Open Issues in Content Distribution
|
|
|
- Avice Letitia Jones
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Open Issues in Content Distribution Pablo Rodriguez Systems and Networking Department Microsoft Research, Cambridge. UK Rodriguez 1 The Problem The Internet has been growing very fast, with a growing number of users accessing a growing amount of content Servers and network links are overloaded Users get frustrated THE INTERNET Rodriguez 2
2 Content Distribution History... With 25 years of Internet experience, we ve learned exactly one way to deal with the exponential growth: Caching. (1997, Van Jacobson) and he was right, but with a different business model Rodriguez 3 Content Distribution History... Web Proxy Caching: ISP Web Cache INTERNET Servers Caches save ISPs bandwidth, reduce clients latency, and avoid flash crowds and bandwidth usage in the origin servers access link Web caching gives good performance because very often» a single client repeatedly accesses the same document» a nearby client also accesses the same document Cache Hit ratio increases logarithmically with number of users Rodriguez 4
3 Content Distribution History... ISP Backbone ISP Servers INTERNET ISP Rodriguez 5 What went wrong with Web Caches? Web protocols evolved extensively to accommodate caching, e.g. HTTP 1.1 However, Web caching was developed with a strong ISP perspective, leaving content providers out of the picture It is the ISP who places a cache and controls it ISPs only interest to use Web caches is to reduce bandwidth In the USA: Bandwidth was very cheap. No interest for ISPs in Caching In Europe, there were many more Web caches However, ISPs can arbitrarily tune Web caches to deliver stale content European Union tried to ban Web caching. Some US content providers started suing ISPs using Web caching Rodriguez 6
4 Content Provider s Point of View Content providers care about User experience latency Content freshness Avoid flash crowds Minimize bandwidth usage in their access link Accurate access statistics In an ideal world, all ISPs would use cooperative caches with enough capacity, delivering fresh content, and reporting accurate access statistics However, the real world is that many ISPs did not implement caching and the ones that did, abused of it Content providers defeated caches (Pragma: No-cache) and started thinking about building infrastructures to deliver their content Rodriguez 7 Content Distribution History... Some large content providers decided to use their network of Mirror Servers» But content providers prefer to outsource the distribution to a third party...» Plus, it is more cost effective (no need to dimension all systems for the pick) Content Distribution Networks (CDNs) build an overlay networks of caches to provide fast, costeffective, and reliable content delivery, while working tightly with content providers Rodriguez 8
5 Why are CDNs important? Content Distribution Networks: Provide control over content Bypass bottlenecks to reduce latency and provide more reliable performance Offload servers from flash crowds Provide economy of scale and reduce infrastructure and management cost (sharing) Allow for more sophisticated Web content authoring Eliminate needs to dimension all servers for pick (multiplexing) Shield servers from denial of attacks Provide application-level agreements CDNs are used to: Relieve end-user latency for the most important Web sites (e.g. CNN, Yahoo) Minimize impact of flash crowd events (e.g. Olympics, US Open) Provide significant bandwidth savings (e.g %) Distribute enterprise content (e.g. remote learning) Rodriguez 9 Content Distribution Middleware Apps Web Streaming Distant Learning File Swapping Games Wireless Grid CDN Content Distribution Components Web Caching Multicast Cache-Sharing Load Balancing Satellite Overlays P2P Content Redirection Error Correction Techniques Content Management TCP/IP Layer MAC Layer Rodriguez 10
6 CDN Case Study: Akamai Akamai (AH kuh my) is Hawaiian for intelligent, clever and informally cool. Founded Apr 99, Boston MA by MIT students [Nasdaq: AKAM], had an explosive opening-day gain of % on October 29 th, 2000 Akamai can be considered to be the first CDN in the Internet (others also at the time: Sandpiper, Digital Island) More than 1250 content providers use their network servers in 40 countries Still fewer countries than UN Delivers text/images as well as streaming of stored and life media. $2000 per Mbps/month. $300 for region-specific service Rodriguez 11 Akamai: How it works? Origin Server Name: IP: GET Pull/Push Images IP: ) Akamai Caches Name: ag12.akamai.net IP:? IP: In-lined Images 3) HTTP OK index.html <html> <img SRC= <img SRC= </html> 1) IP: DNS Query Name: aq12.akamai.net Process index.html 2) Akamai DNS DNS response Name: aq12.akamai.net IP: TTL: 10 sec Rodriguez 12
7 More Akamai information URL akamaization is becoming obsolete and only supported for legacy reasons Currently most content providers prefer to use DNS CNAME techniques to get all their content served from the Akamai servers» Still content providers need to run their origin servers Akamai Evolution: Files/Streaming Secure pages and whole pages Dynamic Page assembly at the edge (ESI) Distributed applications» First step is to replicate read-only databases Rodriguez 13 Akamai: How to avoid flash crowds? Origin Server Name: IP: Akamai Caches Rodriguez 14
8 Akamai: How to avoid flash crowds? Origin Server Name: IP: Hierarchical Caching Akamai Caches Rodriguez 15 CDN Challenges. Distributing Web content has proven to be an easier problem than expected Bandwidth and servers are becoming cheaper and cheaper P2P is a becoming a serious alternative to using CDNs Multimedia content is still waiting for the last-mile Plus no clear business model After the bubble burst, there are fewer content providers Content concentration. Fewer chances for statistical multiplexing Lots of content tends to be of local interest only (no need to have global presence) Few nodes with well connected links can provide most of the benefit (e.g. data centers in major countries) Managing a large number of servers around the world is difficult and expensive Rodriguez 16
9 CND s future. The edge is shrinking: Most ISPs can reach content providers within only few hops» Bottleneck is moving towards the servers Not much sense for world-wide CDNs with huge number of servers Left over from the bubble s era Cost inefficient Most likely CDNs will use much fewer servers placed only in wellconnected data hosting centers» Provides better multiplexing since sharing happens at fewer points» These servers will enable dynamic resource allocation for efficient infrastructure sharing CDNs will still be deployed in enterprises and countries with bandwidth problems P2P will take over part of the CDN s business, specially in the enterprise market Dynamic content delivery will not require moving the processing power to the edge Processing at the edge does not reduce the processing time Rodriguez 17 Research: Been there, done that Cache replacement policies Inter-Cache sharing protocols Redirection Mechanisms Content Management Rodriguez 18
10 Several Possible Research Areas Distributing Dynamic Content CDNs for Interactive Applications Wireless Content Distribution Minimizing maintenance/deployment costs Rodriguez 19 Content Distribution Issues How to scale the distribution of content to the network edge How to ensure that the content is up-to-date How to automatically redirect clients to the best edge servers Rodriguez 20
