRICTION CONNECTION USING HIGH STRENGTH BOLTS
 Nordic Steel Construction Conference 212 Hotel Bristol, Oslo, Norway 5-7 September 212 ANALYSIS OF A LAP JOINT FRICTION CONNECTION USING HIGH STRENGTH BOLTS Marouene Limam a, Christine Heistermann a and
Nordic Steel Construction Conference 212 Hotel Bristol, Oslo, Norway 5-7 September 212 ANALYSIS OF A LAP JOINT FRICTION CONNECTION USING HIGH STRENGTH BOLTS Marouene Limam a, Christine Heistermann a and
Structural Integrity Analysis
 Structural Integrity Analysis 1. STRESS CONCENTRATION Igor Kokcharov 1.1 STRESSES AND CONCENTRATORS 1.1.1 Stress An applied external force F causes inner forces in the carrying structure. Inner forces
Structural Integrity Analysis 1. STRESS CONCENTRATION Igor Kokcharov 1.1 STRESSES AND CONCENTRATORS 1.1.1 Stress An applied external force F causes inner forces in the carrying structure. Inner forces
New approaches in Eurocode 3 efficient global structural design
 New approaches in Eurocode 3 efficient global structural design Part 1: 3D model based analysis using general beam-column FEM Ferenc Papp* and József Szalai ** * Associate Professor, Department of Structural
New approaches in Eurocode 3 efficient global structural design Part 1: 3D model based analysis using general beam-column FEM Ferenc Papp* and József Szalai ** * Associate Professor, Department of Structural
SEISMIC DESIGN. Various building codes consider the following categories for the analysis and design for earthquake loading:
 SEISMIC DESIGN Various building codes consider the following categories for the analysis and design for earthquake loading: 1. Seismic Performance Category (SPC), varies from A to E, depending on how the
SEISMIC DESIGN Various building codes consider the following categories for the analysis and design for earthquake loading: 1. Seismic Performance Category (SPC), varies from A to E, depending on how the
Numerical modelling of shear connection between concrete slab and sheeting deck
 7th fib International PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 2008 September 10-13, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Numerical modelling of shear connection between concrete slab and sheeting deck Noémi Seres
7th fib International PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 2008 September 10-13, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Numerical modelling of shear connection between concrete slab and sheeting deck Noémi Seres
SPECIFICATIONS, LOADS, AND METHODS OF DESIGN
 CHAPTER Structural Steel Design LRFD Method Third Edition SPECIFICATIONS, LOADS, AND METHODS OF DESIGN A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Part II Structural
CHAPTER Structural Steel Design LRFD Method Third Edition SPECIFICATIONS, LOADS, AND METHODS OF DESIGN A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Part II Structural
bi directional loading). Prototype ten story
 NEESR SG: Behavior, Analysis and Design of Complex Wall Systems The laboratory testing presented here was conducted as part of a larger effort that employed laboratory testing and numerical simulation
NEESR SG: Behavior, Analysis and Design of Complex Wall Systems The laboratory testing presented here was conducted as part of a larger effort that employed laboratory testing and numerical simulation
CSA S16-09 Design of Steel Structures Canada
 CSA S16-09 Design of Steel Structures Canada Ed Whalen, P.Eng CISC President CSA S16-09 1 CSA Standard S16-09 Standard, Design of Steel Structures. Sets out minimum requirements used by engineers in the
CSA S16-09 Design of Steel Structures Canada Ed Whalen, P.Eng CISC President CSA S16-09 1 CSA Standard S16-09 Standard, Design of Steel Structures. Sets out minimum requirements used by engineers in the
STRENGTH AND DUCTILITY OF WELDED JOINTS SUBJECTED TO OUT OF PLANE BENDING
 STRENGTH AND DUCTILITY OF WELDED JOINTS SUBJECTED TO OUT OF PLANE BENDING by Ivan Gomez Amit Kanvinde University of California, Davis Yu Kay Kwan Gilbert Grondin University of Alberta Final Report Presented
STRENGTH AND DUCTILITY OF WELDED JOINTS SUBJECTED TO OUT OF PLANE BENDING by Ivan Gomez Amit Kanvinde University of California, Davis Yu Kay Kwan Gilbert Grondin University of Alberta Final Report Presented
Bearing strength of stainless steel bolted plates in tension
 NSCC29 Bearing strength of stainless steel bolted plates in tension G. KIYMAZ 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Istanbul Kultur University, Ataköy Campus, Bakırköy, Istanbul, Turkey ABSTRACT: A study
NSCC29 Bearing strength of stainless steel bolted plates in tension G. KIYMAZ 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Istanbul Kultur University, Ataköy Campus, Bakırköy, Istanbul, Turkey ABSTRACT: A study
NOTCHES AND THEIR EFFECTS. Ali Fatemi - University of Toledo All Rights Reserved Chapter 7 Notches and Their Effects 1
 NOTCHES AND THEIR EFFECTS Ali Fatemi - University of Toledo All Rights Reserved Chapter 7 Notches and Their Effects 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Background Stress/Strain Concentrations S-N Approach for Notched Members
NOTCHES AND THEIR EFFECTS Ali Fatemi - University of Toledo All Rights Reserved Chapter 7 Notches and Their Effects 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Background Stress/Strain Concentrations S-N Approach for Notched Members
Miss S. S. Nibhorkar 1 1 M. E (Structure) Scholar,
 Volume, Special Issue, ICSTSD Behaviour of Steel Bracing as a Global Retrofitting Technique Miss S. S. Nibhorkar M. E (Structure) Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering
Volume, Special Issue, ICSTSD Behaviour of Steel Bracing as a Global Retrofitting Technique Miss S. S. Nibhorkar M. E (Structure) Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering
SEISMIC RETROFITTING TECHNIQUE USING CARBON FIBERS FOR REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS
 Fracture Mechanics of Concrete Structures Proceedings FRAMCOS-3 AEDIFICA TIO Publishers, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany SEISMIC RETROFITTING TECHNIQUE USING CARBON FIBERS FOR REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS H.
