Injury Biomechanics of the Cervical Spine in Car Collisions - Some needs for further research
|
|
|
- Brent McKinney
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Injury Biomechanics of the Cervical Spine in Car Collisions - Some needs for further research Mats Y. Svensson Crash Safety Division, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden Background The incidence of soft tissue neck injuries in car collisions has been on the increase during the last two decades and these injuries cause enormous costs to the society and the insurance business today. This is the reason behind the intensified research efforts and the great number of important publications in this field in recent years. Youganandan and Pintar (2000a) present a condensed overview of the latest development in the field. Accident data have been collected in a number of studies and we are beginning to get a clearer view of the injury incidence as a function of various parameters. The injury risk appears to be the greatest in rear-end collisions but frontal collisions as well as side collisions stand for a significant portion of these injuries (Krafft, 2000; Temming and Zobel, 1998; Jakobsson et al., 2000b). The neck injury symptoms appear to be very similar for all impact directions (Minton et al., 2000). The injury risk differs between seating positions. In rear-end collisions the rear seat generally is safer (Lövsund et al., 1988; Jakobsson et al., 2000a). The risk of initial neck symptoms increases with velocity change (delta-v) but among those initially injured the acceleration pulse appears to be more important than the delta-v as a predictor of risk of long term consequences (Krafft, 2000; Kullgren et al., 2000). The neck injury risk differs significantly between different car models of similar size in rear impacts (Krafft, 2000). Taller drivers have an increased injury risk in rear impacts (Jakobsson, 2000) and the injury risk increases if the vehicle occupant is unaware of the impending accident (Ryan et al., 1994). A number of experimental studies on volunteers and post mortem human subjects have been reported. There is a relatively good view of the overall body kinematics in different crash directions. The typical neck loading in a car accident is caused by the acceleration of the torso resulting in a neck bending motion illustrated in Figure 1. The thoracic spine normally undergoes some type of bending motion in this type of event. In rear end collisions the thoracic kyphosis is straightened resulting in an elevation and a rearward tilt of the T1 vertebra (Davidsson et al., 1998; van den Kroonenberg, 1998; Ono et al., 2000). Several studies have focused also on the detailed motion of the cervical spinal segments during rear-end impact loading (Ono et al., 1997; Panjabi et al., 1999; Winkelstein et al., 1999; Youganandan and Pintar, 2000b; Deng et al., 2000). The intervertebral motion appears to deviate from normal physiologic human neck bending motion. Two new crash dummy prototypes for rear-end collision testing have been presented, BioRID (Davidsson, 1999; Davidsson, 2000; Davidsson et al., 1999) and RID2 (Cappon et al., 2000). The dummies enable more detailed assessment of the human body kinematics in rear end impacts. This will for instance improve the prediction of the contact conditions between the head and the head-restraint. In the future, with this type of dummy and with appropriate dummy instrumentation, it will hopefully be possible to measure injury criteria that correlate to neck injury risk. Soft tissue injuries have been found in several different structures and locations in the neck region in experimental studies and autopsy studies. In a recent study Yoganandan et al. (2000) reported injuries to several ligaments, the intervertebral discs and the facet joint structures. Siegmund and Brault (2000) and Brault et al. (2000) presented indications of muscle injury due to eccentric muscle loading in the early phase of the neck motion in rear impacts. Taylor et al. (1998) reported interstitial haemorrhage in cervical dorsal root ganglia in an autopsy study of victims who had sustained severe inertial neck loading during impacts to the torso or to the head. The structures around the ganglia were mostly uninjured. These findings correlate to experimental findings in pigs of nerve cell membrane dysfunction in cervical spinal root ganglia reported by Svensson et al. (2000).
