Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
- Ambrose Farmer
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVIEW ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis Wilson Campos Tavares Junior 1, Renata Rolim 2, Adriana Maria Kakehasi 3 ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory polyarthritis that often leads to progressive joint destruction and disability. The treatment and management of RA has been based on early identification of the disease and intervention with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Changes in management have resulted in significant improvements for patients with RA, including reduction of signs and symptoms of disease, joint preservation, and reduction of structural damage progression. In addition, sensitive methods to assess treatment response and predict the course of disease are required. Regarding early diagnosis of RA, longitudinal studies have demonstrated that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is more sensitive than X-rays to demonstrate the presence and progression of bone erosions. On the other hand, many factors of poor prognostics have been linked to RA, including demographic, genetic, environmental, clinical, immunological, and radiographic. This paper presents considerations on the use of MRI in RA regarding diagnose, monitoring, and prognostic of disease. Keywords: arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, magnetic resonance imaging Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved. THE IMPORTANCE OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory polyarthritis, which frequently leads to progressive joint destruction and disability. Regarding early diagnosis of RA, longitudinal studies have demonstrated that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is more sensitive than radiography in demonstrating progressive erosive joint damage. 1 MRI is an important imaging technique that provides multiplanar images and is able to visualize a range of joint structures, including synovium, tendons, ligaments, bone, and cartilage. It does not use radiation, so it can be repeated as much as necessary, and allows longitudinal assessment. With the advances in sequence analysis software and lower costs, MRI is likely to become more accessible. MRI is recognized as the imaging technology of choice for visualization of the inflamed synovial membrane and bone edema. 2 Furthermore, MRI has been shown to be a sensitive, non-invasive method for detection and quantification of bone erosions. 3 Erosions are visible on MRI on average two years before they are visible on radiographs and may become consistently visualized on radiographs of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints only when 20% 30% of the bone is eroded on MRI. 1 To assess and quantify the disease manifestation in RA, the degree of synovial inflammation (synovitis), bone marrow edema, erosions, and tenosynovitis, several scoring systems have been suggested, and the Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid-Arthritis Clinical Trials (OMERACT) and Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Image Scoring system (RAMRIS) are the most studied and used in clinical practice. 1,4 Received on 12/25/2010. Approved on 08/30/2011. Authors declare no conflict of interests. Hospital das Clínicas of the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais HC/UFMG. 1. Physician Assistant of Radiology at the Hospital das Clínicas of the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais HC/UFMG; Radiologist Physician of the Ecoar Medicina Diagnóstica 2. Resident Physician at the HC/UFMG 3. Doctor, Professor of Rheumatology at Faculdade de Medicina da UFMG Correspondence to: Wilson Campos Tavares Junior. Rua Gonçalves Dias, 750/1803 Funcionários. CEP: Belo Horizonte, MG, Brasil. [email protected] Rev Bras Reumatol 2011;51(6):
2 Tavares Junior et al. Ultrasound (US) is commonly used to assess soft tissue disease or detect articular fluid collection. High-frequency US transducers enable ultrasonographic assessment of small joints. It can also be used to visualize others structures, such as cartilage and bone surface, and can detect cortical defects, extensor tendon sheath thickening and synovial proliferation. However, the diagnostic ultrasound does not provide useful information on intraosseous pathologies. Adequate skill of the sonographers is another requirement for this method. Few studies have investigated the differential diagnostic value of MRI, with divergent results. The use of MRI for detection of synovitis in hands and wrists have shown some improvement in diagnostic accuracy (94% vs. 83%) in early undifferentiated arthritis patients. 5 In a study of patients with RA, systemic lupus erythematosus, and primary Sjögren s syndrome with polyarthralgia involving the hand, the presence of bone edema in the MCP joints was much more common in RA patients. 6 Among 41 polyartrhitis patients who were unclassified despite clinical, biochemical and radiographic examinations, the application of the correct MRI classification as RA or non-ra was shown in 39 of 41 patient, when a revision was made after two years using the 1987 American College of Rheumatoloy (ACR) criteria. 7 Results from a recent systematic review showed that anticyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-ccp2) antibodies in patients with RA for less than two years have almost identical sensitivity to rheumatoid factor (56% vs. 58%), although with considerably higher specificity. In early RA, a positive anti-ccp2 test showed a positive likelihood ratio of 12.7, but sensitivity was higher in studies of established RA. Sensitivity for predicting RA before symptom onset seems lower, although specificity remains high. 8 MRI TECHNIQUE In early RA, wrist and hand involvement are usually bilateral. Some authors perform bilateral MRI of the wrists or hands, but the study of the dominant or more painful wrist is routinely used, assuming that the joint involvement in this wrist will be higher than in the other wrist and hand. The use of MRI in a single hand reduces time, cost and discomfort for the patient. The areas of interest are wrists, MCP joints, and proximal interphalangeal joints. The distal radius and ulna, the carpal bones, and the MCP joints can be visualized together within a Field of View of mm. 9 Usually, MRI studies of RA patients have focused on one or two joint regions most frequently the wrist and on the second through fifth MCP joints. Consequently, MRI may reduce the sample size of joints and follow-up time in exams, due to greater sensitivity in distinguishing between responders and non-responders, as corroborated in clinical trials. 