EE122 Project 2B: P2P tiny World of Warcraft. Instructor: Prof. Ion Stoica
|
|
|
- Spencer Harper
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE122 Project 2B: P2P tiny World of Warcraft Instructor: Prof. Ion Stoica TAs: Junda Liu DK Moon David Due: 11:50pm on December 11, 2009 through bspace Version History: 0.4 Update sec 5 bullet Change error code of P2P_BKUP_RESPONSE. Bonus has 10 points. 0.2 Correct section 3.3 bullet 1. Delete section 4 bullet 5. Add new section 4 bullet First release 1. Overview In part A, you solved the scalability problem by partitioning workload among servers. As you deploy many servers, hardware failures are inevitable. And if a server crashes, all user data on that server are lost (assuming hard drive also fails if user data are stored in files). In this part, you will build a P2P data storage between servers to solve this problem. The basic idea is simple: duplicate and distribute. Each server makes copies of its data and sends them to other servers as backup. It also sends update messages to keep backups up-to-date. The client is the same as part A. The tracker is almost the same except the hash function is slightly modified. To reduce workload, you are NOT required to modify your tracker. You can just use the reference tracker. You are required to add following features to server: 1. Calculate P2P_ID from IP and TCP port 2. Connect to other servers' TCP port, and send/receive P2P messages 3. Receive P2P messages from TCP port and process them 4. Detect backup server failure and find another server as backup 2. Details Servers use a simplified P2P network to exchange messages. When a server starts, in addition to procedures described in project 1 and project 2 part A, it computes a unique P2P_ID from its IP address and TCP port, and joins the P2P network. Every server stores some user data and a copy on its backup server, so it can recover user data after crash. 2.1 P2P_ID Every server has a unique P2P_ID, and servers talk with each other using this P2P_ID. The P2P_ID space is [0, 1023]. If a server realizes it has the same P2P_ID with an
2 existing server, it must exits (More details in Section 2.4). For every player, there is also a P2P_ID calculated from player name using the same function. Each server decides which player data it should store based on its own P2P_ID and player's P2P_ID. Calculate P2P_ID: Input Player: unsigned char pointer of player name string. Server: 7-byte unsigned char array, first 4 bytes are non-local IP address, following 2 bytes are TCP port number, last byte is always 0x00. Note: is local IP and should NOT be used. Example: IP= , TCP port=12345, the array in hex format: Function Output 0x80 0x20 0x2A 0xC5 0x30 0x39 0x00 Slightly modified hash function from part A: unsigned int calc_p2p_id(unsigned char *s) { unsigned int hashval; for( hashval=0;*s!=0;s++) hashval=*s + 31*hashval; return hashval % 1024; } The difference is shown in bold. Note:When s is a pointer to player name string, this function calculates player's P2P_ID. P2P_ID of server or player, an unsigned integer id and 0 id Primary and backup server Every player has a primary and a backup server to store its data. Select primary server: 1. Use calc_p2p_id(player name pointer) to get the player's P2P_ID, assume it's idx 2. Among the servers whose P2P_ID is not smaller than idx, the one with smallest P2P_ID is primary server 3. If idx is bigger than all server P2P_IDs, the server with smallest P2P_ID is the primary server Below is an example. Numbers inside the circle is the P2P_ID of that server. The circle is only for illustration, and doesn't imply any actual toplogy or transmission. If idx is 56, then server with P2P_ID 123 is the primary server. If idx is 456, then server with P2P_ID 456 is the primary server. If idx is 1010, then server with P2P_ID 123 is the primary server. Backup server: Every server finds a backup server for its data. For server with P2P_ID x: 1. If no other server exists, do not use backup server 2. Among all servers that have P2P_ID bigger than x, the one with smallest P2P_ID is backup server 3. If all other servers have smaller P2P_ID, the one with smallest P2P_ID is backup server As shown below, server 456 is the backup server for server 123, and server 123 is backup server for server If server A is B's backup server, we call A is B's successor, and B is A's predecessor. When P2P network only has 2 servers, they are both successor and predecessor to each other. TCP connection for backup is always from
3 predecessor to successor. Following above principles, each server has a primary range and a backup range. If A is B's successor, then A's primary range is: [B id +1, A id ], if B id < A id [B id +1, 1023] and [0, A id ], if B id > A id 2.3 Server goes up/down When server A comes up (either first time or after a crash) A joins P2P network by following steps: A reads peers.lst and finds predecessor B and successor C A connects to B and C and sends P2P_JOIN_REQUEST (If B and C are the same server, A only establishes one connection and send one request) A receives P2P_JOIN_RESPONSE from B and C A closes connection to B but keep the connection to C B does the following: B sends back P2P_JOIN_RESPONSE containing all user data in its primary range B closes connection to previouse successor B connects to A's TCP port and keeps the connection C does the following: C modifies its primary and backup range C finds which players now should be primarily stored on A C sends back P2P_JOIN_RESPONSE containing players from previous step If B and C are the same server, the server does C's steps first, then B's steps. So it sends two P2P_JOIN_RESPONSE messages back to A. When server A fails: Its successor C will take requests (assume tracker can detect this and return the backup server to client. See Section 5 for more details). But for simplicity, backup server doesn't change its primary or backup range.
4 Its predecessor B detects this because of broken TCP connection. It reads peers.lst and follows above principles to find another server (usually C) as backup. Then it connects to the new backup server and sends P2P_BKUP_REQUEST when necessary. The primay and backup range on every server will change only when other server joins P2P network. They stay the same when server fails. In this design, data will be still lost if two P2P_ID-adjacent servers both fail. 2.4 What's new when server starts In addition to listening on TCP and UDP ports, the server gets its non-local IP address, computes the P2P_ID, and tries to read a file peers.lst. peers.lst may be a local file or stored on NFS and shared among servers. It contains one server information per line, see below for example. If peers.lst doesn't exist, it means the server is the first in the P2P network. It creates peers.lst file and writes its "P2P_ID IP TCPport\n" (space delimited, without quote) into the file. IP address uses dotted-quad notation. Example: If the file exists, the server reads the file and checks all P2P_IDs in it. If the server doesn't find its P2P_ID in the file, it appends its "P2P_ID IP TCPport\n" to peers.lst, and sends messages to join P2P network. If it finds same P2P_ID, but IP or TCPport is different, server prints out "P2P_ID conflicts." and exits. If it finds itself in the file, it sends messages to join P2P network. Packet formats are described in Section Protocol All P2P messages are TCP. MsgVer is one byte, and always 0x P2P_JOIN_REQUEST MsgVer(1B)=0x04 MsgLength(2B) MsgType(1B) Server P2P_ID(4B) 1. Sent from new coming server to its successor and predecessor. 2. MsgLength: 0x08 3. MsgType: 0x10 4. Server P2P_ID: network order P2P_ID of the sender 3.2 P2P_JOIN_RESPONSE MsgVer(1B)=0x04 MsgLength(2B) MsgType(1B) User Number(4B) User Data(20B) Sent from existing servers to new coming server 2. MsgType: 0x11 3. User Number: how many users this message contains, network order unsigned int.
