IMPROVING THE RESISTANCE OF A SERIES 60 VESSEL WITH A CFD CODE
|
|
|
- Gordon Fleming
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 V European Conference on Compuaonal Flud Dynamcs ECCOMAS CFD 2010 J. C. F. Perera and A. Sequera (Eds) Lsbon, Porugal, June 2010 IMPROVING THE RESISTANCE OF A SERIES 60 VESSEL WITH A CFD CODE J. M. A. Fonfach *, C. Guedes Soares * Cenre for Marne Technology and Engneerng (CENTEC) Techncal nversy of Lsbon, Insuo Superor Técnco Av. Rovsco Pas, Lsboa, Porugal e-mal: [email protected], [email protected] Key words: Compuaonal Flud Dynamcs, Shp Hydrodynamcs, Free Surface Flow, Turbulen Models, Hull Shape Opmzaon Absrac. An hydrodynamc sudy was carred ou of a seres 60 vessel model usng a CFD RANS (Reynolds Averaged Naver-Soes Equaons) based code, wh he am of calculang he pressure graden and shear sresses of he flow around he vessel, and he assocaed wave ran generaed a he nerface of wo fluds (free Surface), for Froude numbers n he range of 0.18 o The daa were valdaed wh prevous publshed epermenal ess. Dfferen mesh sze was used n he presen sudy o deermne he mos approprae one. The use of a zone wh urbulen properes s a fundamenal aspec n vscous flow smulaon. For he soluon of he governng equaons wo urbulence models for he urbulen vscosy are evaluaed. They are: Shear Sress Transpor (SST) and he K- model. Subsequen o obanng hese resuls, a sudy o opmze he hydrodynamc ressance was conduced, so ha he hull of he shp was modfed by addng a bow bulb, whch were analyzed wh wo dfferen lenghs, obanng he bes alernave
2 1 INTRODCTION The desgn and opmzaon of he hull lnes have radonally been performed on he bass of scaled models esed n owng ans. Ths mehod s oday he mos relable n he predcon of hydrodynamc properes of he shp. Analycal mehods are no used due o he compley of he governng equaons of real flows complcaed by he esence of free surface, vscous phenomena and he comple shp geomery. In hese days wh he developmen of new numerc ools, he advances n compuer echnology and he ncrease capably of daa processng, Compuaonal Flud Dynamc (CFD) has made remarable progress and allowed good resuls o be obaned. The neres and demand of he ndusry o mplemen new mehods s one of he mos mporan reasons ha nfluence he developmen of CFD. Shps have been bul wh bulbous bows as par of he hull, bu he hydrodynamc desgn of bulbous bows s sll dffcul, because of epensve an ess necessary n he desgn of he bows, even a he prelmnary desgn sage. I s val o defne he hydrodynamc performance of he hull, o calculae he engne power, capable o overcome he hydrodynamc ressance produced by he neracon of he hull wh he flow. Thus s mporan o desgn he hull forms such ha hey can operae economcally [1-2]. I s necessary o undersand he complcaed flow characerscs for an opmal hull desgn, whch ncludes a low drag and hgh propulsve effcency. For beer nowledge of he flow around he hull, s mporan o have relable and accurae daa, abou he physcal phenomena n he neracon flow-shp. The daa of he epermenal ess whch descrbe he local flow deals are nvaluable for he valdaon of he CFD models. There have been some epermenal daa of he flow around he shp models avalable for valdaon of CFD. The nernaonal owng an conference (ITTC) summarzed avalable benchmar daa base for CFD Valdaon for ressance and propulson of a shp, for he cargo-conaner shp, seres 60 and urbulen measuremen es case are gven n [3-4]. Prevously wo worshops were presened for he compuaonal analyss flow around shps, HSVA/Dyne aner and a seres 60 model were chosen for he es case [5]. However he progress ha has been acheved n he epermenal ess has no decreased he neres of nowng n deal he flow feld, wh beer nformaon of he near-wall flow, assocaed wh he moon of hull. Ths nformaon s no offered by he epermenal mehod; on he oher hand CFD have a good performance n gvng characerscs of he behavor of he flow ha ofen mprove developmen of he hull form. The cos and me requred for he compuaon are lower han for an ess. The CFD has been negraed n o researchng and he ndusry, for eample s beng used n desgn of shps for he predcon of vscous flow wh free surface around he hull, he flow separaon o desgn appendces and propeller-hull neracon. Vscous flow compuaon for shps began n he 60 s, wh he smplfed boundary layer equaon beng solved. In hs approach, he boundary layer can be calculaed accepably n he hull, however, hs formulaon faled n he predcng flow a sern. In he 80 s a large number of RANS (Reynolds Averaged Naver-Soes) mehods were developed for shp sern flow. The sern flow predcon capables were mproved raher remarably around However, CFD smulaons near he propeller were less sasfacory, due o shape of he boundary layer n he propeller zone. Laer, was realzed, ha he reason for he nably o predc was he nadequae modelng of urbulence. Ths lead o he mplemenaon of more advanced models, such as he -ω urbulence model and he Reynolds sress model [6]. 2
3 The modern vscous flow codes, whch solve he RANSE, have he ably o smulae effcenly he urbulen flow problems around shps. The wo models mos used n CFD o solve he urbulen phenomena, are he sandard - model and he Shear Sress ranspor (SST) -ω, he performance of whch models was suded n [7] dealng wh he predcon of he reaachmen lengh of flow. The -ω model gave very good comparson o epermenal daa whle he - model predced a sgnfcanly shorer lengh. However, he -ωmodel overpredced he spreadng raes around he free shear layer due o naccurae predcon of eddy vscosy value. Free surface problems such as he wave mang problem were smulaed wh vscous flow codes dependng on wheher he compuaonal grd adaps o he shape or he poson of he free surface. Therefore, wo maor approaches wdely appled o he free surface compuaons are he so-called nerface-racng mehod, e.g. a movng mesh and he nerface-capurng mehod, e.g. he volume of flud mehod (VOF) proposed by Hr and Nchols [8] o deal wh free surface boundary problems. The am of hs sudy s he use of CFD code for a shp desgn. For ha effec, he performance of he seres 60 shp model was mproved as a resul of changes n he hull form. Frs a sudy of he naed hull was performed, whch analyzed he mesh sensvy and valdaed numercal daa. Then wo dfferen bulbs were desgned o reduce he ressance of he hull. The models were calculaed wh he commercal sofware CFX verson MATHEMATICAL MODEL In CFX, he Reynolds-averaged Naver Soes (RANS) equaons for he momenum ranspor and connuy equaon for mass conservaon are equaons governng he moon of a hree-dmensonal seady, ncompressble and vscous urbulen flow. The homogenous mulphase Euleran Euleran flud approach ulzes Volume of Flud mehod (VOF) o descrbe he free surface flow problem mahemacally. The ulzed VOF mehod s a fed grd echnque desgned for wo or more fluds, where n each cell of a mesh s necessary o use only one value for each dependen varable defnng he flud sae, whch can be defned by a funcon α (where q represen he fracon of volume; q = 1, 2,..).The value of hs varable s uny a any pon occuped by flud and zero n he oher case. The average value of α n a cell represens he poson of he nerface of he flud. In parcular, a un value of α would correspond o a cell full of flud, whle a zero value would ndcae ha he cell s empy, so he cells wh α values beween zero and one mus, he conan a free surface. The racng of he nerface s accomplshed by solvng he connuy equaon of he volume fracon. For he q lqud, hs equaon s wren as follow: q α q u where he consrans are gven by: α q = 0 (1) n q= 1 α q = and for ncompressble flows, he frs erm of he connuy equaon s: α q = 0 1 (2) (3) 3
4 The densy of he whole flud n each cell s evaluaed by he volume-fraconaverage of all lquds n he cell: ρ = α ρ q q (4) All oher properes (e.g., vscosy ) are compued n he same way. The momenum equaon s dependen on he volume fracons of all lquds hrough he properes ρ and. The Naver-Soes equaon can be wren n Caresan ensor form as follows: u u 1 p u u = ρ where for seady flow, he velocy-me can be wren as: (5) u = 0 (6) where u s he velocy n he sream drecon,ρ s he flud densy,s he nemac vscosy of he flow and p s he pressure. The Naver-Soes equaon canno be resolved properly for he effecs of hgh frequency urbulence, because he compuaonal resources do no allow he curren generaon of suffcenly fne mesh o properly resolve he small-scale vorce lengh. For hs reason, he effors n Compuaonal Flud Dynamcs are dreced o he soluon of he Reynolds equaons. These equaons are obaned usng he defnon of average me. The flow s separaed no mean ( ) and flucuang (u )componens n he RANS approach o urbulence: = u' (7) he me averagng velocy componen s defned as: T 1 = d (8) T 0 where T s he averagng me of he smulaon, usually chosen o be large compared o he ypcal mescale of urbulen flucuaons. Subsung no he Naver-Soes equaons n seady flow for me averagng, one obans he me averaged Naver- Soes equaons: u 1 p u u = u u (9) ρ where, he sascal averagng of he Naver-Soes equaons gve rses o he unnown erm, s defned n eq.(10): u u 2 u u = δ (10) 3 whch are he correlaon beween he flucuang velocy componens and s nown as he Reynolds Sress erm. The esence of he Reynolds sress means here s no longer 4
5 5 a closed se of equaons, and urbulence model assumpons are needed o esmae he unnowns o solve hs closure problem Two models were used o calculae he urbulen vscosy. In CFD, he sandard - and Shear Sress Transpor -ω are he wo mos wdely used models n hs caegory. The sandard - urbulence model solves he flow based on he assumpon ha he rae of producon and dsspaon of urbulen flows are n near-balance n energy ransfer. The dsspaon rae, of he energy s wren as: L 3/2 = (11) where s he nec energy of he flow and L s he lengh scale nvolved. Ths s hen relaed o he urbulen vscosy based on he Prandl mng lengh model: ρc 2 µ = (12) where µ C s an emprcal consan and ρ s he densy he flow, applyng hs o he equaons governng flud flow, he equaon of he sandard - model s wren as: ( ) ρ σ ρ = (13) and he equaon: ( ) ρc C σ ρ = (14) based on eensve eamnaon of a wde range of urbulen flows, he consan parameers used n he equaons ae he followng values, 0.09 C µ = ; 1.44 C 1 = ; 1.92 C 2 = ; 1.0 σ = ; 1.3 σ = Shear Sress Transpor -ω wo equaons model was developed as an alernave o cover he defcences of he sandard - model a he walls. The Shear Sress Transpor -ωs smlar n srucure o he - model bu he varable s replaced by he dsspaon rae per un nec energy. The equaons n he Shear Sress Transpor model are wren as: ( ) ρω σ ρ = (15) and he ω equaon: ( ) 2 βρω ω α ω σ ρ = (16) where: ω ρ = (17) Alhough he wo equaon models (-ω and - ) provde a good compromse beween compley and accuracy among RANS models, he applcaons are resrced
6 o seady ype of flow. Thus, soluon s sough o acheve boh compuaonal effcency and he capably of predcng he chaoc naure of flow such as vore sheddng. 3 SHIP MODEL The shp model used for hs sudy s a seres 60 wh bloc coeffcen (C B ) of 0.6, whch s a sngle-propeller merchan ype shp and s a sandard for shp-hydrodynamcs research, and was chosen because, s one of used by ITTC research program. The characersc of naed hull model used for he epermenal and compuaonal es are, gven bellow, and he longudnal profle of he 3D model s shown n Fgure 1. Lengh beween perpendcular (Lbp) [m] Breadh (B) [m] Draf (T) [m] Dsplacemen ( ) [m 3 ] Weed Surface Area (S) [m 2 ] 4 EXPERIMENTAL SETP Fgure 1: longudnal profle of he 3D model. To compare and valdae he numercal resuls, use have been made of he epermenal resuls presened by he ITTC Cooperave Epermen on a Seres 60 Model, a he Shp Research Insue n he sudy Flow Measuremen and Ressance Tes [4]. In he epermens, he ressance es was carred ou under free condon. The range of Froude number (Fn) was 0.07 o 0.34 and s sep s The ressance force was measured by a ressance dynamomeer of he sran gauge ype whch has he capacy of 20g and a olerance of 0.05% of he full scale. The wave profles along he hull surface were measured by phoographs a values of Fn = 0.18; 0.22; 0.25; 0.28; 0.30; 0.32 and The horzonal and vercal scales were drawn on he model surface for hs purpose. The phoographs were aen by he hree 35mm cameras. The vscous flow feld was measured usng 5-hole Po ube, whch s he NPL ype (ape angle s 100 deg.) and s dameer s 5mm. The shp model was fed o he owng carrage n order o assure he accuracy of measurng poson. The Froude number was se o 0.18, for calbraon. The waer condons n he owng an are shown n Table 1: T C ρ gs /m m 2 /s Table 1: The envronmen condon measured n he Towng an. 5 COMPTATIONAL DOMAIN AND GRID GENERATION The geomery of he hull and he volume of conrol of he grd were obaned n approprae eernal sofware, and he molded offses of he ransverse secon of he model were obaned from he polynomal defnon of he cross secon for seres 60. 6
7 The modeled surface of hull was compared wh he epermenal model; he dfference was only 0.2%, and hus was consdered ha he surface was modeled opmally by he generaed mesh. The volume of conrol was chosen o be of bo shape. The hegh of he compuaonal doman s 1.25L bp and s wdh s aen o be of 1.5L bp due o he symmery of he problem. The doman nle boundary s a a dsance of 1.5L ahead of he shp, whle he oule boundary s locaed a 2.6L bp from he shp sern. The grd generaor ICEM CFD was used for meshng he compuaonal doman wh unsrucured erahedral grd and dfferen mesh szes were consdered for he analyss of ressance n naed hull condon. The mesh sze for he hull and free surface are summarzed n Table 2 and are shown n Fgures 3 and 4. Mesh sensvy sudes were performed o eplore he effec of dfferen opology and local refnemen o observer accuracy on he resul, In ICEM CFD he opon Low ranson was chosen o refne he mesh gradually n he zone of neres unl a remoe zone of he doman. nsrucured erahedral grd was chosen because s easly adusable o comple geomery; however hs ype of mesh ncreases he compuaonal cos. Mesh N Hull Sze F.S. Sze Doman N Node Mesh N 1 2%L 2%L 425,940 Mesh N 2 0.5%L 2%L 596,313 Mesh N 3 0.5%L 1%L 1,874,160 Mesh N %L 1%L 2,391,549 Table 2: Dfferen sze mesh used n he hull and Free Surface (F.S.). L s he Lengh beween perpendculars. In he free surface and hull surface a prsmac layer mesh was appled (see Fgure 2), wh an eponenal ncremen beween layers. The nal hegh and he number of layers are presened n he Table 3. The parameer seleced was ha he oal layer hegh n he nerface zone s wce he draf of he hull, and he oal hcness around o hull appromaely equal o one quarer of draf. The prsmac layer mesh has been used n he all cases ecep for mesh N 1. Iem N Layers Inal hegh Hull F. S Table 3: Parameers for Prsm layer mesh appled n he hull and Free Surface. Fgure 2: Scheme of grd used n he compuaonal doman. 7
8 Fgure 3: Compuaonal Grd on Seres 60 surface, a dfferen sze mesh. Fgure 4: Compuaonal Grd on Waer surface around Seres 60 shp model, a dfferen sze mesh. 6 BONDARY CONDITIONS AND SIMLATION CRITERIA For free surface calculaons, he ar and waer flow around he seres 60 shp model was smulaed usng he sandard homogenous Volume of Flud (VOF) model (or free surface model) avalable n CFX In he VOF model, a sngle momen equaons s shared by he flud volume fracon of each of he fluds n each compuaonal cell s raced hroughou he doman, surface enson was no appled n he models. The coupled volume fracon soluon algorhm was used o mprove he convergence. The sn and rm of he hull was no aen no accoun, hus was consdered ha he hull was fed and he compuaons were run seady n me. The sandard - and shear sress ranspor -ω urbulen model was employed n he CFD smulaons wh he sandard coeffcen. Boh urbulence models are wdely used n he marne and hydrodynamcs applcaon and hese models have a good performance for hgh accuracy boundary layer smulaons. The waer condon was modeled as n he epermenal es, whch means fresh waer a 21.5 Celsus degree, (Densy = 999g/m 3, Dynamc Vscous = 1.137E- 3g/m/s). The ar was assumed compressble (for compuaonal sably reason) and was modeled wh a molecular mass of 28.96g/mole and a Dynamc Vscosy of 1.8E-5 g/m/s. Buoyancy forces due o flud densy dfference were modeled n he analyss. The boundary condon was employed o smulae he condon on he owng an. A velocy nle boundary condon was used upsream; he flow velocy was consdered equal o he velocy epermenal of he model usng he cases of epermenal measuremen o wave profle. The free surface elevaon was fed a he nle. A hydrosac pressure oule boundary condon was used downsream; he hydrosac pressure a he oule was calculaed assumng an undsurbed free surface. Smooh walls wh a free-slp condon were assumed for he op, floor and he sde wall, only half of he model was consdered n he smulaons by usng a symmery plane condon a Y = 0. Smooh walls wh a non-slp condon (u, v, w = 0) were assumed n he enre hull. 8
9 Convergence was assessed by plong he flowng parameers agans he number of eraon: Resduals for mass, momenum and urbulence (arge crera = 1E-4) and Drag forces (X drecons). The mamum number of eraons was equal o 500. However, f he convergence crera are reached for all resduals, he smulaon was sopped before reachng 500 eraons. For mos smulaons, convergence of all resduals forces and monorng pons was acheved n around 300 eraons [9]. 7 NMERIC RESISTANCE VALIDATION OF THE BARE HLL The oal ressance coeffcens were obaned from he numercal resuls and compared wh he epermenal value. No blocage correcon was made for epermenal daa [4]. The speed relave o waer s used n he calculaon. The oal ressance coeffcen s: R C = (17) 2 0.5ρ. S where R s he oal ressance. The oal ressance coeffcen for dfferen mesh and urbulen model are show n Fgures 5 and 6. Fgure 5: Toal coeffcen a mesh N 1 and N 2 for -ω and - urbulen model, for dfferen Fn. Fgure 6: Toal coeffcen a mesh N 3 and N 4 for SST urbulen models for dfferen Fn. To valdae he resul he percenages of dfference beween he numercal and epermenal daa, were calculaed and are summarzed n Table 4. Fn / Mesh N Mesh N 1 (SST) Mesh N 1 (-e) Mesh N 2 (SST) Mesh N 2 (-e) Mesh N 3 (SST) Mesh N 4 (SST) Table 4: Dfference n percenage beween C num and C ep 9
10 The wave paern generaed for he shp when advancng n calm waer, whch generae he waves on he dsurbed ar-waer nerface (free surface), s due o he shp ha has o supply he energy connuously o generae he wave paern ha followng he shp. Thus, he shp should overcome he drag nduced by he wave generaon on he free surface. The so-called wave ressance (drag) relaes o hs mporan phenomenon. The comparson beween he numercal and epermenal resul of he wave profle along of he hull wh dfferen Froude number and mesh sze are shown n Fgures 7 o 9 and he global vew o he wave paern are show n he Fgure 10 and 11, a Fn = 0.32 for he dfferen mesh sze. Fgure 7: Predced wave profle for Fn = by CFX. Fgure 8: Predced wave profle for Fn = by CFX. Fgure 9: Predced wave profle a Fn = by CFX. Fgure 10: Epermenal and predced wave conour for mesh N 2, a Fn = Fgure 11: Predced wave conour for mesh N 3 and N 4, a Fn =
11 From he obaned resuls, was observed ha he use of prsmac mesh mproves he predcon of he urbulen boundary layer, where he SST model was he bes appromaon. In hgher Froude Number, he predced ressance s more eac, defnng a velocy range where he CFD code gves accurae resuls whou requrng a grea compuaonal cos. For he lower Froude Number, s necessary o use a fne mesh capable o consder small dfferences n he graden of pressure and free surface deformaon. The fne mesh n he nerface of he flud perms a good appromaon of he wave paern by he shp. However he fne mesh n he hull mproves he predcon of he ressance beer han he fne mesh n he free surface. 8 DEFINITION AND PERFORMACE OF THE IMPROVED CASES The man obecve s o mnmze s he oal ressance of he Seres 60 model shp, n calm waer a dfferen speed for ranges of Froude number beween 0.18 and The bow of he shp was modfed ncludng wo bulbs wh dfferen lengh. The frs layou of he bulb was consdered as cylnder, n whch he ransversal area of he cylnder was esmaed as 20% of he md shp secon area and he lengh was consdered beween 0.04L bp <<0.06L bp, from he fore perpendcular. Laer he shape of he bulb was modfed unl he proper desgn was acheved. The wo desgned bulbs are shown n Fgure 11 and are compared wh he naed hull. Fgure 11: Perspecve vew of he bow and bulb geomery, naed hull, hull N 1, hull N 2 The used mesh for he hull was mesh N 2, whch was used n he numercal smulaon of he naed hull. For he bulb a fne mesh accordng o mesh N 4 was used, as show n Fgure 12. The boundary condon was he same as n he prevous case. Fgure 12: Mesh on he hall and free surface for he opmzed cases. The bulb reduces wave generaon around he bow regon. The wave generaed by he bow bulb under free surface neracs wh he wave generaed by he desgn waerlne. The wave ressance can be reduced f he bow bulb s properly locaed. The analyss of he hull wh bulb, was compared wh he naed hull smulaon, he parameers consdered n he analyss were he oal ressance coeffcen, he wave paern, he wave profle along he hull, pressure n he hull and sream lne n he hull, ha were repored n he Fgures 13 o 18 and Table 5. 11
12 Fgure 13: Toal coeffcen for bare hull and Hull N 1 and Hull N 2. Fn / Hull N Hull N Hull N Table 5: Dfference percenage of oal coeffcen beween bare hull and hull N 1 and hull N 2 Fgure 14: Predced wave profle for hull N 1 and N, a Fn = by CFX. Fgure 15: Predced wave profle for hull N 1 and N, Fn = by CFX. Fgure 16: Predced wave conour for hull N 1 and N 2, a Fn = Fgure 17: Pressure n he bare hull, hull N 1 and N 2, a Fn =
13 Fgure 18: Seam Lnes n he bare hull, hull N 1 and N 2, a Fn = The ressance n boh mproved hulls was reduced when a Froude number over 0.28 s used. Ths s observed on he compued wave paern, as he dsrbuon of wave feld by he cussed bow bulb s globally sof and has a smaller bow wave. The low amplude of waves s an ndcaon ha he wave ressance componen of he shp s ressance was reduced. Boh mproved models reduced he amplude of he bow wave, alhough hs s more noceable n hull N 2. In addon, he seepness of he frs wave and he frs rough around boh models are sofer. Wh he bulb volume a low pressure feld shows mprovemens n he pressure coeffcen dsrbuon. The pressure paern on he bow vares more genly and he pressure gradens are reduced n he modfed regon. In he wo new cases he slope of he sream lnes are larger. Fnally a lowes ressance was calculaed from he sream flow bulb when ncreasng he lengh bu hs dfference s margnal beween boh bulbs. The sgnfcan dfference wh he nal desgn s caused only by he pressure ressance, because he hree cases have he same frconal ressance. 9 CONCLSIONS Ths wor shows he poenal of Compuaonal Flud Dynamcs applcaons n shp hydrodynamc desgn. CFD s an effecve ool allowng he opmzaon of he hull, whch decreases he cos n he frs sages of desgn. The vscous flow wh free surface around Seres 60 Model Shp was smulaed for wo dfferen urbulen models a dfferen Froude number. A comparson of hese resuls wh epermenal daa showed good agreemen. The accuracy of he naed ressance predcons s ncreased when s usng a mesh fner han a 0.5%L n he hull. The obaned resuls are whn 10% of he epermenal resuls. Two dfferen bulbs were esed n CFD and provded an mprovemen n he hull ressance a hgh Froude numbers. REFERENCES [1] Emlo F. Campana, Danele Per, Yusue Tahara and Frederc Sern, Shape opmzaon n shp hydrodynamcs usng compuaonal flud dynamcs, Journal Compu. Mehods Appl. Mech. Engr.196, (2006) [2] W. J. Km, S. H. Van and D. H. Km, Measuremen of flows around modern commercal shp models, Epermens n Fluds (2001) [3] Suzu H, Suzu T, Myazas S, Turbulence measuremen n sern flow feld of a shp model sere 60, C B = 0.60, Kansa Soc Nav Arch, (1997) [4] H. Taesh, T. Hno, M. Hnasu, Y. Tsuada and J. Fusawa, Flow Measuremens and ressance Tess, ITTC Cooperave Epermens on a Seres 60 Model A shp Research Insue, Proc. 17 h Towng Tan Conference, (ITTC), (1987) 13
14 [5] Berram V, Chap K-Y, Lammers G, Laundan, Epermenal valdaon daa freesurface flow for cargo vessel. In: Kodoma Y (ed) Proccedngs of CFD Worshop, Toyo Japan, (1994). [6] Zhang Zh-rong, Lu Hu, Zhu Song-png and Zhao Feng, Applcaon of CFD In shp engneerng desgn pracce and shp hydrodynamcs, Chna Shp Scenfc Research Cener, Wu , Chna (1996) [7] Wlco D C, Turbulence Modellng for CFD, DCW Indusres Inc., Calforna, (1993) [8] Hr, C. W and Nchols B.D., Volume of Flud (VOF) mehod for he dynamcs of free boundares, Journal of Compuaonal Physcs,39, (1981) [9] C. Craddoc, A. Lebas, and A. Ganguly, se of CFD For hull form and appendage desgn assessmen on an offshore vessel and he denfcaon of a wae focusng effec, Proceedngs RINA Marne CFD Symposum, Souhampon, K, (2008) 14
Spline. Computer Graphics. B-splines. B-Splines (for basis splines) Generating a curve. Basis Functions. Lecture 14 Curves and Surfaces II
 Lecure 4 Curves and Surfaces II Splne A long flexble srps of meal used by drafspersons o lay ou he surfaces of arplanes, cars and shps Ducks weghs aached o he splnes were used o pull he splne n dfferen
Lecure 4 Curves and Surfaces II Splne A long flexble srps of meal used by drafspersons o lay ou he surfaces of arplanes, cars and shps Ducks weghs aached o he splnes were used o pull he splne n dfferen
HEAT CONDUCTION PROBLEM IN A TWO-LAYERED HOLLOW CYLINDER BY USING THE GREEN S FUNCTION METHOD
 Journal of Appled Mahemacs and Compuaonal Mechancs 3, (), 45-5 HEAT CONDUCTION PROBLEM IN A TWO-LAYERED HOLLOW CYLINDER BY USING THE GREEN S FUNCTION METHOD Sansław Kukla, Urszula Sedlecka Insue of Mahemacs,
Journal of Appled Mahemacs and Compuaonal Mechancs 3, (), 45-5 HEAT CONDUCTION PROBLEM IN A TWO-LAYERED HOLLOW CYLINDER BY USING THE GREEN S FUNCTION METHOD Sansław Kukla, Urszula Sedlecka Insue of Mahemacs,
Analyzing Energy Use with Decomposition Methods
 nalyzng nergy Use wh Decomposon Mehods eve HNN nergy Technology Polcy Dvson [email protected] nergy Tranng Week Pars 1 h prl 213 OCD/ 213 Dscusson nergy consumpon and energy effcency? How can energy consumpon
nalyzng nergy Use wh Decomposon Mehods eve HNN nergy Technology Polcy Dvson [email protected] nergy Tranng Week Pars 1 h prl 213 OCD/ 213 Dscusson nergy consumpon and energy effcency? How can energy consumpon
Lecture 40 Induction. Review Inductors Self-induction RL circuits Energy stored in a Magnetic Field
 ecure 4 nducon evew nducors Self-nducon crcus nergy sored n a Magnec Feld 1 evew nducon end nergy Transfers mf Bv Mechancal energy ransform n elecrc and hen n hermal energy P Fv B v evew eformulaon of
ecure 4 nducon evew nducors Self-nducon crcus nergy sored n a Magnec Feld 1 evew nducon end nergy Transfers mf Bv Mechancal energy ransform n elecrc and hen n hermal energy P Fv B v evew eformulaon of
Analysis of intelligent road network, paradigm shift and new applications
 CONFERENCE ABOUT THE STATUS AND FUTURE OF THE EDUCATIONAL AND R&D SERVICES FOR THE VEHICLE INDUSTRY Analyss of nellgen road nework, paradgm shf and new applcaons Péer Tamás "Smarer Transpor" - IT for co-operave
CONFERENCE ABOUT THE STATUS AND FUTURE OF THE EDUCATIONAL AND R&D SERVICES FOR THE VEHICLE INDUSTRY Analyss of nellgen road nework, paradgm shf and new applcaons Péer Tamás "Smarer Transpor" - IT for co-operave
APPLICATION OF CHAOS THEORY TO ANALYSIS OF COMPUTER NETWORK TRAFFIC Liudvikas Kaklauskas, Leonidas Sakalauskas
 The XIII Inernaonal Conference Appled Sochasc Models and Daa Analyss (ASMDA-2009) June 30-July 3 2009 Vlnus LITHUANIA ISBN 978-9955-28-463-5 L. Sakalauskas C. Skadas and E. K. Zavadskas (Eds.): ASMDA-2009
The XIII Inernaonal Conference Appled Sochasc Models and Daa Analyss (ASMDA-2009) June 30-July 3 2009 Vlnus LITHUANIA ISBN 978-9955-28-463-5 L. Sakalauskas C. Skadas and E. K. Zavadskas (Eds.): ASMDA-2009
Capacity Planning. Operations Planning
 Operaons Plannng Capacy Plannng Sales and Operaons Plannng Forecasng Capacy plannng Invenory opmzaon How much capacy assgned o each producon un? Realsc capacy esmaes Sraegc level Moderaely long me horzon
Operaons Plannng Capacy Plannng Sales and Operaons Plannng Forecasng Capacy plannng Invenory opmzaon How much capacy assgned o each producon un? Realsc capacy esmaes Sraegc level Moderaely long me horzon
How To Calculate Backup From A Backup From An Oal To A Daa
 6 IJCSNS Inernaonal Journal of Compuer Scence and Nework Secury, VOL.4 No.7, July 04 Mahemacal Model of Daa Backup and Recovery Karel Burda The Faculy of Elecrcal Engneerng and Communcaon Brno Unversy
6 IJCSNS Inernaonal Journal of Compuer Scence and Nework Secury, VOL.4 No.7, July 04 Mahemacal Model of Daa Backup and Recovery Karel Burda The Faculy of Elecrcal Engneerng and Communcaon Brno Unversy
Genetic Algorithm with Range Selection Mechanism for Dynamic Multiservice Load Balancing in Cloud-Based Multimedia System
 ISSN : 2347-8446 (Onlne) Inernaonal Journal of Advanced Research n Genec Algorhm wh Range Selecon Mechansm for Dynamc Mulservce Load Balancng n Cloud-Based Mulmeda Sysem I Mchael Sadgun Rao Kona, II K.Purushoama
ISSN : 2347-8446 (Onlne) Inernaonal Journal of Advanced Research n Genec Algorhm wh Range Selecon Mechansm for Dynamc Mulservce Load Balancng n Cloud-Based Mulmeda Sysem I Mchael Sadgun Rao Kona, II K.Purushoama
Sensor Nework proposeations
 008 Inernaoal Symposum on Telecommuncaons A cooperave sngle arge rackng algorhm usng bnary sensor neworks Danal Aghajaran, Reza Berang Compuer Engneerng Deparmen, Iran Unversy of Scence and Technology,
008 Inernaoal Symposum on Telecommuncaons A cooperave sngle arge rackng algorhm usng bnary sensor neworks Danal Aghajaran, Reza Berang Compuer Engneerng Deparmen, Iran Unversy of Scence and Technology,
GUIDANCE STATEMENT ON CALCULATION METHODOLOGY
 GUIDANCE STATEMENT ON CALCULATION METHODOLOGY Adopon Dae: 9/28/0 Effecve Dae: //20 Reroacve Applcaon: No Requred www.gpssandards.org 204 CFA Insue Gudance Saemen on Calculaon Mehodology GIPS GUIDANCE STATEMENT
GUIDANCE STATEMENT ON CALCULATION METHODOLOGY Adopon Dae: 9/28/0 Effecve Dae: //20 Reroacve Applcaon: No Requred www.gpssandards.org 204 CFA Insue Gudance Saemen on Calculaon Mehodology GIPS GUIDANCE STATEMENT
MORE ON TVM, "SIX FUNCTIONS OF A DOLLAR", FINANCIAL MECHANICS. Copyright 2004, S. Malpezzi
 MORE ON VM, "SIX FUNCIONS OF A DOLLAR", FINANCIAL MECHANICS Copyrgh 2004, S. Malpezz I wan everyone o be very clear on boh he "rees" (our basc fnancal funcons) and he "fores" (he dea of he cash flow model).
MORE ON VM, "SIX FUNCIONS OF A DOLLAR", FINANCIAL MECHANICS Copyrgh 2004, S. Malpezz I wan everyone o be very clear on boh he "rees" (our basc fnancal funcons) and he "fores" (he dea of he cash flow model).
Kalman filtering as a performance monitoring technique for a propensity scorecard
 Kalman flerng as a performance monorng echnque for a propensy scorecard Kaarzyna Bjak * Unversy of Souhampon, Souhampon, UK, and Buro Informacj Kredyowej S.A., Warsaw, Poland Absrac Propensy scorecards
Kalman flerng as a performance monorng echnque for a propensy scorecard Kaarzyna Bjak * Unversy of Souhampon, Souhampon, UK, and Buro Informacj Kredyowej S.A., Warsaw, Poland Absrac Propensy scorecards
THE USE IN BANKS OF VALUE AT RISK METHOD IN MARKET RISK MANAGEMENT. Ioan TRENCA *
 ANALELE ŞTIINłIFICE ALE UNIVERSITĂłII ALEXANDRU IOAN CUZA DIN IAŞI Tomul LVI ŞnŃe Economce 009 THE USE IN BANKS OF VALUE AT RISK METHOD IN MARKET RISK MANAGEMENT Ioan TRENCA * Absrac In sophscaed marke
ANALELE ŞTIINłIFICE ALE UNIVERSITĂłII ALEXANDRU IOAN CUZA DIN IAŞI Tomul LVI ŞnŃe Economce 009 THE USE IN BANKS OF VALUE AT RISK METHOD IN MARKET RISK MANAGEMENT Ioan TRENCA * Absrac In sophscaed marke
12/7/2011. Procedures to be Covered. Time Series Analysis Using Statgraphics Centurion. Time Series Analysis. Example #1 U.S.
 Tme Seres Analyss Usng Sagraphcs Cenuron Nel W. Polhemus, CTO, SaPon Technologes, Inc. Procedures o be Covered Descrpve Mehods (me sequence plos, auocorrelaon funcons, perodograms) Smoohng Seasonal Decomposon
Tme Seres Analyss Usng Sagraphcs Cenuron Nel W. Polhemus, CTO, SaPon Technologes, Inc. Procedures o be Covered Descrpve Mehods (me sequence plos, auocorrelaon funcons, perodograms) Smoohng Seasonal Decomposon
An Anti-spam Filter Combination Framework for Text-and-Image Emails through Incremental Learning
 An An-spam Fler Combnaon Framework for Tex-and-Image Emals hrough Incremenal Learnng 1 Byungk Byun, 1 Chn-Hu Lee, 2 Seve Webb, 2 Danesh Iran, and 2 Calon Pu 1 School of Elecrcal & Compuer Engr. Georga
An An-spam Fler Combnaon Framework for Tex-and-Image Emals hrough Incremenal Learnng 1 Byungk Byun, 1 Chn-Hu Lee, 2 Seve Webb, 2 Danesh Iran, and 2 Calon Pu 1 School of Elecrcal & Compuer Engr. Georga
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
 IJSM, Volume, Number, 0 ISSN: 555-4 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT SPONSORED BY: Angelo Sae Unversy San Angelo, Texas, USA www.angelo.edu Managng Edors: Professor Alan S. Khade, Ph.D. Calforna
IJSM, Volume, Number, 0 ISSN: 555-4 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT SPONSORED BY: Angelo Sae Unversy San Angelo, Texas, USA www.angelo.edu Managng Edors: Professor Alan S. Khade, Ph.D. Calforna
Pedro M. Castro Iiro Harjunkoski Ignacio E. Grossmann. Lisbon, Portugal Ladenburg, Germany Pittsburgh, USA
 Pedro M. Casro Iro Harjunkosk Ignaco E. Grossmann Lsbon Porugal Ladenburg Germany Psburgh USA 1 Process operaons are ofen subjec o energy consrans Heang and coolng ules elecrcal power Avalably Prce Challengng
Pedro M. Casro Iro Harjunkosk Ignaco E. Grossmann Lsbon Porugal Ladenburg Germany Psburgh USA 1 Process operaons are ofen subjec o energy consrans Heang and coolng ules elecrcal power Avalably Prce Challengng
TURBULENCE MODELING FOR BEGINNERS
 TURBULENCE MODELING FOR BEGINNERS by TONY SAAD UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE SPACE INSTITUTE [email protected] hp://ed.nows. The purpose of hs ny gude s o summarze he basc conceps of urbulence modelng and o a comple
TURBULENCE MODELING FOR BEGINNERS by TONY SAAD UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE SPACE INSTITUTE [email protected] hp://ed.nows. The purpose of hs ny gude s o summarze he basc conceps of urbulence modelng and o a comple
Linear Extension Cube Attack on Stream Ciphers Abstract: Keywords: 1. Introduction
 Lnear Exenson Cube Aack on Sream Cphers Lren Dng Yongjuan Wang Zhufeng L (Language Engneerng Deparmen, Luo yang Unversy for Foregn Language, Luo yang cy, He nan Provnce, 47003, P. R. Chna) Absrac: Basng
Lnear Exenson Cube Aack on Sream Cphers Lren Dng Yongjuan Wang Zhufeng L (Language Engneerng Deparmen, Luo yang Unversy for Foregn Language, Luo yang cy, He nan Provnce, 47003, P. R. Chna) Absrac: Basng
Cost- and Energy-Aware Load Distribution Across Data Centers
 - and Energy-Aware Load Dsrbuon Across Daa Ceners Ken Le, Rcardo Banchn, Margare Maronos, and Thu D. Nguyen Rugers Unversy Prnceon Unversy Inroducon Today, many large organzaons operae mulple daa ceners.
- and Energy-Aware Load Dsrbuon Across Daa Ceners Ken Le, Rcardo Banchn, Margare Maronos, and Thu D. Nguyen Rugers Unversy Prnceon Unversy Inroducon Today, many large organzaons operae mulple daa ceners.
A Background Layer Model for Object Tracking through Occlusion
 A Background Layer Model for Obec Trackng hrough Occluson Yue Zhou and Ha Tao Deparmen of Compuer Engneerng Unversy of Calforna, Sana Cruz, CA 95064 {zhou,ao}@soe.ucsc.edu Absrac Moon layer esmaon has
A Background Layer Model for Obec Trackng hrough Occluson Yue Zhou and Ha Tao Deparmen of Compuer Engneerng Unversy of Calforna, Sana Cruz, CA 95064 {zhou,ao}@soe.ucsc.edu Absrac Moon layer esmaon has
An Optimisation-based Approach for Integrated Water Resources Management
 20 h Euroean Symosum on Comuer Aded Process Engneerng ESCAPE20 S Perucc and G Buzz Ferrars (Edors) 2010 Elsever BV All rghs reserved An Omsaon-based Aroach for Inegraed Waer Resources Managemen Songsong
20 h Euroean Symosum on Comuer Aded Process Engneerng ESCAPE20 S Perucc and G Buzz Ferrars (Edors) 2010 Elsever BV All rghs reserved An Omsaon-based Aroach for Inegraed Waer Resources Managemen Songsong
An Architecture to Support Distributed Data Mining Services in E-Commerce Environments
 An Archecure o Suppor Dsrbued Daa Mnng Servces n E-Commerce Envronmens S. Krshnaswamy 1, A. Zaslavsky 1, S.W. Loke 2 School of Compuer Scence & Sofware Engneerng, Monash Unversy 1 900 Dandenong Road, Caulfeld
An Archecure o Suppor Dsrbued Daa Mnng Servces n E-Commerce Envronmens S. Krshnaswamy 1, A. Zaslavsky 1, S.W. Loke 2 School of Compuer Scence & Sofware Engneerng, Monash Unversy 1 900 Dandenong Road, Caulfeld
Introductory Turbulence Modeling
 Inrodcory Trblence Modelng Lecres Noes by Ismal B. Cel Wes Vrgna nversy Mechancal & Aerospace Engneerng Dep..O. Bo 606 Morganown, WV 6506-606 December 999 TABLE OF CONTENT age TABLE OF CONTENT... NOMENCLATRE...v.0
Inrodcory Trblence Modelng Lecres Noes by Ismal B. Cel Wes Vrgna nversy Mechancal & Aerospace Engneerng Dep..O. Bo 606 Morganown, WV 6506-606 December 999 TABLE OF CONTENT age TABLE OF CONTENT... NOMENCLATRE...v.0
HEURISTIC ALGORITHM FOR SINGLE RESOURCE CONSTRAINED PROJECT SCHEDULING PROBLEM BASED ON THE DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING
 Yugoslav Journal o Operaons Research Volume 19 (2009) Number 2, 281-298 DOI:10.2298/YUJOR0902281S HEURISTIC ALGORITHM FOR SINGLE RESOURCE CONSTRAINED PROJECT SCHEDULING PROBLEM BASED ON THE DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING
Yugoslav Journal o Operaons Research Volume 19 (2009) Number 2, 281-298 DOI:10.2298/YUJOR0902281S HEURISTIC ALGORITHM FOR SINGLE RESOURCE CONSTRAINED PROJECT SCHEDULING PROBLEM BASED ON THE DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING
Time Series. A thesis. Submitted to the. Edith Cowan University. Perth, Western Australia. David Sheung Chi Fung. In Fulfillment of the Requirements
 Mehods for he Esmaon of Mssng Values n Tme Seres A hess Submed o he Faculy of Communcaons, ealh and Scence Edh Cowan Unversy Perh, Wesern Ausrala By Davd Sheung Ch Fung In Fulfllmen of he Requremens For
Mehods for he Esmaon of Mssng Values n Tme Seres A hess Submed o he Faculy of Communcaons, ealh and Scence Edh Cowan Unversy Perh, Wesern Ausrala By Davd Sheung Ch Fung In Fulfllmen of he Requremens For
The Virtual Machine Resource Allocation based on Service Features in Cloud Computing Environment
 Send Orders for Reprns o [email protected] The Open Cybernecs & Sysemcs Journal, 2015, 9, 639-647 639 Open Access The Vrual Machne Resource Allocaon based on Servce Feaures n Cloud Compung Envronmen
Send Orders for Reprns o [email protected] The Open Cybernecs & Sysemcs Journal, 2015, 9, 639-647 639 Open Access The Vrual Machne Resource Allocaon based on Servce Feaures n Cloud Compung Envronmen
SPC-based Inventory Control Policy to Improve Supply Chain Dynamics
 Francesco Cosanno e al. / Inernaonal Journal of Engneerng and Technology (IJET) SPC-based Invenory Conrol Polcy o Improve Supply Chan ynamcs Francesco Cosanno #, Gulo Gravo #, Ahmed Shaban #3,*, Massmo
Francesco Cosanno e al. / Inernaonal Journal of Engneerng and Technology (IJET) SPC-based Invenory Conrol Polcy o Improve Supply Chan ynamcs Francesco Cosanno #, Gulo Gravo #, Ahmed Shaban #3,*, Massmo
RESOLUTION OF THE LINEAR FRACTIONAL GOAL PROGRAMMING PROBLEM
 Revsa Elecrónca de Comuncacones y Trabajos de ASEPUMA. Rec@ Volumen Págnas 7 a 40. RESOLUTION OF THE LINEAR FRACTIONAL GOAL PROGRAMMING PROBLEM RAFAEL CABALLERO [email protected] Unversdad de Málaga
Revsa Elecrónca de Comuncacones y Trabajos de ASEPUMA. Rec@ Volumen Págnas 7 a 40. RESOLUTION OF THE LINEAR FRACTIONAL GOAL PROGRAMMING PROBLEM RAFAEL CABALLERO [email protected] Unversdad de Málaga
MULTI-WORKDAY ERGONOMIC WORKFORCE SCHEDULING WITH DAYS OFF
 Proceedngs of he 4h Inernaonal Conference on Engneerng, Projec, and Producon Managemen (EPPM 203) MULTI-WORKDAY ERGONOMIC WORKFORCE SCHEDULING WITH DAYS OFF Tar Raanamanee and Suebsak Nanhavanj School
Proceedngs of he 4h Inernaonal Conference on Engneerng, Projec, and Producon Managemen (EPPM 203) MULTI-WORKDAY ERGONOMIC WORKFORCE SCHEDULING WITH DAYS OFF Tar Raanamanee and Suebsak Nanhavanj School
Pavel V. Shevchenko Quantitative Risk Management. CSIRO Mathematical & Information Sciences. Bridging to Finance
 Pavel V. Shevchenko Quanave Rsk Managemen CSIRO Mahemacal & Informaon Scences Brdgng o Fnance Conference Quanave Mehods n Invesmen and Rsk Managemen: sourcng new approaches from mahemacal heory and he
Pavel V. Shevchenko Quanave Rsk Managemen CSIRO Mahemacal & Informaon Scences Brdgng o Fnance Conference Quanave Mehods n Invesmen and Rsk Managemen: sourcng new approaches from mahemacal heory and he
Estimating intrinsic currency values
 Cung edge Foregn exchange Esmang nrnsc currency values Forex marke praconers consanly alk abou he srenghenng or weakenng of ndvdual currences. In hs arcle, Jan Chen and Paul Dous presen a new mehodology
Cung edge Foregn exchange Esmang nrnsc currency values Forex marke praconers consanly alk abou he srenghenng or weakenng of ndvdual currences. In hs arcle, Jan Chen and Paul Dous presen a new mehodology
A Real-time Adaptive Traffic Monitoring Approach for Multimedia Content Delivery in Wireless Environment *
 A Real-e Adapve Traffc Monorng Approach for Muleda Conen Delvery n Wreless Envronen * Boonl Adpa and DongSong Zhang Inforaon Syses Deparen Unversy of Maryland, Balore Couny Balore, MD, U.S.A. [email protected],
A Real-e Adapve Traffc Monorng Approach for Muleda Conen Delvery n Wreless Envronen * Boonl Adpa and DongSong Zhang Inforaon Syses Deparen Unversy of Maryland, Balore Couny Balore, MD, U.S.A. [email protected],
Proceedings of the 2008 Winter Simulation Conference S. J. Mason, R. R. Hill, L. Mönch, O. Rose, T. Jefferson, J. W. Fowler eds.
 Proceedngs of he 008 Wner Smulaon Conference S. J. Mason, R. R. Hll, L. Mönch, O. Rose, T. Jefferson, J. W. Fowler eds. DEMAND FORECAST OF SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS BASED ON TECHNOLOGY DIFFUSION Chen-Fu Chen,
Proceedngs of he 008 Wner Smulaon Conference S. J. Mason, R. R. Hll, L. Mönch, O. Rose, T. Jefferson, J. W. Fowler eds. DEMAND FORECAST OF SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS BASED ON TECHNOLOGY DIFFUSION Chen-Fu Chen,
THE IMPACT OF UNSECURED DEBT ON FINANCIAL DISTRESS AMONG BRITISH HOUSEHOLDS. Ana del Río and Garry Young. Documentos de Trabajo N.
 THE IMPACT OF UNSECURED DEBT ON FINANCIAL DISTRESS AMONG BRITISH HOUSEHOLDS 2005 Ana del Río and Garry Young Documenos de Trabajo N.º 0512 THE IMPACT OF UNSECURED DEBT ON FINANCIAL DISTRESS AMONG BRITISH
THE IMPACT OF UNSECURED DEBT ON FINANCIAL DISTRESS AMONG BRITISH HOUSEHOLDS 2005 Ana del Río and Garry Young Documenos de Trabajo N.º 0512 THE IMPACT OF UNSECURED DEBT ON FINANCIAL DISTRESS AMONG BRITISH
Testing techniques and forecasting ability of FX Options Implied Risk Neutral Densities. Oren Tapiero
 Tesng echnques and forecasng ably of FX Opons Impled Rsk Neural Denses Oren Tapero 1 Table of Conens Absrac 3 Inroducon 4 I. The Daa 7 1. Opon Selecon Crerons 7. Use of mpled spo raes nsead of quoed spo
Tesng echnques and forecasng ably of FX Opons Impled Rsk Neural Denses Oren Tapero 1 Table of Conens Absrac 3 Inroducon 4 I. The Daa 7 1. Opon Selecon Crerons 7. Use of mpled spo raes nsead of quoed spo
MODEL-BASED APPROACH TO CHARACTERIZATION OF DIFFUSION PROCESSES VIA DISTRIBUTED CONTROL OF ACTUATED SENSOR NETWORKS
 MODEL-BASED APPROACH TO CHARACTERIZATION OF DIFFUSION PROCESSES IA DISTRIBUTED CONTROL OF ACTUATED SENSOR NETWORKS Kevn L. Moore and YangQuan Chen Cener for Self-Organzng and Inellgen Sysems Uah Sae Unversy
MODEL-BASED APPROACH TO CHARACTERIZATION OF DIFFUSION PROCESSES IA DISTRIBUTED CONTROL OF ACTUATED SENSOR NETWORKS Kevn L. Moore and YangQuan Chen Cener for Self-Organzng and Inellgen Sysems Uah Sae Unversy
How To Understand The Theory Of The Power Of The Market
 Sysem Dynamcs models for generaon expanson plannng n a compeve framework: olgopoly and marke power represenaon J.J. Sánchez, J. Barquín, E. Ceneno, A. López-Peña Insuo de Invesgacón Tecnológca Unversdad
Sysem Dynamcs models for generaon expanson plannng n a compeve framework: olgopoly and marke power represenaon J.J. Sánchez, J. Barquín, E. Ceneno, A. López-Peña Insuo de Invesgacón Tecnológca Unversdad
Methodology of the CBOE S&P 500 PutWrite Index (PUT SM ) (with supplemental information regarding the CBOE S&P 500 PutWrite T-W Index (PWT SM ))
 ehodology of he CBOE S&P 500 PuWre Index (PUT S ) (wh supplemenal nformaon regardng he CBOE S&P 500 PuWre T-W Index (PWT S )) The CBOE S&P 500 PuWre Index (cker symbol PUT ) racks he value of a passve
ehodology of he CBOE S&P 500 PuWre Index (PUT S ) (wh supplemenal nformaon regardng he CBOE S&P 500 PuWre T-W Index (PWT S )) The CBOE S&P 500 PuWre Index (cker symbol PUT ) racks he value of a passve
PARTICLE FILTER BASED VEHICLE TRACKING APPROACH WITH IMPROVED RESAMPLING STAGE
 ISS: 0976-910(OLIE) ICTACT JOURAL O IMAGE AD VIDEO PROCESSIG, FEBRUARY 014, VOLUME: 04, ISSUE: 03 PARTICLE FILTER BASED VEHICLE TRACKIG APPROACH WITH IMPROVED RESAMPLIG STAGE We Leong Khong 1, We Yeang
ISS: 0976-910(OLIE) ICTACT JOURAL O IMAGE AD VIDEO PROCESSIG, FEBRUARY 014, VOLUME: 04, ISSUE: 03 PARTICLE FILTER BASED VEHICLE TRACKIG APPROACH WITH IMPROVED RESAMPLIG STAGE We Leong Khong 1, We Yeang
Linear methods for regression and classification with functional data
 Lnear mehods for regresson and classfcaon wh funconal daa Glber Sapora Chare de Sasue Appluée & CEDRIC Conservaore Naonal des Ars e Méers 9 rue San Marn, case 44 754 Pars cedex 3, France [email protected]
Lnear mehods for regresson and classfcaon wh funconal daa Glber Sapora Chare de Sasue Appluée & CEDRIC Conservaore Naonal des Ars e Méers 9 rue San Marn, case 44 754 Pars cedex 3, France [email protected]
Market-Clearing Electricity Prices and Energy Uplift
 Marke-Clearng Elecrcy Prces and Energy Uplf Paul R. Grbk, Wllam W. Hogan, and Susan L. Pope December 31, 2007 Elecrcy marke models requre energy prces for balancng, spo and shor-erm forward ransacons.
Marke-Clearng Elecrcy Prces and Energy Uplf Paul R. Grbk, Wllam W. Hogan, and Susan L. Pope December 31, 2007 Elecrcy marke models requre energy prces for balancng, spo and shor-erm forward ransacons.
A GENERALIZED FRAMEWORK FOR CREDIT RISK PORTFOLIO MODELS
 A GENERALIZED FRAMEWORK FOR CREDIT RISK PORTFOLIO MODELS H. UGUR KOYLUOGLU ANDREW HICKMAN Olver, Wyman & Company CSFP Capal, Inc. * 666 Ffh Avenue Eleven Madson Avenue New Yor, New Yor 10103 New Yor, New
A GENERALIZED FRAMEWORK FOR CREDIT RISK PORTFOLIO MODELS H. UGUR KOYLUOGLU ANDREW HICKMAN Olver, Wyman & Company CSFP Capal, Inc. * 666 Ffh Avenue Eleven Madson Avenue New Yor, New Yor 10103 New Yor, New
A Hybrid AANN-KPCA Approach to Sensor Data Validation
 Proceedngs of he 7h WSEAS Inernaonal Conference on Appled Informacs and Communcaons, Ahens, Greece, Augus 4-6, 7 85 A Hybrd AANN-KPCA Approach o Sensor Daa Valdaon REZA SHARIFI, REZA LANGARI Deparmen of
Proceedngs of he 7h WSEAS Inernaonal Conference on Appled Informacs and Communcaons, Ahens, Greece, Augus 4-6, 7 85 A Hybrd AANN-KPCA Approach o Sensor Daa Valdaon REZA SHARIFI, REZA LANGARI Deparmen of
Y2K* Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé. Rutgers Uni ersity, 75 Hamilton Street, New Brunswick, New Jersey 08901 E-mail: [email protected].
 Revew of Economc Dynamcs 2, 850856 Ž 1999. Arcle ID redy.1999.0065, avalable onlne a hp:www.dealbrary.com on Y2K* Sephane Schm-Grohé Rugers Unersy, 75 Hamlon Sree, New Brunswc, New Jersey 08901 E-mal:
Revew of Economc Dynamcs 2, 850856 Ž 1999. Arcle ID redy.1999.0065, avalable onlne a hp:www.dealbrary.com on Y2K* Sephane Schm-Grohé Rugers Unersy, 75 Hamlon Sree, New Brunswc, New Jersey 08901 E-mal:
A Hybrid Wind-Solar Energy System: A New Rectifier Stage Topology
 A Hybr n-solar Energy Sysem: A New Recfer Sage Topology Joanne Hu*, IEEE Suen Member, Alreza Bakhsha IEEE Senor Member, an Praveen K. Jan, IEEE Fellow Deparmen of Elecrcal an Compuer Engneerng Queen s
A Hybr n-solar Energy Sysem: A New Recfer Sage Topology Joanne Hu*, IEEE Suen Member, Alreza Bakhsha IEEE Senor Member, an Praveen K. Jan, IEEE Fellow Deparmen of Elecrcal an Compuer Engneerng Queen s
PerfCenter: A Methodology and Tool for Performance Analysis of Application Hosting Centers
 PerfCener: A Mehodology and Tool for Performance Analyss of Applcaon Hosng Ceners Rukma P. Verlekar, Varsha Ape, Prakhar Goyal, Bhavsh Aggarwal Dep. of Compuer Scence and Engneerng Indan Insue of Technology
PerfCener: A Mehodology and Tool for Performance Analyss of Applcaon Hosng Ceners Rukma P. Verlekar, Varsha Ape, Prakhar Goyal, Bhavsh Aggarwal Dep. of Compuer Scence and Engneerng Indan Insue of Technology
Anomaly Detection in Network Traffic Using Selected Methods of Time Series Analysis
 I. J. Compuer Nework and Informaon Secury, 2015, 9, 10-18 Publshed Onlne Augus 2015 n MECS (hp://www.mecs-press.org/) DOI: 10.5815/jcns.2015.09.02 Anomaly Deecon n Nework Traffc Usng Seleced Mehods of
I. J. Compuer Nework and Informaon Secury, 2015, 9, 10-18 Publshed Onlne Augus 2015 n MECS (hp://www.mecs-press.org/) DOI: 10.5815/jcns.2015.09.02 Anomaly Deecon n Nework Traffc Usng Seleced Mehods of
The Rules of the Settlement Guarantee Fund. 1. These Rules, hereinafter referred to as "the Rules", define the procedures for the formation
 Vald as of May 31, 2010 The Rules of he Selemen Guaranee Fund 1 1. These Rules, herenafer referred o as "he Rules", defne he procedures for he formaon and use of he Selemen Guaranee Fund, as defned n Arcle
Vald as of May 31, 2010 The Rules of he Selemen Guaranee Fund 1 1. These Rules, herenafer referred o as "he Rules", defne he procedures for he formaon and use of he Selemen Guaranee Fund, as defned n Arcle
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMETRICS AND BUSINESS STATISTICS. Exponential Smoothing for Inventory Control: Means and Variances of Lead-Time Demand
 ISSN 440-77X ISBN 0 736 094 X AUSTRALIA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMETRICS AND BUSINESS STATISTICS Exponenal Smoohng for Invenory Conrol: Means and Varances of Lead-Tme Demand Ralph D. Snyder, Anne B. Koehler,
ISSN 440-77X ISBN 0 736 094 X AUSTRALIA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMETRICS AND BUSINESS STATISTICS Exponenal Smoohng for Invenory Conrol: Means and Varances of Lead-Tme Demand Ralph D. Snyder, Anne B. Koehler,
Cooperative Distributed Scheduling for Storage Devices in Microgrids using Dynamic KKT Multipliers and Consensus Networks
 Cooperave Dsrbued Schedulng for Sorage Devces n Mcrogrds usng Dynamc KK Mulplers and Consensus Newors Navd Rahbar-Asr Yuan Zhang Mo-Yuen Chow Deparmen of Elecrcal and Compuer Engneerng Norh Carolna Sae
Cooperave Dsrbued Schedulng for Sorage Devces n Mcrogrds usng Dynamc KK Mulplers and Consensus Newors Navd Rahbar-Asr Yuan Zhang Mo-Yuen Chow Deparmen of Elecrcal and Compuer Engneerng Norh Carolna Sae
A Heuristic Solution Method to a Stochastic Vehicle Routing Problem
 A Heursc Soluon Mehod o a Sochasc Vehcle Roung Problem Lars M. Hvaum Unversy of Bergen, Bergen, Norway. [email protected] Arne Løkkeangen Molde Unversy College, 6411 Molde, Norway. [email protected]
A Heursc Soluon Mehod o a Sochasc Vehcle Roung Problem Lars M. Hvaum Unversy of Bergen, Bergen, Norway. [email protected] Arne Løkkeangen Molde Unversy College, 6411 Molde, Norway. [email protected]
A Reverse Logistics Model for the Distribution of Waste/By-products. Hamid Pourmohammadi, Maged Dessouky*, and Mansour Rahimi
 A Reverse Logscs Model for he Dsrbuon of Wase/By-producs Hamd Pourmohammad, Maged Dessouy*, and Mansour Rahm Unversy of Souhern Calforna Epsen Deparmen of Indusral and Sysems Engneerng 375 McClnoc Avenue,
A Reverse Logscs Model for he Dsrbuon of Wase/By-producs Hamd Pourmohammad, Maged Dessouy*, and Mansour Rahm Unversy of Souhern Calforna Epsen Deparmen of Indusral and Sysems Engneerng 375 McClnoc Avenue,
Fundamental Analysis of Receivables and Bad Debt Reserves
 Fundamenal Analyss of Recevables and Bad Deb Reserves Mchael Calegar Assocae Professor Deparmen of Accounng Sana Clara Unversy e-mal: [email protected] February 21 2005 Fundamenal Analyss of Recevables
Fundamenal Analyss of Recevables and Bad Deb Reserves Mchael Calegar Assocae Professor Deparmen of Accounng Sana Clara Unversy e-mal: [email protected] February 21 2005 Fundamenal Analyss of Recevables
Attribution Strategies and Return on Keyword Investment in Paid Search Advertising
 Arbuon Sraeges and Reurn on Keyword Invesmen n Pad Search Adversng by Hongshuang (Alce) L, P. K. Kannan, Sva Vswanahan and Abhshek Pan * December 15, 2015 * Honshuang (Alce) L s Asssan Professor of Markeng,
Arbuon Sraeges and Reurn on Keyword Invesmen n Pad Search Adversng by Hongshuang (Alce) L, P. K. Kannan, Sva Vswanahan and Abhshek Pan * December 15, 2015 * Honshuang (Alce) L s Asssan Professor of Markeng,
Network Effects on Standard Software Markets: A Simulation Model to examine Pricing Strategies
 Nework Effecs on Sandard Sofware Markes Page Nework Effecs on Sandard Sofware Markes: A Smulaon Model o examne Prcng Sraeges Peer Buxmann Absrac Ths paper examnes sraeges of sandard sofware vendors, n
Nework Effecs on Sandard Sofware Markes Page Nework Effecs on Sandard Sofware Markes: A Smulaon Model o examne Prcng Sraeges Peer Buxmann Absrac Ths paper examnes sraeges of sandard sofware vendors, n
An Ensemble Data Mining and FLANN Combining Short-term Load Forecasting System for Abnormal Days
 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE, VOL. 6, NO. 6, JUNE 0 96 An Ensemble Daa Mnng and FLANN Combnng Shor-erm Load Forecasng Sysem for Abnormal Days Mng L College of Auomaon, Guangdong Unversy of Technology, Guangzhou,
JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE, VOL. 6, NO. 6, JUNE 0 96 An Ensemble Daa Mnng and FLANN Combnng Shor-erm Load Forecasng Sysem for Abnormal Days Mng L College of Auomaon, Guangdong Unversy of Technology, Guangzhou,
A New Method to Evaluate Equity-Linked Life Insurance
 Coneporary Manageen Research Pages -, Vol. 0, No., March 04 do:0.790/cr.097 A New Mehod o Evaluae Equy-Lnked Lfe Insurance Mng-Shann Tsa Naonal Unversy of Kaohsung E-Mal: [email protected] Shh-Cheng Lee Yuan-Ze
Coneporary Manageen Research Pages -, Vol. 0, No., March 04 do:0.790/cr.097 A New Mehod o Evaluae Equy-Lnked Lfe Insurance Mng-Shann Tsa Naonal Unversy of Kaohsung E-Mal: [email protected] Shh-Cheng Lee Yuan-Ze
Information-based trading, price impact of trades, and trade autocorrelation
 Informaon-based radng, prce mpac of rades, and rade auocorrelaon Kee H. Chung a,, Mngsheng L b, Thomas H. McInsh c a Sae Unversy of New York (SUNY) a Buffalo, Buffalo, NY 426, USA b Unversy of Lousana
Informaon-based radng, prce mpac of rades, and rade auocorrelaon Kee H. Chung a,, Mngsheng L b, Thomas H. McInsh c a Sae Unversy of New York (SUNY) a Buffalo, Buffalo, NY 426, USA b Unversy of Lousana
Payout Policy Choices and Shareholder Investment Horizons
 Payou Polcy Choces and Shareholder Invesmen Horzons José-Mguel Gaspar* Massmo Massa** Pedro Maos*** Rajdeep Pagr Zahd Rehman Absrac Ths paper examnes how shareholder nvesmen horzons nfluence payou polcy
Payou Polcy Choces and Shareholder Invesmen Horzons José-Mguel Gaspar* Massmo Massa** Pedro Maos*** Rajdeep Pagr Zahd Rehman Absrac Ths paper examnes how shareholder nvesmen horzons nfluence payou polcy
The Incentive Effects of Organizational Forms: Evidence from Florida s Non-Emergency Medicaid Transportation Programs
 The Incenve Effecs of Organzaonal Forms: Evdence from Florda s Non-Emergency Medcad Transporaon Programs Chfeng Da* Deparmen of Economcs Souhern Illnos Unversy Carbondale, IL 62901 Davd Denslow Deparmen
The Incenve Effecs of Organzaonal Forms: Evdence from Florda s Non-Emergency Medcad Transporaon Programs Chfeng Da* Deparmen of Economcs Souhern Illnos Unversy Carbondale, IL 62901 Davd Denslow Deparmen
Insurance. By Mark Dorfman, Alexander Kling, and Jochen Russ. Abstract
 he Impac Of Deflaon On Insurance Companes Offerng Parcpang fe Insurance y Mar Dorfman, lexander Klng, and Jochen Russ bsrac We presen a smple model n whch he mpac of a deflaonary economy on lfe nsurers
he Impac Of Deflaon On Insurance Companes Offerng Parcpang fe Insurance y Mar Dorfman, lexander Klng, and Jochen Russ bsrac We presen a smple model n whch he mpac of a deflaonary economy on lfe nsurers
ANALYSIS OF SOURCE LOCATION ALGORITHMS Part I: Overview and non-iterative methods
 ANALYSIS OF SOURCE LOCATION ALGORITHMS Par I: Overvew and non-erave mehods MAOCHEN GE Pennsylvana Sae Unversy, Unversy Park PA 1680 Absrac Ths arcle and he accompanyng one dscuss he source locaon heores
ANALYSIS OF SOURCE LOCATION ALGORITHMS Par I: Overvew and non-erave mehods MAOCHEN GE Pennsylvana Sae Unversy, Unversy Park PA 1680 Absrac Ths arcle and he accompanyng one dscuss he source locaon heores
Applying the Theta Model to Short-Term Forecasts in Monthly Time Series
 Applyng he Thea Model o Shor-Term Forecass n Monhly Tme Seres Glson Adamczuk Olvera *, Marcelo Gonçalves Trenn +, Anselmo Chaves Neo ** * Deparmen of Mechancal Engneerng, Federal Technologcal Unversy of
Applyng he Thea Model o Shor-Term Forecass n Monhly Tme Seres Glson Adamczuk Olvera *, Marcelo Gonçalves Trenn +, Anselmo Chaves Neo ** * Deparmen of Mechancal Engneerng, Federal Technologcal Unversy of
Ground rules. Guide to the calculation methods of the FTSE Actuaries UK Gilts Index Series v1.9
 Ground rules Gude o he calculaon mehods of he FTSE Acuares UK Gls Index Seres v1.9 fserussell.com Ocober 2015 Conens 1.0 Inroducon... 4 1.1 Scope... 4 1.2 FTSE Russell... 5 1.3 Overvew of he calculaons...
Ground rules Gude o he calculaon mehods of he FTSE Acuares UK Gls Index Seres v1.9 fserussell.com Ocober 2015 Conens 1.0 Inroducon... 4 1.1 Scope... 4 1.2 FTSE Russell... 5 1.3 Overvew of he calculaons...
The Prediction Algorithm Based on Fuzzy Logic Using Time Series Data Mining Method
 The Predcon Algorhm Based on Fuzzy Logc Usng Tme Seres Daa Mnng Mehod I Aydn, M Karakose, and E Akn Asrac Predcon of an even a a me seres s que mporan for engneerng and economy prolems Tme seres daa mnng
The Predcon Algorhm Based on Fuzzy Logc Usng Tme Seres Daa Mnng Mehod I Aydn, M Karakose, and E Akn Asrac Predcon of an even a a me seres s que mporan for engneerng and economy prolems Tme seres daa mnng
Distribution Channel Strategy and Efficiency Performance of the Life insurance. Industry in Taiwan. Abstract
 Dsrbuon Channel Sraegy and Effcency Performance of he Lfe nsurance Indusry n Tawan Absrac Changes n regulaons and laws he pas few decades have afeced Tawan s lfe nsurance ndusry and caused many nsurers
Dsrbuon Channel Sraegy and Effcency Performance of he Lfe nsurance Indusry n Tawan Absrac Changes n regulaons and laws he pas few decades have afeced Tawan s lfe nsurance ndusry and caused many nsurers
The Definition and Measurement of Productivity* Mark Rogers
 The Defnon and Measuremen of Producvy* Mark Rogers Melbourne Insue of Appled Economc and Socal Research The Unversy of Melbourne Melbourne Insue Workng Paper No. 9/98 ISSN 1328-4991 ISBN 0 7325 0912 6
The Defnon and Measuremen of Producvy* Mark Rogers Melbourne Insue of Appled Economc and Socal Research The Unversy of Melbourne Melbourne Insue Workng Paper No. 9/98 ISSN 1328-4991 ISBN 0 7325 0912 6
SHIPPING ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR ULTRA LARGE CONTAINERSHIP
 Journal of he Easern Asa Socey for Transporaon Sudes, Vol. 6, pp. 936-951, 2005 SHIPPING ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR ULTRA LARGE CONTAINERSHIP Chaug-Ing HSU Professor Deparen of Transporaon Technology and Manageen
Journal of he Easern Asa Socey for Transporaon Sudes, Vol. 6, pp. 936-951, 2005 SHIPPING ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR ULTRA LARGE CONTAINERSHIP Chaug-Ing HSU Professor Deparen of Transporaon Technology and Manageen
Optimization of Nurse Scheduling Problem with a Two-Stage Mathematical Programming Model
 Asa Pacfc Managemen Revew 15(4) (2010) 503-516 Opmzaon of Nurse Schedulng Problem wh a Two-Sage Mahemacal Programmng Model Chang-Chun Tsa a,*, Cheng-Jung Lee b a Deparmen of Busness Admnsraon, Trans World
Asa Pacfc Managemen Revew 15(4) (2010) 503-516 Opmzaon of Nurse Schedulng Problem wh a Two-Sage Mahemacal Programmng Model Chang-Chun Tsa a,*, Cheng-Jung Lee b a Deparmen of Busness Admnsraon, Trans World
A robust optimisation approach to project scheduling and resource allocation. Elodie Adida* and Pradnya Joshi
 In. J. Servces Operaons and Informacs, Vol. 4, No. 2, 2009 169 A robus opmsaon approach o projec schedulng and resource allocaon Elode Adda* and Pradnya Josh Deparmen of Mechancal and Indusral Engneerng,
In. J. Servces Operaons and Informacs, Vol. 4, No. 2, 2009 169 A robus opmsaon approach o projec schedulng and resource allocaon Elode Adda* and Pradnya Josh Deparmen of Mechancal and Indusral Engneerng,
Efficiency of General Insurance in Malaysia Using Stochastic Frontier Analysis (SFA)
 Inernaonal Journal of Modern Engneerng Research (IJMER) www.jmer.com Vol., Issue.5, Sep-Oc. 01 pp-3886-3890 ISSN: 49-6645 Effcency of General Insurance n Malaysa Usng Sochasc Froner Analyss (SFA) Mohamad
Inernaonal Journal of Modern Engneerng Research (IJMER) www.jmer.com Vol., Issue.5, Sep-Oc. 01 pp-3886-3890 ISSN: 49-6645 Effcency of General Insurance n Malaysa Usng Sochasc Froner Analyss (SFA) Mohamad
This research paper analyzes the impact of information technology (IT) in a healthcare
 Producvy of Informaon Sysems n he Healhcare Indusry Nrup M. Menon Byungae Lee Lesle Eldenburg Texas Tech Unversy, College of Busness MS 2101, Lubbock, Texas 79409 [email protected] The Unversy of Illnos a
Producvy of Informaon Sysems n he Healhcare Indusry Nrup M. Menon Byungae Lee Lesle Eldenburg Texas Tech Unversy, College of Busness MS 2101, Lubbock, Texas 79409 [email protected] The Unversy of Illnos a
Performance Measurement for Traditional Investment
 E D H E C I S K A N D A S S E T M A N A G E M E N T E S E A C H C E N T E erformance Measuremen for Tradonal Invesmen Leraure Survey January 007 Véronque Le Sourd Senor esearch Engneer a he EDHEC sk and
E D H E C I S K A N D A S S E T M A N A G E M E N T E S E A C H C E N T E erformance Measuremen for Tradonal Invesmen Leraure Survey January 007 Véronque Le Sourd Senor esearch Engneer a he EDHEC sk and
A binary powering Schur algorithm for computing primary matrix roots
 Numercal Algorhms manuscr No. (wll be nsered by he edor) A bnary owerng Schur algorhm for comung rmary marx roos Federco Greco Bruno Iannazzo Receved: dae / Acceed: dae Absrac An algorhm for comung rmary
Numercal Algorhms manuscr No. (wll be nsered by he edor) A bnary owerng Schur algorhm for comung rmary marx roos Federco Greco Bruno Iannazzo Receved: dae / Acceed: dae Absrac An algorhm for comung rmary
Levy-Grant-Schemes in Vocational Education
 Levy-Gran-Schemes n Vocaonal Educaon Sefan Bornemann Munch Graduae School of Economcs Inernaonal Educaonal Economcs Conference Taru, Augus 26h, 2005 Sefan Bornemann / MGSE Srucure Movaon and Objecve Leraure
Levy-Gran-Schemes n Vocaonal Educaon Sefan Bornemann Munch Graduae School of Economcs Inernaonal Educaonal Economcs Conference Taru, Augus 26h, 2005 Sefan Bornemann / MGSE Srucure Movaon and Objecve Leraure
Working Paper Tracking the new economy: Using growth theory to detect changes in trend productivity
 econsor www.econsor.eu Der Open-Access-Publkaonsserver der ZBW Lebnz-Informaonszenrum Wrschaf The Open Access Publcaon erver of he ZBW Lebnz Informaon Cenre for Economcs Kahn James A.; Rch Rober Workng
econsor www.econsor.eu Der Open-Access-Publkaonsserver der ZBW Lebnz-Informaonszenrum Wrschaf The Open Access Publcaon erver of he ZBW Lebnz Informaon Cenre for Economcs Kahn James A.; Rch Rober Workng
IMES DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES
 IMS DISCUSSION PPR SRIS Rsk Managemen for quy Porfolos of Japanese Banks kra ID and Toshkazu OHB Dscusson Paper No. 98--9 INSTITUT FOR MONTRY ND CONOMIC STUDIS BNK OF JPN C.P.O BOX 23 TOKYO 1-863 JPN NOT:
IMS DISCUSSION PPR SRIS Rsk Managemen for quy Porfolos of Japanese Banks kra ID and Toshkazu OHB Dscusson Paper No. 98--9 INSTITUT FOR MONTRY ND CONOMIC STUDIS BNK OF JPN C.P.O BOX 23 TOKYO 1-863 JPN NOT:
Return Persistence, Risk Dynamics and Momentum Exposures of Equity and Bond Mutual Funds
 Reurn Perssence, Rsk Dynamcs and Momenum Exposures of Equy and Bond Muual Funds Joop Hu, Marn Marens, and Therry Pos Ths Verson: 22-2-2008 Absrac To analyze perssence n muual fund performance, s common
Reurn Perssence, Rsk Dynamcs and Momenum Exposures of Equy and Bond Muual Funds Joop Hu, Marn Marens, and Therry Pos Ths Verson: 22-2-2008 Absrac To analyze perssence n muual fund performance, s common
Reading assignment: Chapter 4 of Aris
 Chaper 4 - The Knemacs of Flud Moon Parcle pahs and maeral dervaves Sreamlnes Sreaklnes Dlaaon Reynolds ranspor heorem Conservaon of mass and he equaon of connuy Deformaon and rae of sran Physcal nerpreaon
Chaper 4 - The Knemacs of Flud Moon Parcle pahs and maeral dervaves Sreamlnes Sreaklnes Dlaaon Reynolds ranspor heorem Conservaon of mass and he equaon of connuy Deformaon and rae of sran Physcal nerpreaon
HAND: Highly Available Dynamic Deployment Infrastructure for Globus Toolkit 4
 HAND: Hghly Avalable Dynamc Deploymen Infrasrucure for Globus Toolk 4 L Q 1, Ha Jn 1, Ian Foser,3, Jarek Gawor 1 Huazhong Unversy of Scence and Technology, Wuhan, 430074, Chna [email protected]; [email protected]
HAND: Hghly Avalable Dynamc Deploymen Infrasrucure for Globus Toolk 4 L Q 1, Ha Jn 1, Ian Foser,3, Jarek Gawor 1 Huazhong Unversy of Scence and Technology, Wuhan, 430074, Chna [email protected]; [email protected]
Calculating and interpreting multipliers in the presence of non-stationary time series: The case of U.S. federal infrastructure spending
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SOCIAL AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCES ISSN Prn: 156-1540, ISSN Onlne: 151-1559, do:10.551/ajsms.010.1.1.4.38 010, ScenceHuβ, hp://www.schub.org/ajsms Calculang and nerpreng mulplers n he presence
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SOCIAL AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCES ISSN Prn: 156-1540, ISSN Onlne: 151-1559, do:10.551/ajsms.010.1.1.4.38 010, ScenceHuβ, hp://www.schub.org/ajsms Calculang and nerpreng mulplers n he presence
Modeling state-related fmri activity using change-point theory
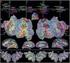 Modelng sae-relaed fmri acvy usng change-pon heory Marn A. Lndqus 1*, Chrsan Waugh and Tor D. Wager 3 1. Deparmen of Sascs, Columba Unversy, New York, NY, 1007. Deparmen of Psychology, Unversy of Mchgan,
Modelng sae-relaed fmri acvy usng change-pon heory Marn A. Lndqus 1*, Chrsan Waugh and Tor D. Wager 3 1. Deparmen of Sascs, Columba Unversy, New York, NY, 1007. Deparmen of Psychology, Unversy of Mchgan,
A Hybrid Method for Forecasting Stock Market Trend Using Soft-Thresholding De-noise Model and SVM
 A Hybrd Mehod for Forecasng Sock Marke Trend Usng Sof-Thresholdng De-nose Model and SVM Xueshen Su, Qnghua Hu, Daren Yu, Zongxa Xe, and Zhongyng Q Harbn Insue of Technology, Harbn 150001, Chna [email protected]
A Hybrd Mehod for Forecasng Sock Marke Trend Usng Sof-Thresholdng De-nose Model and SVM Xueshen Su, Qnghua Hu, Daren Yu, Zongxa Xe, and Zhongyng Q Harbn Insue of Technology, Harbn 150001, Chna [email protected]
