Business Process Redesign Training
|
|
|
- Gwen York
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Business Process Redesign Training Participant s Guide and Presentation Materials Informatics Capacity Meeting July 2007
2
3 A program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Business Process Redesign Training Participant s Guide Informatics Capacity Meeting July 2007
4 Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Agenda: Day One...1 Agenda: Day Two...2 Ten Steps in Business Process Redesign...3 Choosing a Process to Analyze...4 Setting Priorities: Process Condition and Strategic Importance...5 Choosing a Process to Redesign...6 Immunization Task Flow...7 Choosing Measures of Process Quality and Efficiency...8 Application: Choosing a Process to Redesign and Selecting Measures Identifying the Value Chain Application: Identifying the Value Chain Redesign Principles and Thought Joggers Application: Redesigning a Process Change Management Strategies Change Concepts and the Plan-Do-Study-Act Cycle PDSA Case Story: Acme Health Department PDSA Worksheet Communication Plan Next Steps Notes... 24
5
6 A program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Business Process Redesign Training Informatics Capacity Meeting July 9-10, 2007 Columbus, Ohio Agenda: Day One Introduction and Overview 8:30 Welcome and Overview 9:35 Overview of BPR 9:55 Break Selecting Processes for Redesign 10:15 Choosing Processes to Analyze 10:45 Choosing Processes to Redesign Establishing Measures for Processes 11:00 Measurement Concepts 11:45 Lunch 1:00 Team application: Processes and Measures Identifying Types of Tasks 2:30 What is a Value Chain? 3:00 Break 3:15 Team Application: Identifying the Value Chain Ways to Improve Processes, Part I 4:15 Principles of Redesign 4:40 Day One Closing Page 1
7 Agenda: Day Two Ways to Improve Processes, Part II 8:30 Introduction and Review 9:00 Redesign application: Immunization Task Flow 10:00 Break 10:15 Team Application: Redesign 11:45 Lunch 1:00 Redesign Sharing and Feedback Change Management and Implementation 1:45 Barriers to Change 3:00 Break 3:15 Barriers to Change (continued) 3:35 PDSA Cycle 4:05 Team planning 4:35 Conclusion Page 2
8 Ten Steps in Business Process Redesign Choose a process to redesign. Identify appropriate measures of process quality and efficiency. Gather data related to measures to establish a baseline. Identify the purpose of all tasks in the process, in order to identify the value chain and possible process improvements. Brainstorm ways to improve the process. Create potential new task flows. Work with stakeholders to get input and approval on new task flows. Develop a plan for testing new task flows. Implement new task flows and gather data on quality and effectiveness. Cycle back through process as indicated by findings in test. Page 3
9 Choosing a Process to Analyze Directions: Develop a list of possible processes to analyze. Then, use the scales below to rate each process on importance and condition,. As a group, select a facilitator to lead a discussion of these processes. Work together to reach a consensus involving all stakeholders about the ratings for each process. Then, add each task to the matrix on the next page. After all tasks are on the matrix, analyze the tasks beginning with the high importance/low quality tasks (the lower right quadrant). # Process Condition Importance Process Condition Rating Description 6 Key measures of the process and the process outcomes are predictable. The products and services from the process consistently meeting needs and expectations of customers. 5 The process has been formally improved during the part year. On-going measures exist for the process, including supplier input and customer feedback. 4 The process is well defined and measures of process performance and quality of outcomes are used to monitor the process. 3 The process has been defined by stakeholders. The intent of the process is understood. Documentation of the process exists, such as process flows, procedures, policies, etc. 2 There is a general understanding about the process by those who work in it. No documentation or process standards exist. 1 The process is not defined. This is a new process that needs to be designed and documented. Strategic Importance Rating Description 6 We must focus on this process or product to accomplish the strategic objective. 4 Focusing on this process or product will have a direct impact on the strategic objective. 2 Focusing on this process or product will have an indirect impact on the strategic objective. 0 No impact on the strategic objective is expected from focusing on this process or product. Page 4
10 Setting Priorities: Process Condition and Strategic Importance Condition Low importance/high condition Leave alone Low importance /Low condition Low priority High importance /High condition Leave alone, but monitor High importance /Low condition Highest priority analyze first Importance Page 5
11 Choosing a Process to Redesign Directions: Consider the strategic importance and process condition, as described on previous pages. Also, you should consider the following questions to determine the likelihood that redesign will make a difference. Is it inefficient? Waste of money, effort, or time Results in excessive errors or rework Requires amount of resources disproportionate to its importance Is it inconsistent? Unpredictable results Unpredictable quality Is it antiquated? The way we ve always done things Manual process being automated New technology is being introduced (upgrade of software or other tools) Do we need to document this process? People need to be trained People need jobs aids or other resources to complete the work An organization restructuring requires documentation in case new people are assigned to this process Is it feasible and likely that redesign will succeed and have a positive impact? Strategically important Within our ability to change Page 6
12 Immunization Task Flow Immunization Task Flow Xx insert task flow here. Page 7
13 Choosing Measures of Process Quality and Efficiency Key Question: What can we measure that will show us differences in performance between the old process and the redesigned process? Measurement is a critical part of testing and implementing changes; measures tell a team whether the changes they are making actually lead to improvement. 1 Look at the information in the business process matrix, particularly the objective and outcome for the process. Also, consider using a balanced set of measures for all improvement efforts: Customer Outcome Measures (voice of the customer): How is the system performing? What is the result? Process Efficiency Measures (voice of the organization): How do we know if the process is efficient? Balancing Measures (looking at a system from different directions/dimensions): Are changes designed to improve one part of the system causing new problems in other parts of the system? Here are some of the indicators that business analysts have found helpful in establishing outcome, process, and balancing measures: Time and efficiency: Cycle time, delays, amount of time to appointment, amount of time to get test results, amount of waiting time, number of contacts required Volume: Throughput, percentage of population affected/reached, number of people seen, production rate Cost: Person hours, materials, number of handoffs and reviews, duplicated efforts, unnecessary efforts, amount of waste, missed opportunities, clinician hours devoted to clinical work Quality: Defect rate, errors, standardization, inventory levels, customer satisfaction measures, re-do s required, public health outcomes See the next page for some sample measures. Note that sample measures included on the chart relate to the processes in your Taking Care of Business book. Page 8
14 Sample Measures Process Customer Outcome Process Efficiency Balancing Billing & Accounts Receivable Communicable Disease & Clinical Intervention & Treatment Community Health Assessment Environmental & Safety Inspection Immunization Administration Grantee Administration Client receives timely invoices Timely diagnosis and treatment of disease Public health practitioners develop projects that target current population trends based on health assessment reports Decrease in exposure to environmental hazards Reduce vaccine preventable disease incidence Funder receives timely financial reports Decrease the time between visit/procedure and processing invoice Timely receipt of lab results Increase timely development and dissemination of reports Increase timely inspection of facilities with possible environmental hazards Increase the percentage of people vaccinated Decrease the time for approval of expenditures Accuracy of invoices are not compromised when increasing number of timely invoices Accuracy of lab reports are not compromised in increasing timeliness Accuracy and completeness of the report is not compromised due to increase in timeliness If number of facilities inspected increases, quality of reports are not compromised Other clinical services are not overlooked When decreasing time of approval, expenditures meet grant requirements 2 Use this checklist to make sure that you have chosen the most practical, useful measures to use in your redesign project: Is it related directly to this process? Will it show differences in performance when we change the process? Is it logical, relevant, and easy to understand? Can data be collected as a natural part of the process? Is the level of detail sufficient to identify and analyze problems and opportunities? Have we used measures like this successfully in the past? Note: Measures may evolve as you identify changes and potential effects of changes. Page 9
