COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT DIAGNOSTIC MODALITIES IN EVALUATION OF INFECTION OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY. Summary
|
|
|
- Nora Eaton
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Biomed Clin Res Volume 2 Number 1, 2009 Original Article COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT DIAGNOSTIC MODALITIES IN EVALUATION OF INFECTION OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY Plamen S. Kinov, 1 Teodor Z. Petrov, 1 Dilyana Vasileva, Peter N. Tivchev Clinic of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Queen Giovanna University Hospital - ISUL, Medical University-Sofia, Bulgaria 1 Central Laboratory of Nuclear Medicine Alexandrovska University Hospital, Medical University-Sofia, Bulgaria Summary Loosening is the most common late complication of total hip arthroplasty. Although rare, low-grade infection often presents as prosthetic loosening and could be missed. There is controversy about the diagnostic value of bone scintigraphy and laboratory tests in patients suspected of having loosening. In this retrospective study, we evaluated the sensitivity and the specificity of different diagnostic modalities in patients suspected of having loosening of the hip arthroplasty. Seventeen patients (20 hips) with total hip arthroplasty and possible prosthetic loosening were examined with conventional radiography and three-phase bone scintigraphy. Results of microbiological examinations of joint aspiration and surgical specimens (9 patients), plus C-reactive protein level (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, as well as clinical follow-up were evaluated in the twenty hips. Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy values were calculated. Five hips had septic, and three hips had aseptic loosening. In twelve cases, neither loosening nor infection was confirmed. For diagnosing infection with conventional radiography and bone scintigraphy, respectively, sensitivity values were 62.5% and 87.5%; specificity - 80% and 91.6%; and accuracy 85% and 90%. For ESR and CRP, respectively, sensitivity values were 60% and 100%; specificity - 100% and 70%; and accuracy % and 75%. In a study population of patients suspected of having infected total hip replacements, threephase bone scintigraphy performed better than conventional radiography, ESR and CRP tests. Key words: scintigraphy, hip arthroplasty. Introduction Corresponding Author: Plamen Kinov Dept. of Orthopedics Univ. Hosp. Queen Giovanna- ISUL 8, Bialo more str. Sofia, 1527 Bulgaria plamenkinov@yahoo.com Received: January 05, 2009 Revision received: May 28, 2009 Accepted: July 06, 2009 Loosening is the most common late complication of total hip arthroplasty (THA) [1]. Although rare, lowgrade infection often presents as prosthetic loosening and could be missed. After the considerable decrease from 9% in the initial series of Charnley [2], the reported rate of infection after primary implantation and revision arthroplasty of hip prostheses is between 1% and 4% [3]. Although rare, infection is a serious complication in reconstructive joint surgery. The diagnosis of an infected hip endoprosthesis is usually made using clinical methods, radiographic techniques, and biopsy. However, there is no absolutely 36
2 Kinov et al. Comparison of different diagnostic modalities precise diagnostic test. A complicating factor is that the accuracy of imaging investigations depends on the expertise of the interpreters [4, 5]. Moreover, the relative utility of bone scintigraphy and laboratory examinations is controversial [6, 7]. The aim of our retrospective study was to evaluate the diagnostic value of bone scintigraphy, C-reactive protein level (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), in patients suspected of having aseptic or septic loosening of the hip arthroplasty. Material and Methods From the database of the Clinic of Orthopedics and Traumatology, 20 total hip arthroplasties, examined with bone scintigraphy, were reviewed retrospectively. The series included eleven females and six males, mean age 63.7±8.2 years (age range 51-81). Three arthroplasties were bilateral; five hips were scheduled for revision because of infection, and three because of aseptic loosening. In another nine cases, bone scintigraphy was performed for evaluation of periprosthetic remodeling after revision with impaction allografting. In three of the cases, patients complained of hip pain. The average time between the index surgery and bone scintigraphy was 3.3±4.6 years (range years). The patients were evaluated clinically [1], radiographically [1, 8, 9], and scintigraphically [7]. Differential white blood cell count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP) and fibrinogen were measured shortly before the examination. ESR levels above 40 mm/hr were considered abnormal. CRP levels were considered abnormal according to the local laboratory standard (above 0.8 mg/dl). No patient received antibiotic treatment at the time of imaging. Demographic data on the patients in the series are shown in Table 1. Imaging evaluation included standard radiographs and 99Tc-MDP bone scans. Table 1. Characteristics of the patients in the series. Parameter Demographics Primary diagnosis N,% Results Age (yrs) 63.7 (51 to 81) Weight (kg) 73.9 (47 to 115) Height (cm) (145 to 185) Gender (M/F; %) 6/11 (35.3%/64.7%) Osteoarthritis 14 (70%) Fracture 3 (15%) Osteonecrosis 2 (10%) Others 1 (5%) Primary/Revision HA (N, %) 9/11 (45%/55%) Involved hip (R/L, N, %) 15/5 (75%/25%) Follow-up (yrs) 3.3 (0.5 to 16) Conventional Radiography Implant stability was assessed radiographically according to the criteria proposed by Engh et al. [8] for cementless, and by Harris and McGann [9] for cemented implants. Radiolucency was defined as a radiolucent line >2 mm and parallel to the implant. Subsidence was defined as a decrease of at least 5 mm in the distance between the top of the stem and the greater trochanter. Cup migration >5 mm was defined by measuring the distance from the teardrop line. The diagnosis of infection [3, 10] was rendered when at least one of the following criteria was present: rapid prosthetic migration (of at least 2 mm within 6-12 months), rapidly progressing periprosthetic osteolysis, and/or irregular periprosthetic osteolysis. The diagnosis of loosening (without infection) [1, 8, 9] was rendered when at least one of the following criteria was present: migration (of less than 5 mm), periprosthetic lucency (in a smooth area of 2 mm or greater in diameter), periosteal reaction (of the solid type), and/or cement fracture. In the patients with only one set of radiographs, the diagnosis of infection or loosening was based on the same morphologic criteria, without information regarding migration. 37
