USER Guide to ICD-10 Coding
|
|
|
- Alexia Pearson
- 3 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USER GUIDE Technical User Guide compiled by the Ministerial ICD-10 Task Team to define standards and guidelines for ICD-10 coding implementation Date: 18 October 2012 Final Version 1.00 Page 1 of 18
2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction Overview and Background Objective(s) Definitions, Acronyms and Abbreviations Acknowledgements ICD-10 Implementation Phases ICD-10 Terminology Definitions Master Industry Table (MIT) Coding Definitions Primary Diagnosis (PDX) - Morbidity Primary Code Secondary Diagnosis (SDX) - Morbidity Secondary Code Valid Code Complete Code / Level of Specificity Complications Co-morbid Conditions Maternity Codes Morphology Codes (ICD-O) Combination Coding Sequelae Codes External Cause Codes (ECC) Dagger (+) and Asterisk (*) Codes Local Infections Sequencing of ICD-10 Codes Placement of ICD-10 Codes on Claims General Treating / Attending / Admitting Healthcare Provider Claims Referring Healthcare Providers Diagnoses Hospital Claims ICD-10 codes and Modifiers ICD-10 codes and Dental Laboratory Claims Clinical Validation General PMB Conditions Different ICD-10 codes on Different Claims Pre-authorisation versus Claims ICD-10 codes not appropriate for patient age ICD-10 codes not appropriate for patient gender Use of Morphology Codes (ICD-O) Appendix A: Communication with Stakeholders Appendix B: Notices Published by the National Department of Health Appendix C: Explanatory Notes on MIT Page 2 of 18
3 1. Introduction 1.1 Overview and Background ICD-10 (International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems Tenth Revision) is a diagnostic coding standard owned and maintained by the World Health Organisation (WHO). The coding standard was adopted by the National Health Information System of South Africa (NHISSA), and forms part of the health information strategy of the National Department of Health (NDoH). The standard currently serves as the diagnostic coding standard of choice in both the public and private healthcare sectors for morbidity coding. The purpose of ICD-10 coding is to translate diagnoses of diseases and other health related problems from descriptions into an alphanumerical code, which permits easy storage, retrieval and analysis of the data. It also allows for the establishment of the systematic recording, analysis, interpretation and comparison of morbidity and mortality data collected within the country but also with other countries. ICD-10 coding communicates heath data in a predictable, consistent and reproducible manner. Regulation 5(f) of the Medical Schemes Act 131 of 1998 prescribes the manner of submission of claims by healthcare providers and determines that all claims must contain the relevant diagnostic code that relates to the health service. The Council for Medical Schemes (CMS) will provide assistance to the ICD- 10 Task Team and measure compliance against Regulation 5(f) of the Medical Schemes Act 131 of 1998 as part of the accreditation of managed healthcare organisations and medical scheme administrators in future The implementation of the Medical Schemes Act 131 of 1998 also saw the emergence of a minimum set of guaranteed benefits to be covered by medical schemes referred to as Prescribed Minimum Benefits (PMBs). Entitlement to these benefits is diagnoses-driven and is appropriately identified using ICD-10 coding. To support the NHI (National Health Insurance) and for the purpose of accurate disease statistics, a Ministerial ICD-10 Task Team has been established to advise the Minister of Health on matters pertaining to ICD-10. One of the responsibilities of this Task Team is to ensure that phase 3 and 4.1 of ICD-10 is fully implemented by 1 January Objective(s) The following table describes the main objectives of the Ministerial ICD-10 Task Team s Technical User Guide: O3. Defining clear technical requirements to ensure easy understanding of Phase 3 implementation requirements. O1.1 Ensure the equal compliance within the public and private healthcare sectors. Implementation of ICD-10 Clinical Validation. O2.1 Assist in a smooth and successful transition from ICD-10 Coding Implementation Phase 3 to Phase 4. Ensuring high compliance and accurate ICD-10 statistics by medical schemes, medical scheme administrators and managed healthcare organisations, and by default healthcare service providers in both the public and private healthcare sectors. O3.1 A detailed review of the current ICD-10 compliance data will be undertaken by Council for Medical Schemes (CMS) on behalf of the NDoH. O3.2 Findings of O3.1 must be analysed and reported with specific focus on the outstanding requirements of Phase 4 of the implementation process. Page 3 of 18
4 1.3 Definitions, Acronyms and Abbreviations Abbreviation BHF CMS ECC ICD-10 ICD-O ICD-10 TT LOA LOS MIT MVA NHISSA NHI PDX PMA PMB SDX WHO Term / Definition Board of Healthcare Funders Council for Medical Schemes External Cause Codes Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems Tenth Revision International Classification for Oncology National ICD-10 Task Team Level of Acuity Length of Stay Master Industry Table Motor Vehicle Accident National Health Information System of South Africa National Health Insurance Primary Diagnosis Practice Management Application Prescribed Minimum Benefits Secondary Diagnosis World Health Organisation 1.4 Acknowledgements The NDoH would like to thank all those participating in the ICD-10 Task Team for offering their time and expertise in the development of the implementation plan. Page 4 of 18
5 2. ICD-10 Implementation Phases A phased approach starting on 1 July 2005 has been followed to implement ICD-10 coding in South Africa as described in the CMS Circular 32 of Phase 1: Implementation period from 1 July 2005 to 30 September 2005 Phase 2: Implementation period from 1 October 2005 to 31 December 2005 Phase 3: Implementation period from 1 January 2006 to 01 January 2014 Phase 4: Implementation has been further phased into 4.1. and 4.2. Phase 4.1: Implementation period starts with displaying warning messages from 01 June 2013 based on the new data requirements i.e. age, gender, morphology codes. This phase will be fully implemented on 1 January 2014 with full claim validation rejections. Phase 4.2: Implementation details will be finalised in 2013 and communicated to all healthcare stakeholders In order to be fully compliant with the ICD-10 coding implementation plan, stakeholders must have successfully implemented phase 3 and 4.1 by 01 January The requirements for implementation of the phases are described as follows:- Implementation Requirements Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Use all codes (primary and secondary) from the Master Industry Table (MIT) Level of specificity of ICD-10 code(s) Minimum 3-characters Maximum level of specificity (3 rd, 4 th and 5 th characters) for all primary and secondary codes Sequencing of multiple ICD-10 codes Valid Primary code in first position, followed by secondary codes to a maximum of 10 codes per line item for Medical, Allied and Support Health Professionals and a Valid Primary code in first position, followed by a maximum of 29 codes on a head level for hospital providers Codes invalid for use in first position: Asterisk, Sequelae, or External Cause Code (ECC), etc Page 5 of 18
6 Implementation Requirements Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Healthcare Providers mandated to submit ICD-10 codes. All diagnosing healthcare providers for all claim items. All non-diagnosing healthcare providers (pharmacists, clinical support and allied healthcare providers) for all PMB claim items. All non-diagnosing healthcare providers (pharmacists, clinical support and allied healthcare providers) for all non-pmb claim items. Hospital claims mandated to submit on highest / header / claim level only. Referral diagnoses to be submitted highest / header / claim level only when available. ICD-10 codes per claim item. At least 1 code Full clinical encounter coding For example: two codes describing the disease or condition e.g. injuries with an ECC; irrespective of whether the injury code is in the primary or secondary position, and ECC must follow somewhere in the secondary string Clinical Validation Contractual arrangements PMB conditions ICD-10 code not appropriate for Patient age ICD-10 code not appropriate for Patient gender Use of Morphology codes (ICD-O) 3. ICD-10 Terminology Definitions Using the above mentioned table describing the requirements for implementation of the different ICD-10 phases, the following sections explain the different ICD-10 terminology in more detail. 3.1 Master Industry Table (MIT) The MIT is considered the healthcare industry standard for ICD-10 codes and contains all the ICD-10 codes to be used in South Africa. The MIT is distributed as a Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet. The current version of the MIT in use in South Africa is dated September The updated MIT will be published on 01 January 2013 for implementation on 01 June Please refer to Appendix C for full details regarding the content of the MIT. Page 6 of 18
7 3.2 Coding Definitions Primary Diagnosis (PDX) - Morbidity Definition: The Primary Diagnosis is the main condition being treated. The condition that was diagnosed at the end of the episode of healthcare mainly responsible for the patient s need for treatment or investigation. If there is more than one main condition treated, then the most clinically severe or life threatening condition should be selected as the main condition in the primary position. If this cannot be established then the condition that is responsible for the greatest use of resources should be selected. Where there is more than one main condition being treated and no information is available to determine which of the conditions is the most severe / life threatening, or which one is responsible for the greatest use of resources go back to the default rule that stipulate the selection of the first condition documented by the treating provider. If no diagnosis was made, the main symptom, abnormal finding or problem should be selected as the main condition. Episodes of healthcare or contact with health services are not restricted to the treatment or investigation of current illness or injury. Episodes may also occur when someone who may not currently be sick requires or receives limited care or services; the details of the relevant circumstances should be recorded as the main condition. There can only be one primary diagnosis at the end of the episode of healthcare, primarily responsible for the patient s need for treatment or investigation. Resources equates to money or overall financial costs. This includes Level of Acuity (LOA), Length of Stay (LOS), equipment, medication etc. as part of the patient s treatment and care. All services will therefore total up to resource use for the event or the episode of care Primary Code Definition: The primary code is the code that describes the primary diagnosis, and must appear in the first (primary) position on a claim. Many patient encounters involve complications or sequelae (late effects) of primary conditions, however a primary underlying condition still exists and this is the condition that defines the primary code Secondary Diagnosis (SDX) - Morbidity Definition: This is an additional condition that affects patient care or may co-exist with the main condition and may require: Clinical evaluation; or Therapeutic treatment; or Diagnostic procedures; or Extended length of hospital stay; or Increased nursing care and/or monitoring Increased intensity of nursing care ECC also fall under secondary diagnoses. Examples are specified in the South African ICD-10 Coding Standards and Guidelines document. Page 7 of 18
