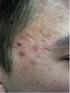
Comparison efficacy of azithromycin vs. doxycycline in patients with acne vulgaris
|
|
|
- Kenneth McKinney
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: Volume 4 Number 2 (2015) pp Original Research Article Comparison efficacy of azithromycin vs. doxycycline in patients with acne vulgaris Ameneh Yazdanfar 1* and MahsaSaleki 2 1 Department of Dermatology, School of medicine, Hamedan University of Medical Sciences, Hamedan, Iran 2 Department of clinical psychology, Islamic Azad University, Science and research center, Tehran, Iran *Corresponding author A B S T R A C T K eywo rd s Acne vulgaris, Doxycycline, Azithromycin Comparing the efficacy of doxycycline and azithromycin in the treatment of patients with acne vulgaris. A total of 120 patients with moderate to severe acne vulgaris participated in this randomized, double-blinded clinical trial and were randomly assigned to two groups (azithromycin and doxycycline). global scoreswere determined and recorded at baseline. Patients were followed up for three months Clinical assessment was made at baseline and at the end of each month and a global score was determined at each visit. Data was analyzed using SPSS, P value <0.05 was considered significant. There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of demographic data and baseline global scores. Based on global acne grading system, mean percentage of improvement of the lesions was 75.33% in azithromycin group and 73.23% in doxycycline group. statistical analysis showed that at the end of the first and second months, azithromycin was more effective than doxycycline and the difference was found significan (P=0.005) for the second month, that might reflect the faster and more effective improvement of acne with azithromycin, although the difference wasn t significant at the end of the treatment period. Side effects for Doxycycline was 7 (11.7%) for gastrointestinal and3 (5%) for dermatologic that was higher than azithromycin 2 (3.3%) and 1 (1.7%) respectively. Our results showed that azithromycin a long acting macrolide has faster and more effective improvement with lower side effects and can be a suitable alternative for doxycycline in treatment of acne vulgaris. Introduction Acne vulgaris is a multifactorial disorder of pilosebaceous unit. Clinical presentations vary from mild acne with comedones to systemic inflammatory disease. Although acne might affect all age groups, it is primarily considered an adolescence disease (1). Characteristics of this disorder include, comedone, erythematose papules and pustules and nodules, deep pustules or psuedocysts and sometimes scarring. Acne 1002
2 has been reported to be most prevalent in years old females (45% of them are affected) and years old males (35% of them are affected). In cases with very mild acne, it is considered a physiologic problem which is found in nearly 24% of female teenagers. Female patients present with acne earlier than males due to lower puberty age. The disease improves gradually after years, although in 7-17% of patients it persists after 25 years. Acne might persist to fourth decade in 1% of male and 5% of female patients (2). Four main factors are involved in pathogenesis of acne vulgaris: increase in production of sebum, increase in keratinocytes of pilosebaceouse follicle, change in microbial floraof the skin (proliferation of Propionibacterium acnes) and inflammation (3). Impact of genetic factors has been proved through monozygotic and dizygotic twin studies. They showed that the number of comedones and the severity of acne is similar in monozygotic twins in contrast to dizygotic twins (4). A study reported 45% frequency of acne in the parents of boys affected with acne while only 8% of parents of healthy boys had acne. Patients with persistent acne after 30 years were found to have stronger family history than those with adolescence acne (5). Association of severe acne with XXY syndrome has been reported (6). Studies on various races have also showed the impact of genetic and environmental factors together. Acne in African-Americans is more severe than Caucasians. In addition, severity of acne in Japanese is found to be lower than Caucasians. Incidence of acne has been shown to increase in Eskimos changing their diet from fish to processed foods containing saturated lipids. Same findings have been seen in Japanese immigrants in Hawaii taking American diet 1003 habits (6). Without treatment, acne vulgaris might lead to complications such as inflammatory lesions, post inflammation hyperpigmentation (PIH), inflammatory painful nodules, nodular hypertrophic scars, cystic lesions and etc. It might also result in very ugly shaped exudative or hemorrhagic nodules. In rare cases, there might be sinus tracts between deep nodules or pustules. Lesions in severe acne vulgaris might become very painful, chronic and refractory to treatment and even cause psychological complications particularly in young females (7). Mild cases of acne are treated using topical agents such as retinoids or topical antibiotics. Systemic antibiotics including doxycycline are used in treatment of moderate and moderate to severe acne, mild acne in depressive and dysphoric patients, and PIH. During the past three decades, oral broad spectrum antibiotics such as tetracyclines (doxycycline and ) and macrolides have been used in treatment of inflammatory acne, which have required administration of several doses daily for a long period (at least 6 months) due to short half-life. In addition, systemic antibiotics might result in several side effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances. Azithromycin is a derivative of Erythromycin with a long half-life and thus it can be prescribed in less frequent doses and according to the studies, it has minor side effects, is cost effective and well tolerated with a high patient compliance rate (8,12). In 2001 Fernandez and Obregon investigated the role of azithromycin in treatment of acne and found that it was effective in more than 80% of the cases, while other therapeutic agents including tetracycline, erythromycin, minocycline and doxycycline were averagely effective in
3 77.1% of the cases, however, the difference wasn t statistically significant (9). In another study in 1998, Gruber et al compared therapeutic effects of azithromycin and minocycline in acne vulgaris. Satisfactory results were found in 75.8% of patients treated by azithromycin and 70.5% of patients receiving minocycline at the end of the treatment period. Both antibiotics were well tolerated, minor adverse effects were found in 10.3% of patients in azithromycin group and 11.7% in minocycline group. They concluded that in acne treatment, azithromycin is at least as effective and tolerable as minocycline (10). In the study of Fernandez et al in 1997, patients were satisfied by azithromycin treatment, no side effects was observed and up to 80% improvement was found after four weeks of treatment (11). Kapadia and Talib in their study in 2004 found significant improvement in more than 82.9% of patients after four weeks of treatment with azithromycin. Maximum improvement was detected after 12 weeks of treatment. Adverse effects including nausea, and heart burn were only seen in 11.4% of cases (13). Rafiei and Yaghubi in 2006 investigated therapeutic effects of tetracycline and azithromycin in acne patients. Their results showed considerable improvement in both groups, while azithromycin was found to be somewhat more effective than tetracycline in reducing inflammatory lesions (84.7% vs. 79.8%). They concluded that azithromycin is a safe and efficient therapeutic choice in inflammatory acne (15). In another study by Lucky et al in 2008, azithromycin was shown to result in significant improvement in 80% of patients after four weeks of treatment, without causing any serious side effects, while in doxycycline group, improvement was found in only 53% of patients (14) Given the high prevalence of acne in adolescence particularly in females, and the mentioned literature review, we decided to conduct a randomized clinical trial with the aim of comparing the effect of azithromycin and doxycycline in treatment of moderate to severe acne. Materials and Methods This double- blinded randomized clinical trial was conducted on patients with moderate to severe acne vulgaris Referred to Farshchian Hospital. Diagnosis was confirmed due to clinical criteria. Patients with multiple papules, pustules and nodules or scars on face or trunk were considered to have moderate to severe acne. The severity of acne was determined according to global acne grading system (GAGS) developed by Dermatology Department of Harvard University. Study population consisted of all patients with moderate to severe acne vulgaris attending dermatology clinic and department of Farshchian Hospital. Patients who met the diagnostic criteria were enrolled in the study if they didn t have a history of taking systemic and topical treatment for their acne during the past four and two weeks respectively and hadn t received oral isotertinoin for the past 6 months. Female patients all required to have a negative pregnancy test and were asked to use a safe contraception method other than OCP during the study period. Exclusion criteria were history of drug sensitivity, medical diseases including endocrine or gastrointestinal, smoking and hyperandrogenism manifestations in girls. After taking informed consents, patients were enrolled in the study and randomly assigned to two treatment groups: case group received 250 mg azithromycin daily
