Low dose rate brachytherapy for the treatment of prostate cancer
|
|
|
- Joan Clarke
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Low dose rate brachytherapy for the treatment of prostate cancer Information for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit
2 Low dose rate brachytherapy for the treatment of prostate cancer This information booklet has been written to give you information about low dose rate brachytherapy for prostate cancer. This booklet is intended as a guide to your treatment at this hospital. If you have any questions you may want to discuss them further with the urology/oncology nurse specialists who can be contacted on Monday-Friday 07:30-16:30. There is also an answer phone available. What is brachytherapy? Brachytherapy is the insertion of radioactive Iodine 125 (I125) seeds directly into the prostate gland. These seeds will slowly give off a low level of radiotherapy to the prostate over a period of 9 months. The procedure is normally carried out whilst you are anaesthetised as the seeds are inserted through the skin behind the scrotum and in front of the anus. This area is called the perineum. The seeds measure half a centimetre (5mm) in length and are half a millimetre (0.5mm) thick. They are held together by a strand which allows the seeds to be implanted easier. 2
3 The iodine seeds have a half life of 60 days which means that after 60 days half of the radioactivity will have left the seeds. After a further 60 days the remaining radioactivity will have halved again. This means there will be some radioactivity from the seeds for approximately 9 months in total. After this period of time the seeds are effectively inactive but remain permanently in the prostate gland. This should not cause you any problems. The seeds are implanted with a very high degree of accuracy using transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) guidance from a probe inserted in the rectum (back passage) to show images of the prostate gland on a television monitor. The doctors work as a team during the procedure. One doctor (the urologist) uses the ultrasound probe to image the prostate and one doctor (the oncologist) inserts the seeds into the prostate. By working together the doctors can identify where each seed has been placed within the prostate gland. 3
4 Are there any alternatives to brachytherapy? There are other treatment options available for your prostate cancer, which include: Active monitoring This option includes regular Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) blood tests, Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) and repeat prostate biopsies to monitor the activity of the prostate cancer. Laparoscopic/open radical retropubic prostatectomy This is the surgical removal of the prostate gland either via key hole surgery or a larger surgical incision to remove the prostate gland and the cancer in it. Radical external beam radiotherapy This option involves high energy X-rays being focused on the prostate gland to kill the prostate cancer cells within the prostate gland. It often follows a 3 month period of hormone therapy (see Hormone Therapy). There are information booklets on these treatment options available from your doctor, Clinical Nurse Specialist team and The Patrick Room on request. Who is brachytherapy suitable for? Like all treatments for prostate cancer the more information about you and your cancer we have the better advice we can give about the available treatments. The information we will need about your cancer is: Your PSA value Your cancer grade Your cancer stage Your cancer volume There is other information we need to know in addition to this, which includes: What is your urinary function like? 4
5 What is your general health like? Have you had any prostate surgery? How big is your prostate gland? These are explained in more detail below: Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) A patient with a PSA value of less than 10 ng/ml at diagnosis is ideal although a value of up to 20 ng/ml will be considered for brachytherapy. Grade Prostate cancer is graded by a histopathologist to assess how aggressively the cancer may behave. It is given a number measured on the Gleason Scale. The primary pattern of cancer cells and the secondary pattern of cancer cells are given a number between 1 (lowest grade) and 5 (highest grade). These grades are then added together to give the Gleason score which is measured between 2 (lowest score) and 10 (highest score). In practice, there are rarely scores of less than 6 when prostate biopsy specimens are assessed. Ideally the grade of the prostate cancer should be 7 or less for brachytherapy. Stage The stage of prostate cancer is an assessment of where the prostate cancer is. Some patients are not suitable for all potential treatments because there is evidence that the prostate cancer has spread (metastasised) to other areas of the body. Brachytherapy is only suitable for patients that have localised (organ confined) disease. To assess the stage of the cancer you will be given a digital rectal examination (DRE). To be suitable for the treatment the assessment of cancer should be T1 or T2 on DRE which means that the urologist can not feel any cancer within the prostate gland. Further assessment of the stage of the prostate cancer is done with an Magnetic Resonance Image scan (MRI) which will show the structure of the prostate gland, the areas of cancer within 5