11 Selecting the Best Server The copy selected should ideally have the lowest access time Techniques for server selection use Client origination address Geographical proximity Number of hops RTT Server load Application level measurements Problems High complexity and overhead» periodic measurements, statistics The selected copy may not always be the best one Rodriguez 21 Parallel Downloads Instead consider parallel-downloads! Speeds-up download times Relaxes server selection Performs load balancing and increases fault-tolerance Replica Servers Popular Document Rodriguez 22
12 Requirements Documents should be large enough Replicated content must be bit-by-bit identical Clients and servers are able to utilize range requests as specified in HTTP 1.1 Clients and servers implement persistent connections to avoid TCP slow-start Rodriguez 23 How to choose the block size? The number of blocks should be larger than the number of mirror sites accessed in parallel Each block should be small enough to rapidly adapt to changing conditions and ensure that the last block requested from each server terminates at about the same time Each block should be sufficient large to reduce the influence of the idle times and reduce the number of negotiations (transmission time>>rtt) Client Get block i Block i Get block i+j Mirror Site Transmission of block i Idle time Client Get block i Block i Get block i+j Pipeline Mirror Site Transmission of block i idle time Rodriguez 24
13 Cost of Parallel-Access Processing overhead at the client for scheduling block assignments There are already several products that do a parallel-access to a single server It is easy to scale the client Additional network traffic generated by the block request messages Can be reduced by adaptively increasing the block size Higher number of TCP connections opened to the mirror sites For large files, TCP set-up is relatively insignificant TCP connections last for a smaller period of time Drop TCP connections for slow servers Use idle-servers in different time-zones Parallel-Access: Experiment Client written in Java. We used 9 NLANR mirror sites as the mirror servers We computed the average delay of the parallel-access system every 15 minutes during a period of 10 days UK Slovakia Portugal Greece Spain Japan Austria Australia Israel Eurecom, France Rodriguez 26
14 Parallel-access: Performance Smoothes out bandwidth variations, increases resilience against congestion and failures, and reduces downloading times Rodriguez 27 Small Documents For small documents, the connection time accounts for most of the download time Pipelining is difficult due to the small transmission times Rodriguez 28
15 Parallel-Access on a Modem line No Pipelining Pipelining Parallel-access over a modem line gives as good performance as the fastest server with no server selection, however, idle times are more relevant Using pipelining, the parallel-rate is very close to the best possible rate Rodriguez 29 Parallel-Access: Multiple sites vs One site If the wrong server is chosen, the performance is worse than a parallelaccess. Using a single server there is no load balancing and there is still the problem of server selection Rodriguez 30
16 Large Scale Deployment What if everybody does parallel-downloads? If all clients share the same bottleneck => Speedup is reduced Servers congested Close to bottleneck Spare capacity Still,» Client s experience is more uniform across clients and within a single client» Load is automatically distributed among servers» No need for a server selection algorithm Fairness Ideal Case simple Real Case simple overall overall parallel parallel 100 clients, 10 servers, 100 routers, NS2 (average loaded system) As more users perform parallel-downloads, the overall download time decreases but the performance of simple-downloads is slightly reduced => Overhead of having many connections and block requests Rodriguez 32
17 Peer-to-Peer Parallel-Donwloads Parallel-access works very well in peer-to-peer applications Peer-servers performance fluctuates Content tends to be quite large Clients become new sources: Efficient way to scale a parallelaccess Number of Parallel-Servers Rodriguez 33 Future Extensions Parallel-downloads under P2P systems Applications to streaming audio and video Rodriguez 34
18 Further Reading On the scale and performance of cooperative Web proxy caching. Alec Wolman, Geoffrey M. Voelker, Nitin Sharma, Neal Cardwell, Anna Karlin, and Henry M. Levy. In Proceedings of SOSP '99 Lee Breslau, Pei Cao, Li Fan, Graham Phillips, and Scott Shenker. Web caching and Zipf-like distributions: Evidence and implications. In Proceedings of the INFOCOM '99 conference, March 1999 Pablo Rodriguez, Andreas Kirpal, and Ernst W. Biersack. Parallel-access for mirror sites in the Internet. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM'2000, March 2000 Distribution of Stored Information in the Web. A tutorial on Web caching. Keith Ross ( Content Distribution Networks Overview : Web Caching and Replication. Rabinovich and Spatscheck. Addison Wesley. Rodriguez 35 Conclusions Content Distribution is an important part of today s Internet Content Distribution needs to take a step forward to accommodate new applications and bottlenecks Interactivity, distributed applications, reduced maintenance/deployment costs Wireless networks bring a new set of problems that can be overcome with intelligent CDN techniques Rodriguez 36
How To Understand The Power Of A Content Delivery Network (Cdn)
 Overview 5-44 5-44 Computer Networking 5-64 Lecture 8: Delivering Content Content Delivery Networks Peter Steenkiste Fall 04 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/5-44-f4 Web Consistent hashing Peer-to-peer CDN Motivation
Overview 5-44 5-44 Computer Networking 5-64 Lecture 8: Delivering Content Content Delivery Networks Peter Steenkiste Fall 04 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/5-44-f4 Web Consistent hashing Peer-to-peer CDN Motivation
Internet Content Distribution
 Internet Content Distribution Chapter 2: Server-Side Techniques (TUD Student Use Only) Chapter Outline Server-side techniques for content distribution Goals Mirrors Server farms Surrogates DNS load balancing
Internet Content Distribution Chapter 2: Server-Side Techniques (TUD Student Use Only) Chapter Outline Server-side techniques for content distribution Goals Mirrors Server farms Surrogates DNS load balancing
CSC2231: Akamai. http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~stefan/courses/csc2231/05au. Stefan Saroiu Department of Computer Science University of Toronto
 CSC2231: Akamai http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~stefan/courses/csc2231/05au Stefan Saroiu Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Administrivia Project proposals due today!!! No lecture on Monday:
CSC2231: Akamai http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~stefan/courses/csc2231/05au Stefan Saroiu Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Administrivia Project proposals due today!!! No lecture on Monday:
Measuring the Web: Part I - - Content Delivery Networks. Prof. Anja Feldmann, Ph.D. Dr. Ramin Khalili Georgios Smaragdakis, PhD
 Measuring the Web: Part I - - Content Delivery Networks Prof. Anja Feldmann, Ph.D. Dr. Ramin Khalili Georgios Smaragdakis, PhD Acknowledgement Material presented in these slides is borrowed from presentajons
Measuring the Web: Part I - - Content Delivery Networks Prof. Anja Feldmann, Ph.D. Dr. Ramin Khalili Georgios Smaragdakis, PhD Acknowledgement Material presented in these slides is borrowed from presentajons
Web Caching and CDNs. Aditya Akella
 Web Caching and CDNs Aditya Akella 1 Where can bottlenecks occur? First mile: client to its ISPs Last mile: server to its ISP Server: compute/memory limitations ISP interconnections/peerings: congestion
Web Caching and CDNs Aditya Akella 1 Where can bottlenecks occur? First mile: client to its ISPs Last mile: server to its ISP Server: compute/memory limitations ISP interconnections/peerings: congestion