8 3.2.4 Secondary Code Definition: Secondary codes are codes that further describe the patient s condition or the cause of the patient encounter. The secondary codes must follow the primary code and appear in the second to tenth position on a claim line. Examples include diabetic retinopathy, motor vehicle accident (MVA), etc. The rules and conventions of ICD-10 coding as set out by the WHO are applied to assign these codes appropriately (ICD-10 Volume 2 Instruction Manual, Chapter 3) Valid Code Definition: A valid code is an ICD-10 code that is published in the MIT based on the WHO rules and conventions. Example of valid Primary ICD-10 code up to maximum level of specificity: ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description Valid as a Primary Code M65.3 Trigger finger NO M65.34 Trigger finger, hand YES N63 Unspecified lump in breast YES Example of valid Secondary ICD-10 code: ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description Valid as a Primary Code W01 Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling NO W01.0 Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling, NO home W01.00 Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling, home while engaged in sports activity YES Complete Code / Level of Specificity Definition: A complete code is an ICD-10 code specified to its maximum level of specificity as published in the MIT based on the WHO rules and conventions. While most ICD-10 codes are valid up to four and even five characters, there are codes that are valid up to three characters only e.g. I10. Example of Primary ICD-10 code up to maximum level of specificity: ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description Maximum Specificity M65.3 Trigger finger NO M65.34 Trigger finger, hand YES N63 Unspecified lump in breast YES Example of Secondary ICD-10 code up to maximum level of specificity: ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description Maximum Specificity W01 Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling NO W01.0 Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling, NO home W01.00 Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling, home while engaged in sports activity YES Page 8 of 18
9 3.2.7 Complications Definition: A complication usually arises subsequent to: an existing condition, disease, pregnancy, injury, etc.; treatments and procedures; adverse reactions to drugs and / or chemicals. A complication may become a primary diagnosis despite it not being the reason for medical treatment. Examples are specified in the South African ICD-10 Coding Standards and Guidelines document Co-morbid Conditions Definition: A pre-existing condition that may or may not increase resource usage and it may co-exist with the main diagnosis. A co-morbid condition may become a primary diagnosis if it is the main condition being treated Maternity Codes Codes O80-O84 (Delivery section in the WHO ICD-10 Volume 1 in chapter XV) should only be used for primary morbidity coding if no other condition classifiable to Chapter XV: Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium is recorded Morphology Codes (ICD-O) The morphology code records the kind of tumour that has developed and how it behaves. This means that Morphology codes will need to be supplied with all WHO ICD-10 Volume 1 Chapter 2 (Neoplasm) codes where surgery has been performed or where pathology /laboratory investigations have been done to confirm the underlying cell type of the neoplasm. 3.3 Combination Coding Definition: There are certain diseases or conditions that require a set of two codes to correctly or accurately describe a particular disease or condition. The following are the four most common examples of Combination Coding: Sequelae Codes Definition: Sequelae is the late effect of a condition that is no longer present as the current illness. The initial condition occurred one or more years ago. A sequelae code can NEVER be used on its own or in the primary position. Example 1: Dysphagia due to stroke. Note: PDX: R13 Dysphagia SDX: I69.4 Sequelae of stroke, not specified as haemorrhage or infarction The primary diagnosis (PDX) is the late effect: Dysphagia and the secondary diagnosis (SDX) is the initial or sequelae condition: Due to stroke. Example 2: The patient presents with osteonecrosis of the pelvic region due to a hip replacement performed 18 months ago after a fracture of the femur was sustained in a motor vehicle accident. Page 9 of 18
10 PDX: M87.25 Osteonecrosis due to previous trauma, pelvic region and thigh SDX: T93.1 Sequelae of fracture of femur SDX: Y85.0 Sequelae of motor-vehicle accident Note: The primary diagnosis (PDX) is the late effect: Dysphagia and the secondary diagnosis (SDX) is the initial or sequelae condition: Due to stroke External Cause Codes (ECC) Definition: ECC allow for the classification of environmental events, circumstances and conditions as the cause of injury, poisoning and other adverse effects. The South African standard stipulates that all S and T codes must be accompanied by the ECC. ECC must always be used to the maximum level of specificity. Refer the WHO ICD-10 Volume 1 Chapter XIX on Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes (S00 T98). ECC is found in the MIT and also in the WHO ICD-10 Volume 1 Chapter XX External causes of morbidity and mortality (V01 Y98). The primary diagnosis (PDX) is the injury or poisoning code and the ECC is the secondary diagnosis (SDX). An ECC code can NEVER be used on its own or in the primary position. For example: Open fracture neck of femur due to fall from tree, at home, whilst gardening. PDX: S72.01: Open fracture neck of femur SDX: W14.03: Fall from tree, at home, whilst engaged in other types of work Note: The ECC section requires coding to the maximum level of specificity Dagger (+) and Asterisk (*) Codes Definition: Codes marked with a dagger (+) are considered the primary code indicating the underlying disease, while codes marked with an asterisk (*) are considered optional or secondary codes indicating the manifestation. A dagger code (+) can be used on its own when there is no manifestation. An asterisk code (*) can NEVER be used on its own or in the primary position. There are 83 special asterisk categories listed at the start of the relevant chapters in the WHO ICD-10 Volume 1 book. For example: Tuberculous peritonitis PDX: A18.3+: Tuberculosis of intestines, peritoneum and mesenteric glands SDX: K67.3*: Tuberculous peritonitis Note: Note: The dagger (+) is the primary diagnosis (PDX) and the asterisk (*) is the secondary diagnosis (SDX). Not all dagger codes are marked with the symbol (+) and any code, as appropriate, may become a dagger code. Medical schemes may not reject a claim for the reason that a code not marked as such was used as a dagger code together with an asterisk (*) code. All codes to be used for the manifestation are marked with the symbol (*) to indicate that these are asterisks codes. Page 10 of 18
11 3.3.4 Local Infections Definition: Coding of some infections requires an additional code in order to identify the organism(s) that is causing the infection. For example: Acute cystitis due to E.coli infection PDX: N30.0: SDX: B96.2: Acute cystitis Escherichia [E.coli] as cause of diseases classified to other chapters Note: The site of infection is coded as the primary diagnosis (PDX) and the infecting organism as the secondary diagnosis (SDX). 3.4 Sequencing of ICD-10 Codes Definition: Determine whether the first code in the primary position on a claim is valid and complete. A maximum of 10 (ten) ICD-10 codes in total must be allowed for per line item and / or referral diagnoses. 3.5 Placement of ICD-10 Codes on Claims It is important to understand how to include ICD-10 codes on claims, whether on paper or electronic format General Each ICD-10 code could consist of a maximum of 10 characters. The primary code is always the first code followed by the secondary / other codes. The dagger (+) and asterisk (*) symbols are left off all claims. An upper-or lowercase X is used as a placeholder for the 4 th character where a code does not have a 4 th character but does have a valid 5 th character. The dot, which is an integral part of an ICD-10 code, is retained in all paper and electronic claim submissions. Descriptions of diagnoses codes may not be transmitted or printed. Only the ICD-10 codes itself should be transmitted in order to protect patients privacy and confidentiality. 3-character codes should not contain any dots (.), spaces or hyphens (-). 4- and 5-character codes MUST contain the dot (.) after the 3 rd character but SHOULD NOT contain any spaces or hyphens (-). Electronic claims submission formats typically dictate the separator to be used between multiple codes: o Comma- delimited: Use a forward slash (/) without any additional separators like spaces between ICD-10 codes. o MEDCLM / EDIFACT: Use a forward slash (/) without any additional separators like spaces between ICD-10 codes. o XML: Different tags will be used for multiple ICD-10 codes Paper claims: Allow for code, space, forward slash (*/) space, code, repeating until a maximum of 10 ICD-10 codes. Third parties i.e. switching companies or pharmaceutical benefit management (PBM) companies must maintain the integrity of ICD-10 codes in its original format. Furthermore, the order of the ICD-10 codes may not be changed during transmission and / or translation of data. Non-disclosure of a diagnosis by the member of a medical scheme or a healthcare provider (U98.- range) Page 11 of 18