5 4. User Data:20 bytes user info, same as project 2 part A: Name(10B) HP(4B) EXP(4B) X(1B) Y(1B) 5. One message may contain multiple user data, and spans multiple TCP packets 6. When server receives this message, it updates local user data 3.3 P2P_BKUP_REQUEST MsgVer(1B)=0x04 MsgLength(2B) MsgType(1B) User Data(20B) 1. Sent from a server to its successor to store or update user data. A server needs to send this message when it gets SAVE_STATE_REQUEST (defined in part A) from client. 2. MsgLength: 0x18 3. MsgType: 0x12 4. User Data: 20 bytes, same as above 3.4 P2P_BKUP_RESPONSE MsgVer(1B)=0x04 MsgLength(2B) MsgType(1B) ErrorCode(1B) Padding(3B) 1. Sent from successor to predecessor, in response to P2P_BKUP_REQUEST. 2. MsgLength: 0x08 3. MsgType: 0x13 4. ErrorCode: 1. Success: 0x00 2. Error: 0x02 4. Evaluation 1. Tracker will NOT be tested in this part, unless you implement bonus features. 2. Game logic will NOT be tested in this part. 3. Test script will frequently start and kill multiple server processes. 4. Test script sends SIGTERM signal to kill server process. It's best that your server can handle this signal and exit gracefully. 5. Same as part A, your sever should read/write "users/playername" file for player data 5. Bonus (10 points) To reduce workload, we assume that tracker can detect server status and return the backup one to client if primary server fails, but current tracker doesn't support this. Your team can implement the following for extra credit (10 points): 1. Tracker reads a config file (generated from peers.lst) and uses calc_p2p_id(player name) to decide which server to return. (Reference tracker already implements this) 2. Heartbeat message from tracker to server or other method to detect failed server
6 3. If primary server fails, tracker will return backup server to client If your team implement bonus features, please explain how they are implemented in your submitted readme file. 6. Appendix 6.1 Get non-local IP address Call gethostname(name), then gethostbyname(name). h_addr_list[0] has IP address and inet_ntoa converts it to dotted-quad string.
Implementing and testing tftp
 CSE123 Spring 2013 Term Project Implementing and testing tftp Project Description Checkpoint: May 10, 2013 Due: May 29, 2013 For this project you will program a client/server network application in C on
CSE123 Spring 2013 Term Project Implementing and testing tftp Project Description Checkpoint: May 10, 2013 Due: May 29, 2013 For this project you will program a client/server network application in C on
Follow these steps to prepare the module and evaluation board for testing.
 2 Getting Started 2.1. Hardware Installation Procedure Follow these steps to prepare the module and evaluation board for testing. STEP1: Plug the EG-SR-7100A module into the sockets on the test board.
2 Getting Started 2.1. Hardware Installation Procedure Follow these steps to prepare the module and evaluation board for testing. STEP1: Plug the EG-SR-7100A module into the sockets on the test board.
CS 557- Project 1 A P2P File Sharing Network
 Assigned: Feb 26, 205 Due: Monday, March 23, 205 CS 557- Project A P2P File Sharing Network Brief Description This project involves the development of FreeBits, a file sharing network loosely resembling
Assigned: Feb 26, 205 Due: Monday, March 23, 205 CS 557- Project A P2P File Sharing Network Brief Description This project involves the development of FreeBits, a file sharing network loosely resembling
HP Service Virtualization
 HP Service Virtualization Fixed Length Protocol Virtualization SV Training September 2014 Fixed Length Protocol Virtualization Technology Description Use Cases Supported Message Structures SV Service Description
HP Service Virtualization Fixed Length Protocol Virtualization SV Training September 2014 Fixed Length Protocol Virtualization Technology Description Use Cases Supported Message Structures SV Service Description
Lecture 8b: Proxy Server Load Balancing
 Internet and Intranet Protocols and Applications Lecture 8b: Proxy Server Load Balancing March, 2004 Arthur Goldberg Computer Science Department New York University artg@cs.nyu.edu Load Balancing Problem:
Internet and Intranet Protocols and Applications Lecture 8b: Proxy Server Load Balancing March, 2004 Arthur Goldberg Computer Science Department New York University artg@cs.nyu.edu Load Balancing Problem:
Lab 5: BitTorrent Client Implementation
 Lab 5: BitTorrent Client Implementation Due: Nov. 30th at 11:59 PM Milestone: Nov. 19th during Lab Overview In this lab, you and your lab parterner will develop a basic BitTorrent client that can, at minimal,
Lab 5: BitTorrent Client Implementation Due: Nov. 30th at 11:59 PM Milestone: Nov. 19th during Lab Overview In this lab, you and your lab parterner will develop a basic BitTorrent client that can, at minimal,
Exam 1 Review Questions
 CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks Exam 1 Review Questions Jon Turner 10/2013 1. A user in St. Louis, connected to the internet via a 20 Mb/s (b=bits) connection retrieves a 250 KB (B=bytes) web
CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks Exam 1 Review Questions Jon Turner 10/2013 1. A user in St. Louis, connected to the internet via a 20 Mb/s (b=bits) connection retrieves a 250 KB (B=bytes) web
A Client Server Transaction. Introduction to Computer Systems 15 213/18 243, fall 2009 18 th Lecture, Nov. 3 rd
 A Client Server Transaction Introduction to Computer Systems 15 213/18 243, fall 2009 18 th Lecture, Nov. 3 rd 4. Client handles response Client process 1. Client sends request 3. Server sends response
A Client Server Transaction Introduction to Computer Systems 15 213/18 243, fall 2009 18 th Lecture, Nov. 3 rd 4. Client handles response Client process 1. Client sends request 3. Server sends response
Application Note: AN00121 Using XMOS TCP/IP Library for UDP-based Networking
 Application Note: AN00121 Using XMOS TCP/IP Library for UDP-based Networking This application note demonstrates the use of XMOS TCP/IP stack on an XMOS multicore micro controller to communicate on an ethernet-based
Application Note: AN00121 Using XMOS TCP/IP Library for UDP-based Networking This application note demonstrates the use of XMOS TCP/IP stack on an XMOS multicore micro controller to communicate on an ethernet-based
Communications and Networking
 Communications and Networking History and Background telephone system local area networks Internet architecture: what the pieces are and how they fit together names and addresses: what's your name and
Communications and Networking History and Background telephone system local area networks Internet architecture: what the pieces are and how they fit together names and addresses: what's your name and
Firewalls with IPTables. Jason Healy, Director of Networks and Systems
 Firewalls with IPTables Jason Healy, Director of Networks and Systems Last Updated Mar 18, 2008 2 Contents 1 Host-based Firewalls with IPTables 5 1.1 Introduction.............................. 5 1.2 Concepts...............................
Firewalls with IPTables Jason Healy, Director of Networks and Systems Last Updated Mar 18, 2008 2 Contents 1 Host-based Firewalls with IPTables 5 1.1 Introduction.............................. 5 1.2 Concepts...............................
Tutorial on Socket Programming
 Tutorial on Socket Programming Computer Networks - CSC 458 Department of Computer Science Seyed Hossein Mortazavi (Slides are mainly from Monia Ghobadi, and Amin Tootoonchian, ) 1 Outline Client- server
Tutorial on Socket Programming Computer Networks - CSC 458 Department of Computer Science Seyed Hossein Mortazavi (Slides are mainly from Monia Ghobadi, and Amin Tootoonchian, ) 1 Outline Client- server
Teldat Router. DNS Client
 Teldat Router DNS Client Doc. DM723-I Rev. 10.00 March, 2003 INDEX Chapter 1 Domain Name System...1 1. Introduction...2 2. Resolution of domains...3 2.1. Domain names resolver functionality...4 2.2. Functionality
Teldat Router DNS Client Doc. DM723-I Rev. 10.00 March, 2003 INDEX Chapter 1 Domain Name System...1 1. Introduction...2 2. Resolution of domains...3 2.1. Domain names resolver functionality...4 2.2. Functionality
Workload Firewall Management
 Workload Firewall Management Setup Guide Contents: About Halo Workload Firewalls Implementing Halo Workload Firewalls Creating Firewall Policies Define Firewall-Related Components Create Inbound Rules
Workload Firewall Management Setup Guide Contents: About Halo Workload Firewalls Implementing Halo Workload Firewalls Creating Firewall Policies Define Firewall-Related Components Create Inbound Rules
The Answer to the 14 Most Frequently Asked Modbus Questions
 Modbus Frequently Asked Questions WP-34-REV0-0609-1/7 The Answer to the 14 Most Frequently Asked Modbus Questions Exactly what is Modbus? Modbus is an open serial communications protocol widely used in
Modbus Frequently Asked Questions WP-34-REV0-0609-1/7 The Answer to the 14 Most Frequently Asked Modbus Questions Exactly what is Modbus? Modbus is an open serial communications protocol widely used in
µtasker Document FTP Client
 Embedding it better... µtasker Document FTP Client utaskerftp_client.doc/1.01 Copyright 2012 M.J.Butcher Consulting Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. FTP Log-In...4 3. FTP Operation Modes...4 4.
Embedding it better... µtasker Document FTP Client utaskerftp_client.doc/1.01 Copyright 2012 M.J.Butcher Consulting Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. FTP Log-In...4 3. FTP Operation Modes...4 4.
IP Network Layer. Datagram ID FLAG Fragment Offset. IP Datagrams. IP Addresses. IP Addresses. CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP
 CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP IP Network Layer Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina IP Datagrams IP is the network layer packet delivery
CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP IP Network Layer Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina IP Datagrams IP is the network layer packet delivery
Importing data from Linux LDAP server to HA3969U
 Importing data from Linux LDAP server to HA3969U Application Notes Abstract: This document describes how to import data and records from Linux LDAP servers to Storageflex HA3969U systems, and by doing
Importing data from Linux LDAP server to HA3969U Application Notes Abstract: This document describes how to import data and records from Linux LDAP servers to Storageflex HA3969U systems, and by doing
CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks. Exam 2 Solutions. Your name: 10/31/2013
 CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks Jon Turner Exam Solutions Your name: 0/3/03. (0 points). Consider a circular DHT with 7 nodes numbered 0,,...,6, where the nodes cache key-values pairs for 60
CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks Jon Turner Exam Solutions Your name: 0/3/03. (0 points). Consider a circular DHT with 7 nodes numbered 0,,...,6, where the nodes cache key-values pairs for 60
SYMETRIX SOLUTIONS: TECH TIP August 2015
 String Output Modules The purpose of this document is to provide an understanding of operation and configuration of the two different String Output modules available within SymNet Composer. The two different
String Output Modules The purpose of this document is to provide an understanding of operation and configuration of the two different String Output modules available within SymNet Composer. The two different
3.5. cmsg Developer s Guide. Data Acquisition Group JEFFERSON LAB. Version
 Version 3.5 JEFFERSON LAB Data Acquisition Group cmsg Developer s Guide J E F F E R S O N L A B D A T A A C Q U I S I T I O N G R O U P cmsg Developer s Guide Elliott Wolin wolin@jlab.org Carl Timmer timmer@jlab.org
Version 3.5 JEFFERSON LAB Data Acquisition Group cmsg Developer s Guide J E F F E R S O N L A B D A T A A C Q U I S I T I O N G R O U P cmsg Developer s Guide Elliott Wolin wolin@jlab.org Carl Timmer timmer@jlab.org
Technical Support Bulletin Nr.18 Modbus Tips
 Technical Support Bulletin Nr.18 Modbus Tips Contents! Definitions! Implemented commands! Examples of commands or frames! Calculating the logical area! Reading a signed variable! Example of commands supported
Technical Support Bulletin Nr.18 Modbus Tips Contents! Definitions! Implemented commands! Examples of commands or frames! Calculating the logical area! Reading a signed variable! Example of commands supported
Introduction to Socket Programming Part I : TCP Clients, Servers; Host information
 Introduction to Socket Programming Part I : TCP Clients, Servers; Host information Keywords: sockets, client-server, network programming-socket functions, OSI layering, byte-ordering Outline: 1.) Introduction
Introduction to Socket Programming Part I : TCP Clients, Servers; Host information Keywords: sockets, client-server, network programming-socket functions, OSI layering, byte-ordering Outline: 1.) Introduction
Websense SQL Queries. David Buyer June 2009 Be281@bfn.org
 Websense SQL Queries David Buyer June 2009 Be281@bfn.org Introduction The SQL queries that are listed here I have been using for a number of years now. I use them almost exclusively as an alternative to
Websense SQL Queries David Buyer June 2009 Be281@bfn.org Introduction The SQL queries that are listed here I have been using for a number of years now. I use them almost exclusively as an alternative to
Network Attached Storage. Jinfeng Yang Oct/19/2015
 Network Attached Storage Jinfeng Yang Oct/19/2015 Outline Part A 1. What is the Network Attached Storage (NAS)? 2. What are the applications of NAS? 3. The benefits of NAS. 4. NAS s performance (Reliability
Network Attached Storage Jinfeng Yang Oct/19/2015 Outline Part A 1. What is the Network Attached Storage (NAS)? 2. What are the applications of NAS? 3. The benefits of NAS. 4. NAS s performance (Reliability
F2103 GPRS DTU USER MANUAL
 F2103 GPRS DTU USER MANUAL Add:J1-J2,3rd Floor,No.44,GuanRi Road,SoftWare Park,XiaMen,China 1 Zip Code:361008 Contents Chapter 1 Brief Introduction of Product... 3 1.1 General... 3 1.2 Product Features...
F2103 GPRS DTU USER MANUAL Add:J1-J2,3rd Floor,No.44,GuanRi Road,SoftWare Park,XiaMen,China 1 Zip Code:361008 Contents Chapter 1 Brief Introduction of Product... 3 1.1 General... 3 1.2 Product Features...
Google File System. Web and scalability
 Google File System Web and scalability The web: - How big is the Web right now? No one knows. - Number of pages that are crawled: o 100,000 pages in 1994 o 8 million pages in 2005 - Crawlable pages might
Google File System Web and scalability The web: - How big is the Web right now? No one knows. - Number of pages that are crawled: o 100,000 pages in 1994 o 8 million pages in 2005 - Crawlable pages might
Configuring Health Monitoring
 CHAPTER4 Note The information in this chapter applies to both the ACE module and the ACE appliance unless otherwise noted. The features that are described in this chapter apply to both IPv6 and IPv4 unless
CHAPTER4 Note The information in this chapter applies to both the ACE module and the ACE appliance unless otherwise noted. The features that are described in this chapter apply to both IPv6 and IPv4 unless
WIZnet S2E (Serial-to-Ethernet) Device s Configuration Tool Programming Guide
 WIZnet S2E (Serial-to-Ethernet) Device s Configuration Tool Programming Guide Rev 0.2 This document describes how to make your own Configuration Tool for WIZ100SR, WIZ105SR and WIZ110SR of WIZnet. And
WIZnet S2E (Serial-to-Ethernet) Device s Configuration Tool Programming Guide Rev 0.2 This document describes how to make your own Configuration Tool for WIZ100SR, WIZ105SR and WIZ110SR of WIZnet. And
AN-POV-011 SNMP use with POV
 Introduction This document describes the SNMP Interface provided with Point of View (POV). Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a popular protocol for network management. It is used for collecting
Introduction This document describes the SNMP Interface provided with Point of View (POV). Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a popular protocol for network management. It is used for collecting
Configuring System Message Logging
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Cisco 4700 Series Application Control Engine (ACE) appliance. Each ACE contains a number of log files that retain records
CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Cisco 4700 Series Application Control Engine (ACE) appliance. Each ACE contains a number of log files that retain records
Fault Tolerance in the Internet: Servers and Routers
 Fault Tolerance in the Internet: Servers and Routers Sana Naveed Khawaja, Tariq Mahmood Research Associates Department of Computer Science Lahore University of Management Sciences Motivation Client Link
Fault Tolerance in the Internet: Servers and Routers Sana Naveed Khawaja, Tariq Mahmood Research Associates Department of Computer Science Lahore University of Management Sciences Motivation Client Link
360-FAAR Design Goals
 360-FAAR Design Goals Overview of Design Goals and General Principals Purpose of This Document This document presents a generalised overview of the design goals of 360-FAAR. It is hoped that the information
360-FAAR Design Goals Overview of Design Goals and General Principals Purpose of This Document This document presents a generalised overview of the design goals of 360-FAAR. It is hoped that the information
Kiwi SyslogGen. A Freeware Syslog message generator for Windows. by SolarWinds, Inc.
 Kiwi SyslogGen A Freeware Syslog message generator for Windows by SolarWinds, Inc. Kiwi SyslogGen is a free Windows Syslog message generator which sends Unix type Syslog messages to any PC or Unix Syslog
Kiwi SyslogGen A Freeware Syslog message generator for Windows by SolarWinds, Inc. Kiwi SyslogGen is a free Windows Syslog message generator which sends Unix type Syslog messages to any PC or Unix Syslog
architecture: what the pieces are and how they fit together names and addresses: what's your name and number?
 Communications and networking history and background telephone system local area networks Internet architecture: what the pieces are and how they fit together names and addresses: what's your name and
Communications and networking history and background telephone system local area networks Internet architecture: what the pieces are and how they fit together names and addresses: what's your name and
COMP 112 Assignment 1: HTTP Servers
 COMP 112 Assignment 1: HTTP Servers Lead TA: Jim Mao Based on an assignment from Alva Couch Tufts University Due 11:59 PM September 24, 2015 Introduction In this assignment, you will write a web server
COMP 112 Assignment 1: HTTP Servers Lead TA: Jim Mao Based on an assignment from Alva Couch Tufts University Due 11:59 PM September 24, 2015 Introduction In this assignment, you will write a web server
CLOUD-BASED COMPUTING BY JARED MILLER 3/9/15
 CLOUD-BASED COMPUTING BY JARED MILLER 3/9/15 THE TERM CLOUD Where did this term cloud actually come from? What is this term used to describe? When did this term become populuar? WHERE DID THE TERM COME
CLOUD-BASED COMPUTING BY JARED MILLER 3/9/15 THE TERM CLOUD Where did this term cloud actually come from? What is this term used to describe? When did this term become populuar? WHERE DID THE TERM COME
File Transfer And Access (FTP, TFTP, NFS) Chapter 25 By: Sang Oh Spencer Kam Atsuya Takagi
 File Transfer And Access (FTP, TFTP, NFS) Chapter 25 By: Sang Oh Spencer Kam Atsuya Takagi History of FTP The first proposed file transfer mechanisms were developed for implementation on hosts at M.I.T.
File Transfer And Access (FTP, TFTP, NFS) Chapter 25 By: Sang Oh Spencer Kam Atsuya Takagi History of FTP The first proposed file transfer mechanisms were developed for implementation on hosts at M.I.T.
Apache Hadoop. Alexandru Costan
 1 Apache Hadoop Alexandru Costan Big Data Landscape No one-size-fits-all solution: SQL, NoSQL, MapReduce, No standard, except Hadoop 2 Outline What is Hadoop? Who uses it? Architecture HDFS MapReduce Open
1 Apache Hadoop Alexandru Costan Big Data Landscape No one-size-fits-all solution: SQL, NoSQL, MapReduce, No standard, except Hadoop 2 Outline What is Hadoop? Who uses it? Architecture HDFS MapReduce Open
Chapter 2: Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
 Chapter 2: Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Gustavo Alonso Computer Science Department Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETHZ) alonso@inf.ethz.ch http://www.iks.inf.ethz.ch/ Contents - Chapter 2 - RPC
Chapter 2: Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Gustavo Alonso Computer Science Department Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETHZ) alonso@inf.ethz.ch http://www.iks.inf.ethz.ch/ Contents - Chapter 2 - RPC
Network Address Translation (NAT) Adapted from Tannenbaum s Computer Network Ch.5.6; computer.howstuffworks.com/nat1.htm; Comer s TCP/IP vol.1 Ch.
 Network Address Translation (NAT) Adapted from Tannenbaum s Computer Network Ch.5.6; computer.howstuffworks.com/nat1.htm; Comer s TCP/IP vol.1 Ch.20 Long term and short term solutions to Internet scalability
Network Address Translation (NAT) Adapted from Tannenbaum s Computer Network Ch.5.6; computer.howstuffworks.com/nat1.htm; Comer s TCP/IP vol.1 Ch.20 Long term and short term solutions to Internet scalability
Chapter 1 - Web Server Management and Cluster Topology
 Objectives At the end of this chapter, participants will be able to understand: Web server management options provided by Network Deployment Clustered Application Servers Cluster creation and management
Objectives At the end of this chapter, participants will be able to understand: Web server management options provided by Network Deployment Clustered Application Servers Cluster creation and management
Managing Latency in IPS Networks
 Application Note Revision B McAfee Network Security Platform Managing Latency in IPS Networks Managing Latency in IPS Networks McAfee Network Security Platform provides you with a set of pre-defined recommended
Application Note Revision B McAfee Network Security Platform Managing Latency in IPS Networks Managing Latency in IPS Networks McAfee Network Security Platform provides you with a set of pre-defined recommended
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions 1. Q: What is the Network Data Tunnel? A: Network Data Tunnel (NDT) is a software-based solution that accelerates data transfer in point-to-point or point-to-multipoint network
Frequently Asked Questions 1. Q: What is the Network Data Tunnel? A: Network Data Tunnel (NDT) is a software-based solution that accelerates data transfer in point-to-point or point-to-multipoint network
Cluster APIs. Cluster APIs
 Cluster APIs Cluster APIs Cluster APIs include: Cluster Control APIs Cluster Resource Group APIs Cluster Resource Group Exit Program Topics covered here are: Cluster APIs Cluster Resource Services Characteristics
Cluster APIs Cluster APIs Cluster APIs include: Cluster Control APIs Cluster Resource Group APIs Cluster Resource Group Exit Program Topics covered here are: Cluster APIs Cluster Resource Services Characteristics
Moven Studio realtime. streaming
 Moven Studio realtime network streaming UDP protocol specification Document MV0305P Revision B, 19 December 2007 Xsens Technologies B.V. phone +31 88 XSENS 00 Pantheon 6a +31 88 97367 00 P.O. Box 559 fax
Moven Studio realtime network streaming UDP protocol specification Document MV0305P Revision B, 19 December 2007 Xsens Technologies B.V. phone +31 88 XSENS 00 Pantheon 6a +31 88 97367 00 P.O. Box 559 fax
Network FAX Driver. Operation Guide
 Network FAX Driver Operation Guide About this Operation Guide This Operation Guide explains the settings for the Network FAX driver as well as the procedures that are required in order to use the Network
Network FAX Driver Operation Guide About this Operation Guide This Operation Guide explains the settings for the Network FAX driver as well as the procedures that are required in order to use the Network
Building a Highly Available and Scalable Web Farm
 Page 1 of 10 MSDN Home > MSDN Library > Deployment Rate this page: 10 users 4.9 out of 5 Building a Highly Available and Scalable Web Farm Duwamish Online Paul Johns and Aaron Ching Microsoft Developer
Page 1 of 10 MSDN Home > MSDN Library > Deployment Rate this page: 10 users 4.9 out of 5 Building a Highly Available and Scalable Web Farm Duwamish Online Paul Johns and Aaron Ching Microsoft Developer
BookKeeper overview. Table of contents
 by Table of contents 1 BookKeeper overview...2 1.1 BookKeeper introduction... 2 1.2 In slightly more detail...2 1.3 Bookkeeper elements and concepts...3 1.4 Bookkeeper initial design... 3 1.5 Bookkeeper
by Table of contents 1 BookKeeper overview...2 1.1 BookKeeper introduction... 2 1.2 In slightly more detail...2 1.3 Bookkeeper elements and concepts...3 1.4 Bookkeeper initial design... 3 1.5 Bookkeeper
RTP / RTCP. Announcements. Today s Lecture. RTP Info RTP (RFC 3550) I. Final Exam study guide online. Signup for project demos
 Announcements I. Final Exam study guide online RTP / RTCP Internet Protocols CSC / ECE 573 Fall, 2005 N. C. State University II. III. Signup for project demos Teaching evaluations at end today copyright
Announcements I. Final Exam study guide online RTP / RTCP Internet Protocols CSC / ECE 573 Fall, 2005 N. C. State University II. III. Signup for project demos Teaching evaluations at end today copyright
Arduino Internet Connectivity: Maintenance Manual Julian Ryan Draft No. 7 April 24, 2015
 Arduino Internet Connectivity: Maintenance Manual Julian Ryan Draft No. 7 April 24, 2015 CEN 4935 Senior Software Engineering Project Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Software Engineering Program Florida
Arduino Internet Connectivity: Maintenance Manual Julian Ryan Draft No. 7 April 24, 2015 CEN 4935 Senior Software Engineering Project Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Software Engineering Program Florida
Measuring the performance of a Wired network
 Measuring the performance of a Wired network slide 1 note throughout the following tutorial the courier font indicates the terminal output whereas the courier bold indicates keyboard input. and italic
Measuring the performance of a Wired network slide 1 note throughout the following tutorial the courier font indicates the terminal output whereas the courier bold indicates keyboard input. and italic
IP Addressing. -Internetworking (with TCP/IP) -Classful addressing -Subnetting and Supernetting -Classless addressing
 IP Addressing -Internetworking (with TCP/IP) -Classful addressing -Subnetting and Supernetting -Classless addressing Internetworking The concept of internetworking: we need to make different networks communicate
IP Addressing -Internetworking (with TCP/IP) -Classful addressing -Subnetting and Supernetting -Classless addressing Internetworking The concept of internetworking: we need to make different networks communicate
MBA Dedicated Servers: A How-to Guide
 MBA Dedicated Servers: A How-to Guide 1. If you are behind a firewall, see the Router configuration section below for information on setting up port forwarding. 2. Launch the STEAM client. The Steam client
MBA Dedicated Servers: A How-to Guide 1. If you are behind a firewall, see the Router configuration section below for information on setting up port forwarding. 2. Launch the STEAM client. The Steam client
20 Using Scripts. (Programming without Parts) 20-1
 20 Using Scripts (Programming without Parts) This chapter explains the basics of creating and using programming scripts in GP-Pro EX. Please start by reading 20.1 Settings Menu (page 20-2) and then turn
20 Using Scripts (Programming without Parts) This chapter explains the basics of creating and using programming scripts in GP-Pro EX. Please start by reading 20.1 Settings Menu (page 20-2) and then turn
Hadoop and Map-Reduce. Swati Gore
 Hadoop and Map-Reduce Swati Gore Contents Why Hadoop? Hadoop Overview Hadoop Architecture Working Description Fault Tolerance Limitations Why Map-Reduce not MPI Distributed sort Why Hadoop? Existing Data
Hadoop and Map-Reduce Swati Gore Contents Why Hadoop? Hadoop Overview Hadoop Architecture Working Description Fault Tolerance Limitations Why Map-Reduce not MPI Distributed sort Why Hadoop? Existing Data
orrelog SNMP Trap Monitor Software Users Manual
 orrelog SNMP Trap Monitor Software Users Manual http://www.correlog.com mailto:info@correlog.com CorreLog, SNMP Trap Monitor Software Manual Copyright 2008-2015, CorreLog, Inc. All rights reserved. No
orrelog SNMP Trap Monitor Software Users Manual http://www.correlog.com mailto:info@correlog.com CorreLog, SNMP Trap Monitor Software Manual Copyright 2008-2015, CorreLog, Inc. All rights reserved. No
Socket Programming. Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur
 Socket Programming Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur Background Demultiplexing Convert host-to-host packet delivery service into a process-to-process communication channel
Socket Programming Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur Background Demultiplexing Convert host-to-host packet delivery service into a process-to-process communication channel
Firewall Implementation
 CS425: Computer Networks Firewall Implementation Ankit Kumar Y8088 Akshay Mittal Y8056 Ashish Gupta Y8410 Sayandeep Ghosh Y8465 October 31, 2010 under the guidance of Prof. Dheeraj Sanghi Department of
CS425: Computer Networks Firewall Implementation Ankit Kumar Y8088 Akshay Mittal Y8056 Ashish Gupta Y8410 Sayandeep Ghosh Y8465 October 31, 2010 under the guidance of Prof. Dheeraj Sanghi Department of
Redundant Storage Cluster
 Redundant Storage Cluster For When It's Just Too Big Bob Burgess radian 6 Technologies MySQL User Conference 2009 Scope Fundamentals of MySQL Proxy Fundamentals of LuaSQL Description of the Redundant Storage
Redundant Storage Cluster For When It's Just Too Big Bob Burgess radian 6 Technologies MySQL User Conference 2009 Scope Fundamentals of MySQL Proxy Fundamentals of LuaSQL Description of the Redundant Storage
Last Class: Communication in Distributed Systems. Today: Remote Procedure Calls
 Last Class: Communication in Distributed Systems Structured or unstructured? Addressing? Blocking/non-blocking? Buffered or unbuffered? Reliable or unreliable? Server architecture Scalability Push or pull?
Last Class: Communication in Distributed Systems Structured or unstructured? Addressing? Blocking/non-blocking? Buffered or unbuffered? Reliable or unreliable? Server architecture Scalability Push or pull?
Monitoring QNAP NAS system
 Monitoring QNAP NAS system eg Enterprise v6 Restricted Rights Legend The information contained in this document is confidential and subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced
Monitoring QNAP NAS system eg Enterprise v6 Restricted Rights Legend The information contained in this document is confidential and subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced
Managing Virtual Servers
 CHAPTER 4 Content Switching Module Device Manager (CVDM-CSM) displays details of existing virtual servers and enables users to perform detailed tasks that include creating or deleting virtual servers,
CHAPTER 4 Content Switching Module Device Manager (CVDM-CSM) displays details of existing virtual servers and enables users to perform detailed tasks that include creating or deleting virtual servers,
EMC Integrated Infrastructure for VMware
 EMC Integrated Infrastructure for VMware Enabled by EMC Celerra NS-120 Reference Architecture EMC Global Solutions Centers EMC Corporation Corporate Headquarters Hopkinton MA 01748-9103 1.508.435.1000
EMC Integrated Infrastructure for VMware Enabled by EMC Celerra NS-120 Reference Architecture EMC Global Solutions Centers EMC Corporation Corporate Headquarters Hopkinton MA 01748-9103 1.508.435.1000
Chapter 11. User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
 Chapter 11 User Datagram Protocol (UDP) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000 1 CONTENTS PROCESS-TO-PROCESS COMMUNICATION USER DATAGRAM CHECKSUM UDP OPERATION USE OF UDP UDP PACKAGE The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 11 User Datagram Protocol (UDP) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000 1 CONTENTS PROCESS-TO-PROCESS COMMUNICATION USER DATAGRAM CHECKSUM UDP OPERATION USE OF UDP UDP PACKAGE The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chord. A scalable peer-to-peer look-up protocol for internet applications
 Chord A scalable peer-to-peer look-up protocol for internet applications by Ion Stoica, Robert Morris, David Karger, M. Frans Kaashoek, Hari Balakrishnan Overview Introduction The Chord Algorithm Construction
Chord A scalable peer-to-peer look-up protocol for internet applications by Ion Stoica, Robert Morris, David Karger, M. Frans Kaashoek, Hari Balakrishnan Overview Introduction The Chord Algorithm Construction
CSE331: Introduction to Networks and Security. Lecture 12 Fall 2006
 CSE331: Introduction to Networks and Security Lecture 12 Fall 2006 Announcements Midterm I will be held Friday, Oct. 6th. True/False Multiple Choice Calculation Short answer Short essay Project 2 is on
CSE331: Introduction to Networks and Security Lecture 12 Fall 2006 Announcements Midterm I will be held Friday, Oct. 6th. True/False Multiple Choice Calculation Short answer Short essay Project 2 is on
Cloud Optimize Your IT
 Cloud Optimize Your IT Windows Server 2012 Michael Faden Partner Technology Advisor Microsoft Schweiz 1 Beyond Virtualization virtualization The power of many servers, the simplicity of one Every app,
Cloud Optimize Your IT Windows Server 2012 Michael Faden Partner Technology Advisor Microsoft Schweiz 1 Beyond Virtualization virtualization The power of many servers, the simplicity of one Every app,
Introduction to Wireshark Network Analysis
 Introduction to Wireshark Network Analysis Page 2 of 24 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION 4 Overview 4 CAPTURING LIVE DATA 5 Preface 6 Capture Interfaces 6 Capture Options 6 Performing the Capture 8 ANALYZING
Introduction to Wireshark Network Analysis Page 2 of 24 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION 4 Overview 4 CAPTURING LIVE DATA 5 Preface 6 Capture Interfaces 6 Capture Options 6 Performing the Capture 8 ANALYZING
Lecture 15. IP address space managed by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
 Lecture 15 IP Address Each host and router on the Internet has an IP address, which consist of a combination of network number and host number. The combination is unique; no two machines have the same
Lecture 15 IP Address Each host and router on the Internet has an IP address, which consist of a combination of network number and host number. The combination is unique; no two machines have the same
Internet Firewall CSIS 4222. Packet Filtering. Internet Firewall. Examples. Spring 2011 CSIS 4222. net15 1. Routers can implement packet filtering
 Internet Firewall CSIS 4222 A combination of hardware and software that isolates an organization s internal network from the Internet at large Ch 27: Internet Routing Ch 30: Packet filtering & firewalls
Internet Firewall CSIS 4222 A combination of hardware and software that isolates an organization s internal network from the Internet at large Ch 27: Internet Routing Ch 30: Packet filtering & firewalls
SSC - Communication and Networking Java Socket Programming (II)
 SSC - Communication and Networking Java Socket Programming (II) Shan He School for Computational Science University of Birmingham Module 06-19321: SSC Outline Outline of Topics Multicast in Java User Datagram
SSC - Communication and Networking Java Socket Programming (II) Shan He School for Computational Science University of Birmingham Module 06-19321: SSC Outline Outline of Topics Multicast in Java User Datagram
The new frontier of the DATA acquisition using 1 and 10 Gb/s Ethernet links. Filippo Costa on behalf of the ALICE DAQ group
 The new frontier of the DATA acquisition using 1 and 10 Gb/s Ethernet links Filippo Costa on behalf of the ALICE DAQ group DATE software 2 DATE (ALICE Data Acquisition and Test Environment) ALICE is a
The new frontier of the DATA acquisition using 1 and 10 Gb/s Ethernet links Filippo Costa on behalf of the ALICE DAQ group DATE software 2 DATE (ALICE Data Acquisition and Test Environment) ALICE is a
NAT & IP Masquerade. Internet NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION INTRODUCTION. NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5. Internal PC 192.168.0.25
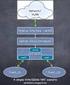 NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
Thick Client Application Security
 Thick Client Application Security Arindam Mandal (arindam.mandal@paladion.net) (http://www.paladion.net) January 2005 This paper discusses the critical vulnerabilities and corresponding risks in a two
Thick Client Application Security Arindam Mandal (arindam.mandal@paladion.net) (http://www.paladion.net) January 2005 This paper discusses the critical vulnerabilities and corresponding risks in a two
Computer Networks Network architecture
 Computer Networks Network architecture Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York - Networks are like onions - They stink? - Yes, no, they have layers Shrek and Donkey 1 Introduction
Computer Networks Network architecture Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York - Networks are like onions - They stink? - Yes, no, they have layers Shrek and Donkey 1 Introduction
User-ID Features. PAN-OS New Features Guide Version 6.0. Copyright 2007-2015 Palo Alto Networks
 User-ID Features PAN-OS New Features Guide Version 6.0 Contact Information Corporate Headquarters: Palo Alto Networks 4401 Great America Parkway Santa Clara, CA 95054 http://www.paloaltonetworks.com/contact/contact/
User-ID Features PAN-OS New Features Guide Version 6.0 Contact Information Corporate Headquarters: Palo Alto Networks 4401 Great America Parkway Santa Clara, CA 95054 http://www.paloaltonetworks.com/contact/contact/
ENABLING RPC OVER HTTPS CONNECTIONS TO M-FILES SERVER
 M-FILES CORPORATION ENABLING RPC OVER HTTPS CONNECTIONS TO M-FILES SERVER VERSION 2.3 DECEMBER 18, 2015 Page 1 of 15 CONTENTS 1. Version history... 3 2. Overview... 3 2.1. System Requirements... 3 3. Network
M-FILES CORPORATION ENABLING RPC OVER HTTPS CONNECTIONS TO M-FILES SERVER VERSION 2.3 DECEMBER 18, 2015 Page 1 of 15 CONTENTS 1. Version history... 3 2. Overview... 3 2.1. System Requirements... 3 3. Network
Monitoring System Status
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to monitor the health and activities of the system. It covers these topics: About Logged Information, page 14-121 Event Logging, page 14-122 Monitoring Performance,
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to monitor the health and activities of the system. It covers these topics: About Logged Information, page 14-121 Event Logging, page 14-122 Monitoring Performance,
GSM. Quectel Cellular Engine. GSM TCPIP Application Notes GSM_TCPIP_AN_V1.1
 GSM Cellular Engine GSM TCPIP Application Notes GSM_TCPIP_AN_V1.1 Document Title GSM TCPIP Application Notes Version 1.1 Date 2011-09-22 Status Document Control ID Release GSM_TCPIP_AN_V1.1 General Notes
GSM Cellular Engine GSM TCPIP Application Notes GSM_TCPIP_AN_V1.1 Document Title GSM TCPIP Application Notes Version 1.1 Date 2011-09-22 Status Document Control ID Release GSM_TCPIP_AN_V1.1 General Notes
2015/02/07 05:41 1/23 WIZ550WEB Users' Guide
 2015/02/07 05:41 1/23 WIZ550WEB Users' Guide WIZ550WEB Users' Guide Overview WIZ550web provides the lightweight webserver operating. It controls digital output or monitors digital and analogue input through
2015/02/07 05:41 1/23 WIZ550WEB Users' Guide WIZ550WEB Users' Guide Overview WIZ550web provides the lightweight webserver operating. It controls digital output or monitors digital and analogue input through
DHCP Failover. Necessary for a secure and stable network. DHCP Failover White Paper Page 1
 DHCP Failover Necessary for a secure and stable network DHCP Failover White Paper Page 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Basic DHCP Redundancy... 3 3. VitalQIP Failover Solution... 5 4. VitalQIP
DHCP Failover Necessary for a secure and stable network DHCP Failover White Paper Page 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Basic DHCP Redundancy... 3 3. VitalQIP Failover Solution... 5 4. VitalQIP
KLV encoder / decoder library for STANAG 4609
 KLV (Key-Length-Value) is a data encoding standard used for binary data byte-packing and metadata embedding into video feeds. KLV encoder/decoder C++ library (available for both Windows and Linux) allows
KLV (Key-Length-Value) is a data encoding standard used for binary data byte-packing and metadata embedding into video feeds. KLV encoder/decoder C++ library (available for both Windows and Linux) allows
Network Management. What is network management?
 Network Management Introduction to network management motivation major components Internet network management framework MIB: management information base SMI: data definition language SNMP: protocol for
Network Management Introduction to network management motivation major components Internet network management framework MIB: management information base SMI: data definition language SNMP: protocol for
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. TCP/IP Part I. Prof Indranil Sengupta Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology
 Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur TCP/IP Part I Prof Indranil Sengupta Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture 3: TCP/IP Part I On completion, the student
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur TCP/IP Part I Prof Indranil Sengupta Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture 3: TCP/IP Part I On completion, the student
Accelerating Network Virtualization Overlays with QLogic Intelligent Ethernet Adapters
 Enterprise Strategy Group Getting to the bigger truth. ESG Lab Review Accelerating Network Virtualization Overlays with QLogic Intelligent Ethernet Adapters Date: June 2016 Author: Jack Poller, Senior
Enterprise Strategy Group Getting to the bigger truth. ESG Lab Review Accelerating Network Virtualization Overlays with QLogic Intelligent Ethernet Adapters Date: June 2016 Author: Jack Poller, Senior
Monitoring Coyote Point Equalizers
 Monitoring Coyote Point Equalizers eg Enterprise v6 Restricted Rights Legend The information contained in this document is confidential and subject to change without notice. No part of this document may
Monitoring Coyote Point Equalizers eg Enterprise v6 Restricted Rights Legend The information contained in this document is confidential and subject to change without notice. No part of this document may
Different Ways of Connecting to. 3DLevelScanner II. A.P.M Automation Solutions LTD. www.apm-solutions.com Version 3.0
 3DLevelScanner II Different Ways of Connecting to 3DLevelScanner II A.P.M Automation Solutions LTD. www.apm-solutions.com Version 3.0 2 Different Ways of Connecting to 3DLevelScanner II Version 3.0 Table
3DLevelScanner II Different Ways of Connecting to 3DLevelScanner II A.P.M Automation Solutions LTD. www.apm-solutions.com Version 3.0 2 Different Ways of Connecting to 3DLevelScanner II Version 3.0 Table
Voice over IP: RTP/RTCP The transport layer
 Advanced Networking Voice over IP: /RTCP The transport layer Renato Lo Cigno Requirements For Real-Time Transmission Need to emulate conventional telephone system Isochronous output timing same with input
Advanced Networking Voice over IP: /RTCP The transport layer Renato Lo Cigno Requirements For Real-Time Transmission Need to emulate conventional telephone system Isochronous output timing same with input
On-Net Surveillance Systems, Inc. Triggering Software Generic Events from the Windows Scheduler
 Triggering Software Generic Events from the Windows Scheduler Background OnSSI s NetDVR and NetDVMS NVR software platforms have the ability to change certain settings based on external events. As an example,
Triggering Software Generic Events from the Windows Scheduler Background OnSSI s NetDVR and NetDVMS NVR software platforms have the ability to change certain settings based on external events. As an example,
Understanding and Configuring NAT Tech Note PAN-OS 4.1
 Understanding and Configuring NAT Tech Note PAN-OS 4.1 Revision C 2012, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Scope... 3 Design Consideration... 3 Software requirement...
Understanding and Configuring NAT Tech Note PAN-OS 4.1 Revision C 2012, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Scope... 3 Design Consideration... 3 Software requirement...
UNIX Sockets. COS 461 Precept 1
 UNIX Sockets COS 461 Precept 1 Clients and Servers Client program Running on end host Requests service E.g., Web browser Server program Running on end host Provides service E.g., Web server GET /index.html
UNIX Sockets COS 461 Precept 1 Clients and Servers Client program Running on end host Requests service E.g., Web browser Server program Running on end host Provides service E.g., Web server GET /index.html
>>> SOLUTIONS <<< c) The OSI Reference Model has two additional layers. Where are these layers in the stack and what services do they provide?
 Midterm Exam for Computer Networks (CNT 4004) Fall 2013 >>> SOLUTIONS
Midterm Exam for Computer Networks (CNT 4004) Fall 2013 >>> SOLUTIONS
Introduction to IP v6
 IP v 1-3: defined and replaced Introduction to IP v6 IP v4 - current version; 20 years old IP v5 - streams protocol IP v6 - replacement for IP v4 During developments it was called IPng - Next Generation
IP v 1-3: defined and replaced Introduction to IP v6 IP v4 - current version; 20 years old IP v5 - streams protocol IP v6 - replacement for IP v4 During developments it was called IPng - Next Generation
Measurement Study of Wuala, a Distributed Social Storage Service
 Measurement Study of Wuala, a Distributed Social Storage Service Thomas Mager - Master Thesis Advisors: Prof. Ernst Biersack Prof. Thorsten Strufe Prof. Pietro Michiardi Illustration: Maxim Malevich 15.12.2010
Measurement Study of Wuala, a Distributed Social Storage Service Thomas Mager - Master Thesis Advisors: Prof. Ernst Biersack Prof. Thorsten Strufe Prof. Pietro Michiardi Illustration: Maxim Malevich 15.12.2010
EMC DOCUMENTUM xplore 1.1 DISASTER RECOVERY USING EMC NETWORKER
 White Paper EMC DOCUMENTUM xplore 1.1 DISASTER RECOVERY USING EMC NETWORKER Abstract The objective of this white paper is to describe the architecture of and procedure for configuring EMC Documentum xplore
White Paper EMC DOCUMENTUM xplore 1.1 DISASTER RECOVERY USING EMC NETWORKER Abstract The objective of this white paper is to describe the architecture of and procedure for configuring EMC Documentum xplore
The English translation Of MBA Standard 0301
 MBA 文 書 0603 号 MBA Document 0603 The English translation Of MBA Standard 0301 MISAUTH Protocol Specification The authoritive specification is Japansese one, MBA Standard 0203 (June 2004). The Protocol
MBA 文 書 0603 号 MBA Document 0603 The English translation Of MBA Standard 0301 MISAUTH Protocol Specification The authoritive specification is Japansese one, MBA Standard 0203 (June 2004). The Protocol
Chapter 11. Using MAX II User Flash Memory for Data Storage in Manufacturing Flow
 Chapter 11. Using MAX II User Flash Memory for Data Storage in Manufacturing Flow MII51011-1.1 Introduction Small capacity, non-volatile memory is commonly used in storing manufacturing data (e.g., manufacturer
Chapter 11. Using MAX II User Flash Memory for Data Storage in Manufacturing Flow MII51011-1.1 Introduction Small capacity, non-volatile memory is commonly used in storing manufacturing data (e.g., manufacturer
Acano solution. Third Party Call Control Guide. March 2015 76-1055-01-E
 Acano solution Third Party Call Control Guide March 2015 76-1055-01-E Contents Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 How to Use this Guide... 3 1.1.1 Commands... 4 2 Example of Configuring a SIP Trunk to CUCM...
Acano solution Third Party Call Control Guide March 2015 76-1055-01-E Contents Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 How to Use this Guide... 3 1.1.1 Commands... 4 2 Example of Configuring a SIP Trunk to CUCM...
A REST API for Arduino & the CC3000 WiFi Chip
 A REST API for Arduino & the CC3000 WiFi Chip Created by Marc-Olivier Schwartz Last updated on 2014-04-22 03:01:12 PM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Hardware configuration Installing the library
A REST API for Arduino & the CC3000 WiFi Chip Created by Marc-Olivier Schwartz Last updated on 2014-04-22 03:01:12 PM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Hardware configuration Installing the library