6 it and if the capsule (edges) of the prostate gland is intact. This is important because prostate cancer that is bulging against or through the prostate capsule may not be effectively treated with the seeds. There is often a number of weeks wait for MRI scans but this is clinically acceptable for low risk prostate cancer. Your team will arrange for your scan to be done as soon as possible. Some patients will also require an Isotope Bone Scan to assess for potential prostate cancer spread to the bones. If you are unsure whether you need any of these scans please ask your doctor or your specialist nurse. Cancer volume The volume of prostate cancer within the prostate gland can be estimated by the histopathologist when the biopsy is analysed. Ideally patients should have an estimated small volume of prostate cancer although larger volumes can also be treated. Urinary function Patients that have a strong urinary flow and are able to empty their bladders well tend to recover better from the treatment rather than patients that have a poor urinary flow or other urinary symptoms. Other symptoms of poor urinary function include frequency (urinating often), urgency (urinating with little or no warning), nocturia (rising at night to urinate) and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. These symptoms will be assessed before you have brachytherapy. You will be expected to complete a short questionnaire about your symptoms and also urinate (at least 150mls) into a special machine (flow rate machine) that measures the strength of your urinary flow. You will then have an ultrasound scan of your bladder to assess how much urine is left behind in the bladder (post void residual) where ultrasound gel is put on your lower abdomen to assess how empty it is. Patients that have a strong urinary flow 6
7 (greater than 15mls/sec) and have a small post void residual (less than 100mls) are less likely to have urinary problems following brachytherapy. Some patients may be advised to take medication before their brachytherapy to improve the strength of their flow and the bladder s emptying capabilities (see alpha-blockers). In these instances, your General Practitioner (GP) will be informed. General health It is important to determine how fit patients are prior to having a general anaesthetic. Your doctor will ask you about any previous or current medical problems that you have. The doctor will want to know if you have any blood clotting disorders, any major operations, your current medications and any chronic disease such as diabetes or breathing problems. For patients whom it is considered unsafe to offer a general anaesthetic, a different treatment option such as external beam radiotherapy or active monitoring may be offered. Previous prostate surgery Patients that have had previous surgery to the prostate are usually offered a different treatment such as radical prostatectomy, external beam radiotherapy or active monitoring. When prostate tissue is removed during a Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) a cavity is made in the prostate which improves urinary symptoms. It also reduces the accuracy and certainty of placing the seeds during brachytherapy and there is a risk that not all of the prostate gland will be adequately treated with the appropriate radiotherapy dose. Prostate gland size Brachytherapy is only suitable for patients that have a prostate gland that is smaller than 50cc (cubic centimetres) when measured with a trans rectal ultrasound probe. This measurement is often routinely done at the same time that prostate biopsies are taken but patients that have a prostate 7
8 which appears large may require a repeat TRUS (transrectal ultrasound) measurement. Brachytherapy is unsuitable for patients with large prostates because a large prostate will be partially shielded by the pelvic bones. This means that access to the prostate is difficult. Patients that have a prostate gland measured greater than 50cc may be offered a 3-6 month period of hormone therapy (see hormone therapy) which may reduce the size of the prostate sufficiently enabling complete access to the whole of the gland. Once all of the pre-treatment information is available you will receive an appointment to see the oncology (cancer) doctors to discuss whether you are suitable for bracytherapy and a decision on your treatment will be made. A date for the brachytherapy will shortly follow for your admission to the hospital. The treatment Brachytherapy treatment can be carried out either as a one stage procedure or as a two stage procedure. The treatment is the same regardless of which method is offered. Brachytherapy is divided into two stages which can be done on two separate admissions to the hospital or in a single visit. Both the one stage and the two stage procedure will require bowel preparation (enema to clear the bowel) prior to a general anaesthetic. This allows accurate and clear pictures of the prostate to be taken. A catheter is inserted into your bladder through your urethra to help the urologist identify the structures around the prostate gland. The catheter is removed in the operating theatre before you are woken up. Stage one the volume study In order to make sure that the correct amount of seeds are implanted into the prostate gland and in the correct location, an accurate picture of the prostate gland is needed. This is done with a TRUS in the operating theatre whilst you are anaesthetised. The urologist is able to save pictures of the 8
9 shape and size of your prostate gland. These pictures are then converted to a three dimensional image. This image is then used by physicists (radiotherapy scientists), to plan the exact location of the seeds to ensure all of the prostate gland receives the appropriate radiation dose. Once the location of seeds is known the physicists can calculate how many seeds are needed for the implant stage. The volume study stage takes no longer than half an hour. Urethra Prostate Template Implant needle Bladder Rectum Ultrasound Probe Stage two the implant When the physicists have planned the location and amount of seeds required, the oncologist will then be able to start the implant stage. The seeds are loaded inside hollow needles which are then inserted through the skin in the perineum (the area between the testes and the anus). A metal grid attached to the operating table ensures that the needles are inserted into the correct area of the prostate gland. The urologist will use the TRUS to identify the prostate gland and the location of the needles within the prostate gland. This 9
