Defending Computer Networks Lecture 7: Port Scanning. Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science
|
|
|
- Jessica Daniela Freeman
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Defending Computer Networks Lecture 7: Port Scanning Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science
2
3 Logis;cs Aim to give out HW2 on Thursday
4
5
6 Main Goals for Today TCP Portscanning Detec;on of Portscanning
7 Refresh: 3- way handshake Syn Packet Syn- ack Packet Client Ack Packet Normal data exchange Server
8 Refresh: IP Address Space Different organiza;ons get different amounts Class A: x.0.0.0/8 (2 24 = 16,777,216) x is in, as is x ) Huge org eg (DOD is /8 IBM is /8) Class B: x.y.0.0/16 (2 16 = 65536) Mid- sized organiza;on eg Cornell has /16, /16, /16 and /16 Class C: x.y.z.0/24 (2 8 = 256) Small organiza;ons. Can also have intermediate bitmasks. eg /22
9 Port Scan Scenarios Bad guy wants to map an address space Old style: across the internet S;ll happens for internet facing servers But rarely can map en;re networks any more Newer style: has a compromised machine on an internal network Wants to know what servers are here? Specifically, which machines have open ports?
10 Class B Portscan Example 2^16 addresses Say bad guy just scans on port 80 Eg say he knows an IIS or Apache exploit. Send out 2 16 syn packets to port 80 x.y.0.0, x.y.0.1, x.y.0.2, x.y Horizontal scan on port 80 See who sends back a syn- ack. Means they have a process answering on port 80. Find all the web servers this way. Agack em! Start with sending an ack pkt to establish conn. Or not if we don t send the 3 rd handshake, system typically won t log. Half- open connec;on
11 Ver;cal Port Scan of 1 IP Targelng a single IP address. Scan all 2 16 ports. Find all ports answering
12 What Happens if Port Not Open No machine at all. Typically get an ICMP response from a router Special protocol for Internet error message packets Saying no host at this address Machine but with closed port Typically get a reset packet Like a syn- ack, but with R set instead of S and A Seman;cs stop this immediately Security system (firewall) Silence (depending on configura;on)
13 Visualizing Scans Port IP Address
14 Small Piece of a Large Random Scan Port IP Address
15 Let s try it sudo nmap - n ss
16 What s Happening on The Wire sudo tcpdump - n - i en3 sudo nmap - n ss
17
18
19 TCP Fin Flag Used to indicate orderly close of a connec;on. Fin (F) 0x0x in TCP header flags field Either side may issue a packet with FIN in. Can be a data packet. Other side should respond with a FIN pkt. Connec;on is then over and no more pkts should be sent.
20 FIN Scanning
21 Let s try these and compare tcpdump - n - i en0 nmap - n ss nmap - n sf If ;me nmap - n sx nmap - n sn
22 What is Advantage Some early packet filters Network access control devices Would just examine syns to enforce policy Eg if we want to block inbound , No syns to port 25. Allow all non- syn pkts through on the theory that end- host will not actually allow a connec;on with no syn. But, end- host might respond to FIN scan, allowing agacker to portscan it through filter.
23 Let s look at everything nmap can do Just for kicks May not work, is slow/flaky at ;mes sudo nmap - n A T
24 hgps://nakedsecurity.sophos.com/2015/09/11/ us- agency- in- charge- of- power- grid- and- nukes- keeps- gelng- breached/
25 Algorithms to Detect Portscans First brush with Network Intrusion Detec;on General art/science of detec;ng badness by watching packets fly by. Invented at UC Davis Todd Heberlein et al circa 1989 Network Security Monitor Portscan detec;on is a nice sample problem. Illustrates many of the issues in an easy- to- follow context.
26 Firstly We Need to Get Packets Old Promiscuously monitor a hub/wire Modern Span port on switch Network tap device Detec;on device itself inline IPS Intrusion Preven;on System For CS 5434 purposes, libpcap man pcap will get you started.
27 Then we need a data structure Simplest possible thing is a hash table keyed on client IP With per- connec;on counts of relevant stuff Eg just count syns Portscanners will issue more syns than average. Alert when count goes over threshold But what s likely to go wrong? : : :1
28 Another possibility Look for the actual sequen;al behavior Syn- > Syn- > Syn- > Implement by having a last dest field in table entry Keep counts of number of increment- by- ones Fragile What could go wrong?
29 Keep track of unique dests/src? Now have to have a way to know what is a unique dst for that src? : : :1
30 Beger Idea Key off the idea that port- scanners make a lot of failed connec;ons. Legit users make only a few So keep track of failed- succeed count Alert when goes over threshold. How can the agacker game this? Doesn t work in the presence of packet- filter/ firewalls.
31 Another Idea Learn the probability of a syn (say) being to a des;na;on: P(D) Popular servers will have high P(D) (say 5% or 1%) Non- servers will have very low P(D) (1 in 10 6 or 10 9 ) Take log(p(d)) and accumulate that in hash table Anomaly score Portscanners will accumulate a lot of anomaly score Alert if over a threshold Harder for agackers to game don t know P(D) Otherwise wouldn t need to portscan
32 Extending the basic idea Keep flow table state Know when we see things like unexpected F Give that a high anomaly score F 23 F 97 F : : :1
Defending Computer Networks Lecture 6: TCP and Scanning. Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science
 Defending Computer Networks Lecture 6: TCP and Scanning Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science Logis;cs HW1 due tomorrow First quiz will be Tuesday September 23 rd. Half hour quiz at start
Defending Computer Networks Lecture 6: TCP and Scanning Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science Logis;cs HW1 due tomorrow First quiz will be Tuesday September 23 rd. Half hour quiz at start
Port Scanning. Objectives. Introduction: Port Scanning. 1. Introduce the techniques of port scanning. 2. Use port scanning audit tools such as Nmap.
 Port Scanning Objectives 1. Introduce the techniques of port scanning. 2. Use port scanning audit tools such as Nmap. Introduction: All machines connected to a LAN or connected to Internet via a modem
Port Scanning Objectives 1. Introduce the techniques of port scanning. 2. Use port scanning audit tools such as Nmap. Introduction: All machines connected to a LAN or connected to Internet via a modem
Introduction to Firewalls Open Source Security Tools for Information Technology Professionals
 Introduction to Firewalls Open Source Security Tools for Information Technology Professionals School of Professional Studies (SPS) The City University of New York (CUNY) Aron Trauring Adjunct Professor
Introduction to Firewalls Open Source Security Tools for Information Technology Professionals School of Professional Studies (SPS) The City University of New York (CUNY) Aron Trauring Adjunct Professor
Firewall Testing. Cameron Kerr Telecommunications Programme University of Otago. May 16, 2005
 Firewall Testing Cameron Kerr Telecommunications Programme University of Otago May 16, 2005 Abstract Writing a custom firewall is a complex task, and is something that requires a significant amount of
Firewall Testing Cameron Kerr Telecommunications Programme University of Otago May 16, 2005 Abstract Writing a custom firewall is a complex task, and is something that requires a significant amount of
An Introduction to Nmap with a Focus on Information Gathering. Ionuț Ambrosie
 An Introduction to Nmap with a Focus on Information Gathering Ionuț Ambrosie January 12, 2015 During the information gathering phase of a penetration test, tools such as Nmap can be helpful in allowing
An Introduction to Nmap with a Focus on Information Gathering Ionuț Ambrosie January 12, 2015 During the information gathering phase of a penetration test, tools such as Nmap can be helpful in allowing
FIREWALLS. Firewall: isolates organization s internal net from larger Internet, allowing some packets to pass, blocking others
 FIREWALLS FIREWALLS Firewall: isolates organization s internal net from larger Internet, allowing some packets to pass, blocking others FIREWALLS: WHY Prevent denial of service attacks: SYN flooding: attacker
FIREWALLS FIREWALLS Firewall: isolates organization s internal net from larger Internet, allowing some packets to pass, blocking others FIREWALLS: WHY Prevent denial of service attacks: SYN flooding: attacker
Network Traffic Analysis
 2013 Network Traffic Analysis Gerben Kleijn and Terence Nicholls 6/21/2013 Contents Introduction... 3 Lab 1 - Installing the Operating System (OS)... 3 Lab 2 Working with TCPDump... 4 Lab 3 - Installing
2013 Network Traffic Analysis Gerben Kleijn and Terence Nicholls 6/21/2013 Contents Introduction... 3 Lab 1 - Installing the Operating System (OS)... 3 Lab 2 Working with TCPDump... 4 Lab 3 - Installing
Intrusion Detection & SNORT. Fakrul Alam [email protected]
 Intrusion Detection & SNORT Fakrul Alam [email protected] Sometimes, Defenses Fail Our defenses aren t perfect Patches weren t applied promptly enough Antivirus signatures not up to date 0- days get through
Intrusion Detection & SNORT Fakrul Alam [email protected] Sometimes, Defenses Fail Our defenses aren t perfect Patches weren t applied promptly enough Antivirus signatures not up to date 0- days get through
FIREWALL AND NAT Lecture 7a
 FIREWALL AND NAT Lecture 7a COMPSCI 726 Network Defence and Countermeasures Muhammad Rizwan Asghar August 3, 2015 Source of most of slides: University of Twente FIREWALL An integrated collection of security
FIREWALL AND NAT Lecture 7a COMPSCI 726 Network Defence and Countermeasures Muhammad Rizwan Asghar August 3, 2015 Source of most of slides: University of Twente FIREWALL An integrated collection of security
Firewalls. Firewalls. Idea: separate local network from the Internet 2/24/15. Intranet DMZ. Trusted hosts and networks. Firewall.
 Firewalls 1 Firewalls Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Firewall Intranet Router DMZ Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks 2 1 Castle and
Firewalls 1 Firewalls Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Firewall Intranet Router DMZ Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks 2 1 Castle and
Firewalls 1 / 43. Firewalls
 What s a Firewall Why Use? Tradttional by Analogy Should We Fix the Network Protocols Instead? Firewall Advantages Schematic of a Firewall Conceptual Pieces The DMZ Positioning Why Administrative Domains?
What s a Firewall Why Use? Tradttional by Analogy Should We Fix the Network Protocols Instead? Firewall Advantages Schematic of a Firewall Conceptual Pieces The DMZ Positioning Why Administrative Domains?