4 and control group received 100 mg doxycycline daily for three months. All patient received instructions about correct method of taking the drugs. Clinical assessment was made at baseline and at the end of each month and a global score was determined at each visit. The score for each area (Local score) is calculated by multiplying a factor assigned to each area of the body (according to GAGS) in the grade of severity of the lesions (0-4). Global score is the sum of local scores. A score of 0 means no lesions; 1-18 is considered mild acne; 19-30, moderate acne; 31-38, severe acne; and higher than 39 very severe acne. Drug side effects including gastrointestinal, neurologic and dermatologic signs and symptoms were checked and recorded during each visit. Patients were asked to evaluate the treatment at the end of the third month by grading: 0, worse; 1, no change; 2, mild improvement; 3, moderate improvement; 4, considerable improvement. Study was designed as double blinded so that patients were not informed of the study structure and researchers didn t know about the type of the treatment each patient was receiving and just studied the manifestations of the disease and complications of the treatment. Medications were prescribed by dermatology attending and then patients were referred to the research unit. Data was analyzed using SPSS. Mean global scores were compared using t-test. Qualitative variables were compared using chi-2 test. As shown on the table, gastrointestinal side effects are more frequently seen with doxycycline (11.7%) than azithromycin (3.3%). According to the table, dermatologic adverse effects of doxycycline (5%) is higher than azithromycin (1.7%), however. No patients demonstrated neurologic side effects. Accordingly patients evaluation of treatment is moderate to good in 95% of patients in azithromycin group and 93.3% of patients in doxycycline group and the difference isn t significant. According to the table, change in mean global score from baseline to the end of the third month of therapy was from to 6.51 in doxycycline group and from to 6.15 in azithromycin group, showing similar efficacy for two drugs. The difference between mean global scores at baseline and at the end of the first and third months not found to be statistically significant, however, at the end of the second month azithromycin group had a significantly lower mean global score than doxycycline that was significant (P=0.005). Result and Discussion Statistical analysis showed no significant difference between the two groups regarding demographic characteristics and mean global score at baseline, therefore comparison of the results between the two groups was more precise. As mentioned, few patients were excluded from the study due to medication side effects or inability to afford azithromycin and were substituted with new cases. Mean GS at the end of each month of treatment was significantly decreased when compared with baseline which indicates the therapeutic efficacy of both drugs. Moreover, statistical analysis showed that at the end of the first and second months, azithromycin was more effective than doxycycline and the difference was found significant for the second month that might reflect the faster and more effective 1005
5 improvement of acne with azithromycin, although the difference wasn t significant at the end of the treatment period. Fernandez and Obregon in 2001 investigated efficacy of azithromycin in acne treatment. In their study a total of 99 inflammatory episodes of acne were treated in 79 patients using several antimicrobial medications including tetracycline, azithromycin, minocycline, and doxycycline. Patients who could not tolerate any of the mentioned drugs were treated using azithromycin. Azithromycin was administered as 250 mg/day. Side effects of all drugs were evaluated. It was shown that azithromycin was effective in 85.7% of patients while the other three antibiotics had anaverage efficacy of 77.1%; however, the difference wasn t statistically significant (9). Kapadia and Talib in 2004 studied the effect of 250 mg azithromycin daily for 12 weeks on 35 patients with moderate to severe acne and found considerable improvement in 82.9% of them with maximum improvement (more than 80%) being recorded after 12 weeks of treatment. Side effects including nausea and heart burn were only seen in 4 (11.4%) patients. This study reported daily 250 mg azithromycin as a safe therapeutic regimen for acne with minor side effects (13). Their study period was 3 months similar to ours and they also found maximum improvement after 12 weeks of therapy. They reported gastrointestinal adverse effects of azithromycin in 4 patients while we foundonecase of abdominal pain and one case of nausea in our study. Yucelten in 2005 compared the efficacy of azithromycin and doxycycline in acne treatment on 50 patients assigned randomly to two therapy groups: azithromycin group received azithromycin 500 mg/day on 3 consecutive days per week in the first, on 2 consecutive days in the second and on 1 day 1006 per week in the third month. The second group took doxycycline twice a day for the first month, and daily for the second and third months. Clinical response to therapy was similar in the two groups and persisted 3 months after discontinuation of the treatment. Three cases of diarrhea were reported in azithromycin group while two patients in doxycycline group developed photosensitivity. This study suggested that azithromycin is at least as effective as doxycycline in treatment of acne (14). Consistently in our study, gastrointestinal side effects were found in azithromycin group including 2 cases with abdominal pain and nausea, and dermatologic side effects were seen in doxycycline group including two cases of photosensitivity and one case of skin rash. Rafiei and Yaghoobi in 2006 compared tetracycline and azithromycin in treatment of acne on 290 patients for three months. Azithromycin was administered 500 mg/day for 3 consecutive days per week on the first and 250 mg/day every other day for the next two months. The results showed improvements of the lesions in both groups, however, azithromycin was slightly more effective than doxycycline in reducing inflammatory lesions (84.7% vs. 79.7%) and it was concluded that azithromycin is a safe and effective alternative in treatment of inflammatory acne (15). Study population in their investigation was larger than ours which is more appropriate statistically. The schedule in their study was 3 consecutive days for azithromycin and every other day for doxycycline, but in our study both drugs were administered daily. Lucky et al (2008) studied the effect of azithromycin 500 mg/day and doxycycline 100mg/day on 70 patients with acne. After 2 months of therapy, satisfaction rate was 60% in doxycycline group and 80% in azithromycin group. Therapeutic effect was
6 65% and 80% in doxycycline and azithromycin groups, respectively (14). Study population was similar to our study; however, they administered azithromycin 500 mg/day and doxycycline 100 mg/day for three months. Nevertheless it is interesting that they found azithromycin to be significantly more effective than doxycycline while in our study the efficacy was similar and only in second month of administration was significant. Muron in 2009 studied the effect of azithromycin and doxycycline on acne treatment in years old adolescents for a six-month period. Ninety patients received 250 mg azithromycin and ninety other were given 100 mg doxycycline daily. Therapeutic effect of the two drugs was nearly 79% and similar. Side effects were found in 15% of the patients in doxycycline group including abdominal pain and vomiting and 5% of patients in azithromycin group including nausea (16). Efficacy of the medications in this study was similar to ours (79%) and also the reported adverse events were almost like our findings in the twogroups in terms of type (gastrointestinal and dermatologic). Knaggs et al in 2011 studied the effect of azithromycin and doxycycline in 40 patients for 2 months. Twenty five patients received 100 mg/day doxycycline and fifteen patients received 250 mg azithromycin every other day. Therapeutic effect in both groups was almost 71%. Patient s satisfaction for treatment was 70% in doxycycline group and 82% in azithromycin group. Side effects in doxycycline group included skin rashes in 10% of the patients while in azithromycin skin rashes were found in 4% (17). Treatment period was 2 months in this study while it was 3 months for our study. Patient s satisfaction level in our study was 95% for azithromycin and 93.3% for doxycycline. In a study in 2012 Speroff et al compared azithromycin 500 mg every 1007 other day with doxycycline 200 mg daily on 80 patients in two groups of 40 patients each containing 20 male and 20 female patients. Therapeutic effect of the drugs after four months was 81.1% in azithromycin group and 76% in doxycycline group and the difference was not statistically significant. Treatment side effects in doxycycline group included skin rash and photosensitivity in 18% and headache in 5%. In azithromycin group dermatologic (skin rash) and neurologic adverse effects were found in 10% and 2%, respectively (18). In consistent to our study, patients in this investigation were equally assigned to the two groups and the number of male and female patients in the two groups was similar. Frequency of neurologic side effects was 5% in doxycycline group and 2% in azithromycin group in this study; however, no cases of neurologic complications were seen in our study. Ellis and Krach in a study compared the effect of 250 mg/day azithromycin and 100 mg/day doxycycline in treatment of acne for a three-month period. Therapeutic response was similar and nearly 78.5% in both groups and persisted for 3 months after treatment discontinuation. Nausea and vomiting was reported in four patients in doxycycline group and two patients in azithromycin group. Photosensitivity was seen in four patients in doxycycline group but not azithromycin group. Patients in this study were 15 to 28 years old (19), while in our study they were years old. Therapeutic effect in this study was close to our results (78.5%). Mean improvement of acne in our study according to the global acne grading system was 74% in both study groups highlighting the high efficacy of both of these drugs. Quantitative evaluation of the acne according to GAGS scale was performed at the end of each month of treatment and