15 3 Follow through and implement your measures. Keep in mind that measures and redesign support each other. That is, choosing measures will help shape the nature of the redesign, but you may also find that your redesign shapes your measures. For example, if you decide that increasing cycle time is an important measure, then you will try to create a redesigned process that has a reduced cycle time. If, while creating your redesign, you develop a task flow that you hope will increase the number of customers you can serve, then you will probably want to add a measure for that purpose. The following guidelines should help you implement whatever measures you choose. Plot data over time. Improvement requires change, and change is, by definition, a temporal phenomenon. Much information about a system and how to improve it can be obtained by plotting data over time, such as data on length of stay, volume, patient satisfaction and then observing trends and other patterns. Tracking a few key measures over time is the single most powerful tool a team can use. Seek usefulness, not perfection. Remember, measurement is not the goal; improvement is the goal. In order to move forward to the next step, a team needs just enough data to know whether changes are leading to improvement. Use sampling. Sampling is a simple, efficient way to help a team understand how a system is performing. In cardiac surgery, the patient volume is typically low enough to allow tracking of key measures for all patients. However, sampling can save time and resources while accurately tracking performance. For example, instead of monitoring the time from catheterization to cardiac surgery continuously, measure a random sample of 10 to 20 cardiac surgery patients per month. Integrate measurement into the daily routine. Useful data are often easy to obtain without relying on information systems. Don t wait two months to receive data on patients average length of stay in the hospital from the information systems department. Develop a simple data collection form, and make collecting the data part of someone s job. Often, a few simple measures will yield all the information you need. Use qualitative and quantitative data. In addition to collecting quantitative data, be sure to collect qualitative data, which often are easier to access and highly informative. For example, ask the nursing staff how weaning from medications is going or how to improve the sedation protocol. Or, in order to focus your efforts on improving patient and family satisfaction, ask patients and their families about their experience of the cardiac surgery process. Adapted from Page 10
16 Application: Choosing a Process to Redesign and Selecting Measures I: Choose a process to redesign. Use the information on pages 4-6 to guide your discussion. Record your chosen process, along with your rationale, on the chart below. II: Choose balanced measures. A. Read the information on page 8 and the chart on page 9 to understand what you need to do. B. Get out your business process matrix and study the details for the process you have chosen. C. As a team, brainstorm a list of possible measures. Brainstorming means generating as many ideas as you can without evaluation or elaboration. D. Discuss the items on the list you brainstormed. E. Read the information on the bottom of page 8 and all of page 9. This information will help inform your final decision. F. Select at least one outcome, one process, and one balancing measure you may have more than one of each and record them on the chart below. Process to Redesign: Rationale for Redesign: Balanced Measures Customer Outcome Process Efficiency Balancing Page 11
17 III: Create a flipchart of your work. Your flipchart may look like the chart on the previous page, or it may take another form of your choosing. Your flipchart should show your chosen process, rationale, and balanced measures. This flipchart will be a tool for looking at the big picture of your work. IV: Be a critical friend. Critical friends are the people we trust to push our thinking and help us move forward in a positive direction. Critical friends help us think about an issue more thoroughly. Critical friends do this by gently asking probing questions and giving positive constructive feedback. The role of a critical friend can help you be more thoughtful in your planning process. In this part of the exercise, you will work with two other teams, sharing work and serving as critical friends to each other. Each team will present its work, and the other teams will provide feedback and ask probing questions to help move the work forward. Some examples of questions you might ask (and others might ask of you) include: Why did you choose this process for redesign, instead of the others? What did you learn from your stakeholders that helped you with this decision? Do you think your stakeholders will support this decision? Why? What were your key concerns in choosing these measures? What are you trying to achieve? Did you have any redesign ideas in mind when you chose these measures? If so, what were they? Do you think there will be changes to your business process matrix after redesign? What other measures did you consider? Why? Why did you not use them? How do you think you can gather data related to these measures to establish a base line and then measure the new process? What help will you need from stakeholder to gather data related to these measures? How do you plan to get it? Can data be collected on these measures as a natural part of the process? Is the level of detail sufficient to identify and analyze problems and opportunities? Have you used measures like this successfully in the past? V: Summarize and share your learning points. The three teams working together should create a second flipchart with issues we faced, insights we gained, and questions we still have. Choose a speaker to present your poster to the large group for further discussion. Page 12
18 Identifying the Value Chain Types of Tasks Typically, business processes include all three types of tasks listed below: Value-added tasks: Tasks that must be performed in order to reach the process objective(s). Required, non-value added tasks: These tasks do not contribute directly to the process objective but are necessary because they are required by law or regulation, required by business necessity, or the process would be in jeopardy if they were removed. These tasks include: Some quality tasks (tasks performed make sure the process meets standards related to things such as accuracy, completeness, or compliance) Some administrative tasks (tasks that help the organization run smoothly) Enabling tasks (tasks that make it possible for the process to occur) Mandated tasks (those required by policy, law, or regulation) Non-value added waste tasks: These tasks are neither required nor essential. They may include: Some quality tasks Some administrative tasks Rework Handling Setup Storage The Value Chain When redesigning a business process, we need to identify the value chain. The value chain is the minimum set of tasks that are essential to reach the process objective(s). Note: If you change the objective, then the value chain will change as well. Page 13
19 Application: Identifying the Value Chain I: Identify task types. Use the information on the previous page, label each of the tasks in your process as valueadded, required non-value added, or waste tasks. II: Label the value chain. Highlight, circle, or otherwise identify the tasks in the value chain. III: Pair and share. Join with one other team and show them your process, how you labeled tasks, and your value chain. Ask for feedback. Switch places and repeat. IV: Summarize learning points. Record any thoughts and insights you have that might help with redesign: Insights to keep in mind for redesign: Each pair should be prepared to share one insight with the large group. Page 14
20 Redesign Principles and Thought Joggers Products and services are produced by processes. How does work flow in these processes? What is the plan to get work through a process? Are the various steps in the process arranged and prioritized to obtain quality outcomes at low costs? How can we change the work flow so that the process is less reactive and more planned? Improving Processes Popular methods of improving overall flow include identifying best practices found in similar processes standardizing repeatable task series, forms, and instructions; use co-located teams to resolve complex issues; combine operations; reduce/eliminate handoffs; move sequential activities close together; identify alternatives to the process. For instance, is it more efficient to have a vendor perform this service? Below are some redesign principles to consider as you look at ways to improve a given process. Eliminate non-value added waste tasks. Ensure that every task is value-added. For every task, ask, Would a reasonable customer pay for this if he or she knew it was being done? Each task should accomplish a state change in the direction of completion, which usually excludes moving and checking. Streamline non-value added required tasks. Make individual tasks rich enough that people are working up to their potential. Consider grouping administrative tasks across several departments, if possible. Perform steps in parallel rather than in sequence. Many processes are designed so that tasks are done in series or a linear sequence. The second task is not begun until the first task is completed. This is especially true when different groups in the organization are involved in the different steps of a process. Sometimes improvements in time and costs can be gained from designing the system to do some or all tasks in parallel. For example, the work on step 5 can begin as soon as step 1 is complete, rather than wait until steps 2, 3, and 4 are done. Use multiple versions of the same process for special situations. Minimize handoffs. Many systems require that elements (e.g., a customer, a form, a product) be transferred to multiple people, offices, or work stations to complete the processing or service. The handoff from one stage to the next can result in increased time and costs and cause quality problems. The work flow can be rearranged to minimize any handoff in the process. Redesign the process so that any worker is only involved one time in an iteration of a process. Sometimes changes in organization structure or position descriptions can minimize handoffs. Page 15