10 teamwork ensures that the correct placement of the seeds is monitored for accuracy throughout the implant procedure. Most implants will use between 80 and 120 seeds (depending on the prostate size) using needles. The implant stage will take between one and a half hours and two hours to complete. An X-ray of the location of the seeds is also taken in the operating theatre to ensure the seeds are correctly positioned. The doctors will look at the X-ray to ensure this. An ice pack is placed over the area of the perineum where the seeds have been inserted. This will reduce the swelling and bruising. Your urine will be monitored for blood content after the implant stage and if there is very little or no blood present it will be removed prior to you being woken up. Sometimes there is blood present in your urine that requires a bladder washout. Warmed sterile water is inserted into your bladder through the catheter and then removed with a syringe until the blood is less obvious. When the doctors are sure the bleeding has reduced sufficiently the catheter is then removed in the operating theatre. For some patients with heavy bleeding the catheter will be removed a few hours later when they are awake and back on the ward. In most cases patients will be allowed home later on the same day when they have recovered from the anaesthetic or the following morning. You will not be able to drive for 24 hours 10
11 after the anaesthetic so alternative travel arrangements will be needed. After discharge you should avoid heavy lifting and rigorous exercise for 2-3 days. After this period normal activity can be resumed. Alpha-blockers Alpha-blockers is the name of a group of medicines that are useful for men with urinary problems. Alpha-blockers are tablets or capsules that are taken daily. They relax the smooth muscle in the urethra and increase the strength of urinary flow. Tamsulosin (Flomax, Flomaxtra) is commonly used in this hospital. These are taken daily (one dose per day). You will be discharged following your brachytherapy with a week s supply. You will need to take these for 3 months or longer until your symptoms settle. You will need to see your GP who will prescribe you a further supply of the tablets. Antibiotics You have a risk of developing a urinary infection after brachytherapy and to reduce this risk you will be discharged with a course of antibiotics. Ciprofloxacin is an antibiotic tablet that is taken twice daily. After the course of antibiotics has been completed there is no need to arrange a repeat prescription. You will be told if a longer course of antibiotics is required. Side effects There are a number of side effects from the brachytherapy which the doctors will explain to you prior to you having your treatment. Many of the side effects are related to urinary symptoms, that is why you undergo a thorough assessment before the procedure. The immediate side effects following brachytherapy can be: Soreness, bruising and discolouration to the perineal area 11
12 Blood in the urine and semen A burning sensation when urinating There are other side effects that may become more intense or apparent when the radiation reaction from the seeds begins. This is usually after 1 or 2 weeks following the procedure. The urethra becomes inflamed as a response to the radiation. These side effects are: Stinging and burning when urinating Increased frequency and urgency of urinating These symptoms can be mild for many patients but some patients may have more severe side effects. Some patients will need medication to help relieve their symptoms. Usually these side effects last for between 4 and 6 weeks. They will gradually reduce in severity over the following months. Other side effects of brachytherapy include: Poor urinary flow The prostate becomes swollen as a response to the implantation of the radioactive seeds that then causes a restriction. It is advised that you drink between 2 and 2.5 litres of clear fluids (combination of water and squashes) to relieve this side effect. Drinking plenty of fluid can also reduce the chances of developing a urine infection. After 2 weeks the amount of fluid can be reduced to 1.5 litres. Urgency and frequency of urination Caffeine rich drinks such as tea, coffee and cola can irritate the bladder and cause increased frequency and urgency in wanting to pass urine. Reducing the amount of these drinks or changing to decaffeinated tea and coffee may help. Urinary patterns will usually return to normal by 6 to 9 months following the brachytherapy. Urinary retention Some patients will have more severe side effects after treatment. 12
13 1 in 20 patients may be unable to empty their bladder satisfactorily after their treatment and require a catheter. The symptoms of this are a dull ache in the lower abdomen and a feeling of wanting to urinate but being unable to do so. If this happens you should either contact the nurse specialist (either at your local hospital or at the Queen Elizabeth) or attend your local accident and emergency department to be assessed by the doctors. A catheter will be inserted into your bladder through your penis to relieve the symptoms. This will need to stay in place for a few weeks until the prostate swelling reduces. It is unlikely that it will need to stay in longer than this. Bowels Immediately after brachytherapy some patients feel as though they are constipated. This is possibly due to the swelling of the prostate. A high fibre diet and increased fluid intake can reduce the feeling. Some patients may prefer medicines (Lactulose) to reduce the sensation and should be prescribed by the GP. Some patients may also have an increase in their bowel frequency and notice that it is a softer motion. This is usually temporary and can be managed with a lower fibre diet or Imodium. Blood from the rectum is noticed by a few patients and although it can be alarming it is usually for a short period and stops on its own. Severe cases may need additional medication such as steroid suppositories which can be prescribed from your GP. Erectile dysfunction As with most of the treatments for prostate cancer, brachytherapy has a risk of impotence (inability to achieve satisfactory erections). This can occur in approximately 1 in 4 men and is more common if there are already problems getting an erection before treatment. Older men (over 60) also may be at an increased risk of impotence. There are however medications that are available via your GP s for the treatment 13