7 showed higher efficacy of azithromycin in comparison to doxycycline during the first two months in acne treatment, although at the end of the three-month period the effect of the both drugs was almost similar. Subjective evaluation of the two treatment regimens asked from patients showed that nearly 94% assessed therapeutic effect moderate to good reflecting their satisfaction. Therefore, azithromycin is a long acting drug with minor side effects and high patient compliance. On the other hand, it costs more than older antibiotics which is a compliance limiting factor in patients from lower economic levels. Results of the presents study and previous investigations demonstrated that azithromycin, a long acting macrolide, can be an acceptable alternative for the classic doxycycline in treatment of inflammatory acne and given the long half-life and low complications, it has higher patient compliance while its short-term effects are better than doxycycline. Table.1 Frequency of gastrointestinal side effects in the study population Gastrointestinal side effects Type of therapy Yes N (%) No N (%) Doxycycline 7 (11.7%) 53 (88.3%) Azithromycin 2 (3.3%) 58 (96.7%) Total 9 (7.5%) 111 (92.5%) As shown on the table, gastrointestinal side effects are more frequently seen with doxycycline (11.7%) than azithromycin (3.3%). Table.2 Frequency of dermatologic side effects in the study population Dermatologic side effects Type of therapy Yes N (%) No N (%) Doxycycline 3 (5%) 57 (95%) Azithromycin 1 (1.7%) 59 (89.3%) Total 4 (3.3%) 116 (96.7%) According to the table, dermatologic adverse effects of doxycycline (5%) is higher than azithromycin (1.7%), however. No patients demonstrated neurologic side effects. Table.3 Comparison of patients evaluation about their treatment in the two groups Patients evaluation Type of No Mild Moderate Good therapy improvement improvement improvement improvement Doxycycline 2 (3.3%) 2 (3.3%) 24 (40%) 32 (53.3%) Azithromycin 1 (1.7%) 2 (3.3%) 27 (45%) 30 (50%) Total 3 (2.5%) 4 (3.3%) 51 (42.5%) 62 (51.7%) Accordingly patients evaluation of treatment is moderate to good in 95% of patients in azithromycin group and 93.3% of patients in doxycycline group and the difference isn t significant. 1008
8 Table.4 Comparison of mean final score of the patients at the end of first, second and third months of treatment Baseline First month Second month Third month Doxycycline Azithromycin Acknowledgement Present study is done in Department Dermatology of Farshchian hospital of Hamedan university of medical sciences. References 1)Andrea L Zaennglein.Acnevulgaris.In: Jean L Bolognia, Joseph L Jorizzo, Ronald PRapini. Dermatology, Mosby, Second Edition, 2008: )N.B.Simpson&W.J.Cuncliffe.Disorders of the sebaceous glands.in: Rook, Wilkinson,Ebling: textbook of Dermatology. Champion. Black well sience, 2004: )Gloor M, Hubs Cher HL. UntersuchungensurexternenBehandlung der Acne vulgarismit tetracycline und estrogen.haut arzt.1994; 25: ) Walton s, Wyatt E, cunliffe WJ. Genetic Control of sebum excretion and acne.a twinstudy. Br JDermatol 2002; 18: ) Goulden V, Clark SM. Cnnliffe WJ. Post adolescent acne: a review of clinical FeaturesBr, J Dermatol 2007; 136: ) Voorhees s JJ, Wilkins J W J r, Hayes E et al. Nodulo Cystic acne as a phonotypic feature of the xyy genotype. Report of five cases, review of all known xyy subjects with severacne, and discussion of xyycytodiagnosis.brjdermatol 1999; 105: Good felloe A, Alagh band-zadeh J, Carter G, et al. Oral spironolactone improves acne vulgaris and reduces sebum excretion. Br J Dermatol2007 ; 111: Zouboulis CC, Piguero-Martin J. update and future of systemic acne treatment. Dermatol 2003; 206: ) Fernandez. Obregon, A. Azithromycin for the treatment of acne. Int J Dermatol1997;36: ) Gruber F, Grubisic Greblo H, kastelam M, Brajac I, Lenkovic M, Famolo G, Azithromycin Compared with minocyline in treatment of acne. Come donica and papulo-pustulosa. J chemother Dec; 10(6): ) Fernandez Obregon A. Azithromycin for the treatment of acne.int J Dermatol 2001;39: ) Parsad D, Pandhi R, Nagpal R, Negiks. Azithromycin monthly pulses VS daily doxycyline in the treatment of ance vulgaris.j Dermatol Jan ; 28(7) : ) Kapadia N, talib A. acne treated successfully with azithromycin. IntDermatol Oct;43(10): Lucky j, Kus S, yucelten D, aytug A. comparison of efficacy of azithromycin VS doxcycylin in treatment of acne vulgaris. Cline ExpDermatol 2005 May ; 30(3) : ) Rafiei R, yaghoobi R, Azithromycin versus tetracycline in treatment of acne vulgaris. JDermatology treat. 2006; 17(4): Muuron JL, Ashman D. Acne vulgaris in a public school. Trans st John s HospDermatolSoc 2009;49: Knaggs He- Holland DB, Morrisc. et al. Autoantification of cellular proliferation in using the monoclonal antibody Ki-67-J sac invest-dermatol 2011;102: ) SperoffL,DecherneyA.Evaluation of azithromycin and doxycyclin in acne obstet Gynecol.2012;91: ) Ellis C,KrachM.Uses and complication of doxycyclin in acne vulgaris. J Cutan Med.2012;12:
ASSESSMENT OF ORAL AZITHROMYCIN MONOTHERPY IN THE TREATMENT OF SEVERE NODULOCYSTIC ACNE: A PROSPECTIVE CLINICAL STUDY
 IJMPS Sci. Journal Impact Factor 5.001 Research Article ASSESSMENT OF ORAL AZITHROMYCIN MONOTHERPY IN THE TREATMENT OF SEVERE NODULOCYSTIC ACNE: A PROSPECTIVE CLINICAL STUDY Samer A. Dhaher 1, Najih M.
IJMPS Sci. Journal Impact Factor 5.001 Research Article ASSESSMENT OF ORAL AZITHROMYCIN MONOTHERPY IN THE TREATMENT OF SEVERE NODULOCYSTIC ACNE: A PROSPECTIVE CLINICAL STUDY Samer A. Dhaher 1, Najih M.
Acne. Sofia Chaudhry M.D. Histology of an inflamed comedo. Bolognia, 2008.
 Acne Sofia Chaudhry M.D. Histology of an inflamed comedo. Bolognia, 2008. Acne Vulgaris (Common Acne) Multifactorial disorder of pilosebaceous unit Affects 40-50 million individuals annually in U.S. alone
Acne Sofia Chaudhry M.D. Histology of an inflamed comedo. Bolognia, 2008. Acne Vulgaris (Common Acne) Multifactorial disorder of pilosebaceous unit Affects 40-50 million individuals annually in U.S. alone
Objective: To compare the efficacy of isotretinoin vs. weekly pulse dose azithromycin in the treatment of moderate to severe acne.
 Original Article Isotretinoin versus weekly pulse dose azithromycin in the treatment of acne-a comparative study Md Abdul Wahab, M. Hasibur Rahman*, Nasrin Sultana Monamie**, Mohammad Jamaluddin, Lubna
Original Article Isotretinoin versus weekly pulse dose azithromycin in the treatment of acne-a comparative study Md Abdul Wahab, M. Hasibur Rahman*, Nasrin Sultana Monamie**, Mohammad Jamaluddin, Lubna
1. ACNE 1. Lisa Schmidt, MPH, Eve A. Kerr, MD, and Kenneth Clark, MD
 1. ACNE 1 Lisa Schmidt, MPH, Eve A. Kerr, MD, and Kenneth Clark, MD The general approach to summarizing the key literature on acne was to review relevant sections of two medical text books (Vernon and
1. ACNE 1 Lisa Schmidt, MPH, Eve A. Kerr, MD, and Kenneth Clark, MD The general approach to summarizing the key literature on acne was to review relevant sections of two medical text books (Vernon and
Pathogenesis 10/04/2015. Acne
 Deepani Rathnayake MBBS, MD, FACD Acne Affects >80% of adolescents >40% of adults Associated with Disfigurement Loss of confidence Depression Affects quality of life Pathogenesis i) increased sebum production,
Deepani Rathnayake MBBS, MD, FACD Acne Affects >80% of adolescents >40% of adults Associated with Disfigurement Loss of confidence Depression Affects quality of life Pathogenesis i) increased sebum production,
Acne. Objectives. Conflicts of Interest. Acne 05/18/2015
 Objectives Acne Jonathan A. Dyer, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Child Health University of Missouri Discuss acne pathogenesis Recognize common acne subtypes Implement a treatment plan based
Objectives Acne Jonathan A. Dyer, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Child Health University of Missouri Discuss acne pathogenesis Recognize common acne subtypes Implement a treatment plan based
Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris. Emerging Applications
 Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Emerging Applications About Acne Vulgaris Very common - Affects 80% of population Almost every person experiences acne Most common reason to visit dermatologist
Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Emerging Applications About Acne Vulgaris Very common - Affects 80% of population Almost every person experiences acne Most common reason to visit dermatologist
Summary Acne vulgaris is a chronic, treatable disease but response to treatment may be delayed.