3 J Biomed Clin Res Volume 2 Number 1, Bone Scintigraphy Three-phase bone scintigraphy was performed with a gamma camera equipped with a lowenergy, high-resolution, parallel-hole collimator by using a 20% window centered on the 140-keV photopeak after intravenous injection of MBq of 99mTc-MDP (Methylene Diphosphonate). In the dynamic phase, images of the hip were acquired in a 3-second exposure up to 2 minutes after injection. The blood pool phase consisted of acquisition of a static spot image of the hip (anterior view) 5 minutes after intravenous tracer injection. The third phase (i.e. the bone mineral metabolism study) was performed 24 hours after injection, and anterior and posterior spot views of the hip were again obtained. The images were analyzed by a nuclear physician (T.P. and D.V.), blinded to the results from the other studies (radiographs and laboratory tests). The appearance (focal or diffuse) of the increased radionuclide uptake was described [6, 11]. Focally or diffusely increased periprosthetic uptake in all three phases of bone scintigraphy was considered diagnostic for infection. Increased radionuclide uptake limited to the third phase was considered to indicate a loosened but not infected total hip replacement. Diagnosis of Infection Our criterion for infection was based on detecting microorganisms in cultures. If no microorganisms were found, the detection of local abscess formation and the presence of neutrophilic granulocytes were also considered. In the eight hips revised, at the time of revision surgery, biopsy specimens were collected. Each was put in a separate, dry, sterile glass container and taken to the laboratory for immediate processing. Standard bacteriological techniques were used to identify isolates and determine antibiotic sensitivity. For eight of the 20 cases, results from the analysis of additional histologic specimens of capsular tissue were available. The final diagnosis of septic/aseptic loosening was based on surgical, histologic, laboratory, and bacteriologic data and follow-up. No infection was assumed to be present in patients who had negative microbiologic results at revision (for the eight revised hips); normal ESR, CRP level and white blood cell count; and improvement in their clinical symptoms for more than 6 months. Statistical Analysis The sensitivity of the different tests was defined as the number of true-positive results divided by the sum of true-positive and false-negative; specificity - as the number of true-negatives divided by the sum of true-negatives and falsepositives; accuracy was defined as the sum of true-positives and true-negatives divided by the total number of cases. Data were compared using a sign test. Statistical analysis was performed with the SPSS statistical package Version 10.0 (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois, USA). Significance was defined as a p value of <0.05. Results Five hips were diagnosed as having an infection on the basis of the correlation between positive pre- and intra-operative cultures, and laboratory and histological findings showing acute or chronic inflammation of tissue (Fig. 1); the appearance of the tissue intraoperatively; radiographic findings; and the clinical course. Three hips were diagnosed radiographically as septically loose. There were seven positive and thirteen negative bone scans. In four cases, bone scintigraphy yielded positive result for sepsis; on the other hand, one of the four hips with negative intraoperative culture was diagnosed as septic. Clinical, radiographic, and pre- and intraoperative findings showed aseptic loosening in three hips (two cups 2/15, 13.3%) and two stems (2/15, 13.3%) (Fig. 2). The sensitivity of conventional radiography was 62.5%; specificity was 80%, and accuracy 85%. The sensitivity of bone scintigraphy was 87.5%; specificity was 91.6%; and accuracy - 90%. The observed differences were not statistically significant. Data were also evaluated with respect to the predictive value of ESR and CRP for independent evaluation of infection (Table 2). For ESR, there were three positive and twelve negative results. For CRP, there were eight positive and seven negative results. The mean ESR value for the 15 patients with measurement was 22.9 mm/h (range, 6 to 63 mm/h, SD ±19.5), and the mean value for CRP for the 16 patients with measurement was 1.84 mg/dl (range, 0.24 to 7.2 mg/dl, SD ±2.03). However, differences were not significant (p>0.05). Differential white blood count and fibrinogen measurements did not show correlation with loosening (septic or aseptic).
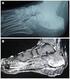
4 Kinov et al. Comparison of different diagnostic modalities Figure 1. P.B, 57-year-old female 26 months after left total hip replacement. Infection was diagnosed by microbiological evaluation of a surgical specimen. Results of conventional radiography, bone scintigraphy, and ESR and CRP were true-positive. A) Bone scintigraphy. Increased radionuclide uptake. B), C) Conventional anteroposterior radiographs of the left hip show rapid development of osteolysis (arrows) at the bone-prosthesis and cement-bone interfaces. (B was obtained 6 months prior to C). Figure 2. T.I., 67-year-old female 6 months after right revision total hip replacement with osteoplasty and cementing technique. Aseptic loosening of the cup. Result of conventional radiography was false-negative (A), whereas this of bone scintigraphy true-positive (B). ESR and CRP within normal range. Table 2. Ability of different modalities to predict infection of hip arthroplasty. Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) Accuracy (%) Radiography Scintigraphy ESR CSR
5 J Biomed Clin Res Volume 2 Number 1, 2009 Discussion Improvements in prosthetic materials and surgical techniques have led to marked decreases in the prevalence of infection and aseptic loosening in patients with hip replacements. Identifying the cause of loosening is important, as it will determine the extent of surgery required. In the presence of infection, implant removal and radical debridement of infected soft tissue and bone is often indicated. The use of bone grafts is controversial. Radiographic diagnosis of infected hip arthroplasty versus aseptic loosening is difficult because there is considerable morphologic overlap between the two diagnoses. In aseptic loosening, wear debris (composed of polymethylmethacrylate, polyethylene, or metal) lead to macrophage activation, which in turn releases bone-resorbing products like interleukins and prostaglandin E2 [1]. This occurs in areas of progressive bone loss and granuloma formation, which may simulate abnormalities relating to infection. The course bone resorption takes in time, however, may serve as an important tool in differentiating an aseptic loosening from a septic one [11]. A negative bone scan suggested the absence of loosening. However, a positive result was regarded as controversial for the diagnosis of both aseptic and septic complications. Focally increased radionuclide uptake around the prosthesis is commonly considered to represent