21 Find and remove bottlenecks. Smooth work flow to redistribute work during peak demand periods. Avoid cumbersome translations and interfaces such as re-keying data from one system to another. Use automation. Seek straight-through processing and automate clerical activities, especially those that move a transaction from one system to another. Help all participants in the process feel ownership of the process. Measure outcomes, not tasks or handoffs Symptoms of Inefficiency Duplication of effort common tasks performed in different places of the process or by more than one entity. Quality checkpoints too far removed from process Unnecessary tasks: Each task not in the value chain should be evaluated to determine if it is needed for the process to meet the objective. Some tasks are no longer required do to changes in an organization, but are still performed. Long cycle times that can be shortened by eliminating sequential activities, hand offs, checkpoints and waiting time (idle) between tasks? Data is input multiple times or transformed repeated from secondary sources Excessive errors resulting in re-work Participants in the process do not understand how it is done, why, or the impact of their performance Process is structured to meet some objective not related to the strategic goals of the organization Process is not standardized. Adapted from: The change concepts included here were developed by Associates in Process Improvement. The Improvement Guide. Langley GJ, Nolan KM, Nolan TW, Norman CL, Provost LP. San Francisco, California, USA: Jossey-Bass Publishers, Inc.; Page 16
22 Application: Redesigning a Process I: Redesign your process. Redesign the process that you selected yesterday. This means creating a new task flow that will help you improve the measures you selected. (You may also need to add or change measures based on your redesign.) Post your redesign on a flipchart. II: Revise matrix as needed. Revisit the row of your business process matrix that contains information on this process. Is it still accurate? Do you need to revise it based on your redesign? Make revisions as needed. III: Create a flipchart of your work. Your flipchart may look like the chart on the next page, or it may take another form of your choosing. Your flipchart should represent your thinking and your final decisions. IV: Be a critical friend. Work with two other teams, sharing work and serving as critical friends to each other. Each team will present its work, and the other teams will provide feedback and ask probing questions to help move the work forward. Some examples of questions include: What were some of the problems with the existing process? What did you hope to achieve with this redesign? Do you think your stakeholders will support this decision? Why? How do you plan to involve them? What were the changes to your business process matrix after redesign? What other redesigns did you consider? Why? Why did you not use them? How do you think you can gather data to measure the new process? What concerns do you have about this redesign? V: Summarize and share your learning points. The three teams working together should create a flipchart with issues we faced, insights we gained, and questions we still have. Choose a speaker to present your poster to the large group for further discussion. Page 17
23 Change Management Strategies Possible Barriers to Implementation Strategies for Overcoming Barriers Page 18
24 Change Concepts and the Plan-Do-Study-Act Cycle While all changes do not lead to improvement, all improvement requires change. The ability to develop, test, and implement changes is essential for any individual, group, or organization that wants to continuously improve. Run Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles to test a change or group of changes on a small scale to see if they result in improvement. If they do, expand the tests and gradually incorporate larger and larger samples until you are confident that the changes should be adopted more widely. 1 Plan 2 Do 3 Study 4 Act Plan the test or observation, including a plan for collecting data. State the objective of the test. Make predictions about what will happen and why. Develop a plan to test the change. (Who? What? When? Where? What data need to be collected?) Try out the test on a small scale. Carry out the test. Document problems and unexpected observations. Begin analysis of the data. Set aside time to analyze the data and study the results. Complete the analysis of the data. Compare the data to your predictions. Summarize and reflect on what was learned. Refine the change, based on what was learned from the test. Determine what modifications should be made. Prepare a plan for the next test. Source: Institute for Health Care Improvement, Page 19
25 PDSA Case Story: Acme Health Department Opportunity and Goal Baseline Changes What Happened To address the bacterial outbreak in their community, the ACME Health Department decided to initiate a school immunization requirement for the new vaccine. Their goal is to have 90% of school-aged children vaccinated against the bacteria within five years. Public health officials predicted that there would be a high level of compliance with first-time enrollees such as kindergarteners, first-graders and transfer students where immunization requirements are enforced more stringently as a part of the registration process. The expectation was that there would be lower numbers of compliance in grades two to four (ages seven-nine) where most children are past the initial booster and school registration stage. Their predictions proved to be true: Early analysis showed that more than 90% of kindergarten and first-graders eligible for the vaccine had up-to-date immunization records on file. However, only 22% of the second through fourth graders had the latest vaccination on their immunization records. The Health Department decided to focus on increasing immunization rates among this age group by adding a step in the registration process to assess the vaccination status of siblings in the affected age range and to refer those unvaccinated to the immunization clinic. They added a check box to the intake checklist to make sure this was done. A one-year pilot test of this sibling referral initiative was conducted in Parkhill Elementary School. This school was selected because it resides in the heart of the outbreak vicinity and they use a registration database and filing system, making the student immunization information more readily accessible than that from a paper filing system. Preliminary data from the pilot test shows that the percentage of children between ages seven and nine that receive the vaccination increased from 22%-73% after introducing the sibling referral program into the current process. What s Next Given the success of the initiative, ACME staff is determining how to redesign the student registration process to incorporate review and referral for immunization of non-siblings. Page 20
26 PDSA Worksheet Directions: Use this worksheet to plan, implement, and evaluate tests of changes. This worksheet provides an easy-to-understand one-page summary of your process to use with all stakeholders. 1 Plan Write your goal (what you hope to accomplish through this test of change) and measure(s) Tasks/activities needed to set up and implement test of change Who When Where 2 Do Describe what happened when you ran the test: 3 Study Describe measured results and how they compared to predictions: 4 Act Describe what modifications to the plan will be made for the next cycle from what you learned: Page 21
27 Communication Plan Person s Name/Position Review Approve Contribute Be Informed Project objective Communication objective Key messages for each quadrant Communication strategies/vehicles Page 22
28 Next Steps Throughout this training, we have provided you with a new way of thinking about the opportunities to improve your work products, flow of work, or get more from information systems. In the first phase of training, beginning in February, we defined your work processes and activities using business process analysis. As we train you for the second phase of your projects, we have discussed the business process redesign approach that will guide you in improving the process. Business analysis employs a variety of tools and methods, beyond what we have been able to present in our short time together. Depending on the complexity of your organization and the scope of proposed changes to your business process, you may need additional knowledge about business analysis, or you may need a dedicated business analyst to support your efforts. As we move forward, some organizations may choose to hire a business analyst on staff or as a consultant. The business analyst would provide the necessary objectivity and understanding of your specific project and operating environment to support your next steps. However, for short-term projects, that may not be a feasible option. In that case, we propose that you identify a staff member who can be committed to learning business analysis tools and approaches in greater depth. As background, and to support your efforts, we will provide a resource library on ConnectionsZone with reference materials related to business analysis approaches and tools. The Institute staff is here to support your efforts and provide continued feedback on your progress. Page 23
29 Notes Page 24
30 Public Health Informatics Institute 750 Commerce Drive, Suite 400 Decatur, GA TEL: FAX: Public Health Informatics Institute. All rights reserved. Page 25
Quality Improvement Primers. Change Concepts and Ideas
 Quality Improvement Primers Change Concepts and Ideas ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This workbook is the result of the efforts of the Health Quality Ontario (HQO). For additional information about other resources,
Quality Improvement Primers Change Concepts and Ideas ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This workbook is the result of the efforts of the Health Quality Ontario (HQO). For additional information about other resources,
Lean Six Sigma: Redesigning the Cancer Care Delivery Process. 2014 Community Oncology Conference
 Lean Six Sigma: Redesigning the Cancer Care Delivery Process 2014 Community Oncology Conference Disclosure Medical Directorship, The US Oncology Network, compensated A Typical Oncology Clinic (Does this
Lean Six Sigma: Redesigning the Cancer Care Delivery Process 2014 Community Oncology Conference Disclosure Medical Directorship, The US Oncology Network, compensated A Typical Oncology Clinic (Does this
