d/d or D/deaf: used as a collective noun to refer to both those Deaf people who identify with the Deaf culture and those deaf people who do not.
|
|
|
- Frederica Todd
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Glossary Use of Deaf/deaf; Hard of Hearing/hard of Hearing; D/d. D/deaf; D/D/HH Committee members discussed what would be the most appropriate, respectful and understandable usages of the above terminology (and other possible combinations of terms). The conventions from researchers, local and national organizations, CBE, Alberta Education as well as strongly held personal beliefs were all considered. The purpose of the document is neither history nor terminology, rather the future and best outcomes for students. Therefore, for this framework, it was agreed that Deaf and Hard of Hearing (D/HH) will be used, except when specifically referencing a source which uses something different. Numerous slightly different definitions of the terms that follow are available, some of which also contain specific numeric ranges. The ones that follow are in general taken from the Canadian Association of the Deaf's website and will be used as appropriate when Deaf and Hard of Hearing (D/HH) cannot be used without changing meaning. Hard of Hearing (HH): used to refer to a hearing loss at a level that significantly limits but does not preclude perception of spoken language through audition alone. Includes most people with hearing loss from the mild to severe range. deaf: a medical/audiological term referring to those people who have little or no functional hearing. May also be used as a collective noun to refer to people who are medically deaf but who do not necessarily identify with the Deaf community Deaf: a sociological term referring to those individuals who are medically deaf or hard of hearing who identify with and participate in the culture, society and language of Deaf people, which is based on Sign language. d/d or D/deaf: used as a collective noun to refer to both those Deaf people who identify with the Deaf culture and those deaf people who do not. Accommodations: a change or alteration in the way a student is expected to participate in schooling or demonstrate their learning. This may include, but is not limited to, special teaching or assessment strategies, equipment, personnel, content support, or extra time for examinations. Acoustics: having to do with sound, the sense of hearing, or the science of sound. As used in this framework, the term refers to the qualities of an auditorium, classroom, or other space that affect the sound quality. Acoustic Room Treatment: the use of sound-absorbing materials (such as carpets and acoustical tile) to reduce room noise and sound reflection. Adapted programming: programming that retains the learning outcomes of the Program of Studies, where adjustments to the instructional process are provided to address the special education needs of the student. (Standards for Special Education, p. 3) Adaptive/Assistive technology for learning (ATL): the devices, media and services used by students with physical, sensory, cognitive, speech, learning or behavioural disabilities to actively engage in learning
2 and to achieve their individual learning goals. ATL is a subset of a broad range of technologies that enhance students learning. ( For the purposes of this report, adaptive technology will be used. Alternative program: has a specific meaning within the School Act. D/HH programming within CBE is not considered an "alternative program" in the Alberta Education meaning of the word. Traditional Learning Centre (philosophy of teaching), Mandarin Bilingual (language) or Science School (content delivery) would be examples of alternative programs. Alternative program status for ASL, as is the case for the Edmonton School for the Deaf, only occurs when there is a board approved ASL second language program. Second Language programs are governed by both provincial and CBE protocols for language programs. American Sign Language (ASL): a visual language in which the shape, placement, and movement of the hands, as well as facial expressions and body movements, all play important parts in conveying information. ASL has its own unique rules of grammar and syntax. Amplification: includes hearing aids, cochlear implants, Personal FM systems, and Classroom Audio Distribution Systems (CADS). Assistive Technology: technology used by individuals in order to perform functions that might otherwise be difficult or impossible. This can include but is not limited to hardware, software and peripherals to access information technologies. (Essential Components, pg. 11) Auditory/Oral programs: programs which focus on the use of residual hearing through amplification (hearing aids or cochlear implants and FM systems), augmenting residual hearing with speechreading and spoken language. This approach normally excludes the use of ASL, although natural gestures may be used. See also Auditory/Oral education; Auditory-Verbal Auditory/Oral Education: an approach based on the principle that most Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing children can be taught to listen and speak with early intervention and consistent training. The focus of this educational approach is to use the auditory channel (or hearing) to acquire speech and oral language. See also Auditory/Oral-programs; Auditory Verbal Auditory-Verbal: this approach is similar to the auditory/oral approach, except it does not encourage speechreading. This method emphasizes the exclusive use of auditory skills through one-on-one teaching. It excludes the use of any type of sign language. See also Auditory/Oral entries Bilateral hearing loss: hearing loss in both ears. Bimodal-bilingual: this approach supports the acquisition and use of a visual (ASL) and spoken language. The development of a visual language, ASL, is promoted as a first language and used as the medium of instruction and communication. English is primarily addressed through reading, writing, and through the auditory modality. See also Bicultural/Bilingual Bi-lingual/Bi-cultural: this approach focuses on language accessibility and Deaf cultural identity development. ASL is promoted as a first language and used as the medium of instruction and communication. English is primarily addressed through reading and writing. Spoken English and listening may also be incorporated into classroom activities.
3 Classroom Audio Distribution System (CADS): consists of a microphone/transmitter that the teacher wears. The receiver is a speaker that is either mounted to a wall or placed on a surface in the classroom. CADS includes both infra-red and sound-field FM systems. CADS provides an improved signal-to-noise ratio. The signal-to-noise ratio improvement is not sufficient to overcome the obstacles of distance, noise, and reverberation in children who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing; as such. CADS is typically only used when the student does not wear hearing aids or cochlear implants. See also personal FM system Closed Captioning: is a technology that encodes captions within video, including descriptions of sounds. Communication Development: is used broadly to refer to the child's auditory skills, visual skills, receptive and expressive language skills, (spoken and/or sign) language development, pragmatics and turn taking. (Moeller et al., 2013) Communication Access Realtime Translation (CART): is live-event captioning; a way to transcribe the spoken word into readable English text using a stenotype machine, notebook computer, and realtime software. The text appears on a computer monitor or other display. CART provides a complete translation of all spoken words and environmental sounds for the benefit of an individual consumer or larger group in a variety of settings including classrooms. Increasingly, CART is being provided remotely via the Internet or a telephone connection. (National Court Reporters' Association) CI/ Cochlear Implant: A cochlear implant is an electronic device that is designed to provide hearing to those with profound deafness. Part of the device is surgically implanted into the inner ear and part is worn externally. As a prosthetic device, the cochlear implant stimulates the auditory or hearing nerve directly, bypassing the damaged part of the inner ear or cochlea. Many viable nerve fibres remain in the auditory nerve even in cases of profound deafness, and the cochlear implant can restore activity to this nerve and the hearing pathway. (Canadian Academy of Audiology) Classroom Placement: the educational setting that a student attends, as a result of collaboration between Calgary Board of Education personnel, agencies, parents, and students as developmentally appropriate, in order to best meets the student s current needs. Complex Learners/Co-morbidity//Deaf+: are all terms used to describe learners who have more than one factor impacting their educational/physical/social growth. For D/HH students, this would mean a D/HH diagnosis as well as one or more other compounding factors. For the purposes of this report, complex learner or a student with complex needs will be used. Community School Setting: the school within the child s home community, or the school that the student is bussed to that is designated as their home community school, that the student attends. The D/HH student in a regular classroom and is supported by a Strategist for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing Congregated Programs: are normally directly supported by at least two professionals in a classroom: a trained Teacher of the Deaf (ToD) and a support staff member. The program is supported by and accountable to the school principals at SJS, QEE and QEHS and supported by Area and system level staff, as well as service providers from outside agencies, such as Alberta Health Services. D/HH Program class: the Deaf and Hard of Hearing System class is an educational environment which offers communicative supports and services to students who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing.