Content Delivery Networks. Shaxun Chen April 21, 2009
 Content Delivery Networks Shaxun Chen April 21, 2009 Outline Introduction to CDN An Industry Example: Akamai A Research Example: CDN over Mobile Networks Conclusion Outline Introduction to CDN An Industry
Content Delivery Networks Shaxun Chen April 21, 2009 Outline Introduction to CDN An Industry Example: Akamai A Research Example: CDN over Mobile Networks Conclusion Outline Introduction to CDN An Industry
Distributed Systems 19. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu
 Distributed Systems 19. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Motivation Serving web content from one location presents problems Scalability Reliability Performance Flash
Distributed Systems 19. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Motivation Serving web content from one location presents problems Scalability Reliability Performance Flash
Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Dr. Yingwu Zhu
 Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Dr. Yingwu Zhu Web Cache Architecure Local ISP cache cdn Reverse Reverse Proxy Reverse Proxy Reverse Proxy Proxy L4 Switch Content Content Content Server Content Server
Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Dr. Yingwu Zhu Web Cache Architecure Local ISP cache cdn Reverse Reverse Proxy Reverse Proxy Reverse Proxy Proxy L4 Switch Content Content Content Server Content Server
Internet Content Distribution
 Internet Content Distribution Chapter 4: Content Distribution Networks (TUD Student Use Only) Chapter Outline Basics of content distribution networks (CDN) Why CDN? How do they work? Client redirection
Internet Content Distribution Chapter 4: Content Distribution Networks (TUD Student Use Only) Chapter Outline Basics of content distribution networks (CDN) Why CDN? How do they work? Client redirection
Distributed Systems. 23. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University. Fall 2015
 Distributed Systems 23. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2015 November 17, 2015 2014-2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Motivation Serving web content from one location presents
Distributed Systems 23. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2015 November 17, 2015 2014-2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Motivation Serving web content from one location presents
DATA COMMUNICATOIN NETWORKING
 DATA COMMUNICATOIN NETWORKING Instructor: Ouldooz Baghban Karimi Course Book: Computer Networking, A Top-Down Approach, Kurose, Ross Slides: - Course book Slides - Slides from Princeton University COS461
DATA COMMUNICATOIN NETWORKING Instructor: Ouldooz Baghban Karimi Course Book: Computer Networking, A Top-Down Approach, Kurose, Ross Slides: - Course book Slides - Slides from Princeton University COS461
Indirection. science can be solved by adding another level of indirection" -- Butler Lampson. "Every problem in computer
 Indirection Indirection: rather than reference an entity directly, reference it ( indirectly ) via another entity, which in turn can or will access the original entity A x B "Every problem in computer
Indirection Indirection: rather than reference an entity directly, reference it ( indirectly ) via another entity, which in turn can or will access the original entity A x B "Every problem in computer
Distributed Systems. 24. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) 2013 Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University. Fall 2013
 Distributed Systems 24. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2013 November 27, 2013 2013 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Motivation Serving web content from one location presents
Distributed Systems 24. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2013 November 27, 2013 2013 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Motivation Serving web content from one location presents
The old Internet. Software in the Network: Outline. Traditional Design. 1) Basic Caching. The Arrival of Software (in the network)
 The old Software in the Network: What Happened and Where to Go Prof. Eric A. Brewer UC Berkeley Inktomi Corporation Local networks with local names and switches IP creates global namespace and links the
The old Software in the Network: What Happened and Where to Go Prof. Eric A. Brewer UC Berkeley Inktomi Corporation Local networks with local names and switches IP creates global namespace and links the
Distributed Systems. 25. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) 2014 Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University. Fall 2014
 Distributed Systems 25. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2014 November 16, 2014 2014 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Motivation Serving web content from one location presents
Distributed Systems 25. Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2014 November 16, 2014 2014 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Motivation Serving web content from one location presents
Lecture 3: Scaling by Load Balancing 1. Comments on reviews i. 2. Topic 1: Scalability a. QUESTION: What are problems? i. These papers look at
 Lecture 3: Scaling by Load Balancing 1. Comments on reviews i. 2. Topic 1: Scalability a. QUESTION: What are problems? i. These papers look at distributing load b. QUESTION: What is the context? i. How
Lecture 3: Scaling by Load Balancing 1. Comments on reviews i. 2. Topic 1: Scalability a. QUESTION: What are problems? i. These papers look at distributing load b. QUESTION: What is the context? i. How
Content Distribu-on Networks (CDNs)
 Content Distribu-on Networks (CDNs) Jennifer Rexford COS 461: Computer Networks Lectures: MW 10-10:0am in Architecture N101 hjp://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr12/cos461/ Second Half of the Course
Content Distribu-on Networks (CDNs) Jennifer Rexford COS 461: Computer Networks Lectures: MW 10-10:0am in Architecture N101 hjp://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr12/cos461/ Second Half of the Course
Overview. Tor Circuit Setup (1) Tor Anonymity Network
 8-345: Introduction to Telecommunication Networks Lectures 8: Delivering Content Web, Peer-Peer, CDNs Peter Steenkiste Spring 05 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/nets-ece Web Peer-to-peer Motivation Architectures TOR
8-345: Introduction to Telecommunication Networks Lectures 8: Delivering Content Web, Peer-Peer, CDNs Peter Steenkiste Spring 05 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/nets-ece Web Peer-to-peer Motivation Architectures TOR
Real-Time Analysis of CDN in an Academic Institute: A Simulation Study
 Journal of Algorithms & Computational Technology Vol. 6 No. 3 483 Real-Time Analysis of CDN in an Academic Institute: A Simulation Study N. Ramachandran * and P. Sivaprakasam + *Indian Institute of Management
Journal of Algorithms & Computational Technology Vol. 6 No. 3 483 Real-Time Analysis of CDN in an Academic Institute: A Simulation Study N. Ramachandran * and P. Sivaprakasam + *Indian Institute of Management
High volume Internet data centers. MPLS-based Request Routing. Current dispatcher technology. MPLS-based architecture
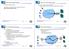 MPLS-based Request Routing High volume Internet data centers MPLS-based Request Routing Arup Acharya, Anees Shaikh, Renu Tewari, Dinesh Verma IBM TJ Watson Research Center Web server cluster + front-end
MPLS-based Request Routing High volume Internet data centers MPLS-based Request Routing Arup Acharya, Anees Shaikh, Renu Tewari, Dinesh Verma IBM TJ Watson Research Center Web server cluster + front-end