 TREATMENT OF ACNE VULGARIS Summary Acne vulgaris is a chronic, treatable disease but response to treatment may be delayed. Topical agents are useful as monotherapy for mild acne and in combination with
TREATMENT OF ACNE VULGARIS Summary Acne vulgaris is a chronic, treatable disease but response to treatment may be delayed. Topical agents are useful as monotherapy for mild acne and in combination with
ACNE AND ROSACEA. Disclosure. Distribution of Acne 6/12/2014. NJAFP 2014 Summer Celebration & Scientific Assembly 1
 ACNE AND ROSACEA Everett Schlam, MD Assistant Director, Mountainside Hospital Family Medicine Residency Program, Verona, NJ Disclosure Dr. Schlam has indicated that he has nothing to disclose relevant
ACNE AND ROSACEA Everett Schlam, MD Assistant Director, Mountainside Hospital Family Medicine Residency Program, Verona, NJ Disclosure Dr. Schlam has indicated that he has nothing to disclose relevant
Acne breakouts vulgaris is one of the commonest skin conditions, which dermatologists treat and it
 Introduction Acne breakouts vulgaris is one of the commonest skin conditions, which dermatologists treat and it mostly impacts teens, though it might appear at any sort of age. Acne breakouts cause necessarily
Introduction Acne breakouts vulgaris is one of the commonest skin conditions, which dermatologists treat and it mostly impacts teens, though it might appear at any sort of age. Acne breakouts cause necessarily
Therapeutic Overview Topical Acne Agents
 Therapeutic Overview Topical Acne Agents Overview/Summary Acne vulgaris, a disease of the pilosebaceous follicles, is the most common cutaneous dermatological disorder and primarily affects adolescents
Therapeutic Overview Topical Acne Agents Overview/Summary Acne vulgaris, a disease of the pilosebaceous follicles, is the most common cutaneous dermatological disorder and primarily affects adolescents
Acne (Acne Vulgaris) A common type of bacteria that lives on the skin, known as Propionibacterium acnes, sometimes
 Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Acne, clinically known as acne vulgaris, is the most common skin disease. It affects 85% of teenagers, some as young as 12, and often continues into adulthood. It is also called pimples,
Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Acne, clinically known as acne vulgaris, is the most common skin disease. It affects 85% of teenagers, some as young as 12, and often continues into adulthood. It is also called pimples,
Comparison of the Effect of Azelaic Acid 20% And Clindamycin 1% In the Treatment of Mild And Moderate Acne. Abstract
 Original Article Comparison of the Effect of Azelaic Acid 20% And Clindamycin 1% In the Treatment of Mild And Moderate Acne Soudabeh Tirgar Tabari, MD Ali Akbar Moghadam Nia, PharmD Karimollah Hajian Amirmajid
Original Article Comparison of the Effect of Azelaic Acid 20% And Clindamycin 1% In the Treatment of Mild And Moderate Acne Soudabeh Tirgar Tabari, MD Ali Akbar Moghadam Nia, PharmD Karimollah Hajian Amirmajid
ACNE TOP TIPS FOR GPs! Louise Moss GP Moss Valley Medical Practice, Eckington, GPwSI for NDCCG Sept 2013
 ACNE TOP TIPS FOR GPs! Louise Moss GP Moss Valley Medical Practice, Eckington, GPwSI for NDCCG Sept 2013 Acne-an important condition Aim for today To have a better understanding of how to treat Acne well,
ACNE TOP TIPS FOR GPs! Louise Moss GP Moss Valley Medical Practice, Eckington, GPwSI for NDCCG Sept 2013 Acne-an important condition Aim for today To have a better understanding of how to treat Acne well,
74 Full Text Available On www.ijupls.com. Medical Sciences. Original Article!!!
 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Life Sciences 2(2): March-April 2012 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES Medical Sciences Original Article!!! Received: 18-04-2012;
International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Life Sciences 2(2): March-April 2012 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES Medical Sciences Original Article!!! Received: 18-04-2012;
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn- 2278-4802, pissn- 2278-4748/ Vol. 3/ Issue 52/Oct 13, 2014 Page 12179
 PRESCRIPTION AUDIT OF ACNE VULGARIS IN SKIN OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENT OF A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL Vishal Prakash Giri 1, Shubhra Kanodia 2, Om Prakash Giri 3, Ataul Haque 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
PRESCRIPTION AUDIT OF ACNE VULGARIS IN SKIN OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENT OF A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL Vishal Prakash Giri 1, Shubhra Kanodia 2, Om Prakash Giri 3, Ataul Haque 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
How To Treat Acne
 THE IMPORTANCE OF EARLY DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF ACNE* Adelaide Ann Hebert, MD, FAAD ABSTRACT Several topical and systemic agents are available for acne treatment. Commonly used topical therapies include
THE IMPORTANCE OF EARLY DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF ACNE* Adelaide Ann Hebert, MD, FAAD ABSTRACT Several topical and systemic agents are available for acne treatment. Commonly used topical therapies include
acne Dr. M. Goeteyn Dermatologie AZ Sint-Jan Brugge-Oostende AV marleen.goeteyn@azsintjan.be
 acne Dr. M. Goeteyn Dermatologie AZ Sint-Jan Brugge-Oostende AV marleen.goeteyn@azsintjan.be Why should you treat acne? -Impact on the quality of life -scarring What is acne? Acne is an inflammatory disease
acne Dr. M. Goeteyn Dermatologie AZ Sint-Jan Brugge-Oostende AV marleen.goeteyn@azsintjan.be Why should you treat acne? -Impact on the quality of life -scarring What is acne? Acne is an inflammatory disease
Neutral Superoxidized solution vs. benzoyl peroxide gel 5% in the treatment of. Superoxidized solution (SOS) is an electrochemically processed aqueous
 Neutral Superoxidized solution vs. benzoyl peroxide gel 5% in the treatment of acne vulgaris: a randomized open-label clinical trial. Summary. Superoxidized solution (SOS) is an electrochemically processed
Neutral Superoxidized solution vs. benzoyl peroxide gel 5% in the treatment of acne vulgaris: a randomized open-label clinical trial. Summary. Superoxidized solution (SOS) is an electrochemically processed
Available online www.jocpr.com. Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(2):736-741 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 A comparative study of efficacy and safety of combination
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(2):736-741 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 A comparative study of efficacy and safety of combination
ACNE GUIDELINES: Management of Acne Vulgaris: Clinical Recommendations & Isotretinoin Position Statement. American Academy of Dermatology
 O ACNE GUIDELINES: Management of Acne Vulgaris: Clinical s & Isotretinoin Position Statement American Academy of Dermatology s s for systems for the grading and classification of acne Clinicians may find
O ACNE GUIDELINES: Management of Acne Vulgaris: Clinical s & Isotretinoin Position Statement American Academy of Dermatology s s for systems for the grading and classification of acne Clinicians may find
4/18/2014 ACNE: THEN & NOW 25 YEARS OF INNOVATION ACNE VULGARIS ETIOLOGY OF ACNE. Jenifer Lloyd, DO, FAAD Professor of Internal Medicine
 ACNE: THEN & NOW 25 YEARS OF INNOVATION Jenifer Lloyd, DO, FAAD Professor of Internal Medicine ACNE VULGARIS The most common disease of the pilosebaceous unit. Commonly affects the face, chest & back.
ACNE: THEN & NOW 25 YEARS OF INNOVATION Jenifer Lloyd, DO, FAAD Professor of Internal Medicine ACNE VULGARIS The most common disease of the pilosebaceous unit. Commonly affects the face, chest & back.
A comparison of efficacy and safety of topical 0.1% adapalene and 4% benzoyl peroxide in the treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris
 Original Article A comparison of efficacy and safety of topical 0.1% adapalene and 4% benzoyl peroxide in the treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris Usma Iftikhar, Shahbaz Aman, Muhammad Nadeem, Atif
Original Article A comparison of efficacy and safety of topical 0.1% adapalene and 4% benzoyl peroxide in the treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris Usma Iftikhar, Shahbaz Aman, Muhammad Nadeem, Atif
A 3-PRODUCT SALICYLIC ACID REGIMEN EFFECTIVELY TREATS ACNE VULGARIS IN POST- ADOLESCENT WOMEN
 A 3-PRODUCT SALICYLIC ACID REGIMEN EFFECTIVELY TREATS ACNE VULGARIS IN POST- ADOLESCENT WOMEN J. R. Kaczvinsky 1, C. E. Mack 1, L. L. Griffin 1, J. Li 1, R. A. Rose-Mansfield 1, S. C. Weitz 1, M. J. Marmor
A 3-PRODUCT SALICYLIC ACID REGIMEN EFFECTIVELY TREATS ACNE VULGARIS IN POST- ADOLESCENT WOMEN J. R. Kaczvinsky 1, C. E. Mack 1, L. L. Griffin 1, J. Li 1, R. A. Rose-Mansfield 1, S. C. Weitz 1, M. J. Marmor
Advances in Acne Management. ABP Objectives for ACNE. Case 1 5/13/11
 Advances in Acne Management Advances and Controversies in Pediatrics 2011 Erin Mathes, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics UCSF ABP Objectives for ACNE Plan for the treatment
Advances in Acne Management Advances and Controversies in Pediatrics 2011 Erin Mathes, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics UCSF ABP Objectives for ACNE Plan for the treatment
Comparative study between topical Zanco J. Med. Sci., Vol. 18, No. (3), 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.15218/zjms.2014.0036
 Comparative study between topical clindamycin solution (1%) versus combination of clindamycin (1%)/adapalene (0.1%) gel in the treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris Received: 27/4/2013 Accepted:
Comparative study between topical clindamycin solution (1%) versus combination of clindamycin (1%)/adapalene (0.1%) gel in the treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris Received: 27/4/2013 Accepted:
ACNE. Nisakorn Saewan, Ph.D.
 ACNE, Ph.D. Contents Definition Cause of acne Type of acne Acne grades Acne treatments Objectives To explain the definition of acne To elucidate cause of acne To identify type and grade of acne To explain
ACNE, Ph.D. Contents Definition Cause of acne Type of acne Acne grades Acne treatments Objectives To explain the definition of acne To elucidate cause of acne To identify type and grade of acne To explain
Acne can appear on the face. back, chest, neck. shoulders, and upper arms. ----.-----. WHAT CAUSES ACNE?
 Cysts Nodules Acne can appear on the face. back, chest, neck. shoulders, and upper arms. pore becomes inflamed (red and swollen). Sometimes the inflammation can damage the lining of the pore and then the
Cysts Nodules Acne can appear on the face. back, chest, neck. shoulders, and upper arms. pore becomes inflamed (red and swollen). Sometimes the inflammation can damage the lining of the pore and then the
Acne Vulgaris Medicines Consultation Toolkit
 Introduction Acne is a very common skin condition, which affects more than 80% of people at some point in their life. 1 Furthermore, it is a chronic condition, which along with eczema and psoriasis, accounts
Introduction Acne is a very common skin condition, which affects more than 80% of people at some point in their life. 1 Furthermore, it is a chronic condition, which along with eczema and psoriasis, accounts
Name of Policy: Laser Treatment of Active Acne
 Name of Policy: Laser Treatment of Active Acne Policy #: 394 Latest Review Date: January 2015 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: Effective January 1, 2015: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular
Name of Policy: Laser Treatment of Active Acne Policy #: 394 Latest Review Date: January 2015 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: Effective January 1, 2015: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular
X-Plain Acne Reference Summary
 X-Plain Acne Reference Summary Introduction Nearly 17 million people in the United States have acne, making it one of the most common skin diseases in the USA. Although acne is not a serious health threat,
X-Plain Acne Reference Summary Introduction Nearly 17 million people in the United States have acne, making it one of the most common skin diseases in the USA. Although acne is not a serious health threat,
Indication under review: cutaneous treatment of acne vulgaris when comedones, papules and pustules are present.
 Resubmission adapalene 0.1%/benzoyl peroxide 2.5% gel (Epiduo ) SMC No. (682/11) Galderma UK Ltd 07 March 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
Resubmission adapalene 0.1%/benzoyl peroxide 2.5% gel (Epiduo ) SMC No. (682/11) Galderma UK Ltd 07 March 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
Acne Vulgaris: Basic Facts
 Acne 1 Module Instructions The following module contains hyperlinked information which serves to offer more information on topics you may or may not be familiar with. We encourage that you read all the
Acne 1 Module Instructions The following module contains hyperlinked information which serves to offer more information on topics you may or may not be familiar with. We encourage that you read all the
Annex II. Scientific conclusions and grounds for refusal presented by the European Medicines Agency
 Annex II Scientific conclusions and grounds for refusal presented by the European Medicines Agency 5 Scientific conclusions Overall summary of the scientific evaluation of Ethinylestradiol-Drospirenone
Annex II Scientific conclusions and grounds for refusal presented by the European Medicines Agency 5 Scientific conclusions Overall summary of the scientific evaluation of Ethinylestradiol-Drospirenone
U.S. Scientific Update Aricept 23 mg Tablets. Dr. Lynn Kramer President NeuroScience Product Creation Unit Eisai Inc.
 U.S. Scientific Update Aricept 23 mg Tablets Dr. Lynn Kramer President NeuroScience Product Creation Unit Eisai Inc. Unmet Need in Moderate to Severe Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Ongoing clinical deterioration
U.S. Scientific Update Aricept 23 mg Tablets Dr. Lynn Kramer President NeuroScience Product Creation Unit Eisai Inc. Unmet Need in Moderate to Severe Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Ongoing clinical deterioration
Acne vulgaris, mental health and omega-3 fatty acids. Lipids in Health and Disease. October 13, 2008
 Acne vulgaris, mental health and omega-3 fatty acids 1 Lipids in Health and Disease October 13, 2008 Mark G Rubin, Katherine Kim, Alan C Logan FROM ABSTRACT Acne vulgaris is a common skin condition, one
Acne vulgaris, mental health and omega-3 fatty acids 1 Lipids in Health and Disease October 13, 2008 Mark G Rubin, Katherine Kim, Alan C Logan FROM ABSTRACT Acne vulgaris is a common skin condition, one
A Dose-Finding Study of Azithromycin in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris
 27;15(3):11-17 CLINICAL ARTICLE A Dose-Finding Study of Azithromycin in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Aleksandra Basta-Juzbašić 1, Jasna Lipozenčić 1, Lenka Oremović 2, Lena Kotrulja 2, Franjo Gruber
27;15(3):11-17 CLINICAL ARTICLE A Dose-Finding Study of Azithromycin in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Aleksandra Basta-Juzbašić 1, Jasna Lipozenčić 1, Lenka Oremović 2, Lena Kotrulja 2, Franjo Gruber
New Developments in the Topical Management of Acne
 Clinical Review New Developments in the Topical Management of Acne Abstract Adapalene 0.1%/BPO 2.5% (adapalene/bpo) gel is a novel agent for acne therapy that has recently become available in Canada. This
Clinical Review New Developments in the Topical Management of Acne Abstract Adapalene 0.1%/BPO 2.5% (adapalene/bpo) gel is a novel agent for acne therapy that has recently become available in Canada. This
The effective treatment of acne vulgaris by a high-intensity, narrow band 405 420 nm light source
 J Cosmetic & Laser Ther 2003; 5: 111 116 # J Cosmetic & Laser Ther. All rights reserved ISSN 1476-4172 DOI: 10.1080/14764170310001276 111 The effective treatment of acne vulgaris by a high-intensity, narrow
J Cosmetic & Laser Ther 2003; 5: 111 116 # J Cosmetic & Laser Ther. All rights reserved ISSN 1476-4172 DOI: 10.1080/14764170310001276 111 The effective treatment of acne vulgaris by a high-intensity, narrow
Assessment of Negative Emotional State in Patients with Acne. Vulgaris: A Study on the Emotional Impact of Acne