4 Communication is facilitated by either using American Sign Language (ASL) or an Auditory/Aural approach. The focus of instruction is the development of literacy skills.(see congregated program) D/HH support staff/professional support staff positions: each of these terms has a generally understood meaning, and a specific meaning within the CBE support staff contract. The following definitions represent general usage within CBE: ASL/Sign Language Interpreter: possesses post-secondary training and certification to perform the task of interpreting between two languages, such as spoken English and American Sign Language. CBE interpreters are additionally governed by Standard of Practice for Sign Language Interpreting. They facilitate administration and staff, and parents within the school environment. Educational Audiologist: an audiologist who works with children and teachers in the school setting, and acts as a liaison between the school and medical communities. This may include all aspects of amplification systems, educator in-services, observation of students as well as recommendations regarding modifications of classroom environments. The audiology clerk position supports the educational audiologist. Deaf/Blind Intervener 1 and 11: level 1 is responsible for performing all the responsibilities of and Education Assistant while acquiring the training, skills and experience to be an Intervener Level 11. A deafblind intervener is a person who mediates between a deafblind individual and his or her environment. Using a variety of methods, a deafblind intervener facilitates communication and access to information that is unavailable or distorted due to the individual's dual sensory loss in order to promote independence, engagement, critical thinking, life-skills and social and emotional well-being. Education Assistant D/HH: a person designated to work with students as part of the learning team, under the supervision of a teacher, who is fluent in the language of the specific setting, such as ASL and/or English School Assistant ASL: a person designated, under the supervision of a teacher, to work with students who is fluent in ASL. Speech Language Pathologist: university trained health care professional who works with individuals or groups of students to identify, assess, evaluate, treat manage and educate with regard to speech, language, stuttering, voice health and swallowing disorders. D/HH Certificated (ATA) positions: each of these terms has a generally understood meaning, and a specific meaning within the CBE certificated staff contract. The following definitions represent general usage within CBE: Teacher, D/HH: a certificated teacher with specific responsibility for the instruction of students who are D/HH. Such teachers generally have additional specific training in this field of study. Strategist D/HH: the Strategist is responsible for building the capacity of school learning teams and system personnel working with D/HH students in inclusionary settings. Strategists meet the educational needs of D/HH students by collaborating with school staff and parents through providing advice, strategies, and recommendations for the students programs. Other responsibilities include interpreting audiological assessments, monitoring amplification equipment, and administering assessments. Strategists may provide direct student support in consultation with school personnel.
5 Specialist D/HH: the Specialist is responsible for providing leadership in relation to the personalization of learning, specific to students that are Deaf and Hard of Hearing. Strategic planning, as a result of current and future-oriented research, guides the building of system capacity so that D/HH students can access their learning environments in an inclusionary setting. The Specialist collaborates with key stakeholders for the transitions into the congregated settings, including principals and staff of the schools and agencies involved. Deaf Culture: culture in general is a way of life and learned ways of acting, feeling and thinking based on a group who share common language, beliefs, values, traditions, social norms, and identity in a society. Deaf culture meets all five sociological criteria (language, values, traditions, norms and identity) for defining a culture: ( Language refers to the native visual cultural language of Deaf people, with its own syntax (grammar or form), semantics(vocabulary or content) and pragmatics (social rules of use). Values/beliefs in the Deaf community include the importance of clear communication for all, both in terms of expression and comprehension. Traditions include the stories kept alive through Deaf generations, Deaf experiences and expected participation in Deaf cultural events. Norms refer to rules of behaviour in the Deaf community. All cultures have their own set of behaviours that are deemed acceptable. For Deaf people, it includes getting someone's attention appropriately, using direct eye contact and correct use of shoulder tapping. Identity is one of the key components of the whole person. Accepting that one is Deaf and is proud of his/her culture and heritage and a contributing member of that society is key to being a member of the cultural group. ( Integration/inclusion/co-enrolment/mainstreaming/inclusive setting: are all terms used to describe students with specialized learning needs who receive some or all of their programming in typical classrooms with age appropriate peers, often with some personalized accommodations, adaptations and/or modifications. ( For the purposes of this report, unless citing a quotation: Inclusion: the opportunity to be fully and meaningfully integrated into a typical learning environment. Inclusion also refers to an attitude of acceptance of, and belonging for all students, such that they feel valued as part of the school family (Alberta Education, 2009) Integration: placement of a student who is D/HH with age appropriate hearing peers in a classroom setting IPP/ Individual Program Plan: an IPP is a written commitment of intent by the learning team to ensure appropriate planning for students with special education needs. It is a working document and a record of student progress that contributes to a common understanding and coordination of efforts. (Alberta Education)
6 Language Programming: Bilingual: refers to a language program in which a language other than French or English is used as the language of instruction, to a maximum of 50% of the instructional day. Immersion: refers to a language program, normally French, in which instruction in the second language is up to 100% of the day, especially in the first years. Second Language: three, six, or nine year programs where language instruction occurs during instructional time, the languages being approved by Alberta Education and offered by school districts based on their curricular polices. Locally Developed Course: refers to a course outside the mandated Alberta program of studies which has been developed by a school division(s) and approved for use by Alberta Education. Alternative programs: are defined first by the School Act, and thereafter by the policies of individual boards. Section 21(1) of the Alberta School Act defines alternative programs as an education program that (a) emphasizes a particular language, culture, religion or subject matter, or (b) uses a particular teaching philosophy. The Alberta School for the Deaf operates as an alternative language program (ASL) under the appropriate Alberta Education and Edmonton Public School System regulations. American Sign Language is offered through a variety of courses, although not all of them in Calgary, and only at QEHS. Three were developed by Edmonton Public Schools and one by CBE, and all are Locally Approved Courses. o ASL Language Arts K-12 (Bilingual). This course is taught parallel to the English Language Arts curriculum at QEHS. o ASL Language and Deaf Culture 9 year program o Introduction to ASL and Deaf Culture, Grades 7,8,9 o ASL and Deaf Culture 15/25/35 (high school) offered at QEHS Mediated Education: information transfer between teacher and student is mediated by an interpreter Personal FM system: consists of a microphone/transmitter that the teacher wears, and receivers that attach to the student s hearing aid(s) or cochlear implant(s). A personal FM system provides an improved signal-to-noise ratio and helps to overcome the obstacles of distance, noise, and reverberation in the classroom. This is the FM system of choice when the student has hearing aids or cochlear implants. Program: a program is designed to meet the individual needs of students. For D/HH students, this may include: selection of the communication approach of American Sign Language (ASL) or English, curricular adaptations, amplification, and Speech Language therapy. It is an active process that is based on the student s assessed abilities and needs and is continually monitored and adjusted. Signed English: a sign language system which matches each spoken word of English, using English grammar, syntax and signed vocabulary
7 Sign Supported English: a method that uses some sign, in combination with spoken language, to provide a visual presentation of English vocabulary and/or English language structures as a way to support student access to spoken communication and meaning-making Simultaneous Communication: communicating through the use of spoken words simultaneously with a signed version of the spoken utterance. Sandwiching ASL and English (sign it, say it, sign it OR say it, sign it, say it) or code switching (moving between ASL and English) are strategies used in simultaneous communication. Sound-field FM system: see Classroom Audio Distribution System (CADS) Special Education: students with special needs are described in section 47 of the School Act as being in need of special education programs because of their behavioural, communicational, intellectual, learning or physical characteristics, or students who may require specialized health care services, students who are gifted and talented. IRIS: a custom-built web-based learning application for CBE. The four components include a student learning plan, a learner profile, an educator workspace, and a resource library. Both students and teachers access different areas of the same portal, which means students can have their own space to plan for success and teachers can access a shared knowledge base to collaborate with other teachers. Currently not available in all CBE schools. Modified programming: programming in which the learning outcomes are significantly different from the provincial curriculum and are specifically selected to meet students' special education needs. (Standards for Special Education, pg. 4) Total Communication: an approach that supports the use of all modes of communication and language as needed in different contexts. This includes American Sign Language and more English-based systems of signing (i.e. Signing Exact English), spoken English, mime, facial expressions, and gesture. See also Signed English Transliterate: to write words, or letters, or represent in the characters of one alphabet into another. Unilateral hearing loss: hearing loss in one ear. VRI/ Video Remote Interpreting: when in-person, on-site interpreting services are not available, a solution in the form of off-site interpreting services, called Video Remote Interpreting (VRI) exists. VRI uses videoconferencing technology, equipment, and a high speed internet connection with sufficient bandwidth to provide the services of a qualified interpreter, usually located at a call centre, to people at a different location. While there are many benefits to using VRI services, there are limits to the effectiveness of VRI in some settings including but not limited to medical, legal, and court situations and it must be set up in advance. (National Institute of the Deaf) VRS/Video Relay Services (VRS): basic telecommunications service that enables people with hearing or speech disabilities who use sign language to communicate with voice telephone users. The sign language user connects to a VRS operator using internet-based videoconferencing. The operator then places a voice telephone call to the other party and relays the conversation from sign language to voice and viceversa.