Fracture Mechanics of Concrete Structures Proceedings FRAMCOS-3 AEDIFICA TIO Publishers, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany SEISMIC RETROFITTING TECHNIQUE USING CARBON FIBERS FOR REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS H.
Seismic Risk Prioritization of RC Public Buildings
 Seismic Risk Prioritization of RC Public Buildings In Turkey H. Sucuoğlu & A. Yakut Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey J. Kubin & A. Özmen Prota Inc, Ankara, Turkey SUMMARY Over the past
Seismic Risk Prioritization of RC Public Buildings In Turkey H. Sucuoğlu & A. Yakut Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey J. Kubin & A. Özmen Prota Inc, Ankara, Turkey SUMMARY Over the past
THE EFFECT OF STIRRUPS AND HOOKED STEEL FIBERS INSTEAD ON MOMENT-ROTATION CAPACITY OF BEAM-COLUMN CONNECTIONS
 THE EFFECT OF STIRRUPS AND HOOKED STEEL FIBERS INSTEAD ON MOMENT-ROTATION CAPACITY OF BEAM-COLUMN CONNECTIONS Assist. Prof. Dr. S. KamilAkın 1, Assist. Prof. Dr. Nail Kara 1, 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
THE EFFECT OF STIRRUPS AND HOOKED STEEL FIBERS INSTEAD ON MOMENT-ROTATION CAPACITY OF BEAM-COLUMN CONNECTIONS Assist. Prof. Dr. S. KamilAkın 1, Assist. Prof. Dr. Nail Kara 1, 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW TEST FOR DETERMINATION OF TENSILE STRENGTH OF CONCRETE BLOCKS
 1 th Canadian Masonry Symposium Vancouver, British Columbia, June -5, 013 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW TEST FOR DETERMINATION OF TENSILE STRENGTH OF CONCRETE BLOCKS Vladimir G. Haach 1, Graça Vasconcelos and Paulo
1 th Canadian Masonry Symposium Vancouver, British Columbia, June -5, 013 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW TEST FOR DETERMINATION OF TENSILE STRENGTH OF CONCRETE BLOCKS Vladimir G. Haach 1, Graça Vasconcelos and Paulo
TECHNICAL NOTE. Design of Diagonal Strap Bracing Lateral Force Resisting Systems for the 2006 IBC. On Cold-Formed Steel Construction INTRODUCTION
 TECHNICAL NOTE On Cold-Formed Steel Construction 1201 15th Street, NW, Suite 320 W ashington, DC 20005 (202) 785-2022 $5.00 Design of Diagonal Strap Bracing Lateral Force Resisting Systems for the 2006
TECHNICAL NOTE On Cold-Formed Steel Construction 1201 15th Street, NW, Suite 320 W ashington, DC 20005 (202) 785-2022 $5.00 Design of Diagonal Strap Bracing Lateral Force Resisting Systems for the 2006
Optimum proportions for the design of suspension bridge
 Journal of Civil Engineering (IEB), 34 (1) (26) 1-14 Optimum proportions for the design of suspension bridge Tanvir Manzur and Alamgir Habib Department of Civil Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
Journal of Civil Engineering (IEB), 34 (1) (26) 1-14 Optimum proportions for the design of suspension bridge Tanvir Manzur and Alamgir Habib Department of Civil Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF STRUCTURES
 SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF STRUCTURES RANJITH DISSANAYAKE DEPT. OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF PERADENIYA, SRI LANKA ABSTRACT Many existing reinforced concrete structures in present
SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF STRUCTURES RANJITH DISSANAYAKE DEPT. OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF PERADENIYA, SRI LANKA ABSTRACT Many existing reinforced concrete structures in present
Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra
 Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra Erke Wang, Thomas Nelson, Rainer Rauch CAD-FEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract This paper presents some analytical results and some test results for different
Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra Erke Wang, Thomas Nelson, Rainer Rauch CAD-FEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract This paper presents some analytical results and some test results for different
Objectives. Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity and ductility of given materials.