 Original Article 22 Copyright University of Medicine, Tirana AJMHS 2014; Vol. 2: 22-26 2014 Assessment of Negative Emotional State in Patients with Acne Vulgaris: A Study on the Emotional Impact of Acne
Original Article 22 Copyright University of Medicine, Tirana AJMHS 2014; Vol. 2: 22-26 2014 Assessment of Negative Emotional State in Patients with Acne Vulgaris: A Study on the Emotional Impact of Acne
The treatment of acne is often hampered by
 168 Clinical Pharmacist April 2009 Vol 1 Treatment can help clear acne, minimising scarring and relieving psychosocial stress Acne treatment For personal use only. Not to be reproduced without permission
168 Clinical Pharmacist April 2009 Vol 1 Treatment can help clear acne, minimising scarring and relieving psychosocial stress Acne treatment For personal use only. Not to be reproduced without permission
Acne Vulgaris Introduction What is acne? Factors implicated in the development of acne
 Acne Vulgaris Introduction Acne is a common condition, affecting about 85% of people between the ages of 12-24 years. Although the majority of sufferers grow out of their acne, about 12% of women and 3%
Acne Vulgaris Introduction Acne is a common condition, affecting about 85% of people between the ages of 12-24 years. Although the majority of sufferers grow out of their acne, about 12% of women and 3%
Acne is the most common skin condition PROCEEDINGS CLINICAL UPDATE ON ACNE* Magdalene Dohil, MD ABSTRACT
 CLINICAL UPDATE ON ACNE* Magdalene Dohil, MD ABSTRACT Acne is the most common skin condition in the United States, affecting nearly all adolescents but also a large number of adults. Several pathogenic
CLINICAL UPDATE ON ACNE* Magdalene Dohil, MD ABSTRACT Acne is the most common skin condition in the United States, affecting nearly all adolescents but also a large number of adults. Several pathogenic
Name of Policy: Laser Treatment of Active Acne
 Name of Policy: Laser Treatment of Active Acne Policy #: 394 Latest Review Date: December 2009 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross and
Name of Policy: Laser Treatment of Active Acne Policy #: 394 Latest Review Date: December 2009 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross and
MANAGING ACNE IN PHARMACY
 MANAGING ACNE IN PHARMACY ACNE PREVALENCE Acne is the most common of skin diseases, affecting 85 per cent of Australians aged 15-24 years old. Very few people manage to escape their teenage and young adult
MANAGING ACNE IN PHARMACY ACNE PREVALENCE Acne is the most common of skin diseases, affecting 85 per cent of Australians aged 15-24 years old. Very few people manage to escape their teenage and young adult
Acne Vulgaris: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of a common dermatologic condition
 Acne Vulgaris: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of a common dermatologic condition Dr. Mohamed Emam Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacy Department Faculty of Pharmacy Beni Suef University Hair Pilosebaceous
Acne Vulgaris: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of a common dermatologic condition Dr. Mohamed Emam Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacy Department Faculty of Pharmacy Beni Suef University Hair Pilosebaceous
The Effectiveness oftopical Antibacterials in Acne: A Double-Blind Clinical Study
 J Int Med Res (1978) 6, 72 The Effectiveness oftopical Antibacterials in Acne: A Double-Blind Clinical Study E Franz, MD, 8 Rohde, MD and S Weidner-Strahl, MD, University Department of Dermatology, 34
J Int Med Res (1978) 6, 72 The Effectiveness oftopical Antibacterials in Acne: A Double-Blind Clinical Study E Franz, MD, 8 Rohde, MD and S Weidner-Strahl, MD, University Department of Dermatology, 34
+++#,# & %!"#$%& '"#()*
 +++#,#! "#$#%&"##$!'#&("&!"# $ %& %& & %!"#$%& '"#()* +++#,# Research Article Pharmacology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 COMPARISION OF CLINICAL EFFICACY OF TOPICAL CLINDAMYCIN
+++#,#! "#$#%&"##$!'#&("&!"# $ %& %& & %!"#$%& '"#()* +++#,# Research Article Pharmacology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 COMPARISION OF CLINICAL EFFICACY OF TOPICAL CLINDAMYCIN
Acne Vulgaris: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of a common dermatologic condition
 Acne Vulgaris: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of a common dermatologic condition Latasha Weeks, B.A., B.S. Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate, 2007 University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Learning
Acne Vulgaris: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of a common dermatologic condition Latasha Weeks, B.A., B.S. Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate, 2007 University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Learning
Acne Vulgaris - Current Opinion and New Phototherapeutic Options
 Acne Vulgaris - Current Opinion and New Phototherapeutic Options WILLIAM J. CUNLIFFE, MD FRCP Skin Research Center, Leeds University, Leeds General Infirmary, Leeds, UK INTRODUCTION. Acne is a very common
Acne Vulgaris - Current Opinion and New Phototherapeutic Options WILLIAM J. CUNLIFFE, MD FRCP Skin Research Center, Leeds University, Leeds General Infirmary, Leeds, UK INTRODUCTION. Acne is a very common
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology
 Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
ACUPUNCTURE AND ACNE. About Acne. References Garner SE. Acne vulgaris. In: Williams H (Ed). Evidence Based Dermatology. London: BMJ, 2003.
 ACUPUNCTURE AND ACNE About Acne Acne vulgaris, the most common type of acne, is a chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting hair follicles, and sebaceous glands and ducts. It occurs on the face in 99%
ACUPUNCTURE AND ACNE About Acne Acne vulgaris, the most common type of acne, is a chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting hair follicles, and sebaceous glands and ducts. It occurs on the face in 99%
placebo-controlledcontrolled double-blind, blind,
 Clinical Potential of Minocycline for Depression with Psychotic Features Tsuyoshi Miyaoka Department of Psychiatry Shimane University School of Medicine Minocycline 1. Second-generation tetracycline which
Clinical Potential of Minocycline for Depression with Psychotic Features Tsuyoshi Miyaoka Department of Psychiatry Shimane University School of Medicine Minocycline 1. Second-generation tetracycline which
Adolescent Acne: Effective Therapy for a Serious Condition
 BRIDGET M. BRYER GROFF, MD JENNIFER S. TROMBERG, MD BARBARA B. WILSON, MD University of Virginia Adolescent Acne: Effective Therapy for a Serious Condition Dr Bryer Groff and Dr Tromberg are residents
BRIDGET M. BRYER GROFF, MD JENNIFER S. TROMBERG, MD BARBARA B. WILSON, MD University of Virginia Adolescent Acne: Effective Therapy for a Serious Condition Dr Bryer Groff and Dr Tromberg are residents
Preetha selva et al. / International Journal of Phytopharmacology. 6(1), 2015, 42-46. International Journal of Phytopharmacology
 International Journal of Phytopharmacology Journal homepage: www.onlineijp.com 42 e- ISSN 0975 9328 Print ISSN 2229 7472 IJP A CLINICAL STUDY TO EVALUATE THE EFFECT OF TOPICAL TAZAROTENE IN THE TREATMENT
International Journal of Phytopharmacology Journal homepage: www.onlineijp.com 42 e- ISSN 0975 9328 Print ISSN 2229 7472 IJP A CLINICAL STUDY TO EVALUATE THE EFFECT OF TOPICAL TAZAROTENE IN THE TREATMENT
Efficacy of octenidine dihydrochloride and 2-phenoxyethanol in the topical treatment of inflammatory acne
 P i l o t s t u d y Efficacy of octenidine dihydrochloride and 2-phenoxyethanol in the topical treatment of inflammatory acne S. Mayr-Kanhäuser, B. Kränke, and W. Aberer K E Y WORDS acne, antibiotic resistance,
P i l o t s t u d y Efficacy of octenidine dihydrochloride and 2-phenoxyethanol in the topical treatment of inflammatory acne S. Mayr-Kanhäuser, B. Kränke, and W. Aberer K E Y WORDS acne, antibiotic resistance,
Acne lesions develop in a 2-stage process. PROCEEDINGS THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND PRINCIPLES OF ACNE TREATMENT * Guy F. Webster, MD, PhD ABSTRACT
 THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND PRINCIPLES OF ACNE TREATMENT * Guy F. Webster, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Acne lesions develop as the result of an inflammatory response to bacterial colonization of skin follicles that have
THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND PRINCIPLES OF ACNE TREATMENT * Guy F. Webster, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Acne lesions develop as the result of an inflammatory response to bacterial colonization of skin follicles that have
Acne Skin: Lifestyle or Genetic?