loosening, while diffusely increased uptake is commonly considered to represent infection [7]. However, infection may also be present in prostheses with focal uptake patterns [11]. We described a sensitivity of 87.5% and a specificity of 91.6% for bone scintigraphy in diagnosing infection. Itasaka et al. (2001) described a sensitivity of 83%, a specificity of 79%, and an accuracy of 79% [12]. Bone scintigraphy is of limited value in the diagnosis of loosening and infection in patients who present with it within 12 months after an arthroplasty procedure [13]. The inclusion of seven patients with less than one-year follow-up has probably had effects on our results. Clinical examination, plain radiographs, and bone scintigraphy, as well as combined measurement of CRP, ESR can detect prosthetic loosening and differentiate between low-grade infection and mechanical instability. In Bulgarian literature, there are several studies on bone scintigraphy investigations of THA. Moreover, there are few publications discussing the value of laboratory findings in diagnosing loosening of hip arthroplasty. The results from current studies support the practice of intraoperative cultures, laboratory tests and bone scintigraphy in diagnosing infection of hip arthroplasty. Our study supports previous findings that bone scintigraphy as a method of diagnosing periprosthetic complications has a high sensitivity, and relatively good specificity and accuracy [7]. Our study has certain limitations. The prevalence of infection was low, and this was attributed to the specificity of the Clinic of Orthopedics and Traumatology and the relatively low rate of infection in prosthetic joint surgery. In addition, for obvious reasons, surgery with microbiological evaluation is normally not performed in all patients with a painful total joint replacement. Clinical follow-up sometimes has to be used for evaluation of possible hip infection, which was the case with twelve hips in our study. Conclusion Bone scintigraphy and laboratory tests are useful tools for detecting infection of total hip arthroplasty. Based on the results of our study, it may be concluded that ESR lacks sensitivity, but bone scintigraphy and CRP are accurate enough to predict a periprosthetic infection. However, only CRP can reliably exclude the absence of infection. In a situation in which bone scintigraphy, laboratory studies and clinical picture are equivocal, aspiration biopsy may be helpful in establishing periprosthetic infection. References 1. Kinov P, Tivchev P. The problem of aseptic loosening of total hip arthroplasty. Bulg J Orthop Trauma. 2002;38: Charnley J; Eftekhari N. Postoperative infection in total prosthetic replacement arthroplasty of the hip-joint. With special reference to the bacterial content of the air of the operating room. British J. Surg. 1969;56: Tivchev P. Periprostetic Infections. Diagnosis. Orthop Trauma. 2003;39(3): Kramhoft M, Gehrchen PM, Bodtker S, Wagner A, Jensen F. Inter- and intraobserver study of 40
6 Kinov et al. Comparison of different diagnostic modalities radiographic assessment of cemented total hip arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11: Ore L, Hardoff R, Gips S, Tamir A, Epstein L. Observer variation in the interpretation of bone scintigraphy. J Clin Epidemiol. 1996;49: Levitsky KA, Hozack WJ, Balderston RA, Rothman RH, Gluckman SJ, Maslack MM, et al. Evaluation of the painful prosthetic joint: relative value of bone scan, sedimentation rate, and joint aspiration. J Arthroplasty. 1991;6: Palestro CJ, Torres MA. Radionuclide imaging in orthopedic infections. Semin Nucl Med. 1997;27: Engh CA, Bobyn JD, Glassman AH. Porouscoated hip replacement. The factors governing bone in growth, stress shielding, and clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987;69(1): Harris WH, McGann WA. Loosening of the femoral component after use of the medullaryplug cementing technique. Follow-up note with a minimum five-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68(7): Barrack RL, Harris WH. The value of aspiration of the hip joint before revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75: Aliabadi P, Tumeh SS, Weissman BN, McNeil BJ. Cemented total hip prosthesis: radiographic and scintigraphic evaluation. Radiology. 1989; 173: Itasaka T, Kawai A, Sato T, Mitani S, Inoue H. Diagnosis of infection after total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2001;6: Stumpe KD, Notzli HP, Zanetti M, Kamel EM, Hany TF, Gorres GW, von Schulthess GK, Hodler J. FDG PET for differentiation of infection and aseptic loosening in total hip replacements: comparison with conventional radiography and three-phase bone scintigraphy. Radiology. 2004;231(2):
Although joint arthroplasties were attempted in the nineteenth. Nuclear Medicine and the Infected Joint Replacement
 Nuclear Medicine and the Infected Joint Replacement Charito Love, MD,* Scott E. Marwin, MD,, and Christopher J. Palestro, MD*, Nearly 700,000 hip and knee arthroplasties are performed annually in the United
Nuclear Medicine and the Infected Joint Replacement Charito Love, MD,* Scott E. Marwin, MD,, and Christopher J. Palestro, MD*, Nearly 700,000 hip and knee arthroplasties are performed annually in the United
Clinical performance of endoprosthetic and total hip replacement systems
 Veterans Administration Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development Vol. 24 No. 3 Pages 49 56 Clinical performance of endoprosthetic and total hip replacement systems P. M. SANDBORN, B.S. ; S. D.
Veterans Administration Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development Vol. 24 No. 3 Pages 49 56 Clinical performance of endoprosthetic and total hip replacement systems P. M. SANDBORN, B.S. ; S. D.
The Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty Part 1: Identification and Diagnosis in the Primary Care Setting
 Clinical Review Article The Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty Part 1: Identification and Diagnosis in the Primary Care Setting David J. Jacofsky, MD Mark D. Campbell, MD Deep infection represents one of
Clinical Review Article The Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty Part 1: Identification and Diagnosis in the Primary Care Setting David J. Jacofsky, MD Mark D. Campbell, MD Deep infection represents one of
Kaiser Permanente. National Total Joint Replacement Registry. Liz Paxton Director of Surgical Outcomes & Analysis
 Kaiser Permanente National Total Joint Replacement Registry Liz Paxton Director of Surgical Outcomes & Analysis Overview Background Total Joint Replacement (TJR) Importance of establishing a TJR post-market
Kaiser Permanente National Total Joint Replacement Registry Liz Paxton Director of Surgical Outcomes & Analysis Overview Background Total Joint Replacement (TJR) Importance of establishing a TJR post-market
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Joint Revision Surgery - When Do I Need It?