 Lab 3 Tension Test Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Objectives Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity
Lab 3 Tension Test Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Objectives Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity
B.TECH. (AEROSPACE ENGINEERING) PROGRAMME (BTAE) Term-End Examination December, 2011 BAS-010 : MACHINE DESIGN
 No. of Printed Pages : 7 BAS-01.0 B.TECH. (AEROSPACE ENGINEERING) PROGRAMME (BTAE) CV CA CV C:) O Term-End Examination December, 2011 BAS-010 : MACHINE DESIGN Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : (1)
No. of Printed Pages : 7 BAS-01.0 B.TECH. (AEROSPACE ENGINEERING) PROGRAMME (BTAE) CV CA CV C:) O Term-End Examination December, 2011 BAS-010 : MACHINE DESIGN Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : (1)
Hybrid simulation evaluation of the suspended zipper braced frame
 Hybrid simulation evaluation of the suspended zipper braced frame Tony Yang Post-doctoral scholar University of California, Berkeley Acknowledgements: Andreas Schellenberg, Bozidar Stojadinovic, Jack Moehle
Hybrid simulation evaluation of the suspended zipper braced frame Tony Yang Post-doctoral scholar University of California, Berkeley Acknowledgements: Andreas Schellenberg, Bozidar Stojadinovic, Jack Moehle
Technical Report Example (1) Chartered (CEng) Membership
 Technical Report Example (1) Chartered (CEng) Membership A TECHNICAL REPORT IN SUPPORT OF APPLICATION FOR CHARTERED MEMBERSHIP OF IGEM DESIGN OF 600 (103 BAR) 820MM SELF SEALING REPAIR CLAMP AND VERIFICATION
Technical Report Example (1) Chartered (CEng) Membership A TECHNICAL REPORT IN SUPPORT OF APPLICATION FOR CHARTERED MEMBERSHIP OF IGEM DESIGN OF 600 (103 BAR) 820MM SELF SEALING REPAIR CLAMP AND VERIFICATION
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME 2 ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS
 ENGINEERING COMPONENTS EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS Structural members: struts and ties; direct stress and strain,
ENGINEERING COMPONENTS EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS Structural members: struts and ties; direct stress and strain,
Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures
 Chapter 8 Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures 8.1 Scope Provisions of Sec. 8.1 and 8.2 of Chapter 8 shall apply for detailing of reinforcement in reinforced concrete members, in general. For
Chapter 8 Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures 8.1 Scope Provisions of Sec. 8.1 and 8.2 of Chapter 8 shall apply for detailing of reinforcement in reinforced concrete members, in general. For
DESIGN OF SLABS. 3) Based on support or boundary condition: Simply supported, Cantilever slab,
 DESIGN OF SLABS Dr. G. P. Chandradhara Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering Mysore 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional planar structural element having thickness small compared
DESIGN OF SLABS Dr. G. P. Chandradhara Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering Mysore 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional planar structural element having thickness small compared
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE COLLAR PRODUCTION ON THE PIERCED FLAT SHEET METAL USING LASER FORMING PROCESS
 JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN SCIENCE (ISSN 2322-5009) CODEN (USA): JCRSDJ 2014, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp:277-284 Available at www.jcrs010.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE COLLAR
JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN SCIENCE (ISSN 2322-5009) CODEN (USA): JCRSDJ 2014, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp:277-284 Available at www.jcrs010.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE COLLAR
Requirements for the Use of PRESSS Moment-Resisting Frame Systems
 Requirements for the Use of PRESSS Moment-Resisting Frame Systems Neil M. Hawkins, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Department of Civil Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, Illinois S.
Requirements for the Use of PRESSS Moment-Resisting Frame Systems Neil M. Hawkins, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Department of Civil Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, Illinois S.
FATIGUE CONSIDERATION IN DESIGN
 FATIGUE CONSIDERATION IN DESIGN OBJECTIVES AND SCOPE In this module we will be discussing on design aspects related to fatigue failure, an important mode of failure in engineering components. Fatigue failure
FATIGUE CONSIDERATION IN DESIGN OBJECTIVES AND SCOPE In this module we will be discussing on design aspects related to fatigue failure, an important mode of failure in engineering components. Fatigue failure
Simulation for the Collapse of WTC after Aeroplane Impact
 Simulation for the Collapse of WTC after Aeroplane Impact LU Xinzheng & JIANG Jianjing Department of Civil Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 Abstract: Mechanical simulation and parameter
Simulation for the Collapse of WTC after Aeroplane Impact LU Xinzheng & JIANG Jianjing Department of Civil Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 Abstract: Mechanical simulation and parameter
D1.8 Seismic Supplement Welding Manual. A General Overview of AWS D1.8 Welding Code - Seismic Supplement
 D1.8 Seismic Supplement Welding Manual A General Overview of AWS D1.8 Welding Code - Seismic Supplement 2 D1.8 Seismic Supplement Welding Manual Table of Contents Introduction...2 Background...4 Purpose
D1.8 Seismic Supplement Welding Manual A General Overview of AWS D1.8 Welding Code - Seismic Supplement 2 D1.8 Seismic Supplement Welding Manual Table of Contents Introduction...2 Background...4 Purpose
Draft Table of Contents. Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14