12 o Under such circumstances, the medical scheme is under no obligation to reimburse the member or the healthcare provider as a claim would still not entirely conform to the requirements of the legislation. Any attempt to do so would constitute non-compliance with prevailing legislation Treating / Attending / Admitting Healthcare Provider Claims ICD-10 codes must be supplied on item level. This means that ICD-10 codes must be supplied on tariff level for all procedures and NAPPI level for all medicines. Modifiers and lab slip items are excluded. A maximum of 10 (ten) codes in total must be allowed for per line item Referring Healthcare Providers Diagnoses ICD-10 codes should be included from a referring healthcare provider on a claim rendered by a healthcare provider that might not necessarily have treated a patient but is reporting on a patient s medical condition or has provided medical services, e.g. tests or prosthetics, that will assist the treating healthcare provider in addressing a patient s medical condition. The referral diagnoses could be used to determine a condition(s) of the patient / member in order for the medical scheme to ensure correct benefit allocation. Refer to CMS Circular 28 of 2009: Including ICD-10 code(s) for referring healthcare providers. All parties are requested to ensure that fields containing referral diagnoses data are not discarded in the transmission to or at the medical schemes. Healthcare providers are encouraged to at all times provide ICD-10 code(s) when patients are referred to other healthcare providers. Existence of the field is mandatory. ICD-10 codes must be supplied on header / summary / claim level. A maximum of 10 (ten) codes in total must be allowed for per line item Hospital Claims ICD-10 codes must be supplied on header / summary / claim level. A maximum of 30 (thirty) codes in total must be allowed for per line item ICD-10 codes and Modifiers No ICD-10 code needs to be submitted for modifier items as the modifier can never be used on its own and will inherit the ICD-10 code from its preceding tariff code. The only exception to this rule is Medical modifier 0017 which is used as a tariff code and not strictly as modifier ICD-10 codes and Dental Laboratory Claims All Dental Technician claims must include ICD-10 code(s) on line item level. AND must also include the referral diagnoses as made by the dentist or dental specialist on header / summary / claim level. Dentist and dental specialist claims that include dental laboratory work (code 8099) must include the ICD-10 code(s) on the 8099 line item only. There is no need to repeat this ICD-10 code(s) on the detail of the dental laboratory claim items. Page 12 of 18
13 3.6 Clinical Validation General ICD-10 codes must be included on all claims / accounts / statements regardless of whether the patient or medical scheme is the recipient and of any payment arrangement between any party in the communication channel. Only a healthcare provider treating a specific patient / member can select and include an ICD-10 code(s) on a claim / account / statement. No patient or any other third party may do so. A healthcare provider should use the sign and symptom codes in ICD-10 until such time as he / she can confirm the diagnoses / condition PMB Conditions All members of medical schemes are guaranteed a minimum set of benefits called Prescribed Minimum Benefits (PMBs). The benefits now include a limited set of diagnostic treatment pairs, chronic conditions and emergency medical conditions. The only way to determine if an episode of care constitutes a Prescribed Minimum Benefit is through a diagnosis code. Medical schemes, administrators and managed care organisations must be able to identify the PMB ICD- 10 code, regardless of whether the PMB ICD-10 code is the PDX or SDX Different ICD-10 codes on Different Claims Healthcare providers can not be penalised by medical schemes if their ICD-10 codes differ from that of other healthcare providers treating the same patient at the same time. The issue of determining who should decide on the main diagnosis of a patient is beyond the mandate of the ICD-10 Task Team. The ICD-10 Task Team s role is to assist in slotting in ICD-10 coding into current common practice, and not to interfere with prevailing clinical processes Pre-authorisation versus Claims The following standard response was drafted by the ICD-10 Task Team to explain the use of ICD-10 codes for pre-authorisation versus claim(s) submission: Medical Scheme Regulation 5(f) outlines legislative requirements regarding the manner of submission of a claim. The legislation assumes a discharge diagnosis to be the diagnosis that eventually should be submitted to the medical scheme for reimbursement. It does not however, prescribe the requirements for pre-authorisation. Each medical scheme/administrator should ensure that their internal processes accept ICD-10 codes when submitted by health care providers for the purpose of pre-authorisation or use the verbal description given by the member/health care provider for translation into a pre-authorisation/admission code. The admission code must be updated by the health care provider(s) as the patient s condition progresses or when discharge takes place. Members and healthcare providers may thus not be refused authorisation if no ICD-10 code but only a description of the condition is available ICD-10 codes not appropriate for patient age During phase 4 of the ICD-10 implementation plan, an Age indicator has been included in the new version of the MIT. This Age indicator must be used to determine when a specific ICD-10 code is clinically appropriate for use. This indicator has been compiled based on the WHO Volume 1 Tabular List. Page 13 of 18
14 3.6.6 ICD-10 codes not appropriate for patient gender During phase 4 of the ICD-10 implementation plan, a Gender indicator has been included in the new version of the MIT. This Gender indicator must be used to determine when a specific ICD-10 code is clinically appropriate for use. This indicator has been compiled based on the WHO Volume 2 Instruction manual, chapter 3 and paragraph 3.1.5: Categories with common characteristics, limited to one sex Use of Morphology Codes (ICD-O) A decision was taken to implement the morphology codes as published in ICD-O Version 3. The list will form part of the MIT planned for A crossmap from ICD-10 to ICD-0 has not been developed and supplied, hence any morphology code can be assigned to any ICD-10 code. Page 14 of 18
15 4.1 Appendix A: Communication with Stakeholders Year of Date of Circular Circular Title Publication Publication Reference October /2004 Implementation of ICD-10 coding 17 December /2004 ICD-10 coding process June /2005 Final ICD-10 implementation plan 28 June /2005 ICD-10 coding requirements for clinical support and allied health professionals 25 July /2005 Update on the implementation of ICD-10 coding: all you need to know 18 August /2005 ICD-10 inclusion on claims Guidelines on usage 18 August /2005 National Task team on implementation of ICD-10 published guidelines on ICD-10 submission Guidelines are attached to this Circular 29 September /2005 ICD-10 codes for Multi-drug resistant TB 29 September /2005 Extension for submission of ICD-10 codes by blood transfusion services 3 November /2005 (PMB data) ICD-10 compliance statistics: communication to providers 7 November /2005 National Task team on implementation of ICD-10: collection of high level data from medical schemes 8 December /2005 (PMB data) Most recent circular with ICD-10 coding for PMB conditions May /2006 Postponement of phase 4 of ICD-10 implementation: clinical validation 10 May /2006 Development and use of Quick Reference Code (QRC) lists for ICD July /2006 Validity of Unspecified, Other Specified, Sign & Symptom and Default ICD-10 Codes 28 Sept /2006 ICD-10 Version 2 (2005) products and updating of the BHF/DXS ICD-10 master industry table 28 Sept /2006 ICD-10 Coding of Mixtures on Medicine Claims 15 November /2006 Submission of Aggregated ICD-10 Compliance Data Feb /2007 SA-Specific ICD-10 Codes for Multi and Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis 16 July /2007 Submission of Paper Claims With ICD-10 Codes 16 July /2007 Claims Rejection for Invalid or Incomplete ICD-10 Codes 20 July /2007 ICD-10 Master Industry Table 2007 and BHF/DXS Browser - New Edition Available 13 August /2007 Criteria for Coding Training Companies and Trainers to be listed on the CMS Website and the ICD-10 Task Team Review Documents 24 August /2007 The Use of U98 Non-Disclosure ICD10-Codes 24 August /2007 Inclusion of an ICD-10 code at Header Level by referring Healthcare Providers 04 October /2007 National Task Team on ICD-10 Implementation - X59 Exposure to unspecified factor 06 November /2007 Addendum to Circular Number 24 of Criteria for Coding Training Companies and Trainers to be listed on the CMS Website and the ICD-10 Task Team review documents Page 15 of 18
16 Year of Date of Circular Circular Title Publication Publication Reference March /2008 Changes to ICD-10 Master Industry Table 21 August /2008 ERRATA ON THE ICD-10 MIT 18 December /2008 Submission of aggregated ICD-10 compliance data for July /2009 Validity of Unspecified, Other specified, Sign & symptom, and Default ICD 10 codes 3 September /2009 Proposed ICD-10 coding to be used for H1N1 ("swine flu") 3 September /2009 Criteria for coding training companies and trainers to be listed on the CMS website and the ICD-10 Task Team review document 3 September /2009 Including ICD-10 code(s) on claims for treating and referring healthcare providers 3 September /2009 Including ICD-10 code(s) for referring healthcare providers February /2010 Submission of aggregated ICD-10 compliance data June /2010 Clarification of ICD-10 coding for dental laboratory and technician claims 23 June /2010 ICD-10 codes, pre-authorisation and clinical validation requirements 23 June /2010 ICD-10 coding for non-medical schemes claims 23 June /2010 Purpose of the National ICD-10 Task Team 24 June /2010 The updating of the ICD-10 codes in line with the WHO data 24 June /2010 Review of the ICD-10 Implementation process February /2011 Submission of aggregated ICD-10 compliance data Appendix B: Notices Published by the National Department of Health Date of Notice Title Publication 04 Apr 2012 Appointment of the ICD10 Task Team 15 Jun 2012 ICD-10 coding requirements and training (Circulars 1 and 2 of 2012) Circular 1 of 2012: ICD-10 coding requirements Circular 2 of 2012: Accreditation process of service providers/learners: Diagnostic and procedural coding (SAQA Qualification ID 66389) 15 Jun 2012 South African ICD-10 Coding Standards and Guidelines (Version 5) Page 16 of 18