 Page 1 of 7 Joint Revision Surgery - When Do I Need It? Joint replacement surgery is undoubtedly one of the greatest medical advances of our time. Hip and knee replacements have been performed in millions
Page 1 of 7 Joint Revision Surgery - When Do I Need It? Joint replacement surgery is undoubtedly one of the greatest medical advances of our time. Hip and knee replacements have been performed in millions
The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty. Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan
 Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7
 Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Nuclear medicine has long played an important role in
 Diagnosing Infection in the Failed Joint Replacement: A Comparison of Coincidence Detection F-FDG and 111 In-Labeled Leukocyte/ 99m Tc-Sulfur Colloid Marrow Imaging Charito Love, MD 1 ; Scott E. Marwin,
Diagnosing Infection in the Failed Joint Replacement: A Comparison of Coincidence Detection F-FDG and 111 In-Labeled Leukocyte/ 99m Tc-Sulfur Colloid Marrow Imaging Charito Love, MD 1 ; Scott E. Marwin,
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Imagine being an orthopedic surgeon and knowing that your patient s
 http://www.surgicalproductsmag.com/product-releases/2009/05/safer-methods-internal-bone-fixation Advances in Internal Bone Fixation Sharps safety for orthopedic surgeons by Ron Stoker Imagine being an
http://www.surgicalproductsmag.com/product-releases/2009/05/safer-methods-internal-bone-fixation Advances in Internal Bone Fixation Sharps safety for orthopedic surgeons by Ron Stoker Imagine being an
Introduction to the Bertram Hip Spacer
 Introduction to the Bertram Hip Spacer Approximately 200,000 hip replacement surgeries are done every year in United States. Fortunately the incidence of infection is routinely 0.5 percent-1 percent. However
Introduction to the Bertram Hip Spacer Approximately 200,000 hip replacement surgeries are done every year in United States. Fortunately the incidence of infection is routinely 0.5 percent-1 percent. However
DIAGNOSING INFECTION IN HIP REPLACEMENTS
 DIAGNOSING INFECTION IN HIP REPLACEMENTS THE USE OF FINE-NEEDLE ASPIRATION AND RADIOMETRIC CULTURE P. ROBERTS, A. J. WALTERS, D. J. W. McMINN From the Royal Orthopaedic and Selly Oak Hospitals, Birmingham
DIAGNOSING INFECTION IN HIP REPLACEMENTS THE USE OF FINE-NEEDLE ASPIRATION AND RADIOMETRIC CULTURE P. ROBERTS, A. J. WALTERS, D. J. W. McMINN From the Royal Orthopaedic and Selly Oak Hospitals, Birmingham
INCIDENCE OF REASONS FOR REVISION HIP SURGERY: PRELIMINARY STUDY
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2015 vol. 119, no. 3 SURGERY ORIGINAL PAPERS INCIDENCE OF REASONS FOR REVISION HIP SURGERY: PRELIMINARY STUDY D. Mihăilescu 1*, P. Botez 1,2, Liliana Savin 1, Carmen
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2015 vol. 119, no. 3 SURGERY ORIGINAL PAPERS INCIDENCE OF REASONS FOR REVISION HIP SURGERY: PRELIMINARY STUDY D. Mihăilescu 1*, P. Botez 1,2, Liliana Savin 1, Carmen
RESIDENT TRAINING GOALS AND OBJECTIVES STATEMENTS
 RESIDENT TRAINING GOALS AND OBJECTIVES STATEMENTS Evaluation and treatment of dental emergencies Recognize, anticipate and manage emergency problems related to the oral cavity. Differentiate between those
RESIDENT TRAINING GOALS AND OBJECTIVES STATEMENTS Evaluation and treatment of dental emergencies Recognize, anticipate and manage emergency problems related to the oral cavity. Differentiate between those
From Department of Orthopaedics, Conquest Hospital, The Ridge, East Sussex. n N.A. Sandiford, FRCS (Tr/Orth), MFSEM, Specialist. Registrar.
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 372-379 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary total hip arthroplasty with hydroxyapatite coated titanium femoral stems. Does design philosophy influence long term outcome? : results of a
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 372-379 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary total hip arthroplasty with hydroxyapatite coated titanium femoral stems. Does design philosophy influence long term outcome? : results of a
A 15-year follow-up study of 4606 primary total knee replacements
 Knee A 15-year follow-up study of 466 primary total knee replacements V. I. Roberts, C. N. A. Esler, W. M. Harper From Glenfield General Hospital, Leicester, England This is a 15-year follow-up observational
Knee A 15-year follow-up study of 466 primary total knee replacements V. I. Roberts, C. N. A. Esler, W. M. Harper From Glenfield General Hospital, Leicester, England This is a 15-year follow-up observational
BONE PRESERVATION STEM
 TRI-LOCK BONE PRESERVATION STEM Featuring GRIPTION Technology SURGICAL TECHNIQUE IMPLANT GEOMETRY Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK BONE PRESERVATION STEM Featuring GRIPTION Technology SURGICAL TECHNIQUE IMPLANT GEOMETRY Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
Radiologic Assessment of Total Hip Arthroplasty: Loosening
 March 2004 Radiologic Assessment of Total Hip Arthroplasty: Loosening Grant Garrigues, Harvard Medical School Anatomy Liner Acetabular Component Calcar Stem Femoral Component 2 www.yoursurgery.com/proceduredetails.cfm?br=5&proc=27
March 2004 Radiologic Assessment of Total Hip Arthroplasty: Loosening Grant Garrigues, Harvard Medical School Anatomy Liner Acetabular Component Calcar Stem Femoral Component 2 www.yoursurgery.com/proceduredetails.cfm?br=5&proc=27
Peri-prosthetic Joint Infection
 Therapeutics, Pharmacology and Clinical Toxicology Vol XV, Number 4, December 2011 Pages 293-299 Copyright reserved 2011 ORIGINAL PAPERS Peri-prosthetic Joint Infection - A Diagnostic and Treatment Hospital
Therapeutics, Pharmacology and Clinical Toxicology Vol XV, Number 4, December 2011 Pages 293-299 Copyright reserved 2011 ORIGINAL PAPERS Peri-prosthetic Joint Infection - A Diagnostic and Treatment Hospital
Anterior Hip Replacement
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of hip replacement and arthritis management must be made in
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of hip replacement and arthritis management must be made in
Metallurgical analysis of five failed cast cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloy hip prostheses
 Veterans Administration Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development Vol. 23 No. 4 Pages 27-36 Metallurgical analysis of five failed cast cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloy hip prostheses STEPHEN D.
Veterans Administration Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development Vol. 23 No. 4 Pages 27-36 Metallurgical analysis of five failed cast cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloy hip prostheses STEPHEN D.