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems
 CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Scanning CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Slide #1 Topics 1. Port Scanning 2. Stealth Scanning 3. Version Identification 4. OS Fingerprinting 5. Vulnerability Scanning
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Scanning CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Slide #1 Topics 1. Port Scanning 2. Stealth Scanning 3. Version Identification 4. OS Fingerprinting 5. Vulnerability Scanning
Chapter 8 Security Pt 2
 Chapter 8 Security Pt 2 IC322 Fall 2014 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
Chapter 8 Security Pt 2 IC322 Fall 2014 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
Network Security. Marcus Bendtsen Institutionen för Datavetenskap (IDA) Avdelningen för Databas- och Informationsteknik (ADIT)
 Network Security ICMP, TCP, DNS, Scanning Marcus Bendtsen Institutionen för Datavetenskap (IDA) Avdelningen för Databas- och Informationsteknik (ADIT) Agenda A couple of examples of network protocols that
Network Security ICMP, TCP, DNS, Scanning Marcus Bendtsen Institutionen för Datavetenskap (IDA) Avdelningen för Databas- och Informationsteknik (ADIT) Agenda A couple of examples of network protocols that
System Specification. Author: CMU Team
 System Specification Author: CMU Team Date: 09/23/2005 Table of Contents: 1. Introduction...2 1.1. Enhancement of vulnerability scanning tools reports 2 1.2. Intelligent monitoring of traffic to detect
System Specification Author: CMU Team Date: 09/23/2005 Table of Contents: 1. Introduction...2 1.1. Enhancement of vulnerability scanning tools reports 2 1.2. Intelligent monitoring of traffic to detect
Fuzzy Network Profiling for Intrusion Detection
 Fuzzy Network Profiling for Intrusion Detection John E. Dickerson ([email protected]) and Julie A. Dickerson ([email protected]) Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Iowa State University
Fuzzy Network Profiling for Intrusion Detection John E. Dickerson ([email protected]) and Julie A. Dickerson ([email protected]) Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Iowa State University
Port Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment. ECE4893 Internetwork Security Georgia Institute of Technology
 Port Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment ECE4893 Internetwork Security Georgia Institute of Technology Agenda Reconnaissance Scanning Network Mapping OS detection Vulnerability assessment Reconnaissance
Port Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment ECE4893 Internetwork Security Georgia Institute of Technology Agenda Reconnaissance Scanning Network Mapping OS detection Vulnerability assessment Reconnaissance
A1.1.1.11.1.1.2 1.1.1.3S B
 CS Computer 640: Network AdityaAkella Lecture Introduction Networks Security 25 to Security DoS Firewalls and The D-DoS Vulnerabilities Road Ahead Security Attacks Protocol IP ICMP Routing TCP Security
CS Computer 640: Network AdityaAkella Lecture Introduction Networks Security 25 to Security DoS Firewalls and The D-DoS Vulnerabilities Road Ahead Security Attacks Protocol IP ICMP Routing TCP Security
Firewalls. Ola Flygt Växjö University, Sweden http://w3.msi.vxu.se/users/ofl/ [email protected] +46 470 70 86 49. Firewall Design Principles
 Firewalls Ola Flygt Växjö University, Sweden http://w3.msi.vxu.se/users/ofl/ [email protected] +46 470 70 86 49 1 Firewall Design Principles Firewall Characteristics Types of Firewalls Firewall Configurations
Firewalls Ola Flygt Växjö University, Sweden http://w3.msi.vxu.se/users/ofl/ [email protected] +46 470 70 86 49 1 Firewall Design Principles Firewall Characteristics Types of Firewalls Firewall Configurations
CS5008: Internet Computing
 CS5008: Internet Computing Lecture 22: Internet Security A. O Riordan, 2009, latest revision 2015 Internet Security When a computer connects to the Internet and begins communicating with others, it is
CS5008: Internet Computing Lecture 22: Internet Security A. O Riordan, 2009, latest revision 2015 Internet Security When a computer connects to the Internet and begins communicating with others, it is
Overview of Network Security The need for network security Desirable security properties Common vulnerabilities Security policy designs
 Overview of Network Security The need for network security Desirable security properties Common vulnerabilities Security policy designs Why Network Security? Keep the bad guys out. (1) Closed networks
Overview of Network Security The need for network security Desirable security properties Common vulnerabilities Security policy designs Why Network Security? Keep the bad guys out. (1) Closed networks
CS155: Computer and Network Security
 CS155: Computer and Network Security Programming Project 3 Spring 2005 Shayan Guha [email protected] (with many slides borrowed from Matt Rubens) Project Overview 1) Use standard network monitoring
CS155: Computer and Network Security Programming Project 3 Spring 2005 Shayan Guha [email protected] (with many slides borrowed from Matt Rubens) Project Overview 1) Use standard network monitoring
Host Discovery with nmap
 Host Discovery with nmap By: Mark Wolfgang [email protected] November 2002 Table of Contents Host Discovery with nmap... 1 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 What is Host Discovery?... 4 2. Exploring nmap s Default
Host Discovery with nmap By: Mark Wolfgang [email protected] November 2002 Table of Contents Host Discovery with nmap... 1 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 What is Host Discovery?... 4 2. Exploring nmap s Default
Solution of Exercise Sheet 5
 Foundations of Cybersecurity (Winter 15/16) Prof. Dr. Michael Backes CISPA / Saarland University saarland university computer science Protocols = {????} Client Server IP Address =???? IP Address =????
Foundations of Cybersecurity (Winter 15/16) Prof. Dr. Michael Backes CISPA / Saarland University saarland university computer science Protocols = {????} Client Server IP Address =???? IP Address =????
CS 640 Introduction to Computer Networks. Network security (continued) Key Distribution a first step. Lecture24
 Introduction to Computer Networks Lecture24 Network security (continued) Key distribution Secure Shell Overview Authentication Practical issues Firewalls Denial of Service Attacks Definition Examples Key
Introduction to Computer Networks Lecture24 Network security (continued) Key distribution Secure Shell Overview Authentication Practical issues Firewalls Denial of Service Attacks Definition Examples Key
Remote Network Analysis
 Remote Network Analysis Torsten Hoefler [email protected] (DMZ), mostly between two packet filters and application gateways. The different possibilities to connect DMZ-hosts are also shown in Figure
Remote Network Analysis Torsten Hoefler [email protected] (DMZ), mostly between two packet filters and application gateways. The different possibilities to connect DMZ-hosts are also shown in Figure
Fuzzy Network Profiling for Intrusion Detection
 Fuzzy Network Profiling for Intrusion Detection John E. Dickerson ([email protected]) and Julie A. Dickerson ([email protected]) Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Iowa State University
Fuzzy Network Profiling for Intrusion Detection John E. Dickerson ([email protected]) and Julie A. Dickerson ([email protected]) Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Iowa State University
NETWORK SECURITY WITH OPENSOURCE FIREWALL
 NETWORK SECURITY WITH OPENSOURCE FIREWALL Vivek Kathayat,Dr Laxmi Ahuja AIIT Amity University,Noida [email protected] [email protected] ATTACKER SYSTEM: Backtrack 5r3( 192.168.75.10 ) HOST: Backtrack
NETWORK SECURITY WITH OPENSOURCE FIREWALL Vivek Kathayat,Dr Laxmi Ahuja AIIT Amity University,Noida [email protected] [email protected] ATTACKER SYSTEM: Backtrack 5r3( 192.168.75.10 ) HOST: Backtrack
Host Fingerprinting and Firewalking With hping
 Host Fingerprinting and Firewalking With hping Naveed Afzal National University Of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan Email: [email protected] Naveedafzal gmail.com Abstract: The purpose
Host Fingerprinting and Firewalking With hping Naveed Afzal National University Of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan Email: [email protected] Naveedafzal gmail.com Abstract: The purpose
co Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco R
 co Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco R Table of Contents Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco Routers...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1
co Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco R Table of Contents Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco Routers...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1
WHITE PAPER. FortiGate DoS Protection Block Malicious Traffic Before It Affects Critical Applications and Systems
 WHITE PAPER FortiGate DoS Protection Block Malicious Traffic Before It Affects Critical Applications and Systems Abstract: Denial of Service (DoS) attacks have been a part of the internet landscape for
WHITE PAPER FortiGate DoS Protection Block Malicious Traffic Before It Affects Critical Applications and Systems Abstract: Denial of Service (DoS) attacks have been a part of the internet landscape for
Firewall Firewall August, 2003
 Firewall August, 2003 1 Firewall and Access Control This product also serves as an Internet firewall, not only does it provide a natural firewall function (Network Address Translation, NAT), but it also
Firewall August, 2003 1 Firewall and Access Control This product also serves as an Internet firewall, not only does it provide a natural firewall function (Network Address Translation, NAT), but it also
Network Security - ISA 656 Firewalls & NATs
 Network Security - ISA 656 & NATs Angelos Stavrou Types of Schematic of a Conceptual Pieces Packet UDP Types of Packet Dynamic Packet Application Gateways Circuit Relays Personal /or Distributed Many firewalls
Network Security - ISA 656 & NATs Angelos Stavrou Types of Schematic of a Conceptual Pieces Packet UDP Types of Packet Dynamic Packet Application Gateways Circuit Relays Personal /or Distributed Many firewalls
CSA SDP Working Group
 CSA SDP Working Group An Open Source Code Project for a Software Defined Perimeter to Defend Cloud Applications from DDoS CSA Conference - Berlin November 2015 DHS Problem Addressing the Changing Perimeter
CSA SDP Working Group An Open Source Code Project for a Software Defined Perimeter to Defend Cloud Applications from DDoS CSA Conference - Berlin November 2015 DHS Problem Addressing the Changing Perimeter
Lab 3: Recon and Firewalls
 Lab 3: Recon and Firewalls IP, UDP, TCP and ICMP Before we can create firewall rules, we have to know the basics of network protocols. Here's a quick review... IP ICMP UDP TCP The underlying packet delivery
Lab 3: Recon and Firewalls IP, UDP, TCP and ICMP Before we can create firewall rules, we have to know the basics of network protocols. Here's a quick review... IP ICMP UDP TCP The underlying packet delivery
FortiGate IPS Guide. Intrusion Prevention System Guide. Version 1.0 30 November 2004 01-28007-0080-20041130
 FortiGate IPS Guide Intrusion Prevention System Guide Version 1.0 30 November 2004 01-28007-0080-20041130 Copyright 2004 Fortinet Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication including text, examples,
FortiGate IPS Guide Intrusion Prevention System Guide Version 1.0 30 November 2004 01-28007-0080-20041130 Copyright 2004 Fortinet Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication including text, examples,
Introduction of Intrusion Detection Systems
 Introduction of Intrusion Detection Systems Why IDS? Inspects all inbound and outbound network activity and identifies a network or system attack from someone attempting to compromise a system. Detection:
Introduction of Intrusion Detection Systems Why IDS? Inspects all inbound and outbound network activity and identifies a network or system attack from someone attempting to compromise a system. Detection:
Lecture 5: Network Attacks I. Course Admin
 Lecture 5: Network Attacks I CS 336/536: Computer Network Security Fall 2013 Nitesh Saxena Adopted from previous lectures by Keith Ross Course Admin HW/Lab 1 Due Coming Monday 11am Lab sessions are active
Lecture 5: Network Attacks I CS 336/536: Computer Network Security Fall 2013 Nitesh Saxena Adopted from previous lectures by Keith Ross Course Admin HW/Lab 1 Due Coming Monday 11am Lab sessions are active
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: PACKET CRAFTING
 CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: PACKET CRAFTING Protect your FOSS-based IT infrastructure from packet crafting by learning more about it. In the previous articles in this series, we explored common infrastructure
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: PACKET CRAFTING Protect your FOSS-based IT infrastructure from packet crafting by learning more about it. In the previous articles in this series, we explored common infrastructure
Network Security. Chapter 3. Cornelius Diekmann. Version: October 21, 2015. Lehrstuhl für Netzarchitekturen und Netzdienste Institut für Informatik
 Network Security Chapter 3 Cornelius Diekmann Lehrstuhl für Netzarchitekturen und Netzdienste Institut für Informatik Version: October 21, 2015 IN2101, WS 15/16, Network Security 1 Security Policies and
Network Security Chapter 3 Cornelius Diekmann Lehrstuhl für Netzarchitekturen und Netzdienste Institut für Informatik Version: October 21, 2015 IN2101, WS 15/16, Network Security 1 Security Policies and
Firewalls. Basic Firewall Concept. Why firewalls? Firewall goals. Two Separable Topics. Firewall Design & Architecture Issues
 CS 155 May 20, 2004 Firewalls Basic Firewall Concept Separate local area net from internet Firewall John Mitchell Credit: some text, illustrations from Simon Cooper Router All packets between LAN and internet
CS 155 May 20, 2004 Firewalls Basic Firewall Concept Separate local area net from internet Firewall John Mitchell Credit: some text, illustrations from Simon Cooper Router All packets between LAN and internet
CS 356 Lecture 17 and 18 Intrusion Detection. Spring 2013
 CS 356 Lecture 17 and 18 Intrusion Detection Spring 2013 Review Chapter 1: Basic Concepts and Terminology Chapter 2: Basic Cryptographic Tools Chapter 3 User Authentication Chapter 4 Access Control Lists
CS 356 Lecture 17 and 18 Intrusion Detection Spring 2013 Review Chapter 1: Basic Concepts and Terminology Chapter 2: Basic Cryptographic Tools Chapter 3 User Authentication Chapter 4 Access Control Lists
IDS / IPS. James E. Thiel S.W.A.T.
 IDS / IPS An introduction to intrusion detection and intrusion prevention systems James E. Thiel January 14, 2005 S.W.A.T. Drexel University Overview Intrusion Detection Purpose Types Detection Methods
IDS / IPS An introduction to intrusion detection and intrusion prevention systems James E. Thiel January 14, 2005 S.W.A.T. Drexel University Overview Intrusion Detection Purpose Types Detection Methods
Attacks and Defense. Phase 1: Reconnaissance
 Attacks and Defense Phase 1: Reconnaissance Phase 2: Port Scanning Phase 3: Gaining Access Using Application and Operating System Using Networks Phase 1: Reconnaissance Known as information gathering.
Attacks and Defense Phase 1: Reconnaissance Phase 2: Port Scanning Phase 3: Gaining Access Using Application and Operating System Using Networks Phase 1: Reconnaissance Known as information gathering.
Presented By: Holes in the Fence. Agenda. IPCCTV Attack. DDos Attack. Why Network Security is Important
 Presented By: Holes in the Fence Dave Engebretson, Contributing Technology writer, SDM Magazine Industry Instructor in Fiber and Networking Prevention of Security System breaches of networked Edge Devices
Presented By: Holes in the Fence Dave Engebretson, Contributing Technology writer, SDM Magazine Industry Instructor in Fiber and Networking Prevention of Security System breaches of networked Edge Devices
Network forensics 101 Network monitoring with Netflow, nfsen + nfdump
 Network forensics 101 Network monitoring with Netflow, nfsen + nfdump www.enisa.europa.eu Agenda Intro to netflow Metrics Toolbox (Nfsen + Nfdump) Demo www.enisa.europa.eu 2 What is Netflow Netflow = Netflow
Network forensics 101 Network monitoring with Netflow, nfsen + nfdump www.enisa.europa.eu Agenda Intro to netflow Metrics Toolbox (Nfsen + Nfdump) Demo www.enisa.europa.eu 2 What is Netflow Netflow = Netflow
INTRODUCTION TO FIREWALL SECURITY
 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWALL SECURITY SESSION 1 Agenda Introduction to Firewalls Types of Firewalls Modes and Deployments Key Features in a Firewall Emerging Trends 2 Printed in USA. What Is a Firewall DMZ
INTRODUCTION TO FIREWALL SECURITY SESSION 1 Agenda Introduction to Firewalls Types of Firewalls Modes and Deployments Key Features in a Firewall Emerging Trends 2 Printed in USA. What Is a Firewall DMZ
Presentation_ID. 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Presentation_ID 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 IPv6 Security Considerations Patrick Grossetete [email protected] Dennis Vogel [email protected] 2 Agenda Native security in IPv6 IPv6 challenges
Presentation_ID 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 IPv6 Security Considerations Patrick Grossetete [email protected] Dennis Vogel [email protected] 2 Agenda Native security in IPv6 IPv6 challenges
Introduction. Nmap from an Ethical Hacker's View Part 1. By Kirby Tucker
 Nmap from an Ethical Hacker's View Part 1 By Kirby Tucker Editor's Note: Kirby is a long time contributor and supporter of EH-Net. So when he came to me with the idea to do a more approachable tutorial