2 Phase 1 Phase 2 a) b) c) Figure 1a: Schematic drawing of the head-neck motion during a frontal collision. Phase 1: Protraction motion Phase 2: Flexion motion Phase 1 Phase 2 a) b) c) Figure 1b: Schematic drawing of the head-neck motion during a rear-end collision. Phase 1: Retraction motion Phase 2: Extension motion Several neck injury mechanisms and neck injury criteria have been proposed during recent years. Two criteria, Nij (Kleinberger et al., 1998) and Nkm (Muser et al., 2000), use combinations of neck loads to predict the risk of injury to the skeletal spine. The IV-NIC (Panjabi et al., 1999) uses the angular displacement between adjacent vertebrae to estimate the risk of injury to various structures of the intervertebral joints. The correlation between these three injury criteria and the risk of long term soft tissue neck injury has not (to the author's knowledge) yet been established. The Neck Injury Criterion (NIC) (Boström et al., 2000) uses differential horizontal acceleration between the head and the T1 vertebra to assess the neck injury risk. The NIC was initially based on experimental injury findings summarised by Svensson et al. (2000). NIC would also function as a predictor of other types of injury mechanisms and indications of correlation between NIC and long term neck injury risk have been presented (Boström et al., 2000). The injury symptoms have been described in a large number of papers (e.g. Sturzenegger et al., 1995; Spitzer et al., 1995). It is important to distinguish between initial symptoms and long term symptoms (Krafft, 2000). Long term (chronic) whiplash symptoms appear to be associated with central pain sensitisation (Sheather-Reid and Cohen, 1998; Johansen et al., 1999). The exact origin of this pain sensitisation has not been established. Successful treatment methods could possibly provide a clue. Byrn et al. (1993) reported significantly reduced symptoms during a time period after sub-cutanious sterile water injections on the back of the neck. Bogduk (2000) reported pain relief in about 50 percent of the patients after coagulation of the small nerves that innervate the facet joint that is associated with the painful dermatome.
3 Synthesis It appears likely that several types of neck injury may appear as a result of a whiplash trauma (muscles, ligaments, facet joint, discs, nerve tissue etc.). Several injury types may be present in the same patient at the same time. The relation between these possible injuries and the large set of known whiplash symptoms (neck pain, head ache, shoulder pain, neurological symptoms etc.) is unclear. It would be of particular interest to know which one (ones) of these injuries that would result in long term symptoms and central pain sensitisation. It would then also be of interest to know which injury mechanism is responsible for this particular injury. At the initial symptom stage, arm pain and high symptom intensity seem to correlate to an increased risk of long term consequences (Sturzenegger, 1995; Karlsson et al., 2000). The apparent influence of the crash pulse on the risk of long term consequences in patients with initial symptoms (Krafft, 2000) indicate that there could be a separate injury and a separate injury mechanism behind the long term symptoms. This particular injury could in the acute stage often co-exist with other injuries that normally heal without causing residual pain. Sturzenegger et al. (1995) found a higher risk of long term symptoms in those patients that were injured in a rear end collision and this may indicate that one particular injury (which may cause long term symptoms) is more likely to occur in a rear impact. In more peripheral parts of the body most of these injury types (tissue types) normally recover without long term pain and central pain sensitisation. Is there something special about the neck region that makes one or several of these injuries result in long term pain? Cavanaugh (2000) for instance, explained that the facet joint capsules are particularly rich in nerve endings why an injury at this point would be a likely reason for long