Vitamin D Deficiency: A Global Concern
|
|
|
- Brook King
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vitamin D Deficiency: A Global Concern If you live north of the line connecting San Francisco to Philadelphia and Athens to Beijing, odds are that you don't get enough vitamin D. The same holds true if you don't get outside for at least a 15-minute daily walk in the sun. African-Americans and others with dark skin, as well as older individuals, tend to have much lower levels of vitamin D, as do people who are overweight or obese. The Institute of Medicine's recommended intake of vitamin D is 200 IU up to age 50, 400 IU between the ages of 51 and 70, and 600 IU after age 70. (7) That recommendation is under review and will likely increase, since strong evidence shows optimal intakes are much higher, with at least 1,000-2,000 IU recommended for those over age 2. In extremely high doses hundreds of thousands of IU or more vitamin D is toxic and can even cause death. But in children over the age of 1 and in adults, taking up to 2,000 IU per day as a supplement is safe. Some people may need 3,000 or 4,000 IU per day for adequate blood levels, particularly if they have darker skin, spend winters at higher latitudes (such as the northern U.S.), or have little exposure to direct sunlight. If you fall into one of these groups, ask your doctor to order a vitamin D blood test. To prevent rickets, the American Academy of Pediatrics now recommends vitamin D supplements of 400 IU per day for breastfed infants, as well as for non-breastfed infants and children who do not drink at least a liter of vitamin D fortified milk each day. (6)
2 Worldwide, an estimated 1 billion people have inadequate levels of vitamin D in their blood, and deficiencies can be found in all ethnicities and age groups. (1-3) Indeed, in industrialized countries, doctors are even seeing the resurgence of rickets, the bone-weakening disease that had been largely eradicated through vitamin D fortification. (4-6) Why are these widespread vitamin D deficiencies of such great concern? Because research conducted over the past decade suggests that vitamin D plays a much broader disease-fighting role than once thought. Being D-ficient may increase the risk of a host of chronic diseases, such as osteoporosis, heart disease, some cancers, and multiple sclerosis, as well as infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis and even the seasonal flu. Read more: vitamin D and H1N1 flu Current vitamin D recommendations in the U.S. and Canada were developed more than a decade ago, based on research about what blood levels of vitamin D prevent rickets in young children and osteomalacia ( soft bones ) in adults. (7) The latest science suggests that for chronic disease prevention, we need much more vitamin D than these government guidelines recommend. In light of these findings, the Institute of Medicine has begun reviewing its vitamin D and calcium recommendations, aiming to release a new report in (8) Vitamin D Sources and Function Vitamin D is both a nutrient we eat and a hormone our bodies make. Few foods are naturally rich in vitamin D, so the biggest dietary sources of vitamin D are fortified foods and vitamin supplements.
3 Very few foods naturally contain vitamin D. Good sources include dairy products and breakfast cereals (both of which are fortified with vitamin D), and fatty fish such as salmon and tuna. For most people, the best way to get the enough vitamin D is taking a supplement, but the level in most multivitamins (400 IU) is too low. Encouragingly, some manufacturers have begun adding 800 or 1,000 IU of vitamin D to their standard multivitamin preparations. If the multivitamin you take does not have 1,000 IU of vitamin D, you may want to consider adding a separate vitamin D supplement, especially if you don't spend much time in the sun. The body also manufactures vitamin D from cholesterol, through a process triggered by the action of sunlight on skin, hence its nickname, the sunshine vitamin. Yet some people do not make enough vitamin D from the sun, among them, people who have a darker skin tone, who are overweight, who are older, and who cover up when they are in the sun. (1) Correctly applied sunscreen reduces our ability to absorb vitamin D by more than 90 percent. (9) And not all sunlight is created equal: The sun s ultraviolet B (UVB) rays the so-called tanning rays, and the rays that trigger the skin to produce vitamin D are stronger near the equator and weaker at higher latitudes. So in the fall and winter, people who live at higher latitudes (in the northern U.S. and Europe, for example) can t make much if any vitamin D from the sun. (9)
4 Read more: what may increase your risk for vitamin D deficiency Vitamin D helps ensure that the body absorbs and retains calcium and phosphorus, both critical for building bone. Laboratory studies show that vitamin D can reduce cancer cell growth and plays a critical role in controlling infections. Many of the body s organs and tissues have receptors for vitamin D, and scientists are still teasing out its other possible functions. New Vitamin D Research: Beyond Building Bones Several promising areas of vitamin D research look far beyond vitamin D s role in building bones. And, as you might expect, the news media release a flurry of reports every time another study links vitamin D to some new ailment. What these stories often fail to mention is that vitamin D s role in many of these diseases has not been proven through a randomized trial. That means it s too early to tell if there s merely an association between vitamin D levels and development of the disease, or if high vitamin D levels prevent these diseases. More answers may come from planned trials, such as the VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL), which will enroll 20,000 healthy men and women to see if taking 2,000 IU of vitamin D or 1,000 mg of fish oil daily lowers the risk of cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Here, we provide an overview of some of the more promising areas of vitamin D research, highlighting the complex role of vitamin D in disease prevention and the many unanswered questions that remain. Vitamin D and Bone and Muscle Strength Several studies link low vitamin D levels with an increased risk of fractures in older adults, and they suggest that vitamin D supplementation may prevent such fractures as long as it is taken in a high enough dose. (10-14)