14 of impotence. Tablets such as Viagra and Cialis may increase the quality of erections. The quantity of ejaculate (semen) may decrease following brachytherapy and the first few ejaculates may appear a different colour. This is caused by bleeding in the prostate gland. It will return to normal in a few weeks. Some patients experience a painful ejaculation after treatment but this also settles with time. Condoms are recommended for sexual intercourse for the first 2 or 3 ejaculations. Always ensure the used condom is double wrapped before being put in a dustbin. There are dedicated nurse-led clinics for patients that have erectile dysfunction. These are run in the urology department and referral to these clinics can be arranged by the consultants or the specialist nurse. Follow-up You will be reviewed six weeks following your brachytherapy procedure in the cancer centre clinic where the doctors can assess your side effects. A CT scan will be done between discharge from the ward and this clinic appointment (approximately 4 weeks). This scan is to check the location and quality of the implants. With this information the radiotherapy dose can be calculated. PSA blood tests are not routinely taken until 12 months following the implant. This is because the PSA is expected to be raised after the treatment. However if you are concerned about this you should discuss it with you doctor or nurse specialist. You will then be reviewed 6 months following your implant and then at 12 months. After this period of time follow up can be arranged at your local hospital. 14
15 Radiation safety information Brachytherapy seeds do not pose any risks to your family members or friends. Although the seeds are radioactive you are not. There are some precautions that we would recommend for piece of mind. For the first 2 months you should not sit close to children (under the age of puberty) for longer than a few minutes each day. There is no reason to avoid them completely and it is alright for them to have a brief hug or cuddle. There is no restriction to them staying in the same room as you. Contact with pregnant women should also be restricted to a few minutes a day. Contact with other adults need not be restricted. There are no restrictions to travel although the seeds may affect some security systems at airports, ferry ports and in shops. An information card will be issued explaining how treatment may affect these security systems (see information card). Condoms are recommended for sexual intercourse for the first 2 or 3 ejaculations (see Erectile dysfunction ). Information card An information card will be sent to you after your implantation which will need to be carried with you at all times for 3 years. The card will have information about the implant treatment and contact telephone numbers. It is important that your next of kin knows about the card, so that in the event of you becoming ill, they can tell other doctors about this treatment. It is important that other doctors are aware of the treatment as there is a radiation hazard to them for 3 years after the implant. In the event of death within 3 years of the implant a normal cremation is not allowed due to a radiation hazard. It is also important that hospital staff that carry out post-mortems and funeral directors are aware of the treatment. They will then be able to use the contact information on the card to telephone 15
16 the hospital for advice. Security systems at airports, ferry ports and in some shops may be sensitive to the very low dose of radiation from your implant. The card will instruct staff who they can contact if the security systems are affected. Hormone therapy Hormone therapy is commonly used in the treatment of prostate cancer. This information is about how it is used in this hospital with brachytherapy. Information about the use of hormone therapy (not in combination with brachytherapy) is available from the information room in the Cancer Centre (The Patrick Room). Hormone therapy is useful for reducing the size of the prostate gland. In this hospital 2 types of hormone therapy are used. Firstly, a 2 week supply of an anti-androgen tablet is prescribed and these tablets should be taken according to the dose and frequency on the prescription. Secondly, an LHRH analogue injection is prescribed and will be administered by the specialist nurse towards the end of the 2 week period. The appointment for this injection will be arranged by the specialist nurse. The specialist nurse will also explain the frequency and duration of the hormone therapy. Anti-androgens Anti-androgen tablets are taken for 2 weeks. They block the initial increase in testosterone levels when the LHRH analogue injection is administered. Reported side effects include: Commonly reported: Hot flushes Enlarged breast tissue Less commonly reported: Nausea Vomiting 16
17 Drowsiness Itching Dry skin Sensitive nipples Diarrhoea Abdominal pain Difficulty sleeping Sweating Most people do not have any problems when taking antiandrogens for a short period. Rare side effects include: liver damage (jaundice), chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, weight gain, shortness of breath, difficulty passing urine or back pain. Patients should consult the hospital if these occur. Anti-androgens are safe to be taken with most other medications. You should make sure the doctors are aware of all medications you take regularly. Anti-androgens are safe to be taken with alcohol but drowsiness may be more apparent. Further information about anti-androgens is available on request. LHRH analogues LHRH analogues are injections that are administered every 4 or 12 weeks. They are injected under the skin in the abdomen. It is given after a short period of an anti-androgen. LHRH analogues stop the production of testosterone which prostate cancer cells need to grow and it reduces the size of the prostate gland. Commonly reported side effects include: Hot flushes Reduction in sex drive (libido) Sweats Ability to get an erection Less common side effects include: Joint pain Changes in blood pressure Skin rashes Breast swelling and tenderness These are less common with a short duration of LHRH analogues. Further information about LHRH analogues is available on request. 17