8 Other Acronyms ACH: Alberta Children's Hospital AHS: Alberta Health Services CALM: Career and Life Management (mandatory high school health and finance course in Alberta) CODA: Child(ren) of Deaf adult D2L: Desire to Learn (a secure electronic learning platform) FLIC: Freelance Interpreters Consolidated Inc. FOIP: Freedom of Information and Privacy PUF: Program Unit Funding (provincial) QEE: Queen Elizabeth Elementary School QEHS: Queen Elizabeth High School SJS: Stanley Jones School SIRS: Student Information Record System ToD: Teacher of the Deaf
TOOLS for DEVELOPING Communication PLANS
 TOOLS for DEVELOPING Communication PLANS Students with disabilities, like all students, must have the opportunity to fully participate in all aspects of their education. Being able to effectively communicate
TOOLS for DEVELOPING Communication PLANS Students with disabilities, like all students, must have the opportunity to fully participate in all aspects of their education. Being able to effectively communicate
How To Teach A Deaf Person
 Appendix F. New Hampshire Certification Requirements for Educational Interpreters/Transliterators and for Special Education Teachers in the Area of Deaf and Hearing Disabilities Educational Interpreter/Transliterator
Appendix F. New Hampshire Certification Requirements for Educational Interpreters/Transliterators and for Special Education Teachers in the Area of Deaf and Hearing Disabilities Educational Interpreter/Transliterator
EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN
 EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN Our child has a hearing loss. What happens next? What is early intervention? What can we do to
EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN Our child has a hearing loss. What happens next? What is early intervention? What can we do to
Essential Components. Standards for Special Education. Deaf or Hard of Hearing. Students who are. for. < Amended June 2004 >
 Standards for Special Education < Amended June 2004 > Essential Components OF EDUCATIONAL PROGRAMMING for ACCESS APPROPRIATENESS ACCOUNTABILITY APPEALS Students who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing ALBERTA
Standards for Special Education < Amended June 2004 > Essential Components OF EDUCATIONAL PROGRAMMING for ACCESS APPROPRIATENESS ACCOUNTABILITY APPEALS Students who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing ALBERTA
OCR Levels 2 and 3 in Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools. Unit 39 Support pupils with communication and interaction needs
 OCR Levels 2 and 3 in Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools Unit 39 Support pupils with communication and interaction needs UNIT SUMMARY Who is this unit for? This unit is for those who provide support
OCR Levels 2 and 3 in Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools Unit 39 Support pupils with communication and interaction needs UNIT SUMMARY Who is this unit for? This unit is for those who provide support
Care Pathway for Rehabilitation Team (Following allocation of Cochlear Implant surgery date)
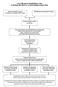 Care Pathway for Rehabilitation Team (Following allocation of Cochlear Implant surgery date) Home information session (Carried out by a member of the CI team) Rehabilitationist allocated to family Cochlear
Care Pathway for Rehabilitation Team (Following allocation of Cochlear Implant surgery date) Home information session (Carried out by a member of the CI team) Rehabilitationist allocated to family Cochlear
NEW YORK STATE TEACHER CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS
 NEW YORK STATE TEACHER CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS TEST DESIGN AND FRAMEWORK September 2014 Authorized for Distribution by the New York State Education Department This test design and framework document
NEW YORK STATE TEACHER CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS TEST DESIGN AND FRAMEWORK September 2014 Authorized for Distribution by the New York State Education Department This test design and framework document
Curriculum Policy for Audiology Primary and Secondary
 ELMFIELD SCHOOL FOR DEAF CHILDREN Curriculum Policy for Audiology Primary and Secondary - 2 - Throughout this document the terms deaf and deafness are used to denote all type and degrees of hearing loss.
ELMFIELD SCHOOL FOR DEAF CHILDREN Curriculum Policy for Audiology Primary and Secondary - 2 - Throughout this document the terms deaf and deafness are used to denote all type and degrees of hearing loss.