5 The latest evidence comes from a combined analysis of 12 fracture prevention trials that included more than 40,000 elderly people, most of them women. Researchers found that high intakes of vitamin D supplements of about 800 IU per day reduced hip and non-spine fractures by 20 percent, while lower intakes (400 IU or less) failed to offer any fracture prevention benefit. (14) Q. What type of vitamin D is best? Two forms of vitamin D are used in supplements: vitamin D2 ( ergocalciferol, or pre-vitamin D) and vitamin D3 ( cholecalciferol ). Vitamin D3 is chemically indistinguishable from the form of vitamin D produced in the body... Read more about what type of vitamin D is best. Vitamin D may also help increase muscle strength, which in turn helps to prevent falls, a common problem that leads to substantial disability and death in older people. (15-17) Once again, vitamin D dose matters: A combined analysis of multiple studies found that taking IU of vitamin D per day lowered the risk of falls by 19 percent, but taking IU per day did not offer any such protection. (18) Vitamin D s muscle-strengthening effects may not be limited to the elderly: There s new evidence that vitamin D may be associated with muscle strength in adolescent girls. (19) Vitamin D and Heart Disease
6 The heart is basically a large muscle, and like skeletal muscle, it has receptors for vitamin D. (20) So perhaps it s no surprise that studies are finding vitamin D deficiency may be linked to heart disease. The Health Professional Follow-Up Study checked the vitamin D blood levels in nearly 50,000 men who were healthy, and then followed them for 10 years. (21) They found that men who were deficient in vitamin D were twice as likely to have a heart attack as men who had adequate levels of vitamin D. Other studies have found that low vitamin D levels were associated with higher risk of heart failure, sudden cardiac death, stroke, overall cardiovascular disease, and cardiovascular death. (22-25) How exactly does vitamin D help prevent heart disease? There s evidence that vitamin D plays a role in controlling blood pressure and preventing artery damage, and this may explain these findings. (26) Vitamin D and Cancer Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed an intriguing relationship between colon cancer deaths and geographic location: People who lived at higher latitudes, such as in the northern U.S., had higher rates of death from colon cancer than people who live closer to the equator. (27) The sun s UVB rays are weaker at higher latitudes, and in turn, people s vitamin D levels in these high latitude locales tend to be lower. This led to the hypothesis that low vitamin D levels might somehow increase colon cancer risk. (27) Vitamin D and Geographic Location
7 Many scientific hypotheses about vitamin D and disease stem from studies that have compared solar radiation and disease rates in different countries. These can be a good starting point for other research but don't provide the most definitive information... Read more about vitamin D studies and geographic location. Since then, dozens of studies suggest an association between low vitamin D levels and increased risks of colon and other cancers. (1,28) The evidence is strongest for colorectal and breast cancers, with most (but not all) observational studies finding that the lower the vitamin D levels, the higher the risk of these diseases. (29-39) Vitamin D levels also seem to predict cancer survival. (28) Yet finding such associations does not necessarily mean that taking vitamin D supplements will lower cancer risk. That requires testing in randomized controlled trials. The VITAL trial will look specifically at whether vitamin D supplements lower cancer risk. It will be years, though, before it releases any results. In the meantime, based on the evidence to date, 16 scientists have circulated a call for action on vitamin D and cancer prevention: (28) Given the high rates of vitamin D deficiency in North America, the potential cancer-fighting benefits of vitamin D, and the low risk of vitamin D supplementation, they recommend widespread vitamin D supplementation of 2000 IU per day. (28) Read more: vitamin D trials for cancer prevention Vitamin D and Immune Function Vitamin D s role in regulating the immune system has led scientists to explore two parallel research paths: Does vitamin D
8 deficiency contribute to the development of multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, and other so-called autoimmune diseases, where the body s immune system attacks its own organs and tissues? And could vitamin D supplements help boost our body s defenses to fight infectious disease, such as tuberculosis and seasonal flu? Vitamin D and Multiple Sclerosis: Multiple sclerosis (MS) rates are much higher far north (or far south) of the equator than in sunnier climes, and researchers suspect that chronic vitamin D deficiencies may be one reason why. One prospective study to look at this question found that among white men and women, those with the highest vitamin D blood levels had a 62 percent lower risk of developing MS than those with the lowest vitamin D levels. (40) The study didn t find this effect among black men and women, most likely because there were fewer black study participants and most of them had low vitamin D levels, making it harder to find any link between vitamin D and MS if one exists. No randomized controlled trials have been conducted on vitamin D and MS, and more research is needed. Vitamin D and Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is another disease that varies with geography a child in Finland is about 400 times more likely to develop it than a child in Venezuela. (41) Evidence that vitamin D may play a role in preventing type 1 diabetes comes from a 30-year study that followed more than 10,000 Finnish children from birth: Children who regularly received vitamin D supplements during infancy had a nearly 90 percent lower risk of developing type 1 diabetes than those who did not receive supplements. (42) Other European case-control studies, when analyzed together, also suggest that vitamin D may help protect against type 1 diabetes. (43) No randomized controlled trials have tested this notion, however, so more research is needed.