Australian Safety and Quality Framework for Health Care
 Activities for MANAGERS Australian Safety and Quality Framework for Health Care Putting the Framework into action: Getting started Contents Principle: Consumer centred Area for action: 1.1 Develop methods
Activities for MANAGERS Australian Safety and Quality Framework for Health Care Putting the Framework into action: Getting started Contents Principle: Consumer centred Area for action: 1.1 Develop methods
IMPROVING PERFORMANCE FOR HEALTH PLAN CUSTOMER SERVICE
 IMPROVING PERFORMANCE FOR HEALTH PLAN CUSTOMER SERVICE A Case Study of a Successful CAHPS Quality Improvement Intervention Excerpt: The Case Study in Brief For a copy of the full report, go to http://www.rand.org/pubs/working_papers/wr7/
IMPROVING PERFORMANCE FOR HEALTH PLAN CUSTOMER SERVICE A Case Study of a Successful CAHPS Quality Improvement Intervention Excerpt: The Case Study in Brief For a copy of the full report, go to http://www.rand.org/pubs/working_papers/wr7/
case study Denver Health & Hospital Authority IT as a Change Agent in the Transformation of Healthcare Summary Introductory Overview ORGANIZATION:
 The Computerworld Honors Program Denver, Colorado, United States Summary For the past nine years, has partnered with Siemens Medical Solutions to further its mission as a safety net city-wide hospital
The Computerworld Honors Program Denver, Colorado, United States Summary For the past nine years, has partnered with Siemens Medical Solutions to further its mission as a safety net city-wide hospital
Develop Project Charter. Develop Project Management Plan
 Develop Charter Develop Charter is the process of developing documentation that formally authorizes a project or a phase. The documentation includes initial requirements that satisfy stakeholder needs
Develop Charter Develop Charter is the process of developing documentation that formally authorizes a project or a phase. The documentation includes initial requirements that satisfy stakeholder needs
Camber Quality Assurance (QA) Approach
 Camber Quality Assurance (QA) Approach Camber s QA approach brings a tested, systematic methodology, ensuring that our customers receive the highest quality products and services, delivered via efficient
Camber Quality Assurance (QA) Approach Camber s QA approach brings a tested, systematic methodology, ensuring that our customers receive the highest quality products and services, delivered via efficient
BENEFITS REALIZATION ENSURES CHANGE DELIVERS GREATER BUSINESS VALUE
 BENEFITS REALIZATION ENSURES CHANGE DELIVERS GREATER BUSINESS VALUE Focusing on the delivery of value-adding benefits is an excellent way to achieve greater ROI from change. Benefits & Value Management
BENEFITS REALIZATION ENSURES CHANGE DELIVERS GREATER BUSINESS VALUE Focusing on the delivery of value-adding benefits is an excellent way to achieve greater ROI from change. Benefits & Value Management
Guide for the Development of Results-based Management and Accountability Frameworks
 Guide for the Development of Results-based Management and Accountability Frameworks August, 2001 Treasury Board Secretariat TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1. Introduction to the Results-based Management and
Guide for the Development of Results-based Management and Accountability Frameworks August, 2001 Treasury Board Secretariat TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1. Introduction to the Results-based Management and
Workshop agenda. Data Quality Metrics and IT Governance. Today s purpose. Icebreaker. Audience Contract. Today s Purpose
 Workshop agenda Strategic Data Quality Management Data Quality Metrics and IT Governance Today s purpose data quality metrics Conclusion Presenter: Micheal Axelsen Director Information Systems Consulting
Workshop agenda Strategic Data Quality Management Data Quality Metrics and IT Governance Today s purpose data quality metrics Conclusion Presenter: Micheal Axelsen Director Information Systems Consulting
The Evolving Role of Process Automation and the Customer Service Experience
 The Evolving Role of Process Automation and the Customer Service Experience Kyle Lyons Managing Director Ponvia Technology Gina Clarkin Product Manager Interactive Intelligence Table of Contents Executive
The Evolving Role of Process Automation and the Customer Service Experience Kyle Lyons Managing Director Ponvia Technology Gina Clarkin Product Manager Interactive Intelligence Table of Contents Executive
Capacity Management: Patient Throughput and Case Management Improvement. February 25, 2015
 Capacity Management: Patient Throughput and Case Management Improvement February 25, 2015 Agenda Introduction Impetus for Change Approach to Improving Case and Capacity Management Client Case Study Key
Capacity Management: Patient Throughput and Case Management Improvement February 25, 2015 Agenda Introduction Impetus for Change Approach to Improving Case and Capacity Management Client Case Study Key
Netstar Strategic Solutions Practice Development Methodology
 Netstar Strategic Solutions Practice Development Methodology Netstar Corporation Abstract This document contains a high level description of the development methodology used by the Netstar Strategic Solutions
Netstar Strategic Solutions Practice Development Methodology Netstar Corporation Abstract This document contains a high level description of the development methodology used by the Netstar Strategic Solutions
Mastering the Iteration: An Agile White Paper
 Rally Software Development Corporation Whitepaper Mastering the Iteration: An Agile White Paper Dean Leffingwell Abstract: The heartbeat of Agile development is the iteration the ability of the team to
Rally Software Development Corporation Whitepaper Mastering the Iteration: An Agile White Paper Dean Leffingwell Abstract: The heartbeat of Agile development is the iteration the ability of the team to
VALUE STREAM MAPPING FOR SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS. Ganesh S Thummala. A Research Paper. Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the
 VALUE STREAM MAPPING FOR SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS by Ganesh S Thummala A Research Paper Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Master of Science Degree In Management Technology
VALUE STREAM MAPPING FOR SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS by Ganesh S Thummala A Research Paper Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Master of Science Degree In Management Technology
Office Efficiency Improving Office Processes and Task Analysis
 Office Efficiency Improving Office Processes and Task Analysis Contents Office Efficiency... 3 Office Efficiency Aim... 3 Sample Office Efficiency Aims... 3 Key Efficiency Measures... 4 Balance Supply
Office Efficiency Improving Office Processes and Task Analysis Contents Office Efficiency... 3 Office Efficiency Aim... 3 Sample Office Efficiency Aims... 3 Key Efficiency Measures... 4 Balance Supply
Adopting Lean Methodology In A Behavioral Healthcare Setting
 Adopting Lean Methodology In A Behavioral Healthcare Setting Organization Name: Sheppard Pratt Health System Type: Specialty Hospital Contact Person: Sunil Khushalani, MD Title: Chair, Medical Executive
Adopting Lean Methodology In A Behavioral Healthcare Setting Organization Name: Sheppard Pratt Health System Type: Specialty Hospital Contact Person: Sunil Khushalani, MD Title: Chair, Medical Executive
CDC UNIFIED PROCESS PRACTICES GUIDE
 Document Purpose The purpose of this document is to provide guidance on the practice of Requirements Definition and to describe the practice overview, requirements, best practices, activities, and key
Document Purpose The purpose of this document is to provide guidance on the practice of Requirements Definition and to describe the practice overview, requirements, best practices, activities, and key
White Paper 10 barriers to effective inventory management
 White Paper 10 barriers to effective inventory management Introduction: Inventory management in an age of health care reform The need to address barriers to effective supply chain management has become
White Paper 10 barriers to effective inventory management Introduction: Inventory management in an age of health care reform The need to address barriers to effective supply chain management has become
The NCCTS Learning Collaborative Model for the Adoption & Implementation of Evidence-Based Mental Health Treatment
 The NCCTS Learning Collaborative Model for the Adoption & Implementation of Evidence-Based Mental Health Treatment NCCTS GUIDELINES FOR CONDUCTING A LEARNING COLLABORATIVE A large gap exists between best
The NCCTS Learning Collaborative Model for the Adoption & Implementation of Evidence-Based Mental Health Treatment NCCTS GUIDELINES FOR CONDUCTING A LEARNING COLLABORATIVE A large gap exists between best
Quality Improvement Process Using Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) Planning for Action
 Quality Improvement Process Using Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) Planning for Action Kathy Hybarger, RN, MSN Connie Steigmeyer, RN, MSN Betsy Lee, RN, MSPH Linda Woolley, RN, MSM Quality Improvement is not
Quality Improvement Process Using Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) Planning for Action Kathy Hybarger, RN, MSN Connie Steigmeyer, RN, MSN Betsy Lee, RN, MSPH Linda Woolley, RN, MSM Quality Improvement is not
(Refer Slide Time: 01:52)
 Software Engineering Prof. N. L. Sarda Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 2 Introduction to Software Engineering Challenges, Process Models etc (Part 2) This
Software Engineering Prof. N. L. Sarda Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 2 Introduction to Software Engineering Challenges, Process Models etc (Part 2) This
Program theory and logic models Evaluation resources from Wilder Research
 Wilder Research Program theory and logic models Evaluation resources from Wilder Research All human service programs are designed to make a difference in the lives of people or to improve our society.
Wilder Research Program theory and logic models Evaluation resources from Wilder Research All human service programs are designed to make a difference in the lives of people or to improve our society.