17 4.3 Appendix C: Explanatory Notes on MIT The following table describes the information contained within the MIT: Column Column Heading Explanation of Headings Data Example A Number Sequential numbering of each entry in the MIT data file used maily for sorting purposes. B Chapter_No Chapter number according to WHO CHAPTER I Volume 1 Tabular List. C Chapter_Desc Chapter description according to WHO Volume 1 Tabular List. Certain infectious and parasitic diseases D Group_Code Group code indicates a group of codes that contain clinically similar conditions and follows the conventions of WHO ICD- 10 Volume 1 referred to as block categories. 001 E Group_Desc Clinical description of the Group Code, referred to as block categories in WHO ICD-10 Volume 1. F ICD10_3_Code ICD-10 3-character code, not considered valid for use unless no 4 th or 5 th character code exists. Used together with Column J Valid_ICD10_ClinicalUse to indicate when valid for use. Intestinal infectious diseases G ICD10_3_Code_Desc ICD-10 3-character code s description Viral and other specified intestinal infections H ICD10_Code ICD-10 code to maximum level of specificity. Used together with Column J Valid_ICD10_ClinicalUse to indicate when valid for use. A08 I WHO_Full_Desc WHO long description for ICD-10 code in its 4- and 5-character format. J Valid_ICD10_ClinicalUse Indicates whether ICD-10 code listed in column H ICD10_Code is valid for clinical use or not. This is to ensure that only codes up to their maximum level of specificity are used. Indicated as: Y = Code VALID for clinical use N = CODE INVALID for clinical use K Valid_ICD10_Primary Indicates whether ICD-10 code is valid in the primary / first position. Indicated as: Y = Code CAN be used in primary / first position N = Code CANNOT be used in primary / first position L Valid_ICD10_Asterisk Indicates whether ICD-10 code is an Asterisk code or not. Indicated as: Y = Code IS an asterisk code N = Code IS NOT an asterisk code Please note that the asterisk (*) symbol is included in column H ICD10_Code. A08 Viral and other specified intestinal infections N N N Page 17 of 18
18 Column Column Heading Explanation of Headings Data Example M Valid_ICD10_Dagger Indicates whether ICD-10 code is a N Dagger code or not. Indicated as: Y = Code IS a dagger code N = Code IS NOT a dagger code N Valid_ICD10_Sequelae Indicates whether ICD-10 code is a N Sequelae code or not. Indicated as: Y = Code IS a sequelae code N = Code IS NOT a sequelae code O Age_Range Age indicator only age information mentioned in WHO Volume 1 (Tabular List) added in range format. P Gender Indicated as: M = Male F = Female U = Unspecified As per WHO Volume 2 Instruction Manual Q Status South African status indicator for each A entry: A = Add D = Discontinue (entry not deleted from file) M = Modify R WHO_Start_Date The WHO effective from date for new entries OR effective from date for change to entry to take effect. Date format = CCYYMMDD S WHO_End_Date WHO discontinued date - when entry is no longer in use. Date format = CCYYMMDD T WHO_Revision_History WHO revision history of changes made per code as per WHO Corrigendas. U SA_Start_Date Blank if code existed prior to 2007 MIT version. Value exists if code was added after 2007 or when modification to code took place to indicate when change takes effect. Date format = CCYYMMDD V SA_End_Date South African discontinued date - when entry is no longer in use. Date format = CCYYMMDD W SA_Revision_History South African revision history of changes made per code. X Comment Additional comments per code. Add new code Page 18 of 18
Questions and answers on ICD10 coding
 Questions and answers on ICD10 coding General overview ICD-10 is a diagnosis coding standard owned and maintained by the World Health Organisation (WHO). This coding standard was adopted by the National
Questions and answers on ICD10 coding General overview ICD-10 is a diagnosis coding standard owned and maintained by the World Health Organisation (WHO). This coding standard was adopted by the National
The ICD-9-CM uses an indented format for ease in reference I10 I10 I10 I10. All information subject to change. 2013 1
 Section I. Conventions, general coding guidelines and chapter specific guidelines The conventions, general guidelines and chapter-specific guidelines are applicable to all health care settings unless otherwise
Section I. Conventions, general coding guidelines and chapter specific guidelines The conventions, general guidelines and chapter-specific guidelines are applicable to all health care settings unless otherwise
ICD-9 Basics Study Guide
 Board of Medical Specialty Coding ICD-9 Basics Study Guide for the Home Health ICD-9 Basic Competencies Examination Two Washingtonian Center 9737 Washingtonian Blvd., Ste. 100 Gaithersburg, MD 20878-7364
Board of Medical Specialty Coding ICD-9 Basics Study Guide for the Home Health ICD-9 Basic Competencies Examination Two Washingtonian Center 9737 Washingtonian Blvd., Ste. 100 Gaithersburg, MD 20878-7364
CIRCULAR 13 OF 2014: MANAGED CARE ACCREDITATION - FINAL MANAGED HEALTH CARE SERVICES DOCUMENT
 CIRCULAR Reference: Classification and naming conventions of Managed Health Care Services Contact person: Hannelie Cornelius Accreditation Manager: Administrators & MCOs Tel: (012) 431 0406 Fax: (012)
CIRCULAR Reference: Classification and naming conventions of Managed Health Care Services Contact person: Hannelie Cornelius Accreditation Manager: Administrators & MCOs Tel: (012) 431 0406 Fax: (012)
Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM. May 29, 2013
 Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM May 29, 2013 Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM A look at the new system and how it compares to ICD-9-CM Presented by Therese
Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM May 29, 2013 Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM A look at the new system and how it compares to ICD-9-CM Presented by Therese
ICD-10-CM Overview and Coding Guidelines. Presented by: Katherine Abel/Rhonda Buckholtz
 ICD-10-CM Overview and Coding Guidelines Presented by: Katherine Abel/Rhonda Buckholtz 1 No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically, electronically,
ICD-10-CM Overview and Coding Guidelines Presented by: Katherine Abel/Rhonda Buckholtz 1 No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically, electronically,
Getting Ready for ICD-10. Part 2: ICD-10 Coding
 Getting Ready for ICD-10 Part 2: ICD-10 Coding Introduction In the United States, on October 1, 2015 the ICD 9 code set used to report medical diagnoses and inpatient procedures will be replaced by International
Getting Ready for ICD-10 Part 2: ICD-10 Coding Introduction In the United States, on October 1, 2015 the ICD 9 code set used to report medical diagnoses and inpatient procedures will be replaced by International
ICD-10 in the Provider Newsletter
 ICD-10 in the Provider Newsletter ICD-10 CM Code Structure, July 2013 ICD-10 Implementation, April 2013 ICD-10 Manual, January 2013 ICD-10 Back on Track, October 2012 ICD-10 Training, July 2012 ICD-10
ICD-10 in the Provider Newsletter ICD-10 CM Code Structure, July 2013 ICD-10 Implementation, April 2013 ICD-10 Manual, January 2013 ICD-10 Back on Track, October 2012 ICD-10 Training, July 2012 ICD-10
Coding with. Snayhil Rana
 Coding with ICD-9-CM CM Snayhil Rana ICD-9-CM CM Index Pre-Test Introduction to ICD-9-CM Coding The Three Volumes of the ICD-9-CM ICD-9-CM Coding Conventions Other ICD-9-CM Sections ICD-9-CM for Claim
Coding with ICD-9-CM CM Snayhil Rana ICD-9-CM CM Index Pre-Test Introduction to ICD-9-CM Coding The Three Volumes of the ICD-9-CM ICD-9-CM Coding Conventions Other ICD-9-CM Sections ICD-9-CM for Claim
Electronic Health Records Next Chapter: Best Practices, Checklists, and Guidelines ICD-10 and Small Practices April 30, 2014.
 Electronic Health Records Next Chapter: Best Practices, Checklists, and Guidelines ICD-10 and Small Practices April 30, 2014 Fallon Health Plan Christine Grondalski, Director Risk Adjustment & Analytics
Electronic Health Records Next Chapter: Best Practices, Checklists, and Guidelines ICD-10 and Small Practices April 30, 2014 Fallon Health Plan Christine Grondalski, Director Risk Adjustment & Analytics
Introduction to ICD-10-CM. An Introduction to the Transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM
 Introduction to ICD-10-CM An Introduction to the Transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM 1 Purpose Explain why the transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD- 10-CM is needed Describe the differences between ICD-9-CM
Introduction to ICD-10-CM An Introduction to the Transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM 1 Purpose Explain why the transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD- 10-CM is needed Describe the differences between ICD-9-CM
Using the ICD-10-CM. The Alphabetic Index helps you determine which section to refer to in the Tabular List. It does not always provide the full code.
 Using the ICD-10-CM Selecting the Correct Code To determine the correct International Classification of Diseases, 10 Edition, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) code, follow these two steps: Step 1: Look
Using the ICD-10-CM Selecting the Correct Code To determine the correct International Classification of Diseases, 10 Edition, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) code, follow these two steps: Step 1: Look
2FORMATS AND CONVENTIONS
 2FORMATS AND CONVENTIONS OF DIAGNOSIS CODING SYSTEMS Learning Outcomes After completing this chapter, students should be able to 2.1 Explain the layout of the ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM manuals. 2.2 Differentiate
2FORMATS AND CONVENTIONS OF DIAGNOSIS CODING SYSTEMS Learning Outcomes After completing this chapter, students should be able to 2.1 Explain the layout of the ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM manuals. 2.2 Differentiate
Ch. 14 - Medical Coding and Claims. A bill sent to the insurance carrier for payment related to patient care
 A bill sent to the insurance carrier for payment related to patient care A claim held or rejected by the insurance carrier due to problems or errors A coding system published by the US department of Health
A bill sent to the insurance carrier for payment related to patient care A claim held or rejected by the insurance carrier due to problems or errors A coding system published by the US department of Health
ICD-10... What Are You Waiting For?