Failure Mechanisms and Closed Reduction of a Constrained Tripolar Acetabular Liner
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 2 2009 Case Report Failure Mechanisms and Closed Reduction of a Constrained Tripolar Acetabular Liner William J. Robertson, MD, Christopher J. Mattern, MD/MBA, John
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 2 2009 Case Report Failure Mechanisms and Closed Reduction of a Constrained Tripolar Acetabular Liner William J. Robertson, MD, Christopher J. Mattern, MD/MBA, John
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model
 Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model Musculoskeletal infections are serious and potentially life-threatening. Musculoskeletal infections include necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis,
Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model Musculoskeletal infections are serious and potentially life-threatening. Musculoskeletal infections include necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis,
An Alternative Conservative Approach to Hip Reconstruction
 Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA An Alternative Conservative Approach to Hip Reconstruction Craig S. Waller, MD* and Timothy McTighe, Dr. H.S. (hc)** Acknow ledgement:
Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA An Alternative Conservative Approach to Hip Reconstruction Craig S. Waller, MD* and Timothy McTighe, Dr. H.S. (hc)** Acknow ledgement:
Hip Resurfacing 2011 ORIGINAL ARTICLE. James W. Pritchett MD. Introduction. Abstract
 1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Resurfacing 2011 James W. Pritchett MD Abstract In 1938 Marion Smith-Peterson placed a cobalt chromium cup on a reshaped femoral head to perform the first hip resurfacing. 15 Also,
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Resurfacing 2011 James W. Pritchett MD Abstract In 1938 Marion Smith-Peterson placed a cobalt chromium cup on a reshaped femoral head to perform the first hip resurfacing. 15 Also,
FEMORAL NECK FRACTURE FOLLOWING TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 1 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURE FOLLOWING TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT László Sólyom ( ), András Vajda & József Lakatos Orthopaedic Department, Semmelweis University, Medical Faculty, Budapest, Hungary Correspondence:
1 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURE FOLLOWING TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT László Sólyom ( ), András Vajda & József Lakatos Orthopaedic Department, Semmelweis University, Medical Faculty, Budapest, Hungary Correspondence:
Clinical Testing for Metal-on-Metal Prosthetic Wear and Tear
 Clinical Testing for Metal-on-Metal Prosthetic Wear and Tear Frederick G. Strathmann, PhD, DABCC (CC, TC) February 8 th, 2013 Disclosures None Objectives Compare heavy metal analysis in synovial fluid
Clinical Testing for Metal-on-Metal Prosthetic Wear and Tear Frederick G. Strathmann, PhD, DABCC (CC, TC) February 8 th, 2013 Disclosures None Objectives Compare heavy metal analysis in synovial fluid
The Right Choice. Exeter. total hip system
 The Right Choice Exeter total hip system Exeter The Right Choice Anatomic Reconstruction Offset The objectives of total hip replacement are to: relieve pain increase mobility and function Achieving a correct
The Right Choice Exeter total hip system Exeter The Right Choice Anatomic Reconstruction Offset The objectives of total hip replacement are to: relieve pain increase mobility and function Achieving a correct
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene
 Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier April 9, 2012 TOC Clinical Value Dossier for Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene 1 Executive Summary 7 2 Burden of
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier April 9, 2012 TOC Clinical Value Dossier for Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene 1 Executive Summary 7 2 Burden of
Analysis of Functional and Radiological Outcome of Total Hip Replacements in Rheumatoid and Osteoarthritis Patients *
 Open Journal of Rheumatology and Autoimmune Diseases, 2013, 3, 246-250 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojra) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojra.2013.34038 Hip Replacements in Rheumatoid
Open Journal of Rheumatology and Autoimmune Diseases, 2013, 3, 246-250 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojra) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojra.2013.34038 Hip Replacements in Rheumatoid
Two-stage Reimplantation of Infected Hip Arthroplasties. Wun-Schen Chen, MD; Te-Hu Fu 1, MD; Jun-Wen Wang, MD
 Original Article 188 Two-stage Reimplantation of Infected Hip Arthroplasties Wun-Schen Chen, MD; Te-Hu Fu 1, MD; Jun-Wen Wang, MD Background: Although two-stage reimplantation for infected hip arthroplasty
Original Article 188 Two-stage Reimplantation of Infected Hip Arthroplasties Wun-Schen Chen, MD; Te-Hu Fu 1, MD; Jun-Wen Wang, MD Background: Although two-stage reimplantation for infected hip arthroplasty
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology
 frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology Recently, you may have seen advertisements from legal companies
frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology Recently, you may have seen advertisements from legal companies
Dr NG FU YUEN Associate Consultant Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital
 Dr NG FU YUEN Associate Consultant Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital Aging Population in Hong Kong Life Expectancy Female 86 Male 81 Figure from Census and Statistics Department,
Dr NG FU YUEN Associate Consultant Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital Aging Population in Hong Kong Life Expectancy Female 86 Male 81 Figure from Census and Statistics Department,
MN Community Measurement Total Knee Replacement Impact and Recommendation Document June 2010
 MN Community Measurement Total Knee Replacement Impact and Recommendation Document June 2010 Degree of Impact Relevance to Consumers, Employers and Payers Annually there are over 500,000 total knee replacement
MN Community Measurement Total Knee Replacement Impact and Recommendation Document June 2010 Degree of Impact Relevance to Consumers, Employers and Payers Annually there are over 500,000 total knee replacement
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks
 Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
False positive PET in lymphoma
 False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
The Journal of Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty 29 (2014) 219 224 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect The Journal of Arthroplasty journal homepage: www.arthroplastyjournal.org One-Component Revision of Failed Hip Resurfacing
The Journal of Arthroplasty 29 (2014) 219 224 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect The Journal of Arthroplasty journal homepage: www.arthroplastyjournal.org One-Component Revision of Failed Hip Resurfacing
Understanding the biological outcomes and responses to orthopaedic surgical implants.
 Understanding the biological outcomes and responses to orthopaedic surgical implants. Dr Catherine Bladen, University of Leeds,UK A report for the Winston Churchill Memorial Trust, 2012 1 Acknowledgements:
Understanding the biological outcomes and responses to orthopaedic surgical implants. Dr Catherine Bladen, University of Leeds,UK A report for the Winston Churchill Memorial Trust, 2012 1 Acknowledgements:
Modular Dual Mobility Acetabular Components: An Important Extension of a Proven Approach to Hip Instability
 Modular Dual Mobility Acetabular Components: An Important Extension of a Proven Approach to Hip Instability Robert Wetzel, MD, Lalit Puri, MD, S. David Stulberg, MD Disclosure In accordance with ACCME
Modular Dual Mobility Acetabular Components: An Important Extension of a Proven Approach to Hip Instability Robert Wetzel, MD, Lalit Puri, MD, S. David Stulberg, MD Disclosure In accordance with ACCME
Propionibacterium Acnes Cause Delayed Surgical Site Infection Only In The Presence Of Implant
 Propionibacterium Acnes Cause Delayed Surgical Site Infection Only In The Presence Of Implant Yuta Shiono 1,2, Ken Ishii 1, Shigenori Nagai 3, Hiroaki Kakinuma 4, Aya Sasaki 5, Mamoru Aizawa 4, Yasunori
Propionibacterium Acnes Cause Delayed Surgical Site Infection Only In The Presence Of Implant Yuta Shiono 1,2, Ken Ishii 1, Shigenori Nagai 3, Hiroaki Kakinuma 4, Aya Sasaki 5, Mamoru Aizawa 4, Yasunori
Risk and Outcome of Infection After Different Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Techniques
 Risk and Outcome of Infection After Different Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Techniques Mehmet S. Binnet, M.D., and Kerem Başarir, M.D. Purpose: Infection after arthroscopic anterior
Risk and Outcome of Infection After Different Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Techniques Mehmet S. Binnet, M.D., and Kerem Başarir, M.D. Purpose: Infection after arthroscopic anterior
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements
 Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Oftentimes, as implant surgeons, we are
 CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
Graphic courtesy of DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. HealthEast Joint Replacement Registry: 20 Year Report
 Graphic courtesy of DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. HealthEast Joint Replacement Registry: 20 Year Report HealthEast Joint Replacement Registry: 20 Year Report Foreword HealthEast Care System began the first
Graphic courtesy of DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. HealthEast Joint Replacement Registry: 20 Year Report HealthEast Joint Replacement Registry: 20 Year Report Foreword HealthEast Care System began the first
Answers to commonly asked questions from patients with metal-on-metal hip replacements / resurfacings. Contents
 Answers to commonly asked questions from patients with metal-on-metal hip replacements / resurfacings John Skinner 1 and Alister Hart 2, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeons and Directors of the London Implant
Answers to commonly asked questions from patients with metal-on-metal hip replacements / resurfacings John Skinner 1 and Alister Hart 2, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeons and Directors of the London Implant
Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis with Kinectiv Technology
 Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis with Kinectiv Technology Hips designed to fit the unique anatomies of men and women Independent control for a natural fit Simple, practical solutions for optimal restoration
Zimmer M/L Taper Hip Prosthesis with Kinectiv Technology Hips designed to fit the unique anatomies of men and women Independent control for a natural fit Simple, practical solutions for optimal restoration
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013
 Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Hip joint replacement surgery has been the most common
 Radiographic Imaging of Hip Replacement Hardware Catherine C. Roberts, MD,* and Felix S. Chew, MD, MBA Hip joint replacement surgery has been the most common type of elective and semi-elective orthopedic
Radiographic Imaging of Hip Replacement Hardware Catherine C. Roberts, MD,* and Felix S. Chew, MD, MBA Hip joint replacement surgery has been the most common type of elective and semi-elective orthopedic
femoral component. RESULTS AT A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS
 N. Sandiford, C. Doctor, S. S. Rajaratnam, S. Ahmed, D. J. East, K. Miles, A. Butler-Manuel, J. A. N. Shepperd From Conquest Hospital, St Leonards on Sea, United Kingdom N. Sandiford, MRCS, MSc(SEM), SpR
N. Sandiford, C. Doctor, S. S. Rajaratnam, S. Ahmed, D. J. East, K. Miles, A. Butler-Manuel, J. A. N. Shepperd From Conquest Hospital, St Leonards on Sea, United Kingdom N. Sandiford, MRCS, MSc(SEM), SpR
Understanding Total Hip Replacement
 Understanding Total Hip Replacement Brian J. White MD Orthopaedic Specialist in Disorders of the Hip Assistant Team Physician Denver Nuggets Western Orthopaedics Denver, Colorado Introduction This is designed
Understanding Total Hip Replacement Brian J. White MD Orthopaedic Specialist in Disorders of the Hip Assistant Team Physician Denver Nuggets Western Orthopaedics Denver, Colorado Introduction This is designed
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for 111 In-Leukocyte Scintigraphy for Suspected Infection/Inflammation
 Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for 111 In-Leukocyte Scintigraphy for Suspected Infection/Inflammation Version 3.0, approved June 2, 2004 Authors: Christopher J. Palestro, MD (Long Island
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for 111 In-Leukocyte Scintigraphy for Suspected Infection/Inflammation Version 3.0, approved June 2, 2004 Authors: Christopher J. Palestro, MD (Long Island
Ultrasound and colour Doppler sonography in acute osteomyelitis in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 590-596 ORIGINAL STUDY Ultrasound and colour Doppler sonography in acute osteomyelitis in children Quamar AZAM, Ibne AHMAD, Mazhar ABBAS, Anjum SYED, Faisal HAQUE From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 590-596 ORIGINAL STUDY Ultrasound and colour Doppler sonography in acute osteomyelitis in children Quamar AZAM, Ibne AHMAD, Mazhar ABBAS, Anjum SYED, Faisal HAQUE From the
Total Hip Joint Replacement. A Patient s Guide
 Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty: Causes and High Incidence of Early Failure
 Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty: Causes and High Incidence of Early Failure David Fabi, MD; Brett Levine, MD; Wayne Paprosky, MD; Craig DellaValle, MD; Scott Sporer, MD; Gregg Klein, MD; Harlan Levine,
Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty: Causes and High Incidence of Early Failure David Fabi, MD; Brett Levine, MD; Wayne Paprosky, MD; Craig DellaValle, MD; Scott Sporer, MD; Gregg Klein, MD; Harlan Levine,
UNILATERAL VS. BILATERAL FIRST RAY SURGERY: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 186 CONSECUTIVE CASES COMPLICATIONS, PATIENT SATISFACTION, AND COST TO SOCIETY
 UNILATERAL VS. BILATERAL FIRST RAY SURGERY: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 186 CONSECUTIVE CASES COMPLICATIONS, PATIENT SATISFACTION, AND COST TO SOCIETY Robert Fridman DPM, Jarrett Cain DPM, Lowell Weil Jr. DPM,
UNILATERAL VS. BILATERAL FIRST RAY SURGERY: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 186 CONSECUTIVE CASES COMPLICATIONS, PATIENT SATISFACTION, AND COST TO SOCIETY Robert Fridman DPM, Jarrett Cain DPM, Lowell Weil Jr. DPM,
C H A P T E R 3 5. Thomas J. Merrill, DPM Riquel Gonzalez, DPM INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 C H A P T E R 3 5 CORTICOSTEROID INDUCED AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF THE RIGHT MEDIAL CUNEIFORM TREATED WITH TRINITY EVOLUTION BONE GRAFT AND ARTHRODESIS: Case Report and Review of the Literature Thomas J. Merrill,
C H A P T E R 3 5 CORTICOSTEROID INDUCED AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF THE RIGHT MEDIAL CUNEIFORM TREATED WITH TRINITY EVOLUTION BONE GRAFT AND ARTHRODESIS: Case Report and Review of the Literature Thomas J. Merrill,
Running head: PSEUDOTUMORS IN ASSOCIATION WITH HIP PROSTHESES 1 PSEUDOTUMORS IN ASSOCIATION WITH HIP PROSTHESES: A LITERTURE REVIEW WITH CASE STUDIES
 Running head: PSEUDOTUMORS IN ASSOCIATION WITH HIP PROSTHESES 1 PSEUDOTUMORS IN ASSOCIATION WITH HIP PROSTHESES: A LITERTURE REVIEW WITH CASE STUDIES November 13, 2013 PSEUDOTUMORS IN ASSOCIATION WITH
Running head: PSEUDOTUMORS IN ASSOCIATION WITH HIP PROSTHESES 1 PSEUDOTUMORS IN ASSOCIATION WITH HIP PROSTHESES: A LITERTURE REVIEW WITH CASE STUDIES November 13, 2013 PSEUDOTUMORS IN ASSOCIATION WITH
Simplified surgery. Personalized performance.
