Microsoft Access 3: Understanding and Creating Queries
|
|
|
- Damian Owens
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
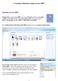
1 Microsoft Access 3: Understanding and Creating Queries In Access Level 2, we learned how to perform basic data retrievals by using Search & Replace functions and Sort & Filter functions. For more complex tasks such as retrieving data records that meet particular criteria, you can use queries. Queries are questions that you ask of your database. By using queries, you can retrieve data from a single table or from multiple tables and display all data together. You can also save and store the queries as reusable Access objects. Open LibraryDatabaseAccess3.accdb. Let s take a look at the Query Design Feature. Click on Create>Query Design (in Other group). In the Show Table window on the right, double click on one or more tables to be included in your query. Or you can select each table by clicking once and then click on the Add button. Click on the Close button after finishing your selection. You will see the Query Design ribbon under the Query Tools tab and the new tab for your query opens up with two segments. The upper segment shows selected tables with existing relationships. Double-clicking on any particular field from the table list will include that field in the Lower Segment of the Query Design View window. You may also drag and drop field names to the lower segment. See below. Click on a table in this segment then press delete key to delete from the query Double-clicking on the asterisk above field names will include all the fields in that table. Field Name Indicates which table the field has been taken from Drag the field onto the lower segment or double click on it to include in your query Check this box for a field to be displayed in results Click on this gray bar to select the entire field then hit delete key on keyboard to delete a field from query Access 3: Queries Page 1 of 18 3/16/2011
2 Let s explore the Query Design Ribbon. Click to run the query Change query type by clicking Click to show list of tables Click to create Totals on Query Include the following fields to run a test query. Title and Publication Year from the Book table Last Name and First Name fields from the Author table Company from the Publisher table You can re-arrange the order of fields by grabbing the entire field and place it on an empty field holder. Position your mouse on the top of a field and click once to select the entire field just like in Excel as to select the entire column. The field will turn black. See sample. Once done, point to the gray bar and grab the entire field with your mouse to move to a new location. Click on the Run command on the ribbon to run your query. Click on the Run command on the Design Ribbon. Your result query should appear in a new tab named Query1 and should look like this: Access 3: Queries Page 2 of 18 3/16/2011
3 You can switch between the Design view and the Table view on the Ribbon to modify the query in the Design view even after you created it. Saving the Query: Click the Save button on the Quick Access Tool bar or by closing out the query tab. That will prompt you to save your query. Give a name that reflects the nature of your query. See the example. Your saved query should display in the Navigation Pane under the Queries object type. Remember: Any change you make in a query (such as adding, deleting, or editing data) will be changed in the tables too!! Creating Subset of a Query: OR Condition: To retrieve the subset of your records in the above query by using the Or condition, you can specify the criteria you want in the Query Design. Not to start from scratch, follow the steps below to copy the existing query and then create a subset out of it as a new query. 1. Right-click on the current query in the navigation pane and select copy. 2. Right-click on the empty area in the navigation pane and click on paste. Give a new name that is meaningful to your new query. 3. A new query with the new name will appear in the navigation pane. Double-click on it to open. Then click on the Design button to edit it in design view. 4. Assume you are only interested in retrieving titles in ascending order published by two companies: Arrows Publication and Beaver Books Ltd regardless of the publication year. o o o Set the sort order to ascending in the Title column. In the Company column, enter Arrows Publication in the first criteria row and Beaver Books Ltd in the next criteria row below. Quotes will be automatically added when you click off. You must enter the entire name NOT a partial name. Deselect the Show checkbox in the Publication Year column. Run your query and note the results. Access 3: Queries Page 3 of 18 3/16/2011
4 See the criteria in design view below. Your result should look like this. Access returns records that have both names in company column And Condition: You can also combine criterion in your query. 1. Follow the first two steps above to create a new query out of our first query Title, Author, and Publisher Details and give a new name And Condition of Title, Author and Publisher Details. See below. 2. Enter Outreach College Press in the criteria row of company column and the year 1991 in the Publication Year. Run your query. You should retrieve one record that meets both of your criteria as shown below. In both conditions above, Access assumes that you are using the comparison operator = (equal). You are looking for records where the text or value in the corresponding field in the datasheet is equal to the text or value that you have entered in the Criteria row in the Query Design grid. There are other comparison operators you can use. See below. Access 3: Queries Page 4 of 18 3/16/2011
5 More on Operators You use the comparison and other special operators in criteria rows to compare values and return a result that is True, False, or Null by using the following operator range. Criteria Definition Example Description & Result < less than <3 Finds records where the field is less than a certain value values less than 3. > greater than >3 Similar to above except finding records that has field value is greater than 3. <= less than or equal to <=#1/12/1936# Finds records where the field value is less than or equal to a certain value records will have dates on or before January 12, Note: Dates are enclosed between # signs. >= greater than or equal to >=#1/12/1936# Similar to above except finding records that has value greater than or equal to a certain value January 12, <> not equal to <>1994 Find records where the field value is not = equal to =Ferguson Ferguson = Ferguson Ferguson Between..And.. between the first and Between 1 and 3 the last value entered (including equal to a certain value Finds records where the value in the field is Ferguson. Notes: In Access 2007, either equal sign or double quotes around your text value are not necessary. Find records where the field is between the two endpoints including 1 and 3. the values) Is Null is empty Is Null Find records where the field is empty. Is Not Null is not empty Is Not Null Find records where the field is not empty. Like Like Like "ferguson" Find records with ferguson in the field. Wild card Characters When using Like and = operators, you can include wild cards characters to represent either individual characters or a string of characters. Two wild card characters are: * used to present a string of characters? used to represent a single character See examples below. Like "*son" - Find records that end in the letters son as in Ferguson, Peterson, etc. Access 3: Queries Page 5 of 18 3/16/2011
6 Like NW1* - Find records that begin with NW1 Like "[a-c]*" - Find records that begins with letters a, b, or c Like *press* - Find records that contain the word press in the field (beginning, middle, or end) Like "??ford" - Find records that begins with two letters but ends with the letters ford in the field. Between..And - This allows a user to put in a range in query, called a parameter query. A parameter query prompts the user for the value of a particular query field, rather than having the value built into the query itself. For example, if you desire to find titles published in a specified range of years, you can create a parameter query. Inside the brackets, type text telling the user what kind of information to enter. In this query, user will put in the first year and the last year of publication. Example shows the search result on titles published between 1990 and 2000 arranged in ascending order by the year. Access 3: Queries Page 6 of 18 3/16/2011
7 Creating a Concatenated field: As in Excel, Access allows you to create a combined [Concatenated] field from more than one field in a new field [column]. Assume you want to combine the Last Names and First Names fields into one field called FullName. Select the original query Title, Author and Publisher Details, copy it and create a new query and give it the name Concatenated field. In Design view, click in a blank column and type the following syntax in the field row. FullName: [FirstName] & " " & [LastName] Use double quotes to create a space between the FirstName and LastName fields. Use square brackets around the field names and & to combine between every two fields. Uncheck the LastName and FirstName columns not to show then run your query. The partial result should look like this: Concatenated field Creating a Calculated field: You can also create a calculated field in a new blank field in the Design form similar to creating a Concatenated field above. Assume you want to find out the total figure of all the copies of each title in the database. You can use normal mathematical operators (+ - * /). See more on Operators in the Appendix. Create a copy of the original query Title, Author and Publisher Details, copy and create a new query and give the name Calculate on Title, Author and Publisher Details. In Design view, delete the LastName and FirstName fields; add Price and Number of Copies fields from the Book table. Select a new field and type in the following syntax in the field row. Run the query. Total Cost: [Number of Copies]*[Price] The partial result should look like this. Access carried out the multiplication operator and provided results in the new calculated field Total Cost column. You can use the Totals function in your query (in datasheet view) by using on the Home ribbon. Simply select the column where you want to see Sum, Average, Count, Maximum, etc. For practice, select Count in Number of Copies column and Sum in Total Cost column or any column you want to see Math function results. Clicking on that Totals function again will turn off those Math function results. Access 3: Queries Page 7 of 18 3/16/2011
8 You can also use the Totals function in your query (in the design grid) by using the Totals function key in the Show/Hide group. The aggregate functions e.g. are sum, average, min, max, and count. You can use this type of function to work out how much you spend on each subject in your library. Create a new query by pulling out the Book and Subject tables. Use the Subject Name field. Create a new field for Total Cost by typing: Total Cost: [Number of Copies]*[Price] Click on Totals function button. A new line called Total will be added. Select sum in the Total Cost field and select Ascending in the sort row of the Subject Name field. Save the query as Totals in Query. Run the query. The result shows how much in total you spend on each subject. On the other hand, if you want to count how many books under each subject, just insert a Number of Copies field. Uncheck the Show checkbox for the Total Cost field and set it to group by the count function under the Number of Copies field. Is Null & Is Not Null: Useful in retrieving records that have blank or non-blank fields. For example, you want to retrieve those publishers with business phone numbers listed in the fields. Create a new query that includes only the Publisher Table. Pull in the Company and BusinessPhone fields in design grid. See partial results below. Save the Query as Null Query. Access 3: Queries Page 8 of 18 3/16/2011
9 Date Function: In Access, the Date() function returns the current date from your computer system as a number in days. You will have to convert days into weeks by using (/7) and into years by using (/365). Say that you wanted to calculate the ages of those living authors. Create a new query by using the Author Table alone. First, you need to pull out the authors into your query whose DateofDeath field is blank (Is Null) and whose DateofBirth field is not blank (Is Not Null). Then create a new blank field to calculate from today s date. See example below. Age=Today s date minus [DateofBirth] then divide by 365 days to convert to years. In the Property Sheet button while in the Age field, limit the field format to Fixed and run the Query. The age field will have two decimals. Go back to Design View and set zero to Decimal places. The result should look like this. (Note: DateofDeath field is unchecked not to show in the result page.) save the query as Author Age Query. Access 3: Queries Page 9 of 18 3/16/2011
10 In level 2, we learned how to set relationships among tables. The lines between the tables that define relationships are called join lines. There are two types of join lines: inner and outer joins. In queries, you can define your joins based on what you need to ask of your database. Create a new query that includes the Publisher and Book Tables. Pull in Company from the Publisher Table and Title from the Book Table. Double-click on a join line to define join properties. Inner Joins: These queries return only those records from both tables in the join that match on the joining field. For example, if you want to retrieve only the titles that have corresponding publisher company names, use inner joins - option 1. Outer Joins: On the other hand, if you want to display all publisher company names, regardless of whether we own any titles from them, use outer joins - option 2 or 3. Inner joins with option 1 Outer joins with option 2 In the outer joins example, the direction of the arrow indicates that every row in the company field in the Publisher table will display whether or not a matching records exist in the title field of the Book table. You can save the query as Join Properties Query. Access 3: Queries Page 10 of 18 3/16/2011
11 Creating a Query using a Wizard: You can build a query by using the Query Wizard as follows: 1. Click the Create tab. 2. Click the Query Wizard button. 3. Click Simple Query Wizard, and then click OK. 4. Select a table or existing query to include in your query. (When you use an existing query to create a new query, the existing one is known as a subquery.) 5. Click to select the fields that you want included in your query. 6. Click Next to continue. 7. If you selected numeric or date fields in step 5, indicate whether you want to see detail or summary information. 8. If you choose Summary, click Summary Options to specify the calculation for each field, and then click OK. 9. Click Next to continue. Access 3: Queries Page 11 of 18 3/16/2011
12 10. In the final wizard dialog box, type the name of the query. 11. Select whether you want to view the results of the query or modify the query design in Design View. 12. Click Finish. Backup Database: You should always create a back-up database before you create any action queries. To do so, follow the steps below. Back up a database 1. Click the Microsoft Office Button, click the arrow next to Manage, and then click Back Up Database. The Save As dialog box appears, and Access appends the current date to the file name. For example, if you have a database named Assets, Access creates the following type of file name: Assets_ Accept the default name and location, or select another name or location, and then click Save. Access closes the original file, creates a backup, and then reopens the original file. Access 3: Queries Page 12 of 18 3/16/2011
13 Appendix (For Self-Learning) (Create a Back-up Database before trying anything) Types of Queries: As you were going through the first step of the Query Wizard, you may notice that there are other types of queries. 1. A Select Query: Queries we have created so far either in Design View or by using the Query Wizard are Select queries. A select query retrieves and displays records in the Table window in Datasheet view. 2. A Crosstab Query: This query type displays summarized values (sums, counts, and averages, etc) from one field in a table, and groups them by one set of fields listed down the left side of the datasheet and by another set of fields listed across the top of the datasheet similar to Spreadsheet. 3. An Action Query: It performs operations on the records that match your criteria. There are four kinds of action queries: a. Delete Queries: delete matching records (Caution: Once done, non-reversible) b. Update Queries: make changes to matching records (Caution: Once done, you cannot easily change them back) c. Append Queries: add new records to the end of a table d. Make-table Queries: create new tables based on matching records 4. A Parameter Query: it allows you to prompt for a single piece of information to use as selection criteria in the query. You can enter the text of the prompt surrounded by square brackets. You can enter multiple criteria in a field by using AND, or use different fields. Example: We have created one by using Between..And.. (see page 6). The following picture shows different query types under the Design tab. Make Table Query: The data that appears after you run a query appears in a table form and Access allows you to work with those results like tables. However, they are not tables. Make Table query is helpful when you want to save the query results to a new table in either the current or a different database. Try the following exercise. Open LibraryDatabaseAccess3.accdb. 1. In Query Design view, create a select query. Add all 4 tables: Subject, Book, Author, and Publisher. 2. Select Subject Name, Title, LastName, Price, and Company fields from the appropriate tables. 3. Set to sort the records - Ascending order by Subject Name. 4. Limit the Company records to Borthwick-Henderson. (Hint: In the Criteria row in the Company field, type in Like "borthwick*".) 5. Click on the Data View button to preview the list of records. 6. If you re satisfied that the appropriate records are displayed, click the Make Table button. Type the name of the table (BorthworkBooks) and indicate you want to place it in the current database. Click OK. 7. Click the Run button. 8. Click Yes when Access asks if you re sure you want to create the new table. 9. Open the new table to view the records resulting from the query. Access 3: Queries Page 13 of 18 3/16/2011
14 10. Close the Query in Design grid. (You actually do not have to save this query unless you need to run it again in future. If you do run it again, Access will delete the existing one first before it presents you with a new table.) Append Query: You can use a query to add records to a table by creating an append query. If the fields you ve selected have the same name in both tables, Access automatically fills the matching name in the Append To row in the design grid. If the fields in the two tables do not have the same name, enter the names of the fields in the Append To row in the design grid. If the table you are appending records to includes a primary key field, the records you are appending must have the same field or an equivalent field of the same data type. Access won t append any of the records if either duplicate or empty values would appear in the primary key field. Try the following example (Source: Steve Johnson, Perspection, Inc. Microsoft Office Access 2007.) 1. Open Vendor.accdb and open the Low Price CL query in Design View. The query basically pulls Price, Vendor Code, and Product from Products Table and Vendor Name from Vendor Table. We are going to append some records from this query into another table by using Append Table query function. 2. In Design View, click the Append button in Query Type group. 3. Type the name of the table to which you want to append the records or click the list arrow and then choose one. Select LightingElectric table. Then click the Current Database option or click the Another Database option and type the name of another database (including the file path, if necessary.) Click OK. 4. Specify which fields will contain the appended values by entering the field names in the Append To row of the design grid. Place Theil s Electric in the Criteria row under the Vendor Name column since you want to add this vendor to the other table. 5. Click the Run button. Click Yes when Access asks if you re sure you want to append records to the table. 6. Open the LightingElectric table to view the appended records at the end. When you close the query, you will be asked to save the changes and if you said yes, your query now has the symbol of Append Query in front of the name. Delete Query: Use Delete Query to remove records from a table based on a criterion or criteria. The delete query searches the table you specify and removes all records that match your criteria. Note: Access permanently deletes these records, so use with caution. You can preview the results by clicking the Datasheet View button before you actually run the query. Let s try the example below. 1. Open Vendor.accdb. Not to change the data in original table, copy the Products Table and paste it in the Table and give a name as Copy of Products. (Hint: right-click to copy and right-click to paste in the Table section.) Access 3: Queries Page 14 of 18 3/16/2011
15 2. Create a Select Query in Design View by selecting Copy of Products table. 3. Double-click on the * in the upper table grid to include every field. Double-click again on Price field alone to specify that you want to delete records from the table where price is less than $ Click on the Design tab under Query Tools. 5. Click the Delete button. The Delete row in the lower grid will indicate a Where location. Type in <0.99 in the Criteria row to indicate all records with less than $0.99 will be deleted. 6. Click the Datasheet View button to preview the list of deleted records. If you are satisfied that the appropriate records would be deleted, click the Design View again and then click the Run button. 7. Click Yes when Access asks if you re sure you want to delete records from the table. See the criteria in design grid below. Update Query: It allows you to make changes to a set of records that match your query s criteria. Assume you want to increase all the prices by a particular vendor in your product table to 25%. Let s try the example below. 1. Open Vendor.accdb. Not to change the data in original table, copy the Products Table and Vendor Table; paste them in the Table area and give names as Copy of Products and Copy of Vendor. (Hint: right-click to copy and right-click to paste in the Table section.) 2. Create a Select Query in Design View by selecting the Copy of Products table and Copy of Vendor. Create a relationship by connecting two Vendor ID fields from these two tables. 3. Select the Product, Price, and Vendor ID fields in the lower grid of the Design grid. 4. Click the Update button. 5. Enter the expression to update the selected field. (Under the Price field, update to price multiplied by 1.25 to increase prices to 25% and limit the criteria under Vendor ID field to LT.) See below. 6. Click the Datasheet View button to preview the list of updated records. Remember once you run the query, records are updated and you cannot change them back. 7. Click the Run button. 8. Click Yes to update the records. Other Specialized Queries: There are other queries that you can explore on your own in the Access help manual by clicking the Help button in the upper right corner of the screen. Find Duplicate Query: Use this query to retrieve duplicate records in a table by displaying a field containing duplicate values alongside additional query fields for comparison purpose. The additional query fields will help you decide whether the record is really a duplicate or not. Access 3: Queries Page 15 of 18 3/16/2011
16 Find Unmatched Query: Use this query to find the unmatched entries between two tables. For example, use this if you want to find out whether there are any products in Products Table that have no match in the Orders Table. Crosstab Query: It allows you to summarize the contents of fields that contain numeric values, such as Date fields or Number fields. The results of the summary calculations are shown at the intersection of rows and columns. The value in a crosstab query cannot be changed in order to change the source data. SQL-Specific Queries: SQL is a powerful database language used in querying, updating, and managing relational databases. Union Query combines related fields from multiple tables into one field, thus combining the data from several tables. Pass-Through - sends SQL commands directly into an SQL database server. This allows you to work with tables on the server instead of linking the tables to your Access database. Data Definition creates, deletes, or alters tables, or creates indexes in a database table. Source: Microsoft.com Operators Arithmetic operators You use the arithmetic operators to calculate a value from two or more numbers or to change the sign of a number from positive to negative or vice versa. Operator Purpose Example + Sum two numbers. [Subtotal]+[SalesTax] - Find the difference between two numbers or indicate the negative value of a number. [Price]-[Discount] * Multiply two numbers. [Quantity]*[Price] / Divide the first number by the second number. [Total]/[ItemCount] \ Round both numbers to integers, divide the first number by the second number, and then truncate the result to an integer. [Registered]\[Rooms] Mod Divide the first number by the second number, and then return only the remainder. [Registered] Mod [Rooms] ^ Raise a number to the power of an exponent. Number ^ Exponent Access 3: Queries Page 16 of 18 3/16/2011
17 Comparison operators You use the comparison operators to compare values and return a result that is True, False, or Null. Operator Purpose Example < Returns True if the first value is less than the second value. Value1 < Value2 <= Returns True if the first value is less than or equal to the second value. Value1 <= Value2 > Returns True if the first value is greater than the second value. Value1 > Value2 >= Returns True if the first value is greater than or equal to the second value. Value1 >= Value2 = Returns True if the first value is equal to the second value. Value1 = Value2 <> Returns True if the first value is not equal to the second value. Value1 <> Value2 Note: In all cases, if either the first value or the second value is null, the result is then also null. Because null represents an unknown value, the result of any comparison with a null value is also unknown. Logical operators You use the logical operators to combine two Boolean values and return a true, false, or null result. Logical operators are also referred to as Boolean operators. Operator Purpose Example And Returns True when Expr1 and Expr2 are true. Expr1 And Expr2 Or Returns True when either Expr1 or Expr2 is true. Expr1 Or Expr2 Eqv Returns True when both Expr1 and Expr2 are true, or when both Expr1 and Expr2 are false. Expr1 Eqv Expr2 Not Returns True when Expr is not true. Not Expr Xor Returns True when either Expr1 is true or Expr2 is true, but not both. Expr1 Xor Expr2 Concatenation operators You use the concatenation operators to combine two text values into one. Operator Purpose Example & Combines two strings to form one string. string1 & string2 + Combines two strings to form one string and propagates null values (if one value is Null, the entire expression evaluates to Null). string1 + string2 Access 3: Queries Page 17 of 18 3/16/2011
18 Special operators You use the special operators to return a True or False result as described in the following table. Operator Purpose Example Is Null or Is Not Null Like "pattern" Between val1 And val2 In(val1,val2...) Determines whether a value is Null or Not Null. Matches string values by using the wildcard operators? and *. Determines whether a numeric or date value is found within a range. Determines whether a value is found within a set of values. Field1 Is Not Null Field1 Like "instruct*" Field1 Between 1 And 10 - OR - Field1 Between # # And # # Field1 In ("red","green","blue") - OR - Field1 In (1,5,7,9) Access 3: Queries Page 18 of 18 3/16/2011
Click to create a query in Design View. and click the Query Design button in the Queries group to create a new table in Design View.
 Microsoft Office Access 2010 Understanding Queries Queries are questions you ask of your database. They allow you to select certain fields out of a table, or pull together data from various related tables
Microsoft Office Access 2010 Understanding Queries Queries are questions you ask of your database. They allow you to select certain fields out of a table, or pull together data from various related tables
Access Queries (Office 2003)
 Access Queries (Office 2003) Technical Support Services Office of Information Technology, West Virginia University OIT Help Desk 293-4444 x 1 oit.wvu.edu/support/training/classmat/db/ Instructor: Kathy
Access Queries (Office 2003) Technical Support Services Office of Information Technology, West Virginia University OIT Help Desk 293-4444 x 1 oit.wvu.edu/support/training/classmat/db/ Instructor: Kathy
Building Queries in Microsoft Access 2007
 Building Queries in Microsoft Access 2007 Description In this class we will explore the purpose, types and uses of Queries. Learn to design a query to retrieve specific data using criteria and operators.
Building Queries in Microsoft Access 2007 Description In this class we will explore the purpose, types and uses of Queries. Learn to design a query to retrieve specific data using criteria and operators.
Microsoft Access 2010 handout
 Microsoft Access 2010 handout Access 2010 is a relational database program you can use to create and manage large quantities of data. You can use Access to manage anything from a home inventory to a giant
Microsoft Access 2010 handout Access 2010 is a relational database program you can use to create and manage large quantities of data. You can use Access to manage anything from a home inventory to a giant
Tutorial 3. Maintaining and Querying a Database
 Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database Microsoft Access 2010 Objectives Find, modify, and delete records in a table Learn how to use the Query window in Design view Create, run, and save queries
Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database Microsoft Access 2010 Objectives Find, modify, and delete records in a table Learn how to use the Query window in Design view Create, run, and save queries
Microsoft Office 2010
 Access Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database Microsoft Office 2010 Objectives Find, modify, and delete records in a table Learn how to use the Query window in Design view Create, run, and save
Access Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database Microsoft Office 2010 Objectives Find, modify, and delete records in a table Learn how to use the Query window in Design view Create, run, and save
Use Find & Replace Commands under Home tab to search and replace data.
 Microsoft Access 2: Managing Data in Tables and Creating Relationships You have created tables in an Access database. Data in Access tables can be added, deleted, and updated to be current (practiced in
Microsoft Access 2: Managing Data in Tables and Creating Relationships You have created tables in an Access database. Data in Access tables can be added, deleted, and updated to be current (practiced in
Database Applications Microsoft Access
 Database Applications Microsoft Access Lesson 4 Working with Queries Difference Between Queries and Filters Filters are temporary Filters are placed on data in a single table Queries are saved as individual
Database Applications Microsoft Access Lesson 4 Working with Queries Difference Between Queries and Filters Filters are temporary Filters are placed on data in a single table Queries are saved as individual
Lab 9 Access PreLab Copy the prelab folder, Lab09 PreLab9_Access_intro
 Lab 9 Access PreLab Copy the prelab folder, Lab09 PreLab9_Access_intro, to your M: drive. To do the second part of the prelab, you will need to have available a database from that folder. Creating a new
Lab 9 Access PreLab Copy the prelab folder, Lab09 PreLab9_Access_intro, to your M: drive. To do the second part of the prelab, you will need to have available a database from that folder. Creating a new
Microsoft Excel 2007 Consolidate Data & Analyze with Pivot Table Windows XP
 Microsoft Excel 2007 Consolidate Data & Analyze with Pivot Table Windows XP Consolidate Data in Multiple Worksheets Example data is saved under Consolidation.xlsx workbook under ProductA through ProductD
Microsoft Excel 2007 Consolidate Data & Analyze with Pivot Table Windows XP Consolidate Data in Multiple Worksheets Example data is saved under Consolidation.xlsx workbook under ProductA through ProductD
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2003
 Introduction to Microsoft Access 2003 Zhi Liu School of Information Fall/2006 Introduction and Objectives Microsoft Access 2003 is a powerful, yet easy to learn, relational database application for Microsoft
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2003 Zhi Liu School of Information Fall/2006 Introduction and Objectives Microsoft Access 2003 is a powerful, yet easy to learn, relational database application for Microsoft
Create a New Database in Access 2010
 Create a New Database in Access 2010 Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 1 CREATING A DATABASE... 1 ADDING TO A DATABASE... 2 CREATE A DATABASE BY USING A TEMPLATE... 2 CREATE A DATABASE WITHOUT USING A TEMPLATE...
Create a New Database in Access 2010 Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 1 CREATING A DATABASE... 1 ADDING TO A DATABASE... 2 CREATE A DATABASE BY USING A TEMPLATE... 2 CREATE A DATABASE WITHOUT USING A TEMPLATE...
Lab Manual. Databases. Microsoft Access. Peeking into Computer Science Access Lab manual
 Lab Manual Databases Microsoft Access 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Introduction to Microsoft Access... 3 Getting started... 3 Tables... 3 Primary Keys... 6 Field Properties... 7 Validation Rules... 11 Input
Lab Manual Databases Microsoft Access 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Introduction to Microsoft Access... 3 Getting started... 3 Tables... 3 Primary Keys... 6 Field Properties... 7 Validation Rules... 11 Input
Querying a Database Using the Select Query Window
 Querying a Database Using the Select Query Window PROJECT CASE PERSPECTIVE Dr. Gernaey and his colleagues are eager for Ashton James College (AJC) to obtain the benefits they anticipated when they set
Querying a Database Using the Select Query Window PROJECT CASE PERSPECTIVE Dr. Gernaey and his colleagues are eager for Ashton James College (AJC) to obtain the benefits they anticipated when they set
Access 2010: Creating Queries Table of Contents INTRODUCTION TO QUERIES... 2 QUERY JOINS... 2 INNER JOINS... 3 OUTER JOINS...
 Access 2010: Creating Queries Table of Contents INTRODUCTION TO QUERIES... 2 QUERY JOINS... 2 INNER JOINS... 3 OUTER JOINS... 3 CHANGE A JOIN PROPERTY... 4 REMOVING A JOIN... 4 CREATE QUERIES... 4 THE
Access 2010: Creating Queries Table of Contents INTRODUCTION TO QUERIES... 2 QUERY JOINS... 2 INNER JOINS... 3 OUTER JOINS... 3 CHANGE A JOIN PROPERTY... 4 REMOVING A JOIN... 4 CREATE QUERIES... 4 THE
Web Intelligence User Guide
 Web Intelligence User Guide Office of Financial Management - Enterprise Reporting Services 4/11/2011 Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Overview... 1 Purpose... 1 Chapter 2 Logon Procedure... 3 Web Intelligence
Web Intelligence User Guide Office of Financial Management - Enterprise Reporting Services 4/11/2011 Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Overview... 1 Purpose... 1 Chapter 2 Logon Procedure... 3 Web Intelligence
MICROSOFT ACCESS 2003 TUTORIAL
 MICROSOFT ACCESS 2003 TUTORIAL M I C R O S O F T A C C E S S 2 0 0 3 Microsoft Access is powerful software designed for PC. It allows you to create and manage databases. A database is an organized body
MICROSOFT ACCESS 2003 TUTORIAL M I C R O S O F T A C C E S S 2 0 0 3 Microsoft Access is powerful software designed for PC. It allows you to create and manage databases. A database is an organized body
Access II 2007 Workshop
 Access II 2007 Workshop Query & Report I. Review Tables/Forms Ways to create tables: tables, templates & design Edit tables: new fields & table properties Import option Link tables: Relationship Forms
Access II 2007 Workshop Query & Report I. Review Tables/Forms Ways to create tables: tables, templates & design Edit tables: new fields & table properties Import option Link tables: Relationship Forms
Chapter 5. Microsoft Access
 Chapter 5 Microsoft Access Topic Introduction to DBMS Microsoft Access Getting Started Creating Database File Database Window Table Queries Form Report Introduction A set of programs designed to organize,
Chapter 5 Microsoft Access Topic Introduction to DBMS Microsoft Access Getting Started Creating Database File Database Window Table Queries Form Report Introduction A set of programs designed to organize,
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2007
 Introduction to Microsoft Access 2007 Introduction A database is a collection of information that's related. Access allows you to manage your information in one database file. Within Access there are four
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2007 Introduction A database is a collection of information that's related. Access allows you to manage your information in one database file. Within Access there are four
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2013
 Introduction to Microsoft Access 2013 A database is a collection of information that is related. Access allows you to manage your information in one database file. Within Access there are four major objects:
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2013 A database is a collection of information that is related. Access allows you to manage your information in one database file. Within Access there are four major objects:
Joins Joins dictate how two tables or queries relate to each other. Click on the join line with the right mouse button to access the Join Properties.
 Lesson Notes Author: Pamela Schmidt Joins Joins dictate how two tables or queries relate to each other. Click on the join line with the right mouse button to access the Join Properties. Inner Joins An
Lesson Notes Author: Pamela Schmidt Joins Joins dictate how two tables or queries relate to each other. Click on the join line with the right mouse button to access the Join Properties. Inner Joins An
Access 2007. Queries
 Access 2007 Queries WORKSHOP DESCRIPTION... 1 Overview 1 Prerequisites 1 Objectives 1 WHAT IS A QUERY?... 2 WHY USE QUERIES?... 2 TERMS TO KNOW... 2 Select Queries 2 Action Queries 2 Crosstab Queries
Access 2007 Queries WORKSHOP DESCRIPTION... 1 Overview 1 Prerequisites 1 Objectives 1 WHAT IS A QUERY?... 2 WHY USE QUERIES?... 2 TERMS TO KNOW... 2 Select Queries 2 Action Queries 2 Crosstab Queries
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2010
 Introduction to Microsoft Access 2010 A database is a collection of information that is related. Access allows you to manage your information in one database file. Within Access there are four major objects:
Introduction to Microsoft Access 2010 A database is a collection of information that is related. Access allows you to manage your information in one database file. Within Access there are four major objects:
Creating and Using Databases with Microsoft Access
 CHAPTER A Creating and Using Databases with Microsoft Access In this chapter, you will Use Access to explore a simple database Design and create a new database Create and use forms Create and use queries
CHAPTER A Creating and Using Databases with Microsoft Access In this chapter, you will Use Access to explore a simple database Design and create a new database Create and use forms Create and use queries
Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction to Access
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction to Access Fall 2014, Version 1.2 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Starting Access...3
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction to Access Fall 2014, Version 1.2 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Starting Access...3
MS Access: Advanced Tables and Queries. Lesson Notes Author: Pamela Schmidt
 Lesson Notes Author: Pamela Schmidt Tables Text Fields (Default) Text or combinations of text and numbers, as well as numbers that don't require calculations, such as phone numbers. or the length set by
Lesson Notes Author: Pamela Schmidt Tables Text Fields (Default) Text or combinations of text and numbers, as well as numbers that don't require calculations, such as phone numbers. or the length set by
Access 2007. Creating Databases - Fundamentals
 Access 2007 Creating Databases - Fundamentals Contents Database Design Objectives of database design 1 Process of database design 1 Creating a New Database... 3 Tables... 4 Creating a table in design view
Access 2007 Creating Databases - Fundamentals Contents Database Design Objectives of database design 1 Process of database design 1 Creating a New Database... 3 Tables... 4 Creating a table in design view
Microsoft Access 2007 - Creating Filters and Tables
 Platform: Windows PC Ref no: USER 165 Date: November 2007 Version: 1 Authors: Derek Sheward, Claire Napier Creating Filters in Microsoft Access 2007 This is the third document in series of five about Microsoft
Platform: Windows PC Ref no: USER 165 Date: November 2007 Version: 1 Authors: Derek Sheward, Claire Napier Creating Filters in Microsoft Access 2007 This is the third document in series of five about Microsoft
MICROSOFT ACCESS A. CREATING A DATABASE B. CREATING TABLES IN A DATABASE
 Prepared for MIS 6326 by Dr. Sumit Sarkar 1 MICROSOFT ACCESS A database is a collection of different types of data, stored in a manner to facilitate use in diverse ways. In Microsoft Access 2000, a database
Prepared for MIS 6326 by Dr. Sumit Sarkar 1 MICROSOFT ACCESS A database is a collection of different types of data, stored in a manner to facilitate use in diverse ways. In Microsoft Access 2000, a database
General User/Technical Guide for Microsoft Access
 General User/Technical Guide for Microsoft Access School of Nursing University of Michigan This guide is the first step in understanding your database. See the list of documentation locations at the end
General User/Technical Guide for Microsoft Access School of Nursing University of Michigan This guide is the first step in understanding your database. See the list of documentation locations at the end
Lab 2: MS ACCESS Tables
 Lab 2: MS ACCESS Tables Summary Introduction to Tables and How to Build a New Database Creating Tables in Datasheet View and Design View Working with Data on Sorting and Filtering 1. Introduction Creating
Lab 2: MS ACCESS Tables Summary Introduction to Tables and How to Build a New Database Creating Tables in Datasheet View and Design View Working with Data on Sorting and Filtering 1. Introduction Creating
Beginning Microsoft Access
 Beginning Microsoft Access A database is a collection of information. Common collections of information that can be entered into a database include the library card catalog, a recipe box, or your personal
Beginning Microsoft Access A database is a collection of information. Common collections of information that can be entered into a database include the library card catalog, a recipe box, or your personal
MICROSOFT ACCESS STEP BY STEP GUIDE
 IGCSE ICT SECTION 11 DATA MANIPULATION MICROSOFT ACCESS STEP BY STEP GUIDE Mark Nicholls ICT Lounge P a g e 1 Contents Task 35 details Page 3 Opening a new Database. Page 4 Importing.csv file into the
IGCSE ICT SECTION 11 DATA MANIPULATION MICROSOFT ACCESS STEP BY STEP GUIDE Mark Nicholls ICT Lounge P a g e 1 Contents Task 35 details Page 3 Opening a new Database. Page 4 Importing.csv file into the
Unit 10: Microsoft Access Queries
 Microsoft Access Queries Unit 10: Microsoft Access Queries Introduction Queries are a fundamental means of accessing and displaying data from tables. Queries used to view, update, and analyze data in different
Microsoft Access Queries Unit 10: Microsoft Access Queries Introduction Queries are a fundamental means of accessing and displaying data from tables. Queries used to view, update, and analyze data in different
Microsoft Access 2010
 IT Training Microsoft Access 2010 Jane Barrett, IT Training & Engagement Team Information System Services Version 3.0 Scope Learning outcomes Learn how to navigate around Access. Learn how to design and
IT Training Microsoft Access 2010 Jane Barrett, IT Training & Engagement Team Information System Services Version 3.0 Scope Learning outcomes Learn how to navigate around Access. Learn how to design and
Excel Database Management Microsoft Excel 2003
 Excel Database Management Microsoft Reference Guide University Technology Services Computer Training Copyright Notice Copyright 2003 EBook Publishing. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may
Excel Database Management Microsoft Reference Guide University Technology Services Computer Training Copyright Notice Copyright 2003 EBook Publishing. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may
Creating tables in Microsoft Access 2007
 Platform: Windows PC Ref no: USER 164 Date: 25 th October 2007 Version: 1 Authors: D.R.Sheward, C.L.Napier Creating tables in Microsoft Access 2007 The aim of this guide is to provide information on using
Platform: Windows PC Ref no: USER 164 Date: 25 th October 2007 Version: 1 Authors: D.R.Sheward, C.L.Napier Creating tables in Microsoft Access 2007 The aim of this guide is to provide information on using
Creating QBE Queries in Microsoft SQL Server
 Creating QBE Queries in Microsoft SQL Server When you ask SQL Server or any other DBMS (including Access) a question about the data in a database, the question is called a query. A query is simply a question
Creating QBE Queries in Microsoft SQL Server When you ask SQL Server or any other DBMS (including Access) a question about the data in a database, the question is called a query. A query is simply a question
Sample- for evaluation only. Introductory Access. TeachUcomp, Inc. A Presentation of TeachUcomp Incorporated. Copyright TeachUcomp, Inc.
 A Presentation of TeachUcomp Incorporated. Copyright TeachUcomp, Inc. 2010 Introductory Access TeachUcomp, Inc. it s all about you Copyright: Copyright 2010 by TeachUcomp, Inc. All rights reserved. This
A Presentation of TeachUcomp Incorporated. Copyright TeachUcomp, Inc. 2010 Introductory Access TeachUcomp, Inc. it s all about you Copyright: Copyright 2010 by TeachUcomp, Inc. All rights reserved. This
Creating and Using Forms in SharePoint
 Creating and Using Forms in SharePoint Getting started with custom lists... 1 Creating a custom list... 1 Creating a user-friendly list name... 1 Other options for creating custom lists... 2 Building a
Creating and Using Forms in SharePoint Getting started with custom lists... 1 Creating a custom list... 1 Creating a user-friendly list name... 1 Other options for creating custom lists... 2 Building a
Search help. More on Office.com: images templates
 Page 1 of 14 Access 2010 Home > Access 2010 Help and How-to > Getting started Search help More on Office.com: images templates Access 2010: database tasks Here are some basic database tasks that you can
Page 1 of 14 Access 2010 Home > Access 2010 Help and How-to > Getting started Search help More on Office.com: images templates Access 2010: database tasks Here are some basic database tasks that you can
Microsoft Access 2007
 How to Use: Microsoft Access 2007 Microsoft Office Access is a powerful tool used to create and format databases. Databases allow information to be organized in rows and tables, where queries can be formed
How to Use: Microsoft Access 2007 Microsoft Office Access is a powerful tool used to create and format databases. Databases allow information to be organized in rows and tables, where queries can be formed
MS Access Lab 2. Topic: Tables
 MS Access Lab 2 Topic: Tables Summary Introduction: Tables, Start to build a new database Creating Tables: Datasheet View, Design View Working with Data: Sorting, Filtering Help on Tables Introduction
MS Access Lab 2 Topic: Tables Summary Introduction: Tables, Start to build a new database Creating Tables: Datasheet View, Design View Working with Data: Sorting, Filtering Help on Tables Introduction
A database is a collection of data organised in a manner that allows access, retrieval, and use of that data.
 Microsoft Access A database is a collection of data organised in a manner that allows access, retrieval, and use of that data. A Database Management System (DBMS) allows users to create a database; add,
Microsoft Access A database is a collection of data organised in a manner that allows access, retrieval, and use of that data. A Database Management System (DBMS) allows users to create a database; add,
Table and field properties Tables and fields also have properties that you can set to control their characteristics or behavior.
 Create a table When you create a database, you store your data in tables subject-based lists that contain rows and columns. For instance, you can create a Contacts table to store a list of names, addresses,
Create a table When you create a database, you store your data in tables subject-based lists that contain rows and columns. For instance, you can create a Contacts table to store a list of names, addresses,
Microsoft Access 2007 Introduction
 Microsoft Access 2007 Introduction Access is the database management system in Microsoft Office. A database is an organized collection of facts about a particular subject. Examples of databases are an
Microsoft Access 2007 Introduction Access is the database management system in Microsoft Office. A database is an organized collection of facts about a particular subject. Examples of databases are an
Access 2010 Intermediate Skills
 Access 2010 Intermediate Skills (C) 2013, BJC HealthCare (St Louis, Missouri). All Rights Reserved. Revised June 5, 2013. TABLE OF CONTENTS OBJECTIVES... 3 UNDERSTANDING RELATIONSHIPS... 4 WHAT IS A RELATIONSHIP?...
Access 2010 Intermediate Skills (C) 2013, BJC HealthCare (St Louis, Missouri). All Rights Reserved. Revised June 5, 2013. TABLE OF CONTENTS OBJECTIVES... 3 UNDERSTANDING RELATIONSHIPS... 4 WHAT IS A RELATIONSHIP?...
Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database
 Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database Microsoft Access 2013 Objectives Session 3.1 Find, modify, and delete records in a table Hide and unhide fields in a datasheet Work in the Query window in
Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database Microsoft Access 2013 Objectives Session 3.1 Find, modify, and delete records in a table Hide and unhide fields in a datasheet Work in the Query window in
Microsoft Office 2010
 Access Tutorial 1 Creating a Database Microsoft Office 2010 Objectives Learn basic database concepts and terms Explore the Microsoft Access window and Backstage view Create a blank database Create and
Access Tutorial 1 Creating a Database Microsoft Office 2010 Objectives Learn basic database concepts and terms Explore the Microsoft Access window and Backstage view Create a blank database Create and
Creating a Database in Access
 Creating a Database in Access Microsoft Access is a database application. A database is collection of records and files organized for a particular purpose. For example, you could use a database to store
Creating a Database in Access Microsoft Access is a database application. A database is collection of records and files organized for a particular purpose. For example, you could use a database to store
What is a database? The parts of an Access database
 What is a database? Any database is a tool to organize and store pieces of information. A Rolodex is a database. So is a phone book. The main goals of a database designer are to: 1. Make sure the data
What is a database? Any database is a tool to organize and store pieces of information. A Rolodex is a database. So is a phone book. The main goals of a database designer are to: 1. Make sure the data
Access Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database. Microsoft Office 2013 Enhanced
 Access Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database Microsoft Office 2013 Enhanced Objectives Session 3.1 Find, modify, and delete records in a table Hide and unhide fields in a datasheet Work in the
Access Tutorial 3 Maintaining and Querying a Database Microsoft Office 2013 Enhanced Objectives Session 3.1 Find, modify, and delete records in a table Hide and unhide fields in a datasheet Work in the
Microsoft Access 2010- Introduction
 Microsoft Access 2010- Introduction Access is the database management system in Microsoft Office. A database is an organized collection of facts about a particular subject. Examples of databases are an
Microsoft Access 2010- Introduction Access is the database management system in Microsoft Office. A database is an organized collection of facts about a particular subject. Examples of databases are an
Microsoft Access 2000
 Microsoft Access 2000 Level 1 Region 4 Teaching, Learning and Technology Center Kaplan, LA Activity 1 Creating a Database 1. Open Microsoft Access 2000 a. Click on START, highlight Programs, point and
Microsoft Access 2000 Level 1 Region 4 Teaching, Learning and Technology Center Kaplan, LA Activity 1 Creating a Database 1. Open Microsoft Access 2000 a. Click on START, highlight Programs, point and
BID2WIN Workshop. Advanced Report Writing
 BID2WIN Workshop Advanced Report Writing Please Note: Please feel free to take this workbook home with you! Electronic copies of all lab documentation are available for download at http://www.bid2win.com/userconf/2011/labs/
BID2WIN Workshop Advanced Report Writing Please Note: Please feel free to take this workbook home with you! Electronic copies of all lab documentation are available for download at http://www.bid2win.com/userconf/2011/labs/
Microsoft Excel 2010 Part 3: Advanced Excel
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Excel 2010 Part 3: Advanced Excel Winter 2015, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Sorting Data...2 Sorting
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Excel 2010 Part 3: Advanced Excel Winter 2015, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Sorting Data...2 Sorting
Planning and Creating a Custom Database
 Planning and Creating a Custom Database Introduction The Microsoft Office Access 00 database wizards make creating databases easy, but you may need to create a database that does not fit any of the predefined
Planning and Creating a Custom Database Introduction The Microsoft Office Access 00 database wizards make creating databases easy, but you may need to create a database that does not fit any of the predefined
Business Objects Version 5 : Introduction
 Business Objects Version 5 : Introduction Page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction About Business Objects Changing Your Password Retrieving Pre-Defined Reports Formatting Your Report Using the Slice and Dice
Business Objects Version 5 : Introduction Page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction About Business Objects Changing Your Password Retrieving Pre-Defined Reports Formatting Your Report Using the Slice and Dice
A Guide to Access 2007
 A Guide to Access 2007 by Adrian Beck Mark Maynard Richard Rodger Software Made Simple PO Box 7068, Rothley, Leicester, UK, LE7 7PT Telephone: 0845 2803121 Fax: 0845 2803121 Internet: www.s-m-s.co.uk email:
A Guide to Access 2007 by Adrian Beck Mark Maynard Richard Rodger Software Made Simple PO Box 7068, Rothley, Leicester, UK, LE7 7PT Telephone: 0845 2803121 Fax: 0845 2803121 Internet: www.s-m-s.co.uk email:
IN THIS PROJECT, YOU LEARN HOW TO
 UNIT 2 PROJECT 11 CREATING A CUSTOMIZED DATABASE IN THIS PROJECT, YOU LEARN HOW TO Examine a Database and Its Objects Create Tables and Set Field Properties in Design View Create Relationships Add and
UNIT 2 PROJECT 11 CREATING A CUSTOMIZED DATABASE IN THIS PROJECT, YOU LEARN HOW TO Examine a Database and Its Objects Create Tables and Set Field Properties in Design View Create Relationships Add and
Ohio University Computer Services Center August, 2002 Crystal Reports Introduction Quick Reference Guide
 Open Crystal Reports From the Windows Start menu choose Programs and then Crystal Reports. Creating a Blank Report Ohio University Computer Services Center August, 2002 Crystal Reports Introduction Quick
Open Crystal Reports From the Windows Start menu choose Programs and then Crystal Reports. Creating a Blank Report Ohio University Computer Services Center August, 2002 Crystal Reports Introduction Quick
BusinessObjects: General Report Writing for Version 5
 BusinessObjects: General Report Writing for Version 5 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...3 1.1 PURPOSE OF COURSE...3 1.2 LEVEL OF EXPERIENCE REQUIRED...3 1.3 TERMINOLOGY...3 1.3.1 Universes...3 1.3.2 Objects...4
BusinessObjects: General Report Writing for Version 5 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...3 1.1 PURPOSE OF COURSE...3 1.2 LEVEL OF EXPERIENCE REQUIRED...3 1.3 TERMINOLOGY...3 1.3.1 Universes...3 1.3.2 Objects...4
EXCEL PIVOT TABLE David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA Dean s Office Oct 2002
 EXCEL PIVOT TABLE David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA Dean s Office Oct 2002 Table of Contents Part I Creating a Pivot Table Excel Database......3 What is a Pivot Table...... 3 Creating Pivot Tables
EXCEL PIVOT TABLE David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA Dean s Office Oct 2002 Table of Contents Part I Creating a Pivot Table Excel Database......3 What is a Pivot Table...... 3 Creating Pivot Tables
ACCESS 2007. Importing and Exporting Data Files. Information Technology. MS Access 2007 Users Guide. IT Training & Development (818) 677-1700
 Information Technology MS Access 2007 Users Guide ACCESS 2007 Importing and Exporting Data Files IT Training & Development (818) 677-1700 training@csun.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 Import Excel
Information Technology MS Access 2007 Users Guide ACCESS 2007 Importing and Exporting Data Files IT Training & Development (818) 677-1700 training@csun.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 Import Excel
Getting Started with Access 2007
 Getting Started with Access 2007 1 A database is an organized collection of information about a subject. Examples of databases include an address book, the telephone book, or a filing cabinet full of documents
Getting Started with Access 2007 1 A database is an organized collection of information about a subject. Examples of databases include an address book, the telephone book, or a filing cabinet full of documents
Microsoft Access 2010 Overview of Basics
 Opening Screen Access 2010 launches with a window allowing you to: create a new database from a template; create a new template from scratch; or open an existing database. Open existing Templates Create
Opening Screen Access 2010 launches with a window allowing you to: create a new database from a template; create a new template from scratch; or open an existing database. Open existing Templates Create
A Basic introduction to Microsoft Access
 A Basic introduction to Microsoft Access By Ojango J.M.K Department of Animal Sciences, Egerton University, Njoro, Kenya and International Livestock Research Institute, Nairobi, Kenya Ms Access is a database
A Basic introduction to Microsoft Access By Ojango J.M.K Department of Animal Sciences, Egerton University, Njoro, Kenya and International Livestock Research Institute, Nairobi, Kenya Ms Access is a database
Lesson 07: MS ACCESS - Handout. Introduction to database (30 mins)
 Lesson 07: MS ACCESS - Handout Handout Introduction to database (30 mins) Microsoft Access is a database application. A database is a collection of related information put together in database objects.
Lesson 07: MS ACCESS - Handout Handout Introduction to database (30 mins) Microsoft Access is a database application. A database is a collection of related information put together in database objects.
Structure a Database. Key Concepts LESSON. Access 380. Lesson 2: Structure a Database. Standards
 LESSON Key Concepts Structure a Database In this lesson, you will continue learning skills to use Access in your daily life. You will learn to create the following elements in this lesson: databases, tables,
LESSON Key Concepts Structure a Database In this lesson, you will continue learning skills to use Access in your daily life. You will learn to create the following elements in this lesson: databases, tables,
Excel 2007 - Using Pivot Tables
 Overview A PivotTable report is an interactive table that allows you to quickly group and summarise information from a data source. You can rearrange (or pivot) the table to display different perspectives
Overview A PivotTable report is an interactive table that allows you to quickly group and summarise information from a data source. You can rearrange (or pivot) the table to display different perspectives
MICROSOFT OFFICE ACCESS 2007 - NEW FEATURES
 MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007 MICROSOFT OFFICE ACCESS 2007 - NEW FEATURES Exploring Access Creating and Working with Tables Finding and Filtering Data Working with Queries and Recordsets Working with Forms Working
MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007 MICROSOFT OFFICE ACCESS 2007 - NEW FEATURES Exploring Access Creating and Working with Tables Finding and Filtering Data Working with Queries and Recordsets Working with Forms Working
Creating a Database using Access 2007
 Creating a Database using Access 2007 Starting Access 2007 Double click on the Access 2007 icon on the Windows desktop (see right), or click-on the Start button in the lower left corner of the screen,
Creating a Database using Access 2007 Starting Access 2007 Double click on the Access 2007 icon on the Windows desktop (see right), or click-on the Start button in the lower left corner of the screen,
Introduction to Microsoft Access
 Welcome to Teach Yourself: Introduction to Microsoft Access This Teach Yourself tutorial explains the basic operations and terminology of Microsoft Access 2003, a database management program. Microsoft
Welcome to Teach Yourself: Introduction to Microsoft Access This Teach Yourself tutorial explains the basic operations and terminology of Microsoft Access 2003, a database management program. Microsoft
Exploring Microsoft Office Access 2007. Chapter 2: Relational Databases and Multi-Table Queries
 Exploring Microsoft Office Access 2007 Chapter 2: Relational Databases and Multi-Table Queries 1 Objectives Design data Create tables Understand table relationships Share data with Excel Establish table
Exploring Microsoft Office Access 2007 Chapter 2: Relational Databases and Multi-Table Queries 1 Objectives Design data Create tables Understand table relationships Share data with Excel Establish table
PROJECT ON MICROSOFT ACCESS (HOME TAB AND EXTERNAL DATA TAB) SUBMITTED BY: SUBMITTED TO: NAME: ROLL NO: REGN NO: BATCH:
 PROJECT ON MICROSOFT ACCESS (HOME TAB AND EXTERNAL DATA TAB) SUBMITTED BY: SUBMITTED TO: NAME: ROLL NO: REGN NO: BATCH: INDEX Microsoft Access- An Overview 2 Datasheet view 4 Create a Table in Datasheet
PROJECT ON MICROSOFT ACCESS (HOME TAB AND EXTERNAL DATA TAB) SUBMITTED BY: SUBMITTED TO: NAME: ROLL NO: REGN NO: BATCH: INDEX Microsoft Access- An Overview 2 Datasheet view 4 Create a Table in Datasheet
ECDL. European Computer Driving Licence. Database Software BCS ITQ Level 1. Syllabus Version 1.0
 ECDL European Computer Driving Licence Database Software BCS ITQ Level 1 Using Microsoft Access 2013 Syllabus Version 1.0 This training, which has been approved by BCS, includes exercise items intended
ECDL European Computer Driving Licence Database Software BCS ITQ Level 1 Using Microsoft Access 2013 Syllabus Version 1.0 This training, which has been approved by BCS, includes exercise items intended
Access 2007. Using Access
 Access 2007 Using Access 1 Contents Introduction to Microsoft Access 2007... 3 Microsoft Access 2007 features 3 Opening a database 4 Database objects 5 Opening objects 6 Working with objects 6 Saving in
Access 2007 Using Access 1 Contents Introduction to Microsoft Access 2007... 3 Microsoft Access 2007 features 3 Opening a database 4 Database objects 5 Opening objects 6 Working with objects 6 Saving in
Database Applications Microsoft Access
 Lesson 1 Tutorial 1 Database Applications Microsoft Access Lesson 1 Introduction For Lesson 1, you will work through Tutorial 1 in your textbook. The tutorial may expose you to more information than is
Lesson 1 Tutorial 1 Database Applications Microsoft Access Lesson 1 Introduction For Lesson 1, you will work through Tutorial 1 in your textbook. The tutorial may expose you to more information than is
How To Create A Powerpoint Intelligence Report In A Pivot Table In A Powerpoints.Com
 Sage 500 ERP Intelligence Reporting Getting Started Guide 27.11.2012 Table of Contents 1.0 Getting started 3 2.0 Managing your reports 10 3.0 Defining report properties 18 4.0 Creating a simple PivotTable
Sage 500 ERP Intelligence Reporting Getting Started Guide 27.11.2012 Table of Contents 1.0 Getting started 3 2.0 Managing your reports 10 3.0 Defining report properties 18 4.0 Creating a simple PivotTable
Check out our website!
 Check out our website! www.nvcc.edu/woodbr idge/computer-lab Contact Us Location: Open Computer Lab Seefeldt Building #336 NOVA Woodbridge Campus Hussna Azamy (OCL Supervisor) Phone: 703-878-5714 E-mail:
Check out our website! www.nvcc.edu/woodbr idge/computer-lab Contact Us Location: Open Computer Lab Seefeldt Building #336 NOVA Woodbridge Campus Hussna Azamy (OCL Supervisor) Phone: 703-878-5714 E-mail:
Business Objects 4.1 Quick User Guide
 Business Objects 4.1 Quick User Guide Log into SCEIS Business Objects (BOBJ) 1. https://sceisreporting.sc.gov 2. Choose Windows AD for Authentication. 3. Enter your SCEIS User Name and Password: Home Screen
Business Objects 4.1 Quick User Guide Log into SCEIS Business Objects (BOBJ) 1. https://sceisreporting.sc.gov 2. Choose Windows AD for Authentication. 3. Enter your SCEIS User Name and Password: Home Screen
How to Concatenate Cells in Microsoft Access
 How to Concatenate Cells in Microsoft Access This tutorial demonstrates how to concatenate cells in Microsoft Access. Sometimes data distributed over multiple columns is more efficient to use when combined
How to Concatenate Cells in Microsoft Access This tutorial demonstrates how to concatenate cells in Microsoft Access. Sometimes data distributed over multiple columns is more efficient to use when combined
Microsoft Access 2010 Advanced Queries
 Microsoft Access 2010 Advanced Queries Email: training@health.ufl.edu Web Page: http://training.health.ufl.edu Microsoft Access 2010: Advanced Queries 2.0 hours This workshop requires completion of "Access:
Microsoft Access 2010 Advanced Queries Email: training@health.ufl.edu Web Page: http://training.health.ufl.edu Microsoft Access 2010: Advanced Queries 2.0 hours This workshop requires completion of "Access:
Intro to Excel spreadsheets
 Intro to Excel spreadsheets What are the objectives of this document? The objectives of document are: 1. Familiarize you with what a spreadsheet is, how it works, and what its capabilities are; 2. Using
Intro to Excel spreadsheets What are the objectives of this document? The objectives of document are: 1. Familiarize you with what a spreadsheet is, how it works, and what its capabilities are; 2. Using
Decision Support AITS University Administration. Web Intelligence Rich Client 4.1 User Guide
 Decision Support AITS University Administration Web Intelligence Rich Client 4.1 User Guide 2 P age Web Intelligence 4.1 User Guide Web Intelligence 4.1 User Guide Contents Getting Started in Web Intelligence
Decision Support AITS University Administration Web Intelligence Rich Client 4.1 User Guide 2 P age Web Intelligence 4.1 User Guide Web Intelligence 4.1 User Guide Contents Getting Started in Web Intelligence
Excel 2013 - Using Pivot Tables
 Overview A PivotTable report is an interactive table that allows you to quickly group and summarise information from a data source. You can rearrange (or pivot) the table to display different perspectives
Overview A PivotTable report is an interactive table that allows you to quickly group and summarise information from a data source. You can rearrange (or pivot) the table to display different perspectives
Word 2007: Mail Merge Learning Guide
 Word 2007: Mail Merge Learning Guide Getting Started Mail merge techniques allow you to create a document which combines repetitive text elements with data drawn from an external data document. To perform
Word 2007: Mail Merge Learning Guide Getting Started Mail merge techniques allow you to create a document which combines repetitive text elements with data drawn from an external data document. To perform
Advanced Excel 10/20/2011 1
 Advanced Excel Data Validation Excel has a feature called Data Validation, which will allow you to control what kind of information is typed into cells. 1. Select the cell(s) you wish to control. 2. Click
Advanced Excel Data Validation Excel has a feature called Data Validation, which will allow you to control what kind of information is typed into cells. 1. Select the cell(s) you wish to control. 2. Click
Working with SQL Server Integration Services
 SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) is a set of tools that let you transfer data to and from SQL Server 2005. In this lab, you ll work with the SQL Server Business Intelligence Development Studio to
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) is a set of tools that let you transfer data to and from SQL Server 2005. In this lab, you ll work with the SQL Server Business Intelligence Development Studio to
Indiana County Assessor Association Excel Excellence
 Indiana County Assessor Association Excel Excellence Basic Excel Data Analysis Division August 2012 1 Agenda Lesson 1: The Benefits of Excel Lesson 2: The Basics of Excel Lesson 3: Hands On Exercises Lesson
Indiana County Assessor Association Excel Excellence Basic Excel Data Analysis Division August 2012 1 Agenda Lesson 1: The Benefits of Excel Lesson 2: The Basics of Excel Lesson 3: Hands On Exercises Lesson
Database File. Table. Field. Datatype. Value. Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences
 Unit 4 Introduction to Spreadsheet and Database, pages 1 of 12 Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 1305 Intro to Computer Technology 15 Module 15: Introduction to Microsoft Access Objectives:
Unit 4 Introduction to Spreadsheet and Database, pages 1 of 12 Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 1305 Intro to Computer Technology 15 Module 15: Introduction to Microsoft Access Objectives:
Using Microsoft Access
 Using Microsoft Access USING MICROSOFT ACCESS 1 Queries 2 Exercise 1. Setting up a Query 3 Exercise 2. Selecting Fields for Query Output 4 Exercise 3. Saving a Query 5 Query Criteria 6 Exercise 4. Adding
Using Microsoft Access USING MICROSOFT ACCESS 1 Queries 2 Exercise 1. Setting up a Query 3 Exercise 2. Selecting Fields for Query Output 4 Exercise 3. Saving a Query 5 Query Criteria 6 Exercise 4. Adding
Learn how to create web enabled (browser) forms in InfoPath 2013 and publish them in SharePoint 2013. InfoPath 2013 Web Enabled (Browser) forms
 Learn how to create web enabled (browser) forms in InfoPath 2013 and publish them in SharePoint 2013. InfoPath 2013 Web Enabled (Browser) forms InfoPath 2013 Web Enabled (Browser) forms Creating Web Enabled
Learn how to create web enabled (browser) forms in InfoPath 2013 and publish them in SharePoint 2013. InfoPath 2013 Web Enabled (Browser) forms InfoPath 2013 Web Enabled (Browser) forms Creating Web Enabled
Tutorial 5 Creating Advanced Queries and Enhancing Table Design
 Tutorial 5 Creating Advanced Queries and Enhancing Table Design Microsoft Access 2013 Objectives Session 5.1 Review object naming standards Use the Like, In, Not, and & operators in queries Filter data
Tutorial 5 Creating Advanced Queries and Enhancing Table Design Microsoft Access 2013 Objectives Session 5.1 Review object naming standards Use the Like, In, Not, and & operators in queries Filter data
Business Objects. Report Writing - CMS Net and CCS Claims
 Business Objects Report Writing - CMS Net and CCS Claims Updated 11/28/2012 1 Introduction/Background... 4 Report Writing (Ad-Hoc)... 4 Requesting Report Writing Access... 4 Java Version... 4 Create A
Business Objects Report Writing - CMS Net and CCS Claims Updated 11/28/2012 1 Introduction/Background... 4 Report Writing (Ad-Hoc)... 4 Requesting Report Writing Access... 4 Java Version... 4 Create A
Advanced Query for Query Developers
 for Developers This is a training guide to step you through the advanced functions of in NUFinancials. is an ad-hoc reporting tool that allows you to retrieve data that is stored in the NUFinancials application.
for Developers This is a training guide to step you through the advanced functions of in NUFinancials. is an ad-hoc reporting tool that allows you to retrieve data that is stored in the NUFinancials application.