Nmap from an Ethical Hacker's View Part 1 By Kirby Tucker Editor's Note: Kirby is a long time contributor and supporter of EH-Net. So when he came to me with the idea to do a more approachable tutorial
CSCE 465 Computer & Network Security
 CSCE 465 Computer & Network Security Instructor: Dr. Guofei Gu http://courses.cse.tamu.edu/guofei/csce465/ Vulnerability Analysis 1 Roadmap Why vulnerability analysis? Example: TCP/IP related vulnerabilities
CSCE 465 Computer & Network Security Instructor: Dr. Guofei Gu http://courses.cse.tamu.edu/guofei/csce465/ Vulnerability Analysis 1 Roadmap Why vulnerability analysis? Example: TCP/IP related vulnerabilities
Security: Attack and Defense
 Security: Attack and Defense Aaron Hertz Carnegie Mellon University Outline! Breaking into hosts! DOS Attacks! Firewalls and other tools 15-441 Computer Networks Spring 2003 Breaking Into Hosts! Guessing
Security: Attack and Defense Aaron Hertz Carnegie Mellon University Outline! Breaking into hosts! DOS Attacks! Firewalls and other tools 15-441 Computer Networks Spring 2003 Breaking Into Hosts! Guessing
Project 2: Firewall Design (Phase I)
 Project 2: Firewall Design (Phase I) CS 161 - Joseph/Tygar November 12, 2006 1 Edits If we need to make clarifications or corrections to this document after distributing it, we will post a new version
Project 2: Firewall Design (Phase I) CS 161 - Joseph/Tygar November 12, 2006 1 Edits If we need to make clarifications or corrections to this document after distributing it, we will post a new version
We will give some overview of firewalls. Figure 1 explains the position of a firewall. Figure 1: A Firewall
 Chapter 10 Firewall Firewalls are devices used to protect a local network from network based security threats while at the same time affording access to the wide area network and the internet. Basically,
Chapter 10 Firewall Firewalls are devices used to protect a local network from network based security threats while at the same time affording access to the wide area network and the internet. Basically,
Introduction to Passive Network Traffic Monitoring
 Introduction to Passive Network Traffic Monitoring CS459 ~ Internet Measurements Spring 2015 Despoina Antonakaki [email protected] Active Monitoring Inject test packets into the network or send packets
Introduction to Passive Network Traffic Monitoring CS459 ~ Internet Measurements Spring 2015 Despoina Antonakaki [email protected] Active Monitoring Inject test packets into the network or send packets
1. Introduction. 2. DoS/DDoS. MilsVPN DoS/DDoS and ISP. 2.1 What is DoS/DDoS? 2.2 What is SYN Flooding?
 Page 1 of 5 1. Introduction The present document explains about common attack scenarios to computer networks and describes with some examples the following features of the MilsGates: Protection against
Page 1 of 5 1. Introduction The present document explains about common attack scenarios to computer networks and describes with some examples the following features of the MilsGates: Protection against
1. Firewall Configuration
 1. Firewall Configuration A firewall is a method of implementing common as well as user defined security policies in an effort to keep intruders out. Firewalls work by analyzing and filtering out IP packets
1. Firewall Configuration A firewall is a method of implementing common as well as user defined security policies in an effort to keep intruders out. Firewalls work by analyzing and filtering out IP packets
VPN Lesson 2: VPN Implementation. Summary
 VPN Lesson 2: VPN Implementation Summary 1 Notations VPN client (ok) Firewall Router VPN firewall VPN router VPN server VPN concentrator 2 Basic Questions 1. VPN implementation options for remote users
VPN Lesson 2: VPN Implementation Summary 1 Notations VPN client (ok) Firewall Router VPN firewall VPN router VPN server VPN concentrator 2 Basic Questions 1. VPN implementation options for remote users
Scanning Tools. Scan Types. Network sweeping - Basic technique used to determine which of a range of IP addresses map to live hosts.
 Scanning Tools The goal of the scanning phase is to learn more information about the target environment and discover openings by interacting with that target environment. This paper will look at some of
Scanning Tools The goal of the scanning phase is to learn more information about the target environment and discover openings by interacting with that target environment. This paper will look at some of
20-CS-6053-00X Network Security Spring, 2014. An Introduction To. Network Security. Week 1. January 7
 20-CS-6053-00X Network Security Spring, 2014 An Introduction To Network Security Week 1 January 7 Attacks Criminal: fraud, scams, destruction; IP, ID, brand theft Privacy: surveillance, databases, traffic
20-CS-6053-00X Network Security Spring, 2014 An Introduction To Network Security Week 1 January 7 Attacks Criminal: fraud, scams, destruction; IP, ID, brand theft Privacy: surveillance, databases, traffic
Exercise 7 Network Forensics
 Exercise 7 Network Forensics What Will You Learn? The network forensics exercise is aimed at introducing you to the post-mortem analysis of pcap file dumps and Cisco netflow logs. In particular you will:
Exercise 7 Network Forensics What Will You Learn? The network forensics exercise is aimed at introducing you to the post-mortem analysis of pcap file dumps and Cisco netflow logs. In particular you will:
Network Security. Network Scanning
 Network Security Network Scanning Module 2 Keith A. Watson, CISSP, CISA IA Research Engineer, CERIAS [email protected] 1 Network Scanning Definition: Sending packets configured to evoke a response
Network Security Network Scanning Module 2 Keith A. Watson, CISSP, CISA IA Research Engineer, CERIAS [email protected] 1 Network Scanning Definition: Sending packets configured to evoke a response
This Lecture. The Internet and Sockets. The Start 1969. If everyone just sends a small packet of data, they can all use the line at the same.