CDN and Traffic-structure
 CDN and Traffic-structure Outline Basics CDN Traffic Analysis 2 Outline Basics CDN Building Blocks Services Evolution Traffic Analysis 3 A Centralized Web! Slow content must traverse multiple backbones
CDN and Traffic-structure Outline Basics CDN Traffic Analysis 2 Outline Basics CDN Building Blocks Services Evolution Traffic Analysis 3 A Centralized Web! Slow content must traverse multiple backbones
1. Comments on reviews a. Need to avoid just summarizing web page asks you for:
 1. Comments on reviews a. Need to avoid just summarizing web page asks you for: i. A one or two sentence summary of the paper ii. A description of the problem they were trying to solve iii. A summary of
1. Comments on reviews a. Need to avoid just summarizing web page asks you for: i. A one or two sentence summary of the paper ii. A description of the problem they were trying to solve iii. A summary of
Evaluating Cooperative Web Caching Protocols for Emerging Network Technologies 1
 Evaluating Cooperative Web Caching Protocols for Emerging Network Technologies 1 Christoph Lindemann and Oliver P. Waldhorst University of Dortmund Department of Computer Science August-Schmidt-Str. 12
Evaluating Cooperative Web Caching Protocols for Emerging Network Technologies 1 Christoph Lindemann and Oliver P. Waldhorst University of Dortmund Department of Computer Science August-Schmidt-Str. 12
AKAMAI WHITE PAPER. Delivering Dynamic Web Content in Cloud Computing Applications: HTTP resource download performance modelling
 AKAMAI WHITE PAPER Delivering Dynamic Web Content in Cloud Computing Applications: HTTP resource download performance modelling Delivering Dynamic Web Content in Cloud Computing Applications 1 Overview
AKAMAI WHITE PAPER Delivering Dynamic Web Content in Cloud Computing Applications: HTTP resource download performance modelling Delivering Dynamic Web Content in Cloud Computing Applications 1 Overview
Dynamic Load Balancing and Node Migration in a Continuous Media Network
 Dynamic Load Balancing and Node Migration in a Continuous Media Network Anthony J. Howe Supervisor: Dr. Mantis Cheng University of Victoria Draft: April 9, 2001 Abstract This report examines current technologies
Dynamic Load Balancing and Node Migration in a Continuous Media Network Anthony J. Howe Supervisor: Dr. Mantis Cheng University of Victoria Draft: April 9, 2001 Abstract This report examines current technologies
Global Server Load Balancing
 White Paper Overview Many enterprises attempt to scale Web and network capacity by deploying additional servers and increased infrastructure at a single location, but centralized architectures are subject
White Paper Overview Many enterprises attempt to scale Web and network capacity by deploying additional servers and increased infrastructure at a single location, but centralized architectures are subject
Demand Routing in Network Layer for Load Balancing in Content Delivery Networks
 Demand Routing in Network Layer for Load Balancing in Content Delivery Networks # A SHRAVANI, 1 M.Tech, Computer Science Engineering E mail: sravaniathome@gmail.com # SYED ABDUL MOEED 2 Asst.Professor,
Demand Routing in Network Layer for Load Balancing in Content Delivery Networks # A SHRAVANI, 1 M.Tech, Computer Science Engineering E mail: sravaniathome@gmail.com # SYED ABDUL MOEED 2 Asst.Professor,
Overlay Networks. Slides adopted from Prof. Böszörményi, Distributed Systems, Summer 2004.
 Overlay Networks An overlay is a logical network on top of the physical network Routing Overlays The simplest kind of overlay Virtual Private Networks (VPN), supported by the routers If no router support
Overlay Networks An overlay is a logical network on top of the physical network Routing Overlays The simplest kind of overlay Virtual Private Networks (VPN), supported by the routers If no router support
Teridion. Rethinking Network Performance. The Internet. Lightning Fast. Technical White Paper July, 2015 www.teridion.com
 Teridion The Internet. Lightning Fast. Rethinking Network Performance Technical White Paper July, 2015 www.teridion.com Executive summary Online services face the growing dual challenge of supporting many
Teridion The Internet. Lightning Fast. Rethinking Network Performance Technical White Paper July, 2015 www.teridion.com Executive summary Online services face the growing dual challenge of supporting many
Content Delivery Networks
 Content Delivery Networks Terena 2000 ftp://ftpeng.cisco.com/sgai/t2000cdn.pdf Silvano Gai Cisco Systems, USA Politecnico di Torino, IT sgai@cisco.com Terena 2000 1 Agenda What are Content Delivery Networks?
Content Delivery Networks Terena 2000 ftp://ftpeng.cisco.com/sgai/t2000cdn.pdf Silvano Gai Cisco Systems, USA Politecnico di Torino, IT sgai@cisco.com Terena 2000 1 Agenda What are Content Delivery Networks?
The Value of a Content Delivery Network
 September 2010 White Paper The Value of a Content Delivery Network Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Performance... 3 The Second Generation of CDNs... 6 Conclusion... 7 About NTT America... 8 Introduction
September 2010 White Paper The Value of a Content Delivery Network Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Performance... 3 The Second Generation of CDNs... 6 Conclusion... 7 About NTT America... 8 Introduction
The Effect of Caches for Mobile Broadband Internet Access
 The Effect of s for Mobile Jochen Eisl, Nokia Siemens Networks, Munich, Germany Haßlinger, Deutsche Telekom Technik,, Darmstadt, Germany IP-based content delivery: CDN & cache architecture Impact of access
The Effect of s for Mobile Jochen Eisl, Nokia Siemens Networks, Munich, Germany Haßlinger, Deutsche Telekom Technik,, Darmstadt, Germany IP-based content delivery: CDN & cache architecture Impact of access
Scaling with Zeus Global Load Balancer
 White Paper Scaling with Zeus Global Load Balancer Zeus. Why wait Contents Introduction... 3 Server Load Balancing within a Datacenter... 3 Global Server Load Balancing between Datacenters... 3 Who might
White Paper Scaling with Zeus Global Load Balancer Zeus. Why wait Contents Introduction... 3 Server Load Balancing within a Datacenter... 3 Global Server Load Balancing between Datacenters... 3 Who might
Making the Internet fast, reliable and secure. DE-CIX Customer Summit - 2014. Steven Schecter <schecter@akamai.com>
 Making the Internet fast, reliable and secure DE-CIX Customer Summit - 2014 Steven Schecter What is a Content Distribution Network RFCs and Internet Drafts define a CDN as: Content
Making the Internet fast, reliable and secure DE-CIX Customer Summit - 2014 Steven Schecter What is a Content Distribution Network RFCs and Internet Drafts define a CDN as: Content
Request Routing, Load-Balancing and Fault- Tolerance Solution - MediaDNS
 White paper Request Routing, Load-Balancing and Fault- Tolerance Solution - MediaDNS June 2001 Response in Global Environment Simply by connecting to the Internet, local businesses transform themselves
White paper Request Routing, Load-Balancing and Fault- Tolerance Solution - MediaDNS June 2001 Response in Global Environment Simply by connecting to the Internet, local businesses transform themselves
FortiBalancer: Global Server Load Balancing WHITE PAPER
 FortiBalancer: Global Server Load Balancing WHITE PAPER FORTINET FortiBalancer: Global Server Load Balancing PAGE 2 Introduction Scalability, high availability and performance are critical to the success
FortiBalancer: Global Server Load Balancing WHITE PAPER FORTINET FortiBalancer: Global Server Load Balancing PAGE 2 Introduction Scalability, high availability and performance are critical to the success
DNS, CDNs Weds March 17 2010 Lecture 13. What is the relationship between a domain name (e.g., youtube.com) and an IP address?