 Simplified surgery. Personalized performance. VISIONAIRE Patient Matched Technology Accuracy Advanced surgical precision, resulting in reproducible outcomes Efficiency Simplifying surgery, reducing costs,
Simplified surgery. Personalized performance. VISIONAIRE Patient Matched Technology Accuracy Advanced surgical precision, resulting in reproducible outcomes Efficiency Simplifying surgery, reducing costs,
Clinically Proven Fiber Metal Material. Power to choose advanced bearing technologies to match patient demands
 Trilogy IT Acetabular System Design Rationale 1 For orthopedic surgeons treating a wide range of patients, the Trilogy IT Acetabular System provides a clinically proven1-5 Fiber Metal Material and the
Trilogy IT Acetabular System Design Rationale 1 For orthopedic surgeons treating a wide range of patients, the Trilogy IT Acetabular System provides a clinically proven1-5 Fiber Metal Material and the
High-Flex Solutions for the MIS Era. Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee System
 High-Flex Solutions for the MIS Era Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee System Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee Built On Success In today s health care environment, meeting patient demands means
High-Flex Solutions for the MIS Era Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee System Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee Built On Success In today s health care environment, meeting patient demands means
chronos BOne VOid Filler Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (b-tcp) bone graft substitute
 chronos BOne VOid Filler Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (b-tcp) bone graft substitute chronos Bone Void Filler Osteoconductive Resorbable Synthetic chronos Granules and Preforms are synthetic, porous, osteoconductive,
chronos BOne VOid Filler Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (b-tcp) bone graft substitute chronos Bone Void Filler Osteoconductive Resorbable Synthetic chronos Granules and Preforms are synthetic, porous, osteoconductive,
Total Hip Replacement
 Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Small stem Exeter total hip replacement: clinical and radiological follow-up over a minimum of 2.5 years
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 148 153 Small stem Exeter total hip replacement: clinical and radiological follow-up over a minimum of 2.5 years S Sivananthan, M Arif, DSK Choon Department
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 148 153 Small stem Exeter total hip replacement: clinical and radiological follow-up over a minimum of 2.5 years S Sivananthan, M Arif, DSK Choon Department
Why an Exactech Hip is Right for You
 Why an Exactech Hip is Right for You Why do I need a total hip replacement? Which surgical approach is best for me? How long will it last? Which implant is right for me? Founded in 1985 by an orthopaedic
Why an Exactech Hip is Right for You Why do I need a total hip replacement? Which surgical approach is best for me? How long will it last? Which implant is right for me? Founded in 1985 by an orthopaedic
Spine and Femoral Head Instrumentation for the Radiologist. Mariam S. Aboian, Gillian Lieberman MBBS
 Spine and Femoral Head Instrumentation for the Radiologist Mariam S. Aboian, Gillian Lieberman MBBS Spine and Hip Instrumentation for the Radiologist Radiologists, Neurosurgeons, Orthopedic Surgeons =
Spine and Femoral Head Instrumentation for the Radiologist Mariam S. Aboian, Gillian Lieberman MBBS Spine and Hip Instrumentation for the Radiologist Radiologists, Neurosurgeons, Orthopedic Surgeons =
SPECT/CT Wrist. Wrist pain 3/27/2012
 Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Exeter. Surgical Technique. V40 Stem Cement-in-Cement. Orthopaedics
 Exeter Orthopaedics V40 Stem Cement-in-Cement Surgical Technique Exeter V40 Stem Cement-in-Cement Surgical Technique Table of Contents Indications and Contraindications...2 Warnings and Precautions...2
Exeter Orthopaedics V40 Stem Cement-in-Cement Surgical Technique Exeter V40 Stem Cement-in-Cement Surgical Technique Table of Contents Indications and Contraindications...2 Warnings and Precautions...2
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
Model Coverage Determination: Total Joint Arthroplasty
 Model Coverage Determination: Total Joint Arthroplasty LCD ID Number LCD Title Major Joint Replacement (Hip and Knee) Indications and Limitations of Coverage and/or Medical Necessity Joint replacement
Model Coverage Determination: Total Joint Arthroplasty LCD ID Number LCD Title Major Joint Replacement (Hip and Knee) Indications and Limitations of Coverage and/or Medical Necessity Joint replacement
PET POSITIVE PLEURAL PLAQUES DECADES AFTER PLEURODESIS: MESOLTHELIOMA? Ellen A. Middleton 1. Jonathan C. Daniel 2. Kenneth S.
 PET POSITIVE PLEURAL PLAQUES DECADES AFTER PLEURODESIS: MESOLTHELIOMA? Ellen A. Middleton 1 Jonathan C. Daniel 2 Kenneth S. Knox 1 Kathleen Williams 1 Departments of Medicine 1 and Surgery 2, University
PET POSITIVE PLEURAL PLAQUES DECADES AFTER PLEURODESIS: MESOLTHELIOMA? Ellen A. Middleton 1 Jonathan C. Daniel 2 Kenneth S. Knox 1 Kathleen Williams 1 Departments of Medicine 1 and Surgery 2, University
Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method
 Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method Christopher Martel, M.Sc., CHP Lisa Thornhill,, NRRPT, RT(NM) Boston University Medical Center Thyroid Carcinoma New cases and deaths in
Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method Christopher Martel, M.Sc., CHP Lisa Thornhill,, NRRPT, RT(NM) Boston University Medical Center Thyroid Carcinoma New cases and deaths in
Acetabular Wedge Augment System
 Orthopaedics Acetabular Wedge Augment System Stryker Hips. Implant with confidence. Restoration Acetabular Wedge Augment System Restoration Acetabular Wedge Augments, united with Tritanium, Trident, MDM
Orthopaedics Acetabular Wedge Augment System Stryker Hips. Implant with confidence. Restoration Acetabular Wedge Augment System Restoration Acetabular Wedge Augments, united with Tritanium, Trident, MDM
The role of nuclear medicine techniques in differentiation between septic and aseptic loosening of total hip and knee arthroplasty
 The role of nuclear medicine techniques in differentiation between septic and aseptic loosening of total hip and knee arthroplasty J.. Jansen, MD 1 F. Smit, MD 2 L.M. Pereira rias-ouda, MD, PhD 2 1 Department
The role of nuclear medicine techniques in differentiation between septic and aseptic loosening of total hip and knee arthroplasty J.. Jansen, MD 1 F. Smit, MD 2 L.M. Pereira rias-ouda, MD, PhD 2 1 Department
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Digital templating facilitates accurate leg length correction in total hip arthroplasty
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 344-349 ORIGINAL STUDY Digital templating facilitates accurate leg length correction in total hip arthroplasty Shivan Sabah JASSIM, Christopher INgHAM, Matthew KEELINg, James
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 344-349 ORIGINAL STUDY Digital templating facilitates accurate leg length correction in total hip arthroplasty Shivan Sabah JASSIM, Christopher INgHAM, Matthew KEELINg, James
IMPLANT CONSENT FORM WHAT ARE DENTAL IMPLANTS?
 IMPLANT CONSENT FORM WHAT ARE DENTAL IMPLANTS? Dental implants are a very successful and accepted treatment option to replace lost or missing teeth. A dental implant is essentially an artificial tooth
IMPLANT CONSENT FORM WHAT ARE DENTAL IMPLANTS? Dental implants are a very successful and accepted treatment option to replace lost or missing teeth. A dental implant is essentially an artificial tooth
Cheryl Richardson, RN, BSN, CIC
 NHSN Surgical Definitions Cheryl Richardson, RN, BSN, CIC Conflict of Interest and Disclosure of Financial Relationships I m an employee of CareFusion. No financial or in-kind contributions have been given
NHSN Surgical Definitions Cheryl Richardson, RN, BSN, CIC Conflict of Interest and Disclosure of Financial Relationships I m an employee of CareFusion. No financial or in-kind contributions have been given
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) through the anterior approach
 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty with a Minimally Invasive Anterior Approach Jonathan G. Yerasimides, MD, and Joel M. Matta, MD Total hip arthroplasty (THA) through the anterior approach is a minimally invasive
Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty with a Minimally Invasive Anterior Approach Jonathan G. Yerasimides, MD, and Joel M. Matta, MD Total hip arthroplasty (THA) through the anterior approach is a minimally invasive
Technology Assessment
 Technology Assessment Horizon Scan on Hip Replacement Surgery Technology Assessment Program Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 540 Gaither Road Rockville, Maryland 20850 December 22, 2006 Horizon
Technology Assessment Horizon Scan on Hip Replacement Surgery Technology Assessment Program Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 540 Gaither Road Rockville, Maryland 20850 December 22, 2006 Horizon
VERILAST Technology for Hip Replacement Implants
 VERILAST Technology for Hip Replacement Implants Surgeon Name Clinic Name Clinic Address Clinic i Address Phone Number Web Address Total Hip Replacement What Is VERILAST Hip Technology? OXINIUM Oxidized
VERILAST Technology for Hip Replacement Implants Surgeon Name Clinic Name Clinic Address Clinic i Address Phone Number Web Address Total Hip Replacement What Is VERILAST Hip Technology? OXINIUM Oxidized
Metal-on-Metal Hip Systems
 Meeting of the Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Devices Advisory Panel June 27-28, 2012 Metal-on-Metal Hip Systems Center for Devices and Radiological Health U.S. Food and Drug Administration Meeting of
Meeting of the Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Devices Advisory Panel June 27-28, 2012 Metal-on-Metal Hip Systems Center for Devices and Radiological Health U.S. Food and Drug Administration Meeting of
The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize
 SPRING 2013 Robot-Guided Spine Surgery Christopher R. Good, M.D., F.A.C.S. and Blair K. Snyder, P.A.-C. The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize patient function and accelerate a return to a
SPRING 2013 Robot-Guided Spine Surgery Christopher R. Good, M.D., F.A.C.S. and Blair K. Snyder, P.A.-C. The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize patient function and accelerate a return to a
St. Charles Hospital Orthopedic Specialists Invent and Refine Surgical Techniques
 St. Charles Hospital Orthopedic Specialists Invent and Refine Surgical Techniques By: Jennifer Webster Tuesday, October 01, 2013 It s one thing to practice advanced surgery. But St. Charles Hospital takes
St. Charles Hospital Orthopedic Specialists Invent and Refine Surgical Techniques By: Jennifer Webster Tuesday, October 01, 2013 It s one thing to practice advanced surgery. But St. Charles Hospital takes
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Total hip replacement and resurfacing arthroplasty for the treatment of pain or disability resulting from end stage arthritis
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Total hip replacement and resurfacing arthroplasty for the treatment of pain or disability resulting from end stage arthritis
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Surgical Technique 2. Indications 4. Product Information 5. 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 2
 Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Surgical Technique 2 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 2 2. Intervertebral Device Implanted 2 3. Buttress Plate Selection 2 4. Awl Insertion 2 5. Screw Insertion
Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS Surgical Technique 2 1. Patient Positioning and Approach 2 2. Intervertebral Device Implanted 2 3. Buttress Plate Selection 2 4. Awl Insertion 2 5. Screw Insertion
Randal S. Ford. ATTORNEY AT LAW (205) 752-4440 attorney@randalsford.com. DePuy ASR Hip Implant Recall Fact Sheet
 DePuy ASR Hip Implant Recall Fact Sheet Recalled Devices: ASR XL Acetabular System on the market since 2004, and sold worldwide. Dates of Implant: July 2003 to 2010 ASR Hip Resurfacing System on the market
DePuy ASR Hip Implant Recall Fact Sheet Recalled Devices: ASR XL Acetabular System on the market since 2004, and sold worldwide. Dates of Implant: July 2003 to 2010 ASR Hip Resurfacing System on the market
Contents. Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1. 2. Spinal Imaging 7. 3. Spinal Biomechanics 23. 4. History and Physical Examination of the Spine 33
 Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
Should I have a knee replacement?
 Introduction Should I have a knee replacement? Knee replacement is an operation to remove the arthritic parts of the knee and replace them with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic. It can either
Introduction Should I have a knee replacement? Knee replacement is an operation to remove the arthritic parts of the knee and replace them with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic. It can either
Integumentary System Individual Exercises
 Integumentary System Individual Exercises 1. A physician performs an incision and drainage of a subcutaneous abscess in his office for a particularly uncooperative established patient. How should this
Integumentary System Individual Exercises 1. A physician performs an incision and drainage of a subcutaneous abscess in his office for a particularly uncooperative established patient. How should this
Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Juvenile Arthritis
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 17 No. 8 2002 Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Long-Term Survivorship and Outcomes Andrew G. Yun, MD,* Scott Martin, MD, David Zurakowski, PhD,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 17 No. 8 2002 Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Long-Term Survivorship and Outcomes Andrew G. Yun, MD,* Scott Martin, MD, David Zurakowski, PhD,
The Immediate Placement of Dental Implants Into Extraction Sites With Periapical Lesions: A Retrospective Chart Review
 IMPLANTS The Immediate Placement of Dental Implants Into Extraction Sites With Periapical Lesions: A Retrospective Chart Review Christopher Lincoln Bell,* David Diehl, Brian Michael Bell, and Robert E.
IMPLANTS The Immediate Placement of Dental Implants Into Extraction Sites With Periapical Lesions: A Retrospective Chart Review Christopher Lincoln Bell,* David Diehl, Brian Michael Bell, and Robert E.
Cover Page. The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/25896 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/25896 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Weegen, Walter van der Title: Metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty : local tissue reactions
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/25896 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Weegen, Walter van der Title: Metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty : local tissue reactions