 This Lecture The Internet and Sockets Computer Security Tom Chothia How the Internet works. Some History TCP/IP Some useful network tools: Nmap, WireShark Some common attacks: The attacker controls the
This Lecture The Internet and Sockets Computer Security Tom Chothia How the Internet works. Some History TCP/IP Some useful network tools: Nmap, WireShark Some common attacks: The attacker controls the
Installing and Configuring Nessus by Nitesh Dhanjani
 Unless you've been living under a rock for the past few years, it is quite evident that software vulnerabilities are being found and announced quicker than ever before. Every time a security advisory goes
Unless you've been living under a rock for the past few years, it is quite evident that software vulnerabilities are being found and announced quicker than ever before. Every time a security advisory goes
CSE331: Introduction to Networks and Security. Lecture 12 Fall 2006
 CSE331: Introduction to Networks and Security Lecture 12 Fall 2006 Announcements Midterm I will be held Friday, Oct. 6th. True/False Multiple Choice Calculation Short answer Short essay Project 2 is on
CSE331: Introduction to Networks and Security Lecture 12 Fall 2006 Announcements Midterm I will be held Friday, Oct. 6th. True/False Multiple Choice Calculation Short answer Short essay Project 2 is on
Wireshark Developer and User Conference
 Wireshark Developer and User Conference Using NetFlow to Analyze Your Network June 15 th, 2011 Christopher J. White Manager Applica6ons and Analy6cs, Cascade Riverbed Technology [email protected] SHARKFEST
Wireshark Developer and User Conference Using NetFlow to Analyze Your Network June 15 th, 2011 Christopher J. White Manager Applica6ons and Analy6cs, Cascade Riverbed Technology [email protected] SHARKFEST
The Transport Layer and Implica4ons for Network Monitoring. CS 410/510 Spring 2014
 The Transport Layer and Implica4ons for Network Monitoring CS 410/510 Spring 2014 Review Preliminaries: Three Principles of Informa4on Security The Three A s Review: Network Protocol Stacks Review: Network
The Transport Layer and Implica4ons for Network Monitoring CS 410/510 Spring 2014 Review Preliminaries: Three Principles of Informa4on Security The Three A s Review: Network Protocol Stacks Review: Network
CMPT 471 Networking II
 CMPT 471 Networking II Firewalls Janice Regan, 2006-2013 1 Security When is a computer secure When the data and software on the computer are available on demand only to those people who should have access
CMPT 471 Networking II Firewalls Janice Regan, 2006-2013 1 Security When is a computer secure When the data and software on the computer are available on demand only to those people who should have access
Configuring Personal Firewalls and Understanding IDS. Securing Networks Chapter 3 Part 2 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA
 Configuring Personal Firewalls and Understanding IDS Securing Networks Chapter 3 Part 2 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA 1 Configuring Personal Firewalls and IDS Learning Objectives Task Statements 1.4 Analyze baseline
Configuring Personal Firewalls and Understanding IDS Securing Networks Chapter 3 Part 2 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA 1 Configuring Personal Firewalls and IDS Learning Objectives Task Statements 1.4 Analyze baseline
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
 Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Defending against Flooding-Based DDoS Attacks: A Tutorial Rocky K. C. Chang Presented by Adwait Belsare ([email protected]) Suvesh Pratapa ([email protected]) Modified by
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Defending against Flooding-Based DDoS Attacks: A Tutorial Rocky K. C. Chang Presented by Adwait Belsare ([email protected]) Suvesh Pratapa ([email protected]) Modified by
Passive Network Traffic Analysis: Understanding a Network Through Passive Monitoring Kevin Timm,
 Passive Network Traffic Analysis: Understanding a Network Through Passive Monitoring Kevin Timm, Network IDS devices use passive network monitoring extensively to detect possible threats. Through passive
Passive Network Traffic Analysis: Understanding a Network Through Passive Monitoring Kevin Timm, Network IDS devices use passive network monitoring extensively to detect possible threats. Through passive
How to protect your home/office network?
 How to protect your home/office network? Using IPTables and Building a Firewall - Background, Motivation and Concepts Adir Abraham [email protected] Do you think that you are alone, connected from
How to protect your home/office network? Using IPTables and Building a Firewall - Background, Motivation and Concepts Adir Abraham [email protected] Do you think that you are alone, connected from
Linux Network Security
 Linux Network Security Course ID SEC220 Course Description This extremely popular class focuses on network security, and makes an excellent companion class to the GL550: Host Security course. Protocols
Linux Network Security Course ID SEC220 Course Description This extremely popular class focuses on network security, and makes an excellent companion class to the GL550: Host Security course. Protocols
Network Security CS 192
 Network Security CS 192 Network Scanning (Idlescan) Department of Computer Science George Washington University Jonathan Stanton 1 Today s topics Discussion of new DNS flaws Network Scanning (Idlescan)
Network Security CS 192 Network Scanning (Idlescan) Department of Computer Science George Washington University Jonathan Stanton 1 Today s topics Discussion of new DNS flaws Network Scanning (Idlescan)
Intrusion Detection Systems. Darren R. Davis Student Computing Labs
 Intrusion Detection Systems Darren R. Davis Student Computing Labs Overview Intrusion Detection What is it? Why do I need it? How do I do it? Intrusion Detection Software Network based Host based Intrusion
Intrusion Detection Systems Darren R. Davis Student Computing Labs Overview Intrusion Detection What is it? Why do I need it? How do I do it? Intrusion Detection Software Network based Host based Intrusion
Carrier/WAN SDN Brocade Flow Optimizer Making SDN Consumable
 Brocade Flow Optimizer Making SDN Consumable Business And IT Are Changing Like Never Before Changes in Application Type, Delivery and Consumption Public/Hybrid Cloud SaaS/PaaS Storage Users/ Machines Device
Brocade Flow Optimizer Making SDN Consumable Business And IT Are Changing Like Never Before Changes in Application Type, Delivery and Consumption Public/Hybrid Cloud SaaS/PaaS Storage Users/ Machines Device
Network Security TCP/IP Refresher
 Network Security TCP/IP Refresher What you (at least) need to know about networking! Dr. David Barrera Network Security HS 2014 Outline Network Reference Models Local Area Networks Internet Protocol (IP)
Network Security TCP/IP Refresher What you (at least) need to know about networking! Dr. David Barrera Network Security HS 2014 Outline Network Reference Models Local Area Networks Internet Protocol (IP)
CS155 - Firewalls. Simon Cooper <[email protected]> CS155 Firewalls 22 May 2003
 CS155 - Firewalls Simon Cooper CS155 Firewalls 22 May 2003 1 Why Firewalls? Need for the exchange of information; education, business, recreation, social and political Need to do something
CS155 - Firewalls Simon Cooper CS155 Firewalls 22 May 2003 1 Why Firewalls? Need for the exchange of information; education, business, recreation, social and political Need to do something
Firewall implementation and testing
 Firewall implementation and testing Patrik Ragnarsson, Niclas Gustafsson E-mail: [email protected], [email protected] Supervisor: David Byers, [email protected] Project Report for Information
Firewall implementation and testing Patrik Ragnarsson, Niclas Gustafsson E-mail: [email protected], [email protected] Supervisor: David Byers, [email protected] Project Report for Information
Looking for Trouble: ICMP and IP Statistics to Watch
 Looking for Trouble: ICMP and IP Statistics to Watch Laura Chappell, Senior Protocol Analyst Protocol Analysis Institute [[email protected]] www.packet-level.com www.podbooks.com HTCIA Member,
Looking for Trouble: ICMP and IP Statistics to Watch Laura Chappell, Senior Protocol Analyst Protocol Analysis Institute [[email protected]] www.packet-level.com www.podbooks.com HTCIA Member,
NAT & IP Masquerade. Internet NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION INTRODUCTION. NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5. Internal PC 192.168.0.25
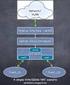 NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
Introduction to Network Security Lab 2 - NMap
 Introduction to Network Security Lab 2 - NMap 1 Introduction: Nmap as an Offensive Network Security Tool Nmap, short for Network Mapper, is a very versatile security tool that should be included in every
Introduction to Network Security Lab 2 - NMap 1 Introduction: Nmap as an Offensive Network Security Tool Nmap, short for Network Mapper, is a very versatile security tool that should be included in every
TCP SYN Flood - Denial of Service Seung Jae Won University of Windsor [email protected]
 TCP SYN Flood - Denial of Service Seung Jae Won University of Windsor [email protected] Abstract TCP SYN flooding attack is a kind of denial-of-service attack. This SYN flooding attack is using the weakness
TCP SYN Flood - Denial of Service Seung Jae Won University of Windsor [email protected] Abstract TCP SYN flooding attack is a kind of denial-of-service attack. This SYN flooding attack is using the weakness
Network Security Monitoring and Behavior Analysis Pavel Čeleda, Petr Velan, Tomáš Jirsík
 Network Security Monitoring and Behavior Analysis Pavel Čeleda, Petr Velan, Tomáš Jirsík {celeda velan jirsik}@ics.muni.cz Part I Introduction P. Čeleda et al. Network Security Monitoring and Behavior
Network Security Monitoring and Behavior Analysis Pavel Čeleda, Petr Velan, Tomáš Jirsík {celeda velan jirsik}@ics.muni.cz Part I Introduction P. Čeleda et al. Network Security Monitoring and Behavior
Cryptography and network security
 Cryptography and network security Firewalls slide 1 Firewalls Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Firewall Intranet Router DMZ Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible
Cryptography and network security Firewalls slide 1 Firewalls Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Firewall Intranet Router DMZ Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible
Snort Installation - Ubuntu FEUP. SSI - ProDEI-2010. Paulo Neto and Rui Chilro. December 7, 2010
 December 7, 2010 Work Proposal The purpose of this work is: Explain a basic IDS Architecture and Topology Explain a more advanced IDS solution Install SNORT on the FEUP Ubuntu distribution and test some
December 7, 2010 Work Proposal The purpose of this work is: Explain a basic IDS Architecture and Topology Explain a more advanced IDS solution Install SNORT on the FEUP Ubuntu distribution and test some
NSC 93-2213-E-110-045
 NSC93-2213-E-110-045 2004 8 1 2005 731 94 830 Introduction 1 Nowadays the Internet has become an important part of people s daily life. People receive emails, surf the web sites, and chat with friends
NSC93-2213-E-110-045 2004 8 1 2005 731 94 830 Introduction 1 Nowadays the Internet has become an important part of people s daily life. People receive emails, surf the web sites, and chat with friends
Announcements. No question session this week
 Announcements No question session this week Stretch break DoS attacks In Feb. 2000, Yahoo s router kept crashing - Engineers had problems with it before, but this was worse - Turned out they were being
Announcements No question session this week Stretch break DoS attacks In Feb. 2000, Yahoo s router kept crashing - Engineers had problems with it before, but this was worse - Turned out they were being
Lecture 2-ter. 2. A communication example Managing a HTTP v1.0 connection. G.Bianchi, G.Neglia, V.Mancuso
 Lecture 2-ter. 2 A communication example Managing a HTTP v1.0 connection Managing a HTTP request User digits URL and press return (or clicks ). What happens (HTTP 1.0): 1. Browser opens a TCP transport
Lecture 2-ter. 2 A communication example Managing a HTTP v1.0 connection Managing a HTTP request User digits URL and press return (or clicks ). What happens (HTTP 1.0): 1. Browser opens a TCP transport
FIREWALLS & CBAC. [email protected]
 FIREWALLS & CBAC [email protected] Implementing a Firewall Personal software firewall a software that is installed on a single PC to protect only that PC All-in-one firewall can be a single device that
FIREWALLS & CBAC [email protected] Implementing a Firewall Personal software firewall a software that is installed on a single PC to protect only that PC All-in-one firewall can be a single device that