 DNS, CDNs Weds March 17 2010 Lecture 13 DNS What is the relationship between a domain name (e.g., youtube.com) and an IP address? DNS is the system that determines this mapping. Basic idea: You contact
DNS, CDNs Weds March 17 2010 Lecture 13 DNS What is the relationship between a domain name (e.g., youtube.com) and an IP address? DNS is the system that determines this mapping. Basic idea: You contact
Traffic delivery evolution in the Internet ENOG 4 Moscow 23 rd October 2012
 Traffic delivery evolution in the Internet ENOG 4 Moscow 23 rd October 2012 January 29th, 2008 Christian Kaufmann Director Network Architecture Akamai Technologies, Inc. way-back machine Web 1998 way-back
Traffic delivery evolution in the Internet ENOG 4 Moscow 23 rd October 2012 January 29th, 2008 Christian Kaufmann Director Network Architecture Akamai Technologies, Inc. way-back machine Web 1998 way-back
ADAPTIVE DISTRIBUTED CACHING WITH MINIMAL MEMORY USAGE
 ADAPTIVE DISTRIBUTED CACHING WITH MINIMAL MEMORY USAGE Markus J. Kaiser, Kwok Ching Tsui and Jiming Liu Department of Computer Science Hong Kong Baptist University Kowloon Tong, Kowloon, Hong Kong ABSTRACT
ADAPTIVE DISTRIBUTED CACHING WITH MINIMAL MEMORY USAGE Markus J. Kaiser, Kwok Ching Tsui and Jiming Liu Department of Computer Science Hong Kong Baptist University Kowloon Tong, Kowloon, Hong Kong ABSTRACT
Guiding Web Proxy and Server Placement for High Performance Internet Content Delivery 1
 Guiding Web Proxy and Server Placement for High Performance Internet Content Delivery 1 Peter Triantafillou (contact author) Department of Computer Engineering and Informatics, University of Patras Rio
Guiding Web Proxy and Server Placement for High Performance Internet Content Delivery 1 Peter Triantafillou (contact author) Department of Computer Engineering and Informatics, University of Patras Rio
How To Understand The Power Of Icdn
 MobiArch 2014 R-iCDN: an Approach Supporting Flexible Content Routing for ISP-operated CDN Song Ci High Performance Network Lab, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline I. Background
MobiArch 2014 R-iCDN: an Approach Supporting Flexible Content Routing for ISP-operated CDN Song Ci High Performance Network Lab, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline I. Background
From Internet Data Centers to Data Centers in the Cloud
 From Internet Data Centers to Data Centers in the Cloud This case study is a short extract from a keynote address given to the Doctoral Symposium at Middleware 2009 by Lucy Cherkasova of HP Research Labs
From Internet Data Centers to Data Centers in the Cloud This case study is a short extract from a keynote address given to the Doctoral Symposium at Middleware 2009 by Lucy Cherkasova of HP Research Labs
Communications Software. CSE 123b. CSE 123b. Spring 2003. Lecture 13: Load Balancing/Content Distribution. Networks (plus some other applications)
 CSE 123b CSE 123b Communications Software Spring 2003 Lecture 13: Load Balancing/Content Distribution Networks (plus some other applications) Stefan Savage Some slides courtesy Srini Seshan Today s class
CSE 123b CSE 123b Communications Software Spring 2003 Lecture 13: Load Balancing/Content Distribution Networks (plus some other applications) Stefan Savage Some slides courtesy Srini Seshan Today s class
Data Center Content Delivery Network
 BM 465E Distributed Systems Lecture 4 Networking (cont.) Mehmet Demirci Today Overlay networks Data centers Content delivery networks Overlay Network A virtual network built on top of another network Overlay
BM 465E Distributed Systems Lecture 4 Networking (cont.) Mehmet Demirci Today Overlay networks Data centers Content delivery networks Overlay Network A virtual network built on top of another network Overlay
Web Email DNS Peer-to-peer systems (file sharing, CDNs, cycle sharing)
 1 1 Distributed Systems What are distributed systems? How would you characterize them? Components of the system are located at networked computers Cooperate to provide some service No shared memory Communication
1 1 Distributed Systems What are distributed systems? How would you characterize them? Components of the system are located at networked computers Cooperate to provide some service No shared memory Communication
Towards a Peer-to-Peer Extended Content Delivery Network
 Towards a Peer-to-Peer Extended Content Delivery Network Daniel Pakkala and Juhani Latvakoski VTT Electronics, Kaitoväylä 1, P.O. Box 1100, FIN-90571 Oulu, Finland E-mail: {Daniel.Pakkala, Juhani.Latvakoski}@vtt.fi
Towards a Peer-to-Peer Extended Content Delivery Network Daniel Pakkala and Juhani Latvakoski VTT Electronics, Kaitoväylä 1, P.O. Box 1100, FIN-90571 Oulu, Finland E-mail: {Daniel.Pakkala, Juhani.Latvakoski}@vtt.fi
A TECHNICAL REVIEW OF CACHING TECHNOLOGIES
 WHITEPAPER Over the past 10 years, the use of applications to enable business processes has evolved drastically. What was once a nice-to-have is now a mainstream staple that exists at the core of business,
WHITEPAPER Over the past 10 years, the use of applications to enable business processes has evolved drastically. What was once a nice-to-have is now a mainstream staple that exists at the core of business,
Hierarchical Content Routing in Large-Scale Multimedia Content Delivery Network
 Hierarchical Content Routing in Large-Scale Multimedia Content Delivery Network Jian Ni, Danny H. K. Tsang, Ivan S. H. Yeung, Xiaojun Hei Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Hong Kong University
Hierarchical Content Routing in Large-Scale Multimedia Content Delivery Network Jian Ni, Danny H. K. Tsang, Ivan S. H. Yeung, Xiaojun Hei Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Hong Kong University
Parallel-Access for Mirror Sites in the Internet
 1 -Access for Mirror Sites in the Internet Pablo Rodriguez Andreas Kirpal Ernst W Biersack Institut EURECOM 2229, route des Crêtes BP 193 694, Sophia Antipolis Cedex, FRANCE rodrigue, kirpal, erbi @eurecomfr
1 -Access for Mirror Sites in the Internet Pablo Rodriguez Andreas Kirpal Ernst W Biersack Institut EURECOM 2229, route des Crêtes BP 193 694, Sophia Antipolis Cedex, FRANCE rodrigue, kirpal, erbi @eurecomfr
networks Live & On-Demand Video Delivery without Interruption Wireless optimization the unsolved mystery WHITE PAPER
 Live & On-Demand Video Delivery without Interruption Wireless optimization the unsolved mystery - Improving the way the world connects - WHITE PAPER Live On-Demand Video Streaming without Interruption
Live & On-Demand Video Delivery without Interruption Wireless optimization the unsolved mystery - Improving the way the world connects - WHITE PAPER Live On-Demand Video Streaming without Interruption
Demystifying CDNs: Building Video Enabled Networks That Maintain Your Network Integrity And Meet User Demand
 An Enterprise Video Communications Industry Lite Paper Demystifying CDNs: Building Video Enabled Networks That Maintain Your Network Integrity And Meet User Demand Overview In recent years video has taken
An Enterprise Video Communications Industry Lite Paper Demystifying CDNs: Building Video Enabled Networks That Maintain Your Network Integrity And Meet User Demand Overview In recent years video has taken
The Application Front End Understanding Next-Generation Load Balancing Appliances
 White Paper Overview To accelerate download times for end users and provide a high performance, highly secure foundation for Web-enabled content and applications, networking functions need to be streamlined.