Chapter 4 SUPPLY CHAIN PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT USING ANALYTIC HIERARCHY PROCESS METHODOLOGY
 Chapter 4 SUPPLY CHAIN PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT USING ANALYTIC HIERARCHY PROCESS METHODOLOGY This chapter highlights on supply chain performance measurement using one of the renowned modelling technique
Chapter 4 SUPPLY CHAIN PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT USING ANALYTIC HIERARCHY PROCESS METHODOLOGY This chapter highlights on supply chain performance measurement using one of the renowned modelling technique
Process Intelligence: An Exciting New Frontier for Business Intelligence
 February/2014 Process Intelligence: An Exciting New Frontier for Business Intelligence Claudia Imhoff, Ph.D. Sponsored by Altosoft, A Kofax Company Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Use Cases... 2 Business
February/2014 Process Intelligence: An Exciting New Frontier for Business Intelligence Claudia Imhoff, Ph.D. Sponsored by Altosoft, A Kofax Company Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Use Cases... 2 Business
Content Sheet 13-1: Overview of Customer Service
 Content Sheet 13-1: Overview of Customer Service Role in quality management system This module will describe basic elements that are essential for developing an effective customer service program. Customer
Content Sheet 13-1: Overview of Customer Service Role in quality management system This module will describe basic elements that are essential for developing an effective customer service program. Customer
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign
 Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign Unit 10.7 Facilitating Implementation Decisions Meeting Unit Objectives Upon successful completion of this unit the student is able to: Plan
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign Unit 10.7 Facilitating Implementation Decisions Meeting Unit Objectives Upon successful completion of this unit the student is able to: Plan
SPECIFICATION BY EXAMPLE. Gojko Adzic. How successful teams deliver the right software. MANNING Shelter Island
 SPECIFICATION BY EXAMPLE How successful teams deliver the right software Gojko Adzic MANNING Shelter Island Brief Contents 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Preface xiii Acknowledgments xxii
SPECIFICATION BY EXAMPLE How successful teams deliver the right software Gojko Adzic MANNING Shelter Island Brief Contents 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Preface xiii Acknowledgments xxii
Step 1: Analyze Data. 1.1 Organize
 A private sector assessment combines quantitative and qualitative methods to increase knowledge about the private health sector. In the analytic phase, the team organizes and examines information amassed
A private sector assessment combines quantitative and qualitative methods to increase knowledge about the private health sector. In the analytic phase, the team organizes and examines information amassed
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE LEADERSHIP AND ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE FOR IMPLEMENTATION (LOCI) DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
 ADDITIONAL FILE 1: DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE LEADERSHIP AND ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE FOR IMPLEMENTATION (LOCI) DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Leadership and organizational change for implementation (LOCI): A randomized
ADDITIONAL FILE 1: DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE LEADERSHIP AND ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE FOR IMPLEMENTATION (LOCI) DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Leadership and organizational change for implementation (LOCI): A randomized
Mid State Health Center Quality Improvement Case Study. Sharon Beaty and John W. Moran 1
 Mid State Health Center Quality Improvement Case Study Sharon Beaty and John W. Moran 1 Introduction: Mid-State Health Center (MSHC) is an independent, non-profit primary care medical practice with offices
Mid State Health Center Quality Improvement Case Study Sharon Beaty and John W. Moran 1 Introduction: Mid-State Health Center (MSHC) is an independent, non-profit primary care medical practice with offices
PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT
 PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT DEFINITION OF A RISK OR RISK EVENT: A discrete occurrence that may affect the project for good or bad. DEFINITION OF A PROBLEM OR UNCERTAINTY: An uncommon state of nature, characterized
PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT DEFINITION OF A RISK OR RISK EVENT: A discrete occurrence that may affect the project for good or bad. DEFINITION OF A PROBLEM OR UNCERTAINTY: An uncommon state of nature, characterized
Tips for Success. Documenting Practice Workflows and Envisioning the Future. 1. Involve All Areas of Practice
 Documenting Practice Workflows and Envisioning the Future Tips for Success The many and varying clinical and administrative processes, workflows and documents that currently drive and control the daily
Documenting Practice Workflows and Envisioning the Future Tips for Success The many and varying clinical and administrative processes, workflows and documents that currently drive and control the daily
Procurement guidance Managing and monitoring suppliers performance
 Procurement guidance Managing and monitoring suppliers performance Procurement guidance: Managing and monitoring suppliers performance Page 2 of 16 Table of contents Table of contents... 2 Purpose of the
Procurement guidance Managing and monitoring suppliers performance Procurement guidance: Managing and monitoring suppliers performance Page 2 of 16 Table of contents Table of contents... 2 Purpose of the
Cisco Unified Communications and Collaboration technology is changing the way we go about the business of the University.
 Data Sheet Cisco Optimization s Optimize Your Solution using Cisco Expertise and Leading Practices Optimizing Your Business Architecture Today, enabling business innovation and agility is about being able
Data Sheet Cisco Optimization s Optimize Your Solution using Cisco Expertise and Leading Practices Optimizing Your Business Architecture Today, enabling business innovation and agility is about being able
Oxford Academic Health Science Network and Buckinghamshire New University: The Innovating in Health Care Settings Programme 2016/17
 Oxford Academic Health Science Network and Buckinghamshire New University: The Innovating in Health Care Settings Programme 2016/17 The programme has been fully funded by Health Education Thames Valley
Oxford Academic Health Science Network and Buckinghamshire New University: The Innovating in Health Care Settings Programme 2016/17 The programme has been fully funded by Health Education Thames Valley
White Paper from Global Process Innovation. Fourteen Metrics for a BPM Program
 White Paper from Global Process Innovation by Jim Boots Fourteen Metrics for a BPM Program This white paper presents 14 metrics which may be useful for monitoring progress on a BPM program or initiative.
White Paper from Global Process Innovation by Jim Boots Fourteen Metrics for a BPM Program This white paper presents 14 metrics which may be useful for monitoring progress on a BPM program or initiative.
How Lean Six Sigma can Change Higher Education. Norma Simons Performance Innovation LLC Secretary ASQ Education Division
 How Lean Six Sigma can Change Higher Education Norma Simons Performance Innovation LLC Secretary ASQ Education Division Learning Outcomes Understand the value of project selection Identify the parameters
How Lean Six Sigma can Change Higher Education Norma Simons Performance Innovation LLC Secretary ASQ Education Division Learning Outcomes Understand the value of project selection Identify the parameters
10426: Large Scale Project Accounting Data Migration in E-Business Suite
 10426: Large Scale Project Accounting Data Migration in E-Business Suite Objective of this Paper Large engineering, procurement and construction firms leveraging Oracle Project Accounting cannot withstand
10426: Large Scale Project Accounting Data Migration in E-Business Suite Objective of this Paper Large engineering, procurement and construction firms leveraging Oracle Project Accounting cannot withstand
BUSINESS PROCESS OPTIMIZATION IN THE CONTACT CENTER
 BUSINESS PROCESS OPTIMIZATION IN THE CONTACT CENTER By Brian Hinton Principal Consultant Strategic Contact, Inc. June 2010 2010 Strategic Contact, Inc. All Rights Reserved WHITE PAPER ABOUT THE AUTHOR
BUSINESS PROCESS OPTIMIZATION IN THE CONTACT CENTER By Brian Hinton Principal Consultant Strategic Contact, Inc. June 2010 2010 Strategic Contact, Inc. All Rights Reserved WHITE PAPER ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Computing Services Network Project Methodology
 Computing Services Network Project Prepared By: Todd Brindley, CSN Project Version # 1.0 Updated on 09/15/2008 Version 1.0 Page 1 MANAGEMENT PLANNING Project : Version Control Version Date Author Change
Computing Services Network Project Prepared By: Todd Brindley, CSN Project Version # 1.0 Updated on 09/15/2008 Version 1.0 Page 1 MANAGEMENT PLANNING Project : Version Control Version Date Author Change
Project Knowledge Areas
 From Houston S: The Project Manager s Guide to Health Information Technology Implementation. Chicago: HIMSS; 2011; pp 27 39. This book is available on the HIMSS online bookstore at www. himss.org/store.
From Houston S: The Project Manager s Guide to Health Information Technology Implementation. Chicago: HIMSS; 2011; pp 27 39. This book is available on the HIMSS online bookstore at www. himss.org/store.