9 Vitamin D, the Flu, and the Common Cold: The flu virus wreaks the most havoc in the winter, abating in the summer months. This seasonality led a British doctor to hypothesize that a sunlight-related seasonal stimulus triggered influenza outbreaks. (44) More than 20 years after this initial hypothesis, several scientists published a paper suggesting that vitamin D may be the seasonal stimulus. (45) Among the evidence they cite: Vitamin D levels are lowest in the winter months. (45) The active form of vitamin D tempers the damaging inflammatory response of some white blood cells, while it also boosts immune cells production of microbe-fighting proteins. (45) Children who have vitamin D-deficiency rickets are more likely to get respiratory infections, while children exposed to sunlight seem to have fewer respiratory infections. (45) Adults who have low vitamin D levels are also more likely to report having had a recent cough, cold, or upper respiratory tract infection. (46) But don t skip your flu shot just yet: No large-scale randomized controlled trials have been done on vitamin D supplements and the flu in general, or on vitamin D and the H1N1 flu virus strain ("swine flu"). Until such studies provide more evidence, it is too early to recommend high doses of vitamin D to prevent or treat colds or flu. (45) Vitamin D and Tuberculosis: Before the advent of antibiotics, sunlight and sun lamps were part of the standard treatment for tuberculosis (TB). (47) More recent research suggests that the sunshine vitamin may be linked to TB risk. Several case-control studies, when analyzed together, suggest that people diagnosed with tuberculosis have lower vitamin D levels than healthy people of similar
10 age and other characteristics. (48) Such studies do not follow individuals over time, so they cannot tell us whether vitamin D deficiency led to the increased TB risk or whether taking vitamin D supplements would prevent TB. There are also genetic differences in the receptor that binds vitamin D, and these differences may influence TB risk. (49) Again, more research is needed. (49) Vitamin D and Risk of Premature Death A promising report in the Archives of Internal Medicine suggests that taking vitamin D supplements may even reduce overall mortality rates: A combined analysis of multiple studies found that taking modest levels of vitamin D supplements was associated with a statistically significant 7 percent reduction in mortality from any cause. (50) The analysis looked at the findings from 18 randomized controlled trials that enrolled a total of nearly 60,000 study participants; most of the study participants took between 400 and 800 IU of vitamin D per day for an average of five years. Keep in mind that this analysis has several limitations, chief among them the fact that the studies it included were not designed to explore mortality in general, or explore specific causes of death. More research is needed before any broad claims can be made about vitamin D and mortality. (51) References 1. Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357: Gordon CM, DePeter KC, Feldman HA, Grace E, Emans SJ. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among healthy adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2004; 158: Lips P, Hosking D, Lippuner K, et al. The prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy amongst women with osteoporosis: an international epidemiological investigation. J Intern Med. 2006; 260:
11 4. Robinson PD, Hogler W, Craig ME, et al. The re-emerging burden of rickets: a decade of experience from Sydney. Arch Dis Child. 2006; 91: Kreiter SR, Schwartz RP, Kirkman HN, Jr., Charlton PA, Calikoglu AS, Davenport ML. Nutritional rickets in African American breast-fed infants. J Pediatr. 2000; 137: Misra M, Pacaud D, Petryk A, Collett-Solberg PF, Kappy M. Vitamin D deficiency in children and its management: review of current knowledge and recommendations. Pediatrics. 2008; 122: Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press, Institute of Medicine. Project information: dietary reference Intakes for vitamin D and calcium. Accessed November 1, Holick MF. Vitamin D: importance in the prevention of cancers, type 1 diabetes, heart disease, and osteoporosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004; 79: Boonen S, Lips P, Bouillon R, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Vanderschueren D, Haentjens P. Need for additional calcium to reduce the risk of hip fracture with vitamin d supplementation: evidence from a comparative metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92: Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Willett WC, Wong JB, Giovannucci E, Dietrich T, Dawson-Hughes B. Fracture prevention with vitamin D supplementation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA. 2005; 293:
12 12. Cauley JA, Lacroix AZ, Wu L, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and risk for hip fractures. Ann Intern Med. 2008; 149: Cauley JA, Parimi N, Ensrud KE, et al. Serum 25 HydroxyVitamin D and the Risk of Hip and Non-spine Fractures in Older Men. J Bone Miner Res Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Willett WC, Wong JB, et al. Prevention of nonvertebral fractures with oral vitamin D and dose dependency: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169: Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Dawson-Hughes B, Willett WC, et al. Effect of Vitamin D on falls: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004; 291: Broe KE, Chen TC, Weinberg J, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Holick MF, Kiel DP. A higher dose of vitamin d reduces the risk of falls in nursing home residents: a randomized, multiple-dose study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007; 55: Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Orav EJ, Dawson-Hughes B. Effect of cholecalciferol plus calcium on falling in ambulatory older men and women: a 3-year randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2006; 166: Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Dawson-Hughes B, Staehelin HB, et al. Fall prevention with supplemental and active forms of vitamin D: a metaanalysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2009; 339:b Ward KA, Das G, Berry JL, et al. Vitamin D status and muscle function in post-menarchal adolescent girls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94: Giovannucci E. Expanding roles of vitamin D. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:
13 21. Giovannucci E, Liu Y, Hollis BW, Rimm EB. 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of myocardial infarction in men: a prospective study. Arch Intern Med. 2008; 168: Pilz S, Marz W, Wellnitz B, et al. Association of vitamin D deficiency with heart failure and sudden cardiac death in a large crosssectional study of patients referred for coronary angiography. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93: Pilz S, Dobnig H, Fischer JE, et al. Low vitamin d levels predict stroke in patients referred to coronary angiography. Stroke. 2008; 39: Wang TJ, Pencina MJ, Booth SL, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and risk of cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2008; 117: Dobnig H, Pilz S, Scharnagl H, et al. Independent association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin d and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d levels with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Arch Intern Med. 2008; 168: Holick MF. The vitamin D deficiency pandemic and consequences for nonskeletal health: mechanisms of action. Mol Aspects Med. 2008; 29: Garland CF, Garland FC. Do sunlight and vitamin D reduce the likelihood of colon cancer? Int J Epidemiol. 1980; 9: Garland CF, Gorham ED, Mohr SB, Garland FC. Vitamin D for cancer prevention: global perspective. Ann Epidemiol. 2009; 19: Yin L, Grandi N, Raum E, Haug U, Arndt V, Brenner H. Metaanalysis: longitudinal studies of serum vitamin D and colorectal cancer risk. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009; 30:
14 30. Wu K, Feskanich D, Fuchs CS, Willett WC, Hollis BW, Giovannucci EL. A nested case control study of plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and risk of colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007; 99: Gorham ED, Garland CF, Garland FC, et al. Optimal vitamin D status for colorectal cancer prevention: a quantitative meta analysis. Am J Prev Med. 2007; 32: Giovannucci E. Epidemiological evidence for vitamin D and colorectal cancer. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22 Suppl 2:V Lin J, Zhang SM, Cook NR, Manson JE, Lee IM, Buring JE. Intakes of calcium and vitamin D and risk of colorectal cancer in women. Am J Epidemiol. 2005; 161: Huncharek M, Muscat J, Kupelnick B. Colorectal cancer risk and dietary intake of calcium, vitamin D, and dairy products: a metaanalysis of 26,335 cases from 60 observational studies. Nutr Cancer. 2009; 61: Bertone-Johnson ER, Chen WY, Holick MF, et al. Plasma 25- hydroxyvitamin D and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and risk of breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005; 14: Garland CF, Gorham ED, Mohr SB, et al. Vitamin D and prevention of breast cancer: pooled analysis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007; 103: Lin J, Manson JE, Lee IM, Cook NR, Buring JE, Zhang SM. Intakes of calcium and vitamin D and breast cancer risk in women. Arch Intern Med. 2007; 167: Robien K, Cutler GJ, Lazovich D. Vitamin D intake and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women: the Iowa Women's Health Study. Cancer Causes Control. 2007; 18:
15 39. Freedman DM, Chang SC, Falk RT, et al. Serum levels of vitamin D metabolites and breast cancer risk in the prostate, lung, colorectal, and ovarian cancer screening trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008; 17: Munger KL, Levin LI, Hollis BW, Howard NS, Ascherio A. Serum 25- hydroxyvitamin D levels and risk of multiple sclerosis. JAMA. 2006; 296: Gillespie KM. Type 1 diabetes: pathogenesis and prevention. CMAJ. 2006; 175: Hypponen E, Laara E, Reunanen A, Jarvelin MR, Virtanen SM. Intake of vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes: a birth-cohort study. Lancet. 2001; 358: Zipitis CS, Akobeng AK. Vitamin D supplementation in early childhood and risk of type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Arch Dis Child. 2008; 93: Hope-Simpson RE. The role of season in the epidemiology of influenza. J Hyg (Lond). 1981; 86: Cannell JJ, Vieth R, Umhau JC, et al. Epidemic influenza and vitamin D. Epidemiol Infect. 2006; 134: Ginde AA, Mansbach JM, Camargo CA, Jr. Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169: Zasloff M. Fighting infections with vitamin D. Nat Med. 2006; 12:
16 48. Nnoaham KE, Clarke A. Low serum vitamin D levels and tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2008; 37: Chocano-Bedoya P, Ronnenberg AG. Vitamin D and tuberculosis. Nutr Rev. 2009; 67: Autier P, Gandini S. Vitamin D supplementation and total mortality: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. 2007; 167: Giovannucci E. Can vitamin D reduce total mortality? Arch Intern Med. 2007; 167:
25-hydroxyvitamin D: from bone and mineral to general health marker
 DIABETES 25 OH Vitamin D TOTAL Assay 25-hydroxyvitamin D: from bone and mineral to general health marker FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Vitamin D Receptors Brain Heart Breast Colon Pancreas Prostate
DIABETES 25 OH Vitamin D TOTAL Assay 25-hydroxyvitamin D: from bone and mineral to general health marker FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Vitamin D Receptors Brain Heart Breast Colon Pancreas Prostate
Key words: Vitamin D Production, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Vitamin D Treatment
 Title: Vitamin D Author: Kerry Lynn Kuffenkam Date: 4-29-09 Key words: Vitamin D Production, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Vitamin D Treatment Abstract: Since the term Vitamin D contains the word vitamin most
Title: Vitamin D Author: Kerry Lynn Kuffenkam Date: 4-29-09 Key words: Vitamin D Production, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Vitamin D Treatment Abstract: Since the term Vitamin D contains the word vitamin most
Vitamin D. Sources of vitamin D
 1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
Vitamin D und seine Bedeutung im Immunsystem und bei der Infektabwehr
 Vitamin D und seine Bedeutung im Immunsystem und bei der Infektabwehr Stefan Pilz Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Medical University of Graz, Austria Department
Vitamin D und seine Bedeutung im Immunsystem und bei der Infektabwehr Stefan Pilz Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Medical University of Graz, Austria Department
D. Vitamin D. 1. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3
 D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease. Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D.
 Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D. Frequently Asked Questions
 Vitamin D Frequently Asked Questions What is vitamin D? What is a vitamin? Why do we need vitamins? Is there more than one form of vitamin D? Where do I get vitamin D? How long should I be outdoors, and
Vitamin D Frequently Asked Questions What is vitamin D? What is a vitamin? Why do we need vitamins? Is there more than one form of vitamin D? Where do I get vitamin D? How long should I be outdoors, and
Selected Questions and Answers on Vitamin D
 Selected Questions and Answers on Vitamin D Joint FAQs to the BfR, German Nutrition Society (DGE) und Max Rubner-Institute (MRI) of 03 December 2014 1 Vitamin D promotes the intake of calcium from the
Selected Questions and Answers on Vitamin D Joint FAQs to the BfR, German Nutrition Society (DGE) und Max Rubner-Institute (MRI) of 03 December 2014 1 Vitamin D promotes the intake of calcium from the
Nutrition for Family Living
 Susan Nitzke, Nutrition Specialist; [email protected] Sherry Tanumihardjo, Nutrition Specialist; [email protected] Amy Rettammel, Outreach Specialist; [email protected] Betsy Kelley,
Susan Nitzke, Nutrition Specialist; [email protected] Sherry Tanumihardjo, Nutrition Specialist; [email protected] Amy Rettammel, Outreach Specialist; [email protected] Betsy Kelley,
Press Information. Vitamin D deficiency
 DSM, Corporate Communications P.O. Box 6500, 6401 HJ Heerlen The Netherlands phone +31 (0) 45 578 2421 www.dsm.com Vitamin D is one of the essential nutrients for human health. Unlike other types of vitamins
DSM, Corporate Communications P.O. Box 6500, 6401 HJ Heerlen The Netherlands phone +31 (0) 45 578 2421 www.dsm.com Vitamin D is one of the essential nutrients for human health. Unlike other types of vitamins
Vitamin D. Why Vitamin D is important and how to get enough
 Vitamin D Why Vitamin D is important and how to get enough Why is vitamin D vital for health? Vitamin D is needed by the body for both physical and mental health, but is best known for making sure bones
Vitamin D Why Vitamin D is important and how to get enough Why is vitamin D vital for health? Vitamin D is needed by the body for both physical and mental health, but is best known for making sure bones
Question I. A vitamin D deficient mother will give birth. A. True B. False. Answer A
 Vitamin D Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Question I A vitamin D deficient mother will give birth to an infant with Vit D deficiency A. True B. False Answer A Question II Human breast milk has adequate amounts
Vitamin D Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Question I A vitamin D deficient mother will give birth to an infant with Vit D deficiency A. True B. False Answer A Question II Human breast milk has adequate amounts
YOUR TRUSTED SOURCE - FOR ALL YOUR VITAMIN D 3 NEEDS
 Vitamin D YOUR TRUSTED SOURCE - FOR ALL YOUR VITAMIN D 3 NEEDS ü Natural form of vitamin D 3, cholecalciferol (from lanolin) ü Strengths from 400 iu to 10,000 iu ü Capsule and liquid forms available ü
Vitamin D YOUR TRUSTED SOURCE - FOR ALL YOUR VITAMIN D 3 NEEDS ü Natural form of vitamin D 3, cholecalciferol (from lanolin) ü Strengths from 400 iu to 10,000 iu ü Capsule and liquid forms available ü
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease. Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D.
 Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Hold the Sunscreen: Your Body Needs that Vitamin D
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hold-the-sunscreen-your-body-needs-that-vitamind/4149/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hold-the-sunscreen-your-body-needs-that-vitamind/4149/
Nutrition and Parkinson s Disease: Can food have an impact? Sarah Zangerle, RD, CD Registered Dietitian Froedtert Memorial Lutheran Hospital
 Nutrition and Parkinson s Disease: Can food have an impact? Sarah Zangerle, RD, CD Registered Dietitian Froedtert Memorial Lutheran Hospital Importance of Nutrition & Parkinson s Disease Good nutrition
Nutrition and Parkinson s Disease: Can food have an impact? Sarah Zangerle, RD, CD Registered Dietitian Froedtert Memorial Lutheran Hospital Importance of Nutrition & Parkinson s Disease Good nutrition
Calcium. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nuf40101 Last reviewed: 02/19/2013 1
 Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
FOR HEALTH. Huldschinsky 1919. Rickets THE D-LIGHTFUL VITAMIN. Solar UV Radiation. Treated VITAMIN D TOXIC OH FROM SUN EXPOSURE. with Mercury Arc Lamp
 THE D-LIGHTFUL VITAMIN W DO YOU MAKE VITAMIN D???? FOR HEALTH Michael F. Holick Boston University Medical Center Solar UV Radiation 7-DHC UV PreD 3 UV UV Tachysterol 3 7-DHC CH2 Vitamin D 3 ΔH PreD 3 Vitamin
THE D-LIGHTFUL VITAMIN W DO YOU MAKE VITAMIN D???? FOR HEALTH Michael F. Holick Boston University Medical Center Solar UV Radiation 7-DHC UV PreD 3 UV UV Tachysterol 3 7-DHC CH2 Vitamin D 3 ΔH PreD 3 Vitamin
Vitamin D and Cardiometabolic risk
 Vitamin D and Cardiometabolic risk 서울의대, 분당서울대병원 내과 최 성 희 2013년 대한당뇨병학회 춘계학술대회 Metabolism Of Vitamin D Risk factors for vitamin D deficiency - Aging decreased concentrations of 7-dehydro-cholesterol in
Vitamin D and Cardiometabolic risk 서울의대, 분당서울대병원 내과 최 성 희 2013년 대한당뇨병학회 춘계학술대회 Metabolism Of Vitamin D Risk factors for vitamin D deficiency - Aging decreased concentrations of 7-dehydro-cholesterol in
Vitamin D deficiency: the cause of everything?
 Health problems linked to vitamin D deficiency: Vitamin D deficiency: the cause of everything? Louise Gagné M.D. Family Physician Saskatoon Community Clinic Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Community
Health problems linked to vitamin D deficiency: Vitamin D deficiency: the cause of everything? Louise Gagné M.D. Family Physician Saskatoon Community Clinic Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Community
The WHI 12 Years Later: What Have We Learned about Postmenopausal HRT?
 AACE 23 rd Annual Scientific and Clinical Congress (2014) Syllabus Materials: The WHI 12 Years Later: What Have We Learned about Postmenopausal HRT? JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, FACP, FACE Chief, Division
AACE 23 rd Annual Scientific and Clinical Congress (2014) Syllabus Materials: The WHI 12 Years Later: What Have We Learned about Postmenopausal HRT? JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, FACP, FACE Chief, Division
Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS
 Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Carlos Healey, diagnosed in 2001 The Three Most Common Eye Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis Blood Pressure & Pulse Height & Weight Complete
Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Carlos Healey, diagnosed in 2001 The Three Most Common Eye Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis Blood Pressure & Pulse Height & Weight Complete
Protecting and improving the nation s health. Vitamin D. Information for healthcare professionals
 Protecting and improving the nation s health Vitamin D Information for healthcare professionals 1 Vitamin D: Information for healthcare professionals Why is vitamin D important? Some of the UK population
Protecting and improving the nation s health Vitamin D Information for healthcare professionals 1 Vitamin D: Information for healthcare professionals Why is vitamin D important? Some of the UK population
Vitamin D and You. By Dr. Sherri Tenpenny www.drtenpenny.com www.osteomed2.com
 Vitamin D and You By Dr. Sherri Tenpenny www.drtenpenny.com www.osteomed2.com What is Vitamin D? Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin produced in the body when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin.
Vitamin D and You By Dr. Sherri Tenpenny www.drtenpenny.com www.osteomed2.com What is Vitamin D? Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin produced in the body when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin.
Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age
 Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
ECONOMIC COSTS OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY
 ECONOMIC COSTS OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY This fact sheet highlights the prevalence and health-consequences of physical inactivity and summarises some of the key facts and figures on the economic costs of
ECONOMIC COSTS OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY This fact sheet highlights the prevalence and health-consequences of physical inactivity and summarises some of the key facts and figures on the economic costs of
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand
 Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
Vitamin D & Iron Dosing Guidelines
 Vitamin D & Iron Dosing Guidelines Ayman Khmour, MD I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program. Objectives Review Ca metabolism Review Recent AAP Guidelines Review CMH
Vitamin D & Iron Dosing Guidelines Ayman Khmour, MD I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program. Objectives Review Ca metabolism Review Recent AAP Guidelines Review CMH
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model
 Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Elderly nursing home residents have a high risk of falls 1
 BRIEF REPORTS A Higher Dose of Vitamin D Reduces the Risk of Falls in Nursing Home Residents: A Randomized, Multiple-Dose Study Kerry E. Broe, MPH, Tai C. Chen, PhD, w Janice Weinberg, ScD, z Heike A.
BRIEF REPORTS A Higher Dose of Vitamin D Reduces the Risk of Falls in Nursing Home Residents: A Randomized, Multiple-Dose Study Kerry E. Broe, MPH, Tai C. Chen, PhD, w Janice Weinberg, ScD, z Heike A.
Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D
 Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D Contents Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D 1. Introduction. 3 2. Product Data Sheet..... 5 3. Product Performances...... 6 4. Product Analysis....... 9 5.
Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D Contents Monoclonal Antibodies to 25OH Vitamin D 1. Introduction. 3 2. Product Data Sheet..... 5 3. Product Performances...... 6 4. Product Analysis....... 9 5.
The Association of Vitamin D Dietary Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Among African Americans in Central Ohio
 The Association of Vitamin D Dietary Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Among African Americans in Central Ohio Presenter: Sin Nee Ng Advisors: Dr. Julie Kennel, Dr. Tonya Orchard Copyright 2014 Sin Nee Ng. All
The Association of Vitamin D Dietary Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Among African Americans in Central Ohio Presenter: Sin Nee Ng Advisors: Dr. Julie Kennel, Dr. Tonya Orchard Copyright 2014 Sin Nee Ng. All
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Healthy Aging Lab: Current Research Abstracts
 Healthy Aging Lab: Current Research Abstracts Arsenic Exposure and Women s Health Environmental exposure to inorganic arsenic is an indisputable source of increased risk of several human cancers and chronic
Healthy Aging Lab: Current Research Abstracts Arsenic Exposure and Women s Health Environmental exposure to inorganic arsenic is an indisputable source of increased risk of several human cancers and chronic
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM
 NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone Number:
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone Number:
A POWERFUL COMBINATION. This educational resource is intended for healthcare professionals.
 A POWERFUL COMBINATION This educational resource is intended for healthcare professionals. 1 oats dairy= FILLING FOOD GAPS essential NUTRIENTS OATS + DAIRY = BETTER TOGETHER Dairy products and oats contain
A POWERFUL COMBINATION This educational resource is intended for healthcare professionals. 1 oats dairy= FILLING FOOD GAPS essential NUTRIENTS OATS + DAIRY = BETTER TOGETHER Dairy products and oats contain
Homework Help Heart Disease & Stroke
 Preventing Heart Disease & Stroke What causes heart disease and stroke? high blood pressure high cholesterol diabetes smoking stress drinking too much alcohol not being physically active being overweight
Preventing Heart Disease & Stroke What causes heart disease and stroke? high blood pressure high cholesterol diabetes smoking stress drinking too much alcohol not being physically active being overweight
Vitamin D (serum, plasma)
 Vitamin D (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Vitamin D 1.2 Alternative names The term vitamin D covers a group of closely related naturally occurring lipid soluble compounds
Vitamin D (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Vitamin D 1.2 Alternative names The term vitamin D covers a group of closely related naturally occurring lipid soluble compounds
GUIDE FOR VITAMIN D IN CHILDHOOD
 GUIDE FOR VITAMIN D IN CHILDHOOD October 2013 Introduction There are many different recommendations for the prevention, detection and treatment of Vitamin D deficiency in the UK. The following is a practical
GUIDE FOR VITAMIN D IN CHILDHOOD October 2013 Introduction There are many different recommendations for the prevention, detection and treatment of Vitamin D deficiency in the UK. The following is a practical
If you were diagnosed with cancer today, what would your chances of survival be?
 Q.1 If you were diagnosed with cancer today, what would your chances of survival be? Ongoing medical research from the last two decades has seen the cancer survival rate increase by more than 40%. However
Q.1 If you were diagnosed with cancer today, what would your chances of survival be? Ongoing medical research from the last two decades has seen the cancer survival rate increase by more than 40%. However
Vitamin D and Calcium Guideline
 Vitamin D and Calcium Guideline Vitamin D Functions of Vitamin D 2 Serum Levels 2 Deficiency 2 Toxicity 2 Dietary Reference Intakes 3 Sources of Vitamin D 3 Therapeutic Options 4 Adults 4 Children (0 18
Vitamin D and Calcium Guideline Vitamin D Functions of Vitamin D 2 Serum Levels 2 Deficiency 2 Toxicity 2 Dietary Reference Intakes 3 Sources of Vitamin D 3 Therapeutic Options 4 Adults 4 Children (0 18
Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
 BONE HEALTH FOR LIFE Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and
BONE HEALTH FOR LIFE Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and
Why you and your Family Should Get the Flu Shot
 Why you and your Family Should Get the Flu Shot Why Get VaCCinated against influenza? Influenza (flu) is a virus that can lead to serious complications, hospitalization, or even death. Even healthy children
Why you and your Family Should Get the Flu Shot Why Get VaCCinated against influenza? Influenza (flu) is a virus that can lead to serious complications, hospitalization, or even death. Even healthy children
The Health Academy e-learning COURSES
 Health Information in Tomorrow s World The Health Academy e-learning COURSES Courses Developed 1 1. All the Way to the Blood Bank Around the world, AIDS is shattering young people's opportunities for healthy
Health Information in Tomorrow s World The Health Academy e-learning COURSES Courses Developed 1 1. All the Way to the Blood Bank Around the world, AIDS is shattering young people's opportunities for healthy
Health Benefits of Grass-Fed Products
 Health Benefits of Grass-Fed Products As you will see, products from pastured animals are ideal for your health. Similar to wild game, they contain the amounts and kinds of nutrients that your body "expects"
Health Benefits of Grass-Fed Products As you will see, products from pastured animals are ideal for your health. Similar to wild game, they contain the amounts and kinds of nutrients that your body "expects"
Evidence-Based Practice for Public Health Identified Knowledge Domains of Public Health
 1 Biostatistics Statistical Methods & Theory Evidence-Based Practice for Public Health Identified Knowledge Domains of Public Health General Public Health Epidemiology Risk Assessment Population-Based
1 Biostatistics Statistical Methods & Theory Evidence-Based Practice for Public Health Identified Knowledge Domains of Public Health General Public Health Epidemiology Risk Assessment Population-Based
Vitamin supplements and you
 Vitamin supplements and you Guidance for pregnant or breastfeeding women, babies and young children Health Improvement About this leaflet Vitamins are really important they are essential nutrients that
Vitamin supplements and you Guidance for pregnant or breastfeeding women, babies and young children Health Improvement About this leaflet Vitamins are really important they are essential nutrients that
Epidemic Vitamin D Deficiency Among Patients in an Elderly Care Rehabilitation Facility Stefan Schilling
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemic Vitamin D Deficiency Among Patients in an Elderly Care Rehabilitation Facility Stefan Schilling SUMMARY Background: Many benefits are ascribed to vitamin D beyond its well-known
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemic Vitamin D Deficiency Among Patients in an Elderly Care Rehabilitation Facility Stefan Schilling SUMMARY Background: Many benefits are ascribed to vitamin D beyond its well-known
Smaller Waistlines, Sharper Minds, Stronger Bones and Healthier Hearts?
 Telephone: (212) 986-9415 Fax: (212) 697-8658 www.teausa.org 362 5th AVENUE, SUITE 801, NEW YORK, NY 10001 Smaller Waistlines, Sharper Minds, Stronger Bones and Healthier Hearts? New Findings Released
Telephone: (212) 986-9415 Fax: (212) 697-8658 www.teausa.org 362 5th AVENUE, SUITE 801, NEW YORK, NY 10001 Smaller Waistlines, Sharper Minds, Stronger Bones and Healthier Hearts? New Findings Released
The Women s Health Initiative: The Role of Hormonal Therapy in Disease Prevention
 The Women s Health Initiative: The Role of Hormonal Therapy in Disease Prevention Robert B. Wallace, MD, MSc Departments of Epidemiology and Internal Medicine University of Iowa College of Public Health
The Women s Health Initiative: The Role of Hormonal Therapy in Disease Prevention Robert B. Wallace, MD, MSc Departments of Epidemiology and Internal Medicine University of Iowa College of Public Health
GUIDE TO THE FORMAT OF PROPOSED FDA 4 CLAIM LEVELS
 GUIDE TO THE FORMAT OF PROPOSED FDA 4 CLAIM LEVELS 1 Product Component Disease Orange Juice Calcium Osteoporosis Pasta Sauce Lycopene (20 mg) Certain cancers, including prostate cancer in men Breakfast
GUIDE TO THE FORMAT OF PROPOSED FDA 4 CLAIM LEVELS 1 Product Component Disease Orange Juice Calcium Osteoporosis Pasta Sauce Lycopene (20 mg) Certain cancers, including prostate cancer in men Breakfast
GUIDELINES FOR THE PRESCRIBING OF VITAMIN D IN ADULTS
 GUIDELINES FOR THE PRESCRIBING OF VITAMIN D IN ADULTS This guidance has been adapted from the North of Tyne Guideline Group guidelines, published in 2011. The treatment of children has been removed, as
GUIDELINES FOR THE PRESCRIBING OF VITAMIN D IN ADULTS This guidance has been adapted from the North of Tyne Guideline Group guidelines, published in 2011. The treatment of children has been removed, as
Fact Sheet: The Affordable Care Act s New Rules on Preventive Care July 14, 2010
 Fact Sheet: The Affordable Care Act s New Rules on Preventive Care July 14, 2010 Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, are responsible for 7 of 10 deaths among Americans each year
Fact Sheet: The Affordable Care Act s New Rules on Preventive Care July 14, 2010 Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, are responsible for 7 of 10 deaths among Americans each year
African Americans & Cardiovascular Diseases
 Statistical Fact Sheet 2013 Update African Americans & Cardiovascular Diseases Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) (ICD/10 codes I00-I99, Q20-Q28) (ICD/9 codes 390-459, 745-747) Among non-hispanic blacks age
Statistical Fact Sheet 2013 Update African Americans & Cardiovascular Diseases Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) (ICD/10 codes I00-I99, Q20-Q28) (ICD/9 codes 390-459, 745-747) Among non-hispanic blacks age
Fact Sheet on Vitamin D
 Fact Sheet on Vitamin D DISCLAIMER: This Fact Sheet Does Not Constitute Medical Advice. This sheet is a compilation of recommendations by top researchers. These recommendations may or may not apply to
Fact Sheet on Vitamin D DISCLAIMER: This Fact Sheet Does Not Constitute Medical Advice. This sheet is a compilation of recommendations by top researchers. These recommendations may or may not apply to
Mediterranean diet: A heart-healthy eating plan Source: mayoclinic.org/mediterranean-diet
 Mediterranean diet: A heart-healthy eating plan Source: mayoclinic.org/mediterranean-diet The heart-healthy Mediterranean is a healthy eating plan based on typical foods and recipes of Mediterranean-style
Mediterranean diet: A heart-healthy eating plan Source: mayoclinic.org/mediterranean-diet The heart-healthy Mediterranean is a healthy eating plan based on typical foods and recipes of Mediterranean-style
Presentation Prepared By: Jessica Rivers, BASc., PTS
 Presentation Prepared By: Jessica Rivers, BASc., PTS Presentation Outline Why should we care about our eating habits? Why is nutrition so important as we age? How do we know if we are eating healthy? What
Presentation Prepared By: Jessica Rivers, BASc., PTS Presentation Outline Why should we care about our eating habits? Why is nutrition so important as we age? How do we know if we are eating healthy? What
Vitamin D and Fracture Reduction: An Evaluation of the Existing Research Susan E. Brown, PhD, CNS
 Reduction: An Evaluation of the Existing Research Susan E. Brown, PhD, CNS Abstract This article re-evaluates the literature on vitamin D and fracture reduction, highlighting the relevance of new understandings
Reduction: An Evaluation of the Existing Research Susan E. Brown, PhD, CNS Abstract This article re-evaluates the literature on vitamin D and fracture reduction, highlighting the relevance of new understandings
HS58A. Healthy Start vitamins and why you need them
 HS58A Healthy Start vitamins and why you need them Folic acid Taking a folic acid supplement before you re pregnant and until the 12th week of your pregnancy is really important because it reduces the
HS58A Healthy Start vitamins and why you need them Folic acid Taking a folic acid supplement before you re pregnant and until the 12th week of your pregnancy is really important because it reduces the
Screening Mammography for Breast Cancer: American College of Preventive Medicine Practice Policy Statement
 Screening Mammography for Breast Cancer: American College of Preventive Medicine Practice Policy Statement Rebecca Ferrini, MD, Elizabeth Mannino, MD, Edith Ramsdell, MD and Linda Hill, MD, MPH Burden
Screening Mammography for Breast Cancer: American College of Preventive Medicine Practice Policy Statement Rebecca Ferrini, MD, Elizabeth Mannino, MD, Edith Ramsdell, MD and Linda Hill, MD, MPH Burden
Using Family History to Improve Your Health Web Quest Abstract
 Web Quest Abstract Students explore the Using Family History to Improve Your Health module on the Genetic Science Learning Center website to complete a web quest. Learning Objectives Chronic diseases such
Web Quest Abstract Students explore the Using Family History to Improve Your Health module on the Genetic Science Learning Center website to complete a web quest. Learning Objectives Chronic diseases such
Vitamin D Status: United States, 2001 2006
 Vitamin D Status: United States, 2001 2006 Anne C. Looker, Ph.D.; Clifford L. Johnson, M.P.H.; David A. Lacher, M.D.; Christine M. Pfeiffer, Ph.D.; Rosemary L. Schleicher, Ph.D.; and Christopher T. Sempos,
Vitamin D Status: United States, 2001 2006 Anne C. Looker, Ph.D.; Clifford L. Johnson, M.P.H.; David A. Lacher, M.D.; Christine M. Pfeiffer, Ph.D.; Rosemary L. Schleicher, Ph.D.; and Christopher T. Sempos,
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Anemia and chronic kidney disease
 Anemia and chronic kidney disease THE KIDNEY FOUNDATION OF CANADA 1 Anemia and chronic kidney disease What is anemia? Anemia is a condition in which the red cells in the blood are at a low level. The red
Anemia and chronic kidney disease THE KIDNEY FOUNDATION OF CANADA 1 Anemia and chronic kidney disease What is anemia? Anemia is a condition in which the red cells in the blood are at a low level. The red
KDIGO. Active and Native Vitamin D
 Active and Native Vitamin D KDIGO Grahame Elder Department of Renal Medicine, Westmead Hospital Osteoporosis & Bone Biology Division, Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Sydney Disclosures Member of
Active and Native Vitamin D KDIGO Grahame Elder Department of Renal Medicine, Westmead Hospital Osteoporosis & Bone Biology Division, Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Sydney Disclosures Member of
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
 Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Us TOO University Presents: Estrogen Deficiency Side Effects Due to Androgen Deprivation Therapy
 Us TOO University Presents: Estrogen Deficiency Side Effects Due to Androgen Deprivation Therapy Today s speaker is Samir Taneja, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible
Us TOO University Presents: Estrogen Deficiency Side Effects Due to Androgen Deprivation Therapy Today s speaker is Samir Taneja, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible
The Skinny on Visceral Fat
 The Skinny on Visceral Fat Fat stored deep in the belly is the most harmful kind. Find out how to cut it down to size. People can carry their extra weight in different places on the body: All over On the
The Skinny on Visceral Fat Fat stored deep in the belly is the most harmful kind. Find out how to cut it down to size. People can carry their extra weight in different places on the body: All over On the
The VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL)
 The VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL) JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH Principal Investigator, VITAL Brigham and Women's Hospital Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women s Health
The VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL) JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH Principal Investigator, VITAL Brigham and Women's Hospital Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women s Health
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis
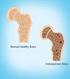 Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels. Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD
 A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD The sunshine vitamin Existed over 500 million years. Prehormone, not only a vitamin. Two major sources:
A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD The sunshine vitamin Existed over 500 million years. Prehormone, not only a vitamin. Two major sources:
chocolate milk Tasty Nutrition
 chocolate milk Tasty Nutrition Nutrition is everything. Good nutrition is vital to our children. Moms want it. Schools want it. Everyone agrees. But are they getting it? Many kids are still falling short
chocolate milk Tasty Nutrition Nutrition is everything. Good nutrition is vital to our children. Moms want it. Schools want it. Everyone agrees. But are they getting it? Many kids are still falling short
Fat-Soluble Vitamins. Quick Facts... Vitamin A. by J. Anderson and L. Young 1 (8/08)
 Fat-Soluble s by J. Anderson and L. Young 1 (8/08) Quick Facts... Small amounts of vitamins A, D, E and K are needed to maintain good health. Foods that contain these vitamins will not lose them when cooked.
Fat-Soluble s by J. Anderson and L. Young 1 (8/08) Quick Facts... Small amounts of vitamins A, D, E and K are needed to maintain good health. Foods that contain these vitamins will not lose them when cooked.
Unintended consequences: Successful social marketing campaign creates health problems
 Unintended consequences: Successful social marketing campaign creates health problems Professor Linda Brennan (corresponding author RMIT, Melbourne Australia ) Professor Gillian Sullivan Mort (presenting
Unintended consequences: Successful social marketing campaign creates health problems Professor Linda Brennan (corresponding author RMIT, Melbourne Australia ) Professor Gillian Sullivan Mort (presenting
Considerations With Calcium And Vitamin D Supplementation
 Considerations With Calcium And Vitamin D Supplementation Activity Preview Calcium is an electrolyte involved in many systems in the body including bone health, nerve signaling pathways, muscle contractions,
Considerations With Calcium And Vitamin D Supplementation Activity Preview Calcium is an electrolyte involved in many systems in the body including bone health, nerve signaling pathways, muscle contractions,
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body. Vitamin A
 What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body Vitamin A Prevents skin disorders, such as acne, wrinkling and age spots. Enhances the immune system protects against colds, flu, and infections to kidney,
What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body Vitamin A Prevents skin disorders, such as acne, wrinkling and age spots. Enhances the immune system protects against colds, flu, and infections to kidney,
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