18 Local sources of further information Good Hope Hospital Cancer Information Centre Good Hope Hospital Rectory Road Sutton Coldfield B75 7RR and ask for the cancer information centre. University Hospitals Birmingham (QE Hospital) The Patrick Room Cancer Centre QE Hospital Birmingham B15 2TH / Sandwell and West Birmingham Hospitals (Sandwell and City Hospital) The Courtyard Centre Sandwell General Hospital Lyndon West Bromwich B71 4HJ Walsall Primary Care Trust Cancer Information Service Challenge Building Hatherton Street Walsall
19 Prostate Cancer Support Groups Sutton Coldfield Prostate Support Group Meet at Good Hope Hospital 2.30pm last Wednesday of the month Joe Dyke Wolverhampton Prostate Cancer Support Group Clare Peterson Urology Outpatients New Cross Hospital Wolverhampton WV10 0ST Prostate Support Group, Sandwell Run by: Sharon Leahy (City)
20 General Support Services Cancer Support The White House 10 Ednam Road Dudley DY1 1JX Solihull Cancer Support Group Solihull Womens Institute 745 Warwick Road Solihull B91 3DG Bridges Support Group SGS House John s Lane Tividale Oldbury B69 3HX Prostate Cancer UK Cambridge House 100 Cambridge Grove London W6 0LE Prostate Cancer Support Association BM Box 9434 London WC1N 3XX
21 National Support Services Macmillan Cancer Support 89 Albert Embankment London SE1 7UQ (Monday-Friday 9am-8pm) The Prostate Cancer Centre Prostate Cancer Centre Stirling Road Guildford Surrey GU2 7RF Prostate Brachytherapy Advisory Group 21
22 The Trust provides free monthly health talks on a variety of medical conditions and treatments. For more information visit or call The Urology Department Queen Elizabeth Hospital Edgbaston, Birmingham, B15 2TH Specialist Nurse Office Telephone: PI12/0808/02 UHB/PI/0808 (Edition 2) Author: Richard Gledhill Date: January 2013 Review date: January 2015
Dynamic prostate brachytherapy
 Dynamic prostate brachytherapy a single visit treatment for prostate cancer This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having brachytherapy to treat your prostate cancer. It explains the benefits,
Dynamic prostate brachytherapy a single visit treatment for prostate cancer This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having brachytherapy to treat your prostate cancer. It explains the benefits,
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Short Course, Pre-operative Radiotherapy for Bowel Cancer
 Short Course, Pre-operative Radiotherapy for Bowel Cancer Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about short course, pre-operative radiotherapy for the treatment of bowel cancer. It explains
Short Course, Pre-operative Radiotherapy for Bowel Cancer Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about short course, pre-operative radiotherapy for the treatment of bowel cancer. It explains
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
Radioactive Seed Implants for Prostate Cancer information for patients and their families
 UROLOGICAL CANCER Radioactive Seed Implants for Prostate Cancer information for patients and their families The Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center 660 South Euclid Avenue, Box 8100 St. Louis, MO 63110-1093
UROLOGICAL CANCER Radioactive Seed Implants for Prostate Cancer information for patients and their families The Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center 660 South Euclid Avenue, Box 8100 St. Louis, MO 63110-1093
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet
 Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer using CyberKnife
 Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer using CyberKnife Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer using CyberKnife Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
University College Hospital. Prostate high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Prostate high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 18 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please
University College Hospital Prostate high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 18 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (T.U.R.B.T)
 Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (T.U.R.B.T) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to help you understand the surgery you are about to undergo. It will give you information
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (T.U.R.B.T) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to help you understand the surgery you are about to undergo. It will give you information
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment. Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Prostate Cancer. An overview of. Treatment. Prolapse. Information and Answers
 Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
Excision or Open Biopsy of a Breast Lump Your Operation Explained
 Excision or Open Biopsy of a Breast Lump Your Operation Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as excision or open biopsy of a breast lump. It explains
Excision or Open Biopsy of a Breast Lump Your Operation Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as excision or open biopsy of a breast lump. It explains
A start to help you understand prostate cancer
 A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
A Patient s Guide to Prostate Brachytherapy
 A Patient s Guide to Prostate Brachytherapy Professor Stephen Langley MS FRCS(Urol) Dr Robert Laing MRCP FRCR Mr John Davies BSc FRCS(Urol) Mr Christopher Eden MS FRCS(Urol) Prostate Cancer Centre, Guildford
A Patient s Guide to Prostate Brachytherapy Professor Stephen Langley MS FRCS(Urol) Dr Robert Laing MRCP FRCR Mr John Davies BSc FRCS(Urol) Mr Christopher Eden MS FRCS(Urol) Prostate Cancer Centre, Guildford
Prostate Brachytherapy Low dose rate permanent seed implant
 Prostate Brachytherapy Low dose rate permanent seed implant A guide for patients and their carers We care, we discover, we teach Contents Introduction.... 1 The prostate gland.... 2 Cancer of the prostate...
Prostate Brachytherapy Low dose rate permanent seed implant A guide for patients and their carers We care, we discover, we teach Contents Introduction.... 1 The prostate gland.... 2 Cancer of the prostate...
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
GreenLight laser prostatectomy
 Ambulatory Care & Local Networks GreenLight laser prostatectomy Information for day surgery patients This information sheet answers some of the questions you may have about having a GreenLight laser prostatectomy.
Ambulatory Care & Local Networks GreenLight laser prostatectomy Information for day surgery patients This information sheet answers some of the questions you may have about having a GreenLight laser prostatectomy.
Patient Information Sheet
 TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF PROSTATE (TURP) Patient Information Sheet Department of Urology Homerton University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Homerton Row, London, E9 6SR Reviewed: June 2012 Next date:
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF PROSTATE (TURP) Patient Information Sheet Department of Urology Homerton University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Homerton Row, London, E9 6SR Reviewed: June 2012 Next date:
Information for patients receiving short-term hormone treatment and radiotherapy for prostate cancer
 Information for patients receiving short-term hormone treatment and radiotherapy for prostate cancer Northern Centre for Cancer Care (NCCC) Freeman Hospital Introduction This leaflet has been written to
Information for patients receiving short-term hormone treatment and radiotherapy for prostate cancer Northern Centre for Cancer Care (NCCC) Freeman Hospital Introduction This leaflet has been written to
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
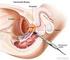 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer
 Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer Treatment Plan Stage of prostate cancer: RADIATION THERAPY Radiation Treatments: Date for planning CT: Date to start radiation
Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer Treatment Plan Stage of prostate cancer: RADIATION THERAPY Radiation Treatments: Date for planning CT: Date to start radiation
A Patient s Guide to TURP Your Prostate Operation
 A Patient s Guide to TURP Your Prostate Operation Mr John Davies BSc FRCS(Urol) Mr Christopher Eden MS FRCS(Urol) Mr Simon Bott FRCS Professor Stephen Langley MS FRCS(Urol) Prostate Cancer Centre, Guildford
A Patient s Guide to TURP Your Prostate Operation Mr John Davies BSc FRCS(Urol) Mr Christopher Eden MS FRCS(Urol) Mr Simon Bott FRCS Professor Stephen Langley MS FRCS(Urol) Prostate Cancer Centre, Guildford
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate)
 Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate) This leaflet is designed to answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate) This leaflet is designed to answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
PATIENT INFORMATION. Brachytherapy for Cancer of the Cervix
 PATIENT INFORMATION Brachytherapy for Cancer of the Cervix Cancer Therapy Centre Locked Mailbag 7103, Liverpool BC, NSW 1871 Telephone: 8738 5180 Facsimile: 8738 5188 August 2013 1. Introduction Radiotherapy
PATIENT INFORMATION Brachytherapy for Cancer of the Cervix Cancer Therapy Centre Locked Mailbag 7103, Liverpool BC, NSW 1871 Telephone: 8738 5180 Facsimile: 8738 5188 August 2013 1. Introduction Radiotherapy
What to Expect While Receiving Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 What to Expect While Receiving Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Princess Margaret Information for patients who are having radiation therapy Read this pamphlet to learn about: The main steps in planning
What to Expect While Receiving Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Princess Margaret Information for patients who are having radiation therapy Read this pamphlet to learn about: The main steps in planning
Your Treatment with Bacillus Calmette- Guérin (BCG)
 Your Treatment with Bacillus Calmette- Guérin (BCG) Patient Information Introduction Your consultant has prescribed BCG for the treatment of your bladder tumour. This booklet does not replace the discussion
Your Treatment with Bacillus Calmette- Guérin (BCG) Patient Information Introduction Your consultant has prescribed BCG for the treatment of your bladder tumour. This booklet does not replace the discussion
The following document includes information about:
 Patient information WHAT TO EXPECT WHILE RECEIVING RADIATION THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER Oncology Vitalité Zone : 1B 4 5 6 Facility : Dr. Léon-Richard Oncology Centre The following document includes information
Patient information WHAT TO EXPECT WHILE RECEIVING RADIATION THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER Oncology Vitalité Zone : 1B 4 5 6 Facility : Dr. Léon-Richard Oncology Centre The following document includes information
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Understanding Locally-Advanced Prostate Cancer
 Understanding Locally-Advanced Prostate Cancer This booklet is to help you and your family understand what it means if you have been diagnosed as having locally-advanced prostate cancer. It gives an outline
Understanding Locally-Advanced Prostate Cancer This booklet is to help you and your family understand what it means if you have been diagnosed as having locally-advanced prostate cancer. It gives an outline
Secondary liver cancer Patient Information Booklet
 Secondary liver cancer Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Secondary liver cancer Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
How to Improve Bladder After Bowler Cancer
 Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Radiotherapy for vulval cancer
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the vulva. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents External radiotherapy Internal
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the vulva. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents External radiotherapy Internal
Information for men considering a male sling procedure
 Information for men considering a male sling procedure Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Information for men considering a male sling procedure Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
The main surgical options for treating early stage cervical cancer are:
 INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
Treating Prostate Cancer
 Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer
 Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer SECTION 1: TREATMENTS This pamphlet provides information about different treatments for prostate cancer including what to expect and any risks and side-effects.
Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer SECTION 1: TREATMENTS This pamphlet provides information about different treatments for prostate cancer including what to expect and any risks and side-effects.
Understanding the PSA test. A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer
 Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Prostate Cancer Information and Facts
 Prostate Cancer Information and Facts Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnutsized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system.
Prostate Cancer Information and Facts Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnutsized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system.
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment
 A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men
 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you
 Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
University College Hospital. Hormone therapy for prostate cancer. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Hormone therapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 10 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please contact
University College Hospital Hormone therapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 10 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please contact
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Low Dose-Rate (LDR) Brachytherapy Procedure
 R.S. McLaughlin Durham Regional Cancer Centre 1 Hospital Court Oshawa, ONT L1G 2B9 905-576-8711, ext. 3856 www.lakeridgehealth.on.ca Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Low Dose-Rate (LDR) Brachytherapy
R.S. McLaughlin Durham Regional Cancer Centre 1 Hospital Court Oshawa, ONT L1G 2B9 905-576-8711, ext. 3856 www.lakeridgehealth.on.ca Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Low Dose-Rate (LDR) Brachytherapy
LIvING WITH Prostate Cancer
 Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Early Prostate Cancer
 Understanding Early Prostate Cancer Caring for people with cancer Understanding Early Prostate Cancer This booklet has been written to help you understand more about early prostate cancer. It has been
Understanding Early Prostate Cancer Caring for people with cancer Understanding Early Prostate Cancer This booklet has been written to help you understand more about early prostate cancer. It has been
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
 Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
Prostate Seed Implant (Brachytherapy) for Prostate Cancer
 www.cpmc.org/learning Prostate Seed Implant (Brachytherapy) for Prostate Cancer What is a Prostate Seed Implant (Brachytherapy)? Radiation therapy is a treatment for cancer that uses high-energy X-rays
www.cpmc.org/learning Prostate Seed Implant (Brachytherapy) for Prostate Cancer What is a Prostate Seed Implant (Brachytherapy)? Radiation therapy is a treatment for cancer that uses high-energy X-rays
External beam radiotherapy
 Treatment Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 External beam radiotherapy In this fact sheet: Who can have radiotherapy? How does radiotherapy treat prostate cancer? What are the advantages and
Treatment Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 External beam radiotherapy In this fact sheet: Who can have radiotherapy? How does radiotherapy treat prostate cancer? What are the advantages and
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology
 Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind
Prostate Cancer. Patient Information
 Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Insertion of a Central Catheter (Hickman/Groshong Catheter)
 Insertion of a Central Catheter (Hickman/Groshong Catheter) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to provide information to patients about to have a central catheter inserted in
Insertion of a Central Catheter (Hickman/Groshong Catheter) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to provide information to patients about to have a central catheter inserted in
Secondary Liver Cancer Information for patients with bowel cancer which has spread to the liver
 Secondary Liver Cancer Information for patients with bowel cancer which has spread to the liver Patient Information Introduction This booklet contains information about secondary liver cancer. It is written
Secondary Liver Cancer Information for patients with bowel cancer which has spread to the liver Patient Information Introduction This booklet contains information about secondary liver cancer. It is written
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
For further information on screening and early detection of prostate cancer, see the Section entitled Screening for Prostate Cancer.
 Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain
 Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. You will find it useful
Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain Temozolomide (oral) with concurrent radiotherapy to the brain This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. You will find it useful
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary
 X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Maintenance BCG for nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer
 Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Maintenance BCG for nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer This information sheet has been given to you to explain the use of maintenance
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Maintenance BCG for nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer This information sheet has been given to you to explain the use of maintenance
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder)
 Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Having a tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) operation for stress urinary incontinence
 Having a tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) operation for stress urinary incontinence This leaflet explains more about tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) including the benefits, risks and any alternatives, and
Having a tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) operation for stress urinary incontinence This leaflet explains more about tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) including the benefits, risks and any alternatives, and
Interstitial Breast Brachytherapy
 Patient Education Questions? Your questions are important. Call your doctor or health care provider if you have questions or concerns. UWMC clinic staff are also available to help at any time. During normal
Patient Education Questions? Your questions are important. Call your doctor or health care provider if you have questions or concerns. UWMC clinic staff are also available to help at any time. During normal
Looking after your urinary catheter at home
 Looking after your urinary catheter at home Information for patients and carers Useful contacts to keep: Name and title of community nurse Single point of access (SPA) for community nursing 24 hour service
Looking after your urinary catheter at home Information for patients and carers Useful contacts to keep: Name and title of community nurse Single point of access (SPA) for community nursing 24 hour service
BRACHYTHERAPY OR RADIOACTIVE SEED IMPLANTATION CANCER OF THE PROSTATE
 BRACHYTHERAPY OR RADIOACTIVE SEED IMPLANTATION CANCER OF THE PROSTATE Prostate cancer, like other cancers, is a disease of the body's cells. Normal cells reproduce themselves by dividing--facilitating
BRACHYTHERAPY OR RADIOACTIVE SEED IMPLANTATION CANCER OF THE PROSTATE Prostate cancer, like other cancers, is a disease of the body's cells. Normal cells reproduce themselves by dividing--facilitating
Surgery for Stress Incontinence
 Directorate of Women s Services Surgery for Stress Incontinence Tension Free Vaginal Tape Information for Patients Direct dial number Ward 40 0191 282 5640 Stress Incontinence Stress incontinence is a
Directorate of Women s Services Surgery for Stress Incontinence Tension Free Vaginal Tape Information for Patients Direct dial number Ward 40 0191 282 5640 Stress Incontinence Stress incontinence is a
Locally advanced prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? How is locally advanced prostate cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? How is locally advanced prostate cancer diagnosed?
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Male urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) you are not alone
 Male urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) you are not alone Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Male urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) you are not alone Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Advanced prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is advanced (metastatic) prostate cancer? What tests are used to diagnose advanced prostate cancer?
Diagnosis Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is advanced (metastatic) prostate cancer? What tests are used to diagnose advanced prostate cancer?
Radiation Management. Of Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Management Of Prostate Cancer An OvervieW Table of Contents THE PROSTATE GLAND....2 PROSTATE CANCER.... 2 PATIENT EVALUATION AND DIAGNOSTIC TESTING......3-5 MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE CANCER AN OVERVIEW
Radiation Management Of Prostate Cancer An OvervieW Table of Contents THE PROSTATE GLAND....2 PROSTATE CANCER.... 2 PATIENT EVALUATION AND DIAGNOSTIC TESTING......3-5 MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE CANCER AN OVERVIEW
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Sex, erectile dysfunction and prostate cancer
 Cancer Information Sheet Sex, erectile dysfunction and prostate cancer The information in this factsheet will help you understand more about erectile dysfunction (ED) and the sexual problems that can follow
Cancer Information Sheet Sex, erectile dysfunction and prostate cancer The information in this factsheet will help you understand more about erectile dysfunction (ED) and the sexual problems that can follow
Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer www.nshealth.ca Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer What is the prostate? The prostate is one of the male sex glands. It makes seminal fluid
Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer www.nshealth.ca Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer What is the prostate? The prostate is one of the male sex glands. It makes seminal fluid
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Localised prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF A BLADDER TUMOUR (TURBT) PATIENT INFORMATION
 TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF A BLADDER TUMOUR (TURBT) PATIENT INFORMATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed FEB 2005 Ubix code UPEB18 1 The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF A BLADDER TUMOUR (TURBT) PATIENT INFORMATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed FEB 2005 Ubix code UPEB18 1 The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you
Prostate Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
PROSTATE CANCER. Get the facts, know your options. Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology
 PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
Having a urinary catheter information for men
 Having a urinary catheter information for men This leaflet explains what a catheter is, why you need it and how you should look after it. If you have any further questions, please contact your district
Having a urinary catheter information for men This leaflet explains what a catheter is, why you need it and how you should look after it. If you have any further questions, please contact your district
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Treatment for bladder tumours - transurethral resection of a bladder tumour (TURBT)
 Treatment for bladder tumours - transurethral resection of a bladder tumour (TURBT) You have had a cystoscopy or other examination that has shown that you have an abnormal area (tumour) in your bladder.
Treatment for bladder tumours - transurethral resection of a bladder tumour (TURBT) You have had a cystoscopy or other examination that has shown that you have an abnormal area (tumour) in your bladder.
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant
 Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
Understanding brachytherapy
 Understanding brachytherapy Brachytherapy Cancer Treatment Legacy Cancer Institute Your health care provider has requested that you receive a type of radiation treatment called brachytherapy as part of
Understanding brachytherapy Brachytherapy Cancer Treatment Legacy Cancer Institute Your health care provider has requested that you receive a type of radiation treatment called brachytherapy as part of
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Radioactive Iodine Therapy Your Treatment Explained
 Radioactive Iodine Therapy Your Treatment Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the treatment known as radioactive iodine therapy. It explains what is involved and some
Radioactive Iodine Therapy Your Treatment Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the treatment known as radioactive iodine therapy. It explains what is involved and some
Why is radiation therapy used to treat prostate cancer? Is there anything that I have to do before my treatment planning appointment?
 2015 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External Beam Treatment for Prostate Cancer Why is radiation therapy used to treat prostate cancer? Prostate cancer may be treated with a combination
2015 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External Beam Treatment for Prostate Cancer Why is radiation therapy used to treat prostate cancer? Prostate cancer may be treated with a combination
The PSA Test for Prostate Cancer Screening:
 For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
University College Hospital. Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
GreenLight Laser Therapy for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
 GreenLight Laser Therapy for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) To learn about this procedure it helps to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm
GreenLight Laser Therapy for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) To learn about this procedure it helps to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm
