Scaling trade-offs between crop productivity, carbon stocks and biodiversity in shifting cultivation landscape mosaics: the FALLOW model
|
|
|
- Neil West
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Keywords: ECOLOGICAL MODELLI NG ELSEVIER Eologial Modelling 149 (22) elsevier oom/loate/eolmodel Saling trade-offs between rop produtivity, arbon stoks and biodiversity in shifting ultivation landsape mosais: the FALLOW model Meine van Noordwijk * International Centre for Researh in Agroforestry, ICRAF SE Asia, PO Box 161, Bogor 161, Indonesia Abstrat Saling rules other than those based on area ('sale-dependene') for 'environmental servie funtions' suh as produtivity, biodiversity and arbon stoks depend on spatial variability and spatial patterns within the landsape, on lateral flows and neighbourhood effets, and on the impat of sale-dependent 'ators' and 'agents'. Previous models of shifting ultivation or rop-fallow rotations have desribed the fate of soil fertility and rop produtivity for an average plot, as a funtion of intensity of land use, without expliit onsideration of the saling rules between plot and landsape. Up to medium land use intensities, a negative tradeoff exists between farmers's interest in rop produtivity per unit area, and environmental interests in arbon stok and other parameters related to age of the fallow vegetation suh as biodiversity. If land use intensity inreases beyond a ritial point, land will further degrade from a farmer's as well as from environmental perspetive. In the Forest, Agroforest, Low-value Lands Or Waste model ('FALLOW?') this desription is applied at landsape sale to a mosai of plots, to investigate the transient behavior under non-equilibrium onditions for different land use intensifiation senario's. The FALLOW model is implemented in the STELLA environment and in the default form keeps trak of the soil fertility hanges in 1 fields, whih may differ in initial fertility and dynamis. During any year in the simulation a number of these fields is ropped, while others are fallowed. During the fallow period aboveground C stoks aumulate and plot-level biodiversity hanges in harater during the suession from pioneer, via early and late seondary vegetation into 'primary' forest. The model user an define the time frames for eah of these transitions, as well as determine the degree of speies overlap between ategories and area-based saling rules within eah ategory, to derive an indiator of landsape-level biodiversity. The model allows omparisons of spatially segregated as well as integrated solutions to multiple funtionality of land use by applying 'forest reserve' rules. Depending on the amount of between-plot variation in parameter values, the trade-off between arbon stok and rop produtivity an shift by a fator 2, even though both properties are diretly related to area. The trade-off between loal and external stakeholder interests for a landsape mosai an thus differ from that derived for a 'representative landsape element'. (!:;) 22 Elsevier Siene B. V. All rights reserved. Agriultural intensifiation; Biodiversity; Carbon stok; Land use hange; Saling; Shifting ultivation.tel.: ; fax: address: m.van-noordwijk@giar.org (M. van Noordwijk) /2/$ -see front matter (!;) 22 Elsevier Siene B.V. All rights reserved. PII: S34-38(1)518-X
2 114 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) Introdution Trenbath (1984, 1989) formulated a simple model of rop-fallow rotations, whih an be solved by algebra when a single 'representative' field is followed over time (Van Noordwijk, 1999). Intensifiation of a rop fallow rotation an be refleted in a redued duration of the fallow and Conerns over the rate of tropial deforestation have led to a renewed ioterest in shifting ultivation systems and early stages of agriultural intensifiation, and their impat on 'environmental servie funtions' suh as produtivity, biodiversity and arbon stoks in the forest margin (Perrings et al., 1995; Van Noordwijk et al., 1998; Tomih et al., 1998a,b, 21). Efforts to 'sale up' from plot-level measurements and assessments to landsape-level impats have to deal expliitly with the saling relations that are likely to differ between the various land funtions, leading to sale-dependene of the trade-offs between these funtions as well. Saling relations depend on spatial variability and spatial patterns within the landsape, on lateral flows and neighborhood effets, and on the impat of sale-dependent 'ators' and 'agents' (Van Noordwijk et al., in press). Use of natural resoures an only be sustained if it balanes the rate of replenishment, and thus sustainable-use strategies require a detailed understanding of the replenishment proesses. Yet, most resoure use problems share a ommon dynamis, with a 'diminishing returns' or 'asymptoti' approah to a maximum resoure availability when the resoure is left alone (not harvested), and a proportional derease due to harvesting, leading to dereasing returns to harvesting effort. This may apply to resoures as different as fisheries, forestry, rubber tapping and soil fertility replenishment by natural vegetation in rop-fallow rotations. Here we fous on a rop-fallow model, but most of its dynamis would, mutatis mutandis, apply to other resoures as well. Whereas 'shifting ultivation' systems in whih a long tree fallow phase alternates with a few years of ropping an sustain rop prodution at aeptable levels and favorable returns to labor, it has been observed in many parts of the world (Hagreis, 193; Nye and Greenland, 196; Ruthenberg, 1976) that with inreased pressure on land and shorter fallow yles, rop prodution will fall short of requirements and the 'system breaks down'. its onsequenes for long term prodution an be evaluated. Intensifiation (inreased use of land for rop prodution) an initially inrease rop yield per unit area under the rotation, while reduing yield per unit ropped area, and the impats on returns to labor depend on the ratio.of labor osts for learing a fallow and those for tending a rop. The highest returns to land are, aording to the Trenbath model, obtained in systems where soil fertility under the fallow is allowed to return to around 55% of the maximum value, independent of other model parameters (Van Noordwijk, 1999). Beyond this point, further intensifiation will lead to a rapid degradation unless a tehnology shift modifies essential parameters of the model. This desription on the basis of a single 'representative' field, however, is not suffiient for judging the transition period of fallow intensifiation, when part of the landsape still has a relatively high fertility as remnant of past fallow lengths. Intensifiation of suh rop-fallow systems will initially inrease yields while dereasing terrestrial arbon stoks in soil and aboveground vegetation, but beyond the ritial intensity both C stok and yield will derease. The trade-off between loal (produtivity) and global (C stok) interests in suh a system, is thus likely to be non-linear. This trade-off is relevant to the urrent debate on the relation between poverty alleviation and environmental protetion, as artiulated in the global 'Alternatives to Slash and Burn' program (Tomih et al., 1998a). Similarly, intensifying fallow rotations an have a non-linear impat on landsape level biodiversity. At low intensities, rop-fallow rotations may inrease the diversity of vegetation types in the form of fallows of various ages, while allowing a substantial share of mature forest to persist. Although the average speies rihness per unit area at field sale is likely to derease, landsape level diversity may initially inrease; while further intensifiation is likely to redue all aspets of biodiversity.
3 2.2. M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) To explore these transition phases and their sale-dependene and test the robustness of the 'ritial fertility' limit, a distributed model was made that: (1) applies the Trenbath model rules for depletion and restoration of soil fertility to a large number of fields, ontributing to a single food (rie) store (2). Deisions on inrease or derease of rop intensity (fration of the land ropped in a single year) are simulated on the basis of the amount of food in the store and expeted to be gained per field, relative to the annual food requirement (3). Deisions on whih fields are to be used in a given year an be based on a number of rules, inluding a partial knowledge of the atual fertility of eah field (4). Four modules representing these aspets jointly drive the dynamis of a landsape mosai, that an be evaluated in terms of arbon stok, biodiversity and food seurity (Fig. 1). Here, we present results of using the spatially distributed model to explore: -impats of spatial heterogeneity in soil properties on the dynamis of the overall system, -impats of various deision rules for intensifiation on system dynamis, -effets of simulating farmer knowledge in seleting the best fields for urrent ropping, -effets of intensifiation on terrestrial C stoks and biodiversity at field and landsape sale, -effets of sale on the trade-off between loal (produtivity) and global (biodiversity and C- stok) benefits. Fig. 1. Overview of the model modules in the FALLOW model. Model 2.1. Model overview The FALLOW model (available via fallow.htm) is a Stella implementation of a set of equations proposed by Trenbath (1984) of a shifting ultivation or rop-fallow rotation system where rie is produed on the basis of soil fertility restoration during fallows, and on,,- sumed on the basis of population density and per-apita food demand. The simulated area an be interpreted as 1 km2, split into 1 fields of 1 ha eah but individual field sizes an vary and a different total area an be simulated as well. Human population density is expressed in persons per km2, rop yields and rie storage inmg. The model has four ore modules that represent the fate of plot-level soil fertility, the rie store, deisions on next years ropping intensity and the spatial implementation of this ropping :plan (Fig. 1). In a yearly time step the program IbOpS through these four modules. Three other modules derive the onsequenes of the farmers land use deisions for food seurity, C stoks and biodiversity. Table 1 provides the definitions, dimensions and default parameter values for the model. Soil fertility module The soil fertility module is based on the Trenbath (1984) model (Van Noordwijk, 1999) and desribes build-up of soil fertility by two parameters, a maximum level S_Finf and a half-reovery time S_Kfert, and deline during ropping as a simple proportion S_FertDepletion. There are two ways of initializing the model: speifying values for eah field in a spreadsheet linked to the Stella model, or by speifying a range of values within whih random hoies are made. If external inputs are used as fertilizer (S_FertilUse? = 1), their effet on soil fertility is represented by the S_Kfertfertil parameter.
4 B_SpeRihPowe R_module: 116 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) Table I Main FALLOW input parameters, their definition and default values Aronym Definition Dimensions Range of value (default value) B_module: Biodiversity B_SpeOverlap Probability (fration) of speies overlap in speies omposition Dimensionless (Vegetation, Vegetation) between two vegetation types -1, arrays B_SpeRih_K B_SpeRihMax (Vegetation) B- VegClassBound (Vegetation) Parameter influening how speies rihness inrease with time, indiation of 'half-enrih-time'. Biodiversity parameter at plot level Maximum of speies rihness (number of speies) per field reahed. Biodiversity parameter at plot level Biodiversity parameter at landsape level: power of relation between number of fields and total rihness for eah vegetation lass Minimum age of vegetation lass. For young seondary forest, old seondary forest, old growth primary forest, early, full and late-produtive AF stage. Values for the first three vegetation lass has to be in asending order. Year 5-1 (3) # Speies/plot 5-5 (2) Dimensionless.1-.4 (.2) Year C_module: arbon stoks C_AumRateF Yearly inrement in C stok during fallow periods mg ha-1 year- C_CropY _Cstok Time-averaged aboveground C stok for ropping years mg ha-1 C_CstokAGMax Maximum aboveground C stok for a forest (end-point of mg ha-1 fallow development) C_StokBGmax Belowground C stok at maximum soil frtility mg ha-1 (5,2,5,1, 2, 45) 2-15 (8) 1-1 (5) 1--4 (25) 2-1 (5) H_module: household deisions H_DistWgtCropping Relative weight of the distane to the village relative to Dimensionless urrent soil fertility in detennining attrativeness of a field for a new ropping yle H_FieldRule Parameter influening deision on whih fiel to rop. I, Dimensionless Deisions on whih fields to rop are not based on urrent fertility; 2, Farmers lassify fields by soil fertility (and distane to village) and hoose the best fields to rop H_ForestResFra Fration of reserved forest area Dimensionless H_RegulMeth Parameter to adjust ropping intensity:, onstant ropping Dimensionless intensity; 1, based on the rie store only; 2, inludes onsumption and yield estimates, based on reent experiene. H_RieStokTarget Target number of years annual rie onsumption an be met Year from the rie store H_StepIntensif Parameter influening maximum hanges in ropping intensity Dimensionless due to deviation of yield from target. Maximum hanges is H_MaxStep x H_IntensifiationStep H_StepMax Parameter influening maximum hanges in ropping intensity Dimensionless due to deviation of yield from target. Maximum hanges is H_MaxStep x H_IntensifiationStep H- TimeCrop Number of onseutive years that a field is ropped, one the Year fallow vegetation has been removed H- YieldMemory Parameter governing farmer's memory of past rop yield:, Dimensionless last years results replae all memory; I, no learning from reent experiene -1 () or 2 (2) -1 (), 1 or 2 (2) -5 (2..5) (.5) (.75) rie store R_ConvEff Conversion effiieny of mineralized nutrients (linked to thederease mg.5-2 (1) in soil fertility in a ropping year) into rop yield
5 .1-1 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) Table (Continued) Range of value (default value) R_CropWorstW Parameter defining weather/limate in relation to rop growth. Dimensionless --{).99 (.5), weather are bad for rop;.99, weather are appropriate for R_LossStoreFra growing rop Fration of rie lost from the store per year r., DlIlleuslouless.1-1 (.15) R_PopDens Human population ] Persons -1 (1) R_ProCapFoodReq Annual food requirement pro apita ] llg per person per.1-1 (.5) year S _module: soil fertility per field S_FertDepletion Fration by whih soil fertility apital stok dereases by Dimensionless mineralization during I year of ropping S_FertiIizUse? Parameter determining use of fertilizer., system not using Dimensionless fertilizer; I, using fertilizer S_Finf_Avg Soil fertility value to whih the soil returns after an infinitely fertility units long fallow period S_Finf_range The range of S_Finf_Avg variation between fields Dimensionless S_InitRFH Parameter defining a maximum multiplier for initial soil fertility units. S_InitRFL Parameter defining a minimum multiplier for initial soil fertility Dimensionless units. Initial soil fertility is varied, relative to F _infinity, within a range of (S_InitRFH-S_InitRFL) S_Kfert_Avg Half reovery time for soil fertility during fallow period. Year Suggested values: Natural fallow, 1-2; Improved fallow, 5-1; Cover rop, 2-5; Fertilizer,.5-2. S_Kfert_Range The range of S_Kfert variation between fields Dimensionless S_Kfertfertil Parameter influening impat of fertilizer use on soil fertility Dimensionless (.2) or I () -2 {to) -2 (.3).2-1 (.95).1-1 (.1) -2 (15) -2 (.3) o.1-1/)(7) 2.3. Rie_store and onsumption module annual food demand ould be met during a simulation run is aumulated and averaged in the food seurity module. Mineralization of stored soil reserves forms the basis of soil fertility during a ropping year and the R- ConvEff parameter indiates the effiieny with whih the atual loss of soil fertility is translated into a rop yield. This effiieny depends on the type of staple rop that is used (named 'rie' in the default example), and on the (arbitrary) units in whih soil fertility is measured (here on a -1 sale). The impat of limati variability on rop yields an be superimposed on the soil fertility based potential yield, by multipliation with a random variable [R_CropWorstW-l]. In the Rie_Store module, we keep trak of the ontents of the rie store, adding all yields and using it to feed people (R_PopDens x R_Pro- CapFoodReq), unless it is lost from the store (at a annual fration of R_StoreLossFra, by unspeified rats, mie-or insets). The degree to whih 2.4. Household deision module The ropping intensity (fration of the land ropped in any given year) is a major ontrol variable in the way the landsape evolved during the simulation. The model provides different routines for simulating household deisions on intensifiation of the rop-fallow rotation in response to the amount of food reserves in the store. If R_RegulMeth = I intensifiation deisions are based on the rie store only, in relation to a target value (H_RieStoktarget); if H_RegulMeth = 2 the deision algorithm inludes onsumption and yield estimates, based on reent experiene (the H- YieldMemory parameter gives weight to previous years and speifies the 'learning style': =
6 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) =..=.. 'C '13 ri) Plot-level rihness Time sine last S&B i J@:'\ Vegetation lasses defined by age, e.g.: -5 pioneer 5-2 Young seondary 2-5 Late seondary > 5 Forest!! Si = S 1 A zi < ' ==-:"::: /,.. Stotal = Li (Si -Lj Pij Sj) Fig. 2. Relations used for deriving total speies rihness of the landsape, Stotal, on the basis of the speies rihness of eah plot (related to its age sine the last S&B event), and the allometri saling rules for speies rihness within eah land over lass (based on its area A and the saling parameter zv and the overlap matrix PI; between land over types. most reent experiene replaes all past experiene, I = initial values not modified, intermediate values provide a mix of past and reent experiene). For either of these regulation methods, there is a maximum value (H_StepMax) to the hange in ropping intensity deemed possible in a single (yearly) timestep. Two methods are provided to implement deisions on ropping intensity. For H_Field_rule = I deisions on whih fields to rop in the oming year are based on the average length of fallow for the given ropping intensity, and a length of eah ropping yle set by H- TimeCrop. The atual implementation to set the or I value for H_Cropped? is 'if mod(time + H_NumbFields- H_FieldNumb[Field], (H- TimeCrop + H- Timefallow» < H- TimeCrop then I else '. For H_Fieldrule = 2 farmers are assumed to lassify fields by soil fertility (in 'standardized normal' lasses, based on the urrent average and S.D.) and distane to the village (H_Dist- WgtCropping), and hoose the best fields urrently available to rop. Via the H_ForestRes- Fra parameter a ertain fration of the landsape an be set aside as forest reserve, not available for growing food rops. Carbon stok module The setors desribed so far generate the dynamis of the landsape mosai and determine whih fields will be ropped in whih years, and over what length of time fallow vegetation will be allowed to grow in the non-ropped fields. The onsequenes of this dynami for C stoks and Biodiversity are based on the length of the fallow period for eah plot. The parameter C_Aum- RateF determines the annual C stok inrement (mg ha -I year-i) in fallow vegetation (Woomer et al., 2), up to an endpoint of C_CStokAG- Max. The C -Crop Y -Cstok parameter speifies the (time-averaged) aboveground C stok for ropping years, Belowground C stoks are assumed to be proportional to the soil fertility indiator and the C_stok BGmax parameter indiates the belowground C stok (in mg ha -I) at maximum soil fertility. Biodiversity module The biodiversity module (Fig. 2) inludes expliit saling rules from plot/field to landsape level. First of all, the speies rihness of eah fallow or forest plot is assumed to be a funtion of the time sine the last field learing ('slash and bum') event. This relation is haraterized by two parameters: a maximum value B_SpeRihMax (number of speies per unit field size) and a B_SpeRihK (year) parameter indiating the time after major disturbane [slash-and-bum (S&B) land learing] required to reah half of the maximum rihness. Data on (higher) plant rihness for a range of tropial land over types were indeed found to relate to time sine disturbane in a similar way (Gillison, 1999). On the basis of the time sine last learing, we an thus derive the plot-level rihness S of eah plot. The next step in the saling proess is to lassify the vegetation into age-lasses, suh as pioneer, young seondary, late seondary or forest vegetation.; the parameter B- VegClassBound allows the model user to adapt the ages used for eah transition. For eah lass an allometri relation between lass-level rihness and the number of fields is derived, driven by the parameters z in Fig. 2 (or
7 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) B_SpeRihPower in the model). This allometri saling rule was introdued by Arrhenius (1921) and is the urrent default model based on island biogeography theory (Rosenzweig, 1995). Finally, a total landsape level rihness is derived by summation over the various vegetation lasses, but orreting for the degree of overlap (the Pif parameter in Fig. 2 or the B_SpeOverlap matrix in the model). Default parameter values Table I speifies the various default parameter values that were hosen to be representative of a situation in the humid tropis where shifting ultivation, rop-fallow rotations, are still viable, at a relatively low population density of 1 persons per km2. While the parameters do not refer to any partiular site, their values were hosen on the basis of measurements in ASB benhmark sites (Gillison, 1999; Van Noordwijk et al., 1998; Woomer et al., 2). Population density in the ASB benhmark areas varies from 3 (Are, Brasil) to 6 (N. Lampung, Indonesia) persons per km2. Graphial output and spatial representation The STELLA environment provides for options on graphial output of timeseries or bi-plots of all variables used in the model. A simple routine was developed in the form of an EXCEL workbook to link maps of input parameters to the model and to onvert plot-level state variables into maps of soil fertility, C stok, vegetation type (Fig. 3) or plant speies rihness. This workbook is available at the same WWW site as the FALLOW model. Results Output for default parameter setting With the default parameters land use intensifies in the initial years (Figs. 3 and 4), but approahes a steady state in whih the relative areas of various suessional land over types remains onstant, although individual plots in the mosai keep hanging. In this default run there is enough to eat in eah year of the simulation (Fig. 4A), while soil fertility delines (Fig. 4B). Primary forest gets replaed by pioneer and young seondary forest-a fration of the land is kept as 'forest reserve' (Fig. 4C). Initially, landsape level rihness in-reases while plot-level rihness delines (Fig. 4D). Landsape level rihness is initially maintained (or shows a slight inrease) while plot level rihness dereases (Fig. 4E). Carbon stoks derease while landsape level diversity initially inreases (Fig. 4F) Critial population density as funtion of fallow type and soil properties When the population density is inreased from the default value of 1 persons per km2 to a value of 17, the default parametrization leads to a rash senario (Fig. 5) after a ertain transition time in whih the soil resoures are depleted. The deline of soil fertility is a non-linear funtion of human population density, as it involves a threshold proess (Fig. 6B)..Within the struture and limitations of the FALLOW model, we an define a ritial human population density ('arrying apaity' for given tehnology and soil harateristis) as the highest population density for whih food suffiieny an be sustained over a IOO-year test period. As the model ontains random weather impats, a number of runs at eah population density is required. The arrying apaity so defined depends on both the S_Kfert (type of fallow) and inherent soil qualities (S_Finf) values (Table 2). Model sensitivity to soil and rop parameters Espeially if a population density is hosen that (just) leads to a rash senario, the influene of soil and rop parameters an be studied (Fig. 6C and D). If low-quality fallow vegetation (with a long half-reovery time for soil fertility, S_Kfert) is replaed by an 'improved' fallow vegetation that leads to more rapid restoration of soil fertility, a rash senario an be returned to a 'stable' domain (for onstant population density). Under the urrent model struture an inrease in the yield potential of the rop, refleted in a hange in
8 3.4. Fig. 12 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) 113-./26 the R_Conveff parameter (Fig. 6D) has a diret impat on.the 'intensifiation' deisions, as the model (impliitly) assumes a subsistene eonomy; growing rie only to supply for loal demand. Aording to the model, higher yielding rops will redue the need for reduing fallow lengths and thus ontribute to the maintenane of higher soil fertility levels. Landsape homogeneity If the routines are used that expliitly selet thefields with the highest urrent soil fertility (H- Fieldrule = 2; Fig. 6A; H_DistWgtCropping = ), the returns on labor will be onsistently higher than with the default (H_Fieldrule = 1). A hange in this setting reflets a more omplete loal knowledge of the fertility status of all plots. and the absene of other onstraints on aess to plots (apart from the H_ForestResFra rule). The setting of this H_Fieldrule parameter influenes the spatial heterogeneity in the landsape and the variation in soil fertility (linked to soil C) as well as aboveground C stok (Fig. 7). As the homogenizing 'reaming off of the landsape (H_Field. rule = 2) leads to higher rie yields, but lower C legend ropped pioneer y_fallow o_fallow forest Time Example of map (time series) showing land over in a five-step lassifiation (ropped land, pioneer vegetation, young fallow,old fallow and forest) for a 'default' run of the FALLOW model; the area in the lower right omer is indiated as 'forest reserve'and is not available for growing food rops.
9 o C. E M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) A kg rie per day of work 1.Cropratio RieStore aa a -.Rie'o ns dj If! to r,-- aa a a %:I C I tiq DC r- I a D 1 C CCC C," I Eo I I r a a-6 a r r ; a r..o CD AreaHighForest AreaOldSe 6 AreaYoungSe AreaPioneer 6 t 6 'U 4.-\ u 6 -j \:66 CI.- 6 I. 6 ' 2 IC B. D..! u GI Landsape SpeHighForest SpeOldSe 6 SpeYoungSe SpePioneer Time, years Time, years F III 4 1 U 35 1 Co 3 III -fa 25 1 > fa C ;) ';: 1 ;) 5 III "C oj D Plot-level speies rihness 1/1.S! U GI Co 1/1 GI > - GI Co a U 1/1 'C a.j Rihness C stok, Mg ha-l. Fig. 4. TilIle series and solile of the lilain trade-offs during a default run with a population density of 1 persons per kin2: A. Cropping intensity and food onsulilption; B. Soil fertility for a 5% salilple of the individual plots plus the landsape level average;c. Land over dynainis (perentage of the total area under various land over types), D. Landsape level speies rihness and the rihness in eah of the vegetation lasses per se (the total is less than the SUlIl of the lasses, beause of speies overlap), E. Trajetory of landsape level rihness versus plot-level rihness; F. trajetory of arbon stoks versus landsape level diversity stoks and biodiversity (results not shown, but similar to those for C stoks), the trade-off between loal benefits (rie yields) and global benefits (C stok and biodiversity) does hange by nearly a fator 2 in year 1. Landsape-versus plot level model preditions The potential impat of an 'improved fallow'versus a 'natural fallow', by reduing the S_Kfertparamete was explored on the relation between
10 4 122 M. van Noordwzjk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) UI 35 QI U 3 QI Q. 25 UI..2.!! 15 Q....1,. 5 -Landsape Rihness SpeHighForest SpeOldSe A D SpeYoungSe Spe Pioneer Time, years UI.! u GI C- UI 35 3 VI > GI VI 25 > ĠI > QI C 2 C - 2. > GI U Co 15 Ie a ";: U..1 u 1 III UI " 'g 5 C Ie..I a -J Plot-level speies rihness III.S? u > Co III 4 3. C stok, M 9 ha-1 Fig. 5. Idem as Fig. 4, for a human population density of 17 persons per km2; NB, the rie store in Fig. 5A represents the situation at the end of eah year, after additions of the new harvest and subtration of the annual onsumption. urrent soil fertility of the plots that are ropped with the returns on labor and the rie yields per total area (Fig. 8A and C, respetively). Both these relations, averaged over a landsape with its variability, are essentially the same as followed from the algebrai analysis of the Trenbath model (Van Noordwijk, 1999). The maximum yields per area are obtained when the relative soil fertility of newly opened fields is about.6, whih is lose to the value of about.55 found in the algebrai steady state solution. The urrent model, however, predits that no simple relation an be found between preeding age of the fallow and the returns to labor or land, in ontrast to steady state solutions where age of fallow would be diretly linked to urrent fertility. At landsape level the
11 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) B 1 >- 8 6 Q).. Q) > 4 < 2 D Kfert = 5 yeari:=::); Years Years 8 1 Fig. 6. Sensitivity analysis for a number of main parameters in the model; A. Yield per unit labor (kg rie per day) for appliation of FieldRule 1 (no plot-level knowledge of soil fertility) and FieldRule 2 (with good knowledge of plot level fertility); B. Changes in landsape level average soil fertility (arbitrary units) for human population densities in the range 1-5 persons per km2); C. idem, for values of the S_Kfert parameter in the range 5-2 year, representing different types of fallow vegetation; D. idem, for three values of the R_ConvEff parameter, that relates food rop (in ri"e equivalents) yields ill mg ha -1 to eah unit derease in soil fertility. Table 2 Sustainability thresholds for human population densities (number of persons per km2) for shifting ultivation systems based on upland rie prodution during a 1-year test period aording to the FALLOW model, depending on the type of fallow vegetation and its typial fertility restoration apaity Kfert, and the inherent properties of the soil, determining the potential soil fertility Finf; riteria for ritial population density in at least five runs for eah parameter setting were: food suffiieny> 9% and landsape-level soil fertility> 5% of initial value Fallow vegetation Kfert (year) Inherent soil quality Degraded forest Good forest Improved fallow Cover rop trajetory of intensifiation, ombined with the individual plot histories, auses a substantial hange in the shape of the fallow-age-fertility relation (Fig. 8B and D), ompared with the results for a sequene of steady states (as in the algebrai solution)
12 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) Disussion The saling up of the plot level Trenbath model to the urrent landsape-level aount, demonstrated that the transient phenomena that may be expeted in an atual landsape mosai under intensifiation an lead to different ratio's between performane parameters, and thus to a different pereption of 'trade-offs', than a omparison of steady state solutions. This onlusion emphasizes the need to interpret field-derived data (as presented by Tomih et al., 21) in the ontext where they were derived, rather than as system properties as suh. A number of the important trade-offs between produtivity, C stok and biodiversity depend on the sale of model appliation, the internal variability in the landsape and the transient behavior under hanges in land use intensity. In the real world, hanges in human population deijsity would add further omplexity to the interpretation of these transients. In developing this model we had to postulate expliit saling rules for speies rihness as indiator of biodiversity. While an abundant literature disusses saling rules within a single vegetation type (Rosenzweig, 1995; Loreau, 2; May and Stumpf, 2) the orretions we use for overlap between vegetation types are speulative and probably represent an area where further researh is urgently needed. Qualitatively, the model an reprodue initial inreases in landsape level speies rihness as a onsequene of 'disturbane' by low-intensity shifting ultivation, even though the average plotlevel rihness will derease. This initially pitive response to disturbane does not exist for the C stoks, and is in line with data olleted for the ASB benhmark sites (Gillison, 1999). The model formulation we use implies that hanges in plot 'E G) Ii. ' II) Years Years Fig. 7. Aboveground C stok (A and B) and soil fertility (C and D) for individual plots and for a landsape-level average (bold line) for simulations where deisions on the fields top be ropped are no diret refletion of plot-level fertility (A and C, H_FieldRule = 1) and for ases where near-perfet knowledge of soil fertility exists and no onstraints in aess to part of the landsape apples (B and D, H_FieldRule = 2).
13 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) ,g -Q) >- 1 "C -; U. CI : a.4... a u Co "': 'C ClO.2 -; > Rei. fertility ropped fields Length of preeding fallow, years Fig. 8. Relationship between returns to labor and land and the relative soil fertility of ropped fields and the age of the pre-eding fallow period, for simulations with Kfert = 15 ('Nat. fallow') and 5 ('Improved fallow'). level speies rihness are fully reversible and that 'time an heal all wounds' from a biodiversity perspetive, without irreversible hanges in the pool from whih reolonization is supposed to our. Future versions of the model may have to more expliitly inorporate onepts of onnetedness within the landsape mosai and its impat on the lateral flow of organisms. We explored two ways of representing the linkage between overall, landsape-level deisions on intensifiation and the plot-level implementation in deisions of whih plots to rop in what year. These different model formulations represent different degrees of perfetion in loal eologial knowledge, and are expeted to have some impat on properties suh as 'returns to labor'. The two versions, however, do not hange the fundamentals of resoure availability in the neighborhood of the 'arrying apaity'. Changes in agriultural tehnology (higher R_ConvEff parameter or fertilizer use) an have a muh more drasti impat, aording to the urrent model. The urrent model requires further parametrization before quantitative 'validation' tests an be performed, but it appears to meet 'sensibility' riteria (predited responses 'make sense') and is sensitive in its overall outome to the main input parameters. The hallenge is to keep the model simple enough t eluidate the main dynamis, but yet allow for saling up. The versions of the model urrently available on the web site inludes options of farmers spending time to ollet forest produts (timber or non-timber) and trade these for rie equivalents. This version of the model also inorporates the option of using a S&B system to start 'agroforests' suh as the rubber or fruit tree agroforests that replaed shifting ultivation in muh of SE Asia (Van Noordwijk et al., 1998; Tomih et al., 1998a; Tomih et al., 2a; Tomih et al., 2b). A water balane module translates the landsape mosai into preditions of total river flow and sediment load. Human deision making based on expliit evaluation of options that arise during the simulation an be represented in the model and its eologial
14 126 M. van Noordwijk / Eologial Modelling 149 (22) onsequenes be explored, but a gradual and stepwise inrease in omplexity from the urrent 'subsistene' eonomy to representations of market integration is desirable. Adding the 'lateral flow;' of human migration will likely reverse the positive environmental impats of introduing options with higher returns to land and labor (ompare the 'Pandora's box' disussion in Tomih et al., 1998a). Aknowledgements The FALLOW model (previously CDFU) was developed during and for a number of training ourses in SE Asia and ourse partiipants in Indonesia, Thailand and Vietnam ontributed to the urrent form of the model through their interest, initiative and questions. Desi Suyamto (IC- SEAjBiotrop, Bogor, Indonesia) helped in the development of the map failities in Exel. Betha Lusiana and Rahmat Mulia assisted in the implementation of the model as urrently available on the WWW site. Referenes Arrhenius,., Speies and area. J. Eol. 9, Gillison, A.N., Impat of different land uses on biodiversity indiators. Aboveground biodiversity assessments working group summary report Alternatives to Slash and Bum projet. International Centre for Researh in Agroforestry (ICRAF), Nairobi. Hagreis, B.J., 193. Ladangbouw [Shifting ultivation]. Landbouw 6, Loreau, M., 2. Are ommunities saturated? On the relationship between (x, 13 and y diversity. Eol. Lett. 3, May, R.M., Stumpf, M.P.H., 2. Speies-area relations in tropial forests. Siene 29, Nye, P.H., Greenland, D.J., 196. The Soil under Shifting Cultivation. Commonwealth Bureau of Soils Teh. Comm. 51, Harpenden, UK. Perrings, C., Maler, K.G., Folke, C., Holling, C.S., Janssen, B.O. (Eds.), Biodiversity Loss: Eonomi and Eologial Issues. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p Rosenzweig, M.L., Speies Diversity in Spae and Time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p Ruthenberg, H., Farming Systems in the Tropis, seond ed. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p Tomih, T.P., Van Noordwijk, M., Vosti, S., Whitover, J., 1998a. Agriultural development with rainforest onservation: methods for seeking Best Bet Alternatives to Slash-and- Bum, with appliations to Brazil and Indonesia. Agri. Eon. 19, Tomih, T.P., Van Noordwijk, M., Budidarseno, S., Gillison, A., Kusumanto, T., Murdiyarso, D., Stolle, F., Fagi, A.M., 1998b. Alternatives to Slash-and-Burn in Indonesia, Summary report and synthesis of Phase II. ICRAF S.E. Asia, Bogor, Indonesia, p Tomih, T.P., Van Noordwijk, M., Budidarseno, S., Gillison, A., Kusumanto, T., Murdiyarso, D., Stolle, F., Fagi, A.M., 21. Agriultural intensifiation, deforestation, and the environment: assessing tradeoffs in Sumatra, Indonesia. In: Lee, D.R., Barrett, C.B. (Eds.), Tradeoffs or Synergies? Agriultural Intensifiation, Eonomi Development and the Environment. CAB-International, Wallingford, pp Trenbath, B.R., Deline of soil fertility and the ollapse of shifting ultivation systems under intensifiation. In: Chadwik, A.C., Sutton, S.L. (Eds.), Tropial Rain-Forest: the Leeds Symposium. Leeds Philosophial and Literary Soiety, Leeds, pp Trenbath, B.R., The use of mathematial models in the development of shifting ultivation. In: Protor, J. (Ed.), Mineral Nutrients in Tropial Forest and Savanna Eosystems. Blakwell, Oxford, pp Van Noordwijk, M., Produtivity of intensified rop fallow rotations in the Trenbath model. Agroforestry Syst. 47, Van Noordwijk, M., Murdiyarso, D., Hairiah, K., Wasrin, U.R., Rahman, A., Tomih, T.P., Forest soils under alternatives to slash-and-burn agriulture in Sumatra, Indonesia. In: Shulte, A., Ruhiyat, D. (Eds.), Soils of Tropial Forest Eosystems: Charateristis, Eology and management. Springer, Berlin, pp Van Noordwijk, M., Poulsen, J., Eriksen, P.M., Filters, flows and fallaies: Methods for quantifying external effets of land use hange. Agriulture Eosystems and Environment in press. Woomer, P.L., Palm, C.A., Alegre, J., Castilla, C., Cordeiro, D.G., Hairiah, K., Kotto-Same, J., Moukam, A., Riese, A., Rodriguez, V., Van Noordwijk, M., 2. Slash and bum effets on arbon stoks in the humid tropis. In: Lal, R., Kimble, J.M., Stewart, B.A. (Eds.), Global Climate Change in Tropial Eosystems. CRC Press, Boa Raton, FL, USA, pp
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Pre-Experience Postgraduate Programmes Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View
 WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual Environments: Classi cation and Comparison of Methods
 Doug A. Bowman bowman@vt.edu Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Doug A. Bowman bowman@vt.edu Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
FIRE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero
 FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
SLA-based Resource Allocation for Software as a Service Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments
 2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
State of Maryland Participation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Accounts
 State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
An Enhanced Critical Path Method for Multiple Resource Constraints
 An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Customer Efficiency, Channel Usage and Firm Performance in Retail Banking
 Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
VOLUME 13, ARTICLE 5, PAGES 117-142 PUBLISHED 05 OCTOBER 2005 DOI: 10.4054/DemRes.2005.13.
 Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Board Building Recruiting and Developing Effective Board Members for Not-for-Profit Organizations
 Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit Organizations Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit
Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit Organizations Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
Paid Placement Strategies for Internet Search Engines
 Paid Plaement Strategies for Internet Searh Engines Hemant K. Bhargava Smeal College of Business Penn State University 342 Beam Building University Park, PA 16802 bhargava@omputer.org Juan Feng Smeal College
Paid Plaement Strategies for Internet Searh Engines Hemant K. Bhargava Smeal College of Business Penn State University 342 Beam Building University Park, PA 16802 bhargava@omputer.org Juan Feng Smeal College
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Practices
 Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Learning Curves and Stochastic Models for Pricing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Services
 T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS
 university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Software Ecosystems: From Software Product Management to Software Platform Management
 Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
The Basics of International Trade: A Classroom Experiment
 The Basis of International Trade: A Classroom Experiment Alberto Isgut, Ganesan Ravishanker, and Tanya Rosenblat * Wesleyan University Abstrat We introdue a simple web-based lassroom experiment in whih
The Basis of International Trade: A Classroom Experiment Alberto Isgut, Ganesan Ravishanker, and Tanya Rosenblat * Wesleyan University Abstrat We introdue a simple web-based lassroom experiment in whih
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Context-Sensitive Adjustments of Cognitive Control: Conflict-Adaptation Effects Are Modulated by Processing Demands of the Ongoing Task
 Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
Online Energy Generation Scheduling for Microgrids with Intermittent Energy Sources and Co-Generation
 Online Energy Generation Sheduling for Mirogrids with Intermittent Energy Soures and Co-Generation Lian Lu Information Engineering Dept. he Chinese Univ. of Hong Kong Jinlong u Information Engineering
Online Energy Generation Sheduling for Mirogrids with Intermittent Energy Soures and Co-Generation Lian Lu Information Engineering Dept. he Chinese Univ. of Hong Kong Jinlong u Information Engineering
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I
 DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
 Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING
 INTERMAN 7 TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING by Douglas A. Ready, Albert A. Viere and Alan F. White RECEIVED 2 7 MAY 1393 International Labour
INTERMAN 7 TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING by Douglas A. Ready, Albert A. Viere and Alan F. White RECEIVED 2 7 MAY 1393 International Labour
An Efficient Network Traffic Classification Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detection Mechanism
 An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
Optimal Sales Force Compensation
 Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
Neural network-based Load Balancing and Reactive Power Control by Static VAR Compensator
 nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
Melbourne Docklands ESD Guide
 Melbourne Doklands ESD Guide Eologially Sustainable Development May 2006 The most signifiant environmental hallenges of our time are global limate hange and fossil fuel dependeny. Rising greenhouse gas
Melbourne Doklands ESD Guide Eologially Sustainable Development May 2006 The most signifiant environmental hallenges of our time are global limate hange and fossil fuel dependeny. Rising greenhouse gas
Improved Vehicle Classification in Long Traffic Video by Cooperating Tracker and Classifier Modules
 Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan
 Form 5500 Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Servie Department of Labor Employee Benefits Seurity Administration Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan
Form 5500 Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Servie Department of Labor Employee Benefits Seurity Administration Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan
Entrepreneur s Guide. Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania FEBRUARY 2015. newpa.com
 Entrepreneur s Guide Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania FEBRUARY 2015 newpa.om The Entrepreneur s Guide: Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania was prepared by the Pennsylvania Department
Entrepreneur s Guide Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania FEBRUARY 2015 newpa.om The Entrepreneur s Guide: Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania was prepared by the Pennsylvania Department
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
International Journal of Supply and Operations Management. Mathematical modeling for EOQ inventory system with advance payment and fuzzy Parameters
 nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
Masters Thesis- Criticality Alarm System Design Guide with Accompanying Alarm System Development for the Radioisotope Production L
 PNNL-18348 Prepared for the U.S. Department of Energy under Contrat DE-AC05-76RL01830 Masters Thesis- Critiality Alarm System Design Guide with Aompanying Alarm System Development for the Radioisotope
PNNL-18348 Prepared for the U.S. Department of Energy under Contrat DE-AC05-76RL01830 Masters Thesis- Critiality Alarm System Design Guide with Aompanying Alarm System Development for the Radioisotope
TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED LEARNING FOR MUSIC WITH I-MAESTRO FRAMEWORK AND TOOLS
 TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED LEARNING FOR MUSIC WITH I-MAESTRO FRAMEWORK AND TOOLS ICSRiM - University of Leeds Shool of Computing & Shool of Musi Leeds LS2 9JT, UK +44-113-343-2583 kia@i-maestro.org www.i-maestro.org,
TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED LEARNING FOR MUSIC WITH I-MAESTRO FRAMEWORK AND TOOLS ICSRiM - University of Leeds Shool of Computing & Shool of Musi Leeds LS2 9JT, UK +44-113-343-2583 kia@i-maestro.org www.i-maestro.org,
Trade Information, Not Spectrum: A Novel TV White Space Information Market Model
 Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
A Theoretical Analysis of Credit Card Reform in Australia *
 A Theoretial Analysis of Credit Card Reform in Australia * by Joshua S. Gans and Stephen P. King Melbourne Business Shool University of Melbourne First Draft: 12 th May, 2001 This Version: 5 th May, 2003
A Theoretial Analysis of Credit Card Reform in Australia * by Joshua S. Gans and Stephen P. King Melbourne Business Shool University of Melbourne First Draft: 12 th May, 2001 This Version: 5 th May, 2003
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY. A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Michal Barzuza*
 Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
From a strategic view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise
 Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
Zentrum für Entwicklungsforschung Center for Development Research Universität Bonn. Oded Stark and C. Simon Fan
 ZEF Bonn Zentrum für Entwiklungsforshung Center for Development Researh Universität Bonn Oded Stark and C. Simon Fan Number 118 Rural-to-Urban Migration, Human Capital, and Agglomeration ZEF Disussion
ZEF Bonn Zentrum für Entwiklungsforshung Center for Development Researh Universität Bonn Oded Stark and C. Simon Fan Number 118 Rural-to-Urban Migration, Human Capital, and Agglomeration ZEF Disussion
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability
 Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com. ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 48 (2014 ) 1096 1109
 Available online at www.sienediret.om SieneDiret Energy Proedia 48 (2014 ) 1096 1109 SHC 2013, International Conferene on Solar Heating and Cooling for Buildings and Industry September 23-25, 2013, Freiburg,
Available online at www.sienediret.om SieneDiret Energy Proedia 48 (2014 ) 1096 1109 SHC 2013, International Conferene on Solar Heating and Cooling for Buildings and Industry September 23-25, 2013, Freiburg,
Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
' R ATIONAL. :::~i:. :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliance with the way you work PRODUCT BRIEF
 ' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detection
 Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Economics
 Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
CARRIER VOICE NETWORK MANAGEMENT
 CARRIER VOICE NETWORK MANAGEMENT Elvis N. Ngah Supervised by: Dr. Sandjai Bhulai Department of Mathematis Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam The Netherlands Deryk Cole Network Operations Center Telesonique Global
CARRIER VOICE NETWORK MANAGEMENT Elvis N. Ngah Supervised by: Dr. Sandjai Bhulai Department of Mathematis Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam The Netherlands Deryk Cole Network Operations Center Telesonique Global
Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System NUR 204 ROLE TRANSITION FOR THE REGISTERED NURSE. Plan Of Instruction
 Alabama Department of Postseonary Euation Representing Alabama s Publi Two-Year ollege System NUR 204 ROLE TRANSITION FOR THE REGISTERED NURSE Plan Of Instrution Effetive Date: 2006 Version Number: 2006-1
Alabama Department of Postseonary Euation Representing Alabama s Publi Two-Year ollege System NUR 204 ROLE TRANSITION FOR THE REGISTERED NURSE Plan Of Instrution Effetive Date: 2006 Version Number: 2006-1
Economic and Antitrust Barriers to Entry
 Eonomi and Antitrust Barriers to Entry R. Preston MAfee, Hugo M. Mialon, and Mihael A. Williams 1 Deember 1, 2003 Abstrat We review the extensive literature on barriers to entry in law and eonomis; we
Eonomi and Antitrust Barriers to Entry R. Preston MAfee, Hugo M. Mialon, and Mihael A. Williams 1 Deember 1, 2003 Abstrat We review the extensive literature on barriers to entry in law and eonomis; we
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS
 RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System
 DOE/EIA-0618(98) Distribution Category UC-950 Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System May 1998 This report was prepared by the, the independent statistial and analytial ageny within
DOE/EIA-0618(98) Distribution Category UC-950 Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System May 1998 This report was prepared by the, the independent statistial and analytial ageny within
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES
 THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
A Context-Aware Preference Database System
 J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, kstef@s.uoi.gr Evaggelia
J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, kstef@s.uoi.gr Evaggelia
Robust Classification and Tracking of Vehicles in Traffic Video Streams
 Proeedings of the IEEE ITSC 2006 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conferene Toronto, Canada, September 17-20, 2006 TC1.4 Robust Classifiation and Traking of Vehiles in Traffi Video Streams
Proeedings of the IEEE ITSC 2006 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conferene Toronto, Canada, September 17-20, 2006 TC1.4 Robust Classifiation and Traking of Vehiles in Traffi Video Streams
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
Chapter 1: Introduction
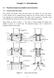 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Procurement auctions are sometimes plagued with a chosen supplier s failing to accomplish a project successfully.
 Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Modelling the Dynamics of Public Attention towards Environmental Issues
 Modelling the Dynamis of Publi ttention towards Environmental Issues Jens Newig, Julia Hesselmann, Institute of Environmental Systems Researh, University of Osnabrük, Germany. E-mail: jens.newig@usf.uni-osnabruek.de
Modelling the Dynamis of Publi ttention towards Environmental Issues Jens Newig, Julia Hesselmann, Institute of Environmental Systems Researh, University of Osnabrük, Germany. E-mail: jens.newig@usf.uni-osnabruek.de
The Optimal Deterrence of Tax Evasion: The Trade-off Between Information Reporting and Audits
 The Optimal Deterrene of Tax Evasion: The Trade-off Between Information Reporting and Audits Yulia Paramonova Department of Eonomis, University of Mihigan Otober 30, 2014 Abstrat Despite the widespread
The Optimal Deterrene of Tax Evasion: The Trade-off Between Information Reporting and Audits Yulia Paramonova Department of Eonomis, University of Mihigan Otober 30, 2014 Abstrat Despite the widespread
Energy Policy 52 (2013) 429 438. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Energy Policy. journal homepage: www.elsevier.
 Energy Poliy 52 (2013) 429 438 Contents lists available at SiVerse SieneDiret Energy Poliy journal homepage: www.elsevier.om/loate/enpol Cost-effetiveness of plug-in hybrid eletri vehile battery apaity
Energy Poliy 52 (2013) 429 438 Contents lists available at SiVerse SieneDiret Energy Poliy journal homepage: www.elsevier.om/loate/enpol Cost-effetiveness of plug-in hybrid eletri vehile battery apaity
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
Unit 12: Installing, Configuring and Administering Microsoft Server
 Unit 12: Installing, Configuring and Administering Mirosoft Server Learning Outomes A andidate following a programme of learning leading to this unit will be able to: Selet a suitable NOS to install for
Unit 12: Installing, Configuring and Administering Mirosoft Server Learning Outomes A andidate following a programme of learning leading to this unit will be able to: Selet a suitable NOS to install for
Table of Contents. Appendix II Application Checklist. Export Finance Program Working Capital Financing...7
 Export Finane Program Guidelines Table of Contents Setion I General...........................................................1 A. Introdution............................................................1
Export Finane Program Guidelines Table of Contents Setion I General...........................................................1 A. Introdution............................................................1
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre
 Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
Picture This: Molecular Maya Puts Life in Life Science Animations
 Piture This: Moleular Maya Puts Life in Life Siene Animations [ Data Visualization ] Based on the Autodesk platform, Digizyme plug-in proves aestheti and eduational effetiveness. BY KEVIN DAVIES In 2010,
Piture This: Moleular Maya Puts Life in Life Siene Animations [ Data Visualization ] Based on the Autodesk platform, Digizyme plug-in proves aestheti and eduational effetiveness. BY KEVIN DAVIES In 2010,
3 Game Theory: Basic Concepts
 3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