 Acne Skin: Lifestyle or Genetic? Yuechan Chen ID: 6786032339 Professor Weiss May 05 2014 ACNE STUDIES CHEN 1 Acne Skin: Lifestyle or Genetic? How can I cure my acne, clear its roots?! Acne is a stubborn
Acne Skin: Lifestyle or Genetic? Yuechan Chen ID: 6786032339 Professor Weiss May 05 2014 ACNE STUDIES CHEN 1 Acne Skin: Lifestyle or Genetic? How can I cure my acne, clear its roots?! Acne is a stubborn
1. Indications for Accutane 2. 2. Contraindications for Accutane 2. 3. Warnings 3. 4. Side Effects 3. 5. Recommended Dosage 4. 6. Patient Management 4
 GUIDELINES FOR ISOTRETINOIN (ACCUTANE) USE FOR THE TREATMENT OF ACNE PAGE 1. Indications for Accutane 2 2. Contraindications for Accutane 2 3. Warnings 3 4. Side Effects 3 5. Recommended Dosage 4 6. Patient
GUIDELINES FOR ISOTRETINOIN (ACCUTANE) USE FOR THE TREATMENT OF ACNE PAGE 1. Indications for Accutane 2 2. Contraindications for Accutane 2 3. Warnings 3 4. Side Effects 3 5. Recommended Dosage 4 6. Patient
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS
 Acne ogist (a doctor who specializes in treating skin problems) about how you can help prevent acne and if treatment would help you. page 1 Q: What is acne? Q: What are the different types of A: Acne is
Acne ogist (a doctor who specializes in treating skin problems) about how you can help prevent acne and if treatment would help you. page 1 Q: What is acne? Q: What are the different types of A: Acne is
A novel, effective, skin-friendly fixed-dose combination topical formulation for adolescents with acne
 A novel, effective, skin-friendly fixed-dose combination topical formulation for adolescents with acne From a satellite symposium held on June 13 th, 2014 at the 12 th Congress of the European Society
A novel, effective, skin-friendly fixed-dose combination topical formulation for adolescents with acne From a satellite symposium held on June 13 th, 2014 at the 12 th Congress of the European Society
A Systematic Review of the Effects and Side Effects of Treatment with Oral Tetracycline in Acne Vulgaris
 A Systematic Review of the Effects and Side Effects of Treatment with Oral Tetracycline in Acne Vulgaris Master Thesis in Medicine Evelina Werner Supervisor Professor Jan Faergemann Department of Dermatology
A Systematic Review of the Effects and Side Effects of Treatment with Oral Tetracycline in Acne Vulgaris Master Thesis in Medicine Evelina Werner Supervisor Professor Jan Faergemann Department of Dermatology
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
***Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Baghdad Teaching Hospital. Baghdad, Iraq.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2015), PP 70-76 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of a Topical Active
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2015), PP 70-76 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of a Topical Active
Clinical Evaluation of Roxithromycin in Patients with Acne
 The Journal of International Medical Research 1996; 24: 109-114 Clinical Evaluation of Roxithromycin in Patients with Acne H AKAMATSU, S NISHIJIMA, M AKAMATSU, I KUROKAWAAND Y ASADA Department of Dermatology,
The Journal of International Medical Research 1996; 24: 109-114 Clinical Evaluation of Roxithromycin in Patients with Acne H AKAMATSU, S NISHIJIMA, M AKAMATSU, I KUROKAWAAND Y ASADA Department of Dermatology,
Active centers: 2. Number of patients/subjects: Planned: 20 Randomized: Treated: 20 Evaluated: Efficacy: 13 Safety: 20
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: sanofi-aventis ClinialTrials.gov
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: sanofi-aventis ClinialTrials.gov
EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE. Dr E Ndabaneze
 EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE Dr E Ndabaneze PLAN 1. Case presentation 2. Topic on Evidence based Treatment of Crohn s disease - Introduction pathology aetiology - Treatment - concept of
EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE Dr E Ndabaneze PLAN 1. Case presentation 2. Topic on Evidence based Treatment of Crohn s disease - Introduction pathology aetiology - Treatment - concept of
National Medicines Information Centre ST. JAMES S HOSPITAL DUBLIN 8 TEL 01-4730589 or 1850-727-727 FAX 01-4730596 www.nmic.ie
 National Medicines Information Centre ST. JAMES S HOSPITAL DUBLIN 8 TEL 01-4730589 or 1850-727-727 FAX 01-4730596 www.nmic.ie VOLUME 14 NUMBER 1 2008 FOR PERSONAL USE ONLY. NOT TO BE REPRODUCED WITHOUT
National Medicines Information Centre ST. JAMES S HOSPITAL DUBLIN 8 TEL 01-4730589 or 1850-727-727 FAX 01-4730596 www.nmic.ie VOLUME 14 NUMBER 1 2008 FOR PERSONAL USE ONLY. NOT TO BE REPRODUCED WITHOUT
EL CAMINO MEDICAL CLINIC
 EL CAMINO MEDICAL CLINIC 1828 El Camino Real, Suite 706 Burlingame, CA 940101 Phone #: (650)777-9117 Acne Acne is a disorder resulting from the action of hormones and other substances on the skin's oil
EL CAMINO MEDICAL CLINIC 1828 El Camino Real, Suite 706 Burlingame, CA 940101 Phone #: (650)777-9117 Acne Acne is a disorder resulting from the action of hormones and other substances on the skin's oil
Two-Year Phase III Data Presented at AAN 61st Annual Meeting Show Positive Outcome of Cladribine Tablets in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 Your contact News Release Barbara Fry Phone +1 905 919 0163 April 29/30, 2009 Two-Year Phase III Data Presented at AAN 61st Annual Meeting Show Positive Outcome of Cladribine Tablets in Patients with Multiple
Your contact News Release Barbara Fry Phone +1 905 919 0163 April 29/30, 2009 Two-Year Phase III Data Presented at AAN 61st Annual Meeting Show Positive Outcome of Cladribine Tablets in Patients with Multiple
Acne. Normal skin. What is acne?
 Acne Acne is extremely common in varying degrees of severity. About 9 out of 10 teenagers develop some degree of acne. However, this does not mean it should be ignored. Acne is a distressing condition
Acne Acne is extremely common in varying degrees of severity. About 9 out of 10 teenagers develop some degree of acne. However, this does not mean it should be ignored. Acne is a distressing condition
Key Messages. Treatment Basics. So preventing acne requires some patience and some experimentation to find the right program for you.
 Treatment Basics Key Messages You don't treat acne, you prevent it. There is no one best or one-size fits all acne treatment. Finding the best topical medications - medications you put on your skin - depends
Treatment Basics Key Messages You don't treat acne, you prevent it. There is no one best or one-size fits all acne treatment. Finding the best topical medications - medications you put on your skin - depends
Is Monotherapy Treatment of Etanercept Effective Against Plaque Psoriasis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2011 Is Monotherapy Treatment of Etanercept
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2011 Is Monotherapy Treatment of Etanercept
THE SCIENCE WHITE PAPER SERIES OF IMAGE SKINCARE: Benzoyl Peroxide for treatment of acne vulgaris
 THE SCIENCE WHITE PAPER SERIES OF IMAGE SKINCARE: Benzoyl Peroxide for treatment of acne vulgaris by Marc A. Ronert MD PhD, Clinical Director Image Skincare ABSTRACT Image Skincare offers products with
THE SCIENCE WHITE PAPER SERIES OF IMAGE SKINCARE: Benzoyl Peroxide for treatment of acne vulgaris by Marc A. Ronert MD PhD, Clinical Director Image Skincare ABSTRACT Image Skincare offers products with