lasting pain. This pain may cause referred pain in e.g. the shoulder region. Facet joint capsule strain and pinching has been shown in post mortem human subjects in rear impact testing (Yoganandan and Pintar, 2000b; Deng et al., 2000). It is however not known whether the same type of mechanisms may occur also in side impacts and frontal impacts. Is there some type of structure that is unique for the neck? The spinal nerve root ganglia would be an example of such a structure. Cavanaugh (2000) explained that injury to the dorsal root ganglia is likely to cause radiating pain to dermatomes of for instance the shoulders and the arms. These symptoms are, as mentioned earlier, known to correlate to increased risk of long term consequences. Cervical dorsal root ganglion injuries have been observed in various impact directions (Svensson et al., 2000, Taylor et al., 1998) and would explain the similarity in symptoms between different impact directions. It can be concluded that we have a lot of exciting research work ahead of us before we get a complete understanding of the whiplash problem. But once we have this understanding, we will have a much better chance of developing accurate diagnosis methods, effective treatment and good preventive measures in vehicles. References Bogduk, N. (2000): An overview of Whiplash. In: Eds. Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A.: Frontiers in Whiplash Trauma. IOS Press, The Netherlands, ISBN , pp. 3-9 Boström, O.; Håland, Y.; Lövsund L.; Svenssom, M.Y. (2000): Neck Injury Criterion (NIC) and its Relevance to Various Possible Neck Injury Mechanisms. In: Eds. Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A.: Frontiers in Whiplash Trauma. IOS Press, The Netherlands, ISBN Brault, J.R.; Siegmund, G.P.; Wheeler, J.B. (2000): Cervical muscle response during whiplash: evidence of a lengthening muscle contraction. Clinical Biomechanics 15 (2000) Byrn C, Olsson I, Falkheden L, Lindh M, Hosterey U, Fogelberg M, Linder LE, Bunketorp (1993): Subcutaneous sterile water injections for chronic neck and shoulder pain following whiplash injuries. Lancet Feb 20;341(8843): Cappon, H.J.; Philippens, M.M.G.R.; van Ratingen, M.R; Wismans, J.S.H.M. (2000): Evaluation of Dummy Behaviour During Low Severeity Rear Impact. Proc. IRCOBI Conf. Montpellier, France, September 20-22, pp
4 Cavanaugh, J.M. (2000): Neurophysiology and Neuroanatomy of Neck Pain. In: Eds. Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A.: Frontiers in Whiplash Trauma. IOS Press, The Netherlands, ISBN , pp Davidsson, J. (1999): BioRID II final report. Crash Safety Division, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden, Report Davidsson, J.; Deutscher, Hell, W.; Linder, A.; Lövsund, P.; Svensson, M.Y. (1998) Human Volunteer Kinematics in Rear-end Sled Collisions. SAE paper no , Proc. Int. IRCOBI Conf., pp Davidsson, J.; Lövsund, P.; Ono, K.; Svensson, M.Y.; Inami, S. (1999): A comparison between volunteer, BioRID P3 and Hybrid III performance in rear impacts International IRCOBI Conference on the Biomechanics of Impact, Barcelona, Spain, SAE paper no (Crash Prevention and Injury Control, accepted) Davidsson, J. (2000): Development of a Mechanical Model for Rear Impacts: Evaluation of Volunteer Responses and Validation of the Model. Dissertation, Crash Safety Division, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden, ISBN Deng, B.; Begeman, P.C.; Yang, K.H.; Tashman, S.; King, A.I. (2000): Kinematics of Human Cadaver Cervical Spine During Low Speed Rear-End Impacts. STAPP Car Crash Journal, Vol. 44, pp Jakobsson, L. (2000): AIS 1 neck injuries in rear-end car impacts, Biomechanical guidelines and evaluation criteria based on accident data and parameter studies. Licentiate Thesis, Crash Safety Division, Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, Jakobsson, L.; Lundell, B.; Norin, H.; Isaksson-Hellman, I. (2000a): WHIPS - Volvo's whiplash protection study. Accident Analysis and Prevention, Vol. 32, pp Jakobsson, L.; Norin, H.; Isaksson-Hellman, I. (2000b) Parameters Influencing the Risk of AIS1 Neck Injuries in Frontal and Side Impacts. Proc. IRCOBI Conf. Montpellier, France, September 20-22, pp Johansen, M.K.