10,11 Basic interpretation of RA changes on MRI among readers is relatively consistent. 12 The OMERACT group recommends starting with a coronal STIR sequence or a Fat Saturated T2 sequence (only available in high-field scanners > 0.6 T) on the wrist and MCP joints for bone marrow edema detection, followed by a 3D isotropic T1-w gradient echo sequence; or a T1 sequence on the coronal and axial plane before and after gadolinium contrast for detection of bone erosions and synovitis. Intravenous contrast is necessary to estimate the degree of synovial inflammation and to differentiate the synovial membrane enhancement from the surrounding tissues. Synovitis tends to be overestimated if it is scored based on the STIR or T2 fat-saturated images, because joint effusion cannot be differentiated from synovitis when using T2 sequences. 1,13 Before the RAMRIS score was developed, manual measurement of the volume of enhancing synovium was used as a measure of treatment response and was recognized as a strong predictor of future disease progression. 1 Table 1 shows the main pattern of MRI in RA. MRI FINDINGS Synovitis The thickening of synovial tissue caused by the rheumatoid inflammatory process may be identified on MRI. Synovitis has Table 1 Main pattern of MRI in RA Characteristics Joints regions examined MRI damage signs Equipment-magnetic type Contrast Sequence Monitoring response therapy (score) Specifications Wrist and second through fifth metacarpophalangeal unilateral, the most painful Edema, synovitis, erosion, tenosynovitis Magnetic field recommendation is 1.5 Tesla Gadolinium Coronal T1, axial T1, coronal T2 with fat saturation, contrast enhanced axial and coronal T1 with fat saturation OMERACT/RAMRIS, synovium volume measurement, scoring contrast-enhanced dynamic OMERACT/RAMRIS: Outcome Measurement Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials/Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System. 630 Rev Bras Reumatol 2011;51(6):
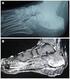
3 Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis an intermediate to low signal intensity on T1-weighted images and, due to the increased water content, high signal intensity on T2-weighted images. 2 MRI signs of synovitis include increased synovial volume, increased water content, contrast enhancement (increased signal intensity after the intravenous injection of gadolinium-based contrast material) (Figure 1). 2 MRI is more sensitive than clinical examination in detecting synovitis in inflammatory arthritis and shows synovial inflammation in early RA. 14,15 On RA, the hypertrophic active synovium can invade and erode contiguous bone and cartilage. Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image is considered very sensitive and specific for assessment of acute synovitis, as reported in an article of Ostendorf et al. 16 When examined the second MCP joint using miniarthroscopy and MRI, it shows enhancement postcontrast in 86% of synovitis patients. 16 McQueen et al. 17 found that 93% of a cohort of 42 RA patients had evidence of MRI synovitis at the wrist within 6 months of the onset of symptoms. Acute synovitis has been shown to enhance rapidly and intensely after the intravenous administration of gadolinium-based contrast material, unlike joint effusion, which does not enhance in the early phase. This early phase lasts approximately 5 minutes after injection. Images obtained from 10 minutes after injection may not accurately delineate the extent of the synovitis, since gadolinium may be excreted into the synovial joint fluid. Fibrotic pannus, which is usually present in end-stage of RA, appears relatively hypovascular after the intravenous administration of gadolinium. Moreover, with T2-weighted sequences, fibrous pannus with intermediate to low signal intensity can be distinguished from acute synovitis and joint fluid. 2,18,19 Bone marrow edema Although bone marrow edema is nonspecific and has been well documented in traumatic, neoplastic, and degenerative bone processes, it is reported to be an important MRI finding in patients with RA, especially in the earlier phases of the disease. Bone edema refers to a unique MRI-detected abnormality with high signal intensity on fat-suppressed MRI sequences and could enhance after contrast administration (Figure 2). Bone edema is defined by OMERACT as a lesion within the trabecular bone with ill-defined margins and signal characteristics of increased water content. 20 When present, it correlates with the severity of adjacent synovitis and it seems to be an independent predictor of erosion development. 21 An image study of the wrist in early RA found that bone edema is a strong predictive aspect of the development of conventional radiography erosions and also predicts functional outcome six years later. 22 Rev Bras Reumatol 2011;51(6): A B (COI) Acq ir 201 Acq Tm Figure 1 Synovitis in a 36-year-old man with early RA of the wrist (eight months duration) and normal radiographic finding. (A) Coronal T1-weighted MRI shows radio carpal synovitis as low signal intensity (arrow). (B) Coronal gadolinium-enhanced fat suppressed T1-weighted MRI shows intense enhancement of the radio carpal synovitis. 5 (COI) Figure 2 Bone marrow edema in a 37-year-old man with early RA of the wrist. Coronal T2-weighted MRI shows pyramidal bone edema represented by high signal intensity (arrow)
4 Tavares Junior et al. Erosions The detection of erosions on MRI is important because it contributes for diagnosis and prognosis in RA patients. 23 MRI could provide an early diagnosis of RA by revealing erosions, whose presence constitutes one of the ACR 1987 diagnostic criteria. MRI erosions have been shown to be predictive of later progression in cohorts followed for up to six years. 24 The MRI definitions of erosions on T1-weighted images are loss of normal low signal intensity of cortical bone and loss of normal high signal intensity of the bone marrow cavity, with enhancement after the administration of gadolinium-based contrast material; and high signal intensity on T2-weighted and STIR images (Figure 3). 13 The contrast enhancement of erosions implies the presence of inflamed synovium and is useful differentiating them from fluid-filled cystic lesions. 2 In the carpal bones the nutrient foramina may be shown in some sequences and could be mistaken for small erosions. Similarly, interosseous ligament insertions at the volar aspect of the carpal bones can simulate erosions. A B A Figure 4 Tenosynovitis in a 53-year-old woman with early RA of the wrist (16 months duration) and normal radiographic finding. (A) Coronal T1-weighted MR. (B) Coronal gadoliniumenhanced fat suppressed T1 MRI shows extensive flexor tenosynovitis with intense enhancement (arrow) and minimal extensor tenosynovitis with mild enhancement (arrow head). B Some attention is required since small erosion-like lesions were identified in two planes in about 2% of metacarpal and wrist bones in healthy subjects, but these lesions did not enhance after the administration of gadolinium-based contrast material and were not associated with bone edema. 25 Tenosynovitis Figure 3 Erosions in a 54-year-old woman with early RA of the wrist (12 months duration). (A) Coronal T1-weighted MR unenhanced and gadolinium enhance fat suppressed T1-weighted MRI in axial and coronal. (B) The erosion in the pyramidal bone that is enhanced after gadolinium (arrow). Synovitis is seen in wrist (*). MRI signs of tenosynovitis include fluid in the tendon sheath, increased thickness and contrast enhancement of the tendon sheath synovium (Figure 4). Small amounts of fluid are usually seen in the tendon sheaths of the wrist in healthy subjects, especially in the extensor compartments. When the diameter of the fluid in the tendon sheath is less than the diameter of the corresponding tendon, the fluid could be considered normal. Contrast enhancement of the tendon sheath synovium is considered a specific sign of tenosynovitis. 632 Rev Bras Reumatol 2011;51(6):
5 Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis Tenosynovitis is clinically significant in early RA because joint synovitis and tenosynovitis represent the same process, and in some patients with early RA, tenosynovitis could predominates over joint synovitis. 26 Dorsal tenosynovitis of the wrist is associated with tendon rupture, wich has been described as the invasion of the tendon by the sheath synovitis and fraying of the tendon against eroded bone margins. 27 Predictors of imaging progression Substantial efforts have been exerted to identify patients with poor prognosis at the time of diagnosis and several promising prognostic markers have been identified. 13,27 MRI erosion score and MRI bone marrow edema score were significantly and independently associated with radiographic progression after two years. The main finding was that MRI bone marrow edema at presentation was the strongest predictor of radiographic progression two years later in patients with early RA. 1 Bone marrow edema is considered an early marker of inflammation, given that its presence is correlated with increased levels of acute phase reactants (erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein) and scales for the clinical evaluation of disease activity. 28,29 MRI bone marrow edema may represent inflammatory infiltrate in the bone marrow of RA patient, and these lesions affect a higher percent of bones in established disease than in early disease. 30 In contrast to radiographic erosions, which reflect bone damage that has already occurred, bone marrow edema thus may represent an important part of the early immunopathological development in RA, and it could be reversed if recommended treatment is introduced. 31,32 Methodological studies have reported that the sensitivity for detecting bone marrow edema may vary within different types of MRI units. 7 Regional MRI could be a predictor of radiographic progression in other anatomical regions according to previous studies. 33 Monitoring disease activity and damage Several prospective follow-up imaging studies performed to compare radiography, US, and MRI findings demonstrate that US and MRI are more sensitive for visualization of inflammatory and destructive changes in joints and have major potential for improved examination compared to X-ray. Both US and MRI are in good agreement with clinical findings. 34,35 Traditional scoring systems developed for X-ray are not directly designed for MRI and US; they are predominantly qualitative and based on visual assessment of data with further Rev Bras Reumatol 2011;51(6): grading according to a given scale. Extraction of quantitative measurements is not trivial. Several scoring systems for MRI and US have been suggested over the years. The aim of the new systems is to counteract the limits of traditional evaluation, which is prone to high personnel costs and human errors. Several authors have used quantitative and semiquantitative analyses of synovial volume, more or less effectively linking it to disease activity. 36 Volume measurement are often performed directly by manually outlining the inflamed synovium or erosions, which is a very time-consuming operation. 37 The OMERACT 2001 test the interreader agreement of synovitis on RA joints using MRI demonstrated a moderate level of agreement. 38 The OMERACT 6 group (2003) found high intrarreader agreement for a trained reader. 39 A longitudinal study assessed intra- and interreader reliability shows good intrarreader correlation. 40 Synovitis, bone edema, and erosions on MRI have been defined by the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) MRI Task Force and a scoring system, termed the RA MRI score (RAMRIS), and has been validated and evaluated for sensitivity to change in a longitudinal setting. The RAMRIS system does not, however, include a scoring system for tendons or a score for cartilage loss; this relates to non adequate image resolution of cartilage in small joints. Recently, Haarvardsholm et al. 41 have published a scoring system for tenosynovitis based on semiquantitative scoring (0 3) of flexor and extensor tenosynovitis at the wrist in 10 anatomical areas. The maximum width of postcontrast enhancement within each anatomical area on axial T1-weighted images was scored, producing a potential maximum score of 30. This system was also tested for reliability in a longitudinal setting and provides a useful adjunct for the conventional RAMRIS. The evaluation of cartilage changes on MRI, however, remains an important research goal. The OMERACT synovitis score is sensitive to change of inflamed synovium over weeks as well as months. 2 MRI is being increasingly used when the treatment is associated with biological agents to measure changes in synovitis. MRI is more sensitive than X-ray for monitoring erosive progression in individual joint regions. 42 The score of each synovitis, bone erosions, and bone marrow edema is made from individual joints; synovitis is scored 0 3 in each of the distal radioulnar, radiocarpal, intercarpal-carpometacarpal, and second through fifth MCP joints. Bone changes are scored in each of the carpal bones, distal radius, distal ulna, and metacarpal bases. Erosions are scored 0 10 and edema 0 3, as a fraction of the bone involved within 1 cm of the joint line. 4,6,43 Although the RAMRIS system is specific for wrist and MCP joints, it has been modified for use in the feet, and there is some 633
6 Tavares Junior et al. evidence to suggest that, as with X-rays, MRI of the feet may be more sensitive, revealing changes in the feet even if the hands are not involved. Scoring of the feet may therefore be of use in early disease, and the parameters are the same used for the hands. CONCLUSION The classification criteria for RA published by the ACR in 1987 are useful to ensure a uniform patient population when comparing experience and clinical treatment results between countries, but is not useful for early diagnosis of RA. In 2010, a new classification criteria were introduced with the aim to facilitate the study of patients at earlier stages of the disease. 26 MRI has the importance of detecting bone damage, particularly when radiographs are normal, contributing with this emerging tool for the diagnosis. With the advent of more powerful treatment strategies, the accurate diagnosis is the central topic related to the ability to select and initiate treatment programs, as is the ability to differentiate between responders and non-responders patients. Surely, the MRI characteristics can provide support in many of these aspects of RA management. 634 Rev Bras Reumatol 2011;51(6):
7 Tavares Junior et al. REFERENCES REFERÊNCIAS 1. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd et al rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69(9): Freeston JE, Bird P, Conaghan PG. The role of MRI in rheumatoid arthritis: research and clinical issues. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2009; 21(2): Wakefield RJ, Conaghan PG, Jarrett S, Emery P. Noninvasive techniques for assessing skeletal changes in inflammatory arthritis: imaging technique. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2004; 16(4): Hodgson RJ, O Connor P, Moots R. MRI of rheumatoid arthritis image quantitation for the assessment of disease activity, progression and response to therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008; 47(1): Sugimoto H, Takeda A, Hyodoh K. Early-stage rheumatoid arthritis: prospective study of the effectiveness of MR imaging for diagnosis. Radiology 2000; 216(2): Boutry N, Hachulla E, Flipo RM, Cortet B, Cotton A. MR imaging findings in hands in early rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with those in systemic lupus erythematosus and primary Sjögren syndrome. Radiology 2005; 236(2): Duer A, Østergaard M, Hørslev-Petersen K, Vallø J. Magnetic resonance imaging and bone scintigraphy in the differential diagnosis of unclassified arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2008; 67(1): Whiting PF, Smidt N, Sterne JA, Harbord R, Burton A, Burke M et al. Systematic review: accuracy of anti-citrullinated Peptide antibodies for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 2010; 152: Narváez JA, Narváez J, De Lama E, De Albert M. MR imaging of early rheumatoid arthritis. Radiographics 2010; 30(1): Ejbjerg BJ, Vestergaard A, Jacobsen S, Thomsen HS, Østergaard M. The smallest detectable difference and sensitivity to change of magnetic resonance imaging and radiographic scoring of structural joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis finger, wrist, and toe joints: a comparison of the OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score applied to different joint combinations and the Sharp/van der Heijde radiographic score. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52(8): Hetland ML, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Junker P, Østergaard M, Ejbjerg BJ, Jacobsen S et al. Radiographic progression and remission rates in early rheumatoid arthritis MRI bone oedema and anti-ccp predicted radiographic progression in the 5-year extension of the double-blind randomised CIMESTRA trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69(10): Conaghan PG, Ejbjerg B, Lassere M, Bird P, Peterfy C, Emery P et al. A multicenter reliability study of extremity-magnetic resonance imaging in the longitudinal evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2007; 34(4): Østergaard M, Ejbjerg B, Szkudlarek M. Imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis: roles of magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasonography, conventional radiography and computed tomography. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2005; 19(1): Forslind K, Larsson EM, Johansson A, Svensson B. Detection of joint pathology by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 1997; 36(6): Rev Bras Reumatol 2011;51(6):
8 15. Sugimoto H, Takeda A, Masuyama J, Furuse M. Early-stage rheumatoid arthritis: diagnostic accuracy of MR imaging. Radiology 1996; 198(1): Ostendorf B, Peters R, Dann P, Becker A, Scherer A, Wedekind F et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and miniarthroscopy of metacarpophalangeal joints: sensitive detection of morphologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2001; 44(11): McQueen FM, Stewart N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, Tan PL et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals a high prevalence of erosions at four months after symptom onset. Ann Rheum Dis 1998; 57(6): König H, Sieper J, Wolf KJ. Rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of hypervascular and fibrous pannus with dynamic MR imaging enhanced with Gd-DTPA. Radiology 1990; 176(2): Tamai K, Yamato M, Yamaguchi T, Ohno W. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging for the evaluation of synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1994; 37(8): Østergaard M, Peterfy C, Conaghan P, McQueen F, Bird P, Ejbjerg B et al. OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Core set of MRI acquisitions, joint pathology definitions, and the OMERACT RA-MRI scoring system. J Rheumatol 2003; 30(6): Raza K, Filer A. Predicting the development of RA in patients with early undifferentiated arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2009; 23(1): Conaghan PG, O Connor P, McGonagle D, Astin P, Wakefield RJ, Gibbon WW et al. Elucidation of the relationship between synovitis and bone damage: a randomized magnetic resonance imaging study of individual joints in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48(1): Bøyesen P, Haavardsholm EA, Østergaard M, Van der Heijde D, Sesseng S, Kvien TK. MRI in early rheumatoid arthritis: synovitis and bone marrow oedema are independent predictors of subsequent radiographic progression. Ann Rheum Dis [Epub 2010 Aug 31]. 24. McQueen FM, Benton N, Perry D, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S et al. Bone edema scored on magnetic resonance imaging scans of the dominant carpus at presentation predicts radiographic joint damage of the hands and feet six years later in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48(7): Ejbjerg B, Narvestad E, Rostrup E, Szkudlarek M, Jacobsen S, Thomsen HS et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of wrist and finger joints in healthy subjects occasionally shows changes resembling erosions and synovitis as seen in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50(4): Eshed I, Feist E, Althoff CE, Hamm B, Konen E, Burmester GR et al. Tenosynovitis of the flexor tendons of the hand detected by MRI: an early indicator of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009; 48(8): Ghozlan R, Vacher H. Where is imaging going in rheumatology? Best Pract Clin Rheumatol 2009; 14(4): Peterfy CG. Magnetic resonance imaging of rheumatoid arthritis: the evolution of clinical applications through clinical trials. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2001; 30(6): Freeston JE, Bird P, Conaghan PG. The role of MRI in rheumatoid arthritis: research and clinical issues. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2009; 21(2): Savnik A, Malmskov H, Thomsen HS, Graff LB, Nielsen H, Danneskiold-Samsøe B et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist and finger joints in patients with inflammatory joint diseases. J Rheumatol 2001; 28(10): Levy G, Chow C, Cimmino MA, Schmidt WA. RA Imaging Study Group: which imaging in rheumatoid arthritis? Joint Bone Spine 2009; 76(4): Hetland ML, Ejbjerg B, Hørslev-Petersen K, Jacobsen S, Vestergaard A, Jurik AG et al. MRI bone oedema is the strongest predictor of the subsequent radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis. Results from a 2-year randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68(3): McQueen FM. Magnetic resonance imaging in early inflammatory arthritis: what is its role? Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000; 39(7): Wiell C, Szkudlarek M, Hasselquist M, Møller JM, Vestergaard A, Nørregaard J et al. Ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, and clinical assessment of inflammatory and destructive changes in fingers and toes of patients with psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2007; 9(6):R119. Erratum in: Arthritis Res Ther 2008; 10(1): Scheel AK, Hermann KG, Ohrndorf S, Werner C, Schirmer C, Detert J et al. Prospective 7 year follow up imaging study comparing radiography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis finger joints. Ann Rheum Dis 2006; 65(5): Østergaard M, Stoltenberg M, Gideon P, Sørensen K, Henriksen O, Lorenzen I. Changes in synovial membrane and joint effusion volumes after intra-articular methylprednisolone. Quantitative assessment of inflammatory and destructive changes in arthritis by MRI. J Rheumatol 1996; 23(7): Østergaard M, Stoltenberg M, Henriksen O, Lorenzen I. Quantitative assessment of synovial inflammation by dynamic gadoliniumenhanced magnetic resonance imaging. A study of the effect of intra-articular methylprednisolone on the rate of early synovial enhancement. Br J Rheumatol 1996; 35(1): Østergaard M, Klarlund M, Lassere M, Conaghan P, Peterfy C, McQueen F et al. Interreader agreement in the assessment of magnetic resonance images of rheumatoid arthritis wrist and finger joints an international multicenter study. J Rheumatol 2001; 28(5): McQueen F, Lassere M, Edmonds J, Conaghan P, Peterfy C, Bird P et al. OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Summary of OMERACT 6 MR Imaging Module. J Rheumatol 2003; 30(6): Haavardsholm EA, Østergaard M, Ejbjerg BJ, Kvan NP, Uhlig TA, Lilleås FG et al. Reliability and sensitivity to change of the OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score in a multireader, longitudinal setting. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52(12): Haavardsholm EA, Bøyesen P, Østergaard M, Schildvold A, Kvien TK. Magnetic resonance imaging findings in 84 patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: bone marrow oedema predicts erosive progression. Ann Rheum Dis 2008; 67(6): Troum OM. Newer imaging technology for the diagnosis of early RA and monitoring of inflammation and joint damage. J Clin Rheumatol 2007; 13(5): Østergaard M, Duer A, Møller U, Ejbjerg B. Magnetic resonance imaging of peripheral joints in rheumatic diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2004; 18(6): Rev Bras Reumatol 2011;51(6):
Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective. Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK
 Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK What is the target? To achieve remission or low disease activity in Rheumatoid
Treat to Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis: UK perspective Dr Deirdre Shawe, North Hampshire Hospital, Basingstoke, UK What is the target? To achieve remission or low disease activity in Rheumatoid
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection
 Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI. Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007
 Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Benedikt Ostendorf, Axel Scherer, Ulrich Mödder, and Matthias Schneider
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 7, July 2004, pp 2094 2102 DOI 10.1002/art.20314 2004, American College of Rheumatology Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Forefeet in Early Rheumatoid
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 7, July 2004, pp 2094 2102 DOI 10.1002/art.20314 2004, American College of Rheumatology Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Forefeet in Early Rheumatoid
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis
 Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis
 Formosan Journal of Rheumatology 2009;23:1-7 Review Article Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis Ying-Chou Chen 1, Tien-Tsai Cheng 1, Shih-Wei Hsu 2 1 Department of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology,
Formosan Journal of Rheumatology 2009;23:1-7 Review Article Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis Ying-Chou Chen 1, Tien-Tsai Cheng 1, Shih-Wei Hsu 2 1 Department of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology,
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
ACT-RAY and MRI substudy
 Tocilizumab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Methotrexate associated with Early Reductions in Tissue Inflammation: 12-Week Results From a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Substudy of a Randomized Controlled
Tocilizumab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Methotrexate associated with Early Reductions in Tissue Inflammation: 12-Week Results From a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Substudy of a Randomized Controlled
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain
 Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: [email protected]
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: [email protected]
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nicole Klett,, M.D.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
1991 :super specialties perceptions
 Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Arthritis of the Hands
 Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective. Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway
 Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway Oslo Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry (ORAR) Very early Arthritis Clinic
Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway Oslo Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry (ORAR) Very early Arthritis Clinic
Systemic condition affecting synovial tissue Hypertrohied synovium destroys. Synovectomy. Tenosynovectomy Tendon Surgery Arthroplasty Arthrodesis
 Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Teodora Serban 1,2, Iulia Satulu 2, Oana Vutcanu 2, Mihaela Milicescu 1,2, Carina Mihai 1,2, Mihai Bojinca 1,2, Victor
ORIGINAL ARTICLES DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Teodora Serban 1,2, Iulia Satulu 2, Oana Vutcanu 2, Mihaela Milicescu 1,2, Carina Mihai 1,2, Mihai Bojinca 1,2, Victor
ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE
 ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
USE OF ULTRASOUND FOR DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW-UP OF PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
 USE OF ULTRASOUND FOR DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW-UP OF PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS Rusmir Husic, 1 Anja Ficjan, 1 Christina Duftner, 2 *Christian Dejaco 1 1. Division of Rheumatology and Immunology, Medical University
USE OF ULTRASOUND FOR DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW-UP OF PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS Rusmir Husic, 1 Anja Ficjan, 1 Christina Duftner, 2 *Christian Dejaco 1 1. Division of Rheumatology and Immunology, Medical University
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Type III Hypersensitivity Response
 NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
Symptoms ongoing for 6/12, initially intermittent in nature.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Multiple Myeloma. Abstract. Introduction
 Multiple Myeloma Abstract Multiple Myeloma is a plasma cell cancer that causes an overproduction of plasma cells. Multiple Myeloma is a difficult disease to diagnosis because symptoms might not be present
Multiple Myeloma Abstract Multiple Myeloma is a plasma cell cancer that causes an overproduction of plasma cells. Multiple Myeloma is a difficult disease to diagnosis because symptoms might not be present
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the third most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the third most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers. Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine
 Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Original Policy Date January /2014
 MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals. RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014
 Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot
 The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: [email protected] Pictorial review Abstract
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: [email protected] Pictorial review Abstract
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital
 Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis Lisa C. Vasanth, MD, MSc a, *, Helene Pavlov, MD b, Vivian Bykerk, BSc, MD, FRCPC c KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Imaging Radiography KEY POINTS Increased awareness of the
Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis Lisa C. Vasanth, MD, MSc a, *, Helene Pavlov, MD b, Vivian Bykerk, BSc, MD, FRCPC c KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Imaging Radiography KEY POINTS Increased awareness of the
Psoriatic Arthritis. Title. Understanding and Managing. in All the Wrong Places. Clinical Features. Etiology of Psoriatic Arthritis
 Focus on CME at Memorial University Understanding and Managing Title Psoriatic Arthritis in All the Wrong Places Proton Rahman MD, MSc, FRCPC Although Baron Jean-Luis Aubert offered the first case description
Focus on CME at Memorial University Understanding and Managing Title Psoriatic Arthritis in All the Wrong Places Proton Rahman MD, MSc, FRCPC Although Baron Jean-Luis Aubert offered the first case description
SPECT/CT Wrist. Wrist pain 3/27/2012
 Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists
 Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Enthesitis: an autoinflammatory lesion linking nail and joint involvement in psoriatic disease
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03363.x JEADV Blackwell Publishing Ltd REVIEW ARTICLE Enthesitis: an autoinflammatory lesion linking nail and joint involvement in psoriatic disease D McGonagle* NIHR, Leeds
DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03363.x JEADV Blackwell Publishing Ltd REVIEW ARTICLE Enthesitis: an autoinflammatory lesion linking nail and joint involvement in psoriatic disease D McGonagle* NIHR, Leeds
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist
 Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bonita S. Libman, M.D.
 The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Evolution of Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do the 2010 Criteria Perform?
 Evolution of Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do the 2010 Criteria Perform? Elizabeth C. Ortiz, MD*, Shuntaro Shinada, MD KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Classification criteria Inflammatory
Evolution of Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do the 2010 Criteria Perform? Elizabeth C. Ortiz, MD*, Shuntaro Shinada, MD KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Classification criteria Inflammatory
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead
 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RA is a common disease: 0.8 per cent of the population RA more common in females: female to male ratio 3:1 RA
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RA is a common disease: 0.8 per cent of the population RA more common in females: female to male ratio 3:1 RA
What s new in clinical assesment of ankylosing spondylitis?
 What s new in clinical assesment of ankylosing spondylitis? Désirée van der Heijde Professor of Rheumatology Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway Content
What s new in clinical assesment of ankylosing spondylitis? Désirée van der Heijde Professor of Rheumatology Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway Content
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 17 December 2003 CPMP/EWP/556/95 rev 1/Final COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 17 December 2003 CPMP/EWP/556/95 rev 1/Final COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
Psoriatic Arthritis. Ewa Olech, MD Division of Rheumatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Las Vegas
 Psoriatic Arthritis Ewa Olech, MD Division of Rheumatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Las Vegas The Spectrum of Spondyloarthritis Characteristics of the Spondyloarthritis Sacroiliac & spinal
Psoriatic Arthritis Ewa Olech, MD Division of Rheumatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Las Vegas The Spectrum of Spondyloarthritis Characteristics of the Spondyloarthritis Sacroiliac & spinal
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Christine Pham MD
 Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
RHEUMATOLOGY ICD-10 CROSSWALK
 RHEUMATOLOGY ICD-10 CROSSWALK ICD is revised periodically and is currently in its tenth edition and will be implemented in the United States on October 1, 2015. There is an annual minor update and three-yearly
RHEUMATOLOGY ICD-10 CROSSWALK ICD is revised periodically and is currently in its tenth edition and will be implemented in the United States on October 1, 2015. There is an annual minor update and three-yearly
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES
 DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
Psoriatic arthritis in practice : How to detect? How to diagnose? Pascal RICHETTE Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris. Copyright
 Psoriatic arthritis in practice : How to detect? How to diagnose? Pascal RICHETTE Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris The patient: a 57 year-old man, with a history of psoriatic nail dystrophy for 10 years Past
Psoriatic arthritis in practice : How to detect? How to diagnose? Pascal RICHETTE Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris The patient: a 57 year-old man, with a history of psoriatic nail dystrophy for 10 years Past
Rheumatoid Arthritis Assessment with Ultrasonography
 10 Rheumatoid Arthritis Assessment with Ultrasonography Thierry Marhadour and Alain Saraux Rheumatology, CHU and University Hospital, La Cavale Blanche, Brest France 1. Introduction Musculoskeletal ultrasound
10 Rheumatoid Arthritis Assessment with Ultrasonography Thierry Marhadour and Alain Saraux Rheumatology, CHU and University Hospital, La Cavale Blanche, Brest France 1. Introduction Musculoskeletal ultrasound
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations
 Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
For rheumatoid arthritis (RA), clinical definitions of
 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Ultrasound-Defined Remission and Active Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Association with Clinical and Serologic Parameters Christian Dejaco, MD, PhD,* Christina Duftner, MD, PhD,
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Ultrasound-Defined Remission and Active Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Association with Clinical and Serologic Parameters Christian Dejaco, MD, PhD,* Christina Duftner, MD, PhD,
Rheumatoid arthritis
 Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Chronic multisystem disease Unknown cause Characteristic feature persistent inflammation of synovia in symmetric peripheral joints Synovial inflammation cartilage
Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Chronic multisystem disease Unknown cause Characteristic feature persistent inflammation of synovia in symmetric peripheral joints Synovial inflammation cartilage
It is worth noting that people with psoriasis can also develop other forms of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
 Psoriatic Arthritis Main Colour - pantone 2597u Research - pantone 206u Children - pantone 123 4 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis.
Psoriatic Arthritis Main Colour - pantone 2597u Research - pantone 206u Children - pantone 123 4 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis.
Ultrasound of the hand and wrist in rheumatology
 Review Medical Ultrasonography 2012, Vol. 14, no. 1, 42-48 Ultrasound of the hand and wrist in rheumatology Violeta Vlad 1, Mihaela Micu 2, Francesco Porta 3, Goran Radunovic 4, Rodina Nestorova 5, Tzvetanka
Review Medical Ultrasonography 2012, Vol. 14, no. 1, 42-48 Ultrasound of the hand and wrist in rheumatology Violeta Vlad 1, Mihaela Micu 2, Francesco Porta 3, Goran Radunovic 4, Rodina Nestorova 5, Tzvetanka
(Intro to Arthritis with a. Arthritis) Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society
 Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
Psoriatic Arthritis. What is psoriatic arthritis? Understanding joints. Who gets psoriatic arthritis? Page 1 of 5
 Page 1 of 5 Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic arthritis causes inflammation, pain, and swelling of joints in some people who have psoriasis. Other parts of the body may also be affected. For example, in many
Page 1 of 5 Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic arthritis causes inflammation, pain, and swelling of joints in some people who have psoriasis. Other parts of the body may also be affected. For example, in many
EFSUMB EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF SOCIETIES FOR ULTRASOUND IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY Building a European Ultrasound Community
 MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 12: Musculoskeletal Musculoskeletal ultrasound comprises a wide range of different examinations increasingly performed
MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 12: Musculoskeletal Musculoskeletal ultrasound comprises a wide range of different examinations increasingly performed
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
Is Your Horse Off Behind?? Hindlimb Facts. Common Hindlimb Lameness. Diagnostic Techniques. Gait Analysis 3/21/2012
 Is Your Horse Off Behind?? Nathaniel A. White II DVM MS DACVS Jean Ellen Shehan Professor and Director Common Hindlimb Lameness Sacroiliac joint pain Hip Lameness Stifle Lameness Stress Fractures Hock
Is Your Horse Off Behind?? Nathaniel A. White II DVM MS DACVS Jean Ellen Shehan Professor and Director Common Hindlimb Lameness Sacroiliac joint pain Hip Lameness Stifle Lameness Stress Fractures Hock
Immune modulation in rheumatology. Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association
 Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis, Management and Monitoring
 Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis, Management and Monitoring Effective Date: September 30, 2012 Scope This guideline is intended to aid in early recognition, intervention and management of patients with
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis, Management and Monitoring Effective Date: September 30, 2012 Scope This guideline is intended to aid in early recognition, intervention and management of patients with
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
How does Vectra DA measure my RA disease activity? What is Vectra DA? The more you and your doctor know about your RA, the better you can manage it
 KNOW YOUR RA SCORE 65 58 50 42 40 35 29 21 15 The advanced blood test that helps you and your doctor better understand your rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease activity with a single score 1 What is Vectra
KNOW YOUR RA SCORE 65 58 50 42 40 35 29 21 15 The advanced blood test that helps you and your doctor better understand your rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease activity with a single score 1 What is Vectra
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION
 Jeff Husband MD Objectives Evaluate, diagnose and manage common wrist injuries due to high energy trauma in athletes Appropriately use radiographs, CT scans and MRI Know when to refer patients for additional
Jeff Husband MD Objectives Evaluate, diagnose and manage common wrist injuries due to high energy trauma in athletes Appropriately use radiographs, CT scans and MRI Know when to refer patients for additional
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Outline. Treatment Goal 4/10/2013. Clinical evaluation New treatment options Future research Discussion
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Robert L. Talbert, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Outline Clinical evaluation New treatment
Rheumatoid Arthritis Robert L. Talbert, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Outline Clinical evaluation New treatment
Reversibility of Acute Demyelinating Lesions in relapsingremitting
 Reversibility of Acute Demyelinating Lesions in relapsingremitting Multiple Sclerosis Omar A. Khan ( Division of Neuroimmunology, Department of Neurology, Neurology and Research Services. Veterans Affairs
Reversibility of Acute Demyelinating Lesions in relapsingremitting Multiple Sclerosis Omar A. Khan ( Division of Neuroimmunology, Department of Neurology, Neurology and Research Services. Veterans Affairs
Outline. Personal profile & research interests. Rheumatology research in Ireland. Current standing. Future plans
 Outline Personal profile & research interests Rheumatology research in Ireland Current standing Future plans Personal profile 1983 MB Queens University 1990-3 ARUK Clinical Research Fellowship 1990-93
Outline Personal profile & research interests Rheumatology research in Ireland Current standing Future plans Personal profile 1983 MB Queens University 1990-3 ARUK Clinical Research Fellowship 1990-93
Imaging of the foot in rheumatoid arthritis
 Imaging of the foot in rheumatoid arthritis Poster No.: C-0033 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Martins, M. Palmeiro, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, Queluz/PT Keywords: Connective tissue
Imaging of the foot in rheumatoid arthritis Poster No.: C-0033 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Martins, M. Palmeiro, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, Queluz/PT Keywords: Connective tissue
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2012. Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2012 Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Report on EULAR 2012 presentations Long-term safety of rituximab: 10-year follow-up in the
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2012 Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Report on EULAR 2012 presentations Long-term safety of rituximab: 10-year follow-up in the
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Effectiveness and Drug Adherence in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Biologic Monotherapy: A prospective observational study in Southern Sweden
 Effectiveness and Drug Adherence in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Biologic Monotherapy: A prospective observational study in Southern Sweden Collaborators: Primary investigators Dr Lars Erik Kristensen,
Effectiveness and Drug Adherence in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Biologic Monotherapy: A prospective observational study in Southern Sweden Collaborators: Primary investigators Dr Lars Erik Kristensen,