PRESCHOOL PLACEMENT CATEGORIES
 PRESCHOOL PLACEMENT CATEGORIES CASEMIS 20 EARLY CHILDHOOD SPECIAL EDUCATION SETTING Early Childhood Special Education Setting: This is a placement setting where children receive all of their special education
PRESCHOOL PLACEMENT CATEGORIES CASEMIS 20 EARLY CHILDHOOD SPECIAL EDUCATION SETTING Early Childhood Special Education Setting: This is a placement setting where children receive all of their special education
Model Communication Plan. Student: DOB: 00 / 00 / 0000
 Model Communication Plan Student: DOB: 00 / 00 / 0000 School: Grade: Grade Primary Area of Eligibility: Secondary Area(s) of Eligibility (if applicable): Date Model Communication Plan Was Completed: 00
Model Communication Plan Student: DOB: 00 / 00 / 0000 School: Grade: Grade Primary Area of Eligibility: Secondary Area(s) of Eligibility (if applicable): Date Model Communication Plan Was Completed: 00
SPECIAL EDUCATION AND RELATED SERVICES
 i SPECIAL EDUCATION AND RELATED SERVICES Updated May 2008 i It is the policy of the South Dakota Department of Education, Office of Educational Services and Supports to provide services to all persons
i SPECIAL EDUCATION AND RELATED SERVICES Updated May 2008 i It is the policy of the South Dakota Department of Education, Office of Educational Services and Supports to provide services to all persons
ARLINGTON PUBLIC SCHOOLS SPECIAL EDUCATION PROGRAMS AND SERVICES
 ARLINGTON PUBLIC SCHOOLS SPECIAL EDUCATION PROGRAMS AND SERVICES Introduction The Arlington Public Schools provides a comprehensive array of programs and services from pre-school through grades 12 designed
ARLINGTON PUBLIC SCHOOLS SPECIAL EDUCATION PROGRAMS AND SERVICES Introduction The Arlington Public Schools provides a comprehensive array of programs and services from pre-school through grades 12 designed
Technical Report #2 Testing Children Who Are Deaf or Hard of Hearing
 Technical Report #2 Testing Children Who Are Deaf or Hard of Hearing September 4, 2015 Lori A. Day, PhD 1, Elizabeth B. Adams Costa, PhD 2, and Susan Engi Raiford, PhD 3 1 Gallaudet University 2 The River
Technical Report #2 Testing Children Who Are Deaf or Hard of Hearing September 4, 2015 Lori A. Day, PhD 1, Elizabeth B. Adams Costa, PhD 2, and Susan Engi Raiford, PhD 3 1 Gallaudet University 2 The River
CHAPTER 3. What children with a cochlear implant need in school. Trends in educational services. Trends in educational services
 10 AN EDUCATOR S GUIDE CHAPTER 3 What children with a cochlear implant need in school Trends in educational services Your student s cochlear implant team Clinical Team surgeon, audiologist Educational
10 AN EDUCATOR S GUIDE CHAPTER 3 What children with a cochlear implant need in school Trends in educational services Your student s cochlear implant team Clinical Team surgeon, audiologist Educational
The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction:
 The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction: As the current CHAIR of the BAEA I felt that it was time for the Role of the Educational Audiologist to be updated. There has been a period of
The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction: As the current CHAIR of the BAEA I felt that it was time for the Role of the Educational Audiologist to be updated. There has been a period of
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS REGARDING SCHOOL AUDIOLOGY SERVICES
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS REGARDING SCHOOL AUDIOLOGY SERVICES The purpose of this document is to respond to questions concerning the role and responsibilities of educational audiologists and how they
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS REGARDING SCHOOL AUDIOLOGY SERVICES The purpose of this document is to respond to questions concerning the role and responsibilities of educational audiologists and how they
Education of Deaf, Hard of Hearing and Deafblind People. Aims and Strategies
 Education of Deaf, Hard of Hearing and Deafblind People Aims and Strategies Education of Deaf, Hard of Hearing and Deafblind People Table of Contents Page Education of Deaf, Hard of Hearing 2 and Deafblind
Education of Deaf, Hard of Hearing and Deafblind People Aims and Strategies Education of Deaf, Hard of Hearing and Deafblind People Table of Contents Page Education of Deaf, Hard of Hearing 2 and Deafblind
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance
 Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
Transition to Preschool For children who are at least 3 years old
 Transition to Preschool For children who are at least 3 years old Once a child who is deaf or hard of hearing turns 3, he or she may be eligible to receive special services when they attend school. Under
Transition to Preschool For children who are at least 3 years old Once a child who is deaf or hard of hearing turns 3, he or she may be eligible to receive special services when they attend school. Under
Provincial Schools Branch
 Provincial Schools Branch Professional Development Opportunities 2009-2010 Supporting School Boards In Meeting the Needs of Deaf and hard of hearing Students Provincial Schools Branch Outreach Programs
Provincial Schools Branch Professional Development Opportunities 2009-2010 Supporting School Boards In Meeting the Needs of Deaf and hard of hearing Students Provincial Schools Branch Outreach Programs
APPENDIX A SCHOOL-BASED RESOURCES
 APPENDIX A SCHOOL-BASED RESOURCES Classroom Teacher - The classroom teacher is responsible for providing a quality education to all students. Duties include: classroom organization and management, assessment,
APPENDIX A SCHOOL-BASED RESOURCES Classroom Teacher - The classroom teacher is responsible for providing a quality education to all students. Duties include: classroom organization and management, assessment,
EARLY LEARNING OCCUPATIONAL THERAPIST (New position)
 Edmonton Catholic Schools is now accepting applications for the position of (10 mth) EARLY LEARNING OCCUPATIONAL THERAPIST (New position) Edmonton Catholic Schools is a large urban school district whose
Edmonton Catholic Schools is now accepting applications for the position of (10 mth) EARLY LEARNING OCCUPATIONAL THERAPIST (New position) Edmonton Catholic Schools is a large urban school district whose
OFFICE OF EDUCATOR LICENSURE SUBJECT MATTER KNOWLEDGE. The Competency Review Made Simple
 OFFICE OF EDUCATOR LICENSURE SUBJECT MATTER KNOWLEDGE The Competency Review Made Simple Meeting and Verifying Subject Matter Competency Requirements December, 2013 Massachusetts Department of Elementary
OFFICE OF EDUCATOR LICENSURE SUBJECT MATTER KNOWLEDGE The Competency Review Made Simple Meeting and Verifying Subject Matter Competency Requirements December, 2013 Massachusetts Department of Elementary
62 Hearing Impaired MI-SG-FLD062-02
 62 Hearing Impaired MI-SG-FLD062-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW OF THE TESTING PROGRAM... 1-1 Contact Information Test Development
62 Hearing Impaired MI-SG-FLD062-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW OF THE TESTING PROGRAM... 1-1 Contact Information Test Development
Interpreting Services
 Interpreting Services User Manual August 2013 Office of Research Services Division of Amenities and Transportation Services Introduction Title 5 USC, Section 3102 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as
Interpreting Services User Manual August 2013 Office of Research Services Division of Amenities and Transportation Services Introduction Title 5 USC, Section 3102 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as
Special Educaton Staff
 Special Educaton Staff The following consultant/support personnel provide service in addition to regular and special subject consultants, coordinators and guidance counselors. Please refer to Appendix
Special Educaton Staff The following consultant/support personnel provide service in addition to regular and special subject consultants, coordinators and guidance counselors. Please refer to Appendix
A Quality Language Arts Program for Deaf and Hard of Hearing Children: Parents in the Driver s Seat
 ASDC Article Winter 2010 Kristin Di Perri, Ed.D. A Quality Language Arts Program for Deaf and Hard of Hearing Children: Parents in the Driver s Seat Often parents of Deaf and Hard-of Hearing (DHH) children
ASDC Article Winter 2010 Kristin Di Perri, Ed.D. A Quality Language Arts Program for Deaf and Hard of Hearing Children: Parents in the Driver s Seat Often parents of Deaf and Hard-of Hearing (DHH) children
Categories of Exceptionality and Definitions
 7. CATEGORIES and DEFINITIONS of EXCEPTIONALITIES Purpose of the standard To provide the ministry with details of the categories and definitions of exceptionalities available to the public, including parents
7. CATEGORIES and DEFINITIONS of EXCEPTIONALITIES Purpose of the standard To provide the ministry with details of the categories and definitions of exceptionalities available to the public, including parents
IDENTIFICATION, EVALUATION AND INTERVENTION FOR ELL STUDENTS WITH COMMUNICATION DISORDERS
 IDENTIFICATION, EVALUATION AND INTERVENTION FOR ELL STUDENTS WITH COMMUNICATION DISORDERS INTRODUCTION Public school systems in the United States have experienced a significant increase in the number of
IDENTIFICATION, EVALUATION AND INTERVENTION FOR ELL STUDENTS WITH COMMUNICATION DISORDERS INTRODUCTION Public school systems in the United States have experienced a significant increase in the number of
Psychological and Social Aspects of Hearing Loss 404.591.1884. www.childrensent.com
 Psychological and Social Aspects of Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com Adjusting to your Child s Diagnosis of Hearing Loss When you learn your child has a hearing loss you may feel grief, shock,
Psychological and Social Aspects of Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com Adjusting to your Child s Diagnosis of Hearing Loss When you learn your child has a hearing loss you may feel grief, shock,
IMPLEMENTING THE DEAF CHILD S BILL OF RIGHTS: GUIDELINES FOR SCHOOLS 1
 IMPLEMENTING THE DEAF CHILD S BILL OF RIGHTS: GUIDELINES FOR SCHOOLS 1 cde The Colorado Department of Education 201 E. Colfax Ave Denver, CO 80203 January, 1999 1 Portions of this document are taken from
IMPLEMENTING THE DEAF CHILD S BILL OF RIGHTS: GUIDELINES FOR SCHOOLS 1 cde The Colorado Department of Education 201 E. Colfax Ave Denver, CO 80203 January, 1999 1 Portions of this document are taken from
PARC: Placement And Readiness Checklists for Students who are Deaf and Hard of Hearing
 PARC: Placement And Readiness Checklists for Students who are Deaf and Hard of Hearing Part 1 Readiness Checklists PARC is a set of placement and readiness checklists designed to assist IEP teams, including
PARC: Placement And Readiness Checklists for Students who are Deaf and Hard of Hearing Part 1 Readiness Checklists PARC is a set of placement and readiness checklists designed to assist IEP teams, including
Special Education Programs, Services, and Personnel
 NIAGARA CATHOLIC DISTRICT SCHOOL BOARD Special Education Programs, Services, and Personnel Inclusion is the students' feeling of belonging in a community of learning that honours equality, student diversity
NIAGARA CATHOLIC DISTRICT SCHOOL BOARD Special Education Programs, Services, and Personnel Inclusion is the students' feeling of belonging in a community of learning that honours equality, student diversity
Indiana Content Standards for Educators
 Indiana Content Standards for Educators EXCEPTIONAL NEEDS DEAF/HARD OF HEARING of hearing are expected to have a broad and comprehensive understanding of the knowledge and skills needed for this educator
Indiana Content Standards for Educators EXCEPTIONAL NEEDS DEAF/HARD OF HEARING of hearing are expected to have a broad and comprehensive understanding of the knowledge and skills needed for this educator
Special Education Coding Criteria 2012/2013. ECS to Grade 12 Mild/Moderate (including Gifted and Talented) Severe
 Special Education Coding Criteria 2012/2013 ECS to Grade 12 Mild/Moderate (including Gifted and Talented) Severe Special Education Coding Criteria 2012/2013 ISSN 1911-4311 Additional copies of this handbook
Special Education Coding Criteria 2012/2013 ECS to Grade 12 Mild/Moderate (including Gifted and Talented) Severe Special Education Coding Criteria 2012/2013 ISSN 1911-4311 Additional copies of this handbook
IDENTIFICATION AND ASSESSMENT OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE LEARNERS
 IDENTIFICATION AND ASSESSMENT OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE LEARNERS CHAPTER 3 INDEX 3.1 PURPOSE AND SCOPE... 3 1 3.2 IDENTIFICATION AND REFERRAL OF ENGLISH LEARNERS SUSPECTED OF HAING A DISABILITY... 3 1 3.3 SPECIAL
IDENTIFICATION AND ASSESSMENT OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE LEARNERS CHAPTER 3 INDEX 3.1 PURPOSE AND SCOPE... 3 1 3.2 IDENTIFICATION AND REFERRAL OF ENGLISH LEARNERS SUSPECTED OF HAING A DISABILITY... 3 1 3.3 SPECIAL
School-based Support Personnel
 L. SUPPORT SERVICES School-based Support Personnel Yukon Education provides both professional and paraprofessional support to schools to address the diverse learning of students. Learning Assistance Program
L. SUPPORT SERVICES School-based Support Personnel Yukon Education provides both professional and paraprofessional support to schools to address the diverse learning of students. Learning Assistance Program
Position Title Deaf Inclusion Worker (DIW) 30.11.10
 Job Description Position Title Deaf Inclusion Worker (DIW) 30.11.10 Location Reporting to Grade Salary Hours OKEHAMPTON COLLEGE SENCO G Point 35 39 12,416-13,930 19 Hours Per Week (Incl PPA time), Term
Job Description Position Title Deaf Inclusion Worker (DIW) 30.11.10 Location Reporting to Grade Salary Hours OKEHAMPTON COLLEGE SENCO G Point 35 39 12,416-13,930 19 Hours Per Week (Incl PPA time), Term
The Audiology and Vocational Rehabilitation partnership
 Audiology on the Job The Audiology and Vocational Rehabilitation partnership Nancy Mascia, Au.D.,CCC-A Alabama Dept of Rehabilitation Dr. Nancy Mascia is an employee of the above organization that provides
Audiology on the Job The Audiology and Vocational Rehabilitation partnership Nancy Mascia, Au.D.,CCC-A Alabama Dept of Rehabilitation Dr. Nancy Mascia is an employee of the above organization that provides
General Information about CU-Boulder
 1 University of Colorado Providing Academic and Research Excellence in the Science Field of Speech-Language Pathology Vernon B. Ingraham, 33, Grand Cross Executive Secretary Scottish Rite Foundation of
1 University of Colorado Providing Academic and Research Excellence in the Science Field of Speech-Language Pathology Vernon B. Ingraham, 33, Grand Cross Executive Secretary Scottish Rite Foundation of
COMPLEX LEARNING DIFFICULTIES AND DISABILITIES RESEARCH PROJECT (CLDD)
 Page 1 This is a general overview of the implications of vision impairment, hearing impairment and multi-sensory impairment. The impact of impairments for individual students with complex learning difficulties
Page 1 This is a general overview of the implications of vision impairment, hearing impairment and multi-sensory impairment. The impact of impairments for individual students with complex learning difficulties
Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss
 With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
MICHIGAN TEST FOR TEACHER CERTIFICATION (MTTC) TEST OBJECTIVES FIELD 062: HEARING IMPAIRED
 MICHIGAN TEST FOR TEACHER CERTIFICATION (MTTC) TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Human Development and Students with Special Educational Needs Hearing Impairments Assessment Program Development and Intervention
MICHIGAN TEST FOR TEACHER CERTIFICATION (MTTC) TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Human Development and Students with Special Educational Needs Hearing Impairments Assessment Program Development and Intervention
Cochlear Implant and Associated Technologies for Hearing
 Cochlear Implant and Associated Technologies for Hearing Mada Assistive Technology Center Tel: 00 974 44594050 Fax: 00 974 44594051 Email: info@mada.org.qa What is a cochlear implant? Cochlear implants
Cochlear Implant and Associated Technologies for Hearing Mada Assistive Technology Center Tel: 00 974 44594050 Fax: 00 974 44594051 Email: info@mada.org.qa What is a cochlear implant? Cochlear implants
2. Provide pricing chart outlining prices for evaluations, direct student services, and other services
 DCBPCS is a learning community that ensures high academic achievement for all in both Spanish and English, develops leadership, and values all cultures. DCBPCS es una comunidad de aprendizaje que asegura
DCBPCS is a learning community that ensures high academic achievement for all in both Spanish and English, develops leadership, and values all cultures. DCBPCS es una comunidad de aprendizaje que asegura
The purpose of this presentation is: To define deafblindness and discuss the impact of combined vision and hearing loss on learning, communication,
 The purpose of this presentation is: To define deafblindness and discuss the impact of combined vision and hearing loss on learning, communication, and overall development To describe the role of interveners
The purpose of this presentation is: To define deafblindness and discuss the impact of combined vision and hearing loss on learning, communication, and overall development To describe the role of interveners
READING SPECIALIST STANDARDS
 READING SPECIALIST STANDARDS Standard I. Standard II. Standard III. Standard IV. Components of Reading: The Reading Specialist applies knowledge of the interrelated components of reading across all developmental
READING SPECIALIST STANDARDS Standard I. Standard II. Standard III. Standard IV. Components of Reading: The Reading Specialist applies knowledge of the interrelated components of reading across all developmental
Two steps are necessary to implement this process. 1. Administer the Home Language survey to all students enrolled in the school corporation.
 INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION Office of English Language Learning & Migrant Education Guidelines to Satisfy Legal Requirements of Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 (42 USCS, 2000d) Lau v. Nichols
INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION Office of English Language Learning & Migrant Education Guidelines to Satisfy Legal Requirements of Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 (42 USCS, 2000d) Lau v. Nichols
How To Communicate With People Who Are Deaf, Deafened Or Hard Of Hearing
 Get Connected to Deaf, Deafened and Hard of Hearing People: A Guide for Service Providers and Businesses This material has been prepared by for the Accessibility Directorate of Ontario, Ministry of Citizenship
Get Connected to Deaf, Deafened and Hard of Hearing People: A Guide for Service Providers and Businesses This material has been prepared by for the Accessibility Directorate of Ontario, Ministry of Citizenship
Reporting of Interpreting as a Related Service. on the PEIMS 163 Student Data Record
 Reporting of Interpreting as a Related Service on the PEIMS 163 Student Data Record 2008-2009 All Local Education Agencies and Charter Schools in Texas must report whether or not a student who is deaf
Reporting of Interpreting as a Related Service on the PEIMS 163 Student Data Record 2008-2009 All Local Education Agencies and Charter Schools in Texas must report whether or not a student who is deaf
Special Education Coding Criteria 2014/2015. ECS to Grade 12 Mild/Moderate Gifted and Talented Severe
 Special Education Coding Criteria 2014/2015 Mild/Moderate Gifted and Talented Severe Special Education Coding Criteria 2014/2015 ISBN 978-1-4601-1902-0 (Print) ISBN 978-1-4601-1903-7 (PDF) ISSN 1911-4311
Special Education Coding Criteria 2014/2015 Mild/Moderate Gifted and Talented Severe Special Education Coding Criteria 2014/2015 ISBN 978-1-4601-1902-0 (Print) ISBN 978-1-4601-1903-7 (PDF) ISSN 1911-4311
Getting Started Kei Te Timata
 Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Intermediate School District 917 CLASSIFICATION DESCRIPTION Educational Audiologist Department: Special Education
 Title of Immediate Supervisor: Assistant Director of Special Education Intermediate School District 917 Department: Special Education FLSA Status: Exempt Accountable For (Job Titles): None Pay Grade Assignment:
Title of Immediate Supervisor: Assistant Director of Special Education Intermediate School District 917 Department: Special Education FLSA Status: Exempt Accountable For (Job Titles): None Pay Grade Assignment:
Ministry of Education. The Individual Education Plan (IEP) A RESOURCE GUIDE IEP
 Ministry of Education The Individual Education Plan (IEP) A RESOURCE GUIDE 2004 IEP CONTENTS Introduction.......................................... 4 What Is an IEP?.........................................
Ministry of Education The Individual Education Plan (IEP) A RESOURCE GUIDE 2004 IEP CONTENTS Introduction.......................................... 4 What Is an IEP?.........................................
Interpreting Legal Discourse and Working in Legal Settings: An AVLIC Position Paper. Synopsis Prepared for ASL Translation Debra Russell - 2013
 Interpreting Legal Discourse and Working in Legal Settings: An AVLIC Position Paper Synopsis Prepared for ASL Translation Debra Russell - 2013 WHY DOES AVLIC HAVE A POSITION PAPER ON LEGAL INTERPRETING?
Interpreting Legal Discourse and Working in Legal Settings: An AVLIC Position Paper Synopsis Prepared for ASL Translation Debra Russell - 2013 WHY DOES AVLIC HAVE A POSITION PAPER ON LEGAL INTERPRETING?
Instruction: Design, Delivery, Assessment Worksheet
 Reading Specialist Instruction: Design, Delivery, Assessment Worksheet Sponsoring Organization University of Massachusetts Amherst Program/Group of Programs Reading Specialist Required Documents Program
Reading Specialist Instruction: Design, Delivery, Assessment Worksheet Sponsoring Organization University of Massachusetts Amherst Program/Group of Programs Reading Specialist Required Documents Program
TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE AND BEST PRACTICES MANUAL Speech-Language Pathology in the Schools
 I. Definition and Overview Central Consolidated School District No. 22 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE AND BEST PRACTICES MANUAL Speech-Language Pathology in the Schools Speech and/or language impairments are those
I. Definition and Overview Central Consolidated School District No. 22 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE AND BEST PRACTICES MANUAL Speech-Language Pathology in the Schools Speech and/or language impairments are those
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan
 Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Audiology as a School Based Service. Purpose. Audiology (IDEA 2004) Arkansas SPED Regulations. IDEA 2004 Part B
 Audiology as a School Based Service 2008 Medicaid in the Schools (MITS) Summit January 24, 2008 Donna Fisher Smiley, Ph.D., CCC-A Audiologist Arkansas Children s Hospital and Conway Public Schools Purpose
Audiology as a School Based Service 2008 Medicaid in the Schools (MITS) Summit January 24, 2008 Donna Fisher Smiley, Ph.D., CCC-A Audiologist Arkansas Children s Hospital and Conway Public Schools Purpose
CALIFORNIA SPECIAL EDUCATION MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM (CASEMIS) SERVICE DESCRIPTIONS. San Diego Unified SELPA
 210 Family training, counseling, and home visits(ages 0-2 only): This service includes: services provided by social workers, psychologists, or other qualified personnel to assist the family in understanding
210 Family training, counseling, and home visits(ages 0-2 only): This service includes: services provided by social workers, psychologists, or other qualified personnel to assist the family in understanding
Chapter 4: Planning Support for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders
 Chapter 4: Planning Support for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders Developing Individualized Program Plans (IPPs) There is considerable variability in how learning and behavioural characteristics
Chapter 4: Planning Support for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders Developing Individualized Program Plans (IPPs) There is considerable variability in how learning and behavioural characteristics
EARLY LEARNING CHILD PSYCHOLOGISTS (Existing positions)
 Edmonton Catholic Schools is now accepting applications for the position of EARLY LEARNING CHILD PSYCHOLOGISTS (Existing positions) Edmonton Catholic Schools is a large urban school district whose mission
Edmonton Catholic Schools is now accepting applications for the position of EARLY LEARNING CHILD PSYCHOLOGISTS (Existing positions) Edmonton Catholic Schools is a large urban school district whose mission
The Disability Tax Credit Certificate Tip sheet for Audiologists
 The Disability Tax Credit Certificate Tip sheet for Audiologists Developed by: The Canadian Academy of Audiology (CAA) & Speech- Language and Audiology Canada (SAC) Purpose of This Document The Canada
The Disability Tax Credit Certificate Tip sheet for Audiologists Developed by: The Canadian Academy of Audiology (CAA) & Speech- Language and Audiology Canada (SAC) Purpose of This Document The Canada
Belmont Public Schools Special Education Programs
 Belmont Public Schools Special Education Programs Preschool Program School: Belmont system wide Population Served: Special Education Students Aged 3 5 Grade: Pre K Program Description: This program is
Belmont Public Schools Special Education Programs Preschool Program School: Belmont system wide Population Served: Special Education Students Aged 3 5 Grade: Pre K Program Description: This program is
West Virginia Department of Education and the Arts DIVISION OF REHABILITATION SERVICES
 2400 INTAKE AND CASE MANAGEMENT 2401 Community Outreach and Referral Source Development. The Division will develop and maintain relationships with organizations, agencies and persons in the community to
2400 INTAKE AND CASE MANAGEMENT 2401 Community Outreach and Referral Source Development. The Division will develop and maintain relationships with organizations, agencies and persons in the community to
Schools for All Children
 Position Paper No. Schools for All Children LOS ANGELES UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT John Deasy, Superintendent Sharyn Howell, Executive Director Division of Special Education Spring 2011 The Los Angeles Unified
Position Paper No. Schools for All Children LOS ANGELES UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT John Deasy, Superintendent Sharyn Howell, Executive Director Division of Special Education Spring 2011 The Los Angeles Unified
The Denver Public Schools Personalized Learning Vision. and Framework Urban Collaborative Fall 2014
 The Denver Public Schools Personalized Learning Vision and Framework Urban Collaborative Fall 2014 -Diann Richardson- Director of Special Education -Gene Bamesberger- Associate Director of Special Education
The Denver Public Schools Personalized Learning Vision and Framework Urban Collaborative Fall 2014 -Diann Richardson- Director of Special Education -Gene Bamesberger- Associate Director of Special Education
Questions and Answers for Parents
 Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
September 13, 2011 ASSEMBLY BILL 114: NONPUBLIC AGENCY CERTIFICATION
 Page 1 September 13, 2011 Dear County and District Superintendents, Special Education Local Plan Area Directors, Special Education Administrators at County Offices of Education, Charter School Administrators,
Page 1 September 13, 2011 Dear County and District Superintendents, Special Education Local Plan Area Directors, Special Education Administrators at County Offices of Education, Charter School Administrators,
Faculty Handbook for Working with Deaf and Hard of Hearing Students
 Faculty Handbook for Working with Deaf and Hard of Hearing Students Table of Contents Disability Laws in Postsecondary Education... 2 SAIC Disability Documentation Requirements... 3 About Hearing Disabilities...
Faculty Handbook for Working with Deaf and Hard of Hearing Students Table of Contents Disability Laws in Postsecondary Education... 2 SAIC Disability Documentation Requirements... 3 About Hearing Disabilities...
College of Education. Special Education
 357 INITIAL PRACTICUM IN SPECIAL EDUCATION. (1) An introductory supervised field experience for special education majors. Students will participate in two special education programs as teacher aides. Placements
357 INITIAL PRACTICUM IN SPECIAL EDUCATION. (1) An introductory supervised field experience for special education majors. Students will participate in two special education programs as teacher aides. Placements
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT. Intervention Programs
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs The Joint Committee on Infant Hearing
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs The Joint Committee on Infant Hearing
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
MILLIKIN TEACHING STANDARDS
 MILLIKIN TEACHING STANDARDS Millikin Teaching Standards are correlated to and modifications of Illinois Professional Teaching Standards. Modifications reflect Millikin s mission and the education unit
MILLIKIN TEACHING STANDARDS Millikin Teaching Standards are correlated to and modifications of Illinois Professional Teaching Standards. Modifications reflect Millikin s mission and the education unit
Understanding Special Education in the OCDSB
 Understanding Special Education in the OCDSB Individual Education Plan Parent Guide Learning Support Services Understanding Special Education in the OCDSB Individual Education Plan Parent Guide Table
Understanding Special Education in the OCDSB Individual Education Plan Parent Guide Learning Support Services Understanding Special Education in the OCDSB Individual Education Plan Parent Guide Table
Monroe Public Schools English Language Learner Program Description and Guidelines Revised, Fall 2012
 Monroe Public Schools Language Learner Program Description and Guidelines Revised, Fall 2012 It is the policy of Monroe Public Schools not to discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin,
Monroe Public Schools Language Learner Program Description and Guidelines Revised, Fall 2012 It is the policy of Monroe Public Schools not to discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin,
Considerations for Teaching a Student Who is Deaf or Hard of Hearing in the Mainstream Setting
 M A N U A L Considerations for Teaching a Student Who is Deaf or Hard of Hearing in the Mainstream Setting Christine Roy, M.S. Ed Table of Contents Part 1 Introduction 4 How should you perceive a student
M A N U A L Considerations for Teaching a Student Who is Deaf or Hard of Hearing in the Mainstream Setting Christine Roy, M.S. Ed Table of Contents Part 1 Introduction 4 How should you perceive a student
Section D: Support Staff and Service
 Section D: Support Staff and Service Student Services Organization and Interdisciplinary Teams D. 1 Autism Services D. 3 Care and Treatment Program Coordinator D. 5 Children s Treatment Network/YRDSB D.
Section D: Support Staff and Service Student Services Organization and Interdisciplinary Teams D. 1 Autism Services D. 3 Care and Treatment Program Coordinator D. 5 Children s Treatment Network/YRDSB D.
Northeast Metro 916. Auditory/Oral Program. Engaging The Whole Child
 Northeast Metro 916 Auditory/Oral Program Engaging The Whole Child Welcome to Northeast Metro 916 Auditory/Oral Program I am proud of what our program has accomplished for children and families in the
Northeast Metro 916 Auditory/Oral Program Engaging The Whole Child Welcome to Northeast Metro 916 Auditory/Oral Program I am proud of what our program has accomplished for children and families in the
Nefertari International Schools IBDP Candidate School Whole School Language Policy
 Nefertari International Schools IBDP Candidate School Whole School Language Policy Release Date: September 2014 To be Reviewed: September 2019 Introduction Before framing the language policy for the International
Nefertari International Schools IBDP Candidate School Whole School Language Policy Release Date: September 2014 To be Reviewed: September 2019 Introduction Before framing the language policy for the International
CHARACTERISTICS FOR STUDENTS WITH: LIMITED ENGLISH PROFICIENCY (LEP)
 CHARACTERISTICS FOR STUDENTS WITH: LIMITED ENGLISH PROFICIENCY (LEP) Research has shown that students acquire a second language in the same way that they acquire the first language. It is an exploratory
CHARACTERISTICS FOR STUDENTS WITH: LIMITED ENGLISH PROFICIENCY (LEP) Research has shown that students acquire a second language in the same way that they acquire the first language. It is an exploratory
Essential Functions for Graduate Students in Speech-Language Pathology
 Essential Functions for Graduate Students in Speech-Language Pathology Introduction The Grand Valley State University Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders speech-language pathology and audiology
Essential Functions for Graduate Students in Speech-Language Pathology Introduction The Grand Valley State University Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders speech-language pathology and audiology
SPECIAL EDUCATION SERVICES. A Manual of Policies, Procedures and Guidelines
 SPECIAL EDUCATION SERVICES A Manual of Policies, Procedures and Guidelines September 2013 BRITISH COLUMBIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION Special Education Services: A Manual of Policies, Procedures and Guidelines
SPECIAL EDUCATION SERVICES A Manual of Policies, Procedures and Guidelines September 2013 BRITISH COLUMBIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION Special Education Services: A Manual of Policies, Procedures and Guidelines
Toolkit for Working with the Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing
 Toolkit for Working with the Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing May 2012 Toolkit for Working with the Deaf and Hard of Hearing Introduction This Toolkit for Working with the Deaf and Hard of Hearing is designed
Toolkit for Working with the Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing May 2012 Toolkit for Working with the Deaf and Hard of Hearing Introduction This Toolkit for Working with the Deaf and Hard of Hearing is designed
Rubric for Evaluating North Carolina s Speech- Language Pathologists
 Rubric for Evaluating North Carolina s Speech- Language Pathologists STANDARD 1: School speech-language pathologists demonstrate leadership, advocacy, collaboration, and ethical practices. School Speech-Language
Rubric for Evaluating North Carolina s Speech- Language Pathologists STANDARD 1: School speech-language pathologists demonstrate leadership, advocacy, collaboration, and ethical practices. School Speech-Language
Section 2.8: Special Education Placements Provided by the Board
 Section 2.8: Special Education Placements Provided by the Board Table of Contents Section 2.8: Special Education Placements Provided by the Board... 1 Special Education Philosophy... 2 Ways in Which SEAC
Section 2.8: Special Education Placements Provided by the Board Table of Contents Section 2.8: Special Education Placements Provided by the Board... 1 Special Education Philosophy... 2 Ways in Which SEAC
Language Development and Deaf Children
 Language Development and Deaf Children What is the difference between speech and language? Language is the words, structures, thoughts and concepts we have in our minds. Speech is one way in which we communicate
Language Development and Deaf Children What is the difference between speech and language? Language is the words, structures, thoughts and concepts we have in our minds. Speech is one way in which we communicate
DSPS ACCOMMODATIONS & INTERPRETING SERVICES. Revised 1/2007 OHLONE COLLEGE FREMONT, CALIFORNIA
 INSTRUCTOR HANDBOOK DSPS ACCOMMODATIONS & INTERPRETING SERVICES Revised 1/2007 OHLONE COLLEGE FREMONT, CALIFORNIA INTRODUCTION The Ohlone College DSP&S Accommodations and Interpreting Services Office provides
INSTRUCTOR HANDBOOK DSPS ACCOMMODATIONS & INTERPRETING SERVICES Revised 1/2007 OHLONE COLLEGE FREMONT, CALIFORNIA INTRODUCTION The Ohlone College DSP&S Accommodations and Interpreting Services Office provides
Global engagement. An International Baccalaureate education for all
 Learning stories Language and learning Inclusive education Global engagement Multiple programme schools Learning stories from the IB continuum share examples of good practice from IB World Schools in order
Learning stories Language and learning Inclusive education Global engagement Multiple programme schools Learning stories from the IB continuum share examples of good practice from IB World Schools in order
Short-Term Programs. A Vital Component for Students who are Blind or Visually Impaired ATLANTIC PROVINCES SPECIAL EDUCATION AUTHORITY
 Short-Term Programs A Vital Component for Students who are Blind or Visually Impaired ATLANTIC PROVINCES SPECIAL EDUCATION AUTHORITY Atlantic Provinces Special Education Authority Commission de l enseignement
Short-Term Programs A Vital Component for Students who are Blind or Visually Impaired ATLANTIC PROVINCES SPECIAL EDUCATION AUTHORITY Atlantic Provinces Special Education Authority Commission de l enseignement
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
MINNESOTA COMPENSATORY SKILLS CHECKLIST FOR STUDENTS WITH HEARING LOSS
 MINNESOTA COMPENSATORY SKILLS CHECKLIST FOR STUDENTS WITH HEARING LOSS Rationale 1 Understanding Hearing Loss 4 Amplification Management 6 Resources/Technology 9 Communication Strategies 12 Personal/Interpersonal
MINNESOTA COMPENSATORY SKILLS CHECKLIST FOR STUDENTS WITH HEARING LOSS Rationale 1 Understanding Hearing Loss 4 Amplification Management 6 Resources/Technology 9 Communication Strategies 12 Personal/Interpersonal
A Parent s Introduction to Exceptional Student Education. in Florida. Florida Department of Education
 A Parent s Introduction to Exceptional Student Education in Florida Florida Department of Education This publication is produced through the Bureau of Exceptional Education and Student Services (BEESS),
A Parent s Introduction to Exceptional Student Education in Florida Florida Department of Education This publication is produced through the Bureau of Exceptional Education and Student Services (BEESS),
Knowledge and Employability Studio Teacher Workstation. Programming for Students with Learning Disabilities Individualized Program Plans
 Individualized Program Plans (IPPs) are required for all students with special needs, including those with learning disabilities. IPPs are: written commitments of intent by education teams to ensure appropriate
Individualized Program Plans (IPPs) are required for all students with special needs, including those with learning disabilities. IPPs are: written commitments of intent by education teams to ensure appropriate
Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230]
![Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230] Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230]](/thumbs/40/21177704.jpg) Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230] STANDARD 1 - Content Knowledge The competent speech-language pathologist understands the philosophical, historical, and legal foundations of speech-language
Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230] STANDARD 1 - Content Knowledge The competent speech-language pathologist understands the philosophical, historical, and legal foundations of speech-language
Parents Guide to SPECIAL EDUCATION
 Parents Guide to SPECIAL EDUCATION DISTRICT SCHOOL BOARD OF NIAGARA Education Centre 905-641-1550 Fax: 905-685-8511 SCHOOL SUPPORT SERVICES SPECIAL EDUCATION SERVICES DEPARTMENT Don Reilly Resource Centre
Parents Guide to SPECIAL EDUCATION DISTRICT SCHOOL BOARD OF NIAGARA Education Centre 905-641-1550 Fax: 905-685-8511 SCHOOL SUPPORT SERVICES SPECIAL EDUCATION SERVICES DEPARTMENT Don Reilly Resource Centre
Models for an Adapted and for a Modified Program
 Models for an Adapted and for a Modified Program Students are assessed to the prescribed learning outcomes Students receive letter grades Adapted Program Instructional practices: Options for: Giving instructions
Models for an Adapted and for a Modified Program Students are assessed to the prescribed learning outcomes Students receive letter grades Adapted Program Instructional practices: Options for: Giving instructions
Register of Students with Severe Disabilities
 Department of Education Learners first, connected and inspired Register of Students with Severe Disabilities Department of Education Register of Students with Severe Disabilities 1. Eligibility Criteria
Department of Education Learners first, connected and inspired Register of Students with Severe Disabilities Department of Education Register of Students with Severe Disabilities 1. Eligibility Criteria
Early Learning Child Psychologist (Existing position)
 1 Early Learning Child Psychologist (Existing position) DEPARTMENT: Learning Services Innovation-Early Learning STATUS/FTE: Out of Scope, Level 7, 10 month or 12 month, 1.0 FTE SALARY RANGE: $63,612-$79,516
1 Early Learning Child Psychologist (Existing position) DEPARTMENT: Learning Services Innovation-Early Learning STATUS/FTE: Out of Scope, Level 7, 10 month or 12 month, 1.0 FTE SALARY RANGE: $63,612-$79,516
Technology in Music Therapy and Special Education. What is Special Education?
 Technology in Music Therapy and Special Education What is Special Education? Disabilities are categorized into the following areas: o Autism, visual impairment, hearing impairment, deaf- blindness, multiple
Technology in Music Therapy and Special Education What is Special Education? Disabilities are categorized into the following areas: o Autism, visual impairment, hearing impairment, deaf- blindness, multiple