Justifying Simulation. Why use simulation? Accurate Depiction of Reality. Insightful system evaluations
 Why use simulation? Accurate Depiction of Reality Anyone can perform a simple analysis manually. However, as the complexity of the analysis increases, so does the need to employ computer-based tools. While
Why use simulation? Accurate Depiction of Reality Anyone can perform a simple analysis manually. However, as the complexity of the analysis increases, so does the need to employ computer-based tools. While
Workflow Redesign for EHRs. College of St. Scholastica
 Workflow Redesign for EHRs Phil Deering Regional Coordinator REACH Pam Oachs, MA, RHIA Assistant Professor College of St. Scholastica 1 Objectives Learn the value of understanding current clinical workflows
Workflow Redesign for EHRs Phil Deering Regional Coordinator REACH Pam Oachs, MA, RHIA Assistant Professor College of St. Scholastica 1 Objectives Learn the value of understanding current clinical workflows
Guidian Healthcare Consulting
 FRONT OFFICE E FFICE EFFICIENCY MAXIMIZING PRACTICE REVENUE STARTING AT THE FRONT D RONT DESK Guidian Healthcare Consulting Guidian Healthcare Consulting Guidian works with Community Health Centers to
FRONT OFFICE E FFICE EFFICIENCY MAXIMIZING PRACTICE REVENUE STARTING AT THE FRONT D RONT DESK Guidian Healthcare Consulting Guidian Healthcare Consulting Guidian works with Community Health Centers to
Ensuring Reliability in Lean New Product Development. John J. Paschkewitz, P.E., CRE
 Ensuring Reliability in Lean New Product Development John J. Paschkewitz, P.E., CRE Overview Introduction and Definitions Part 1: Lean Product Development Lean vs. Traditional Product Development Key Elements
Ensuring Reliability in Lean New Product Development John J. Paschkewitz, P.E., CRE Overview Introduction and Definitions Part 1: Lean Product Development Lean vs. Traditional Product Development Key Elements
NAMD WORKING PAPER SERIES. Advancing Medicare and Medicaid Integration: An Update on Improving State Access to Medicare Data
 NAMD WORKING PAPER SERIES Advancing Medicare and Medicaid Integration: An Update on Improving State Access to Medicare Data May 2012 444 North Capitol Street, Suite 309 Washington, DC 20001 Phone: 202.403.8620
NAMD WORKING PAPER SERIES Advancing Medicare and Medicaid Integration: An Update on Improving State Access to Medicare Data May 2012 444 North Capitol Street, Suite 309 Washington, DC 20001 Phone: 202.403.8620
Examples of Quality Improvement Projects in Adult Immunization
 Examples of Quality Improvement Projects in Adult Immunization The following activities are provided to prompt your thinking about what works best for your practice. When designing a project, consider
Examples of Quality Improvement Projects in Adult Immunization The following activities are provided to prompt your thinking about what works best for your practice. When designing a project, consider
Designing a Modern, Holistic ECM Strategy for Healthcare. How ECM consulting helps healthcare providers thrive in an atmosphere of change.
 Designing a Modern, Holistic ECM Strategy for Healthcare How ECM consulting helps healthcare providers thrive in an atmosphere of change. Executive Summary Today s healthcare industry is undergoing continual
Designing a Modern, Holistic ECM Strategy for Healthcare How ECM consulting helps healthcare providers thrive in an atmosphere of change. Executive Summary Today s healthcare industry is undergoing continual
By Jack Phillips and Patti Phillips How to measure the return on your HR investment
 By Jack Phillips and Patti Phillips How to measure the return on your HR investment Using ROI to demonstrate your business impact The demand for HR s accountability through measurement continues to increase.
By Jack Phillips and Patti Phillips How to measure the return on your HR investment Using ROI to demonstrate your business impact The demand for HR s accountability through measurement continues to increase.
Lean Healthcare Metrics Guide
 Lean Healthcare Metrics Guide Lean Metrics Guide Page 1 This Lean Metrics Guide is a resource to help organizations understand and select metrics to support their implementation of Lean and Six Sigma two
Lean Healthcare Metrics Guide Lean Metrics Guide Page 1 This Lean Metrics Guide is a resource to help organizations understand and select metrics to support their implementation of Lean and Six Sigma two
Building the Business Case for Automated Rapid Testing: Translating the benefits of rapid automated microbial testing into dollars saved
 Building the Business Case for Automated Rapid Testing: Translating the benefits of rapid automated microbial testing into dollars saved A whitepaper by: Opportunities in Micro Quality Control According
Building the Business Case for Automated Rapid Testing: Translating the benefits of rapid automated microbial testing into dollars saved A whitepaper by: Opportunities in Micro Quality Control According
SIX-STEP PROBLEM SOLVING MODEL
 SIX-STEP PROBLEM SOLVING MODEL Problem solving models are used to address many issues that come up on a daily basis in the workplace. These problems may be technical or issue-based. While many of you have
SIX-STEP PROBLEM SOLVING MODEL Problem solving models are used to address many issues that come up on a daily basis in the workplace. These problems may be technical or issue-based. While many of you have
Body of Knowledge for Six Sigma Green Belt
 Body of Knowledge for Six Sigma Green Belt What to Prepare For: The following is the Six Sigma Green Belt Certification Body of Knowledge that the exam will cover. We strongly encourage you to study and
Body of Knowledge for Six Sigma Green Belt What to Prepare For: The following is the Six Sigma Green Belt Certification Body of Knowledge that the exam will cover. We strongly encourage you to study and
CRISP-DM, which stands for Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining, is an industry-proven way to guide your data mining efforts.
 CRISP-DM, which stands for Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining, is an industry-proven way to guide your data mining efforts. As a methodology, it includes descriptions of the typical phases
CRISP-DM, which stands for Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining, is an industry-proven way to guide your data mining efforts. As a methodology, it includes descriptions of the typical phases
Please comply with the Lean Construction Institute s Usage Policies and Attribution Guidelines at http://www.leanconstruction.org/usage.
 Please comply with the Lean Construction Institute s Usage Policies and Attribution Guidelines at http://www.leanconstruction.org/usage.pdf when using this file. Thank you. Target-Value Design: Nine Foundational
Please comply with the Lean Construction Institute s Usage Policies and Attribution Guidelines at http://www.leanconstruction.org/usage.pdf when using this file. Thank you. Target-Value Design: Nine Foundational
Data Conversion Best Practices
 WHITE PAPER Data Conversion Best Practices Thomas Maher and Laura Bloemer Senior Healthcare Consultants Hayes Management WHITE PAPER: Data Conversion Best Practices Background Many healthcare organizations
WHITE PAPER Data Conversion Best Practices Thomas Maher and Laura Bloemer Senior Healthcare Consultants Hayes Management WHITE PAPER: Data Conversion Best Practices Background Many healthcare organizations
An Introduction to Health IT Certification
 January 2009 Table of Contents Wanted: a mechanism to speed up health IT adoption... 3 What CCHIT demands of EHRs... 4 Summarizing the scope of functionality... 5 Building national priorities into EHRs...
January 2009 Table of Contents Wanted: a mechanism to speed up health IT adoption... 3 What CCHIT demands of EHRs... 4 Summarizing the scope of functionality... 5 Building national priorities into EHRs...