White Paper Overview To accelerate download times for end users and provide a high performance, highly secure foundation for Web-enabled content and applications, networking functions need to be streamlined.
Global Server Load Balancing
 White Paper Global Server Load Balancing APV Series Application Delivery Controllers May 2011 Global Server Load Balancing Access. Security. Delivery. Introduction Scalability, high availability and performance
White Paper Global Server Load Balancing APV Series Application Delivery Controllers May 2011 Global Server Load Balancing Access. Security. Delivery. Introduction Scalability, high availability and performance
How To Improve Performance On A Ccdn (Dns)
 Enhanced Content Delivery Network to Improve the QoE 1 Sachendra Singh Solanky, 2 Sandra Brigit Johnson, 3 Vakkalagadda Eswar Praphul 1 M.Tech Student SCSE, VIT University Chennai-600048, 2 M.Tech Student
Enhanced Content Delivery Network to Improve the QoE 1 Sachendra Singh Solanky, 2 Sandra Brigit Johnson, 3 Vakkalagadda Eswar Praphul 1 M.Tech Student SCSE, VIT University Chennai-600048, 2 M.Tech Student
Cisco Application Networking for Citrix Presentation Server
 Cisco Application Networking for Citrix Presentation Server Faster Site Navigation, Less Bandwidth and Server Processing, and Greater Availability for Global Deployments What You Will Learn To address
Cisco Application Networking for Citrix Presentation Server Faster Site Navigation, Less Bandwidth and Server Processing, and Greater Availability for Global Deployments What You Will Learn To address
More efficient content delivery over the Web has become an important
 By George Pallis and Athena Vakali Insight and Perspectives for CONTENT DELIVERY NETWORKS Striking a balance between the costs for Web content providers and the quality of service for Web customers. More
By George Pallis and Athena Vakali Insight and Perspectives for CONTENT DELIVERY NETWORKS Striking a balance between the costs for Web content providers and the quality of service for Web customers. More
q Admin and recap q Case studies: Content Distribution o Forward proxy (web cache) o Akamai o YouTube q P2P networks o Overview
 Outline CS433/533 Computer Networks Lecture 13 CDN & P2P for Scalability q Admin and recap q Case studies: Content Distribution o Forward proxy (web cache) o Akamai o YouTube q P2P networks o Overview
Outline CS433/533 Computer Networks Lecture 13 CDN & P2P for Scalability q Admin and recap q Case studies: Content Distribution o Forward proxy (web cache) o Akamai o YouTube q P2P networks o Overview
How To Test Performance Of A Cdn Server
 On the Use and Performance of Content Distribution Networks Yin Zhang Joint work with Balachander Krishnamurthy and Craig Wills AT&T Labs Research, WPI {yzhang,bala}@research.att.com, cew@cs.wpi.edu ACM
On the Use and Performance of Content Distribution Networks Yin Zhang Joint work with Balachander Krishnamurthy and Craig Wills AT&T Labs Research, WPI {yzhang,bala}@research.att.com, cew@cs.wpi.edu ACM
CHAPTER 4 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CDN IN ACADEMICS
 CHAPTER 4 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CDN IN ACADEMICS The web content providers sharing the content over the Internet during the past did not bother about the users, especially in terms of response time,
CHAPTER 4 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CDN IN ACADEMICS The web content providers sharing the content over the Internet during the past did not bother about the users, especially in terms of response time,
SiteCelerate white paper
 SiteCelerate white paper Arahe Solutions SITECELERATE OVERVIEW As enterprises increases their investment in Web applications, Portal and websites and as usage of these applications increase, performance
SiteCelerate white paper Arahe Solutions SITECELERATE OVERVIEW As enterprises increases their investment in Web applications, Portal and websites and as usage of these applications increase, performance
Reliable Distributed Systems
 Reliable Distributed ystems A glimpse into the world of ontent Distribution Networks Based on a slide set developed by Prof. Paul Francis ontent Routing Principle (a.k.a. ontent Distribution Network) enter
Reliable Distributed ystems A glimpse into the world of ontent Distribution Networks Based on a slide set developed by Prof. Paul Francis ontent Routing Principle (a.k.a. ontent Distribution Network) enter
Get Control of Your Data Center. Application Delivery Controllers
 White Paper Get Control of Your Data Center Application Delivery Controllers May 2011 Get Control of Your Data Center Access. Security. Delivery. Introduction Data center and networking technologies have
White Paper Get Control of Your Data Center Application Delivery Controllers May 2011 Get Control of Your Data Center Access. Security. Delivery. Introduction Data center and networking technologies have
Game Theory Applications for Content Delivery Networks
 Game Theory Applications for Content Delivery Networks Chaki Ng, Harvard University [ chaki@eecs.harvard.edu ] Version 5.5.22 Introduction As Internet topology and user base grow by the minutes, services
Game Theory Applications for Content Delivery Networks Chaki Ng, Harvard University [ chaki@eecs.harvard.edu ] Version 5.5.22 Introduction As Internet topology and user base grow by the minutes, services
WAVE: Popularity-based and Collaborative In-network Caching for Content-Oriented Networks
 WAVE: Popularity-based and Collaborative In-network Caching for Content-Oriented Networks K. D. Cho et al., IEEE INFOCOM 2012 Workshop, pp. 316-321, March 2012. January 17, 2013 Byeong-Gi Kim Park Laboratory,
WAVE: Popularity-based and Collaborative In-network Caching for Content-Oriented Networks K. D. Cho et al., IEEE INFOCOM 2012 Workshop, pp. 316-321, March 2012. January 17, 2013 Byeong-Gi Kim Park Laboratory,
Content Delivery Networks
 Content Delivery Networks Silvano Gai Cisco Systems, USA Politecnico di Torino, IT sgai@cisco.com 1 Agenda What are Content Delivery Networks? DNS based routing Server Load Balancing Content Routers Ethical
Content Delivery Networks Silvano Gai Cisco Systems, USA Politecnico di Torino, IT sgai@cisco.com 1 Agenda What are Content Delivery Networks? DNS based routing Server Load Balancing Content Routers Ethical
Measuring CDN Performance. Hooman Beheshti, VP Technology
 Measuring CDN Performance Hooman Beheshti, VP Technology Why this matters Performance is one of the main reasons we use a CDN Seems easy to measure, but isn t Performance is an easy way to comparison shop
Measuring CDN Performance Hooman Beheshti, VP Technology Why this matters Performance is one of the main reasons we use a CDN Seems easy to measure, but isn t Performance is an easy way to comparison shop
The Application Delivery Controller Understanding Next-Generation Load Balancing Appliances
 White Paper Overview To accelerate response times for end users and provide a high performance, highly secure and scalable foundation for Web applications and rich internet content, application networking