 ICD-10... What Are You Waiting For? What is it? International classification for all general epidemiological, many health management purposes, and clinical use Published by the World Health Organization
ICD-10... What Are You Waiting For? What is it? International classification for all general epidemiological, many health management purposes, and clinical use Published by the World Health Organization
The Official Guidelines for coding and reporting using ICD-9-CM
 Reporting Accurate Codes In the Era of Recovery Audit Contractor Reviews Sue Roehl, RHIT, CCS The Official Guidelines for coding and reporting using ICD-9-CM A set of rules that have been developed to
Reporting Accurate Codes In the Era of Recovery Audit Contractor Reviews Sue Roehl, RHIT, CCS The Official Guidelines for coding and reporting using ICD-9-CM A set of rules that have been developed to
CODING. Neighborhood Health Plan 1 Provider Payment Guidelines
 CODING Policy The terms of this policy set forth the guidelines for reporting the provision of care rendered by NHP participating providers, including but not limited to use of standard diagnosis and procedure
CODING Policy The terms of this policy set forth the guidelines for reporting the provision of care rendered by NHP participating providers, including but not limited to use of standard diagnosis and procedure
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting
 2013 Narrative changes appear in bold text Items underlined have been moved within the guidelines since the 2012 version Italics are used to indicate revisions to heading changes The Centers for Medicare
2013 Narrative changes appear in bold text Items underlined have been moved within the guidelines since the 2012 version Italics are used to indicate revisions to heading changes The Centers for Medicare
ICD-10 for the Chiropractic Procrastinator
 ICD-10 for the Chiropractic Procrastinator Presented By Chiropractic Care of Minnesota, Inc. (CCMI) Authored By Dr. Evan Gwilliam, DC, MBA, BS, CPC, CCPC, NCICS, CCCPC, CPC-I, CPMA, MCS-P Introduction
ICD-10 for the Chiropractic Procrastinator Presented By Chiropractic Care of Minnesota, Inc. (CCMI) Authored By Dr. Evan Gwilliam, DC, MBA, BS, CPC, CCPC, NCICS, CCCPC, CPC-I, CPMA, MCS-P Introduction
Victorian Additions to the Australian Coding Standards
 Victorian Additions to the Australian Coding Standards 1 July 2014 The following are the Victorian Additions to Australian Coding Standards, effective 1 July 2014 (supplementing Australian Coding Standards,
Victorian Additions to the Australian Coding Standards 1 July 2014 The following are the Victorian Additions to Australian Coding Standards, effective 1 July 2014 (supplementing Australian Coding Standards,
Introduction to ICD - 10. Andrea Devlin, CPMA, CPC Alta Partners, LLC 2015
 Introduction to ICD - 10 Andrea Devlin, CPMA, CPC Alta Partners, LLC 2015 Agenda Introduction Benefits of ICD-10 Features of ICD-10 ICD-9 vs. ICD-10 ICD-10 Structure Question & Answer Introducing ICD-10
Introduction to ICD - 10 Andrea Devlin, CPMA, CPC Alta Partners, LLC 2015 Agenda Introduction Benefits of ICD-10 Features of ICD-10 ICD-9 vs. ICD-10 ICD-10 Structure Question & Answer Introducing ICD-10
Breaking the Code: ICD-9-CM Coding in Details
 Breaking the Code: ICD-9-CM Coding in Details ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes are 3- to 5-digit codes used to describe the clinical reason for a patient s treatment. They do not describe the service performed,
Breaking the Code: ICD-9-CM Coding in Details ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes are 3- to 5-digit codes used to describe the clinical reason for a patient s treatment. They do not describe the service performed,
IRF Coding: Changing the Culture to Strengthen the Team
 IRF Coding: Changing the Culture to Strengthen the Team Stephanie Johnson, CCS Sr. HIM Coding Specialist 2014. The UDSMR logo is a trademark of, a division of UB Foundation Activities, Inc. Objectives
IRF Coding: Changing the Culture to Strengthen the Team Stephanie Johnson, CCS Sr. HIM Coding Specialist 2014. The UDSMR logo is a trademark of, a division of UB Foundation Activities, Inc. Objectives
Overview of the national laws on electronic health records in the EU Member States National Report for Lithuania
 Overview of the national laws on electronic health records in the EU Member States and their interaction with the provision of cross-border ehealth services Contract 2013 63 02 Overview of the national
Overview of the national laws on electronic health records in the EU Member States and their interaction with the provision of cross-border ehealth services Contract 2013 63 02 Overview of the national
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS HEALTHCARE IDENTIFIERS BILL 2010
 About Healthcare Identifiers QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS HEALTHCARE IDENTIFIERS BILL 2010 Q1. What is the Healthcare Identifiers Service? The Healthcare Identifiers (HI) Service will implement and maintain a
About Healthcare Identifiers QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS HEALTHCARE IDENTIFIERS BILL 2010 Q1. What is the Healthcare Identifiers Service? The Healthcare Identifiers (HI) Service will implement and maintain a
ICD-10 Readiness for Public Health
 ICD-10 Readiness for Public Health Debbie Widener Sr. Implementation & Training specialist Sonali Luniya, PhD VP, Customer Experience ICD-10 Webinar: Goals ICD-10 Overview and Impacts ICD-9 vs. ICD-10
ICD-10 Readiness for Public Health Debbie Widener Sr. Implementation & Training specialist Sonali Luniya, PhD VP, Customer Experience ICD-10 Webinar: Goals ICD-10 Overview and Impacts ICD-9 vs. ICD-10
It s Time to Transition to ICD-10
 July 22, 2015 It s Time to Transition to ICD-10 What do the changes mean to your SNF? Presented by: Linda S. Little, RN-BSN Clinical Consultant HMM Consulting Office: (631) 265-6289 E-Mail: llittle@horanmm.com
July 22, 2015 It s Time to Transition to ICD-10 What do the changes mean to your SNF? Presented by: Linda S. Little, RN-BSN Clinical Consultant HMM Consulting Office: (631) 265-6289 E-Mail: llittle@horanmm.com
Release: 1. HLTCC402B Complete highly complex clinical coding
 Release: 1 HLTCC402B Complete highly complex clinical coding HLTCC402B Complete highly complex clinical coding Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor Descriptor This unit of competency describes
Release: 1 HLTCC402B Complete highly complex clinical coding HLTCC402B Complete highly complex clinical coding Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor Descriptor This unit of competency describes
Section 6. Medical Management Program
 Section 6. Medical Management Program Introduction Molina Healthcare maintains a medical management program to ensure patient safety as well as detect and prevent fraud, waste and abuse in its programs.
Section 6. Medical Management Program Introduction Molina Healthcare maintains a medical management program to ensure patient safety as well as detect and prevent fraud, waste and abuse in its programs.
HEALTH DEPARTMENT BILLING GUIDELINES
 HEALTH DEPARTMENT BILLING GUIDELINES Acknowledgement: Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ) is copyright 2015 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. No fee schedules, basic units, relative
HEALTH DEPARTMENT BILLING GUIDELINES Acknowledgement: Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ) is copyright 2015 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. No fee schedules, basic units, relative
ICD-10-CM/PCS Transition Fact Sheet
 ICD-10-CM/PCS Transition Fact Sheet Reed Group 10155 Westmoor Drive, Suite 210 Westminster, CO 80021 Notice: 2014 Reed Group, Ltd. All rights reserved. This document is made available for informational
ICD-10-CM/PCS Transition Fact Sheet Reed Group 10155 Westmoor Drive, Suite 210 Westminster, CO 80021 Notice: 2014 Reed Group, Ltd. All rights reserved. This document is made available for informational
HIV/AIDS Care: The Diagnosis Code Series 2. Prepared By: Stacey L. Murphy, MPA, RHIA, CPC AHIMA Approved ICD-10-CM/ICD-10-CM Trainer
 HIV/AIDS Care: The Diagnosis Code Series 2 Prepared By: Stacey L. Murphy, MPA, RHIA, CPC AHIMA Approved ICD-10-CM/ICD-10-CM Trainer Learning Outcomes Identify and explain the difference between ICD-9-CM
HIV/AIDS Care: The Diagnosis Code Series 2 Prepared By: Stacey L. Murphy, MPA, RHIA, CPC AHIMA Approved ICD-10-CM/ICD-10-CM Trainer Learning Outcomes Identify and explain the difference between ICD-9-CM
GENERAL INFORMATION. Adverse Event (AE) Definition (ICH GUIDELINES E6 FOR GCP 1.2):
 Make copies of the blank SAE report form as needed. Retain originals with confirmation of all information faxed to DMID Pharmacovigilance Group Clinical Research Operations and Management Support (CROMS
Make copies of the blank SAE report form as needed. Retain originals with confirmation of all information faxed to DMID Pharmacovigilance Group Clinical Research Operations and Management Support (CROMS
HSE HR Circular 007/2010 26 th April, 2010.
 Office of the National Director of Human Resources Health Service Executive Dr. Steevens Hospital Dublin 8 All Queries to: frank.oleary@hse.ie; Tel: 045 880454 des.williams@hse.ie; Tel: 045 882561 / 01
Office of the National Director of Human Resources Health Service Executive Dr. Steevens Hospital Dublin 8 All Queries to: frank.oleary@hse.ie; Tel: 045 880454 des.williams@hse.ie; Tel: 045 882561 / 01
2014/15 National Tariff Payment System. Annex 7A: Specified services for acute services for local pricing
 2014/15 National Tariff Payment System Annex 7A: Specified services for acute services for local pricing 17 December 2013 Publications Gateway Reference 00883 Annex 7A: Specified services for acute services
2014/15 National Tariff Payment System Annex 7A: Specified services for acute services for local pricing 17 December 2013 Publications Gateway Reference 00883 Annex 7A: Specified services for acute services
WELLCARE CLAIM PAYMENT POLICIES
 WellCare and Harmony Health Plan s claim payment policies are based on publicly distributed guidelines from established industry sources such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the
WellCare and Harmony Health Plan s claim payment policies are based on publicly distributed guidelines from established industry sources such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the
Preparing for ICD-10. What Your Practice Needs to Know
 WRS Health Preparing for ICD-10 2 Executive Summary The healthcare industry is set to undergo an important change on October 1, 2014, when the mandatory adoption of the ICD-10 codes go into effect. The
WRS Health Preparing for ICD-10 2 Executive Summary The healthcare industry is set to undergo an important change on October 1, 2014, when the mandatory adoption of the ICD-10 codes go into effect. The
POLICY STATEMENT 5.17
 POLICY STATEMENT 5.17 DENTAL RECORDS 1 (Including ADA Guidelines for Dental Records) 1. Introduction 1.1 Dentists have a professional and a legal obligation to maintain clinically relevant, accurate and
POLICY STATEMENT 5.17 DENTAL RECORDS 1 (Including ADA Guidelines for Dental Records) 1. Introduction 1.1 Dentists have a professional and a legal obligation to maintain clinically relevant, accurate and
ICD-10-CM Coding Overview AHCA Spring Convention & Trade Show April 21-23, 2015
 ICD-10-CM Coding Overview AHCA Spring Convention & Trade Show April 21-23, 2015 1 Why the Conversion to ICD-10-CM? ICD-10-CM provides more specific data than ICD-9-CM Better reflection of current medical
ICD-10-CM Coding Overview AHCA Spring Convention & Trade Show April 21-23, 2015 1 Why the Conversion to ICD-10-CM? ICD-10-CM provides more specific data than ICD-9-CM Better reflection of current medical
ICD-10 Coding for Audiology
 ICD-10 Coding for Audiology Mary Sue Fino-Szumski, Ph.D., M.B.A. Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Vanderbilt Bill Wilkerson Center Department of Hearing and Speech Sciences Disclosure Financial
ICD-10 Coding for Audiology Mary Sue Fino-Szumski, Ph.D., M.B.A. Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Vanderbilt Bill Wilkerson Center Department of Hearing and Speech Sciences Disclosure Financial
What is your level of coding experience?
 The TrustHCS Academy is dedicated to growing new coders to enter the field of medical records coding while also increasing the ICD-10 skills of seasoned coding professionals. A unique combination of on-line
The TrustHCS Academy is dedicated to growing new coders to enter the field of medical records coding while also increasing the ICD-10 skills of seasoned coding professionals. A unique combination of on-line
Guide to Prescribed Minimum Benefits 2016
 Guide to Prescribed Minimum Benefits 2016 Who we are Remedi Medical Aid Scheme (referred to as 'the Scheme"), registration number 1430, is a non-profit organisation, registered with the Council for Medical
Guide to Prescribed Minimum Benefits 2016 Who we are Remedi Medical Aid Scheme (referred to as 'the Scheme"), registration number 1430, is a non-profit organisation, registered with the Council for Medical
Briefing on ehr Content Hong Kong Clinical Terminology Table (HKCTT) By Maggie LAU Health Informatician, ehriso
 Briefing on ehr Content Hong Kong Clinical Terminology Table (HKCTT) By Maggie LAU Health Informatician, ehriso Agenda Background Application Adoption Management RecognisedTerminologies in ehr Registered
Briefing on ehr Content Hong Kong Clinical Terminology Table (HKCTT) By Maggie LAU Health Informatician, ehriso Agenda Background Application Adoption Management RecognisedTerminologies in ehr Registered
ICD-10-CM KEVIN SOLINSKY, CPC, CPC-I, CEDC, CEMC PRESIDENT HEALTHCARE CODING CONSULTANTS, LLC 480-200-4590
 ICD-10-CM KEVIN SOLINSKY, CPC, CPC-I, CEDC, CEMC PRESIDENT HEALTHCARE CODING CONSULTANTS, LLC 480-200-4590 ICD-10 FINAL RULE Implementation date October 1, 2014. ICD-9-CM codes will not be accepted by
ICD-10-CM KEVIN SOLINSKY, CPC, CPC-I, CEDC, CEMC PRESIDENT HEALTHCARE CODING CONSULTANTS, LLC 480-200-4590 ICD-10 FINAL RULE Implementation date October 1, 2014. ICD-9-CM codes will not be accepted by
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting FY 2016 Page 2 of 115
 Narrative changes appear in bold text Items underlined have been moved within the guidelines since the FY 2014 version Italics are used to indicate revisions to heading changes The Centers for Medicare
Narrative changes appear in bold text Items underlined have been moved within the guidelines since the FY 2014 version Italics are used to indicate revisions to heading changes The Centers for Medicare
South African ICD-10 Coding Standards
 South African ICD-10 Coding Standards Developed to assist the clinical coder in the South African environment Table of Contents South African ICD-10 Coding Standards... 1 Table of Contents... 2 Acknowledgement...
South African ICD-10 Coding Standards Developed to assist the clinical coder in the South African environment Table of Contents South African ICD-10 Coding Standards... 1 Table of Contents... 2 Acknowledgement...
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008
 Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
AHLA. HH. Introduction to Medical Coding for Payment Lawyers
 AHLA HH. Introduction to Medical Coding for Payment Lawyers Robert A. Pelaia Senior University Counsel University of Florida Jacksonville Jacksonville, FL Institute on Medicare and Medicaid Payment Issues
AHLA HH. Introduction to Medical Coding for Payment Lawyers Robert A. Pelaia Senior University Counsel University of Florida Jacksonville Jacksonville, FL Institute on Medicare and Medicaid Payment Issues
Change is Coming in 2014! ICD-10 will replace ICD-9 for Diagnosis Coding
 Change is Coming in 2014! ICD-10 will replace ICD-9 for Diagnosis Coding Clinical Coding Diagnosis Codes Clinicians select ICD-CM codes to describe a patient s diagnoses, symptoms, and clinical findings.
Change is Coming in 2014! ICD-10 will replace ICD-9 for Diagnosis Coding Clinical Coding Diagnosis Codes Clinicians select ICD-CM codes to describe a patient s diagnoses, symptoms, and clinical findings.
Pain Quick Reference for ICD 10 CM
 Pain Quick Reference for ICD 10 CM Coding of acute or chronic pain in ICD 10 CM are located under category G89, Pain, not elsewhere classified. The subcategories are broken down by type, temporal parameter,
Pain Quick Reference for ICD 10 CM Coding of acute or chronic pain in ICD 10 CM are located under category G89, Pain, not elsewhere classified. The subcategories are broken down by type, temporal parameter,
SNOMED CT. The Language of Electronic Health Records
 SNOMED CT The Language of Electronic Health Records Contents SNOMED CT: An overview page 02 What is a Clinical Terminology? What is SNOMED CT? The International Health Terminology Standards Development
SNOMED CT The Language of Electronic Health Records Contents SNOMED CT: An overview page 02 What is a Clinical Terminology? What is SNOMED CT? The International Health Terminology Standards Development
Service Specification Template Department of Health, updated June 2015
 Service Specification Template Department of Health, updated June 2015 Service Specification No. : 2 Service: Commissioner Lead: Provider Lead: Period: Anti-coagulation monitoring Date of Review: 31 st
Service Specification Template Department of Health, updated June 2015 Service Specification No. : 2 Service: Commissioner Lead: Provider Lead: Period: Anti-coagulation monitoring Date of Review: 31 st
Introduction to Medical Coding For Lawyers
 American Health Lawyers Association Institute on Medicare and Medicaid Payment Issues March 20-22, 2013 Introduction to Medical Coding for Payment Lawyers Robert A. Pelaia Senior University Counsel for
American Health Lawyers Association Institute on Medicare and Medicaid Payment Issues March 20-22, 2013 Introduction to Medical Coding for Payment Lawyers Robert A. Pelaia Senior University Counsel for
Maternity Benefit Summary
 Maternity Benefit Summary 2015 How we cover pregnancy and childbirth in 2015 The Maternity Benefit covers day-to-day and in hospital medical expenses for expecting mothers and newborns. Overview This document
Maternity Benefit Summary 2015 How we cover pregnancy and childbirth in 2015 The Maternity Benefit covers day-to-day and in hospital medical expenses for expecting mothers and newborns. Overview This document
How To Get A Blue Cross Code Change
 OVERVIEW 1. What is an ICD Code? The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) code set is used primarily to report medical diagnosis and inpatient procedures. ICD codes are mandated by the Centers
OVERVIEW 1. What is an ICD Code? The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) code set is used primarily to report medical diagnosis and inpatient procedures. ICD codes are mandated by the Centers
What you should know about Data Quality. A guide for health and social care staff
 What you should know about Data Quality A guide for health and social care staff Please note the scope of this document is to provide a broad overview of data quality issues around personal health information
What you should know about Data Quality A guide for health and social care staff Please note the scope of this document is to provide a broad overview of data quality issues around personal health information
ICD-10 Action Plan: Your 12-Step Transition Plan for ICD-10. Written by the AMA CPT Medical Informatics Department
 ICD-10 Action Plan: Your 12-Step Transition Plan for ICD-10 Written by the AMA CPT Medical Informatics Department P R A C T I C E T O O L S E P T E M B E R 2 0 1 2 This resource is for educational purposes
ICD-10 Action Plan: Your 12-Step Transition Plan for ICD-10 Written by the AMA CPT Medical Informatics Department P R A C T I C E T O O L S E P T E M B E R 2 0 1 2 This resource is for educational purposes
Contents QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ALLIED HEALTHCARE
 h QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ALLIED HEALTHCARE Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.....P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.....P.4 OS describe what individuals
h QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ALLIED HEALTHCARE Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.....P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.....P.4 OS describe what individuals
Celebrating ICD-10: A New Tradition of Codes.
 Celebrating ICD-10: A New Tradition of Codes. Delayed. Now What? Stop training entirely? Continue training as originally planned? Alter the course of training? Important Dates January 16, 2009 February
Celebrating ICD-10: A New Tradition of Codes. Delayed. Now What? Stop training entirely? Continue training as originally planned? Alter the course of training? Important Dates January 16, 2009 February
FAQ for Coding Encounters in ICD 10 CM
 FAQ for Coding Encounters in ICD 10 CM Topics: Encounter for Routine Health Exams Encounter for Vaccines Follow Up Encounters Coding for Injuries Encounter for Suture Removal External Cause Codes Tobacco
FAQ for Coding Encounters in ICD 10 CM Topics: Encounter for Routine Health Exams Encounter for Vaccines Follow Up Encounters Coding for Injuries Encounter for Suture Removal External Cause Codes Tobacco
ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS Frequently asked questions for HIM and Patient Financial Services Leaders
 ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS Frequently asked questions for HIM and Patient Financial Services Leaders Executive questions What is the current status of ICD-10? The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS Frequently asked questions for HIM and Patient Financial Services Leaders Executive questions What is the current status of ICD-10? The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
HEALTH INSURANCE CLAIM FORM APPROVED BY THE BERMUDA HEALTH COUNCIL 10/09
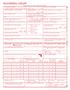 HEALTH INSURANCE CLAIM FORM APPROVED BY THE BERMUDA HEALTH COUNCIL 10/09 1. NAME OF INSURANCE COMPANY PLEASE PRINT OR TYPE IN UPPERCASE LETTERS 1a. INSURED S CERTIFICATE NUMBER ARGUS BF&M COLONIAL FM GEHI
HEALTH INSURANCE CLAIM FORM APPROVED BY THE BERMUDA HEALTH COUNCIL 10/09 1. NAME OF INSURANCE COMPANY PLEASE PRINT OR TYPE IN UPPERCASE LETTERS 1a. INSURED S CERTIFICATE NUMBER ARGUS BF&M COLONIAL FM GEHI
Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for CRNA s and Top 25 Codes
 Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for CRNA s and Top 25 Codes Chapter 2 Neoplasms (C00-D49) Classification improvements Code expansions Significant
Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for CRNA s and Top 25 Codes Chapter 2 Neoplasms (C00-D49) Classification improvements Code expansions Significant
ICD-10-CM Conventions & General Coding Guidelines March 26, 2014
 ICD-10-CM & March 26, 2014 Content Provided by To Receive CPE Credit Individual Attendee Participate in entire webinar Answer polls when they are provided Group Attendees Complete group attendance form
ICD-10-CM & March 26, 2014 Content Provided by To Receive CPE Credit Individual Attendee Participate in entire webinar Answer polls when they are provided Group Attendees Complete group attendance form
CODING CHANGESICD-10!! Presented by: Colleen Grope CPC, CCS-P
 CODING CHANGESICD-10!! Presented by: Colleen Grope CPC, CCS-P 1 AGENDA Differences between ICD-9 and ICD-10 Basic ICD-10 Coding Guidelines Implementation Strategies Potential Revenue Ramifications 2 ICD-9
CODING CHANGESICD-10!! Presented by: Colleen Grope CPC, CCS-P 1 AGENDA Differences between ICD-9 and ICD-10 Basic ICD-10 Coding Guidelines Implementation Strategies Potential Revenue Ramifications 2 ICD-9
Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses of Public Workers: A Review of Employees Compensation Claims from GSIS, 2010-2012
 Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses of Public Workers: A Review of Employees Compensation Claims from GSIS, 2010-2012 Marissa Lomuntad-San Jose, MD, MOH Supervising Occupational Health Officer Occupational
Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses of Public Workers: A Review of Employees Compensation Claims from GSIS, 2010-2012 Marissa Lomuntad-San Jose, MD, MOH Supervising Occupational Health Officer Occupational
Risk Adjustment Data Validation Study Frequently Asked Questions
 Risk Adjustment Data Validation Study Frequently Asked Questions MEDICAL RECORD SUBMISSION Q1: Can medical groups gather all the medical records for the data validation and send them all at once? A1: Please
Risk Adjustment Data Validation Study Frequently Asked Questions MEDICAL RECORD SUBMISSION Q1: Can medical groups gather all the medical records for the data validation and send them all at once? A1: Please
How to Code Well-Care Visits for Children and Adolescents
 How to Code Well-Care Visits for Children and Adolescents to meet NCQA s HEDIS Quality Goals and Receive Appropriate Reimbursement and Credit for Providing Quality Care TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...
How to Code Well-Care Visits for Children and Adolescents to meet NCQA s HEDIS Quality Goals and Receive Appropriate Reimbursement and Credit for Providing Quality Care TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...
How To Transition From Icd 9 To Icd 10
 ICD-10 FAQs for Doctors What is ICD-10? ICD-10 is the 10 th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), used by health care systems to report diagnoses and procedures for purposes of
ICD-10 FAQs for Doctors What is ICD-10? ICD-10 is the 10 th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), used by health care systems to report diagnoses and procedures for purposes of
Medical Terminologies and Classification Systems
 CHAPTER 5 Medical Terminologies and Classification Systems Objectives After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Classify various medical nomenclatures Differentiate common classification systems
CHAPTER 5 Medical Terminologies and Classification Systems Objectives After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Classify various medical nomenclatures Differentiate common classification systems
ICD-10 Provider Preparation
 ICD-10 Provider Preparation After browsing this slide deck, the viewer will become more familiar with the following information: What are the origins of ICD-10? Why transition to ICD-10? Why ICD-10 matters.
ICD-10 Provider Preparation After browsing this slide deck, the viewer will become more familiar with the following information: What are the origins of ICD-10? Why transition to ICD-10? Why ICD-10 matters.
Getting Ready for ICD-10. Dianna Hoskins, OCS Cincinnati Eye Institute
 Dianna Hoskins, OCS Cincinnati Eye Institute Chart Documentation: Will your documentation stand up to ICD-10? Do you always mark which eye, severity or status of the disease (chronic or acute), site, etiology
Dianna Hoskins, OCS Cincinnati Eye Institute Chart Documentation: Will your documentation stand up to ICD-10? Do you always mark which eye, severity or status of the disease (chronic or acute), site, etiology
School of Health Sciences HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
 School of Health Sciences HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Course: HIT 1020 - Basic Diagnosis Coding Credit Hours: 3cr hours Instructor: TBA Office Phone: Division of Allied Health (801) 957-6200 Office Hours:
School of Health Sciences HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Course: HIT 1020 - Basic Diagnosis Coding Credit Hours: 3cr hours Instructor: TBA Office Phone: Division of Allied Health (801) 957-6200 Office Hours:
ICD 10 CM: Presented by:
 ICD 10 CM: Presented by: ICD-10-CM Mission 2014 Why ICD-10? Mechanics of ICD-10 Why ICD-10? Why are we doing this? Here is an excerpt taken from the final ruling [T]he ICD-10 code sets provide a standard
ICD 10 CM: Presented by: ICD-10-CM Mission 2014 Why ICD-10? Mechanics of ICD-10 Why ICD-10? Why are we doing this? Here is an excerpt taken from the final ruling [T]he ICD-10 code sets provide a standard
Are you buying private medical insurance? Take a look at this guide before you decide 2008
 Are you buying private medical insurance? Take a look at this guide before you decide 2008 2 Private medical insurance Private medical insurance 3 Contents 1 About this guide 4 2 What is private medical
Are you buying private medical insurance? Take a look at this guide before you decide 2008 2 Private medical insurance Private medical insurance 3 Contents 1 About this guide 4 2 What is private medical
NHI: a gateway to better health for all
 NHI: a gateway to better health for all TABLE OF CONTENTS The Patient's rights NHI Interim Extension of Services Why NHI? NHI Commitment to YOU Your Commitment to NHI How Do I Become a Member How Do I
NHI: a gateway to better health for all TABLE OF CONTENTS The Patient's rights NHI Interim Extension of Services Why NHI? NHI Commitment to YOU Your Commitment to NHI How Do I Become a Member How Do I
A Comparison of ICD-10-CM and ICD-9-CM for Capturing Domestic Violence
 A Comparison of ICD-10-CM and ICD-9-CM for Capturing Domestic Violence Felicia Cohn, PhD William Rudman, PhD Travis Bankhead, BS Valerie Watzlaf, PhD, FAHIMA, RHIA Objectives Understand the differences
A Comparison of ICD-10-CM and ICD-9-CM for Capturing Domestic Violence Felicia Cohn, PhD William Rudman, PhD Travis Bankhead, BS Valerie Watzlaf, PhD, FAHIMA, RHIA Objectives Understand the differences
SUMMARY PAPER A COMPARISON OF PATIENT CHARTERS IN AUSTRALIA
 SUMMARY PAPER A COMPARISON OF PATIENT CHARTERS IN AUSTRALIA This Summary Paper has been prepared by the Commission office. The range of patient rights and responsibilities that it contains were sourced
SUMMARY PAPER A COMPARISON OF PATIENT CHARTERS IN AUSTRALIA This Summary Paper has been prepared by the Commission office. The range of patient rights and responsibilities that it contains were sourced
5557 FAQs & Definitions
 5557 FAQs & Definitions These Questions and Answers are intended to present information that has been acquired as part of the discovery process and provides necessary context for the Policy Directives
5557 FAQs & Definitions These Questions and Answers are intended to present information that has been acquired as part of the discovery process and provides necessary context for the Policy Directives
10/23/2010. Objectives. Coding Process. What is ICD-9-CM coding? HCPCS. What is CPT-4? Provide a basic understanding of the coding process
 Objectives Medical Coding and Billing HCMT 200 Provide a basic understanding of the coding process Understand the importance of complete, accurate documentation to the coding process Learn the benefits
Objectives Medical Coding and Billing HCMT 200 Provide a basic understanding of the coding process Understand the importance of complete, accurate documentation to the coding process Learn the benefits
General terms of insurance. January 2010 edition. Insurance carrier: Compact Grundversicherungen AG
 Compact One Mandatory basic health insurance (with compulsory initial consultation by phone) pursuant to the Swiss Federal Health Insurance Act (KVG/LAMal) General terms of insurance January 2010 edition
Compact One Mandatory basic health insurance (with compulsory initial consultation by phone) pursuant to the Swiss Federal Health Insurance Act (KVG/LAMal) General terms of insurance January 2010 edition
Data quality checks performed on SUS and HES data
 Data quality checks performed on SUS and HES data Author: HES Data Quality Team Date: 24 th February 2014 1 Copyright 2013, Health and Social Care Information Centre. Version Control Version Date Author
Data quality checks performed on SUS and HES data Author: HES Data Quality Team Date: 24 th February 2014 1 Copyright 2013, Health and Social Care Information Centre. Version Control Version Date Author
9 Expenditure on breast cancer
 9 Expenditure on breast cancer Due to the large number of people diagnosed with breast cancer and the high burden of disease related to it, breast cancer is associated with substantial health-care costs.
9 Expenditure on breast cancer Due to the large number of people diagnosed with breast cancer and the high burden of disease related to it, breast cancer is associated with substantial health-care costs.
AMEX International Healthcare Plan Benefits schedule
 Quality health plans & benefits Healthier living Financial well-being Intelligent solutions AMEX International Healthcare Plan Benefits schedule Effective 1 April 2015 46.06.933.1-EUAM D (4/15) Your flexible
Quality health plans & benefits Healthier living Financial well-being Intelligent solutions AMEX International Healthcare Plan Benefits schedule Effective 1 April 2015 46.06.933.1-EUAM D (4/15) Your flexible
COM Compliance Policy No. 3
 COM Compliance Policy No. 3 THE UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT CHICAGO NO.: 3 UIC College of Medicine DATE: 8/5/10 Chicago, Illinois PAGE: 1of 7 UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS COLLEGE OF MEDICINE CODING AND DOCUMENTATION
COM Compliance Policy No. 3 THE UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT CHICAGO NO.: 3 UIC College of Medicine DATE: 8/5/10 Chicago, Illinois PAGE: 1of 7 UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS COLLEGE OF MEDICINE CODING AND DOCUMENTATION
Keweenaw Holistic Family Medicine Patient Registration Form
 Keweenaw Holistic Family Medicine Patient Registration Form How did you first learn of our Clinic? Circle one: Attended Lecture Internet KHFM website Newspaper Sign in window Yellow Pages Physician Friend
Keweenaw Holistic Family Medicine Patient Registration Form How did you first learn of our Clinic? Circle one: Attended Lecture Internet KHFM website Newspaper Sign in window Yellow Pages Physician Friend
Unit/Standard Number. Proficiency Level Achieved: (X) Indicates Competency Achieved to Industry Proficiency Level
 1 Secondary Task List 100 INTRODUCTION TO HEALTHCARE 101 Identify the roles and educational/credentialing requirements of various health care practitioners. 102 Describe the 's job description, personal
1 Secondary Task List 100 INTRODUCTION TO HEALTHCARE 101 Identify the roles and educational/credentialing requirements of various health care practitioners. 102 Describe the 's job description, personal
ICD 10 ICD 9. 14, 000 codes No laterality Limited severity parameters No placeholders 3-5 digits
 ICD 10 Conversion 1 Why Change? ICD 9 14, 000 codes No laterality Limited severity parameters No placeholders 3-5 digits 1 2 3 4 5 ICD 10 69,000+ codes Indicates Rt or Lt Extensive severity parameters
ICD 10 Conversion 1 Why Change? ICD 9 14, 000 codes No laterality Limited severity parameters No placeholders 3-5 digits 1 2 3 4 5 ICD 10 69,000+ codes Indicates Rt or Lt Extensive severity parameters
ICD 10 ESSENTIALS. Debbie Sarason Manager, Practice Enhancement and Quality Reporting
 ICD 10 ESSENTIALS Debbie Sarason Manager, Practice Enhancement and Quality Reporting October 29, 2015 CHANGING FROM 1CD 9 TO ICD 10 IN 2015 Rest of world has been using ICD 10 for decades World Health
ICD 10 ESSENTIALS Debbie Sarason Manager, Practice Enhancement and Quality Reporting October 29, 2015 CHANGING FROM 1CD 9 TO ICD 10 IN 2015 Rest of world has been using ICD 10 for decades World Health
Challenges for. Health Insurers & TPAs. Data enhancement and information sharing in the health insurance sector
 Challenges for Health Insurers & TPAs Data enhancement and information sharing in the health insurance sector Alam Singh Assistant Managing Director Milliman 86 w w w. e h e a l t h o n l i n e. o r g
Challenges for Health Insurers & TPAs Data enhancement and information sharing in the health insurance sector Alam Singh Assistant Managing Director Milliman 86 w w w. e h e a l t h o n l i n e. o r g
A review of the Condition Present on Admission (CPoA) variable
 A review of the Condition Present on Admission (C) variable Miles Utz, Rachael Wills, Stephanie Callaghan, Taku Endo, Lachlan Mortimer, Sandra Martyn, Trisha Johnston, Corrie Martin Health Statistics Centre,
A review of the Condition Present on Admission (C) variable Miles Utz, Rachael Wills, Stephanie Callaghan, Taku Endo, Lachlan Mortimer, Sandra Martyn, Trisha Johnston, Corrie Martin Health Statistics Centre,
How To Make A Hospice Care Plan
 TOPIC PROPOSED RULE SUMMARY COMMENT Rates and Estimated hospital market basket update: 2.7 percent Aggregate Cap PROPOSAL Impact of ACA Reductions: minus 0.7 percentage points Impact of Wage Index Changes
TOPIC PROPOSED RULE SUMMARY COMMENT Rates and Estimated hospital market basket update: 2.7 percent Aggregate Cap PROPOSAL Impact of ACA Reductions: minus 0.7 percentage points Impact of Wage Index Changes
HEALTH PREFACE. Introduction. Scope of the sector
 HEALTH PREFACE Introduction Government and non-government sectors provide a range of services including general practitioners, hospitals, nursing homes and community health services to support and promote
HEALTH PREFACE Introduction Government and non-government sectors provide a range of services including general practitioners, hospitals, nursing homes and community health services to support and promote
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting FY 2015 Page 2 of 116
 Narrative changes appear in bold text Items underlined have been moved within the guidelines since the FY 2014 version Italics are used to indicate revisions to heading changes The Centers for Medicare
Narrative changes appear in bold text Items underlined have been moved within the guidelines since the FY 2014 version Italics are used to indicate revisions to heading changes The Centers for Medicare
ICD-10-CM TRANSITION WORKBOOK
 ICD-10-CM TRANSITION WORKBOOK The Next Generation of Coding Preparation is the key to success when transitioning your practice from ICD-9 to ICD-10. The federally mandated compliance date is October 1,
ICD-10-CM TRANSITION WORKBOOK The Next Generation of Coding Preparation is the key to success when transitioning your practice from ICD-9 to ICD-10. The federally mandated compliance date is October 1,
1. ICD-10-CM, SKILLED NURSING FACILITIES, AND LAB SERVICES
 1. ICD-10-CM, SKILLED NURSING FACILITIES, AND LAB SERVICES 1.1 ICD-10-CM, SKILLED NURSING FACILITIES, AND LAB SERVICES Welcome to the ICD-10-CM, Skilled Nursing Facilities, and Lab Services training. Please
1. ICD-10-CM, SKILLED NURSING FACILITIES, AND LAB SERVICES 1.1 ICD-10-CM, SKILLED NURSING FACILITIES, AND LAB SERVICES Welcome to the ICD-10-CM, Skilled Nursing Facilities, and Lab Services training. Please
Member Handbook. Mature Membership. This Handbook helps Members fully understand the benefits and limitations of the On Call
 Member Handbook Mature Membership This Handbook helps Members fully understand the benefits and limitations of the On Call Mature Membership and how to properly access them. Eligibility and Participation
Member Handbook Mature Membership This Handbook helps Members fully understand the benefits and limitations of the On Call Mature Membership and how to properly access them. Eligibility and Participation
Section 9. Claims Claim Submission Molina Healthcare PO Box 22815 Long Beach, CA 90801
 Section 9. Claims As a contracted provider, it is important to understand how the claims process works to avoid delays in processing your claims. The following items are covered in this section for your
Section 9. Claims As a contracted provider, it is important to understand how the claims process works to avoid delays in processing your claims. The following items are covered in this section for your