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Olesen, A.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. (1999): Generalised muscular hyperalgesia in chronic whiplash syndrome. Pain 83 (1999) Karlsson, E-L.; Falkheden-Henning, L.; Olsson, I.; Bunketorp, O. (2000): Clinical findings at a primary examination by physiotherapist and the outcome one year after neck sprain in traffic accidents. J Traffic Medicine (2000) Vol. 28, No 2S, p. 47 Kleinberger, M.; Sun, E.; Eppinger, R.; Kuppa, S.; Saul, R. (1998): Development of Improved Injury Criteria for the Assessment of Advanced Automotive Restraint Systems, NHTSA Docket , US Dept. of Transportation, Washington DC Krafft M. (2000): Influence of velocity change and car acceleration on short- and long-term disability risk in rear impact. In: Eds. Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A.: Frontiers in Whiplash Trauma. IOS Press, The Netherlands, ISBN , pp van den Kroonenberg, A.; Philippens, M.; Cappon, H; Wismans, J.; Hell, W.; Langwieder, K. (1998): Human head-neck response during low-speed rear end impacts. SAE paper no , 42nd Annual Stapp Car Crash Conference, Tempe, Arizona, USA Kullgren, A.; Maria Krafft M.; Nygren, A.; Tingvall, C (2000): Neck injuries in frontal impacts: influence of crash pulse characteristics on injury risk. Accident Analysis and Prevention 32 (2000) Lövsund, P.; Nygren, Å.; Salen, B.; Tingvall, C. (1988): Neck Injuries in Rear End Collisions among Front and Rear Seat Occupants. Proc. Int. IRCOBI Conference Biomech. of Impacts, Bergisch- Gladbach, F.R.G., pp Minton, R.; Murray, P.; Stephenson, W.; Galasko C.S.B. (2000) Whiplash injury are current head restraints doing their job?. Accident Analysis and Prevention 32 (2000) Muser, M.; Walz, F.; Zellmer, H. (2000): Biomechanical significance of the rebound phase in low speed rear end impacts International IRCOBI Conference on the Biomechanics of Impact, Montpellier, France, pp
5 Ono, K.; Kaneoka, K.; Wittek, A.; Kajzer, J. (1997): Cervical injury mechanism based on the analysis of human cervical vertebral motion and head-neck-torso kinematics during low-speed rear impacts. 41st Annual Stapp Car Crash Conference, Florida, USA, SAE paper no Ono, K.; Kaneoka, K., Inami, S. (2000): Analysis of Seat Properties on Human Cervical Vertebral Motion in Low-Speed Rear-End Impacts. In: Eds. Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A.: Frontiers in Whiplash Trauma. IOS Press, The Netherlands, ISBN Panjabi, M.M.; Wang, J.L.; Delson, N. (1999): Neck injury criterion based on intervertebral motions and its evaluation using an instrumented neck dummy International IRCOBI Conference on the Biomechanics of Impact, Barcelona, Spain, SAE paper no: Ryan GA, Taylor GW, Moore VM, Dolinis J. (1994): Neck strain in car occupants: injury status after 6 months and crash-related factors. Injury 1994, 25(8): Sheather-Reid, R.B.; Cohen, M.L. (1998): Psychophysical evidence for a neuropathic component of chronic neck pain. Pain 75(1998) Siegmund, G.P.; Brault, J.R. (2000): Role of Cervical Muscles During Whiplash. In: Eds. Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A.: Frontiers in Whiplash Trauma. IOS Press, The Netherlands, ISBN Spitzer, W.O.; Skovron, M.L.; Salmi, L.R. et al. (1995): Scientific Monograph of the Quebec Task Force on Whiplash-Associated Disorders: Redefining "Whiplash" and Its Management. Spine, Supplement 20 Sturzenegger, M.; Radanov, P.B.; Di Stefano, G. (1995): The effect of accident mechanisms and initial findings on the long term course of whiplash. J. Neurol (1995) 242: Svensson, M.Y.; Boström, O.; Davidsson, J.; Hansson, H.-A.; Håland, Y.; Lövsund, p.; Suneson, A.; Säljö, A. (2000): NECK INJURIES IN CAR COLLISIONS - A REVIEW COVERING A POSSIBLE INJURY MECHANISM AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW REAR-IMPACT DUMMY. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 32 (2000) Taylor, J.R.; Twomey, L.T.; Kakulas, B.A. (1998): Dorsal root ganglion injuries in 109 blunt trauma fatalities. Injury, vol. 29, No. 5; pp Temming, J.; Zobel, R. (1998) Frequency and Risk of Cervical Spine Distortion Injuries in Passenger Car Accidents: Significance of Human Factors Data. Int. IRCOBI Conf., pp Winkelstein, B.A.; Nightingale, R.W.; Richardson, W.J.; Myers, B.S. (1999): Cervical facet joint mechanics: Its application to whiplash injury. 43rd Stapp Car Crash Conference, California, USA, SAE Paper no. 99SC15 Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A. (2000a): Frontiers in Whiplash Trauma. IOS Press, The Netherlands, ISBN Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A. (2000b): Mechanics of Head Ache and Neck Pain in Whiplash. In: Eds. Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A.: Frontiers in Whiplash Trauma. IOS Press, The Netherlands, ISBN , pp Yoganandan, N; Pintar, F.A.; Stemper, B.D.; Schlick, M.B.; Philippens,M.; Wismans, J. (2000): Biomechanics of Human Occupants in Simulated Rear Crashes: Documentation of Neck injuries and Comparison of Injury Criteria. STAPP Car Crash Journal, Vol. 44, pp
Neck injuries in car collisions - Injury mechanisms
 Injuries and symptoms Neck injuries in car collisions - Injury mechanisms Mats Svensson Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden The symptoms of injury following neck trauma in rear-end collisions
Injuries and symptoms Neck injuries in car collisions - Injury mechanisms Mats Svensson Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden The symptoms of injury following neck trauma in rear-end collisions
INFLUENCE OF CRASH SEVERITY ON VARIOUS WHIPLASH INJURY SYMPTOMS: A STUDY BASED ON REAL-LIFE REAR-END CRASHES WITH RECORDED CRASH PULSES
 INFLUENCE OF CRASH SEVERITY ON VARIOUS WHIPLASH INJURY SYMPTOMS: A STUDY BASED ON REAL-LIFE REAR-END CRASHES WITH RECORDED CRASH PULSES Maria Krafft*, Anders Kullgren*, Sigrun Malm**, Anders Ydenius* *Folksam
INFLUENCE OF CRASH SEVERITY ON VARIOUS WHIPLASH INJURY SYMPTOMS: A STUDY BASED ON REAL-LIFE REAR-END CRASHES WITH RECORDED CRASH PULSES Maria Krafft*, Anders Kullgren*, Sigrun Malm**, Anders Ydenius* *Folksam
Biomechanics of the Neck in Rear Impacts for improved Seat Design
 Biomechanics of the Neck in Rear Impacts for improved Seat Design Dr.-Ing. Tjark Kreuzinger Regulatory & Technical Affairs Toyota Motor Europe NV/SA Studiedag BEPALING VAN MENSELIJKE SCHADE DOOR SLINGERLETSELS
Biomechanics of the Neck in Rear Impacts for improved Seat Design Dr.-Ing. Tjark Kreuzinger Regulatory & Technical Affairs Toyota Motor Europe NV/SA Studiedag BEPALING VAN MENSELIJKE SCHADE DOOR SLINGERLETSELS
WHIPLASH INJURIES, NOT ONLY A PROBLEM IN REAR-END IMPACT
 WHIPLASH INJURIES, NOT ONLY A PROBLEM IN REAR-END IMPACT Hans Cappon Michiel van Ratingen Jac Wismans TNO Automotive The Netherlands Wolf Hell and Dina Lang German Institute for Vehicle Safety (GDV) Germany
WHIPLASH INJURIES, NOT ONLY A PROBLEM IN REAR-END IMPACT Hans Cappon Michiel van Ratingen Jac Wismans TNO Automotive The Netherlands Wolf Hell and Dina Lang German Institute for Vehicle Safety (GDV) Germany
A NEW TEST METHOD FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF NECK INJURIES IN REAR-END COLLISIONS
 A NEW TEST METHOD FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF NECK INJURIES IN REAR-END COLLISIONS Hans Cappon, Mat Philippens, Jac Wismans TNO Automotive The Netherlands Paper # 242 ABSTRACT Whiplash injuries due to rear-end
A NEW TEST METHOD FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF NECK INJURIES IN REAR-END COLLISIONS Hans Cappon, Mat Philippens, Jac Wismans TNO Automotive The Netherlands Paper # 242 ABSTRACT Whiplash injuries due to rear-end
A multi-body head and neck model for low speed rear impact analysis
 12th IFToMM World Congress, Besançon (France), June18-21, 27 A multi-body head and neck model for low speed rear impact analysis S. Himmetoglu *, M. Acar, A.J. Taylor, K. Bouazza-Marouf Mechanical and
12th IFToMM World Congress, Besançon (France), June18-21, 27 A multi-body head and neck model for low speed rear impact analysis S. Himmetoglu *, M. Acar, A.J. Taylor, K. Bouazza-Marouf Mechanical and