White Paper Overview To accelerate response times for end users and provide a high performance, highly secure and scalable foundation for Web applications and rich internet content, application networking
The Medusa Proxy. A Tool For Exploring User-Perceived Web Performance. Mimika Koletsou and Geoffrey M. Voelker
 The Medusa Proxy A Tool For Exploring User-Perceived Web Performance Mimika Koletsou and Geoffrey M. Voelker Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego 9500 Gilman
The Medusa Proxy A Tool For Exploring User-Perceived Web Performance Mimika Koletsou and Geoffrey M. Voelker Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego 9500 Gilman
Multicast vs. P2P for content distribution
 Multicast vs. P2P for content distribution Abstract Many different service architectures, ranging from centralized client-server to fully distributed are available in today s world for Content Distribution
Multicast vs. P2P for content distribution Abstract Many different service architectures, ranging from centralized client-server to fully distributed are available in today s world for Content Distribution
Choosing a Content Delivery Method
 Choosing a Content Delivery Method Executive Summary Cache-based content distribution networks (CDNs) reach very large volumes of highly dispersed end users by duplicating centrally hosted video, audio
Choosing a Content Delivery Method Executive Summary Cache-based content distribution networks (CDNs) reach very large volumes of highly dispersed end users by duplicating centrally hosted video, audio
Meeting Worldwide Demand for your Content
 Meeting Worldwide Demand for your Content Evolving to a Content Delivery Network A Lucent Technologies White Paper By L. R. Beaumont 4/25/01 Meeting Worldwide Demand for your Content White Paper Table
Meeting Worldwide Demand for your Content Evolving to a Content Delivery Network A Lucent Technologies White Paper By L. R. Beaumont 4/25/01 Meeting Worldwide Demand for your Content White Paper Table
CDN Brokering. Content Distribution Internetworking
 CDN Brokering Alex Biliris, Chuck Cranor, Fred Douglis, Michael Rabinovich, Sandeep Sibal, Oliver Spatscheck, and Walter Sturm AT&T Labs--Research March 12, 2001 Content Distribution Internetworking Definition:
CDN Brokering Alex Biliris, Chuck Cranor, Fred Douglis, Michael Rabinovich, Sandeep Sibal, Oliver Spatscheck, and Walter Sturm AT&T Labs--Research March 12, 2001 Content Distribution Internetworking Definition:
Enabling Media Rich Curriculum with Content Delivery Networking
 Enabling Media Rich Curriculum with Content Delivery Networking Mike McKeown Manager, Education Sector Europe, Middle East, Africa & Latin America mmckeown@cisco.com 1 Media Rich Content & Communication
Enabling Media Rich Curriculum with Content Delivery Networking Mike McKeown Manager, Education Sector Europe, Middle East, Africa & Latin America mmckeown@cisco.com 1 Media Rich Content & Communication
Performance evaluation of redirection schemes in content distribution networks
 Computer Communications 24 (2001) 207 214 www.elsevier.com/locate/comcom Performance evaluation of redirection schemes in content distribution networks J. Kangasharju a, K.W. Ross a, J.W. Roberts b a Institut
Computer Communications 24 (2001) 207 214 www.elsevier.com/locate/comcom Performance evaluation of redirection schemes in content distribution networks J. Kangasharju a, K.W. Ross a, J.W. Roberts b a Institut
Six Steps for Hosting Providers to Sell CDN Services
 Six Steps for Hosting Providers to Sell CDN Services By Rebecca Wetzel March 2013 This report was sponsored by Introduction CDN services are a promising way for many hosting providers to grow their businesses.
Six Steps for Hosting Providers to Sell CDN Services By Rebecca Wetzel March 2013 This report was sponsored by Introduction CDN services are a promising way for many hosting providers to grow their businesses.
TCP and Wireless Networks Classical Approaches Optimizations TCP for 2.5G/3G Systems. Lehrstuhl für Informatik 4 Kommunikation und verteilte Systeme
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Chapter 4 Mobility on the
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Chapter 4 Mobility on the
COMP 631: COMPUTER NETWORKS. How to distribute content without requiring centralized, heavy-duty servers? Peer-to-peer content distribution
 Content Distribution How to distribute content without requiring centralized, heavy-duty servers? Examples: Ø Bittorrent Peer-to-peer content distribution Ø Akamai Content distribution service 20 Bottlenecks
Content Distribution How to distribute content without requiring centralized, heavy-duty servers? Examples: Ø Bittorrent Peer-to-peer content distribution Ø Akamai Content distribution service 20 Bottlenecks
How To Model The Content Delivery Network (Cdn) From A Content Bridge To A Cloud (Cloud)
 Kingston University London In network content caching contributing to the Future Internet Architecture Dissertation submitted for the Degree of Master of Science in Networking and Data Communications By
Kingston University London In network content caching contributing to the Future Internet Architecture Dissertation submitted for the Degree of Master of Science in Networking and Data Communications By
Results-Oriented Application Acceleration with FastView Because Every Second Counts Whitepaper
 Results-Oriented Application Acceleration with FastView Because Every Second Counts Whitepaper Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Why Website Performance Matters...3 What Affects Website Performance...5
Results-Oriented Application Acceleration with FastView Because Every Second Counts Whitepaper Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Why Website Performance Matters...3 What Affects Website Performance...5
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks. Caching, Content Distribution and Load Balancing
 Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Caching, Content Distribution and Load Balancing Motivation Which optimization means do exist? Where should
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Caching, Content Distribution and Load Balancing Motivation Which optimization means do exist? Where should
Peer-to-Peer Networks. Chapter 6: P2P Content Distribution
 Peer-to-Peer Networks Chapter 6: P2P Content Distribution Chapter Outline Content distribution overview Why P2P content distribution? Network coding Peer-to-peer multicast Kangasharju: Peer-to-Peer Networks
Peer-to-Peer Networks Chapter 6: P2P Content Distribution Chapter Outline Content distribution overview Why P2P content distribution? Network coding Peer-to-peer multicast Kangasharju: Peer-to-Peer Networks
AKAMAI WHITE PAPER. Turbo-Charging Dynamic Web Sites with Akamai EdgeSuite SM
 Turbo-Charging Dynamic Web Sites with Akamai EdgeSuite SM 1 Table of Contents Introduction...........................................................3 Next-Generation E-Business Applications...............................
Turbo-Charging Dynamic Web Sites with Akamai EdgeSuite SM 1 Table of Contents Introduction...........................................................3 Next-Generation E-Business Applications...............................
The content delivery network (CDN): Delivering the ultimate Web experience
 The content delivery network (CDN): Delivering the ultimate Web experience White paper April 2010 By Ari Blau Video Solutions Portfolio Leader, Bell and Robert Kevork Associate Director of Marketing. Bell
The content delivery network (CDN): Delivering the ultimate Web experience White paper April 2010 By Ari Blau Video Solutions Portfolio Leader, Bell and Robert Kevork Associate Director of Marketing. Bell
Superior Disaster Recovery with Radware s Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) Solution
 Superior Disaster Recovery with Radware s Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) Solution White Paper January 2012 Radware GSLB Solution White Paper Page 1 Table of Contents 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 2. GLOBAL
Superior Disaster Recovery with Radware s Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) Solution White Paper January 2012 Radware GSLB Solution White Paper Page 1 Table of Contents 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 2. GLOBAL
Protocols. Packets. What's in an IP packet
 Protocols Precise rules that govern communication between two parties TCP/IP: the basic Internet protocols IP: Internet Protocol (bottom level) all packets shipped from network to network as IP packets
Protocols Precise rules that govern communication between two parties TCP/IP: the basic Internet protocols IP: Internet Protocol (bottom level) all packets shipped from network to network as IP packets
Content Distribution over IP: Developments and Challenges
 Content Distribution over IP: Developments and Challenges Adrian Popescu, Blekinge Inst of Technology, Sweden Markus Fiedler, Blekinge Inst of Technology, Sweden Demetres D. Kouvatsos, University of Bradford,
Content Distribution over IP: Developments and Challenges Adrian Popescu, Blekinge Inst of Technology, Sweden Markus Fiedler, Blekinge Inst of Technology, Sweden Demetres D. Kouvatsos, University of Bradford,
Web Application Hosting Cloud Architecture
 Web Application Hosting Cloud Architecture Executive Overview This paper describes vendor neutral best practices for hosting web applications using cloud computing. The architectural elements described
Web Application Hosting Cloud Architecture Executive Overview This paper describes vendor neutral best practices for hosting web applications using cloud computing. The architectural elements described
TCP for Wireless Networks
 TCP for Wireless Networks Outline Motivation TCP mechanisms Indirect TCP Snooping TCP Mobile TCP Fast retransmit/recovery Transmission freezing Selective retransmission Transaction oriented TCP Adapted
TCP for Wireless Networks Outline Motivation TCP mechanisms Indirect TCP Snooping TCP Mobile TCP Fast retransmit/recovery Transmission freezing Selective retransmission Transaction oriented TCP Adapted
FAQs for Oracle iplanet Proxy Server 4.0
 FAQs for Oracle iplanet Proxy Server 4.0 Get answers to the questions most frequently asked about Oracle iplanet Proxy Server Q: What is Oracle iplanet Proxy Server (Java System Web Proxy Server)? A: Oracle
FAQs for Oracle iplanet Proxy Server 4.0 Get answers to the questions most frequently asked about Oracle iplanet Proxy Server Q: What is Oracle iplanet Proxy Server (Java System Web Proxy Server)? A: Oracle
Quantifying the Performance Degradation of IPv6 for TCP in Windows and Linux Networking
 Quantifying the Performance Degradation of IPv6 for TCP in Windows and Linux Networking Burjiz Soorty School of Computing and Mathematical Sciences Auckland University of Technology Auckland, New Zealand
Quantifying the Performance Degradation of IPv6 for TCP in Windows and Linux Networking Burjiz Soorty School of Computing and Mathematical Sciences Auckland University of Technology Auckland, New Zealand
LOAD BALANCING IN WEB SERVER
 LOAD BALANCING IN WEB SERVER Renu Tyagi 1, Shaily Chaudhary 2, Sweta Payala 3 UG, 1,2,3 Department of Information & Technology, Raj Kumar Goel Institute of Technology for Women, Gautam Buddh Technical
LOAD BALANCING IN WEB SERVER Renu Tyagi 1, Shaily Chaudhary 2, Sweta Payala 3 UG, 1,2,3 Department of Information & Technology, Raj Kumar Goel Institute of Technology for Women, Gautam Buddh Technical
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Question: how do packets actually get to their destination? IP routing tables: based on network addresses Ethernet physical interfaces only understand ethernet addresses
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Question: how do packets actually get to their destination? IP routing tables: based on network addresses Ethernet physical interfaces only understand ethernet addresses
Alteon Global Server Load Balancing
 Alteon Global Server Load Balancing Whitepaper GSLB Operation Overview Major Components Distributed Site Monitoring Distributed Site State Protocol Internet Topology Awareness DNS Authoritative Name Server
Alteon Global Server Load Balancing Whitepaper GSLB Operation Overview Major Components Distributed Site Monitoring Distributed Site State Protocol Internet Topology Awareness DNS Authoritative Name Server
HIGH-SPEED BRIDGE TO CLOUD STORAGE
 HIGH-SPEED BRIDGE TO CLOUD STORAGE Addressing throughput bottlenecks with Signiant s SkyDrop 2 The heart of the Internet is a pulsing movement of data circulating among billions of devices worldwide between
HIGH-SPEED BRIDGE TO CLOUD STORAGE Addressing throughput bottlenecks with Signiant s SkyDrop 2 The heart of the Internet is a pulsing movement of data circulating among billions of devices worldwide between
CSCI-1680 CDN & P2P Chen Avin
 CSCI-1680 CDN & P2P Chen Avin Based partly on lecture notes by Scott Shenker and John Jannotti androdrigo Fonseca And Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach - 6th edition Last time DNS & DHT Today: P2P
CSCI-1680 CDN & P2P Chen Avin Based partly on lecture notes by Scott Shenker and John Jannotti androdrigo Fonseca And Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach - 6th edition Last time DNS & DHT Today: P2P
Performance Comparison of low-latency Anonymisation Services from a User Perspective
 Performance Comparison of low-latency Anonymisation Services from a User Perspective Rolf Wendolsky Hannes Federrath Department of Business Informatics University of Regensburg 7th Workshop on Privacy
Performance Comparison of low-latency Anonymisation Services from a User Perspective Rolf Wendolsky Hannes Federrath Department of Business Informatics University of Regensburg 7th Workshop on Privacy
JXTA TM : Beyond P2P File Sharing the Emergence of Knowledge Addressable Networks
 JXTA TM : Beyond P2P File Sharing the Emergence of Knowledge Addressable Networks Bernard Traversat tra@jxta.org JXTA Chief Architect Sun Microsystems 2005 JavaOne SM Conference Session 7208 Extended and
JXTA TM : Beyond P2P File Sharing the Emergence of Knowledge Addressable Networks Bernard Traversat tra@jxta.org JXTA Chief Architect Sun Microsystems 2005 JavaOne SM Conference Session 7208 Extended and
Mobile Communications Chapter 9: Mobile Transport Layer
 Mobile Communications Chapter 9: Mobile Transport Layer Motivation TCP-mechanisms Classical approaches Indirect TCP Snooping TCP Mobile TCP PEPs in general Additional optimizations Fast retransmit/recovery
Mobile Communications Chapter 9: Mobile Transport Layer Motivation TCP-mechanisms Classical approaches Indirect TCP Snooping TCP Mobile TCP PEPs in general Additional optimizations Fast retransmit/recovery
Akamai CDN, IPv6 and DNS security. Christian Kaufmann Akamai Technologies DENOG 5 14 th November 2013
 Akamai CDN, IPv6 and DNS security Christian Kaufmann Akamai Technologies DENOG 5 14 th November 2013 Agenda Akamai Introduction Who s Akamai? Intelligent Platform & Traffic Snapshot Basic Technology Akamai
Akamai CDN, IPv6 and DNS security Christian Kaufmann Akamai Technologies DENOG 5 14 th November 2013 Agenda Akamai Introduction Who s Akamai? Intelligent Platform & Traffic Snapshot Basic Technology Akamai