Evaluating Breastfeeding Programs and Initiatives
 Breastfeeding in Ontario Evaluating Breastfeeding Programs and Initiatives What is evaluation? Evaluation means different things to different people. Fundamentally, evaluation means getting feedback about
Breastfeeding in Ontario Evaluating Breastfeeding Programs and Initiatives What is evaluation? Evaluation means different things to different people. Fundamentally, evaluation means getting feedback about
Electronic Health Records
 What Do Electronic Health Records Mean for Our Practice? What are Electronic Health Records? Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are computer systems that medical practices use instead of paper charts. All
What Do Electronic Health Records Mean for Our Practice? What are Electronic Health Records? Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are computer systems that medical practices use instead of paper charts. All
3 DEVELOP A SHARED VISION, MISSION, AND
 MISSION AND GOALS 34 3 DEVELOP A MISSION, AND GOALS When organizations or individuals decide to join forces and work as a partnership, they do so with a purpose in mind. While the individual partners may
MISSION AND GOALS 34 3 DEVELOP A MISSION, AND GOALS When organizations or individuals decide to join forces and work as a partnership, they do so with a purpose in mind. While the individual partners may
Scioto Paint Valley Mental Health Center. Quality. Assurance Plan
 Scioto Paint Valley Mental Health Center Quality 2015 Assurance Plan SCIOTO PAINT VALLEY MENTAL HEALTH CENTER QUALITY ASSURANCE PLAN OVERVIEW This document presents the comprehensive and systematic plan
Scioto Paint Valley Mental Health Center Quality 2015 Assurance Plan SCIOTO PAINT VALLEY MENTAL HEALTH CENTER QUALITY ASSURANCE PLAN OVERVIEW This document presents the comprehensive and systematic plan
Value Engineering VE with Risk Assessment RA
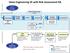 Preparation Conclude & Report Value Engineering VE with Risk Assessment RA yes START Plan for VE and RA Value Engineering Job Plan 1 2 Function Information Analysis 3 Creative 4 Evaluation 5 Develop recommendations
Preparation Conclude & Report Value Engineering VE with Risk Assessment RA yes START Plan for VE and RA Value Engineering Job Plan 1 2 Function Information Analysis 3 Creative 4 Evaluation 5 Develop recommendations
Topic 7: Introduction to quality improvement methods
 Why students need to know about quality improvement methods 1 Students will be familiar with the term evidence-based medicine and the randomized controlled trial, which has enabled medicine to establish
Why students need to know about quality improvement methods 1 Students will be familiar with the term evidence-based medicine and the randomized controlled trial, which has enabled medicine to establish
Introduction to Business Process Improvement
 Introduction to Business Process Improvement Learning Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Define a business process. State the objectives of business process improvement. Explain
Introduction to Business Process Improvement Learning Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Define a business process. State the objectives of business process improvement. Explain
Anatomy of an Enterprise Software Delivery Project
 Chapter 2 Anatomy of an Enterprise Software Delivery Project Chapter Summary I present an example of a typical enterprise software delivery project. I examine its key characteristics and analyze specific
Chapter 2 Anatomy of an Enterprise Software Delivery Project Chapter Summary I present an example of a typical enterprise software delivery project. I examine its key characteristics and analyze specific
The Practical Organization of Automated Software Testing
 The Practical Organization of Automated Software Testing Author: Herbert M. Isenberg Ph.D. Quality Assurance Architect Oacis Healthcare Systems PO Box 3178 Sausalito, CA. 94966 Type: Experience Report
The Practical Organization of Automated Software Testing Author: Herbert M. Isenberg Ph.D. Quality Assurance Architect Oacis Healthcare Systems PO Box 3178 Sausalito, CA. 94966 Type: Experience Report
Advanced Access Works! Improved Patient Satisfaction, Access, and P4P Scores
 Advanced Access Works! Improved Patient Satisfaction, Access, and P4P Scores Mary J. Witt* P ractices continue to struggle with patient scheduling and assuring access to care for their patients. Consequently,
Advanced Access Works! Improved Patient Satisfaction, Access, and P4P Scores Mary J. Witt* P ractices continue to struggle with patient scheduling and assuring access to care for their patients. Consequently,
Webinar Series. Creating Diplomats For Hope. Empathy & Lean. Using Lean Healthcare methodologies to improve upon the patient experience
 Webinar Series Creating Diplomats For Hope Empathy & Lean Using Lean Healthcare methodologies to improve upon the patient experience Webinar Series Creating Diplomats For Hope HOUSEKEEPING AUDIO is available
Webinar Series Creating Diplomats For Hope Empathy & Lean Using Lean Healthcare methodologies to improve upon the patient experience Webinar Series Creating Diplomats For Hope HOUSEKEEPING AUDIO is available
How to Leverage Data Analytics in Healthcare Auditing
 Feature How to Leverage Data Analytics in Healthcare Auditing Unleash the power of the computer to vastly improve your audit reach By Scot Murphy, CFE, CIA, ACDA, and Tom Stec, CIA, ACDA Healthcare auditing
Feature How to Leverage Data Analytics in Healthcare Auditing Unleash the power of the computer to vastly improve your audit reach By Scot Murphy, CFE, CIA, ACDA, and Tom Stec, CIA, ACDA Healthcare auditing
MEDICAL OFFICE SERIES
 MEDICAL OFFICE SERIES Occ. Work Prob. Effective Last Code No. Class Title Area Area Period Date Action 4960 Medical Office Assistant 04 445 6 mo. 07/15/12 New 4961 Medical Office Associate 04 445 6 mo.
MEDICAL OFFICE SERIES Occ. Work Prob. Effective Last Code No. Class Title Area Area Period Date Action 4960 Medical Office Assistant 04 445 6 mo. 07/15/12 New 4961 Medical Office Associate 04 445 6 mo.
How to Develop a Logic Model for Districtwide Family Engagement Strategies
 How to Develop a Logic Model for Districtwide Family Engagement Strategies Helen Westmoreland, Consultant M. Elena Lopez, Senior Consultant Heidi Rosenberg, Senior Research Analyst November, 2009 For questions
How to Develop a Logic Model for Districtwide Family Engagement Strategies Helen Westmoreland, Consultant M. Elena Lopez, Senior Consultant Heidi Rosenberg, Senior Research Analyst November, 2009 For questions
Practice Overview. REQUIREMENTS DEFINITION Issue Date: <mm/dd/yyyy> Revision Date: <mm/dd/yyyy>
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES ENTERPRISE PERFORMANCE LIFE CYCLE FRAMEWORK PRACTIICES GUIIDE REQUIREMENTS DEFINITION Issue Date: Revision Date: Document
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES ENTERPRISE PERFORMANCE LIFE CYCLE FRAMEWORK PRACTIICES GUIIDE REQUIREMENTS DEFINITION Issue Date: Revision Date: Document
How to make your business more flexible & cost effective? Remote Management & Monitoring Solutions for IT Providers
 How to make your business more flexible & cost effective? Remote Management & Monitoring Solutions for IT Providers contents 01 Current situation of the IT Channel 02 Market Trends 03 What would be the
How to make your business more flexible & cost effective? Remote Management & Monitoring Solutions for IT Providers contents 01 Current situation of the IT Channel 02 Market Trends 03 What would be the
Business Analyst Position Description
 Analyst Position Description September 4, 2015 Analysis Position Description September 4, 2015 Page i Table of Contents General Characteristics... 1 Career Path... 2 Explanation of Proficiency Level Definitions...
Analyst Position Description September 4, 2015 Analysis Position Description September 4, 2015 Page i Table of Contents General Characteristics... 1 Career Path... 2 Explanation of Proficiency Level Definitions...
Using Evaluation to Improve Programs. Strategic Planning. www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/evaluation
 Using Evaluation to Improve Programs Strategic Planning www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/evaluation PROGRAM STRATEGIC PLANNING KIT Table of Contents Introduction Part 1: What is strategic planning? Part 2: What
Using Evaluation to Improve Programs Strategic Planning www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/evaluation PROGRAM STRATEGIC PLANNING KIT Table of Contents Introduction Part 1: What is strategic planning? Part 2: What
PUBLIC RELEASE PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE. Inadequate Contractor Transition Risks Increased System Cost and Delays
 PUBLIC RELEASE PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE Inadequate Contractor Transition Risks Increased System Cost and Delays Inspection Report No. OSE-10084-8-0001 / December 1997 Office of Systems Evaluation PTO
PUBLIC RELEASE PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE Inadequate Contractor Transition Risks Increased System Cost and Delays Inspection Report No. OSE-10084-8-0001 / December 1997 Office of Systems Evaluation PTO
 Orange County Health Department STD Quality Improvement Project Storyboard (October 2005 July 2006) Table of Contents The Situation Step 1: Describe the Problem Step 2: Describe the Current Process Step
Orange County Health Department STD Quality Improvement Project Storyboard (October 2005 July 2006) Table of Contents The Situation Step 1: Describe the Problem Step 2: Describe the Current Process Step
15 Principles of Project Management Success
 15 Principles of Project Management Success Project management knowledge, tools and processes are not enough to make your project succeed. You need to get away from your desk and get your hands dirty.
15 Principles of Project Management Success Project management knowledge, tools and processes are not enough to make your project succeed. You need to get away from your desk and get your hands dirty.
