HEPATITIS C. Information Booklet. Dr. Shay Keating, MB, PhD. providing. adapting. nurturing. developing. leading. Informing
|
|
|
- Rosa Victoria Houston
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Information Booklet HEPATITIS C A Guide for Drug Users and their Families providing adapting nurturing developing leading Informing Dr. Shay Keating, MB, PhD.
2
3 Information Booklet HEPATITIS C A GUIDE FOR DRUG USERS AND THEIR FAMILIES Dr. Shay Keating, MB, PhD.
4 FORWARD Through our mission we aim to provide a specialist addiction service in a therapeutic, caring and collaborative way, whilst leading and informing on best practice. As an organisation we are committed to providing a responsive, effective and progressive service. The delivery of Hepatitis information, education and treatment is vital in ensuring that we meet the needs of the client population we serve. I warmly welcome the development of this timely booklet and would like to congratulate Dr. Shay Keating on its publication. I have no doubt that the information provided will be of benefit to those affected by Hepatitis C. Sheila Heffernan General Manager June 2003
5 THE LIVER WHAT AND WHERE IS THE LIVER? The liver is the second largest organ in the body (the skin is considered an organ making it the largest). It is found on the upper right-hand side of the abdomen (belly) under the right lung and protected by the rib cage. It cannot normally be felt. If it becomes inflamed however, it might get bigger and your doctor may be able to feel it by pressing on the abdomen. Unlike the kidneys or lungs, you have only one liver. It is vital that you look after it. You can survive with only one kidney or even one lung but not without your liver. WHAT DOES THE LIVER DO? It stores energy in the form of glucose. This acts as a rapid source of energy; It processes food absorbed in the digestive tract (gut); It makes certain proteins essential, for the control of body fluids; It stores excess amounts of vitamins and minerals, including iron, which are essential for the body to function; It helps in the destruction of old red blood cells; It makes a digestive juice called bile, (which is stored in the gall bladder) and coagulation factors (compounds that help the blood to clot if you bleed); It helps to regulate chemical, hormonal and cholesterol levels; It is essential for detoxifying the blood of many unwanted drugs and waste products; WHAT HAPPENS IF THE LIVER IS BADLY DAMAGED? In severe liver damage the liver Cannot control fluid balance in the body. The abdomen (belly) and legs may swell up; Cannot excrete a compound called bilirubin effectively. Bilirubin is formed from the breakdown of old red blood cells in the body. The bilirubin level in informing the blood rises and the skin and eye membranes look yellow (jaundice). The urine may be very dark and the stools very pale; 3 Cannot make clotting factors so you might bleed more easily;
6 Cannot control the level of certain hormones. Men with advanced liver disease may loose body hair, their testicles may shrink and their breasts may get bigger; Cannot detoxify the blood of certain chemicals and drugs. Patients with advanced hepatitis may be extremely sensitive to the effects of certain drugs and chemicals; 4 Hepatitis C WHAT IS HEPATITIS? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. It can be caused by alcohol, certain chemicals, drugs and viral infections; Viral hepatitis is very common in intravenous drug users; At present, six hepatitis viruses have been identified; they are named hepatitis A, B, C, D, E and G. They differ in how they are transmitted from person to person as well as how long and severely they can affect you. You may be infected with hepatitis A or E when travelling to developing countries without vaccination where water and sewage facilities are poor. You may also contract hepatitis A or hepatitis E when sanitation is poor - not washing hands after going to the toilet, eating contaminated food or after certain sex practices. Both hepatitis A and E cause acute illness, usually with jaundice and flu-like symptoms. They can be severe, especially in the very young or old but recovery is usually complete; The other four hepatitis viruses, B, C, D and G are transmitted mainly by blood and blood products or by sexual activity (mainly hepatitis B); WHAT IS HEPATITIS C? Hepatitis C is a viral infection of the liver. A virus is a tiny organism that may cause disease, infection or inflammation if it enters the body; Hepatitis C was first identified in In Ireland, at present it is estimated that as many as 4 out of every 5 of intravenous drug users are believed to be infected with hepatitis C; World wide approximately 170 million persons are thought to be infected with hepatitis C; Hepatitis C infection is not caused by a single virus but by a family of viruses, that can be further divided into six different subtypes called
7 genotypes. Different genotypes infect different people worldwide. In Ireland genotypes 1 and 3 are the most common forms of hepatitis C seen in drug users, in approximately similar frequencies. HOW CAN A PERSON BECOME INFECTED BY HEPATITIS C? Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus. This means that it is carried in the blood and spread through blood-to-blood contact. In some cases, persons with hepatitis C have no idea how they became infected. The majority of people however can identify a likely way. Some practices are more risky than others; In Ireland sharing injection needles and equipment ( works ) with someone who is infected is the commonest way to become infected with hepatitis C. Sharing filters, spoons or water, frontloading and backloading are also very risky practices. Snorting cocaine has recently been linked with hepatitis C infection. This is thought to be due to sharing of the straw; Not practising safer sex, for example not using a condom during inter course is a possible risk for hepatitis C infection. This is thought to be a low risk. It is easier for women to become infected through unsafe sex than men. The risk of hepatitis C infection is higher in HIV positive persons; Hepatitis C can also be passed on from mother to baby. Once again this is thought to be a relatively low risk (1 in 20) but a risk nonetheless. The chances of a baby becoming infected are higher if the mother has both hepatitis C and HIV. Passing on Hepatitis C to your baby by breast-feeding is not thought to be a risk; Transfusion of blood and blood products can spread hepatitis C. Before 1990, no test was available for the detection of hepatitis C in blood. All blood and blood products are now routinely tested for hepatitis C and recent improvements in blood product screening have greatly reduced the risk of getting hepatitis C in this way; Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes and razor-blades where transfer of blood occurs are low risk ways to become infected, as are unsafe tattooing or body piercing when equipment is not sterile; Exposure to infected blood in the workplace can lead to infection with hepatitis C. Health care workers may have needle stick injuries or may be exposed to infected blood in other ways such as spills; informing Hepatitis C can be transmitted through dried blood because the virus can live outside the body some time; 5
8 YOU CANNOT GET HEPATITIS C FROM: Hugging and kissing; Holding hands; Sharing toilets; Sharing crockery and cutlery; HOW CAN A PERSON PREVENT THE SPREAD OF HEPATITIS C TO OTHERS? Hepatitis C is very infectious. If you are infected with the hepatitis C virus, take the following steps to make sure that you do not spread the virus to others. Never share used needles or works (barrel, filter, spoon, water, etc) with anyone else. Never share needles or works cleaned with bleach. Unlike HIV, the hepatitis C virus does not appear to be killed in the works by bleach. As yet there is no known way of cleaning used works to kill off hepatitis C; Never share the straw if snorting drugs; Wash your hands after injecting. They might have tiny amounts of blood on them; Never donate blood, body organs, other tissues or sperm; Clean all blood spills with paper towels, followed by a detergent and water wash. Then disinfect the area with a solution made up of 10 parts water and 1 part good quality bleach. Dry the area with a clean paper towel; Blood stained articles, such as tampons (except sharp objects such as needles and razors) should be placed in a plastic bag, which is tied at the top before placing in an outside rubbish bin. All sharp objects should be placed in a special sharps container kept out of reach of children; Do not share personal items where blood may be present such as toothbrushes or razors; Cover exposed cut and sores; Use condoms with any new sexual partners. Talk to your doctor about the relative risks with long term sexual partners; Avoid sex during or immediately after your period if you are a female carrier. Hepatitis C is found in menstrual blood; For people receiving ear piercing, tattooing, electrolysis or acupuncture, check that new, disposable needles are being used. This is very important for those in foreign countries; 6
9 Tell your doctor (if he or she doesn t know), your dentist or healthcare worker that you are hepatitis C positive. Anyone who is exposed to blood may be at risk; Remember, unlike hepatitis A and B, there is no vaccine for hepatitis C at present; WHO SHOULD TEST FOR HEPATITIS C INFECTION? All drug users, especially those who have injected drugs or shared works (even once) or snorted drugs from a shared tooter; Those who have been exposed to needle stick injuries; Babies born to hepatitis C positive mothers; Those who feel that they might have received contaminated blood or blood products before testing for hepatitis C in donated blood became routine in this country; Those who have had body piercing or tattooing using improperly sterilised equipment or contaminated ink; DIAGNOSIS OF HEPATITIS C HOW DO I KNOW IF I HAVE BEEN INFECTED WITH THE HEPATITIS C VIRUS? When persons are first infected with hepatitis C they may complain of flu-like symptoms, such as feeling feverish, shivering, nausea or loss of appetite. This is called acute hepatitis and usually lasts a few days or weeks. They may be jaundiced; These symptoms only occur in about 10 to 15% so many do not know that they have been infected; In some people the virus can no longer be detected. We don t know if the virus goes away forever or only for a short time; In most cases (approximately 80%), the infection becomes chronic. This means that the infection lasts for longer than six months; The best way to see if you have been infected is to have a blood test. The providing initial (first) test for hepatitis C is based on the detection of antibodies to the virus, not the virus itself. To help fight viruses, the body produces antibodies. These are found in the blood. Following acute infection it can take some time for these antibodies to appear, usually 2-3 months but in some cases up to 6 months this is referred to as the window period. If antibodies to 7
10 hepatitis C are found it means that the person has been in exposed to the virus at some stage. It does not tell however, if the person still has the virus in the liver or the blood. The virus may be gone but the antibodies can remain for years; Liver enzymes are proteins found in liver cells and are released into the blood if the liver is damaged. High levels of these enzymes in the blood suggest some sort of liver problem. They may be high in persons with Hepatitis C infection. Low levels however, do not necessarily mean that the liver is healthy. A person with hepatitis C and advanced liver damage may have normal liver enzyme levels; A PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test is a better test for the hepatitis virus itself. It will tell if the virus is still detectable in the blood and will show if a person has chronic hepatitis C, or on-going infection. Unfortunately, many persons who are Hepatitis C antibody positive have the virus in the blood and are actively infectious. You and your doctor will decide when is the best time to do a PCR test; Actively infectious means that hepatitis C may be causing liver damage and that you may pass the infection on to others by the ways already described. WHAT ONGOING SYMPTOMS MIGHT I HAVE WHEN INFECTED WITH HEPATITIS C? Flu-like symptoms fever, sweating, nausea, fatigue (tiredness), malaise (generally not feeling well), headache and night sweats; Pains in the joints; Pain around the liver area; Bowel problems such as diarrhoea or constipation; Mood swings, difficulty sleeping or depression; Loss of appetite, especially feeling unwell if you eat fatty foods; Bad reaction to alcohol and increased sensitivity to medication; WILL MY HEPATITIS C INFECTION BECOME CHRONIC? For many patients with hepatitis C, up to 65%, the infection becomes chronic (persists). As mentioned earlier this means that the infection does not go away and the inflammation lasts for a minimum of six months and usually much longer; 8
11 Chronic hepatitis C can lead to serious liver problems, such as fibrosis (scarring of the liver), cirrhosis (irreversible scarring of the liver) or cancer of the liver in some patients; Cirrhosis occurs when normal liver cells are damaged and are irreversibly replaced by scar tissue. At this stage the liver cannot heal itself. This occurs in a minimum of 1 in 5 of persons with hepatitis C, on average about twenty years after becoming infected; With cirrhosis, patients may complain of loss of appetite and weight loss, nausea and vomiting (sometimes blood), jaundice, itching, swelling of the abdomen, increased sensitivity to certain drugs and mental confusion often leading to coma; Approximately 6 8% of persons with hepatitis C develop liver cancer. This appears to develop in those persons with hepatitis C who have cirrhosis and will not generally occur until about twenty years after infection, but could occur earlier; WHAT DO I DO IF I TEST POSITIVE FOR HEPATITIS C? Go to your doctor (G.P. or doctor in the drug treatment clinic). He or She may request a PCR test to see if you still have the virus in your blood. The PCR test must be sent to the laboratory within a couple of hours so your GP may need to refer you onto a specialist clinic for this test. It is most likely that this test will be positive meaning that you still have active infection. If it is negative it means that there is no virus detected in your blood. This means that the infection may be gone for good but it may also mean that the infection is still there but the virus is in very small amounts, which could not be measured in the laboratory. It is recommended that you get another blood test performed 1 year later to see if there is any virus present; Find out which genotype of hepatitis C you have. This may determine what therapy you take and for how long; The hepatologist (liver specialist) may organise an ultrasound test in the x-ray department for you to see if the liver is enlarged or scarred. He or she may also recommend a liver biopsy. This is a technique whereby a small sample of liver is obtained through a tiny cut in the skin above the liver. This is the best way to see how damaged the liver is. It is a relatively low risk procedure but like any medical procedure may have risks. Ask the liver nurturing specialist about these; After the biopsy you might feel some pain in the site of the biopsy or notice pain in the shoulder (referred pain caused by pressure on the nerves in the 9
12 liver and surrounding tissue). If the hepatologist is considering offering you treatment, a biopsy is the best way to see the condition of your liver. It is well worth considering a biopsy. Talk to the hepatologist about any concerns you might have; Learn more about hepatitis C and how it may affect you. This is a newly identified virus. Doctors and scientists are learning more and more about it every day. Keep up to date with information; Talk to a counsellor. There will be questions you may need to ask about living with hepatitis C, it s effect on you and on your family; Learn good infection control practices to prevent the spread of infection; Look at your drug habit. On-going injection of drugs will lessen the chances of your staying healthy with the virus and it will affect your chances of getting treatment. It may also mean that you will infect others; Stop drinking alcohol or reduce your use to a minimum. Alcohol is another cause of hepatitis and may speed the development of liver damage; Look after your general health and diet. Eat sensibly and exercise regularly. WILL I DEVELOP SEVERE LIVER DAMAGE FROM HEPATITIS C? Many factors can worsen the effect hepatitis C may have on you if infected. Excessive drinking of alcohol, as mentioned earlier is another cause of hepatitis, or liver damage. It is advisable for a person who is infected with hepatitis C to stop drinking alcohol. Alcohol worsens liver damage caused by hepatitis C and may speed up the development of cirrhosis (liver scarring) or liver cancer; Many recreational drugs are toxic to the liver and should be avoided. Persons infected by hepatitis C should avoid taking medication when it is not necessary and should consult their doctors or pharmacists when taking any medication even simple painkillers or antibiotics; Infection with another hepatitis virus, for example hepatitis A or B will worsen liver damage. At the moment it is possible to be tested for and vaccinated against hepatitis A and B if you have not already been infected by these viruses. Ask your doctor about this; Infection with HIV may also increase your chances of developing severe liver damage from Hepatitis C. HIV itself can cause liver damage and many of the drugs used to treat HIV are damaging to the liver; 10
13 The hepatitis C virus has many different strains, or genotypes. In Ireland, genotypes 1 and 3 are the commonest. Patients infected with genotype 3 tend to respond better to treatment at present, than those infected by genotype 1; Treatment of hepatitis C IS THERE ANY TREATMENT FOR HEPATITIS C INFECTION? Yes. Current treatment for hepatitis C is with combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin. Interferon is a natural chemical that the body produces in response to viral infections. It is given by injection under the skin (subcutaneously) into a fatty area such as the thighs or stomach. It is a protein so it would be destroyed by the acid in the stomach if swallows so it must be injected. In the past it was given three times a week for six months minimum. Now there is a new form of interferon available termed pegylated interferon. This need only be given once a week; Ribavirin is an antiviral drug currently originally used in the treatment of a particular type of viral pneumonia. Ribavirin appears to prevent the virus from multiplying. When used in the treatment of hepatitis C it works well in combination with interferon. It is taken twice daily in capsule form; The recommended length of treatment is 24 to 48 weeks. Those with genotype non 1 (any of the other five genotypes) are treated for 24 weeks. Treatment of genotype 1 may need longer; A response to treatment is shown by a negative PCR (no virus is found in the blood) at the end of treatment. The specialist will repeat the PCR test six months later to see if it is still negative a sustained viral response. If the patient fails to respond to interferon within three months, therapy may be discontinued; WHO IS OFFERED ANTI-HEPATITIS C THERAPY? Treatment of hepatitis C is recommended for those persons at greatest risk of developing liver cirrhosis. This includes persons with a positive PCR test; leading and not drinking alcohol for a minimum of six months; It is generally recommended that anti-hepatitis C therapy should be offered to those patients who have stable drug or alcohol habits, who are either drug and alcohol free or on a methadone maintenance programme 11
14 Therapy is not routinely offered to a person who is still actively abusing drugs, such as heroin, benzodiazopines (for example valium) or alcohol. Recreational drugs or heavy alcohol drinking, as mentioned earlier are damaging to the liver and it does not make sense to treat one cause of liver damage, the hepatitis C virus and not treat another, the drug or alcohol abuse. It is also pointless to put a patient through the discomfort of interferon therapy if he or she is putting himself or herself at risk of reinfection by active drug use; A person s drug stability can easily be seen on routine urine testing. Dirty urines (opiate or benzodiazepine positive) would suggest that you are not ready to enter into treatment; The treatment of hepatitis C can be uncomfortable for the patient. It is essential that the patient be in adequate accommodation before treatment is started. It would be very difficult for someone to stay on treatment if she or he were homeless; ARE THERE ANY SIDE EFFECTS TO INTERFERON AND RIBAVIRIN THERAPY? Yes. Many commonly used drugs have side effects. Painkillers can cause nausea and antibiotics can cause rashes; Interferon is a very strong drug, which is only given to a patient under the strict supervision of a hepatologist (liver specialist) or infectious disease specialist; Common side effects of interferon are flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, chills, joint pains and weakness, usually 6 to 8 hours after injecting interferon. These symptoms usually lessen after the first few treatments. Some hair loss in seen in 1 in 10 patients. The hair usually grows back as soon as the course of the drug is finished; Patients on combination therapy may loose their appetites or interest in food; Depression while on interferon occurs in approximately 1 in 4 patients on combination therapy. All drug treatment clinics have access to psychiatrists who can help with this; Certain abnormalities in blood cells and thyroid gland function may be seen and regular blood checks are required; Unfortunately many patients feel the symptoms they experience while on interferon are similar to withdrawal from heroin and feel they might 12
15 need to take heroin to overcome these symptoms. If you are offered interferon therapy and experience unwanted symptoms, talk to your doctor. There are many therapies available, which will help to control these effects. Do not use non-prescribed drugs such as heroin; Patients on interferon often complain that they experience the needl buzz again while injecting interferon and that this starts the drug injecting habit all over again. This may be avoided if the person discusses this with the doctor and counsellor. Interferon is now available in specially designed preloaded pens. This should overcome the needle-buzz problem; Side effects of ribavirin are anaemia, which may be severe and may require treatment, dry mouth, nausea, indigestion and tiredness; Ribavirin is very toxic to the unborn baby. Women on ribavirin therapy should practice adequate contraception. They should avoid pregnancy during treatment and for at least four months after treatment is completed. Men should not have unprotected sex while on therapy and for seven months afterwards. SHOULD I HAVE TREATMENT IF IT IS OFFERED TO ME? No two persons with hepatitis C are the same. One person may have ongoing symptoms from hepatitis C while another may feel very well. One person may have a good response to treatment while another may not. One person may find the side effects of treatment very difficult to cope with while another may experience little or no side effects; Unfortunately however, the reality for many persons with hepatitis C is that it will not go away and it s effects can only get worse with time. It is generally felt by liver specialists that treatment is available and should be offered to most patients who are stable, drug wise; With combination drug therapy for hepatitis C, there is a good chance of curing the disease. You should decide with the help of your doctor and counsellor, whether or not you should have treatment if it is offered to you by the liver specialist; Be aware of the risks of going on treatment, the chances of suffering side effects and the risk that your drug habit might destabilise and balance this against the obvious benefit of curing the disease; adapting Do not start therapy until you are ready to do so. Consider treatment sooner rather than later. Persons with low levels of the virus and mild liver disease respond best to treatment. In the long-term, those side effects of combination therapy, which only last a short time, will be a small price to pay for curing this disease. 13
16 CAN I USE COMPLIMENTARY THERAPIES FOR HEPATITIS C? For some people with hepatitis C, complimentary (non-medical) therapies appear to be valuable tools, giving hope and health. They may not be proven to benefit dramatically but may help. Many herbal remedies have been reported as being helpful in the treatment of hepatitis C and it s symptoms. Unfortunately, these may not have undergone the same tests as medical therapies. Discuss this with your doctor. If you are offered medical treatment, do not take any other remedies without first discussing them with your liver specialist. There may be an interaction between both therapies; Massage can be very helpful in relieving stress. Regular relaxation can also make you feel better and control some of the symptoms of infection or side effects of medical therapy; Acupuncture may also relieve stress or help with sleep. If you go for acupuncture, make sure you go to a qualified practitioner and be sure the needles are sterile. HEALTHY EATING WITH HEPATITIS C A healthy diet is important for overall health and well-being. This is even more important if you are suffering from any illness such as hepatitis C or on treatment for this infection. Eating properly helps the liver to stay healthy and aids recovery. Here are some healthy eating tips Eat a well balanced diet and take a vitamin and mineral supplement in times when you diet is not as good as it should be; Eat plenty of fresh fruit, vegetables and salads; Eat less red meats, Substitute with chicken or fish (preferably grilled); Reduce dairy products, use low fat milk and sunflower spreads; Limit eggs to 3 to 4 per week; Reduce salt and sugar intake. Season with herbs instead; Replace white bread, flour and pasta with whole meal alternatives; Avoid greasy, spicy, creamy and sugary foods; 14
17 Cut down on tea and coffee. Drink herbal teas or fruit juices instead; Do not drink alcohol. Many women who are hepatitis C positive and pregnant have special concerns regarding themselves and their unborn babies; CAN I INFECT MY UNBORN BABY IF I AM HEPATITIS C POSITIVE? Yes. It is possible to infect your unborn baby. Transmission is more likely if the amount of virus in the blood is high. Talk to your doctor about this. CAN I RECEIVE TREATMENT FOR HEPATITIS C IF I AM PREGNANT? No. Hepatitis C in Pregnancy At present the two commonly used drugs, approved for treatment of hepatitis C are interferon and ribavirin. Ribavirin is very dangerous to the unborn baby. If you are on combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin it is essential to avoid pregnancy with the appropriate contraception, if required. You must also avoid pregnancy for four months after treatment has ended. If you do become pregnant consult your doctor immediately. Men on combination treatment must avoid unprotected sexual intercourse for the duration of the study and for seven months after treatment has finished. WHAT SHOULD I DO IF I AM HEPATITIS C POSITIVE AND PREGNANT? Try to stay healthy for your own sake and the sake of your baby. Attend your ante-natal appointments as recommended. Do not use drugs if possible or maintain yourself on methadone only. Family and Social Issues HOW MIGHT HEPATITIS C AFFECT MY FAMILY RELATIONSHIPS? Living with hepatitis C isn t easy. Even if you don t have dramatic symptoms, the tiredness associated with hepatitis C infection may be frustrating; All family illness can lead to stress. Family relationships may suffer if a member of the family is infected by hepatitis C. This in turn may lead to developing tension the home until all family members learn to adjust to the disease; Talk to a counsellor either on your own or with the members of your family. In Ireland at present there are many counsellors, trained in the support of 15
18 patients with hepatitis C and their families. Your problems are probably not unusual for a drug user infected with hepatitis C. There may be many questions you might like to ask. Feel free to do so; Try to maintain a normal lifestyle. If you are recently infected it may be years before you may feel unwell as a result of hepatitis C; Change your lifestyle if required. Try to ensure that you do not mistakenly infect a family member. Follow the prevention methods mentioned earlier in this booklet; AS A FAMILY MEMBER, HOW CAN I SUPPORT A PERSON WITH HEPATITIS C? Learn about hepatitis C, how it is contracted and treated; Listen to the person. Don t try to take over and make all the decisions for him or her; Be supportive and not critical of the person; Expect the person with hepatitis C to be moody, worried or depressed from time to time. This is normal for someone with an illness even if he or she is physically well at the time. Try not to focus too much on the family member with hepatitis C, thereby neglecting others in the family; Discuss your concerns with the appropriate people, the doctors and counsellors involved in the care of your family member; Dr. Shay Keating, MB, PhD. 16 The Drug Treatment Centre Board, Trinity Court, Pearse Street, Dublin 2. Tel: Fax: info@dtcb.ie Website: Printed by Quantum Print, Published November 2003.
19
20 The Drug Treatment Centre Board Trinity Court Pearse Street Dublin 2 Tel: Fax: info@dtcb.ie website:
INFORMATION ABOUT HEPATITIS C
 INFORMATION ABOUT HEPATITIS C PATIENT BOOKLET Index 1 About Hepatitis C About Hepatitis C Page 1 Hepatitis C Transmission Page 3 Hepatitis C Disease Progression Page 4 Hepatitis C Diagnosis and Treatment
INFORMATION ABOUT HEPATITIS C PATIENT BOOKLET Index 1 About Hepatitis C About Hepatitis C Page 1 Hepatitis C Transmission Page 3 Hepatitis C Disease Progression Page 4 Hepatitis C Diagnosis and Treatment
HEPATITIS C. The Facts. Get Tested. Get Cured! Health
 HEPATITIS C The Facts Get Tested. Get Cured! Health EVEN IF YOU FEEL HEALTHY, HEPATITIS C MAY BE DAMAGING YOUR LIVER. Your liver keeps you healthy in many ways, such as by removing toxins from your blood
HEPATITIS C The Facts Get Tested. Get Cured! Health EVEN IF YOU FEEL HEALTHY, HEPATITIS C MAY BE DAMAGING YOUR LIVER. Your liver keeps you healthy in many ways, such as by removing toxins from your blood
The Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
 The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) There are 400 million people in the world who live with chronic hepatitis B, including France. Most people don t even know they are infected. But there are several important
The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) There are 400 million people in the world who live with chronic hepatitis B, including France. Most people don t even know they are infected. But there are several important
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC
 BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
Information about hepatitis C for patients and carers
 Information about hepatitis C for patients and carers What is hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is an illness caused by a virus which can be passed through blood from one person to another. It mainly affects the
Information about hepatitis C for patients and carers What is hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is an illness caused by a virus which can be passed through blood from one person to another. It mainly affects the
What you should. know
 H e p a t i t i s C What you should know Table of Contents Hepatitis C: a part of life for many people.......4 What is hepatitis C?.......................6 What does my liver do?....................8 How
H e p a t i t i s C What you should know Table of Contents Hepatitis C: a part of life for many people.......4 What is hepatitis C?.......................6 What does my liver do?....................8 How
Treating Chronic Hepatitis C. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Chronic Hepatitis C A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* has told you that you have chronic hepatitis C.
Treating Chronic Hepatitis C A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* has told you that you have chronic hepatitis C.
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C
 Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
www.hepinfo.ie Are you Hep C aware? awareness information support prevention To find out more visit
 Are you Hep C aware? awareness information support prevention To find out more visit www.hepinfo.ie What is Hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver, causing it to become inflamed
Are you Hep C aware? awareness information support prevention To find out more visit www.hepinfo.ie What is Hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver, causing it to become inflamed
A handbook for people who have injected drugs
 A handbook for people who have injected drugs Introduction This handbook has been written for current and ex-drug injectors. It gives information and advice about the hep C virus, and the tests you can
A handbook for people who have injected drugs Introduction This handbook has been written for current and ex-drug injectors. It gives information and advice about the hep C virus, and the tests you can
Hepatitis C treatment What to expect.
 Hepatitis C treatment What to expect. Anne Glass Hepatitis Clinical Nurse Consultant Liver Clinic SSWAHS Bankstown and Liverpool Hospital Contact 87384074 Monday -Friday What s hepatitis? Hepatitis means
Hepatitis C treatment What to expect. Anne Glass Hepatitis Clinical Nurse Consultant Liver Clinic SSWAHS Bankstown and Liverpool Hospital Contact 87384074 Monday -Friday What s hepatitis? Hepatitis means
New York State Department of Health. 9413 Rev. 10/05
 New York State Department of Health 9413 Rev. 10/05 WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION Did you know that in the United States, at least 1 in 4 people with HIV
New York State Department of Health 9413 Rev. 10/05 WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION Did you know that in the United States, at least 1 in 4 people with HIV
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION
 WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION Did you know that in the United States, at least 1 in 4 people with HIV is also infected with hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION Did you know that in the United States, at least 1 in 4 people with HIV is also infected with hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is
The Facts You Need To Know. Developed by
 The Facts You Need To Know Developed by TODAY YOU LL FIND OUT What s the big deal about the liver? What is hepatitis???? Common types of viral hepatitis How can I protect myself from viral hepatitis? What
The Facts You Need To Know Developed by TODAY YOU LL FIND OUT What s the big deal about the liver? What is hepatitis???? Common types of viral hepatitis How can I protect myself from viral hepatitis? What
GENERAL INFORMATION. Hepatitis B Foundation - Korean Chapter Pg. 3 www.hepb.org
 GENERAL INFORMATION What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is the world's most common liver infection that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which attacks and
GENERAL INFORMATION What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is the world's most common liver infection that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which attacks and
Newly Diagnosed: HEPATITIS C. American Liver Foundation Support Guide
 Newly Diagnosed: HEPATITIS C American Liver Foundation Support Guide T he American Liver Foundation's mission is to facilitate, advocate, and promote education, support, and research for the prevention,
Newly Diagnosed: HEPATITIS C American Liver Foundation Support Guide T he American Liver Foundation's mission is to facilitate, advocate, and promote education, support, and research for the prevention,
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP. Primary Care Provider:
 Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
1.How did I get Hepatitis C?
 1.How did I get Hepatitis C? Sharing needles and syringes ( iv drug use ) or using contaminated straws to snort cocaine Reused needles or medications in a health care setting- (LV endoscopy outbreak, glucometers
1.How did I get Hepatitis C? Sharing needles and syringes ( iv drug use ) or using contaminated straws to snort cocaine Reused needles or medications in a health care setting- (LV endoscopy outbreak, glucometers
Living with HEP C. Facts about Hepatitis C
 Living with HEP C Facts about Hepatitis C IMPORTANT The information in this booklet is intended for people who are newly diagnosed with Hepatitis C (called Hep C for short). It can help you learn more
Living with HEP C Facts about Hepatitis C IMPORTANT The information in this booklet is intended for people who are newly diagnosed with Hepatitis C (called Hep C for short). It can help you learn more
Ribavirin/Pegylated Interferon Combination Therapy for People with Hepatitis C
 Ribavirin/Pegylated Combination Therapy for People with Hepatitis C 1. Introduction 2. What the treatment does 3. When to take it 4. What is? 5. What is interferon? 6. What is pegylated interferon? 7.
Ribavirin/Pegylated Combination Therapy for People with Hepatitis C 1. Introduction 2. What the treatment does 3. When to take it 4. What is? 5. What is interferon? 6. What is pegylated interferon? 7.
Obstetric Cholestasis (itching liver disorder) Information for parents-to-be
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Obstetric Cholestasis (itching liver disorder) Information for parents-to-be page 2 You have been given this leaflet because you have been diagnosed with (or are suspected
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Obstetric Cholestasis (itching liver disorder) Information for parents-to-be page 2 You have been given this leaflet because you have been diagnosed with (or are suspected
Learning about Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Learning about Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease If you have chronic kidney disease (CKD), you want to learn all you can about your disease and what you can
Learning about Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease If you have chronic kidney disease (CKD), you want to learn all you can about your disease and what you can
Take Action Against Hepatitis C For People in Recovery From Mental Illness or Addiction
 Take Action Against Hepatitis C For People in Recovery From Mental Illness or Addiction Attention treatment providers in behavioral health programs! This booklet is intended for use with clients who: Are
Take Action Against Hepatitis C For People in Recovery From Mental Illness or Addiction Attention treatment providers in behavioral health programs! This booklet is intended for use with clients who: Are
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet METHOTREXATE We hope this fact sheet will provide you with some information about Methotrexate and answer some of the questions you may have. Methotrexate is available in tablet
Patient Information Leaflet METHOTREXATE We hope this fact sheet will provide you with some information about Methotrexate and answer some of the questions you may have. Methotrexate is available in tablet
Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox
 What is Ai-Detox? Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox Ai-Detox is a Chinese herbal medicinal formula, produced using state of the art biotechnology, which ensures the utmost standards in quality and safety.
What is Ai-Detox? Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox Ai-Detox is a Chinese herbal medicinal formula, produced using state of the art biotechnology, which ensures the utmost standards in quality and safety.
Hepatitis B. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Hepatitis B U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
What I need to know about Hepatitis B U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
THE A, B, C S OF HEPATITIS. Matt Eidem, M.D. Digestive Health Associates of Texas 1600 Coit Road Suite #301 Plano, Texas 75075 (972) 867-0019
 THE A, B, C S OF HEPATITIS Matt Eidem, M.D. Digestive Health Associates of Texas 1600 Coit Road Suite #301 Plano, Texas 75075 (972) 867-0019 WHAT IS HEPATITIS? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver
THE A, B, C S OF HEPATITIS Matt Eidem, M.D. Digestive Health Associates of Texas 1600 Coit Road Suite #301 Plano, Texas 75075 (972) 867-0019 WHAT IS HEPATITIS? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services
 Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules. What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST?
 MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
Hepatitis C - genotype 2/3
 Hepatitis C - genotype 2/3 Information for you Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other
Hepatitis C - genotype 2/3 Information for you Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other
Bloodborne Pathogens. San Diego Unified School District Nursing & Wellness Program August 2013
 Bloodborne Pathogens San Diego Unified School District Nursing & Wellness Program August 2013 Why Another In-service?? Cal/OSHA mandates that employees with occupational exposure are informed at the time
Bloodborne Pathogens San Diego Unified School District Nursing & Wellness Program August 2013 Why Another In-service?? Cal/OSHA mandates that employees with occupational exposure are informed at the time
Hepatitis C. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Hepatitis C U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
What I need to know about Hepatitis C U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Like cocaine, heroin is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Heroin is highly addictive.
 Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Hepatitis C. Screening, Diagnosis and Linkage to Care
 Hepatitis C Screening, Diagnosis and Linkage to Care Diagnosis If your hepatitis C antibody test is reactive, a second test will be needed to diagnose and determine if you are currently infected. Screening
Hepatitis C Screening, Diagnosis and Linkage to Care Diagnosis If your hepatitis C antibody test is reactive, a second test will be needed to diagnose and determine if you are currently infected. Screening
The most serious symptoms of this stage are:
 The Natural Progression of Hepatitis C The natural history of hepatitis C looks at the likely outcomes for people infected with the virus if there is no medical intervention. However, the process of trying
The Natural Progression of Hepatitis C The natural history of hepatitis C looks at the likely outcomes for people infected with the virus if there is no medical intervention. However, the process of trying
You. guide to tuberculosis treatment and services
 Adapted from TB and You: A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services with permission from Division of Public Health TB Control Program State of North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
Adapted from TB and You: A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services with permission from Division of Public Health TB Control Program State of North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
english facts about hepatitis A, B and C
 english facts about hepatitis A, B and C What is hepatitis? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many viruses can cause liver inflammation, including the hepatitis A, B and C viruses. Some people
english facts about hepatitis A, B and C What is hepatitis? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many viruses can cause liver inflammation, including the hepatitis A, B and C viruses. Some people
Answering your questions on Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML)
 Answering your questions on Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML) Your guide to understanding CML and Glivec (imatinib) treatment The information in this booklet is designed to help you understand chronic myeloid
Answering your questions on Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML) Your guide to understanding CML and Glivec (imatinib) treatment The information in this booklet is designed to help you understand chronic myeloid
MEDICATION GUIDE SYLATRON (SY-LA-TRON) (Peginterferon alfa-2b)
 MEDICATION GUIDE SYLATRON (SY-LA-TRON) (Peginterferon alfa-2b) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking SYLATRON, and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication
MEDICATION GUIDE SYLATRON (SY-LA-TRON) (Peginterferon alfa-2b) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking SYLATRON, and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication
Yes, Tuberculosis is a serious problem all over the world. Between 6 and 10 million in South Africa are infected by the TB germ.
 What is TB? Do many people get tuberculosis (TB)? Yes, Tuberculosis is a serious problem all over the world. Between 6 and 10 million in South Africa are infected by the TB germ. It is infectious, so it
What is TB? Do many people get tuberculosis (TB)? Yes, Tuberculosis is a serious problem all over the world. Between 6 and 10 million in South Africa are infected by the TB germ. It is infectious, so it
MANAGING ANEMIA. When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure. www.kidney.org
 MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
Sofosbuvir, Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C
 Sofosbuvir, Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Department of Hepatology Digestive Diseases Centre Patient Information This leaflet is designed to give you important information
Sofosbuvir, Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Department of Hepatology Digestive Diseases Centre Patient Information This leaflet is designed to give you important information
Viral Liver Disease. The Liver and Its Functions
 Viral Liver Disease The Liver and Its Functions The liver, the body's largest organ weighing about three pounds, is located on the right side of the abdomen, protected by the lower rib cage. It is responsible
Viral Liver Disease The Liver and Its Functions The liver, the body's largest organ weighing about three pounds, is located on the right side of the abdomen, protected by the lower rib cage. It is responsible
Information about. Hepatitis C. What is Hepatitis C? Who should be tested for Hepatitis C?
 Information about Hepatitis C What is Hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting the liver, caused by the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C is now thought to be the most common cause
Information about Hepatitis C What is Hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting the liver, caused by the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C is now thought to be the most common cause
How To Care For A Sick Person
 39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA
 CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA WHAT IS CANCER OF THE LIVER? Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form and it comes from the main type of liver cell, the hepatocyte. About 3 out 4
CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA WHAT IS CANCER OF THE LIVER? Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form and it comes from the main type of liver cell, the hepatocyte. About 3 out 4
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
MEDICATION GUIDE JUXTAPID (JUKS-tuh-pid) (lomitapide) capsules
 MEDICATION GUIDE JUXTAPID (JUKS-tuh-pid) (lomitapide) capsules Read this Medication Guide before your treatment. What is the most important information I should know about JUXTAPID? JUXTAPID is available
MEDICATION GUIDE JUXTAPID (JUKS-tuh-pid) (lomitapide) capsules Read this Medication Guide before your treatment. What is the most important information I should know about JUXTAPID? JUXTAPID is available
Ovarian cancer. Patient information from the BMJ Group. What is ovarian cancer? What are the symptoms?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
MEDICATION GUIDE. PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
Get the Facts About. Disease
 Get the Facts About TB TUBERCULOSIS Disease What s Inside: 3 PAGE Get the facts, then get the cure 4 PAGE 9 PAGE 12 PAGE Learn how TB is spread Treatment for TB disease Talking to family and friends about
Get the Facts About TB TUBERCULOSIS Disease What s Inside: 3 PAGE Get the facts, then get the cure 4 PAGE 9 PAGE 12 PAGE Learn how TB is spread Treatment for TB disease Talking to family and friends about
Alcohol and the Liver
 The facts about... Alcohol and the Liver Five key things you need to know This is a part of your body that regularly works overtime. The liver is our largest organ and it has 500 different roles. One of
The facts about... Alcohol and the Liver Five key things you need to know This is a part of your body that regularly works overtime. The liver is our largest organ and it has 500 different roles. One of
Chemotherapy What It Is, How It Helps
 Chemotherapy What It Is, How It Helps What s in this guide If your doctor has told you that you have cancer, you may have a lot of questions. Can I be cured? What kinds of treatment would be best for me?
Chemotherapy What It Is, How It Helps What s in this guide If your doctor has told you that you have cancer, you may have a lot of questions. Can I be cured? What kinds of treatment would be best for me?
Fairview Specialty Pharmacy. What You Need to Know about Hepatitis C
 Fairview Specialty Pharmacy What You Need to Know about Hepatitis C 2 What You Need to Know about Hepatitis C What is hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is a liver disease. Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver.
Fairview Specialty Pharmacy What You Need to Know about Hepatitis C 2 What You Need to Know about Hepatitis C What is hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is a liver disease. Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver.
Beginner's guide to Hepatitis C testing and immunisation against hepatitis A+B in general practice
 Beginner's guide to Hepatitis C testing and immunisation against hepatitis A+B in general practice Dr Chris Ford GP & SMMGP Clinical Lead Kate Halliday Telford & Wrekin Shared Care Coordinator Aims Discuss:
Beginner's guide to Hepatitis C testing and immunisation against hepatitis A+B in general practice Dr Chris Ford GP & SMMGP Clinical Lead Kate Halliday Telford & Wrekin Shared Care Coordinator Aims Discuss:
Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain
 Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. You will find it useful
Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. You will find it useful
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid.
 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
AUBAGIO Conversation Starter
 AUBAGIO Conversation Starter When you are choosing a multiple sclerosis (MS) treatment for the first time or are considering switching your MS therapy, there can be a lot to think about for both you and
AUBAGIO Conversation Starter When you are choosing a multiple sclerosis (MS) treatment for the first time or are considering switching your MS therapy, there can be a lot to think about for both you and
It is important that you tell your family and the people closest to you of this increased sensitivity to opioids and the risk of overdose.
 MEDICATION GUIDE VIVITROL (viv-i-trol) (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving VIVITROL injections and each time you receive an injection.
MEDICATION GUIDE VIVITROL (viv-i-trol) (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving VIVITROL injections and each time you receive an injection.
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES
 HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
Methamphetamine. Like heroin, meth is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Meth is a highly addictive drug.
 Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
Share the important information in this Medication Guide with members of your household.
 MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
What Is. Norovirus? Learning how to control the spread of norovirus. Web Sites
 Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment
 In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
LIVING WITH CHEPATITIS
 Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment LIVING WITH CHEPATITIS Take control. Learn more. Be sure. It is estimated that 3.9 million Americans are currently living with hepatitis C. If you have
Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment LIVING WITH CHEPATITIS Take control. Learn more. Be sure. It is estimated that 3.9 million Americans are currently living with hepatitis C. If you have
Secondary liver cancer Patient Information Booklet
 Secondary liver cancer Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Secondary liver cancer Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Information for patients receiving short-term hormone treatment and radiotherapy for prostate cancer
 Information for patients receiving short-term hormone treatment and radiotherapy for prostate cancer Northern Centre for Cancer Care (NCCC) Freeman Hospital Introduction This leaflet has been written to
Information for patients receiving short-term hormone treatment and radiotherapy for prostate cancer Northern Centre for Cancer Care (NCCC) Freeman Hospital Introduction This leaflet has been written to
How can you protect yourself from infections?
 How can you protect yourself from infections? Your Infection Prevention Guide www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents Preventing an infection is an important part of your kidney care...3 Things you can do...4
How can you protect yourself from infections? Your Infection Prevention Guide www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents Preventing an infection is an important part of your kidney care...3 Things you can do...4
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
C. difficile Infections
 C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM
 MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM The purpose of preventive exams is to screen for potential health problems and provide education to promote optimal health. It is best practice for chronic health problems
MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM The purpose of preventive exams is to screen for potential health problems and provide education to promote optimal health. It is best practice for chronic health problems
Hepatitis A. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Hepatitis A U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
What I need to know about Hepatitis A U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE)
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
Vincristine by short infusion Doxorubicin by injection Cyclophosphamide by injection Rituximab by an infusion over between 60 minutes to a few hours
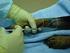 R-CHOP R-CHOP This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce the risk of the cancer coming back, for others
R-CHOP R-CHOP This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce the risk of the cancer coming back, for others
TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY- MEDICAL
 TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY- MEDICAL Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 You have been offered a medical termination of pregnancy using mifepristone. You will have been given some verbal
TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY- MEDICAL Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 You have been offered a medical termination of pregnancy using mifepristone. You will have been given some verbal
Learn about Diabetes. Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. You can learn how to take care of your diabetes.
 Learn about Diabetes You can learn how to take care of your diabetes and prevent some of the serious problems diabetes can cause. The more you know, the better you can manage your diabetes. Share this
Learn about Diabetes You can learn how to take care of your diabetes and prevent some of the serious problems diabetes can cause. The more you know, the better you can manage your diabetes. Share this
Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS
 Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Carlos Healey, diagnosed in 2001 The Three Most Common Eye Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis Blood Pressure & Pulse Height & Weight Complete
Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Carlos Healey, diagnosed in 2001 The Three Most Common Eye Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis Blood Pressure & Pulse Height & Weight Complete
HIV -The Facts BLT 043
 Human Im munodeficiency Virus HIV -The Facts NHS Dumfries & Galloway would like to acknowledge NHS Greater Glasgow for the use of information contained in this leaflet. This leaflet is also available on
Human Im munodeficiency Virus HIV -The Facts NHS Dumfries & Galloway would like to acknowledge NHS Greater Glasgow for the use of information contained in this leaflet. This leaflet is also available on
Testosterone & Testosterone Replacement Therapy
 your PR.i.VATES Testosterone & Testosterone Replacement Therapy www.yourprivates.org.uk CONTENTS TESTOSTERONE & TRT Contents Introduction 3 Purposes of testosterone 4 How will I be affected by an orchidectomy?
your PR.i.VATES Testosterone & Testosterone Replacement Therapy www.yourprivates.org.uk CONTENTS TESTOSTERONE & TRT Contents Introduction 3 Purposes of testosterone 4 How will I be affected by an orchidectomy?
BREAST CANCER TREATMENT
 BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre December 2014 Contents About this booklet 1 Your First Oncology Consultation
BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre December 2014 Contents About this booklet 1 Your First Oncology Consultation
PATIENT INFORMATION INSURANCE INFORMATION
 (mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
(mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
Coping With Alcohol Withdrawal
 Coping With Alcohol Withdrawal Central and North West London NHS Foundation Trust Addictions Services Alcohol withdrawal When a person is dependent on alcohol and suddenly stops drinking there are certain
Coping With Alcohol Withdrawal Central and North West London NHS Foundation Trust Addictions Services Alcohol withdrawal When a person is dependent on alcohol and suddenly stops drinking there are certain
HEPATITIS A, B, AND C
 HEPATITIS A, B, AND C INTRODUCTION Hepatitis is a medical term that means infection and inflammation of the liver, and hepatitis is caused by infection with a virus. There are seven types of hepatitis,
HEPATITIS A, B, AND C INTRODUCTION Hepatitis is a medical term that means infection and inflammation of the liver, and hepatitis is caused by infection with a virus. There are seven types of hepatitis,
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
Understanding. Depression. The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself. Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members
 TM Understanding Depression The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members Understanding Depression Depression is a biological illness. It affects more than
TM Understanding Depression The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members Understanding Depression Depression is a biological illness. It affects more than
Pain and problem drug use
 Pain and problem drug use Information for patients Prepared by the British Pain Society in consultation with the Royal College of Psychiatrists, the Royal College of General Practitioners and the Advisory
Pain and problem drug use Information for patients Prepared by the British Pain Society in consultation with the Royal College of Psychiatrists, the Royal College of General Practitioners and the Advisory
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
Radioactive iodine treatment for thyroid cancer
 Radioactive iodine treatment for thyroid cancer This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding thyroid cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page
Radioactive iodine treatment for thyroid cancer This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding thyroid cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems
 Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine
 Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Introducing hepatitis B
 Introducing hepatitis B 1 Introducing hepatitis B: Contents To jump to the section you require, click on the page number below. Introducing hepatitis B: 10 things you (probably) didn t know about the virus
Introducing hepatitis B 1 Introducing hepatitis B: Contents To jump to the section you require, click on the page number below. Introducing hepatitis B: 10 things you (probably) didn t know about the virus
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
What you need for Your to know Safety about longterm. opioid pain care. What you need to know about long-term opioid
 What you need to know about longterm opioid pain care. What you need to know about long-term opioid and the Safety of Others pain care. TAKING What you OPIOIDS need to know about long-term RESPONSIBLY
What you need to know about longterm opioid pain care. What you need to know about long-term opioid and the Safety of Others pain care. TAKING What you OPIOIDS need to know about long-term RESPONSIBLY
Safe Tattooing How is it done? Things to remember before getting a tattoo: What are the risks? Hepatitis B Hepatitis C: HIV/AIDS:
 Safe Tattooing How is it done? A tattoo consists of pigmentation that is inserted into the second layer of the skin. A vertical vibrating instrument is used to inject the pigment 50 to 3000 times per minute.
Safe Tattooing How is it done? A tattoo consists of pigmentation that is inserted into the second layer of the skin. A vertical vibrating instrument is used to inject the pigment 50 to 3000 times per minute.