 Draft Table of Contents Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14 BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL CONCRETE (ACI 318 14) Chapter 1 General 1.1 Scope of ACI 318
Draft Table of Contents Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14 BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL CONCRETE (ACI 318 14) Chapter 1 General 1.1 Scope of ACI 318
LINKED COLUMN FRAME STEEL SYSTEM PERFORMANCE VALIDATION USING HYBRID SIMULATION
 10NCEE Tenth U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Frontiers of Earthquake Engineering July 21-25, 2014 Anchorage, Alaska LINKED COLUMN FRAME STEEL SYSTEM PERFORMANCE VALIDATION USING HYBRID
10NCEE Tenth U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Frontiers of Earthquake Engineering July 21-25, 2014 Anchorage, Alaska LINKED COLUMN FRAME STEEL SYSTEM PERFORMANCE VALIDATION USING HYBRID
Analysis and Repair of an Earthquake-Damaged High-rise Building in Santiago, Chile
 Analysis and Repair of an Earthquake-Damaged High-rise Building in Santiago, Chile J. Sherstobitoff Ausenco Sandwell, Vancouver, Canada P. Cajiao AMEC, Vancouver, Canada P. Adebar University of British
Analysis and Repair of an Earthquake-Damaged High-rise Building in Santiago, Chile J. Sherstobitoff Ausenco Sandwell, Vancouver, Canada P. Cajiao AMEC, Vancouver, Canada P. Adebar University of British
In-situ Load Testing to Evaluate New Repair Techniques
 In-situ Load Testing to Evaluate New Repair Techniques W.J. Gold 1 and A. Nanni 2 1 Assistant Research Engineer, Univ. of Missouri Rolla, Dept. of Civil Engineering 2 V&M Jones Professor, Univ. of Missouri
In-situ Load Testing to Evaluate New Repair Techniques W.J. Gold 1 and A. Nanni 2 1 Assistant Research Engineer, Univ. of Missouri Rolla, Dept. of Civil Engineering 2 V&M Jones Professor, Univ. of Missouri
CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
 41 CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Simulation is a powerful tool that engineers use to predict the result of a phenomenon or to simulate the working situation in which a part or machine will perform in
41 CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Simulation is a powerful tool that engineers use to predict the result of a phenomenon or to simulate the working situation in which a part or machine will perform in
Numerical models of welded and bolted beam to column connections
 Acta Technica Napocensis: Civil Engineering & Architecture Vol. 55, No.1 (2012) Journal homepage: http://constructii.utcluj.ro/actacivileng Numerical models of welded and bolted beam to column connections
Acta Technica Napocensis: Civil Engineering & Architecture Vol. 55, No.1 (2012) Journal homepage: http://constructii.utcluj.ro/actacivileng Numerical models of welded and bolted beam to column connections
Sheet metal operations - Bending and related processes
 Sheet metal operations - Bending and related processes R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Table of Contents 1.Quiz-Key... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.Bending
Sheet metal operations - Bending and related processes R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Table of Contents 1.Quiz-Key... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.Bending
METU DEPARTMENT OF METALLURGICAL AND MATERIALS ENGINEERING
 METU DEPARTMENT OF METALLURGICAL AND MATERIALS ENGINEERING Met E 206 MATERIALS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 1 Prof. Dr. Rıza GÜRBÜZ Res. Assist. Gül ÇEVİK (Room: B-306) INTRODUCTION TENSION TEST Mechanical testing
METU DEPARTMENT OF METALLURGICAL AND MATERIALS ENGINEERING Met E 206 MATERIALS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 1 Prof. Dr. Rıza GÜRBÜZ Res. Assist. Gül ÇEVİK (Room: B-306) INTRODUCTION TENSION TEST Mechanical testing
Seismic Design of Steel Special Moment Frames:
 NIST GCR 09-917-3 NEHRP Seismic Design Technical Brief No. 2 Seismic Design of Steel Special Moment Frames: A Guide for Practicing Engineers Ronald O. Hamburger Helmut Krawinkler James O. Malley Scott
NIST GCR 09-917-3 NEHRP Seismic Design Technical Brief No. 2 Seismic Design of Steel Special Moment Frames: A Guide for Practicing Engineers Ronald O. Hamburger Helmut Krawinkler James O. Malley Scott
The following sketches show the plans of the two cases of one-way slabs. The spanning direction in each case is shown by the double headed arrow.
 9.2 One-way Slabs This section covers the following topics. Introduction Analysis and Design 9.2.1 Introduction Slabs are an important structural component where prestressing is applied. With increase
9.2 One-way Slabs This section covers the following topics. Introduction Analysis and Design 9.2.1 Introduction Slabs are an important structural component where prestressing is applied. With increase
Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and
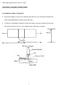 CHAPTER 6. WELDED CONNECTIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTS Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and fused, with supplementary molten metal at the joint. A
CHAPTER 6. WELDED CONNECTIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTS Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and fused, with supplementary molten metal at the joint. A
CRITERIA FOR PRELOADED BOLTS
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center Houston, Texas 77058 REVISION A JULY 6, 1998 REPLACES BASELINE SPACE SHUTTLE CRITERIA FOR PRELOADED BOLTS CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION..............................................
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center Houston, Texas 77058 REVISION A JULY 6, 1998 REPLACES BASELINE SPACE SHUTTLE CRITERIA FOR PRELOADED BOLTS CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION..............................................
Advanced bolt assessment through process automation
 Titelmasterformat Bolt Assessment inside durch ANSYS Klicken bearbeiten Advanced bolt assessment through process automation Contents Short presentation of VDI 2230 Workflow with Bolt Assessment inside
Titelmasterformat Bolt Assessment inside durch ANSYS Klicken bearbeiten Advanced bolt assessment through process automation Contents Short presentation of VDI 2230 Workflow with Bolt Assessment inside
EVALUATION OF SEISMIC RESPONSE - FACULTY OF LAND RECLAMATION AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING -BUCHAREST
 EVALUATION OF SEISMIC RESPONSE - FACULTY OF LAND RECLAMATION AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING -BUCHAREST Abstract Camelia SLAVE University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine of Bucharest, 59 Marasti
EVALUATION OF SEISMIC RESPONSE - FACULTY OF LAND RECLAMATION AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING -BUCHAREST Abstract Camelia SLAVE University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine of Bucharest, 59 Marasti
A Case Study Comparing Two Approaches for Applying Area Loads: Tributary Area Loads vs Shell Pressure Loads
 1 A Case Study Comparing Two Approaches for Applying Area Loads: Tributary Area Loads vs Shell Pressure Loads By Dr. Siriwut Sasibut (Application Engineer) S-FRAME Software Inc. #1158 13351 Commerce Parkway
1 A Case Study Comparing Two Approaches for Applying Area Loads: Tributary Area Loads vs Shell Pressure Loads By Dr. Siriwut Sasibut (Application Engineer) S-FRAME Software Inc. #1158 13351 Commerce Parkway
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL TUTORIAL 4 - COMPLEMENTARY SHEAR STRESS
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL TUTORIAL 4 - COMPLEMENTARY SHEAR STRESS This the fourth and final tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge our progress b completing the self assessment exercises.
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL TUTORIAL 4 - COMPLEMENTARY SHEAR STRESS This the fourth and final tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge our progress b completing the self assessment exercises.
ETABS. Integrated Building Design Software. Concrete Shear Wall Design Manual. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA
 ETABS Integrated Building Design Software Concrete Shear Wall Design Manual Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 8 January 2002 Copyright The computer program ETABS and all
ETABS Integrated Building Design Software Concrete Shear Wall Design Manual Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 8 January 2002 Copyright The computer program ETABS and all
BOLTED RHS END-PLATE JOINTS IN AXIAL TENSION
 Nordic Steel Construction Conference 2012 Hotel Bristol, Oslo, Norway 5-7 September 2012 BOLTED RHS END-PLATE JOINTS IN AXIAL TENSION Fredrik Torp Karlsen a and Arne Aalberg b a Department of Structural
Nordic Steel Construction Conference 2012 Hotel Bristol, Oslo, Norway 5-7 September 2012 BOLTED RHS END-PLATE JOINTS IN AXIAL TENSION Fredrik Torp Karlsen a and Arne Aalberg b a Department of Structural
Introduction to Mechanical Behavior of Biological Materials
 Introduction to Mechanical Behavior of Biological Materials Ozkaya and Nordin Chapter 7, pages 127-151 Chapter 8, pages 173-194 Outline Modes of loading Internal forces and moments Stiffness of a structure
Introduction to Mechanical Behavior of Biological Materials Ozkaya and Nordin Chapter 7, pages 127-151 Chapter 8, pages 173-194 Outline Modes of loading Internal forces and moments Stiffness of a structure
TO BASE PLATES OF HOLLOW SECTIONS COLUMNS
 TO BASE PLATES OF HOLLOW SECTIONS COLUMNS Kamila Horová, Jan Tomšů, František Wald Department of Steel and Civil Structures, Czech Technical University in Prague [email protected]; [email protected];
TO BASE PLATES OF HOLLOW SECTIONS COLUMNS Kamila Horová, Jan Tomšů, František Wald Department of Steel and Civil Structures, Czech Technical University in Prague [email protected]; [email protected];
Nueva Edición del libro clásico para estudiantes de grado.
 Nueva Edición del libro clásico para estudiantes de grado. Ha aparecido la quinta edición del que ya se ha convertido en uno de los libros más vendidos de Diseño de estructuras de Acero para su uso en
Nueva Edición del libro clásico para estudiantes de grado. Ha aparecido la quinta edición del que ya se ha convertido en uno de los libros más vendidos de Diseño de estructuras de Acero para su uso en
SECTION 1 Modeling in Contemporary Software Programs
 SECTION 1 Modeling in Contemporary Software Programs 1.1 General The numerical tools used by expert engineers to analyze seismically isolated structures at the time of this writing represent the state
SECTION 1 Modeling in Contemporary Software Programs 1.1 General The numerical tools used by expert engineers to analyze seismically isolated structures at the time of this writing represent the state
Rehabilitation of a 1985 Steel Moment- Frame Building
 Rehabilitation of a 1985 Steel Moment- Frame Building Gregg Haskell, a) M.EERI A 1985 steel moment frame is seismically upgraded using passive energy dissipation, without adding stiffness to the system.
Rehabilitation of a 1985 Steel Moment- Frame Building Gregg Haskell, a) M.EERI A 1985 steel moment frame is seismically upgraded using passive energy dissipation, without adding stiffness to the system.
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope
 Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Bending, Forming and Flexing Printed Circuits
 Bending, Forming and Flexing Printed Circuits John Coonrod Rogers Corporation Introduction: In the printed circuit board industry there are generally two main types of circuit boards; there are rigid printed
Bending, Forming and Flexing Printed Circuits John Coonrod Rogers Corporation Introduction: In the printed circuit board industry there are generally two main types of circuit boards; there are rigid printed
Technical Notes 3B - Brick Masonry Section Properties May 1993
 Technical Notes 3B - Brick Masonry Section Properties May 1993 Abstract: This Technical Notes is a design aid for the Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (ACI 530/ASCE 5/TMS 402-92) and Specifications
Technical Notes 3B - Brick Masonry Section Properties May 1993 Abstract: This Technical Notes is a design aid for the Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (ACI 530/ASCE 5/TMS 402-92) and Specifications
ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING APDL CONTROL
 ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING AP... Page 1 of 19 ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING APDL CONTROL Yasumasa Shoji, Satoshi Nagata, Toyo Engineering Corporation,
ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING AP... Page 1 of 19 ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING APDL CONTROL Yasumasa Shoji, Satoshi Nagata, Toyo Engineering Corporation,
FEM analysis of the forming process of automotive suspension springs
 FEM analysis of the forming process of automotive suspension springs Berti G. and Monti M. University of Padua, DTG, Stradella San Nicola 3, I-36100 Vicenza (Italy) [email protected], [email protected].
FEM analysis of the forming process of automotive suspension springs Berti G. and Monti M. University of Padua, DTG, Stradella San Nicola 3, I-36100 Vicenza (Italy) [email protected], [email protected].
Chapter 3 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION FEATURES IMPORTANT TO SEISMIC PERFORMANCE
 Chapter 3 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION FEATURES IMPORTANT TO SEISMIC PERFORMANCE To satisfy the performance goals of the NEHRP Recommended Seismic Provisions, a number of characteristics are important to the
Chapter 3 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION FEATURES IMPORTANT TO SEISMIC PERFORMANCE To satisfy the performance goals of the NEHRP Recommended Seismic Provisions, a number of characteristics are important to the
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF A HORIZONTALLY CURVED BRIDGE MODEL
 10NCEE Tenth U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Frontiers of Earthquake Engineering July 21-25, 2014 Anchorage, Alaska NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF A HORIZONTALLY CURVED BRIDGE MODEL K. Kinoshita
10NCEE Tenth U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Frontiers of Earthquake Engineering July 21-25, 2014 Anchorage, Alaska NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF A HORIZONTALLY CURVED BRIDGE MODEL K. Kinoshita
Burst Pressure Prediction of Pressure Vessel using FEA
 Burst Pressure Prediction of Pressure Vessel using FEA Nidhi Dwivedi, Research Scholar (G.E.C, Jabalpur, M.P), Veerendra Kumar Principal (G.E.C, Jabalpur, M.P) Abstract The main objective of this paper
Burst Pressure Prediction of Pressure Vessel using FEA Nidhi Dwivedi, Research Scholar (G.E.C, Jabalpur, M.P), Veerendra Kumar Principal (G.E.C, Jabalpur, M.P) Abstract The main objective of this paper
Optimising plate girder design
 Optimising plate girder design NSCC29 R. Abspoel 1 1 Division of structural engineering, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands ABSTRACT: In the design of steel plate girders a high degree
Optimising plate girder design NSCC29 R. Abspoel 1 1 Division of structural engineering, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands ABSTRACT: In the design of steel plate girders a high degree
Use of Strain Gauge Rosette to Investigate Stress concentration in Isotropic and Orthotropic Plate with Circular Hole
 Use of Strain Gauge Rosette to Investigate Stress concentration in Isotropic and Orthotropic Plate with Circular Hole Mr.V.G.Aradhye 1, Prof.S.S.Kulkarni 2 1 PG Scholar, Mechanical department, SKN Sinhgad
Use of Strain Gauge Rosette to Investigate Stress concentration in Isotropic and Orthotropic Plate with Circular Hole Mr.V.G.Aradhye 1, Prof.S.S.Kulkarni 2 1 PG Scholar, Mechanical department, SKN Sinhgad
Seismically retrofitting reinforced concrete moment resisting frames by using expanded metal panels
 Faculté des Sciences Appliquées Département d'architecture, Géologie, Environnement et Constructions Secteur Ingénierie Structurale Seismically retrofitting reinforced concrete moment resisting frames
Faculté des Sciences Appliquées Département d'architecture, Géologie, Environnement et Constructions Secteur Ingénierie Structurale Seismically retrofitting reinforced concrete moment resisting frames
Hardened Concrete. Lecture No. 14
 Hardened Concrete Lecture No. 14 Strength of Concrete Strength of concrete is commonly considered its most valuable property, although in many practical cases, other characteristics, such as durability
Hardened Concrete Lecture No. 14 Strength of Concrete Strength of concrete is commonly considered its most valuable property, although in many practical cases, other characteristics, such as durability
Objective To conduct Charpy V-notch impact test and determine the ductile-brittle transition temperature of steels.
 IMPACT TESTING Objective To conduct Charpy V-notch impact test and determine the ductile-brittle transition temperature of steels. Equipment Coolants Standard Charpy V-Notched Test specimens Impact tester
IMPACT TESTING Objective To conduct Charpy V-notch impact test and determine the ductile-brittle transition temperature of steels. Equipment Coolants Standard Charpy V-Notched Test specimens Impact tester
CRASH ANALYSIS OF AN IMPACT ATTENUATOR FOR RACING CAR IN SANDWICH MATERIAL
 F2008-SC-016 CRASH ANALYSIS OF AN IMPACT ATTENUATOR FOR RACING CAR IN SANDWICH MATERIAL Boria, Simonetta *, Forasassi, Giuseppe Department of Mechanical, Nuclear and Production Engineering, University
F2008-SC-016 CRASH ANALYSIS OF AN IMPACT ATTENUATOR FOR RACING CAR IN SANDWICH MATERIAL Boria, Simonetta *, Forasassi, Giuseppe Department of Mechanical, Nuclear and Production Engineering, University
Tower Cross Arm Numerical Analysis
 Chapter 7 Tower Cross Arm Numerical Analysis In this section the structural analysis of the test tower cross arm is done in Prokon and compared to a full finite element analysis using Ansys. This is done
Chapter 7 Tower Cross Arm Numerical Analysis In this section the structural analysis of the test tower cross arm is done in Prokon and compared to a full finite element analysis using Ansys. This is done
METHOD OF STATEMENT FOR STATIC LOADING TEST
 Compression Test, METHOD OF STATEMENT FOR STATIC LOADING TEST Tension Test and Lateral Test According to the American Standards ASTM D1143 07, ASTM D3689 07, ASTM D3966 07 and Euro Codes EC7 Table of Contents
Compression Test, METHOD OF STATEMENT FOR STATIC LOADING TEST Tension Test and Lateral Test According to the American Standards ASTM D1143 07, ASTM D3689 07, ASTM D3966 07 and Euro Codes EC7 Table of Contents
Conceptual Design of Buildings (Course unit code 1C2)
 (Course unit code 1C2) Module C Design of Steel Members J.P. Jaspart (University of Liège) 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Bolts are the main type of fasteners used in steel joints. The main geometrical
(Course unit code 1C2) Module C Design of Steel Members J.P. Jaspart (University of Liège) 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Bolts are the main type of fasteners used in steel joints. The main geometrical
Repair of Fatigued Steel Bridge Girders with Carbon Fiber Strips
 2004-02 Final Report Repair of Fatigued Steel Bridge Girders with Carbon Fiber Strips Technical Report Documentation Page 1. Report No. 2. 3. Recipients Accession No. MN/RC 2004-02 4. Title and Subtitle
2004-02 Final Report Repair of Fatigued Steel Bridge Girders with Carbon Fiber Strips Technical Report Documentation Page 1. Report No. 2. 3. Recipients Accession No. MN/RC 2004-02 4. Title and Subtitle
Lap Fillet Weld Calculations and FEA Techniques
 Lap Fillet Weld Calculations and FEA Techniques By: MS.ME Ahmad A. Abbas Sr. Analysis Engineer [email protected] www.advancedcae.com Sunday, July 11, 2010 Advanced CAE All contents Copyright
Lap Fillet Weld Calculations and FEA Techniques By: MS.ME Ahmad A. Abbas Sr. Analysis Engineer [email protected] www.advancedcae.com Sunday, July 11, 2010 Advanced CAE All contents Copyright
The elements used in commercial codes can be classified in two basic categories:
 CHAPTER 3 Truss Element 3.1 Introduction The single most important concept in understanding FEA, is the basic understanding of various finite elements that we employ in an analysis. Elements are used for
CHAPTER 3 Truss Element 3.1 Introduction The single most important concept in understanding FEA, is the basic understanding of various finite elements that we employ in an analysis. Elements are used for
Description of mechanical properties
 ArcelorMittal Europe Flat Products Description of mechanical properties Introduction Mechanical properties are governed by the basic concepts of elasticity, plasticity and toughness. Elasticity is the
ArcelorMittal Europe Flat Products Description of mechanical properties Introduction Mechanical properties are governed by the basic concepts of elasticity, plasticity and toughness. Elasticity is the
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 1 STRESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING. On completion of this tutorial you should be able to do the following.
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTOIAL 1 STESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING This is the first tutorial on bending of beams designed for anyone wishing to study it at a fairly advanced level. You should judge
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTOIAL 1 STESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING This is the first tutorial on bending of beams designed for anyone wishing to study it at a fairly advanced level. You should judge
Performance of Existing Reinforced Concrete Columns under Bidirectional Shear & Axial Loading
 Performance of Existing Reinforced Concrete Columns under Bidirectional Shear & Axial Loading Laura M. Flores University of California, San Diego REU Institution: University of California, Berkeley REU
Performance of Existing Reinforced Concrete Columns under Bidirectional Shear & Axial Loading Laura M. Flores University of California, San Diego REU Institution: University of California, Berkeley REU
CE591 Lecture 8: Shear Walls
 CE591 Lecture 8: Shear Walls Introduction History, examples Benefits Disadvantages Plate Girder Analogy Behavior of Special Plate Shear Walls (SPSW) Design of SPSW Important considerations Special Plate
CE591 Lecture 8: Shear Walls Introduction History, examples Benefits Disadvantages Plate Girder Analogy Behavior of Special Plate Shear Walls (SPSW) Design of SPSW Important considerations Special Plate
REHABILITATION OF THE FIGUEIRA DA FOZ BRIDGE
 REHABILITATION OF THE FIGUEIRA DA FOZ BRIDGE A.Rito Proponte, Lda, Lisbon, Portugal J. Appleton A2P Consult, Lda, Lisbon, Portugal ABSTRACT: The Figueira da Foz Bridge includes a 405 m long cable stayed
REHABILITATION OF THE FIGUEIRA DA FOZ BRIDGE A.Rito Proponte, Lda, Lisbon, Portugal J. Appleton A2P Consult, Lda, Lisbon, Portugal ABSTRACT: The Figueira da Foz Bridge includes a 405 m long cable stayed
Fatigue Performance Evaluation of Forged Steel versus Ductile Cast Iron Crankshaft: A Comparative Study (EXECUTIVE SUMMARY)
 Fatigue Performance Evaluation of Forged Steel versus Ductile Cast Iron Crankshaft: A Comparative Study (EXECUTIVE SUMMARY) Ali Fatemi, Jonathan Williams and Farzin Montazersadgh Professor and Graduate
Fatigue Performance Evaluation of Forged Steel versus Ductile Cast Iron Crankshaft: A Comparative Study (EXECUTIVE SUMMARY) Ali Fatemi, Jonathan Williams and Farzin Montazersadgh Professor and Graduate
CH 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading
 CH 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading Some machine elements are subjected to static loads and for such elements static failure theories are used to predict failure (yielding or fracture).
CH 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading Some machine elements are subjected to static loads and for such elements static failure theories are used to predict failure (yielding or fracture).
DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS OF TUNED/HYBRID MASS DAMPERS USING MULTI-STAGE RUBBER BEARINGS FOR VIBRATION CONTROL OF STRUCTURES
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2243 DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS OF TUNED/HYBRID MASS DAMPERS USING MULTI-STAGE RUBBER BEARINGS FOR
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2243 DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS OF TUNED/HYBRID MASS DAMPERS USING MULTI-STAGE RUBBER BEARINGS FOR
Performance-based Evaluation of the Seismic Response of Bridges with Foundations Designed to Uplift
 Performance-based Evaluation of the Seismic Response of Bridges with Foundations Designed to Uplift Marios Panagiotou Assistant Professor, University of California, Berkeley Acknowledgments Pacific Earthquake
Performance-based Evaluation of the Seismic Response of Bridges with Foundations Designed to Uplift Marios Panagiotou Assistant Professor, University of California, Berkeley Acknowledgments Pacific Earthquake
Deflection Calculation of RC Beams: Finite Element Software Versus Design Code Methods
 Deflection Calculation of RC Beams: Finite Element Software Versus Design Code Methods G. Kaklauskas, Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, 1223 Vilnius, Lithuania ([email protected]) V.
Deflection Calculation of RC Beams: Finite Element Software Versus Design Code Methods G. Kaklauskas, Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, 1223 Vilnius, Lithuania ([email protected]) V.
1.054/1.541 Mechanics and Design of Concrete Structures (3-0-9) Outline 1 Introduction / Design Criteria for Reinforced Concrete Structures
 Prof. Oral Buyukozturk Massachusetts Institute of Technology Outline 1 1.054/1.541 Mechanics and Design of Concrete Structures (3-0-9) Outline 1 Introduction / Design Criteria for Reinforced Concrete Structures
Prof. Oral Buyukozturk Massachusetts Institute of Technology Outline 1 1.054/1.541 Mechanics and Design of Concrete Structures (3-0-9) Outline 1 Introduction / Design Criteria for Reinforced Concrete Structures
A Simple Method of Gripping Prestressing Strands for Tension Tests
 A Simple Method of Gripping Prestressing Strands for Tension Tests Presents a simple technique for gripping a prestressing strand to measure its breaking strength, modulus of elasticity or stress-strain
A Simple Method of Gripping Prestressing Strands for Tension Tests Presents a simple technique for gripping a prestressing strand to measure its breaking strength, modulus of elasticity or stress-strain
THE RELIABILITY OF CAPACITY-DESIGNED COMPONENTS IN SEISMIC RESISTANT SYSTEMS
 THE RELIABILITY OF CAPACITY-DESIGNED COMPONENTS IN SEISMIC RESISTANT SYSTEMS A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRIONMENTAL ENGINEERING AND THE COMMITTEE ON GRADUATE STUDIES OF
THE RELIABILITY OF CAPACITY-DESIGNED COMPONENTS IN SEISMIC RESISTANT SYSTEMS A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRIONMENTAL ENGINEERING AND THE COMMITTEE ON GRADUATE STUDIES OF