Best Practices for Planning and Budgeting. A white paper prepared by PROPHIX Software October 2006
 A white paper prepared by PROPHIX Software October 2006 Executive Summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However,
A white paper prepared by PROPHIX Software October 2006 Executive Summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However,
Business Process Improvement Quick Guide
 Business Process Improvement Quick Guide A modern OPS delivers high-quality public services cost-effectively. To be a high performing organization we must continuously improve. On an ongoing basis, we
Business Process Improvement Quick Guide A modern OPS delivers high-quality public services cost-effectively. To be a high performing organization we must continuously improve. On an ongoing basis, we
An Innovative Approach to Close Cycle Reduction
 An Innovative Approach to Close Cycle Reduction As filing deadlines are accelerated and regulatory requirements become more stringent, companies are discovering that their financial close process does
An Innovative Approach to Close Cycle Reduction As filing deadlines are accelerated and regulatory requirements become more stringent, companies are discovering that their financial close process does
SysAidTM ITIL Package Guide. Change Management, Problem Management and CMDB
 SysAidTM ITIL Package Guide Change Management, Problem Management and CMDB Document Updated: 10 November 2009 Introduction 2 First Chapter: Change Management 5 Chapter 2: Problem Management 33 Chapter
SysAidTM ITIL Package Guide Change Management, Problem Management and CMDB Document Updated: 10 November 2009 Introduction 2 First Chapter: Change Management 5 Chapter 2: Problem Management 33 Chapter
Processing of Insurance Returns. An EMC Lean Six Sigma Project. Author: Aidan Trindle. Editor: Mohan Mahadevan
 Processing of Insurance Returns An EMC Lean Six Sigma Project Author: Aidan Trindle Editor: Mohan Mahadevan EMC Corporation is the world leader in systems, software, services, and solutions for building
Processing of Insurance Returns An EMC Lean Six Sigma Project Author: Aidan Trindle Editor: Mohan Mahadevan EMC Corporation is the world leader in systems, software, services, and solutions for building
Market Analysis Guide
 Market Analysis Guide Toll Free: 1.800.713.3558 Page 1 www.awebusiness.com Table of Contents Demonstration of Your Knowledge of the Industry...3 General Approaches to Market Research...4 Types of Market
Market Analysis Guide Toll Free: 1.800.713.3558 Page 1 www.awebusiness.com Table of Contents Demonstration of Your Knowledge of the Industry...3 General Approaches to Market Research...4 Types of Market
5 PLACES IN YOUR HOSPITAL WHERE ENTERPRISE CONTENT MANAGEMENT CAN HELP
 5 PLACES IN YOUR HOSPITAL WHERE ENTERPRISE CONTENT MANAGEMENT CAN HELP WHAT IS ECM AND WHY MIGHT YOU NEED IT? Although technology continues to improve how healthcare organizations share information both
5 PLACES IN YOUR HOSPITAL WHERE ENTERPRISE CONTENT MANAGEMENT CAN HELP WHAT IS ECM AND WHY MIGHT YOU NEED IT? Although technology continues to improve how healthcare organizations share information both
Best practices for planning and budgeting. A white paper prepared by Prophix
 A white paper prepared by Prophix Executive summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However, common budgeting limitations
A white paper prepared by Prophix Executive summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However, common budgeting limitations
State of Medical Device Development. 2014 State of Medical Device Development seapine.com 1
 State of Medical Device Development 2014 2014 State of Medical Device Development seapine.com 1 Executive Summary The demand for smarter, safer, more connected medical devices has introduced new complexities
State of Medical Device Development 2014 2014 State of Medical Device Development seapine.com 1 Executive Summary The demand for smarter, safer, more connected medical devices has introduced new complexities
WHITE PAPER CREATING A CUSTOMER-CENTRIC COMMUNICATIONS STRATEGY
 WHITE PAPER CREATING A CUSTOMER-CENTRIC COMMUNICATIONS STRATEGY CREATING A CUSTOMER-CENTRIC COMMUNICATIONS STRATEGY Executive Summary This white paper is designed to help you create a customer communications
WHITE PAPER CREATING A CUSTOMER-CENTRIC COMMUNICATIONS STRATEGY CREATING A CUSTOMER-CENTRIC COMMUNICATIONS STRATEGY Executive Summary This white paper is designed to help you create a customer communications
The following outlines an effective, proven process for assuring your practice makes the best, most well informed EHR system and vendor decision:
 Tips for Success Evaluating and Selecting an EHR System The number, variety and complexity of EHR systems in today s market has made the search for a system complex and sometimes intimidating for many
Tips for Success Evaluating and Selecting an EHR System The number, variety and complexity of EHR systems in today s market has made the search for a system complex and sometimes intimidating for many
AUDIT REPORT 03-11 WEB PORTAL SECURITY REVIEW. 2004 FEBRUARY R. D. MacLEAN CITY AUDITOR
 AUDIT REPORT 03-11 WEB PORTAL SECURITY REVIEW 2004 FEBRUARY R. D. MacLEAN CITY AUDITOR Web Portal Security Review Page 2 Audit Report 03-11 Web Portal Security Review INDEX SECTION I EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
AUDIT REPORT 03-11 WEB PORTAL SECURITY REVIEW 2004 FEBRUARY R. D. MacLEAN CITY AUDITOR Web Portal Security Review Page 2 Audit Report 03-11 Web Portal Security Review INDEX SECTION I EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Operationalizing Data Governance through Data Policy Management
 Operationalizing Data Governance through Data Policy Management Prepared for alido by: David Loshin nowledge Integrity, Inc. June, 2010 2010 nowledge Integrity, Inc. Page 1 Introduction The increasing
Operationalizing Data Governance through Data Policy Management Prepared for alido by: David Loshin nowledge Integrity, Inc. June, 2010 2010 nowledge Integrity, Inc. Page 1 Introduction The increasing
Keywords document, agile documentation, documentation, Techno functional expert, Team Collaboration, document selection;
 Volume 4, Issue 4, April 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Document Driven
Volume 4, Issue 4, April 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Document Driven
Guidelines for the Success of a Business Process Management Initiative
 Guidelines for the Success of a Business Process Management Initiative Insert Company Logo June 8 th 2012 Agenda Business Process Management Lifecycle Making change sustainable Business Process Governance
Guidelines for the Success of a Business Process Management Initiative Insert Company Logo June 8 th 2012 Agenda Business Process Management Lifecycle Making change sustainable Business Process Governance
Building the Business Case for BPM Automation in Process Manufacturing
 Building the Business Case for BPM Automation in Process Manufacturing Business process management automation streamlines your enterprise, strengthens your ERP solution and dramatically lowers costs. If
Building the Business Case for BPM Automation in Process Manufacturing Business process management automation streamlines your enterprise, strengthens your ERP solution and dramatically lowers costs. If
3-Step Competency Prioritization Sequence
 3-Step Competency Prioritization Sequence The Core Competencies for Public Health Professionals (Core Competencies), a consensus set of competencies developed by the Council on Linkages Between Academia
3-Step Competency Prioritization Sequence The Core Competencies for Public Health Professionals (Core Competencies), a consensus set of competencies developed by the Council on Linkages Between Academia
LECTURE 1. SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT
 LECTURE 1. SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT 1.1 INFORMATION SYSTEMS System A system is an interrelated set of business procedures used within one business unit working together for a purpose A system has nine characteristics
LECTURE 1. SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT 1.1 INFORMATION SYSTEMS System A system is an interrelated set of business procedures used within one business unit working together for a purpose A system has nine characteristics
Training for Public Health
 Business Common Process Ground: Analysis Training for Public Health Transforming Public Health Information Systems Instructor: Kathy Grantham, MDH Date 2011 Based on Common Ground: Transforming Public
Business Common Process Ground: Analysis Training for Public Health Transforming Public Health Information Systems Instructor: Kathy Grantham, MDH Date 2011 Based on Common Ground: Transforming Public
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PLAN Outline VERSION 0.0 STATUS: OUTLINE DATE:
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT PLAN Outline VERSION 0.0 STATUS: OUTLINE DATE: Project Name Project Management Plan Document Information Document Title Version Author Owner Project Management Plan Amendment History
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PLAN Outline VERSION 0.0 STATUS: OUTLINE DATE: Project Name Project Management Plan Document Information Document Title Version Author Owner Project Management Plan Amendment History
