Table Annex: Detailed information on the impact of the tax system on social expenditure
|
|
|
- Hilary Russell
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 : Detailed information on the impact of the tax system on social expenditure A. Average Itemised Tax Rates (AITR %) B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income C. Tax breaks for social purposes Missing values are presented as follows: m data not available; a data do not exist; x data included in another category. SOCX Manual/Methodology See Part II. (p.88) OECD Social, Employment and Migration Working Papers No. 124, October 2011: Is the European welfare state really more expensive? Indicators on social spending, and a manual to the OECD Social Expenditure database (SOCX)" II.4. Net (after tax) social expenditure
2 AUSTRALIA Table Annex Detailed information on the impact of the tax system on social expenditure A. Average Itemised Tax Rates (AITR %) 2001 (a) 2003 (a) 2005 (b) 2007 (b) 2009 (b) Old-age cash benefits 1a - public pensions Age Pension Wife's Pension na na Widow's B Pension na na na 1b - early retirement benefits 1c - private pensions Superannuation pension Superannuation Lump Sums 2 Survivors' benefits 2a - public pensions Veteran's Service Pensions 3 Incapacity-related benefits na na Disability Support Pension 3c - Sickness payments Sickness Allowance 4 Family cash benefits 4a - Family benefits Parenting Allowance na na Partner Allowance Carer's Payment 4c - Sole parent benefits Sole Parent Widow Allowance 6 Unemployment 6b - unemployment assistance benefit Unemployment Benefits Wage income The AITRs for wage income, superannuation pensions and superannuation lump sums were calculated using a sample file of Australian tax returns in All other AITRs were calculated using the STINMOD model, a static microsimulation model developed by the National Center for Social and Economic Modelling (NATSEM). a.the AITRs were obtained by calculating the amount of tax paid in aggregate with and without the income streams. The difference between the taxes paid was then divided by the value of the income stream to reveal the value of the AITR. b. Tax paid on an income stream was calculated by dividing income from stream by total tax liability and then multiplying it by total tax paid. This amount was then divided by the total income from stream to calculate the AITR. This methodology has been adopted to align with the instructions provided by the OECD. c. Figure is derived from a small sample of observations and caution should be taken with interpretation. Sources: STINMOD distributional model. Revenue Group of The Treasury, Australian Government. B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in millions of Australian dollars (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 9.9% 10.1% 9.8% 9.3% 8.9% 8.7% 8.3% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 13.5% 13.6% 13.0% 12.4% 11.9% 11.9% 11.6% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 15.1% 15.3% 14.7% 14.1% 13.6% 13.6% 13.3% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2, except Government wages from Australian National Accounts (table 40); and OECD Revenue Statistics database ( for lines 3, 4, and 5.
3 AUSTRALIA Table Annex Detailed information on the impact of the tax system on social expenditure C. Tax breaks for social purposes (in millions of Australian dollars) 2001 (d) 2003 (e) 2005 (f) 2007 (g) 2009 (h) Tax breaks similar to cash benefits (i) Family: Tax offsets for taxpayers with dependants Tax offset for housekeeper who cares for a prescribed dependant Tax offset for dependant spouse, child-housekeeper and housekeeper who cares for prescribed dependent Tax offsets for taxpayers supporting a parent, parent-in-law, or invalid relative Other areas: Medical expenses tax offset Exemption of certain income support benefits, pensions or allowances Exemption of Utilities Allowance and Seniors Concession Allowance Exemption of payments made under the First Home Owners Grant Scheme Income averaging for authors, inventors, performing artists, production associates and sportspersons Exemption of post-judgment injury awards in personal injury compensation cases Capped taxation rates for lump sum payments for unused recreation and long service leave (j) Concessional treatment of non-superannuation termination benefits (j) Taxation of five per cent of unused long service leave accumulated by 15 August 1978 (j) Capital gains tax exemption on the sale of a small business at retirement (j) Small business capital gains tax exemption for assets held for more than 15 years (j) Exemption of rent subsidy payments under the Commonwealth/State mortgage and rent relief schemes Tax offset for low income earners For informaton only: these items are not included in the sum of TBSPs as that constitute a double counting with the calculations on Average Direct Tax Rates over benefit income Exemption of the Child Care Rebate (Revenue foregone) Tax offset for child care (Revenue foregone) Exemption of Child Care Benefit (Revenue foregone) Exemption of the Baby Bonus (Revenue foregone) Exemption of the first child tax offset (Baby Bonus) (Revenue foregone) Exemption of Family Tax Benefit, Parts A and B (Revenue foregone) Exemption of certain veterans' pensions, allowances or benefits, compensations, and particular WWII-related payments for persecutions (Revenue foregone) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) This series has been revised to exclude Exemption from the Medicare Levy for residents with a taxable income below a threshold This series has been revised to exclude Exemption from the Medicare Levy for residents with a taxable income below a threshold ($380m), as this was factored into the calculation of AITRs. This series has been revised to exclude Exemption from the Medicare Levy for residents with a taxable income below a threshold ($380m), Mature Age Worker Offset ($425m) and Senior Australian Tax Offset ($606) as this was factored into the calculation of AITRs. Tax breaks provided through GST exemption for child care services has also been removed from the series. Data have been updated using 2011 Tax Expenditure Statement. This series has also been revised to exclude Exemption from the Medicare Levy for residents with a taxable income below a threshold ($446m), Mature Age Worker Offset ($455m) and Senior Australian Tax Offset ($410) as this was factored into the calculation of AITRs. Tax breaks provided through GST exemption for child care services has also been removed from the series. Explanatory notes for these data is available in the sheet "Q4." The rebate for private health insurance has been moved from the category 'Tax breaks similar to cash benefits' to 'Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection' to be consistent with other countries. (j) All series from 2001 to 2007 have been revised to include 'Capped taxation rates for lump sum payments for unused recreation and long service leave', 'Concessional treatment of non-superannuation termination benefits', 'Concessional treatment of non-superannuation termination payments', 'Capital gains tax exemption on the sale of a small business at retirement', and 'Small business capital gains tax exemption for assets held for more than 15 years'. These tax breaks were previously included in the Memorandum Item on Tax breaks for pensions. Source: Australian Government (2011, 2009, 2007,2005, 2003), Tax Expenditure Statement, The Treasury, Canberra. For information only : Exemptions from Goods and Services Tax for social products and services (excluded from total) (j)
4 AUSTRALIA Table Annex Detailed information on the impact of the tax system on social expenditure GST exemption for education supplies (e.g. education sources, student accommodation) GST exemption for drugs and medicinal preparations GST exemption for medical aids and applicances GST exemption for medical and health services GST exemption for private health insurance GST exemption for residential care, community care and other care services (e.g. publicly funded aged care, disability care) GST exemption for child care services (j) The GST is an indirect, broad based consumption tax charged at a rate of 10 per cent. Several goods and services that fall within the OECD's definition of a social product are exempt from this tax. The value of these exemptions are listed above. If this type of tax expenditure in included in the calculation of net social expenditure for other countries, it may be appropriate to similarly incorporate this information in the calculation of net social expenditure in Australia. Estimates of tax expenditure on these concessions is not available for 2003 or Note that tax expenditures relating to GST exemptions was introduced into the Tax Expenditures Statement in For this reason, tax breaks relating to GST exemptions are not available for prior years. Source: Australian Government (2011), Tax Expenditure Statement, The Treasury, Canberra. Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection (not including pensions) % tax offset for expenditure on private health insurance (l) Deduction for gifts to deductible gift recipients Deduction for gifts to approved donees Deduction for contributions with an associated minor benefit Partial rebate for certain non-profit, non-government bodies Capped exemption for public benevolent institutions (excluding public hospitals) Deduction for donations to prescribed private funds (k) Data have been updated using revised estimates published in the 2011 Tax Expenditure Statement. (l) The rebate for private health insurance has been moved from the category 'Tax breaks similar to cash benefits' to 'Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection' to be consistent with other countries. Source: Australian Government (2011, 2009, 2007,2005, 2003), Tax Expenditure Statement, The Treasury, Canberra. Memorandum Items (m) Tax breaks for pensions Superannuation - capital gains tax discount for funds Concessional taxation of employer contributions Concessional taxation of superannuation entity earnings Concessional taxation of funded superannuation Concessional taxation of unfunded superannuation lump sums Superannuation - deduction and concessional taxation of certain personal contributions Superannuation - measures for low-income earners Superannuation - spouse contribution offset Superannuation - tax on funded lump sums relating to post-june 1983 service (l) (m) All series from 2001 to 2007 have been revised to exclude 'Capped taxation rates for lump sum payments for unused recreation and long service leave', 'Concessional treatment of non-superannuation termination benefits', and 'Concessional treatment of non-superannuation termination payments' as these tax concessions are related to employment termination, not pensions. Data have been updated using revised estimates published in the 2011 Tax Expenditure Statement. Source: Australian Government (2011, 2009, 2007,2005, 2003), Tax Expenditure Statement, The Treasury, Canberra. Notes: Data is reported for the financial year commencing on 1 July of the year indicated and finishing on 30 June of the following year and 2011 figures are new and 2009 figures have been updated using estimates published in the 2013 Tax Expenditures Statement.
5 AUSTRIA A. Average Itemised Tax Rates (AITR %) Old-age cash benefits (1 +3) 17.7% - public pensions 17.0% 16.6% 15.9% 15.0% 15.4% 15.8% - private pensions 13.0% 16.6% 15.9% 15.0% 15.4% 15.8% Incapacity-related benefits - Disability pensions 17.7% 17.0% 16.6% 15.9% 15.0% 15.4% 15.8% - Occupational Injury benefits 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% 0.0% - Sickness payments 30.0% 30.0% 29.3% 22.0% 22.0% 22.0% 22.0% Source: Ministry of Finance (Bundesministerium fur Finanzen), Wage Tax Statistics (2001, 2003, 2005, 2007, 2009, 2010, 2011). B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in millions of euros (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 16.7% 16.7% 16.5% 16.3% 16.3% 16.0% 16.0% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 19.3% 19.3% 18.9% 18.6% 18.6% 18.2% 18.3% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 22.4% 22.5% 22.0% 21.8% 22.0% 21.5% 21.5% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2; and OECD Revenue Statistics database ( for lines 3, 4, and 5. C. Tax breaks for social purposes (in millions of euros) Tax breaks similar to cash benefits Family: Tax credits for one-parent families ("Alleinerzieherabsetzbetrag") Other areas: Appliances for the disabled (Befreiung für Versehrten- und Invalidenfahrzeuge) 2 Abs.1 Z 5, Special tax relief (Außergewöhnliche Belastungen) 34, Tax measures to stimulate private social protection (including pensions) Contributions to health, accident and pension insurance (Versicherungsbeiträge) 18 Abs. 1 Z Memorandum Items Tax breaks for pensions Deduction of contributions to private pension insurances or funds as "special expenses" Premium (payable tax credit) for contributions to pension funds Source: Budget Accounts, Foerderungsbericht (2001, 2003, 2005, 2007, 2009, 2010, 2011), Ministry of Finance, Austria.
6 BELGIUM A. Amount of direct tax paid on benefit income (in millions of euros) A.Taxes paid on transfer income (A1 minus A2, then adding local tax rate *) Pensions: PIT Sickness: PIT Early retirement: PIT Unemployment benefits: PIT Total PIT (A1) Pensions: tax credit Sickness: tax credit Early retirement: tax credit Unemployment benefits: tax credit Others Total tax credits (A2) Local tax rate 7.1% 7.4% 7.1% 7.4% 7.3% 7.3% 7.5% B. Social security contributions Total (A + B) * Local tax rate is applied to income tax, which overestimates local tax amount as local taxes are only paid when the amount of the credit does not exhaust income tax. So for 2011, Taxes paid to on tranfers income refer to Total PIT - Total tax credits * local tax (A1 minus A2, then adding local tax rate *) ( )* ( )= B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in millions of euros (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 14.3% 14.4% 15.3% 15.0% 14.0% 14.4% 14.2% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 16.9% 17.1% 17.8% 17.7% 16.6% 17.0% 16.9% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 20.1% 20.5% 21.5% 21.3% 20.4% 20.8% 20.7% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2; and OECD Revenue Statistics database ( for lines 3, 4, and 5.
7 BELGIUM C. Tax breaks for social purposes (in million of Euros) Tax breaks similar to cash benefits Family: Tax credit for children Allowance Childcare expenses Other areas: Compl. Sickness contr Allowance "ALE" Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection (not including pensions) Memorandum Items Tax breaks for pensions Pension savings (3rd pillar) Pension savings (2d pillar) Source: Ministry of Finance, Belgium, from IPP (Impôt des Personnes Physiques).
8 CANADA A. Average Itemised Tax Rates (AITR %) 1 Old-age Cash Benefits a - Public Pensions (OAS) b - Private Pensions Canadian Pension Plan (Retirement) Canadian Pension Plan (Disability) Employment Insurance a - Regular Employment Insurance b - Parental Leave Payments - - n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. 4c - Active Labour Market Programs Worker's Compensation Guaranteed Income Supplement Social Assistance Universal ChildCate Benefits (UCCB) Wage Income * The sample used for the microdataset simulation was a stratified sample of approximately records, weighted to represent all taxfilers in Canada. The sample is provided by the Canada Revenue Agency. B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in millions of Canadian dollars (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 10.5% 10.7% 10.4% 9.6% 8.6% 8.8% 8.9% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 13.5% 13.6% 13.3% 12.5% 11.3% 11.4% 11.6% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 15.4% 15.6% 15.3% 14.4% 13.3% 13.4% 13.5% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2; and OECD Revenue Statistics database ( for lines 3, 4, and 5.
9 CANADA C. Tax breaks for social purposes (in millions of Canadian dollars) 1 Tax breaks similar to cash benefits (total without 5, 8 and 17 below) Family: 2 Infirm dependant/ Caregiver credit Child care expense deduction Adoption Expense Deduction Amount for an eligible dependant Children's fitness tax credit Child tax credit Investment Tax Credit for Child Care Spaces (for Corporations) Child Fitness tax credit Other areas: 1 Disability Tax Credit Infirm dependant credit Disability Supports Deduction Medical expense tax credit Tax credits for employee-paid Canada Pension Plan (CPP) and Quebec Pension Plan (QPP) contributions Tax credits for employee-paid EI and Quebec Parental Insurance Plan (QPIP) contributions Canada Employment credit For information only: not included in total TBSP 5 Canadian Child Tax Benefit/National Child Benefit (amount not included in total TBSP, as already accounted in SOCX ) Age amount (amount not included in total TBSP, as already taken into account when calculating AITRs) Universal child care benefit (amount not included in total TBSP) For information only as refundable credits have been removed from the tax expenditures section as these are now classified as spending measures in public accounts. 6 Refundable Medical Expense Supplement Portion of refundable tax credits that offsets tax liability Working income tax benefit Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection (not including pensions) Non-taxation of employer paid health and dental benefits Deductibility of charitable donations from corporate income tax Charitable donations credit Non-taxation of donations of publicly-listed securities (reduced inclusion rate for capital gains) Memorandum item Tax breaks for pensions (1+2+3) Revenue foregone method: 1 Pension Income Deduction Registered retirement savings plans (RRSPs) Deduction for contributions Non-taxation of investment income Taxation of withdrawals Net tax expenditure Registered pension plans (RPPs) Deduction for contributions Non-taxation of investment income Taxation of withdrawals Net tax expenditure Supplementary information: Present value of tax assistance for retirement savings plans * * The present-value estimates reflect the lifetime cost of a given year s contributions. This definition is different from that used for the cash-flow estimates, and thus the two sets of estimates are not directly comparable. Data supplied by Finance Canada, from Department of Finance Canada (2009, 2004, 2002), Tax Expenditures and Evaluations, Ottawa. 1. Since 2001 Tax expenditures are for federal measures only cannot be considered complete, therefore cannot be compared to some other countries estimates, given that sub-national expenditures are not included. 1. The totals may overestimate total expenditure, as interactions between measures are not taken into account. The sample used for the microdataset simulation was a stratified sample of approximately 450,000 records, weighted to represent all taxfilers in Canada. The sample is provided by Canadian Customs and Revenue Agency.
10 CHILE A. Amount of direct tax paid on benefit income (in millions of Chilean Pesos) Old-age cash benefits (1 +3) - public pensions private pensions Incapacity-related benefits - Disability pensions - Occupational Injury benefits - Sickness payments Note: Figures represent only the income tax paid on pensions. Source: - SII Annual Sworn Statement N 1812 on Revenue from Retirement, Pensions or Pawnshops, and Withholding of Second Category Tax (Income Tax Law). B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in Millions of Chilean Pesos (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 13.9% 14.5% 15.0% 15.0% 13.5% 14.2% 14.3% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 16.7% 16.7% 16.9% 16.8% 15.1% 15.9% 16.0% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 18.4% 18.1% 18.1% 17.9% 16.2% 17.0% 17.1% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2; and OECD Revenue Statistics database ( for lines 3, 4, and 5.
11 CHILE C. Tax breaks for social purposes (in Millions of Chilean Pesos) Tax breaks similar to cash benefits Family Other areas Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection (not including pensions) a), b), c) Item 1 Health insurance (tax deduction) n.a Item 2 Unemploment insurance (tax deduction) n.a Item 3 Donations for social purposes (tax credit and tax deduction) Item 4 Income from renting DFL 2 housing (tax exempt) n.a Item 5 Health services (VAT exempt) n.a Item 6 Contributions to Private Health System (VAT exempt) n.a Item 7 Refund of customs duties when importing equipment for disabled people n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. Item 8 Lower customs duties for disabled people that import vehicles with special features n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. Memorandum Items Tax breaks for pensions d), e) n.a Deduction of contributions to private pensions (e.g occupational pension plans, individual retirement accounts, RRSPs, Superannuation, etc) n.a Non-taxation of investment of private pension funds n.a Source: - SII Annual Sworn Statement N 1812 on Revenue from Retirement, Pensions or Pawnshops, and Withholding of Second Category Tax (Income Tax Law). Tax years 2002, 2004, 2006, 2008, 2010, 2011 and Tax Expenditure Reports elaborated by Servicio de Impuestos Internos (Chilean Internal Revenue Service). Notes: a) Figures in millions of Chilean pesos. b) Tax expenditure measurement began in 2002 and is made on a cash basis. c) Tax breaks concerning pensions (compulsory or voluntary) were excluded. d) Figures in millions of Chilean pesos. e) It is only included the compulsory deduction of contributions to private pensiones
12 CZECH REPUBLIC A. Amount of direct tax paid on benefit income (in millions of Czech koruny) Total tax paid on transfer income old-age pensions Source: Ministry of Finance, Tax Policy Unit; Czech Social Security Administation. B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in millions of Czech koruny (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 14.3% 14.2% 16.6% 16.6% 16.4% 16.5% 17.2% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 16.1% 16.0% 17.8% 17.8% 17.5% 17.5% 18.2% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 20.2% 20.6% 22.8% 22.5% 22.2% 22.3% 23.1% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2; and OECD Revenue Statistics database ( for lines 3, 4, and 5.
13 CZECH REPUBLIC C. Tax breaks for social purposes (in millions of Czech koruny) Tax breaks similar to cash benefits Tax breaks similar to cash benefits 1.1 Tax exemptions (Personal Income Tax): * non-monetary benefits covered from the fund for cultural and social needs or profit after tax provided by an employer to his employee in form of recreational, health care, educational facilities, etc. 1.2 Allowances from the tax base (Personal Income Tax; social insurance contributions are deductible from the tax base): n.a. n.a. Family: * per each dependent child living with the taxpayer in one household * per each handicapped dependent child requiring an escort Other areas: * per handicapped spouse requiring an escort living with taxpayer in one household unless the spouse's own income exceeds low income limit * per handicapped taxpayer requiring an escort * gifts donated to municipalities or to legal entities for financing science, education, culture, schools, police, youth welfare, animal protection, environment, humanitarian projects etc Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection (not including pensions) Corporate Income Tax * tax credits for disabled employees Personal Income Tax * tax credits for disabled employee Memorandum item Tax breaks for pensions Deduction of contributions to private pensions - income tax exemptions and allowances from the tax base * exemption of contributions of employers on behalf of their employees on pension insurance with state contribution from personal income tax up to a ceiling of 5 per cent of employer's gross wage. Until 2009 maximum exemption is CZK for one employee n.a. n.a. * deduction of contributions of employers on behalf of their employees on pension insurance with state contribution from employer's tax base up to a ceiling of 3 per cent of gross wage of the employee. Until 2009 maximum exemption is CZK for one employee n.a. n.a. * contributions of employees on their pension insurance with state contribution * deduction on behalf on pension insurance with state contribution from personal income tax up to a ceiling Non-taxation of investment of private pension funds * there is income tax of 15 % from the returns of private pension funds - standard tax rate is 28 % * reduced 15 % withholding tax on benefits/returns paid by the pension funds to the contributors * reduced 15 % withholding tax on benefits/returns paid by the life insurance to the contributors Sources: Tax Statistics, Czech Ministry of Finance; and the Association of Pension Funds of the Czech Republic. Non-monetary benefits covered from the fund for cultural and social needs or profit after tax provided by an employer to his employee in form of recreational, health care, educational facilities, etc.were estimated based on the previous trend for 2005,2007,2009.
14 DENMARK A. Average Itemised Tax Rates - AITR % Tax and 2005 Tax and 2007 Tax and Tax and 2011 Social Social Social Tax and Social security Social Tax and Social security Tax and Social security 1 Social pension - state old age pension (98%) (98%) (98%) (98%) (98%) ('98%') ('98%') - disability pension (75%) (75%) (77%) (85%) (88%) ('89 %') ('89 %') - anticipated old age pension (84%) (84%) (90%) (76%) (76%) ('76%') ('76 %') 2 Supplementary pensions (ATP) Civil servants pension Early retirement pensions (Delpension) Sickness benefit Parental leave ' 7 Unemployment benefits Early retirement benefits Occupational accidents - except: Occupational accidents and decease ( ) (22%) (23%) (26%) War victims, accidents, sailors ( ) (60%) (40%) (39%) Handicapped children and adults ( ) (47%) (41%) (47%) Survivors Childbirth benefit (barsel) Items under active labour market policy - Measures by regional labour market councils Employment measures for disabled Other, war victims (90%) (90%) (84%) (88%) (89%) ('87%') ('87%') 14 Other, wage earn. Guar. Fond Cash payments to refugees ( ) Low income Transfers taxed as wages In parentheses: proportion of spending subject to taxation if not 100%. B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in millions Danish kroner (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 26.3% 25.9% 26.2% 26.1% 23.5% 23.7% 23.9% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 28.6% 28.2% 28.6% 28.3% 25.6% 25.8% 26.0% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 33.6% 33.2% 33.7% 33.6% 31.0% 31.0% 31.3% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2; and OECD Revenue Statistics database ( for lines 3, 4, and 5.
15 DENMARK C. Tax breaks for social purposes (in millions of Danish kroner) Tax breaks similar to cash benefits Family: Other areas: Supplement for older people "Engangsbelob" (67+) Capital tax reduction for older people (67+) 0 0 Housing for older people "Plejehjem" Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection (not including pensions) Memorandum item Tax breaks for pensions Source: Ministry of Finance, Denmark.
16 ESTONIA A. Average Itemised Tax Rates (AITR %) Total tax paid (including soc. sec. cont.) over transfer income pensions old age pensions disability pension survivor's pension benefits for temporary incapacity for work unemployment benefits income tax: unemployment insurance benefit insurance benefit upon lay-off benefit upon insolvency of employer social security contributions: insurance benefit upon lay-off benefit upon insolvency of employer family benefits maternity benefit parental benefit B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in Millions of Estonian kroon (EEK). (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 20.4% 21.8% 21.4% 21.9% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 21.4% 22.8% 22.3% 22.8% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 24.1% 26.6% 26.1% 26.5% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2; and OECD Revenue Statistics database ( for lines 3, 4, and 5.
17 ESTONIA C. Tax breaks for social purposes (in Millions of EUR). Tax breaks similar to cash benefits Family: Increased basic exemption upon provision of maintenance to child Additional allowance for 2nd+ children, accrual Deduction from tax base: educational expenses, accrual Deduction from tax base: education loan interests, accrual Not included in the total Additional allowance for couple, accrual Other areas: Deduction from tax base: mortgage interest payments, accrual Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection (not including pensions) Deduction from tax base: contributions to voluntary pension funds, accrual Memorandum Items Tax breaks for pensions Additional allowance for pensioners, this is not cash benefit but tax expenditure Source: Estonian Tax and Customs Board
18 FINLAND A. Average Itemised Tax Rates (%) 1 Old-age cash benefits 1a - public pensions c - private pensions Survivors' benefits 2a - public pensions Incapacity-related benefits 3a - Disability pensions b - Occupational Injury benefits c - Sickness payments Family cash benefits 4a - Family benefits b - Maternity and parental leave payments Active labour market policies 5a - benefits while on training Unemployment 6a - unemployment insurance benefit b - unemployment assistance benefit The micro-simulation model used in the Ministry of Finance is based on a representative sample of some individual taxpayers. The model is used for the planning of national tax policies and for estimating the effect of tax policy alterations on tax revenues and on the income tax liabilities of taxpayers at different income levels. The information is in principle collected for the Income Distribution Survey from Statistics Finland. The sample covers about 0,5% of the total taxpayer population, but the model has been made representative for the total taxpayer population. The dataset is updated annually.there is a break in series in 2009 for unemployment average itemised tax rates resulting from a change in definition. Source : Ministry of Finance. B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in millions of euros (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 21.1% 21.3% 20.7% 19.8% 18.6% 18.4% 19.6% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 23.2% 23.5% 22.8% 21.9% 20.7% 20.4% 21.6% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 26.8% 27.3% 26.7% 25.6% 24.6% 24.2% 25.6% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2; and OECD Revenue Statistics database ( for lines 3, 4, and 5.
19 FINLAND C. Tax breaks for social purposes (in millions of euros) Tax breaks similar to cash benefits Family: Other areas: Tax breaks to stimulate private social protection (not including pensions) Cash donations to Charities Memorandum Items Tax breaks for pension Deduction of contributions to private pensions Source: Ministry of Finance, Finland.
20 I.A.2.1 FRANCE A. Amount of direct tax paid on benefit income (in millions of euros) Total (income tax + social security contributions) a Old-age, survivors' benefits, disability pensions b Occupational Injury benefits c Sickness payments a-4c Family and sole parent cash benefits b Maternity and parental leave payments Active labour market policies Unemployment Housing Note: Data for 2009 have been estimated. There is a break in the series in 2010 due to the underlying model used to derive estimates. Sources 2010: DREES, based on estimates from INES model (DREES/INSEE) and the Comptes de la protection sociale (DREES). New methodology is presented in A. Renoux (2013), «Les prélèvements obligatoires directs réduisent de 5 % le montant brut des prestations de protection sociales», La protection sociale en France et en Europe en 2011 édition 2013, DREES, document de travail série statistique n 181, June 2013 ( pp ). Sources : DREES/INSEE, based on estimates from ACOSS and the Comptes de la protection sociale (DREES). B. Average implicit indirect tax rates of consumption out of benefit income Indirect taxes paid out of consumption of cash transfers, in millions of euros (1) Private final consumption expenditure (2) Private consumption plus Government consumption minus Government wages (3) General consumption taxes plus excise duties ( ) General taxes Excises (4) Taxes on production sale transfer (5100) (5) Taxes on Goods and Services (5000) Implicit average indirect tax rate on consumption out of benefit income: (6) using general consumption taxes plus excise duties (3)/(2) 15.2% 14.9% 15.0% 14.7% 13.7% 13.8% 14.0% (7) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base (5)/(2) 16.9% 16.5% 16.6% 16.2% 15.3% 15.4% 15.8% (8) using a broad concept of the indirect tax base and ignoring government consumpion (5)/(1) 19.7% 19.5% 19.7% 19.2% 18.3% 18.5% 18.9% Source: OECD on-line National Accounts database ( for lines 1 and 2; and OECD Revenue Statistics database
Australia. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors. Australia. Exchange rate: US$1.00 equals 1.32 Australian dollars (A$). Qualifying Conditions
 Australia Exchange rate: US$1.00 equals 1.32 Australian dollars (A$). Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First laws: 1908 (old-age and disability) and 1942 (widows). Current laws: 1991 (social security),
Australia Exchange rate: US$1.00 equals 1.32 Australian dollars (A$). Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First laws: 1908 (old-age and disability) and 1942 (widows). Current laws: 1991 (social security),
Description of tax expenditures
 Appendix A Description of tax expenditures This Appendix provides further information on the tax expenditures identified in Table 5.1, including legislative references and, in some cases, an expanded description
Appendix A Description of tax expenditures This Appendix provides further information on the tax expenditures identified in Table 5.1, including legislative references and, in some cases, an expanded description
How To Tax On Pension Income For Older People In European Countries
 Austria Belgium Czech Republic Tax credit of EUR 400 for low pension income up to EUR 17,000; the tax credit is fully phased out once pension income equals EUR 25,000. pension income of maximum EUR 1,901.19.
Austria Belgium Czech Republic Tax credit of EUR 400 for low pension income up to EUR 17,000; the tax credit is fully phased out once pension income equals EUR 25,000. pension income of maximum EUR 1,901.19.
PENSIONS AT A GLANCE 2011: RETIREMENT-INCOME SYSTEMS IN OECD COUNTRIES AUSTRALIA
 PENSIONS AT A GLANCE 2011: RETIREMENT-INCOME SYSTEMS IN OECD COUNTRIES Online Country Profiles, including personal income tax and social security contributions AUSTRALIA Australia: pension system in 2008
PENSIONS AT A GLANCE 2011: RETIREMENT-INCOME SYSTEMS IN OECD COUNTRIES Online Country Profiles, including personal income tax and social security contributions AUSTRALIA Australia: pension system in 2008
NET SOCIAL EXPENDITURE INDICATORS: QUESTIONNAIRE
 NET SOCIAL EXPENDITURE INDICATORS: QUESTIONNAIRE 1. Introduction 1. The OECD Social Expenditure database (SOCX) contains information on public and private social expenditure in OECD countries (Adema, Fron
NET SOCIAL EXPENDITURE INDICATORS: QUESTIONNAIRE 1. Introduction 1. The OECD Social Expenditure database (SOCX) contains information on public and private social expenditure in OECD countries (Adema, Fron
FEDERAL BUDGET 2009 SUMMARY
 FEDERAL BUDGET 2009 SUMMARY 13 May 2009 As widely expected, last nightʼs Federal Budget contained a number of proposals that will affect clients. Importantly, the proposals will require passage of legislation
FEDERAL BUDGET 2009 SUMMARY 13 May 2009 As widely expected, last nightʼs Federal Budget contained a number of proposals that will affect clients. Importantly, the proposals will require passage of legislation
FEDERAL BUDGET 2009 UPDATE BRIEF SUMMARY
 Wealth Management Federal Budget 2009 FEDERAL BUDGET 2009 UPDATE BRIEF SUMMARY The Government has delivered what it says is one of the most difficult Budgets since the great depression, with many winners
Wealth Management Federal Budget 2009 FEDERAL BUDGET 2009 UPDATE BRIEF SUMMARY The Government has delivered what it says is one of the most difficult Budgets since the great depression, with many winners
Work Injury: Benefits, 2010
 Austria Belgium Temporary disability The insured receives the cash sickness benefit until a decision on permanent disability is made. The employer pays 100% of earnings for up to 12 weeks (plus additional
Austria Belgium Temporary disability The insured receives the cash sickness benefit until a decision on permanent disability is made. The employer pays 100% of earnings for up to 12 weeks (plus additional
United Kingdom. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors. United Kingdom. Exchange rate: US$1.00 = 0.64 pounds ( ). Qualifying Conditions
 United Kingdom Exchange rate: US$1.00 = 0.64 pounds ( ). Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First laws: 1908 (old-age pension), 1911 (disability insurance), and 1925 (old-age and survivors insurance).
United Kingdom Exchange rate: US$1.00 = 0.64 pounds ( ). Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First laws: 1908 (old-age pension), 1911 (disability insurance), and 1925 (old-age and survivors insurance).
CLIENT FACT SHEET. If you are under age 65 you may make personal contributions to superannuation on your own behalf.
 CLIENT FACT SHEET July 2010 Understanding superannuation and superannuation contributions Superannuation is an investment vehicle designed to assist Australians in saving for their retirement. The Government
CLIENT FACT SHEET July 2010 Understanding superannuation and superannuation contributions Superannuation is an investment vehicle designed to assist Australians in saving for their retirement. The Government
Health Systems: Type, Coverage and Financing Mechanisms
 Health Systems: Type, Coverage and Mechanisms Austria Belgium Bulgaria (2007) Czech Republic Denmark (2007) Estonia (2008). Supplementary private health Complementary voluntary and private health Public
Health Systems: Type, Coverage and Mechanisms Austria Belgium Bulgaria (2007) Czech Republic Denmark (2007) Estonia (2008). Supplementary private health Complementary voluntary and private health Public
Understanding Superannuation
 Understanding Superannuation Client Fact Sheet July 2012 Superannuation is an investment vehicle designed to assist Australians save for retirement. The Federal Government encourages saving through superannuation
Understanding Superannuation Client Fact Sheet July 2012 Superannuation is an investment vehicle designed to assist Australians save for retirement. The Federal Government encourages saving through superannuation
Taxation measures. Medicare low income thresholds. Changes to tax rates for non-residents. Changes to the net medical expenses tax offset
 2012-2013 Federal Budget Report May 2012 This year s Federal Budget was returned to surplus while ensuring families and small business share in the benefits of the resource boom. Cor sae por restiam adis
2012-2013 Federal Budget Report May 2012 This year s Federal Budget was returned to surplus while ensuring families and small business share in the benefits of the resource boom. Cor sae por restiam adis
PENSIONS AT A GLANCE 2009: RETIREMENT INCOME SYSTEMS IN OECD COUNTRIES UNITED STATES
 PENSIONS AT A GLANCE 29: RETIREMENT INCOME SYSTEMS IN OECD COUNTRIES Online Country Profiles, including personal income tax and social security contributions UNITED STATES United States: pension system
PENSIONS AT A GLANCE 29: RETIREMENT INCOME SYSTEMS IN OECD COUNTRIES Online Country Profiles, including personal income tax and social security contributions UNITED STATES United States: pension system
2016/17 Budget. 1. Effective Budget Night 7.30pm (AEST) 3 May 2016. 1.1 New lifetime cap for non-concessional superannuation contributions
 2016/17 Budget Superannuation reform changes 1. Effective Budget Night 7.30pm (AEST) 3 May 2016 1.1 New lifetime cap for non-concessional superannuation contributions The government will introduce a $500,000
2016/17 Budget Superannuation reform changes 1. Effective Budget Night 7.30pm (AEST) 3 May 2016 1.1 New lifetime cap for non-concessional superannuation contributions The government will introduce a $500,000
RECENT INCOME TAX CHANGES
 RECENT INCOME TAX CHANGES Increased Medicare Levy Low Income Thresholds The Medicare Levy low-income thresholds for families and dependent child-student component of the threshold have been changed to
RECENT INCOME TAX CHANGES Increased Medicare Levy Low Income Thresholds The Medicare Levy low-income thresholds for families and dependent child-student component of the threshold have been changed to
Reliance Super. Taxation Supplement. 14 March 2014. a membership category of Maritime Super
 Taxation Supplement 14 March 2014 Contents Tax on contributions 2 Tax on rollovers 3 Tax on investment earnings 3 Tax on super benefits 3 Spouse tax offset 7 Tax deductions for the self-employed 7 Low
Taxation Supplement 14 March 2014 Contents Tax on contributions 2 Tax on rollovers 3 Tax on investment earnings 3 Tax on super benefits 3 Spouse tax offset 7 Tax deductions for the self-employed 7 Low
FINLAND. Nomenclature
 FINLAND Nomenclature KEL KIEL KVTEL LEL MEL MYEL PEL TAEL TEL VEL VPEL YEL The National Pension Act (old age, disability) The Evangelical-Lutheran church Pension Act The Local Government Employees Pension
FINLAND Nomenclature KEL KIEL KVTEL LEL MEL MYEL PEL TAEL TEL VEL VPEL YEL The National Pension Act (old age, disability) The Evangelical-Lutheran church Pension Act The Local Government Employees Pension
// BRIEF STATISTICS 2014
 // BRIEF STATISTICS 2014 // TAXATION IN FINLAND Finland s taxation is subject to decisions by the Finnish Parliament, the European Union and the municipalities of Finland. It is governed by tax legislation,
// BRIEF STATISTICS 2014 // TAXATION IN FINLAND Finland s taxation is subject to decisions by the Finnish Parliament, the European Union and the municipalities of Finland. It is governed by tax legislation,
SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTIONS
 OECD TAX DATABASE EXPLANATORY ANNEX PART III. SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTIONS (Document updated May 2015) 1 Table of contents PART III, TABLE 1 EMPLOYEE SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTION RATES 4 III.1. AUSTRIA
OECD TAX DATABASE EXPLANATORY ANNEX PART III. SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTIONS (Document updated May 2015) 1 Table of contents PART III, TABLE 1 EMPLOYEE SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTION RATES 4 III.1. AUSTRIA
SALARY PACKAGING SUPERANNUATION GUIDE TO EMPLOYEES
 SALARY PACKAGING SUPERANNUATION GUIDE TO EMPLOYEES Superannuation Introducing Salary Packaging Salary packaging has been made available to all staff of the University through the Enterprise Agreement process.
SALARY PACKAGING SUPERANNUATION GUIDE TO EMPLOYEES Superannuation Introducing Salary Packaging Salary packaging has been made available to all staff of the University through the Enterprise Agreement process.
CHAPTER 4 - TAX PREFERENCES FOR SUPERANNUATION AND LIFE INSURANCE SAVINGS
 45 CHAPTER 4 - TAX PREFERENCES FOR SUPERANNUATION AND LIFE INSURANCE SAVINGS 4.1 Introduction In general, superannuation and life insurance have not been subject to the normal income tax treatment for
45 CHAPTER 4 - TAX PREFERENCES FOR SUPERANNUATION AND LIFE INSURANCE SAVINGS 4.1 Introduction In general, superannuation and life insurance have not been subject to the normal income tax treatment for
An explanation of social assistance, pension schemes, insurance schemes and similar concepts
 From: OECD Framework for Statistics on the Distribution of Household Income, Consumption and Wealth Access the complete publication at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/9789264194830-en An explanation of social
From: OECD Framework for Statistics on the Distribution of Household Income, Consumption and Wealth Access the complete publication at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/9789264194830-en An explanation of social
RECENT INCOME TAX CHANGES
 RECENT INCOME TAX CHANGES Financial Institution Details Required From 1 July 2013, when preparing your income tax returns we will need to include your nominated Australian bank account details when a refund
RECENT INCOME TAX CHANGES Financial Institution Details Required From 1 July 2013, when preparing your income tax returns we will need to include your nominated Australian bank account details when a refund
Super taxes, caps, payments, thresholds and rebates
 Fact Sheet Super taxes, caps, payments, thresholds and rebates This fact sheet provides a useful one-stop reference guide to the tax rates, caps, thresholds and rebates that apply or are related to superannuation
Fact Sheet Super taxes, caps, payments, thresholds and rebates This fact sheet provides a useful one-stop reference guide to the tax rates, caps, thresholds and rebates that apply or are related to superannuation
Colombia. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors. Regulatory Framework. Qualifying Conditions. Coverage. Source of Funds. Colombia
 Colombia Exchange rate: US$1.00 equals 2,338.14 pesos. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First law: 1946, implemented in 1965. Current law: 1993 (social insurance), implemented in 1994, with 2003 amendments.
Colombia Exchange rate: US$1.00 equals 2,338.14 pesos. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First law: 1946, implemented in 1965. Current law: 1993 (social insurance), implemented in 1994, with 2003 amendments.
Fundamentals of Australian Taxation. Snehal Shah Director GMK Partners Pty Ltd
 Fundamentals of Australian Taxation Snehal Shah Director GMK Partners Pty Ltd Disclaimer This presentation is of a general nature only and is not intended to be relied upon as, nor to be a substitute for,
Fundamentals of Australian Taxation Snehal Shah Director GMK Partners Pty Ltd Disclaimer This presentation is of a general nature only and is not intended to be relied upon as, nor to be a substitute for,
AustChoice Super general reference guide (ACH.02)
 AustChoice Super general reference guide (ACH.02) Issued: 28 May 2015 This guide contains important information not included in the AustChoice Super PDS. We recommend you read this entire guide. The information
AustChoice Super general reference guide (ACH.02) Issued: 28 May 2015 This guide contains important information not included in the AustChoice Super PDS. We recommend you read this entire guide. The information
2 Voluntary retirement module specification
 2 Voluntary retirement module specification As part of its research on Superannuation Policy for Post-Retirement the Commission has developed a model referred to as the Productivity Commission Retirement
2 Voluntary retirement module specification As part of its research on Superannuation Policy for Post-Retirement the Commission has developed a model referred to as the Productivity Commission Retirement
The Expatriate Financial Guide to
 The Expatriate Financial Guide to Australian Tax Facts Australia Introduction Tax Year Assessment Basis Income Tax Taxation in Australia is mostly at a national/federal level with property taxes (council
The Expatriate Financial Guide to Australian Tax Facts Australia Introduction Tax Year Assessment Basis Income Tax Taxation in Australia is mostly at a national/federal level with property taxes (council
Social Security. Social Security Payments and the Taxation System. Technical Series Number One
 Social Security Social Security Payments and the Taxation System Technical Series Number One Social Security Payments and the Taxation System Technical Series No.1 Josh Polette (revised by Kate Chan) Social
Social Security Social Security Payments and the Taxation System Technical Series Number One Social Security Payments and the Taxation System Technical Series No.1 Josh Polette (revised by Kate Chan) Social
Tax offsets QUESTION 19 SPOUSE TAX OFFSETS STOP NOTE. Did you have a spouse married or de facto?
 Tax offsets 19 QUESTION 19 SPOUSE TAX OFFSETS Did you have a spouse married or de facto? STOP If you maintained a child or a student, you cannot complete your tax return using Retirees TaxPack 2004 see
Tax offsets 19 QUESTION 19 SPOUSE TAX OFFSETS Did you have a spouse married or de facto? STOP If you maintained a child or a student, you cannot complete your tax return using Retirees TaxPack 2004 see
Fact Sheet Tax on Super 2009/10
 It pays to belong TM Key Focus A tax of 15% applies to concessional (i.e. before tax) contributions. All employer and salary sacrifice contributions will be taxed at the top marginal rate if your super
It pays to belong TM Key Focus A tax of 15% applies to concessional (i.e. before tax) contributions. All employer and salary sacrifice contributions will be taxed at the top marginal rate if your super
Chapter 2. The Temporary Budget Repair Levy
 Chapter 2 The Temporary Budget Repair Levy 2.1 This chapter discusses the legislation introduced by the package of Temporary Budget Repair Levy (the Levy) bills. 2.2 The committee first gives a brief overview
Chapter 2 The Temporary Budget Repair Levy 2.1 This chapter discusses the legislation introduced by the package of Temporary Budget Repair Levy (the Levy) bills. 2.2 The committee first gives a brief overview
Structuring & Tax. Ensuring your plans for your super become a reality. By Ben Andreou Partner Head of Structuring & Tax
 Structuring & Tax Ensuring your plans for your super become a reality By Ben Andreou Partner Head of Structuring & Tax December 2015 Table of Contents Page Why should you read this paper?... 3 Background...
Structuring & Tax Ensuring your plans for your super become a reality By Ben Andreou Partner Head of Structuring & Tax December 2015 Table of Contents Page Why should you read this paper?... 3 Background...
CANADA 2003. 1. Overview of the system
 CANADA 2003 1. Overview of the system The system of benefits and incentives in Canada comprises a number of programs, including benefit programs and tax assistance. Some are the responsibility of the federal
CANADA 2003 1. Overview of the system The system of benefits and incentives in Canada comprises a number of programs, including benefit programs and tax assistance. Some are the responsibility of the federal
Centrelink payments and entitlements, pension bonus scheme and work bonus
 Centrelink payments and entitlements, pension bonus scheme and work bonus 1 January 2014 While there are many different Centrelink payments and entitlements available, in this flyer we have outlined the
Centrelink payments and entitlements, pension bonus scheme and work bonus 1 January 2014 While there are many different Centrelink payments and entitlements available, in this flyer we have outlined the
- on termination due to redundancy
 The Increased Tax on Lump Sum Termination Payments By Ray Stevens (USA) INTRODUCTION In May, 1983, the Government announced increases in the taxation payable on lump sum superannuation benefits and on
The Increased Tax on Lump Sum Termination Payments By Ray Stevens (USA) INTRODUCTION In May, 1983, the Government announced increases in the taxation payable on lump sum superannuation benefits and on
LWK. Chartered Accountants. Individual Tax Return Checklist
 LWK Pty. Limited ACN 121 288 373 Chartered Accountants Business Advisers and Consultants Business Advisers an Individual Tax Return Checklist This checklist has been prepared by LWK Pty Limited Chartered
LWK Pty. Limited ACN 121 288 373 Chartered Accountants Business Advisers and Consultants Business Advisers an Individual Tax Return Checklist This checklist has been prepared by LWK Pty Limited Chartered
Rates of Tax 2011/12 Resident Individuals
 s of Tax 2011/12 Resident Individuals The following rates apply to individuals who are residents of Australia for tax purposes for the entire income year. 1 Tax Payable 2, 3 0 6,000 Nil 6,001 37,000 15
s of Tax 2011/12 Resident Individuals The following rates apply to individuals who are residents of Australia for tax purposes for the entire income year. 1 Tax Payable 2, 3 0 6,000 Nil 6,001 37,000 15
Australia: Retirement Income and Annuities Markets. Contractual Savings Conference April 2008 Greg Brunner
 Australia: Retirement Income and Annuities Markets Contractual Savings Conference April 2008 Greg Brunner Pension system Age pension in place since 1908, funded on a payas-you go basis Means testing. The
Australia: Retirement Income and Annuities Markets Contractual Savings Conference April 2008 Greg Brunner Pension system Age pension in place since 1908, funded on a payas-you go basis Means testing. The
China. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors. China. Exchange rate: US$1.00 = 6.78 yuan. Regulatory Framework. Coverage. Qualifying Conditions
 China Exchange rate: US$1.00 = 6.78 yuan. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First law: 1951. Current laws: 1953 (regulations); 1978, 1995, 1997, 1999, and 2005 (directives); and 2009 (guideline on rural
China Exchange rate: US$1.00 = 6.78 yuan. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First law: 1951. Current laws: 1953 (regulations); 1978, 1995, 1997, 1999, and 2005 (directives); and 2009 (guideline on rural
Year-end Tax Planning Guide - 30 June 2013 BUSINESSES
 Year-end Tax Planning Guide - 30 The end of the financial year is fast approaching. In the lead up to 30 June, this newsletter covers some of the year-end tax planning matters for your consideration. BUSINESSES
Year-end Tax Planning Guide - 30 The end of the financial year is fast approaching. In the lead up to 30 June, this newsletter covers some of the year-end tax planning matters for your consideration. BUSINESSES
German Tax Facts. The Expatriate Financial Guide to Germany
 The Expatriate Financial Guide to Germany German Tax Facts Introduction Tax Year Assessment Basis Income Tax Taxation in Germany occurs at a national and municipal level. The Ministry of Finance controls
The Expatriate Financial Guide to Germany German Tax Facts Introduction Tax Year Assessment Basis Income Tax Taxation in Germany occurs at a national and municipal level. The Ministry of Finance controls
Tax deductible superannuation contributions
 Tax deductible superannuation contributions TB 35 TECHNICAL SERVICES ISSUED ON 29 OCTOBER 2014 ADVISER USE ONLY VERSION 1.1 Summary Employers and certain individuals can claim a tax deduction for contributions
Tax deductible superannuation contributions TB 35 TECHNICAL SERVICES ISSUED ON 29 OCTOBER 2014 ADVISER USE ONLY VERSION 1.1 Summary Employers and certain individuals can claim a tax deduction for contributions
TAX TUTOR INSIDE IS YOUR TAX GUIDE FOR 2013-2014
 TAX TUTOR INSIDE IS YOUR TAX GUIDE FOR 2013-2014 PERSONAL TAX PERSONAL INCOME TAX RATES 2013-2014 & 2012-2013 Taxable Income $0 - $18,200 Nil Tax Payable $18,201 - $37,000 19% of excess over $18,200 $37,001
TAX TUTOR INSIDE IS YOUR TAX GUIDE FOR 2013-2014 PERSONAL TAX PERSONAL INCOME TAX RATES 2013-2014 & 2012-2013 Taxable Income $0 - $18,200 Nil Tax Payable $18,201 - $37,000 19% of excess over $18,200 $37,001
taxation Current to June 20, 2013 What s Inside www.bdo.ca
 www.bdo.ca taxation Tax Facts 2013 Current to June 20, 2013 Tax Facts 2013 provides you with a summary of 2013 personal income tax rates and amounts, as well as corporate tax rates (as at July 1, 2013),
www.bdo.ca taxation Tax Facts 2013 Current to June 20, 2013 Tax Facts 2013 provides you with a summary of 2013 personal income tax rates and amounts, as well as corporate tax rates (as at July 1, 2013),
Income, Gift, and Estate Tax Update
 Income, Gift, and Estate Tax Update Individual Income Tax Rates p. 1 Phil Harris Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics University of Wisconsin-Madison Marriage Penalty Relief p. 1 Capital Gains
Income, Gift, and Estate Tax Update Individual Income Tax Rates p. 1 Phil Harris Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics University of Wisconsin-Madison Marriage Penalty Relief p. 1 Capital Gains
Superannuation 2010 2011
 RESEARCH PAPER NO. 3, 2010 11 9 September 2010 Superannuation 2010 2011 Leslie Nielson Economics Section Executive summary This paper, updated for the 2010 11 financial year, is designed to provide readers
RESEARCH PAPER NO. 3, 2010 11 9 September 2010 Superannuation 2010 2011 Leslie Nielson Economics Section Executive summary This paper, updated for the 2010 11 financial year, is designed to provide readers
2009/10 Federal Budget in Brief
 2009/10 Federal Budget in Brief The 2009/10 Federal Budget is characterised by a $57.6 billion deficit, with the Government expecting to see the budget return to a surplus position in 2015/16. The focus
2009/10 Federal Budget in Brief The 2009/10 Federal Budget is characterised by a $57.6 billion deficit, with the Government expecting to see the budget return to a surplus position in 2015/16. The focus
Social protection of the self-employed
 Social protection of the self-employed Country analysis Bulgaria Czech Republic Estonia Hungary Latvia Lithuania Poland Romania Slovak Republic Slovenia Comparative analysis 323 General principles The
Social protection of the self-employed Country analysis Bulgaria Czech Republic Estonia Hungary Latvia Lithuania Poland Romania Slovak Republic Slovenia Comparative analysis 323 General principles The
End of financial year planning tips May 2014
 End of financial year planning tips May 2014 With the end of the financial year fast approaching, it is a good time to review financial planning strategies with a view to optimising your outcomes. This
End of financial year planning tips May 2014 With the end of the financial year fast approaching, it is a good time to review financial planning strategies with a view to optimising your outcomes. This
Superannuation. A Financial Planning Technical Guide
 Superannuation A Financial Planning Technical Guide 2 Superannuation Contents Superannuation overview 4 Superannuation contributions 4 Superannuation taxation 7 Preservation 9 Beneficiary nomination 9
Superannuation A Financial Planning Technical Guide 2 Superannuation Contents Superannuation overview 4 Superannuation contributions 4 Superannuation taxation 7 Preservation 9 Beneficiary nomination 9
Korea, South. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors. Korea, South. Exchange rate: US$1.00 equals 945.30 won. Qualifying Conditions. Regulatory Framework
 Korea, South Exchange rate: US$1.00 equals 945.30 won. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First law: 1973 (national welfare pension). Current law: 1986 (national pension), with 1989, 1993, 1995, 1997,
Korea, South Exchange rate: US$1.00 equals 945.30 won. Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First law: 1973 (national welfare pension). Current law: 1986 (national pension), with 1989, 1993, 1995, 1997,
receive the full amount of any of the qualifying benefits and allowances for the full year, and have no other taxable income.
 Page 1 of 9 Guide to tax offsets Overview Tax offsets (sometimes also referred to as rebates) directly reduce the amount of tax you must pay. They are not the same as tax deductions. Deductions only reduce
Page 1 of 9 Guide to tax offsets Overview Tax offsets (sometimes also referred to as rebates) directly reduce the amount of tax you must pay. They are not the same as tax deductions. Deductions only reduce
2 Social security and welfare expenses
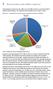 2 Social security and welfare expenses Total spending on social security and welfare was $131.9 billion in 2012-13, or around one third of total government spending. The composition of this spending is
2 Social security and welfare expenses Total spending on social security and welfare was $131.9 billion in 2012-13, or around one third of total government spending. The composition of this spending is
Employment Injuries and Occupational Diseases: Benefits (Permanent Incapacity) a), 2005
 Austria Belgium 20% (50% for pupils and students). Accident insurance fund. Review at any time possible in the first two years; thereafter at intervals of at least 1 year. No minimum level. Employment
Austria Belgium 20% (50% for pupils and students). Accident insurance fund. Review at any time possible in the first two years; thereafter at intervals of at least 1 year. No minimum level. Employment
THE TAX INSTITUTE. Tax Rates Table 2013-14
 THE TAX INSTITUTE Tax Rates Table 2013-14 taxinstitute.com.au Individual income tax rates Residents 2012-13 2013-14 Taxable income Marginal rate Tax on this income $0 $18,200 Nil Nil $18,201 $37,000 19%
THE TAX INSTITUTE Tax Rates Table 2013-14 taxinstitute.com.au Individual income tax rates Residents 2012-13 2013-14 Taxable income Marginal rate Tax on this income $0 $18,200 Nil Nil $18,201 $37,000 19%
Tax Rates & Thresholds Handy Guide
 Tax Rates & Thresholds Handy Guide 2014/15 Income Year Issued August 2014 Taxation of Superannuation Benefits Superannuation benefits from a taxed source Age of recipient Lump Sum Income stream 60 and
Tax Rates & Thresholds Handy Guide 2014/15 Income Year Issued August 2014 Taxation of Superannuation Benefits Superannuation benefits from a taxed source Age of recipient Lump Sum Income stream 60 and
AUSTRALIA. 1. Overview of the system
 AUSTRALIA 1. Overview of the system Australia has flat-rate, means-tested unemployment benefits. An administrative distinction is made between long-term and initial benefits, although this does not affect
AUSTRALIA 1. Overview of the system Australia has flat-rate, means-tested unemployment benefits. An administrative distinction is made between long-term and initial benefits, although this does not affect
Introduction... Distinctive Features of the Benefits Environment... Key Changes in Recent Years...
 Table of Contents Introduction... Distinctive Features of the Benefits Environment... Key Changes in Recent Years... 2 3 4 Statutory/Mandatory Programs... 5... 5 Retirement Benefits... 6 Death Benefits...
Table of Contents Introduction... Distinctive Features of the Benefits Environment... Key Changes in Recent Years... 2 3 4 Statutory/Mandatory Programs... 5... 5 Retirement Benefits... 6 Death Benefits...
Contents. Introduction. Introduction 1. Top five Budget proposals 2. Taxation 7. Social security and aged care 10.
 Contents Introduction 1 Top five Budget proposals 2 Taxation 7 Social security and aged care 10 Other measures 15 Introduction After weeks of speculation, the Federal Treasurer Joe Hockey handed down the
Contents Introduction 1 Top five Budget proposals 2 Taxation 7 Social security and aged care 10 Other measures 15 Introduction After weeks of speculation, the Federal Treasurer Joe Hockey handed down the
Living and Working in Austria. 1 l Income tax in Austria 2 l Social Security in Austria 3 l Residence And Work Permits in Austria
 Tax l Accounting l Audit l Advisory Living and Working in Austria 1 l Income tax in Austria 2 l Social Security in Austria 3 l Residence And Work Permits in Austria We are pleased to present you in our
Tax l Accounting l Audit l Advisory Living and Working in Austria 1 l Income tax in Austria 2 l Social Security in Austria 3 l Residence And Work Permits in Austria We are pleased to present you in our
Retirement incomes. Aisur. Submission to the Tax White Paper Task Force. July 2015
 Retirement incomes Submission to the Tax White Paper Task Force July 2015 Executive summary 2015 1 Background The Australian retirement income system comprises three pillars: a publicly funded means tested
Retirement incomes Submission to the Tax White Paper Task Force July 2015 Executive summary 2015 1 Background The Australian retirement income system comprises three pillars: a publicly funded means tested
Individual Tax Interview Checklist - 2010 Income Tax Return
 Where reply is Yes, supply supporting information 2009/2010 refers to the period from 1 July 2009 to 30 June 2010 Unless otherwise stated, this checklist refers to events occurring in 2009/2010 Client
Where reply is Yes, supply supporting information 2009/2010 refers to the period from 1 July 2009 to 30 June 2010 Unless otherwise stated, this checklist refers to events occurring in 2009/2010 Client
Year-end Tax Planning Guide - 30 June 2014 BUSINESSES
 Year-end Tax Planning Guide - 30 The end of the financial year is fast approaching. In the lead up to 30 June, this newsletter covers some of the year-end tax planning matters for your consideration. BUSINESSES
Year-end Tax Planning Guide - 30 The end of the financial year is fast approaching. In the lead up to 30 June, this newsletter covers some of the year-end tax planning matters for your consideration. BUSINESSES
Australia. Qualifying conditions. Benefit calculation. Defined contribution. Key indicators: Australia. Australia: Pension system in 2014
 11. PENSIONS AT A GLANCE 215: COUNTRY PROFILES AUSTRALIA Australia Australia: Pension system in 214 Australia s retirement income system has three components: a means-tested Age Pension funded through
11. PENSIONS AT A GLANCE 215: COUNTRY PROFILES AUSTRALIA Australia Australia: Pension system in 214 Australia s retirement income system has three components: a means-tested Age Pension funded through
Tax on contributions. Non-concessional (after tax) contribution caps. Age at 1 July 2015 Annual cap Tax rate Under 65 $180,000* Nil 65-74 $180,000 Nil
 This section summarises the main Federal Government taxes that apply to superannuation at the time of preparation. For more information, contact MyLife MySuper on 1300 MYLIFE (695 433) or the Australian
This section summarises the main Federal Government taxes that apply to superannuation at the time of preparation. For more information, contact MyLife MySuper on 1300 MYLIFE (695 433) or the Australian
baggetta & co accountants financial planners self managed super funds 2013 Individual Tax Return Checklist
 baggetta & co accountants financial planners self managed super funds 2013 Individual Tax Return Checklist Provide all supporting documentation to substantiate your claims Such as copies of receipts, tax
baggetta & co accountants financial planners self managed super funds 2013 Individual Tax Return Checklist Provide all supporting documentation to substantiate your claims Such as copies of receipts, tax
SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTIONS
 OECD TAX DATABASE EXPLANATORY ANNEX PART III. SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTIONS (Document updated May 2014) 1 Table of contents PART III. SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTION TABLES 4 Part III, Table 1 4 III.1. AUSTRIA
OECD TAX DATABASE EXPLANATORY ANNEX PART III. SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTIONS (Document updated May 2014) 1 Table of contents PART III. SOCIAL SECURITY CONTRIBUTION TABLES 4 Part III, Table 1 4 III.1. AUSTRIA
General reference guide
 General reference guide (TPS.01) Issued: 1 July 2015 The Portfolio Service Super Essentials The Portfolio Service Superannuation Plan The Portfolio Service Retirement Income Plan This guide contains important
General reference guide (TPS.01) Issued: 1 July 2015 The Portfolio Service Super Essentials The Portfolio Service Superannuation Plan The Portfolio Service Retirement Income Plan This guide contains important
All persons gainfully employed under age 60. Self-employed are covered also.
 Prepared by First Life Financial Company. I SUMMARY Social Security Eligibility Retirement Contributions All persons gainfully employed under age 60. Self-employed are covered also. 60M/F To Social Security:
Prepared by First Life Financial Company. I SUMMARY Social Security Eligibility Retirement Contributions All persons gainfully employed under age 60. Self-employed are covered also. 60M/F To Social Security:
NB: receipt of an allowance does not automatically entitle an employee to a deduction. Compare to ATO Portal report.
 INCOME (PLEASE OBTAIN EVIDENCE WHERE APPLICABLE) 1. Salary and wages NB: have you received all your payment summaries from all your employers? Obtain and attach PAYG summaries. Non cash benefits received
INCOME (PLEASE OBTAIN EVIDENCE WHERE APPLICABLE) 1. Salary and wages NB: have you received all your payment summaries from all your employers? Obtain and attach PAYG summaries. Non cash benefits received
Topics. AMA Private Health Insurance Comparison 2016 Budget Breakdown Top Ten Tax Tips for 2016. AMA Private Health Insurance Comparison
 Prime Time Advisory News Update May 2016 Newsletter Topics AMA Private Health Insurance Comparison 2016 Budget Breakdown Top Ten Tax Tips for 2016 AMA Private Health Insurance Comparison Recent price increases
Prime Time Advisory News Update May 2016 Newsletter Topics AMA Private Health Insurance Comparison 2016 Budget Breakdown Top Ten Tax Tips for 2016 AMA Private Health Insurance Comparison Recent price increases
NEWSLETTER MAY 2014 2 0 1 4 T A X P L A N N I N G 2 0 1 4 F E D E R A L B U D G E T U P D A T E. www.mgh.com.au 1
 NEWSLETTER MAY 2014 2 0 1 4 T A X P L A N N I N G The end of the financial year is fast approaching. We encourage you to make an appointment with our office so we can formulate personalised tax strategies
NEWSLETTER MAY 2014 2 0 1 4 T A X P L A N N I N G The end of the financial year is fast approaching. We encourage you to make an appointment with our office so we can formulate personalised tax strategies
How Can You Reduce Your Taxes?
 RON GRAHAM AND ASSOCIATES LTD. 10585 111 Street NW, Edmonton, Alberta, T5M 0L7 Telephone (780) 429-6775 Facsimile (780) 424-0004 Email rgraham@rgafinancial.com How Can You Reduce Your Taxes? Tax Brackets.
RON GRAHAM AND ASSOCIATES LTD. 10585 111 Street NW, Edmonton, Alberta, T5M 0L7 Telephone (780) 429-6775 Facsimile (780) 424-0004 Email rgraham@rgafinancial.com How Can You Reduce Your Taxes? Tax Brackets.
Provinces and territories also impose income taxes on individuals in addition to federal taxes
 Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 Canada Local information Tax Authority Website Tax Year Tax Return due date Is joint filing possible Are tax return extensions possible Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 Canada Local information Tax Authority Website Tax Year Tax Return due date Is joint filing possible Are tax return extensions possible Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
1 General facts on postings abroad and social security 2 Posting to EU or EEA countries or other agreement countries
 Posting abroad 2010 Introduction This booklet is intended as a guide for employers and employees when planning a posting abroad. The booklet answers the following questions: Which country are the social
Posting abroad 2010 Introduction This booklet is intended as a guide for employers and employees when planning a posting abroad. The booklet answers the following questions: Which country are the social
The benefits of insuring through super. Macquarie Life
 The benefits of insuring through super Macquarie Life While your clients are accumulating wealth, they also need to ensure adequate insurance cover is in place so they and their families are looked after
The benefits of insuring through super Macquarie Life While your clients are accumulating wealth, they also need to ensure adequate insurance cover is in place so they and their families are looked after
Private health insurance policy details
 Private health insurance policy details PRIVATE HEALTH INSURANCE YOU NEED TO KNOW The information on this page will help you complete Private health insurance policy details on page 4 of your tax return.
Private health insurance policy details PRIVATE HEALTH INSURANCE YOU NEED TO KNOW The information on this page will help you complete Private health insurance policy details on page 4 of your tax return.
3.1: Overview of the individuals income tax system
 3: Individuals Overview This chapter gives an overview of Australia s individuals income tax system and issues arising in the current system that may present scope for reform. Key points Individuals income
3: Individuals Overview This chapter gives an overview of Australia s individuals income tax system and issues arising in the current system that may present scope for reform. Key points Individuals income
SMSF Facts Sheet. July 2015
 SMSF Facts Sheet July 2015 Key Superannuation Rates and Thresholds - 2015/16 Contributions The tables below contain the amounts of concessional and non-concessional contributions you may make to your superannuation
SMSF Facts Sheet July 2015 Key Superannuation Rates and Thresholds - 2015/16 Contributions The tables below contain the amounts of concessional and non-concessional contributions you may make to your superannuation
Pension rules for the self-employed in the EU, 2014 a)
 Austria Belgium Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Austria used to have a comprehensive special scheme both for farmers and for craftsmen and retailers until 31 Dec 2004. As of 1 Jan 2005 all pension systems were
Austria Belgium Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Austria used to have a comprehensive special scheme both for farmers and for craftsmen and retailers until 31 Dec 2004. As of 1 Jan 2005 all pension systems were
TAX PLAN G TAX PLAN G ANNEX 83
 TAX PLAN G TAX PLAN G ANNEX 83 TABLE OF CONTENTS TAX PLAN Overview.... 85 Health Care Contribution Levy.... 86 Personal Income Tax.... 88 Additional Support For Working Families... 89 Charitable Donations
TAX PLAN G TAX PLAN G ANNEX 83 TABLE OF CONTENTS TAX PLAN Overview.... 85 Health Care Contribution Levy.... 86 Personal Income Tax.... 88 Additional Support For Working Families... 89 Charitable Donations
Statement of formulas for calculating amounts to be withheld
 Schedule Pay as you go (PAYG) withholding NAT 00 Statement of formulas for calculating amounts to be withheld For payments made on or after July 0 This document is a withholding schedule made by the Commissioner
Schedule Pay as you go (PAYG) withholding NAT 00 Statement of formulas for calculating amounts to be withheld For payments made on or after July 0 This document is a withholding schedule made by the Commissioner
Social assistance: 2% of covered payroll. Government. Social insurance: None; contributes as an employer. Social assistance: Any deficit.
 Barbados Exchange rate: US$1.00 = 2.02 Barbadian dollars (B$). Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First law: 1937 (social assistance). Current law: 1966 (social insurance). Type of program: Social insurance
Barbados Exchange rate: US$1.00 = 2.02 Barbadian dollars (B$). Old Age, Disability, and Survivors First law: 1937 (social assistance). Current law: 1966 (social insurance). Type of program: Social insurance
2014 Federal Budget Analysis
 For adviser use only. Not for public distribution. 2014 Federal Budget Analysis In one of the more highly anticipated Federal Budgets, the Government announced major changes that should be discussed with
For adviser use only. Not for public distribution. 2014 Federal Budget Analysis In one of the more highly anticipated Federal Budgets, the Government announced major changes that should be discussed with
Individual tax return instructions 2013
 Instructions for taxpayers Individual tax return instructions 03 To help you complete your tax return July 0 30 June 03 Now available on tablets NAT 7050-06.03 OUR COMMITMENT TO YOU We are committed to
Instructions for taxpayers Individual tax return instructions 03 To help you complete your tax return July 0 30 June 03 Now available on tablets NAT 7050-06.03 OUR COMMITMENT TO YOU We are committed to
Rates of Tax 2013/14 Resident Individuals
 July Supplement 2014 Rates of Tax 2013/14 Resident Individuals The following rates apply to individuals who are residents of Australia for tax purposes for the entire income year. 1 Tax Payable 2,3 0 18,200
July Supplement 2014 Rates of Tax 2013/14 Resident Individuals The following rates apply to individuals who are residents of Australia for tax purposes for the entire income year. 1 Tax Payable 2,3 0 18,200
TAXPACK. Income. Deductions. Losses. Tax offsets. Private health insurance. Medicare levy. Adjustments CHOOSE E-TAX AND LODGE OVER THE INTERNET.
 NOT FOR SALE Income Deductions Losses Tax offsets Private health insurance CHOOSE E-TAX AND LODGE OVER THE INTERNET. see page 6 YOU MAY ALSO NEED SUPPLEMENT. see page 5 LODGE YOUR TAX RETURN BY 31 OCTOBER
NOT FOR SALE Income Deductions Losses Tax offsets Private health insurance CHOOSE E-TAX AND LODGE OVER THE INTERNET. see page 6 YOU MAY ALSO NEED SUPPLEMENT. see page 5 LODGE YOUR TAX RETURN BY 31 OCTOBER
G E N C S V A L T E R S L A W F I R M B A L T I C T A X C A R D 2 0 1 5
 PERSONAL INCOME TAX IN BALTICS Personal Income Tax Rates in Baltics Country Social Tax- employee share Social Tax- employer share Personal Income Tax Latvia 10.50% 23.59% 23% Lithuania 9% 30.98% - 32.6%
PERSONAL INCOME TAX IN BALTICS Personal Income Tax Rates in Baltics Country Social Tax- employee share Social Tax- employer share Personal Income Tax Latvia 10.50% 23.59% 23% Lithuania 9% 30.98% - 32.6%
INDIVIDUAL TAX INTERVIEW CHECKLIST 2013 INCOME TAX RETURN
 INDIVIDUAL TAX INTERVIEW CHECKLIST 2013 INCOME TAX RETURN CLIENT DETAILS Tax File Number: ABN: Surname or family name: First given name: Other given names: Postal address: Suburb/town/locality: State/territory:
INDIVIDUAL TAX INTERVIEW CHECKLIST 2013 INCOME TAX RETURN CLIENT DETAILS Tax File Number: ABN: Surname or family name: First given name: Other given names: Postal address: Suburb/town/locality: State/territory:
The Cypriot Pension System: Adequacy and Sustainability
 Cyprus Economic Policy Review, Vol. 6, No. 2, pp. 49-58 (2012) 1450-4561 49 The Cypriot Pension System: Adequacy and Sustainability Philippos Mannaris Aon Hewitt Abstract The fundamental objective of pension
Cyprus Economic Policy Review, Vol. 6, No. 2, pp. 49-58 (2012) 1450-4561 49 The Cypriot Pension System: Adequacy and Sustainability Philippos Mannaris Aon Hewitt Abstract The fundamental objective of pension
AUSTRALIA SUMMARY. Social Security. Prepared by Hannover Life Re of Australasia.
 Prepared by Hannover Life Re of Australasia. I SUMMARY Social Security Eligibility Retirement Age Contributions Retirement To qualify as an Australian resident a person must be living in Australia as:
Prepared by Hannover Life Re of Australasia. I SUMMARY Social Security Eligibility Retirement Age Contributions Retirement To qualify as an Australian resident a person must be living in Australia as:
Tax return for individuals 2015 1 July 2014 to 30 June 2015
 Use Individual tax return instructions 2015 to fill in this tax return n Print clearly using a black pen only n Use BLOCK LETTERS and print one character in each box S M I T H S T Individual information
Use Individual tax return instructions 2015 to fill in this tax return n Print clearly using a black pen only n Use BLOCK LETTERS and print one character in each box S M I T H S T Individual information
Superannuation: dealing with life s changes
 Booklet 2 Superannuation: dealing with life s changes MAStech Smart technical solutions made simple Contents Introduction 01 Introduction 03 Accessing your superannuation benefits 04 Conditions of release
Booklet 2 Superannuation: dealing with life s changes MAStech Smart technical solutions made simple Contents Introduction 01 Introduction 03 Accessing your superannuation benefits 04 Conditions of release
The social security system is organized and implemented at national level by state bodies/ public institutions.
 1 March 2009 PRESENTATION OF THE CROATIAN PENSION SYSTEM Croatian social security system is mostly the insurance based, with exception of family benefits (children allowance- doplatak za djecu) and the
1 March 2009 PRESENTATION OF THE CROATIAN PENSION SYSTEM Croatian social security system is mostly the insurance based, with exception of family benefits (children allowance- doplatak za djecu) and the
2015 rates and thresholds guide
 Client Information Newsletter - Tax & Super 2015 rates and thresholds guide October 2015 Table of Contents Individual tax rates for residents... 2 Individual tax rates for non-residents.... 2 2014-15 resident
Client Information Newsletter - Tax & Super 2015 rates and thresholds guide October 2015 Table of Contents Individual tax rates for residents... 2 Individual tax rates for non-residents.... 2 2014-15 resident
Dover Individual Income Tax Return Checklist
 Dover Individual Income Tax Return Checklist For the year ending (insert income year) 1. Advisor/Accountant Details Company/Firm name: Contact name: Contact email: Contact phone: 2. Client Details Full
Dover Individual Income Tax Return Checklist For the year ending (insert income year) 1. Advisor/Accountant Details Company/Firm name: Contact name: Contact email: Contact phone: 2. Client Details Full