2. The prescribing clinician will register with the designated manufacturer.
 Clozapine Management Program Description Magellan of Arizona Pharmacy Program Background: Magellan Health Services of Arizona recognizes the importance of a clozapine program. Clozapine received increased
Clozapine Management Program Description Magellan of Arizona Pharmacy Program Background: Magellan Health Services of Arizona recognizes the importance of a clozapine program. Clozapine received increased
F r e q u e n t l y A s k e d Q u e s t i o n s
 Acne who specializes in treating skin problems) about how you can help prevent acne and if treatment would help you. Q: What is acne? A: Acne is a disorder that causes outbreaks of skin lesions commonly
Acne who specializes in treating skin problems) about how you can help prevent acne and if treatment would help you. Q: What is acne? A: Acne is a disorder that causes outbreaks of skin lesions commonly
Guidelines of Care for Acne Vulgaris Management Technical Report
 Guidelines of Care for Acne Vulgaris Management Technical Report 2 Acne Vulgaris Table of Contents Page No. ntroduction... 3 Clinical questions... 3 evaluation of evidence... 4 Grading and classification
Guidelines of Care for Acne Vulgaris Management Technical Report 2 Acne Vulgaris Table of Contents Page No. ntroduction... 3 Clinical questions... 3 evaluation of evidence... 4 Grading and classification
Helmut Schöfer 1 Arno Göllner 3 Werner Kusche 2 Ulrich Schwantes 3
 Effectiveness and Tolerance of Topical Nadifloxacin in the Therapy of Acne Vulgaris (grade I-II): Results of a Non-interventional Trial in 555 Patients Helmut Schöfer 1 Arno Göllner 3 Werner Kusche 2 Ulrich
Effectiveness and Tolerance of Topical Nadifloxacin in the Therapy of Acne Vulgaris (grade I-II): Results of a Non-interventional Trial in 555 Patients Helmut Schöfer 1 Arno Göllner 3 Werner Kusche 2 Ulrich
Comparative Study of Effectiveness of Clindamycin Monotherapy and Clindamycin - Benzoyl Peroxide Combination Therapy in Grade II Acne Patients
 Indian Journal of Pharmacy Practice Association of Pharmaceutical Teachers of India Comparative Study of Effectiveness of Clindamycin Monoerapy and Clindamycin - Benzoyl Peroxide Combination Therapy in
Indian Journal of Pharmacy Practice Association of Pharmaceutical Teachers of India Comparative Study of Effectiveness of Clindamycin Monoerapy and Clindamycin - Benzoyl Peroxide Combination Therapy in
Potulaca (Portulaca oleracea) detergent and other formulations that disrupt the active anthraquinones by regulating the Nitric
 Natural effective support for acne, oily and inflamed skin care At the heart of Frutarom's TopicRange for oily and acne skin problems, we focus Z-Care - a botanical blend based on traditions of Chinese
Natural effective support for acne, oily and inflamed skin care At the heart of Frutarom's TopicRange for oily and acne skin problems, we focus Z-Care - a botanical blend based on traditions of Chinese
Biologic Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF BioBeam TM Acne
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF BioBeam TM Acne BioBeam ACNE is a Class 2A phototherapeutic medical device and complies with Annex VI of the Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC and is CE certified (CE 0473). BioBeam
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF BioBeam TM Acne BioBeam ACNE is a Class 2A phototherapeutic medical device and complies with Annex VI of the Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC and is CE certified (CE 0473). BioBeam
to Part of Dossier: Name of Active Ingredient: Title of Study: Quality of life study with adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. ESCALAR.
 2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Adalimumab (HUMIRA) (For National Authority Use Only) Name of Active Ingredient: Adalimumab Title
2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Adalimumab (HUMIRA) (For National Authority Use Only) Name of Active Ingredient: Adalimumab Title
The Relationship of Salivary Free Testosterone Concentration with Acne Vulgaris
 American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2015; 3(2): 73-77 Published online April 9, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajcem) doi: 10.11648/j.ajcem.20150302.15 ISSN: 2330-8125
American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2015; 3(2): 73-77 Published online April 9, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajcem) doi: 10.11648/j.ajcem.20150302.15 ISSN: 2330-8125
PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain
 P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
Guidance for Industry Acne Vulgaris: Developing Drugs for Treatment
 Guidance for Industry Acne Vulgaris: Developing Drugs for Treatment DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this draft document
Guidance for Industry Acne Vulgaris: Developing Drugs for Treatment DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this draft document
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Adjunctive psychosocial intervention. Conditions requiring dose reduction. Immediate, peak plasma concentration is reached within 1 hour.
 Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Naltrexone Hydrochloride in alcohol dependence Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist,
Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Naltrexone Hydrochloride in alcohol dependence Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist,
Antipsychotic drugs are the cornerstone of treatment
 Article Effectiveness of Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, and Ziprasidone in Patients With Chronic Schizophrenia Following Discontinuation of a Previous Atypical Antipsychotic T. Scott Stroup, M.D.,
Article Effectiveness of Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, and Ziprasidone in Patients With Chronic Schizophrenia Following Discontinuation of a Previous Atypical Antipsychotic T. Scott Stroup, M.D.,
Progress in MS: Current and Emerging Therapies
 Progress in MS: Current and Emerging Therapies Presented by: Dr. Kathryn Giles, MD MSc FRCPC The MS Society gratefully acknowledges the grant received from Biogen Idec Canada, which makes possible the
Progress in MS: Current and Emerging Therapies Presented by: Dr. Kathryn Giles, MD MSc FRCPC The MS Society gratefully acknowledges the grant received from Biogen Idec Canada, which makes possible the
Committee Approval Date: December 12, 2014 Next Review Date: December 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru299 Topic: Tecfidera, dimethyl fumarate Date of Origin: May 16, 2013 Committee Approval Date: December 12, 2014 Next Review Date: December 2015 Effective Date: January
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru299 Topic: Tecfidera, dimethyl fumarate Date of Origin: May 16, 2013 Committee Approval Date: December 12, 2014 Next Review Date: December 2015 Effective Date: January
Acne. Acne. Pediatric Update. Pediatric Update 18/09/2013. Chris Keeling Bio. Keystone Dermatology 23rd Ave & 111St. September 21, 2013
 Pediatric Update Acne Chris Keeling MSc MD FRCPC Dermatology Mohs Micrographic Surgery Keystone Dermatology 23rd Ave & 111St September 21, 2013 Chris Keeling Bio BSc Honours 87-91 University of New Brunswick
Pediatric Update Acne Chris Keeling MSc MD FRCPC Dermatology Mohs Micrographic Surgery Keystone Dermatology 23rd Ave & 111St September 21, 2013 Chris Keeling Bio BSc Honours 87-91 University of New Brunswick
Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
To determine the appropriate treatment, a thorough
 Guidelines for Treating Acne ANDREAS. D. KATSAMBAS, MD CHRISTINA STEFANAKI, MD WILLIAM J. CUNLIFFE, MD, FRCP Abstract: Acne, a chronic inflammatory disease of the pilosebaceous units of the face, neck,
Guidelines for Treating Acne ANDREAS. D. KATSAMBAS, MD CHRISTINA STEFANAKI, MD WILLIAM J. CUNLIFFE, MD, FRCP Abstract: Acne, a chronic inflammatory disease of the pilosebaceous units of the face, neck,
Salicylic Acid Peel Incorporating Triethyl Citrate and Ethyl Linoleate in the Treatment of Moderate Acne: A New Therapeutic Approach
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Salicylic Acid Peel Incorporating Triethyl Citrate and Ethyl Linoleate in the Treatment of Moderate Acne: A New Therapeutic Approach BEATRICE RAONE, MD,* STEFANO VERALDI, MD, ROBERTA
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Salicylic Acid Peel Incorporating Triethyl Citrate and Ethyl Linoleate in the Treatment of Moderate Acne: A New Therapeutic Approach BEATRICE RAONE, MD,* STEFANO VERALDI, MD, ROBERTA
Version History. Previous Versions. Policy Title. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields
Thank you for downloading this free report!
 Thank you for downloading this free report! Feel free to share this report with other people! Marthine B. Green www.acnebuzz.com 2 Page The Truth About Acne There are so many misconceptions about what
Thank you for downloading this free report! Feel free to share this report with other people! Marthine B. Green www.acnebuzz.com 2 Page The Truth About Acne There are so many misconceptions about what
A Phase 2 Study of Interferon Beta-1a (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis
 A Phase 2 Study of (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis - Study Results - ClinicalTrials.gov A Phase 2 Study of (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis This study has been completed. Sponsor: Biogen Idec Information
A Phase 2 Study of (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis - Study Results - ClinicalTrials.gov A Phase 2 Study of (Avonex ) in Ulcerative Colitis This study has been completed. Sponsor: Biogen Idec Information
SYNOPSIS. Risperidone: Clinical Study Report CR003274
 SYNOPSIS Protocol No: CR003274 Title of Study: An Open-Label, Long-Term Trial of Risperidone Long-Acting Microspheres in the Treatment of Subjects Diagnosed with Schizophrenia Coordinating Investigator:
SYNOPSIS Protocol No: CR003274 Title of Study: An Open-Label, Long-Term Trial of Risperidone Long-Acting Microspheres in the Treatment of Subjects Diagnosed with Schizophrenia Coordinating Investigator:
