Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): NFC-based Electronic Data Capture Systems The Case of a Quality of Life
|
|
|
- Benjamin Pierce
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): NFC-based Electronic Data Capture Systems The Case of a Quality of Life Questionnaire. In: Proceedings of the 20th European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS), Barcelona, Spain.
2 NFC-BASED ELECTRONIC DATA CAPTURE SYSTEMS THE CASE OF A QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTIONNAIRE Prinz, Andreas, Information Systems, Kassel University, Pfannkuchstraße 1, Kassel, Germany, prinz@uni-kassel.de Menschner, Philipp, Information Systems, Kassel University, Pfannkuchstraße 1, Kassel, Germany, menschner@uni-kassel.de Leimeister, Jan Marco, Information Systems, Kassel University, Pfannkuchstraße 1, Kassel, Germany, leimeister@uni-kassel.de Abstract In this paper, we present a Near Field Communication (NFC)-based electronic data capture prototype for patient self-reported rating scales. Such scales are valuable feedback for medical treatment and care processes. As traditional paper-based questionnaires are time- and cost-consuming and may be affected by low patient compliance, our prototype allows patient monitoring and electronic data acquisition directly from the patient s home. It enables real time representation and analysis of patient data and thus allows direct medical intervention by physicians. In developing the prototype, we followed a design science approach, developed design goals for the special case of patients suffering from impaired motor skills, and tested the prototype in a field study over the course of twelve weeks. We chose NFC since the interaction paradigm is intuitive and quickly learned, without prior knowledge being necessary. Our results indicate that NFC is almost as simple as filling out a paperbased questionnaire. During the study patients used the prototype autonomously and with minimal errors. Further, NFC technology was perceived as very intuitive and the information quality of each patient s health status could be improved. Based on the findings we derive recommendations for future research and applications of NFC based electronic data capture systems. Keywords: Electronic Data Capture, NFC, Information Quality, Design Science.
3 1 Introduction Patients suffering from chronic diseases often have to cope with limitations and a reduced quality of life. This is particularly applicable for patients with limited or impaired fine motor skills, which can occur from chronic diseases such as motor neuron disease, dementia, Parkinson s disease or multiple sclerosis. For most diseases of this kind, a cure remains elusive, despite availability of certain medications to treat symptoms. The protracted course of the diseases has a major impact on the quality of life of patients and their families (Welsh et al., 2003, Löser et al., 2007). In order to guarantee the best possible treatment procedures, physicians need up-to-date information about their patients actual state and well-being. Yet, it is well recognized that capturing, archiving, analysing and interpreting health status information involves logistic challenges (Wolfe and Pincus, 1995). For patients living at home, this implies an even greater challenge, as contemporaneous information, which can be efficiently and effectively used for therapeutic decision-making, is not available. The insufficient information logistics amongst physicians, patients and nursing staff concerning the well-being of patients could be improved by using mobile networks and information systems for electronic data capture (EDC) of health status information. As mobile devices have achieved a high level of public acceptance, they are increasingly considered to be integrated in health care (Leimeister et al., 2005). Telecommunication networks allow a flexible, location-independent monitoring of the patients status. Additionally, costs can be reduced as patients take over data acquisition tasks. In this paper, we describe the development and evaluation of a mobile Near Field Communication (NFC)-based electronic data capture (EDC) system for patient self-reported questionnaires. NFC, is a short-range high frequency wireless communication technology, based on the frequency of 13,56 MHz, which enables the exchange of data between devices within 10 centimetres (around 4 inches) distance (ECMA-340, 2004, Want, 2006). Therefore, the objective of our work was to provide a simple, effective and efficient self-reporting system of the current well-being status, which would allow patients a cost-efficient and easy-to-handle reporting system of their current condition. We have identified a scenario that can benefit from applying EDC techniques, both from an economic perspective as well as having an impact on the patients health status and quality of life. These are rating scales and disease progress questionnaires. The paper is structured as follows. We first provide an overview of related work on NFC technology and EDC methods used in patient care, clinical trials, and Ambient Assisted Living (AAL) scenarios. This is followed by a presentation of the design goals that guided our development and our research approach. Then, we shortly describe our insert (Self-Reporting questionnaire) prototype system and present the results of the field test evaluation. This includes a discussion and insights into the design of contactless electronic capture of self-reported patient data. We close with a discussion of the contributions from this research, the implications and the derived recommendations for future research. 2 Related Work In health care, the provision of appropriate treatment often depends on self-reported states, characteristics and behaviours of patients in order to understand disease progression or treatment outcomes. Over the last decades, there has been steady progress in the development of measurement techniques for all kinds of diseases. A wide variety of rating scales is used to determine the state of patients, ranging from impairment scales to health-related quality of life instruments (e.g., (Kaufmann et al., 2005, Grauer and Birnbom, 1975, Welsh et al., 2003)). Studies have shown their importance in measuring the impact of different diseases and their treatment on patients (Guyatt et al., 1993). The results of the rating scales and questionnaires are then used to adapt and optimize therapeutic options. Several studies have evaluated the effectiveness of patient self-rating for different kinds of diseases (Strömgren et al., 2001). They show that the validity and reliability are of a sufficient level in order to serve as a ba-
4 sis for treatment decision-making. Follow-up costs of inadequate treatment are hard to measure, and the negative impact on patients quality of life is manifest. Health status information has traditionally been captured using paper-based questionnaires. However, traditional paper-based medical patient surveys or questionnaires for health status information are time- and cost-consuming, and can suffer from contaminating effects, such as time-delay or inaccuracy due to disregard, which can lead to unsuited or out-of-date treatment. Electronic-based questionnaires overcome these deficits by allowing to aggregate and calculate the data, which potentially reduces the time to acquire data and can hence increase the patient s compliance (Nyholm et al., 2004). Further, electronically captured, self-reported patient data can instantly be compiled and can be available for physicians and clinical personnel in almost real time. This provides indications for possible medical interventions, even in-between appointments (Velikova et al., 1999). Currently, there are considerable studies on various occurrences of electronic data capture (EDC) (Bischoff-Ferrari HA. et al., 2005, Richter et al., 2006, Palmblad M. and B., 2004, Dale O. and KB., 2007, Koene et al., 2010, Blake, 2008). The application of NFC technology to provide EDC for patient self-reporting is, however, comparatively novel and not widely implemented. NFC makes many tasks easier and more convenient by providing access to systems and services simply by touch. Morak et al. (2007), use NFC-technology as a self-management process for monitoring heart failure patients and Iglesias et al. (2009) describe an NFC-based health monitoring system to improve quality of life for elderly patients. Patients transmit health related data to a central database by touching medical devices with a mobile telephone. Physicians or nurses can view the entire data and guide the patient to the best possible health status. Bravo et al. (2008) use NFC for supporting nurse activities in an Alzheimer s day centre. NFC-based nutrition management for elderly patients is suggested by Prinz et al. (2009). In a clinical context, NFC is used by various researchers. Lahtela et al. (2008) have developed an NFCbased solution to avoid medication errors in hospitals. As an additional path of medical data acquisition, Fikry et al. (2006) and Morak et al. (2009) describe different NFC-based solutions which allow physicians or nurses to collect data by easily touching medical devices with a mobile phone. Yet, none of these studies focus on usability for patients suffering from impaired fine motor skills. 3 Development and Research Approach For the specific use case we worked in cooperation with a German hospital which is specialized on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), which is a form of motor neuron disease. ALS is a progressive, fatal, neurodegenerative disease caused by the degeneration of motor neurons, the nerve cells in the central nervous system that control voluntary muscle movement. Death usually occurs within two to five years of diagnosis. In particular, ALS patients suffer from progressive paralysis, so they need to be provided with an easy to handle system. As patients attribute an important role to the interactive applications interface design, the overall process of our approach to user-centered design (UCD) is based on evaluating the usability of insert in small iterative steps. 3.1 Design Goals The design goals have been identified in discussions and observations with physicians and patients and formed the basis for developing our solution idea for an electronic data capture system. In this specific case we had several challenges. As continuous tracking and surveillance of health status did not exist thus far, means for patients to report on their current state had to be integrated. Another particularity was the progressive paralysis of patients. Due to impaired fine motor skills, it was difficult for these patients to use commonly available user interfaces such as mouse or multi touch devices. Hence, in view of accounting for the patients physical state, the NFC-based solution was preferred. Our concept of insert, an easy-to-use electronic data capture system for patients with impaired fine motor skills, is based on the following main goals:
5 Increase the usability (a) ease of use & (b) perceived usefulness: A major problem in mobile user-interface (UI) design practice is that current approaches cannot directly be applied to mobile phones. According to Subramanya et al. (2006), in general, the UI should be intuitive and easy to use. The usability is important for creating applications which are easy to use and which fulfill the needs of the targeted user-group. Ease of use and perceived usefulness derive directly from the TAM (Davis et al., 1989). Increase intention to use: The dimension intention to use is a predictor of future usage, it derives directly from the TAM (Davis et al., 1989). Increase confirmation: The questions about confirmation are an important dimension for explaining IS continuance intention (Bhattacherjee, 2001). Providing a very efficient and intuitive way of interaction suited to patients with impaired fine motor skills: It is important that patients with impaired fine motor skills are able to use the system. Otherwise, it is no guarantee that the data will be entered reliably. Improve information quality: Are the results useful to serve as medical decision-making basis and facilitate the additional information of physician daily work? 3.2 Research Approach We used a design science approach (Jones and Gregor, 2007, Hevner et al., 2004) which aims to develop solutions to organizational problems through design and evaluation of novel artefacts. The design process generally consists of analyses, design, implementation and evaluation of an artefact (Simon, 1996, Hevner et al., 2004), in our case the prototype insert. As users generally had no prior experience with mobile EDC services, and user involvement in system development is still an acknowledged success factor, we adopted the AAL service design approach (AALSDA) approach by (Menschner et al., 2011). Figure 1. AALSDA approach (Menschner et al., 2011). We began with an in-depth analysis of treatment and care processes of patients suffering from ALS. Background information on the problem was obtained through a review of relevant literature, case studies, interviews, questionnaires, observations and document analyses. Based on the findings from the analyses and our design goals, we developed a design concept and a low fidelity prototype which was then evaluated in focus groups as well as in workshops (Prinz et al., 2011). We then developed a fully functional proof-of-concept prototype which was tested in a long-term field study in a German hospital.
6 4 The Design of the insert Prototype A mobile phone application that allows the reading of NFC-tags on a smart poster with NFC-enabled mobile phones is used. By touching a tag with an NFC-enabled mobile phone, this information can be read and displayed to the user (Forum, 2006). The transmitted and aggregated data is processed and stored in the central unit of the insert system and can be analyzed by physicians and nurses. 4.1 Smart Poster and Mobile Application In the tests we executed during the design process, we show that the NFC solution outperforms iphone and PC-solutions as well as a paper-based protocol with respect to the following criteria on pragmatic and hedonistic aspects (Prinz et al., 2012). The easy to learn touch metaphor of NFC interaction makes NFC, particularly for the target group (elderly people and people with impaired fine motor skills) who are not familiar with the use of mobile phones or computers, an interesting technology. Figure 2. NFC Smart poster for patient self-reporting Figure 2 shows the self-rating questionnaire smart poster of the well-established ALS-functional rating scale (Kaufmann et al., 2005). The smart poster contains twelve questions (three sections to bulbar symptoms, motor activity and respiratory dysfunction) with five possible answers in each case (Kasarskis et al., 1999). The poster has images printed in front and NFC-tags glued to the back. To start the application, a touch on the start icon or interaction field is sufficient. After the application is launched, the patient has to touch one of the twelve questions. As shown in figure 3, patients have to follow four simple steps to answer the question via insert.
7 Figure 3. Rating process of insert Once contact is made, the mobile device gives audible, haptic and visual feedback to the user. For audible feedback, the title of the chosen question is spoken; for haptic feedback, the phone vibrates; and for visual feedback, the chosen headline of the question appears on the display. After each question the patient has to respond to a five-point Likert scale (0 to 4). Once the answering process for the chosen question is completed, the application reminds the patient to answer the next question. Again, the mobile device confirms the transmission of data with audible, haptic and visual feedback. The icon of the interaction field is based on generic NFC tags (Arnall, 2006). To help patients navigate to the interactive areas, the inner circle is coloured red. The size of the interaction field of 35 x 35 millimetres is dependent on the used passive NFC tags. The client is implemented as a Java J2ME midlet which controls the NFC-reader device of the Nokia 6212 phone through an API provided by Nokia. J2ME is an optimized Java Edition for programming mobile devices (Java, 2010). The multimedia files, such as photos and audio data corresponding to the twelve questions, are stored on the mobile device. In order to start the application, an NFC-Tag, storing a specific NFC Data Exchange Format (NDEF) record-type is used. The URN can be assigned to a Java class in the mobile phone. If the mobile device detects an NFC tag with the stored URN, the mobile phone selects the assigned java class and executes it. If the patient wants to send a message to the hospital, he can use the tag which prompts the midlet to generate a special enquiry to the server. 4.2 Physician Dashboard To allow physicians the management of the patient scoring data, a so-called physician dashboard has been implemented through which physicians can extract relevant information about their patients. In order for the information to be available anytime and anywhere, a web portal has been implemented for access by both stationary computers and smart phones. The dashboard is structured as follows: On one side there is a category patients providing patient relevant data. On the opposite side there is a category mobile devices referring to the mobile phone data handed out. In the patients category, physicians get an overview representation of the patient data, where they can see information about all participating patients. This is where patients can be added or deleted. Next to the personal data, such as name and date of birth, is the place where the ID assigned to each patient can be found. This ID is also provided on the smart phone to uniquely and anonymously identify a patient. In addition to the ID, the data referring to the responsible physicians can be obtained. The display can be customised as a table or as a figure, depending on the user s preferences.
8 Figure 4. Physicians dashboard: Patient Scoring Data Figure 4 depicts the answers of the last questionnaire entries. The diagram clearly illustrates the changes in the assessment of patients over their period of scoring. In addition to the content preparation for patients, the IDs assigned to dedicated patients in the category mobile devices can be edited. Thus, it is possible to allot a certain beginning and end point for when the ID can be used. In addition to the access for physicians, the dashboard contains a special administrator access. This area allows assigning of access privileges to specific people in different roles. It is thus possible to define the physicians responsible for patients or further administrators can be allotted. The administrator access also allows adding additional questionnaires. Therefore, a part from the existing system of evaluating a questionnaire concerning motor diseases, further smart poster and tele-medical applications can be appended following similar principles. 4.3 Technical Description and Process Routine To gather data in a centralised way and to easily monitor the data, a client server architecture is chosen. In this architecture, the mobile phone acts as a client gathering the data and passing it on to a server. The choice of client application, rather than purely server-side architecture, is based on the fact that, especially in rural areas, mobile communication networks are insufficiently developed for broadband connection, needed to exchange intensive multimedia data between the server and mobile devices (BMWi, 2009). The client software is implemented on a Nokia 6212 classic NFC-enabled mobile phone. The data-flow from mobile device to the server can be detailed as follows: By touching a tag, the insert midlet application is automatically started, and the mobile receives the identifier of the poster. The mobile device then requests an enquiry to the server. This enquiry incorporates the Poster-ID as well as a unique hash value. The server matches the hash value with the ones issued to the patients. If the hash value exists, it sends the tag-ids available on the poster to the mobile phone. This gives the phone the semantics of which tag corresponds to what meaning. The mobile phone sends the data to the server once the patient completes the evaluation and touches the send-tag twice. In this implementation, the intermediary server is first being addressed, and it eventually composes the respective messages using scripting and Java servlets. In the hospital, the transmitted data is merged with the patient data using the delivered ID. The central unit of the electronic data capture solution is a server which stores the patients response to the questionnaire and can be accessed through a web interface. Since the user data contain sensitive information about patients, data security has to be considered. This is achieved in the following way: There
9 is separation between the master data and transaction data. Transaction data is delivered by secured mechanisms to the hospital. However, master data (in the form of information about the patients) is located in a shielded domain in a secured area inside the server architecture. 5 Evaluation Setting The prototype was evaluated in a field study at patients home with 18 patients (amongst them 7 female), ranging in age from 55 to 70 years, of a German hospital over the course of 12 weeks. First, the physicians received a 45 minutes hands-on training to use and explain the system. After that, the physicians gave a training session to the patients, so that the patients were able to use the system at home. Patients received a fixed day of the week on which they should conduct their health status with the prototype. The hospital provided patient access for us, yet they took over the distribution process of the NFC-enabled mobile phones and smart posters. We had two drop outs, one of them died during the field test, the other one had usage problems the power on/off button of the mobile phone was too small. The objectives of this field study were (1) a test of the technical feasibility and (2) an evaluation of the practicability, according to our design goals. Test of the technical feasibility of the NFC-based electronic data capture system for patients with impaired fine motor skills: The relevant issue in this case was to find out whetherthe patients are able to use the NFC-based mobile phones with the smart poster with an acceptable error rate. Evaluations of the practicability of the electronic data capture system: In order for the proposed system to be beneficial in capturing patient data,the system would have to be able to run stable at patients home without attendance, aside from assembly and disassembly. Furthermore, it needs to be assessed whether the prototype application was capable of gathering patient data at patients home. Every participant received an NFC-enabled mobile phone and a smart poster containing twelve questions about the level of functional impairment in performing one of twelve common tasks, e.g. climbing stairs, speaking or breathing. Each task is rated on a five-point scale from 0 = can't do, to 4 = normal ability. The patient has to rate him- or herself once a week on a fixed day. This poster represents the ALS-FRS rating scale, which is well-established for ALS-patients (Kaufmann et al., 2005). After twelve weeks, the patients fill in a questionnaire (regarding usability, intention to use, confirmation & interaction) with a 7-point likert scale and post it together with the mobile phone and smart poster in a prepaid package to us. We received all distributed mobile phones and smart posters, but only 13 of 18 questionnaires. 6 Evaluation Results The results of the evaluation are structured using the design goals (1) increasing usability, (2) intention to use, (3) confirmation, (4) providing a very efficient and intuitive way of interaction suited to patients with impaired fine motor skills and (5) improving information quality. Interpretations are accompanied by information gathered during telephone interviews with patients and physicians. We conducted evaluations on a technological (technical feasibility), user (practicability) and physician s basis. 6.1 Overall Impression The evaluation shows that the prototype has great potential to improve the information logistics problem between physicians, home care nurses, and patients with impairment of fine motor skills. Through the active participation and integration of patients, better documentation and an improved basis for medical treatment and nursing care could be achieved. Further, through an intensified integration, pa-
10 tients were enabled to better understand their medical condition and could participate more actively in the treatment and consultation processes. Our results indicate that customer (in our case patients) integration can lead to modifications for an enhanced patient-physician relationship enabled by improved patient information and autonomy. We also surmise that the prototype can improve productivity of medical processes not only by accounting for improved standards of medical care and quality of life, but also by being more cost efficient. The use of insert is almost as simple as filling in a paperbased questionnaire One of the patients died during the field study; with the help of the captured data this could have been anticipated by a physician shortly before. Generally, a healthy person starts with an ALSFRS base score of 48. Our patients had an average score of 31,15 points, starting with an average of 33,72 and finished after twelve weeks with an average of 30,61. If the score is less than 20 points, the patient will normally die within the next few weeks. The mentioned patient started with a score of 24 and fell below the threshold of 20 within a few weeks. Furthermore, we received requests from three patients whether they could continue to use the system even after the end of the field test. The physicians feedback was positive and there were no complaints. The subjectively assessed values have been regarded as realistic by the physicians. They checked the transmitted data with values before and after the field test. With the help of the transmitted data, we have an accurate data base on the individual patient. Before we used the system, we have examined the patient every three to six months and in the meantime we have received no information about the patients health status. The additional data allows us to adjust the treatment if the patient s condition changes. 6.2 Evaluation according to design goals The results of the evaluation are structured according to the five design goals. The average values of the individual items can be found in table 1. Increase the usability (1a) ease of use & (1b) perceived usefulness: The overall feedback of the user acceptance is very high. Thus, it can be assumed that the operation with the prototype is easy to learn and comprehend. The patients scored the used EDC system as a system which is easy to use for them. The interaction with the system did not require a lot of mental effort. The perceived usefulness has been rated as high, with the use of insert the documentation frequency of disease progression would increase. Furthermore, the usefulness for documenting the disease progression has been rated high. The patients could use the system without the help of relatives or nursing staff. Increase intention to use (2): As we can see in the evaluation results, the intention to use has been rated high. The results match the statements of telephone interviews and showed that some patients are interested in keeping the system in use after the field study. Increase confirmation (3): The confirmation of the system has been rated high. The functionalities of the system were better than the patients had expected. Overall, the expectations of the system were fulfilled. In summary, we could say that all the basic features were present and the patients did not miss any main functionality. Providing a very efficient and intuitive way of interaction suited to patients with impaired fine motor skills (4): With insert we can show, that the system provides a very efficient and intuitive way of interaction suited to patients with impaired fine motor skills. The patients have rated the use of NFC technology very high, the use of buttons to interact with the system scored worse. The vibration and acoustic statement of the mobile phone by touching an interactive field was a helpful functionality. Improve information quality (5): As a test of the technical feasibility of the systems, the mentioned field study was a great success. We received (average) records per patients with a standard deviation of A total of 2328 values were transmitted, with an error rate of 0.34 percent (8 data points), which have been caused by a double assessment or missing data point. The average assessment interval was 176:40:24 hours with a standard deviation of 64:23:41 hours. With the collected data, the physicians have a weekly picture of the patient s condition. Before they used the system, they generated this data only when the patients came to the hospital during regular appointments every three to six months.
11 Goal Variable (Source) (1a) Ease of use (Davis et al., 1989) (1b) Perceived usefulness (Davis et al., 1989) 2 Intention to use (Davis et al., 1989) 3 Confirmation (Bhattache rjee, 2001) 4 Intuitive way of interaction Table 1. Measurement Items (Range 1 to 7) AVG SD Learning to operate with insert is easy for me Interacting with insert requires a lot of mental effort I find insert easy to use Using insert would increase the frequency of documentation of disease progression. I find insert to be useful for documenting my disease progression Assuming that I have access to insert, I intend to use it Given that INSERT is available to me, I predict that I will use it. The functionality provided by insert was better than what I had expected. Overall, most of my expectations of using insert were confirmed. I prefer the use of insert via NFC (touching interactive fields on the poster) I prefer the use of insert via button (without touching interactive fields on the poster). The acoustic statement of each question section was helpful functionality. The vibration of the mobile phone by touching a question has been a helpful functionality. Evaluation results of insert , The prototype further revealed some design principles for NFC-based EDC in general. These include the importance of feedback (audible, visible and haptic), a comprehensible and coherent poster structure and measurements to ensure data security. Noted was the appreciation of the automated reminders and warnings. Patient responses in our study showed that this gave them a feeling of being cared for. We assume that the prototype system could be applied to other contexts or groups of patients in health care, such as elderly people who face similar difficulties in handling electronic devices. 7 Conclusion and future work Because of the rarity of the disease, we only had a very small number of cases and a generalisation is not always possible. This research paper describes the development, implementation and evaluation of an application that allows patients with impaired fine motor skills to assess their health status, based on an established rating scale. We therefore adapted NFC technology to a quality of life questionnaire. We focused on engineering an easy to use interaction. Our evaluation showed that patients with impaired fine motor skills accepted insert as a system that is easy to use and effective for reporting the patient s current condition. Through the active participation and integration of patients, improved documentation as well as an improved basis for medical treatment and nursing care could be achieved. Further, through an intensified integration, patients gained better understanding of their medical condition and were able to participate more actively and cooperate in the treatment and consultation processes. The example of insert shows the potentials and possibilities that technical support systems can offer to patients. The latter exemplary extension is based upon literature documenting that the completion of specific questionnaires enable improved forecasts of disease progression (Kaufmann et al., 2005). The recent integration of sensors (e.g., motion sensor) and additional technical devices (e.g., global positioning system (GPS) devices) in new generations of mobile phones additionally enable completely novel medical applications (Schweiger et al., 2007), which could extend our work. To
12 conclude, the use of mobile services and information technology can have a great impact on medical processes and services. Improvements of communication and interaction processes have a positive influence on the quality of patients lives. A modified patient-physician relationship, as a result of improved patient information and autonomy, offers new possibilities for the design of novel medical services which are only made possible by modern technical support systems. References Arnall, T. (2006). A graphic language for touch-based interactions. 8th conference on Humancomputer interaction with mobile devices and services Helsinki, Finland: ACM. Bhattacherjee, A. (2001). Understanding Information Systems Continuance: An Expectation- Confirmation Model. MIS Quarterly, 25 (3), Bischoff-Ferrari HA., Vondechend M., Bellamy N. and R., T. (2005). Validation and patient acceptance of a computer touch screen version of the WOMAC 3.1 Osteoarthritis Index. Ann Rheum Dis., 64 (1), Blake, H. (2008). Innovation in practice: mobile phone technology in patient care. Br J Community Nurs., 13 (4), 160, BMWi (2009). Breitbandstrategie der Bundesregierung. Berlin: Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie (BMWi). Bravo, J., López-de-Ipiña, D., Fuentes, C., Hervás, R., Peña, R., Vergara, M. and Casero, G. (2008). Enabling NFC Technology for Supporting Chronic Diseases: A Proposal for Alzheimer Caregivers. In Ambient Intelligence. (Aarts, E., Crowley, J., De Ruyter, B., Gerhäuser, H., Pflaum, A., Schmidt, J. and Wichert, R. Eds.), , Springer Berlin / Heidelberg. Dale O. and KB., H. (2007). Despite technical problems personal digital assistants outperform pen and paper when collecting patient diary data. J Clin Epidemiol, 60, Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P. and Warshaw, P. R. (1989). User acceptance of computer technology: a comparison of two theoretical models. Manage. Sci., 35 (8), ECMA-340 (2004). Near Field Communication Interface and Protocol (NFCIP-1). Fikry, M., Karim, A. and Muhamad, R. (2006). Integration of Near Field Communication (NFC) and Bluetooth Technology for Medical Data Acquisition System Computational Geometry & Artificial Vision, Forum, N. (2006). Smart Poster Record Type Definition. Available: [Accessed ] Grauer, H. and Birnbom, F. (1975). A Geriatric Functional Rating Scale to determine the need for institutional care. J Am Geriatrics Soc, 23, Guyatt, G. H., Feeny, D. H. and Patrick, D. L. (1993). Measuring health-related quality of life. Ann Intern Med, 118 (8), Hevner, A. R., March, S. T. and Park, J. (2004). Design science in information systems research. Management Information Systems Quarterly, 28 (1), Iglesias, R., Parra, J., Cruces, C. and Segura, N. G. d. (2009). Experiencing NFC-based touch for home healthcare. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Pervasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments. Corfu, Greece: ACM. Java (2010). What is J2ME or Java ME?. Available: [Accessed ] Jones, D. and Gregor, S. (2007). The Anatomy of a Design Theory. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 8 (5), Kasarskis, E. J., Scarlata, D., Hill, R., Fuller, C., Stambler, N. and Cedarbaum, J. M. (1999). A retrospective study of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in ALS patients during the BDNF and CNTF trials. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 169 (1-2), Kaufmann, P., Levy, G., Thompson, J. L. P., DelBene, M. L., Battista, V., Gordon, P. H., Rowland, L. P., Levin, B. and Mitsumoto, H. (2005). The ALSFRSr predicts survival time in an ALS clinic population. Neurology, 64,
13 Koene, P., Köbler, F., Burgner, P., Resatsch, F., Sandner, U., Leimeister, J. M. and Krcmar, H. (2010). RFID-based media usage panels in supportive environments. 18th European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS). Pretoria, South Africa. Lahtela, A., Hassinen, M. and Jylha, V. (2008). RFID and NFC in healthcare: Safety of hospitals medication care Second International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare. Tampere, Finland. Leimeister, J. M., Krcmar, H., Horsch, A. and Kuhn, K. (2005). Mobile IT-Systeme im Gesundheitswesen, mobile Systeme für Patienten. HMD Praxis der Wirtschaftsinformatik, 41 (244), Löser, C., Lübbers, H., Mahlke, R. and Lankisch, P. G. (2007). Der ungewollte Gewichtsverlust des alten Menschen. Dtsch Arztebl, 104 (49), Menschner, P., Prinz, A., Koene, P., Köbler, F., Altmann, M., Krcmar, H. and Leimeister, J. (2011). Reaching into patients homes participatory designed AAL services. Electronic Markets, Morak, J., Hayn, D., Kastner, P., Drobics, M. and Schreier, G. (2009). Near Field Communication Technology as the Key for Data Acquisition in Clinical Research. First International Workshop on Near Field Communication. Hagenberg, Austria. Morak, J., Kollmann, A., Hayn, D., Kastner, P., Humer, G. and Schreier, G. (2007). Improving telemonitoring of heart failure patients with NFC technology. Proceedings of the fifth IASTED International Conference: biomedical engineering. Innsbruck, Austria. Nyholm, D., Kowalski, J. and Aquilonius, S.-M. (2004). Wireless real-time electronic data capture for self-assessment of motor function and quality of life in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders, 19 (4), Palmblad M. and B., T. (2004). Electronic diaries and questionnaires: designing user interfaces that are easy for all patients to use. Qual Life Res., 13, Prinz, A., Menschner, P., Altmann, M. and Leimeister, J. M. (2011). insert - an NFC-based Self- Reporting Questionnaire for Patients with Fine Motor Diseases. 3rd International Workshop on Near Field Communication - NFC2011 Hagenberg. Prinz, A., Menschner, P. and Leimeister, J. M. (2009). NFC-basiertes Ernährungsmanagement für ältere, pflegebedürftige Menschen. Informatik Im Focus das Leben. Jahrestagung der Gesellschaft für Informatik. Lübeck: GI - Gesellschaft für Informatik, GI Lecture Notes in Informatics. Prinz, A., Menschner, P. and Leimeister, J. M. (2012). Has NFC the Potential to Revolutionize Selfreported Electronic Data Capture? An Empirical Comparison of Different Interaction Concepts CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Austin, USA: ACM. Richter, J. G., Nixdorf, M., Koch, T., Schneider, M., Becker, A. and Monser, R. (2006). Mobile Computing instead of paper based documentation in German Rheumatology. Proceedings of the International Conference on Mobile Business IEEE Computer Society. Schweiger, A., Sunyaev, A., Leimeister, J. M. and Krcmar, H. (2007). Toward seamless healthcare with software agents. Communications of the Association for Information Systems (CAIS), 19, Simon, H. A The Sciences of the Artificial (3rd ed.), Cambridge, MA, MIT Press. Strömgren, A. S., Groenvold, M., Sorensen, A. and Andersen, L. (2001). Symptom recognition in advanced cancer. A comparison of nursing records against patient self-rating. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 45 (9), Subramanya, S. R. and Yi, B. K. (2006). User interfaces for mobile content. Computer, 39 (4), Velikova, G., Wright, E. P., Smith, A. B., Cull, A., Gould, A., Forman, D., Perren, T., Stead, M., Brown, J. and Selby, P. J. (1999). Automated Collection of Quality-of-Life Data: A Comparison of Paper and Computer Touch-Screen Questionnaires. J Clin Oncol, 17 (3), Want, R. (2006). An Introduction to RFID Technology Pervasive Computing, 6, Welsh, M., McDermott, M. P., Holloway, R. G., Plumb, S., Pfeiffer, R. and Hubble, J. (2003). Development and testing of the Parkinson's disease quality of life scale. Movement Disorders, 18 (6), Wolfe, F. and Pincus, T. (1995). Data collection in the clinic. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America, 21 (2),
How To Create An Electronic Data Capture System For Health Care
 Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): Electronic Data Capture in HealthCare - NFC as Easy Way for Self reported Health Status Information. In: Health Policy and Technology,
Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): Electronic Data Capture in HealthCare - NFC as Easy Way for Self reported Health Status Information. In: Health Policy and Technology,
Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P.; Altmann, M. & Leimeister, J. M. (2011): insert - An NFC-based Self-Reporting Questionnaire for Patients
 Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P.; Altmann, M. & Leimeister, J. M. (2011): insert - An NFC-based Self-Reporting Questionnaire for Patients with Fine Motor Diseases. In: Third International Workshop
Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P.; Altmann, M. & Leimeister, J. M. (2011): insert - An NFC-based Self-Reporting Questionnaire for Patients with Fine Motor Diseases. In: Third International Workshop
Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): Has NFC the potential to revolutionize self-reported electronic data capture?
 Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): Has NFC the potential to revolutionize self-reported electronic data capture? - An empirical comparison of different interaction concept.
Please quote as: Prinz, A.; Menschner, P. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): Has NFC the potential to revolutionize self-reported electronic data capture? - An empirical comparison of different interaction concept.
Please quote as: Menschner, P.; Prinz, A.; Koene, P.; Köbler, F.; Altmann, M.; Krcmar, H. & Leimeister, J. M. (2011): Reaching into patients homes -
 Please quote as: Menschner, P.; Prinz, A.; Koene, P.; Köbler, F.; Altmann, M.; Krcmar, H. & Leimeister, J. M. (2011): Reaching into patients homes - participatory designed AAL services. In: Electronic
Please quote as: Menschner, P.; Prinz, A.; Koene, P.; Köbler, F.; Altmann, M.; Krcmar, H. & Leimeister, J. M. (2011): Reaching into patients homes - participatory designed AAL services. In: Electronic
Please quote as: Resatsch, F.; Sandner, U.; Höchst, C.; Michelis, D.; Schildhauer, T.; Leimeister, J. M. & Krcmar, H. (Hrsg.) (2007): Easymeeting -
 Please quote as: Resatsch, F.; Sandner, U.; Höchst, C.; Michelis, D.; Schildhauer, T.; Leimeister, J. M. & Krcmar, H. (Hrsg.) (2007): Easymeeting - Prototyping ubiquitous computing in offices. Erscheinungsjahr/Year:
Please quote as: Resatsch, F.; Sandner, U.; Höchst, C.; Michelis, D.; Schildhauer, T.; Leimeister, J. M. & Krcmar, H. (Hrsg.) (2007): Easymeeting - Prototyping ubiquitous computing in offices. Erscheinungsjahr/Year:
Please quote as: Köbler, F.; Koene, P.; Krcmar, H.; Altmann, M. & Leimeister, J. M. (2010): LocaTag - An NFC-based system enhancing instant messaging
 Please quote as: Köbler, F.; Koene, P.; Krcmar, H.; Altmann, M. & Leimeister, J. M. (2010): LocaTag - An NFC-based system enhancing instant messaging tools with real-time user location. In: 2. International
Please quote as: Köbler, F.; Koene, P.; Krcmar, H.; Altmann, M. & Leimeister, J. M. (2010): LocaTag - An NFC-based system enhancing instant messaging tools with real-time user location. In: 2. International
PROJECT: HEALTH DASHBOARD
 PROJECT OVERVIEW The Health Dashboard was my senior year capstone project for my major in Engineering Psychology at Tufts University. The goal of this project, which was sponsored by Cambridge Consultants,
PROJECT OVERVIEW The Health Dashboard was my senior year capstone project for my major in Engineering Psychology at Tufts University. The goal of this project, which was sponsored by Cambridge Consultants,
MoCoShoP: supporting mobile and collaborative shopping and planning of interiors
 MoCoShoP: supporting mobile and collaborative shopping and planning of interiors Julian Seifert 1, Dennis Schneider 2 and Enrico Rukzio 1 1 Ulm University, Ulm, Germany {julian.seifert, enrico.rukzio}@uni-ulm.de
MoCoShoP: supporting mobile and collaborative shopping and planning of interiors Julian Seifert 1, Dennis Schneider 2 and Enrico Rukzio 1 1 Ulm University, Ulm, Germany {julian.seifert, enrico.rukzio}@uni-ulm.de
STORE VIEW: Pervasive RFID & Indoor Navigation based Retail Inventory Management
 STORE VIEW: Pervasive RFID & Indoor Navigation based Retail Inventory Management Anna Carreras Tànger, 122-140. anna.carrerasc@upf.edu Marc Morenza-Cinos Barcelona, SPAIN marc.morenza@upf.edu Rafael Pous
STORE VIEW: Pervasive RFID & Indoor Navigation based Retail Inventory Management Anna Carreras Tànger, 122-140. anna.carrerasc@upf.edu Marc Morenza-Cinos Barcelona, SPAIN marc.morenza@upf.edu Rafael Pous
NFC Based Equipment Management Inventory System
 Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing c 2015 ISSN 2073-4212 Ubiquitous International Volume 6, Number 6, November 2015 NFC Based Equipment Management Inventory System Rung-Shiang
Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing c 2015 ISSN 2073-4212 Ubiquitous International Volume 6, Number 6, November 2015 NFC Based Equipment Management Inventory System Rung-Shiang
NFC: Enabler for Innovative Mobility and Payment NFC: MOBILIDADE E MEIOS DE PAGAMENTO
 NFC: Enabler for Innovative Mobility and Payment Cards Brazil Sao Paulo, April 3rd to 5th 2007 Rodolfo Gomes - 1st Level Customer Application Support NFC&RFID Europe A new Company has reborn Few months
NFC: Enabler for Innovative Mobility and Payment Cards Brazil Sao Paulo, April 3rd to 5th 2007 Rodolfo Gomes - 1st Level Customer Application Support NFC&RFID Europe A new Company has reborn Few months
Please quote as: Hartmann, M.; Bretschneider, U. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): Making patients to innovators - The case of the Ideenschmiede.
 Please quote as: Hartmann, M.; Bretschneider, U. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): Making patients to innovators - The case of the Ideenschmiede. In: R&D Management Conference 2012, Grenoble, France. Making
Please quote as: Hartmann, M.; Bretschneider, U. & Leimeister, J. M. (2012): Making patients to innovators - The case of the Ideenschmiede. In: R&D Management Conference 2012, Grenoble, France. Making
DropTheBeat a tangible user interface for cloud computing resources
 DropTheBeat a tangible user interface for cloud computing resources Philip Koene philip.koene@in.tum.de Felix Köbler felix.koebler@in.tum.de Suparna Goswami suparna.goswami@in.tum.de Copyright is held
DropTheBeat a tangible user interface for cloud computing resources Philip Koene philip.koene@in.tum.de Felix Köbler felix.koebler@in.tum.de Suparna Goswami suparna.goswami@in.tum.de Copyright is held
Ambient Intelligence: technological solutions for wellness and supporting to daily activities
 Tenth LACCEI Latin American and Caribbean Conference (LACCEI 2012), Megaprojects: Building Infrastructure by fostering engineering collaboration, efficient and effective integration and innovative planning,
Tenth LACCEI Latin American and Caribbean Conference (LACCEI 2012), Megaprojects: Building Infrastructure by fostering engineering collaboration, efficient and effective integration and innovative planning,
MOBILE PHONE APPLICATION TO SUPPORT THE ELDERLY
 International Journal of Cyber Society and Education Pages 51-56, Vol. 6, No. 1, June 2013 doi: 10.7903/ijcse.1047 MOBILE PHONE APPLICATION TO SUPPORT THE ELDERLY Maria Panou L. Mesogion 357-359, Athens,
International Journal of Cyber Society and Education Pages 51-56, Vol. 6, No. 1, June 2013 doi: 10.7903/ijcse.1047 MOBILE PHONE APPLICATION TO SUPPORT THE ELDERLY Maria Panou L. Mesogion 357-359, Athens,
Single Level Drill Down Interactive Visualization Technique for Descriptive Data Mining Results
 , pp.33-40 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijgdc.2014.7.4.04 Single Level Drill Down Interactive Visualization Technique for Descriptive Data Mining Results Muzammil Khan, Fida Hussain and Imran Khan Department
, pp.33-40 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijgdc.2014.7.4.04 Single Level Drill Down Interactive Visualization Technique for Descriptive Data Mining Results Muzammil Khan, Fida Hussain and Imran Khan Department
Semester 2 Semester 1 Quartile 2A Quartile 2B Quartile 1A Quartile 1B 5EC 5EC 5EC. Master Thesis and (if applicable) Internship (35EC)
 Master s programme Psychology 2015-2016 The Master s programme in Psychology (60EC, 1 year) offers five (specialization) tracks in the field of psychology: Human Factors & Engineering Psychology (in English)
Master s programme Psychology 2015-2016 The Master s programme in Psychology (60EC, 1 year) offers five (specialization) tracks in the field of psychology: Human Factors & Engineering Psychology (in English)
The Conceptualization of Integrated Consumer Health Informatics Utilization Framework
 The Conceptualization of Integrated Consumer Health Informatics Utilization Framework Norfadzila, S.W.A., Balakrishnan, V., A. Abrizah Abstract The purpose of this paper is to propose an integrated consumer
The Conceptualization of Integrated Consumer Health Informatics Utilization Framework Norfadzila, S.W.A., Balakrishnan, V., A. Abrizah Abstract The purpose of this paper is to propose an integrated consumer
COCIR GLOSSARY OF TERMS
 COCIR GLOSSARY OF TERMS 2 European Coordination Committee of the Radiological, 13 COCIR TELEMEDICINE TOOLKIT 2011 Part 2 GLOSSARY OF TERMS Introduction.............................. 14 Part I: Telemedicine
COCIR GLOSSARY OF TERMS 2 European Coordination Committee of the Radiological, 13 COCIR TELEMEDICINE TOOLKIT 2011 Part 2 GLOSSARY OF TERMS Introduction.............................. 14 Part I: Telemedicine
Mobile Haptics. A project funded by Tekes in 2006 2009
 Mobile Haptics A project funded by Tekes in 2006 2009 Mobile Haptics: Academic Research Groups TAUCHI Multimodal Interaction Research Group (MMIG), University of Tampere Prof. Roope Raisamo, coordinator
Mobile Haptics A project funded by Tekes in 2006 2009 Mobile Haptics: Academic Research Groups TAUCHI Multimodal Interaction Research Group (MMIG), University of Tampere Prof. Roope Raisamo, coordinator
Getting Clinicians Involved: Testing Smartphone Applications to Promote Behavior Change in Health Care
 Getting Clinicians Involved: Testing Smartphone Applications to Promote Behavior Change in Health Care Xiaomu Zhou 4 Huntington Street xmyzhou@rutgers.edu Lora Appel 4 Huntington Street lappel@eden.rutgers.edu
Getting Clinicians Involved: Testing Smartphone Applications to Promote Behavior Change in Health Care Xiaomu Zhou 4 Huntington Street xmyzhou@rutgers.edu Lora Appel 4 Huntington Street lappel@eden.rutgers.edu
Patient Trajectory Modeling and Analysis
 Patient Trajectory Modeling and Analysis Jalel Akaichi and Marwa Manaa Higher Institute of Management of tunis, 41 Rue de la Liberté, Cité Bouchoucha, 2000 Bardo, Tunisia j.akaichi@gmail.com, manaamarwa@gmail.com
Patient Trajectory Modeling and Analysis Jalel Akaichi and Marwa Manaa Higher Institute of Management of tunis, 41 Rue de la Liberté, Cité Bouchoucha, 2000 Bardo, Tunisia j.akaichi@gmail.com, manaamarwa@gmail.com
The preliminary design of a wearable computer for supporting Construction Progress Monitoring
 The preliminary design of a wearable computer for supporting Construction Progress Monitoring 1 Introduction Jan Reinhardt, TU - Dresden Prof. James H. Garrett,Jr., Carnegie Mellon University Prof. Raimar
The preliminary design of a wearable computer for supporting Construction Progress Monitoring 1 Introduction Jan Reinhardt, TU - Dresden Prof. James H. Garrett,Jr., Carnegie Mellon University Prof. Raimar
Getting Serious About a Platform Independent Application for the Usage of Mobile Moodle Quizzes: A Case Study
 Getting Serious About a Platform Independent Application for the Usage of Mobile Moodle Quizzes: A Case Study Stefan Geisler, Marc Jansen 1 Contents Introduction The System The Case Study Summary and Outlook
Getting Serious About a Platform Independent Application for the Usage of Mobile Moodle Quizzes: A Case Study Stefan Geisler, Marc Jansen 1 Contents Introduction The System The Case Study Summary and Outlook
WAITER: A Wearable Personal Healthcare and Emergency Aid System
 Sixth Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications WAITER: A Wearable Personal Healthcare and Emergency Aid System Wanhong Wu 1, Jiannong Cao 1, Yuan Zheng 1, Yong-Ping
Sixth Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications WAITER: A Wearable Personal Healthcare and Emergency Aid System Wanhong Wu 1, Jiannong Cao 1, Yuan Zheng 1, Yong-Ping
Store Logistics and Payment with Near Field Communication
 with www.stolpan.com Store Logistics and Payment with Near Field Communication Hagenberg, Hagenberg, March March 20. 2007 20. 2007. Dr. László Kutor, Dr. BMF László Kutor, BMF 19/1 StoLPaN Project Summary
with www.stolpan.com Store Logistics and Payment with Near Field Communication Hagenberg, Hagenberg, March March 20. 2007 20. 2007. Dr. László Kutor, Dr. BMF László Kutor, BMF 19/1 StoLPaN Project Summary
Evaluation of an Electronic Charting System in the BCIT Nursing Simulation Lab
 Evaluation of an Electronic Charting System in the BCIT Nursing Simulation Lab Prepared by: Johanne Mattie Research Associate, Technology and Product Evaluation Group As part of the Stage 3 ehealth Go
Evaluation of an Electronic Charting System in the BCIT Nursing Simulation Lab Prepared by: Johanne Mattie Research Associate, Technology and Product Evaluation Group As part of the Stage 3 ehealth Go
Customer Timeline - New in Summer 2012. Web Lead Capture - New in Summer 2012. Built-In Dashboards - New in Summer 2012
 What s New Maximizer CRM 12 Features New Mobile Access User Interface Enhanced Mobile Access Appointment Management Enhanced Web Access User Interface Improved Web Access Speed & Navigation LinkedIn Integration
What s New Maximizer CRM 12 Features New Mobile Access User Interface Enhanced Mobile Access Appointment Management Enhanced Web Access User Interface Improved Web Access Speed & Navigation LinkedIn Integration
Healthcare Delivery. Transforming. through Mobility Solutions. A Solution White Paper - version 1.0
 Transforming Healthcare Delivery through Mobility Solutions A Solution White Paper - version 1.0 HTC Global Services HTC Towers, No. 41, GST Road, Guindy, Chennai - 600 032, India. Ph: +91 44 4345 3500
Transforming Healthcare Delivery through Mobility Solutions A Solution White Paper - version 1.0 HTC Global Services HTC Towers, No. 41, GST Road, Guindy, Chennai - 600 032, India. Ph: +91 44 4345 3500
AMA, an application for Monitoring, Analysis and Monitoring A tool to better understand autism
 AMA, an application for Monitoring, Analysis and Monitoring A tool to better understand autism MAS 771: Autism Theory & Technology Akane Sano (akanes@mit.edu) Javier Hernandez (javierhr@mit.edu) Introduction
AMA, an application for Monitoring, Analysis and Monitoring A tool to better understand autism MAS 771: Autism Theory & Technology Akane Sano (akanes@mit.edu) Javier Hernandez (javierhr@mit.edu) Introduction
Towards a Transparent Proactive User Interface for a Shopping Assistant
 Towards a Transparent Proactive User Interface for a Shopping Assistant Michael Schneider Department of Computer Science, Saarland University, Stuhlsatzenhausweg, Bau 36.1, 66123 Saarbrücken, Germany mschneid@cs.uni-sb.de
Towards a Transparent Proactive User Interface for a Shopping Assistant Michael Schneider Department of Computer Science, Saarland University, Stuhlsatzenhausweg, Bau 36.1, 66123 Saarbrücken, Germany mschneid@cs.uni-sb.de
Mobile Assistant for Monitoring Plant Pests and Diseases
 Mobile Assistant for Monitoring Plant Pests and Diseases Christian Kuhn 1, Juliane Schmitt 1, Manfred Röhrig 2 1 ZEPP Central Institution for Decision Support Systems in Crop Protection Rüdesheimer Str.
Mobile Assistant for Monitoring Plant Pests and Diseases Christian Kuhn 1, Juliane Schmitt 1, Manfred Röhrig 2 1 ZEPP Central Institution for Decision Support Systems in Crop Protection Rüdesheimer Str.
How To Help A Family With Dementia
 NHS Highland area: Specialist dementia support for families, carers & communities Research Project Executive Summary Supported by Argyll & Bute Council, the Highland Council and NHS Highland 1. Introduction
NHS Highland area: Specialist dementia support for families, carers & communities Research Project Executive Summary Supported by Argyll & Bute Council, the Highland Council and NHS Highland 1. Introduction
Cellular Wireless technology: Creating a link between people and the healthcare community
 Cellular Wireless technology: Creating a link between people and the healthcare community Introduction Demands on health-care systems worldwide have increased to the point where the delivery and cost of
Cellular Wireless technology: Creating a link between people and the healthcare community Introduction Demands on health-care systems worldwide have increased to the point where the delivery and cost of
Using Physical Mobile Interaction for
 Using Physical Mobile Interaction for the Personalization of Ubiquitous Services Sonja Finkenzeller, Diploma Thesis Final Presentation Duration: 30.11.2008 31.05.2009 Responsible Supervisor: Dipl.-Medieninf.
Using Physical Mobile Interaction for the Personalization of Ubiquitous Services Sonja Finkenzeller, Diploma Thesis Final Presentation Duration: 30.11.2008 31.05.2009 Responsible Supervisor: Dipl.-Medieninf.
Please quote as: Köbler, F.; Goswami, S.; Koene, P.; Leimeister, J. M. & Krcmar, H. (2011): Using NFriendConnector to Extend Facebook to the Real
 Please quote as: Köbler, F.; Goswami, S.; Koene, P.; Leimeister, J. M. & Krcmar, H. (2011): Using NFriendConnector to Extend Facebook to the Real World. In: Wirtschaftsinformatik Konferenz (WI) 2011, Zürich,
Please quote as: Köbler, F.; Goswami, S.; Koene, P.; Leimeister, J. M. & Krcmar, H. (2011): Using NFriendConnector to Extend Facebook to the Real World. In: Wirtschaftsinformatik Konferenz (WI) 2011, Zürich,
Internationalization Processes for Open Educational Resources
 Internationalization Processes for Open Educational Resources Henri Pirkkalainen 1, Stefan Thalmann 2, Jan Pawlowski 1, Markus Bick 3, Philipp Holtkamp 1, Kyung-Hun Ha 3 1 University of Jyväskylä, Global
Internationalization Processes for Open Educational Resources Henri Pirkkalainen 1, Stefan Thalmann 2, Jan Pawlowski 1, Markus Bick 3, Philipp Holtkamp 1, Kyung-Hun Ha 3 1 University of Jyväskylä, Global
Analyzing lifelong learning student behavior in a progressive degree
 Analyzing lifelong learning student behavior in a progressive degree Ana-Elena Guerrero-Roldán, Enric Mor, Julià Minguillón Universitat Oberta de Catalunya Barcelona, Spain {aguerreror, emor, jminguillona}@uoc.edu
Analyzing lifelong learning student behavior in a progressive degree Ana-Elena Guerrero-Roldán, Enric Mor, Julià Minguillón Universitat Oberta de Catalunya Barcelona, Spain {aguerreror, emor, jminguillona}@uoc.edu
Reading with Mobile Phone & Large Display
 Reading with Mobile Phone & Large Display Roswitha Gostner Computing Department Lancaster University, gostner@lancs.ac.uk Hans Gellersen Computing Department Lancaster University Lancaster, LA1 4WY, UK
Reading with Mobile Phone & Large Display Roswitha Gostner Computing Department Lancaster University, gostner@lancs.ac.uk Hans Gellersen Computing Department Lancaster University Lancaster, LA1 4WY, UK
EHRs and Contexts of Use
 2 EHRs and Contexts of Use A Providers Perspective on EHR User Experience Presented by March 2013 1 EHRs and Contexts of Use It s not a new concept. Most modern EHRs, descending from products designed
2 EHRs and Contexts of Use A Providers Perspective on EHR User Experience Presented by March 2013 1 EHRs and Contexts of Use It s not a new concept. Most modern EHRs, descending from products designed
User-centered Requirements Elicitation for Business Intelligence Solutions
 User-centered Requirements Elicitation for Business Intelligence Solutions Hendrik Meth and Alexander Mädche University of Mannheim Chair of Information Systems IV - Enterprise Information Systems 68131
User-centered Requirements Elicitation for Business Intelligence Solutions Hendrik Meth and Alexander Mädche University of Mannheim Chair of Information Systems IV - Enterprise Information Systems 68131
Bachelor of Games and Virtual Worlds (Programming) Subject and Course Summaries
 First Semester Development 1A On completion of this subject students will be able to apply basic programming and problem solving skills in a 3 rd generation object-oriented programming language (such as
First Semester Development 1A On completion of this subject students will be able to apply basic programming and problem solving skills in a 3 rd generation object-oriented programming language (such as
TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT ACKNOWLEDGEMENT LIST OF FIGURES LIST OF TABLES
 TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT ACKNOWLEDGEMENT LIST OF FIGURES LIST OF TABLES ii iii x xiv CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION 1 1.0 Background 1 1.1 Research Motivation 4 1.2 Research Objectives 5 1.3 Project Scope 6
TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT ACKNOWLEDGEMENT LIST OF FIGURES LIST OF TABLES ii iii x xiv CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION 1 1.0 Background 1 1.1 Research Motivation 4 1.2 Research Objectives 5 1.3 Project Scope 6
How To Make A Light Bulb For Older People
 Ambient Lighting Assistance New lighting technology for enhancing the wellbeing of older people Project Information The Specific Targeted Research Project (STREP) Ambient Lighting Assistance for an Ageing
Ambient Lighting Assistance New lighting technology for enhancing the wellbeing of older people Project Information The Specific Targeted Research Project (STREP) Ambient Lighting Assistance for an Ageing
Web of Things Use Cases and Solutions at FZI
 Web of Things Use Cases and Solutions at FZI Speaker: Benedikt Kämpgen (FZI) Location: W3C Web of Things Workshop, Munich Date: 20.04.2015 FZI FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM INFORMATIK Semantic Web vs Web of Things
Web of Things Use Cases and Solutions at FZI Speaker: Benedikt Kämpgen (FZI) Location: W3C Web of Things Workshop, Munich Date: 20.04.2015 FZI FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM INFORMATIK Semantic Web vs Web of Things
Online Tools for Co-design User Involvement through the Innovation Process
 PAPER I Online Tools for Co-design User Involvement through the Innovation Process In: Karahasanovic, A. and Følstad, A. (Eds.). The NordiCHI 2008 Workshops: New Approaches to Requirements Elicitation
PAPER I Online Tools for Co-design User Involvement through the Innovation Process In: Karahasanovic, A. and Følstad, A. (Eds.). The NordiCHI 2008 Workshops: New Approaches to Requirements Elicitation
Digia was among the first. Applying User-Centered Design. to Mobile Application Development
 Applying User-Centered Design Digia was among the first companies to develop third-party software applications that can be installed in Symbian smart phones by service providers or end users [3]. In 2001,
Applying User-Centered Design Digia was among the first companies to develop third-party software applications that can be installed in Symbian smart phones by service providers or end users [3]. In 2001,
A Comparison of Mobile Peer-to-peer File-sharing Clients
 1. ABSTRACT A Comparison of Mobile Peer-to-peer File-sharing Clients Imre Kelényi 1, Péter Ekler 1, Bertalan Forstner 2 PHD Students 1, Assistant Professor 2 Budapest University of Technology and Economics
1. ABSTRACT A Comparison of Mobile Peer-to-peer File-sharing Clients Imre Kelényi 1, Péter Ekler 1, Bertalan Forstner 2 PHD Students 1, Assistant Professor 2 Budapest University of Technology and Economics
The Personal Medical Unit A Ubiquitous Computing Infrastructure for Personal Pervasive Healthcare
 The Personal Medical Unit A Ubiquitous Computing Infrastructure for Personal Pervasive Healthcare Jakob E. Bardram Centre for Pervasive Healthcare Department of Computer Science, University of Aarhus Aabogade
The Personal Medical Unit A Ubiquitous Computing Infrastructure for Personal Pervasive Healthcare Jakob E. Bardram Centre for Pervasive Healthcare Department of Computer Science, University of Aarhus Aabogade
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Andreas Schrader
 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Andreas Schrader Ambient Computing Group Institute of Telematics University of Lübeck www.itm.uni-luebeck.de schrader@itm.uni-luebeck.de Working Group Ambient Computing Institute for Telematics,
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Andreas Schrader Ambient Computing Group Institute of Telematics University of Lübeck www.itm.uni-luebeck.de schrader@itm.uni-luebeck.de Working Group Ambient Computing Institute for Telematics,
Smartphone Applications for Medication Management
 Smartphone Applications for Medication Management Introduction and Overview: The objective of the Computer Science Design Laboratory this semester is to provide exposure to a wide range of emerging technologies
Smartphone Applications for Medication Management Introduction and Overview: The objective of the Computer Science Design Laboratory this semester is to provide exposure to a wide range of emerging technologies
Remote Usability Evaluation of Mobile Web Applications
 Remote Usability Evaluation of Mobile Web Applications Paolo Burzacca and Fabio Paternò CNR-ISTI, HIIS Laboratory, via G. Moruzzi 1, 56124 Pisa, Italy {paolo.burzacca,fabio.paterno}@isti.cnr.it Abstract.
Remote Usability Evaluation of Mobile Web Applications Paolo Burzacca and Fabio Paternò CNR-ISTI, HIIS Laboratory, via G. Moruzzi 1, 56124 Pisa, Italy {paolo.burzacca,fabio.paterno}@isti.cnr.it Abstract.
Mobile Devices Accelerate Patient Centric Healthcare
 Mobile Devices Accelerate Patient Centric Healthcare Steven F. Owens 1, MedNest, LLC As this web enabled digital age evolves from desktop computers with modems to mobile computing devices and sensors capable
Mobile Devices Accelerate Patient Centric Healthcare Steven F. Owens 1, MedNest, LLC As this web enabled digital age evolves from desktop computers with modems to mobile computing devices and sensors capable
Transforming Healthcare in Emerging Markets with EMR adoption
 Transforming Healthcare in Emerging Markets with EMR adoption Author Ann Geo Thekkel User Experience. Accenture, India Ann.geothekkel@accenture.com Abstract Compromising 24 countries, 35 percent of the
Transforming Healthcare in Emerging Markets with EMR adoption Author Ann Geo Thekkel User Experience. Accenture, India Ann.geothekkel@accenture.com Abstract Compromising 24 countries, 35 percent of the
A Study of the Design of Wireless Medical Sensor Network based u- Healthcare System
 , pp.91-96 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijbsbt.2014.6.3.11 A Study of the Design of Wireless Medical Sensor Network based u- Healthcare System Ronnie D. Caytiles and Sungwon Park 1* 1 Hannam University 133
, pp.91-96 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijbsbt.2014.6.3.11 A Study of the Design of Wireless Medical Sensor Network based u- Healthcare System Ronnie D. Caytiles and Sungwon Park 1* 1 Hannam University 133
GIM Capital Goods / B2B. Heidelberg, April 2015
 GIM Capital Goods / B2B Heidelberg, April 2015 04/2015 AGENDA 1. GIM Profile 2. GIM Capital Goods / B2B 3. Potential Methodological Approach GIM in a Nutshell GIM is one of the biggest and most experienced
GIM Capital Goods / B2B Heidelberg, April 2015 04/2015 AGENDA 1. GIM Profile 2. GIM Capital Goods / B2B 3. Potential Methodological Approach GIM in a Nutshell GIM is one of the biggest and most experienced
Telecommunication (120 ЕCTS)
 Study program Faculty Cycle Software Engineering and Telecommunication (120 ЕCTS) Contemporary Sciences and Technologies Postgraduate ECTS 120 Offered in Tetovo Description of the program This master study
Study program Faculty Cycle Software Engineering and Telecommunication (120 ЕCTS) Contemporary Sciences and Technologies Postgraduate ECTS 120 Offered in Tetovo Description of the program This master study
Contents The College of Information Science and Technology 2011-2012 Undergraduate Course Descriptions
 Contents The College of Information Science and Technology 2011-2012 Undergraduate Course Descriptions Information Science & Systems Courses INFO 101 - Introduction to Information Technology Introduces
Contents The College of Information Science and Technology 2011-2012 Undergraduate Course Descriptions Information Science & Systems Courses INFO 101 - Introduction to Information Technology Introduces
How To Write Long Term Care Insurance
 By Lori Boyce, AVP Risk Management and R&D Underwriting long term care insurance: a primer Every day Canadians die, are diagnosed with cancer, have heart attacks and become disabled and our insurance solutions
By Lori Boyce, AVP Risk Management and R&D Underwriting long term care insurance: a primer Every day Canadians die, are diagnosed with cancer, have heart attacks and become disabled and our insurance solutions
Enabling Integrated Care
 Enabling Integrated Care Harnessing personal health systems for better outcomes across the care continuum Briefing Note for a SmartPersonalHealth Workshop WoHIT, Thursday 18 March 2010, 13:00-17:00, Barcelona
Enabling Integrated Care Harnessing personal health systems for better outcomes across the care continuum Briefing Note for a SmartPersonalHealth Workshop WoHIT, Thursday 18 March 2010, 13:00-17:00, Barcelona
Summary chapter 2 chapter 2
 Summary Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the brain and the spinal cord. The cause of MS is unknown. MS usually starts in young adulthood. In the course of the disease progression of neurological
Summary Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the brain and the spinal cord. The cause of MS is unknown. MS usually starts in young adulthood. In the course of the disease progression of neurological
T3.1. Independent Living Applications Portfolio. Henk Herman Nap: h.h.nap@smart-homes.nl. Ad van Berlo: a.vberlo@smart-homes.nl
 T3.1 Independent Living Applications Portfolio Henk Herman Nap: h.h.nap@smart-homes.nl Ad van Berlo: a.vberlo@smart-homes.nl Richard Pasmans: r.pasmans@smart-homes.nl 2013 Roll-out with 7000 users in real
T3.1 Independent Living Applications Portfolio Henk Herman Nap: h.h.nap@smart-homes.nl Ad van Berlo: a.vberlo@smart-homes.nl Richard Pasmans: r.pasmans@smart-homes.nl 2013 Roll-out with 7000 users in real
MAGPIE: An Agent Platform for the Development of Mobile Applications for Pervasive Healthcare
 MAGPIE: An Agent Platform for the Development of Mobile Applications for Pervasive Healthcare Albert Brugués 1,2, Stefano Bromuri 1, Josep Pegueroles 2, and Michael Schumacher 1 1 University of Applied
MAGPIE: An Agent Platform for the Development of Mobile Applications for Pervasive Healthcare Albert Brugués 1,2, Stefano Bromuri 1, Josep Pegueroles 2, and Michael Schumacher 1 1 University of Applied
THE ROLE OF HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN PATIENT-CENTERED CARE COLLABORATION. 2012 Louisiana HIPAA & EHR Conference Presenter: Chris Williams
 THE ROLE OF HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN PATIENT-CENTERED CARE COLLABORATION 2012 Louisiana HIPAA & EHR Conference Presenter: Chris Williams Agenda Overview Impact of HIT on Patient-Centered Care (PCC)
THE ROLE OF HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN PATIENT-CENTERED CARE COLLABORATION 2012 Louisiana HIPAA & EHR Conference Presenter: Chris Williams Agenda Overview Impact of HIT on Patient-Centered Care (PCC)
Framework for Near-Field- Communication-Based Geo-Localization and Personalization for Android-Based Smartphones Application in Hospital Environments
 ehealth2014 Health Informatics Meets ehealth A. Hörbst et al. (Eds.) 2014 The authors and IOS Press. This article is published online with Open Access by IOS Press and distributed under the terms of the
ehealth2014 Health Informatics Meets ehealth A. Hörbst et al. (Eds.) 2014 The authors and IOS Press. This article is published online with Open Access by IOS Press and distributed under the terms of the
Health Informatics and Artificial Intelligence: the next big thing in health/aged care
 Health Informatics and Artificial Intelligence: the next big thing in health/aged care Professor Michael Blumenstein Griffith University ACSA National Conference, Adelaide Tuesday, September 9 th 2014
Health Informatics and Artificial Intelligence: the next big thing in health/aged care Professor Michael Blumenstein Griffith University ACSA National Conference, Adelaide Tuesday, September 9 th 2014
Loyalty Systems over Near Field Communication (NFC)
 Loyalty Systems over Near Field Communication (NFC) Diogo Simões IST - Technical University of Lisbon Av. Prof. Cavaco Silva Tagus Park 2780-990 Porto Salvo, Portugal diogo.simoes@tagus.ist.utl.pt Abstract.
Loyalty Systems over Near Field Communication (NFC) Diogo Simões IST - Technical University of Lisbon Av. Prof. Cavaco Silva Tagus Park 2780-990 Porto Salvo, Portugal diogo.simoes@tagus.ist.utl.pt Abstract.
Towards Persuasive Technologies for Improved Software Quality
 Towards Persuasive Technologies for Improved Software Quality Sophie Steinparz 1, Alexander Felfernig 1, Ingo Pribik 2, and Gerhard Leitner 3 1 Institute for Software Technology, Applied Software Engineering,
Towards Persuasive Technologies for Improved Software Quality Sophie Steinparz 1, Alexander Felfernig 1, Ingo Pribik 2, and Gerhard Leitner 3 1 Institute for Software Technology, Applied Software Engineering,
ENHANCING MOBILE PEER-TO-PEER ENVIRONMENT WITH NEIGHBORHOOD INFORMATION
 ENHANCING MOBILE PEER-TO-PEER ENVIRONMENT WITH NEIGHBORHOOD INFORMATION Arto Hämäläinen and Jari Porras Lappeenranta University of Technology Laboratory of Communications Engineering P.O. Box 20 53851
ENHANCING MOBILE PEER-TO-PEER ENVIRONMENT WITH NEIGHBORHOOD INFORMATION Arto Hämäläinen and Jari Porras Lappeenranta University of Technology Laboratory of Communications Engineering P.O. Box 20 53851
PREDICTING ACCEPTANCE OF ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS: WHAT FACTORS MATTER MOST?
 PREDICTING ACCEPTANCE OF ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS: WHAT FACTORS MATTER MOST? Shanan G. Gibson & Elaine D. Seeman College of Business, East Carolina University gibsons@ecu.edu; seemane@ecu.edu ABSTRACT
PREDICTING ACCEPTANCE OF ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS: WHAT FACTORS MATTER MOST? Shanan G. Gibson & Elaine D. Seeman College of Business, East Carolina University gibsons@ecu.edu; seemane@ecu.edu ABSTRACT
A Framework of Context-Sensitive Visualization for User-Centered Interactive Systems
 Proceedings of 10 th International Conference on User Modeling, pp423-427 Edinburgh, UK, July 24-29, 2005. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2005 A Framework of Context-Sensitive Visualization for User-Centered
Proceedings of 10 th International Conference on User Modeling, pp423-427 Edinburgh, UK, July 24-29, 2005. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2005 A Framework of Context-Sensitive Visualization for User-Centered
Agenda. ARITHMOS Presents: Introduction to epro. EDC and epro integration General Overview. epro and ecrf Integration: a case study
 Agenda ARITHMOS Presents: epro and ecrf Integration: a case study Introduction to epro EDC and epro integration General Overview From epro to ipro: Technology trend in Pharma epro EDC integration: A case
Agenda ARITHMOS Presents: epro and ecrf Integration: a case study Introduction to epro EDC and epro integration General Overview From epro to ipro: Technology trend in Pharma epro EDC integration: A case
Wireless Multimedia Technologies for Assisted Living
 Second LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCEI 2004) Challenges and Opportunities for Engineering Education, Research and Development 2-4 June
Second LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCEI 2004) Challenges and Opportunities for Engineering Education, Research and Development 2-4 June
Open Access Research and Design for Mobile Terminal-Based on Smart Home System
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2015, 7, 479-484 479 Open Access Research and Design for Mobile Terminal-Based on Smart Home System
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2015, 7, 479-484 479 Open Access Research and Design for Mobile Terminal-Based on Smart Home System
 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
What Do Master s Thesis Titles Inform about Media Technology?
 What Do Master s Thesis Titles Inform about Media Technology? Oittinen, P. Aalto University, School of Science (Aalto SCI), Department of Media Technology, P.O.Box 15500, FIN-00076 Aalto, Finland, http://media.tkk.fi
What Do Master s Thesis Titles Inform about Media Technology? Oittinen, P. Aalto University, School of Science (Aalto SCI), Department of Media Technology, P.O.Box 15500, FIN-00076 Aalto, Finland, http://media.tkk.fi
Personalized Fall Risk Assessment Tool by using the Data Treasure contained in Mobile Electronic Patient Records
 Personalized Fall Risk Assessment Tool by using the Data Treasure contained in Mobile Electronic Patient Records Elif ERYILMAZ a,1, Sebastian AHRNDT a, Johannes FÄHNDRICH a and Sahin ALBAYRAK a a DAI Lab,
Personalized Fall Risk Assessment Tool by using the Data Treasure contained in Mobile Electronic Patient Records Elif ERYILMAZ a,1, Sebastian AHRNDT a, Johannes FÄHNDRICH a and Sahin ALBAYRAK a a DAI Lab,
Key factors for personal health monitoring and diagnosis devices
 Key factors for personal health monitoring and diagnosis devices Schwaibold M, Gmelin M, von Wagner G, Schöchlin J, Bolz A {schwaibold schoechlin bolz}@fzi.de Germany Abstract: The current common goal
Key factors for personal health monitoring and diagnosis devices Schwaibold M, Gmelin M, von Wagner G, Schöchlin J, Bolz A {schwaibold schoechlin bolz}@fzi.de Germany Abstract: The current common goal
Communication Support System Between Persons with Dementia and Family Caregivers using Memories
 Communication Support System Between Persons with Dementia and Family Caregivers using Memories Kazuhiro Yamasaki Graduate School of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Shiga, Japan
Communication Support System Between Persons with Dementia and Family Caregivers using Memories Kazuhiro Yamasaki Graduate School of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Shiga, Japan
The Importance of User-Centered Design
 Research Statement Chaiwoo Lee As I study topics around user-centered product design and development, I always try to keep the broader implications of my research in mind. Research on user-centered design
Research Statement Chaiwoo Lee As I study topics around user-centered product design and development, I always try to keep the broader implications of my research in mind. Research on user-centered design
Modelling user acceptance of wireless medical technologies
 Modelling user acceptance of wireless medical technologies Katrin Arning, Sylvia Kowalewski, and Martina Ziefle Human Computer Interaction Center (HCIC), RWTH Aachen University Theaterplatz 14, 52062 Aachen,
Modelling user acceptance of wireless medical technologies Katrin Arning, Sylvia Kowalewski, and Martina Ziefle Human Computer Interaction Center (HCIC), RWTH Aachen University Theaterplatz 14, 52062 Aachen,
Fig. 1 BAN Architecture III. ATMEL BOARD
 Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2014 ISSN: 2321 7782 (Online) International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2014 ISSN: 2321 7782 (Online) International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
Building on our strengths through technology. Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital Technology Strategy
 Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital Technology Strategy Building on our strengths through technology Advanced technology in rehabilitation is exploding as new and innovative approaches to therapy emerge and
Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital Technology Strategy Building on our strengths through technology Advanced technology in rehabilitation is exploding as new and innovative approaches to therapy emerge and
Power & Environmental Monitoring
 Data Centre Monitoring Made Easy Power & Environmental Monitoring Features & Benefits Packet Power provides the easiest, most cost effective way to capture detailed power and temperature information for
Data Centre Monitoring Made Easy Power & Environmental Monitoring Features & Benefits Packet Power provides the easiest, most cost effective way to capture detailed power and temperature information for
Table of contents. 1. About the platform 3. 2. MetaTrader 4 platform Installation 4. 3. Logging in 5 - Common log in problems 5
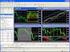 Table of contents 1. About the platform 3 2. MetaTrader 4 platform Installation 4 3. Logging in 5 - Common log in problems 5 4. How to change your password 6 5. User Interface and Customization 7 - Toolbars
Table of contents 1. About the platform 3 2. MetaTrader 4 platform Installation 4 3. Logging in 5 - Common log in problems 5 4. How to change your password 6 5. User Interface and Customization 7 - Toolbars
Building Open-Source Based Architecture of Enterprise Applications for Business Intelligence
 Building Open-Source Based Architecture of Enterprise Applications for Business Intelligence TOMAS CHLOUBA Department of Informatics and Quantitative Methods University of Hradec Kralove Rokitanskeho 62,
Building Open-Source Based Architecture of Enterprise Applications for Business Intelligence TOMAS CHLOUBA Department of Informatics and Quantitative Methods University of Hradec Kralove Rokitanskeho 62,
Licensed Healthcare Providers Guidelines for Telemedicine Using the MyDocNow Platform
 Contents 1. Scope of These Guidelines... 2 2. What is Telemedicine?... 2 3. Introduction... 3 4. What Are the Benefits of Telemedicine?... 3 5. Frequently Asked Questions Physician Care and Treatment...
Contents 1. Scope of These Guidelines... 2 2. What is Telemedicine?... 2 3. Introduction... 3 4. What Are the Benefits of Telemedicine?... 3 5. Frequently Asked Questions Physician Care and Treatment...
Enhancing Mobile Browsing and Reading
 Enhancing Mobile Browsing and Reading Chen-Hsiang Yu MIT CSAIL 32 Vassar St Cambridge, MA 02139 chyu@mit.edu Robert C. Miller MIT CSAIL 32 Vassar St Cambridge, MA 02139 rcm@mit.edu Abstract Although the
Enhancing Mobile Browsing and Reading Chen-Hsiang Yu MIT CSAIL 32 Vassar St Cambridge, MA 02139 chyu@mit.edu Robert C. Miller MIT CSAIL 32 Vassar St Cambridge, MA 02139 rcm@mit.edu Abstract Although the
Patient Empowerment Framework for Cardiac Patients
 Patient Empowerment Framework for Cardiac Patients Robert Mulrenin a, Manuela Plößnig a, Mihai Radulescu a, Gökçe Banu Laleci b, Catherine Chronaki c and Yildiray Kabak b a Salzburg Research Forschungsgesellschaft,
Patient Empowerment Framework for Cardiac Patients Robert Mulrenin a, Manuela Plößnig a, Mihai Radulescu a, Gökçe Banu Laleci b, Catherine Chronaki c and Yildiray Kabak b a Salzburg Research Forschungsgesellschaft,
Donnellan, Brian Gleasure, Rob Helfert, Markus Kenneally, Jim Rothenberger, Marcus Chiarini Tremblay, Monica VanderMeer, Debra Winter, Robert
 Title Author(s) Editor(s) ITSM ProcessGuide a longitudinal and multi-method field study for real-world DSR artifact evaluation Morana, Stefan; Schacht, Silvia; Gerards, Timo; Maedche, Alexander Donnellan,
Title Author(s) Editor(s) ITSM ProcessGuide a longitudinal and multi-method field study for real-world DSR artifact evaluation Morana, Stefan; Schacht, Silvia; Gerards, Timo; Maedche, Alexander Donnellan,
Overview of Dutch working conditions 2014. Summary
 Overview of Dutch working conditions 2014 Summary Overview of Dutch working conditions 2014 Summary Authors Marjolein Douwes Anita Venema Seth van den Bossche Publisher TNO, Leiden, 2015 Commissioned by
Overview of Dutch working conditions 2014 Summary Overview of Dutch working conditions 2014 Summary Authors Marjolein Douwes Anita Venema Seth van den Bossche Publisher TNO, Leiden, 2015 Commissioned by
Tele-monitoring as a medical application of Ubiquitous Computing
 Tele-monitoring as a medical application of Ubiquitous Computing C. Kunze, W. Stork, K.D. Müller-Glaser Institut für Technik der Informationsverarbeitung Universität Karlsruhe Engesserstr. 5 76128 Karlsruhe
Tele-monitoring as a medical application of Ubiquitous Computing C. Kunze, W. Stork, K.D. Müller-Glaser Institut für Technik der Informationsverarbeitung Universität Karlsruhe Engesserstr. 5 76128 Karlsruhe
Dr Louise Schaper, PhD CEO, Health Informatics Society of Australia
 Dr Louise Schaper, PhD CEO, Health Informatics Society of Australia Megatrend One: Older population Megatrend One: Older population Megatrend One: Older population Megatrend Two: Digital technology in
Dr Louise Schaper, PhD CEO, Health Informatics Society of Australia Megatrend One: Older population Megatrend One: Older population Megatrend One: Older population Megatrend Two: Digital technology in
Business Intelligence in E-Learning
 Business Intelligence in E-Learning (Case Study of Iran University of Science and Technology) Mohammad Hassan Falakmasir 1, Jafar Habibi 2, Shahrouz Moaven 1, Hassan Abolhassani 2 Department of Computer
Business Intelligence in E-Learning (Case Study of Iran University of Science and Technology) Mohammad Hassan Falakmasir 1, Jafar Habibi 2, Shahrouz Moaven 1, Hassan Abolhassani 2 Department of Computer
NetVision. NetVision: Smart Energy Smart Grids and Smart Meters - Towards Smarter Energy Management. Solution Datasheet
 Version 2.0 - October 2014 NetVision Solution Datasheet NetVision: Smart Energy Smart Grids and Smart Meters - Towards Smarter Energy Management According to analyst firm Berg Insight, the installed base
Version 2.0 - October 2014 NetVision Solution Datasheet NetVision: Smart Energy Smart Grids and Smart Meters - Towards Smarter Energy Management According to analyst firm Berg Insight, the installed base
The Six A s. for Population Health Management. Suzanne Cogan, VP North American Sales, Orion Health
 The Six A s for Population Health Management Suzanne Cogan, VP North American Sales, Summary Healthcare organisations globally are investing significant resources in re-architecting their care delivery
The Six A s for Population Health Management Suzanne Cogan, VP North American Sales, Summary Healthcare organisations globally are investing significant resources in re-architecting their care delivery
THE NATURE OF MEDICAL DEVICE SERVICES A Multiple-Case Study
 THE NATURE OF MEDICAL DEVICE SERVICES A Multiple-Case Study Christian Mauro, Helmut Krcmar Information Systems, Technische Universität München, Boltzmannstr. 3, 85748 Garching, Germany mauro@in.tum.de,
THE NATURE OF MEDICAL DEVICE SERVICES A Multiple-Case Study Christian Mauro, Helmut Krcmar Information Systems, Technische Universität München, Boltzmannstr. 3, 85748 Garching, Germany mauro@in.tum.de,
RHODE ISLAND SERVICES FOR THE BLIND AND VISUALLY IMPAIRED ORS/DHS THE INDEPENDENT LIVING FOR OLDER BLIND PROGRAM
 RHODE ISLAND SERVICES FOR THE BLIND AND VISUALLY IMPAIRED ORS/DHS THE INDEPENDENT LIVING FOR OLDER BLIND PROGRAM FINAL EVALUATION REPORT OCTOBER 1, 2005 - SEPTEMBER 30, 2006 Prepared by Kristine L. Chadwick,
RHODE ISLAND SERVICES FOR THE BLIND AND VISUALLY IMPAIRED ORS/DHS THE INDEPENDENT LIVING FOR OLDER BLIND PROGRAM FINAL EVALUATION REPORT OCTOBER 1, 2005 - SEPTEMBER 30, 2006 Prepared by Kristine L. Chadwick,