A NEW NECK INJURY CRITERION CANDIDATE FOR REAR-END COLLISIONS TAKING INTO ACCOUNT SHEAR FORCES AND BENDING MOMENTS
 A NEW NECK INJURY CRITERION CANDIDATE FOR REAR-END COLLISIONS TAKING INTO ACCOUNT SHEAR FORCES AND BENDING MOMENTS K.-U. Schmitt 1,2, M. H. Muser 2 and P. Niederer 1 1 Institute of Biomedical Engineering,
A NEW NECK INJURY CRITERION CANDIDATE FOR REAR-END COLLISIONS TAKING INTO ACCOUNT SHEAR FORCES AND BENDING MOMENTS K.-U. Schmitt 1,2, M. H. Muser 2 and P. Niederer 1 1 Institute of Biomedical Engineering,
Assessing the Female Neck Injury Risk
 Content 1 Assessing the Female Neck Injury Risk 3 Thesis About why Females are at Greater Risk of Sustaining Whiplash Injuries Assessing the Female Neck Injury Risk 4 High Speed X-Ray Motion Analysis of
Content 1 Assessing the Female Neck Injury Risk 3 Thesis About why Females are at Greater Risk of Sustaining Whiplash Injuries Assessing the Female Neck Injury Risk 4 High Speed X-Ray Motion Analysis of
Euro NCAP Whiplash Rating - Toyota Position & Proposal. May 2011
 Euro NCAP Whiplash Rating - Toyota Position & Proposal May 2011 1 Content Background and Priority J-NCAP Extended Review Overall Conclusion 2 Schedule 2011 February June 7 14 21 28 Folksam Chalmers TNO
Euro NCAP Whiplash Rating - Toyota Position & Proposal May 2011 1 Content Background and Priority J-NCAP Extended Review Overall Conclusion 2 Schedule 2011 February June 7 14 21 28 Folksam Chalmers TNO
Biomechanics of Neck Injuries Resulting from Rear-End Vehicle Collisions
 Received: 09.09.2013 / Accepted: 27.11.2013 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.9218-13.1 Review Biomechanics of Neck Injuries Resulting from Rear-End Vehicle Collisions Otomobil Kazalarında Boyun Yaralanmaları
Received: 09.09.2013 / Accepted: 27.11.2013 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.9218-13.1 Review Biomechanics of Neck Injuries Resulting from Rear-End Vehicle Collisions Otomobil Kazalarında Boyun Yaralanmaları
Necessary Components of Whiplash Injuries
 A STUDY OF CURRENT NECK INJURY CRITERIA USED FOR WHIPLASH ANALYSIS. PROPOSAL OF A NEW CRITERION INVOLVING UPPER AND LOWER NECK LOAD CELLS. D. Muñoz 1, A. Mansilla 1,2, F. López-Valdés 1,2. R. Martín 1
A STUDY OF CURRENT NECK INJURY CRITERIA USED FOR WHIPLASH ANALYSIS. PROPOSAL OF A NEW CRITERION INVOLVING UPPER AND LOWER NECK LOAD CELLS. D. Muñoz 1, A. Mansilla 1,2, F. López-Valdés 1,2. R. Martín 1
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 AN EVALUATION OF EXISTING AND PROPOSED INJURY CRITERIA WITH VARIOUS DUMMIES TO DETERMINE THEIR ABILITY TO PREDICT THE LEVELS OF SOFT TISSUE NECK INJURY SEEN IN REAL WORLD ACCIDENTS Frank Heitplatz Raimondo
AN EVALUATION OF EXISTING AND PROPOSED INJURY CRITERIA WITH VARIOUS DUMMIES TO DETERMINE THEIR ABILITY TO PREDICT THE LEVELS OF SOFT TISSUE NECK INJURY SEEN IN REAL WORLD ACCIDENTS Frank Heitplatz Raimondo
ABSTRACT INJURY CRITERION TO ASSESS WHIPLASH INJURY IN FMVSS NO. 202 DYNAMIC TEST OPTION
 KINEMATICALLY BASED WHIPLASH INJURY CRITERION Shashi Kuppa, James Saunders, Jason Stammen National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Ann Mallory Transportation Research Center Inc. U.S.A 05-0211 ABSTRACT
KINEMATICALLY BASED WHIPLASH INJURY CRITERION Shashi Kuppa, James Saunders, Jason Stammen National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Ann Mallory Transportation Research Center Inc. U.S.A 05-0211 ABSTRACT
ENHANCEMENT OF SEAT PERFORMANCE IN LOW-SPEED REAR IMPACT
 ENHANCEMENT OF SEAT PERFORMANCE IN LOW-SPEED REAR IMPACT Harald Zellmer Michael Stamm Alexander Seidenschwang Autoliv GmbH, Elmshorn, Germany Anton Brunner Winterthur Insurance Corp., Dep. of Accident
ENHANCEMENT OF SEAT PERFORMANCE IN LOW-SPEED REAR IMPACT Harald Zellmer Michael Stamm Alexander Seidenschwang Autoliv GmbH, Elmshorn, Germany Anton Brunner Winterthur Insurance Corp., Dep. of Accident
How To Understand The Injury From A Whiplash
 Chinese Journal of Traumatology 2009; 12(5):305-314. 305. Review Biomechanics of whiplash injury CHEN Hai-bin 陈 海 斌 *, King H YANG and WANG Zheng-guo 王 正 国 Despite a large number of rear-end collisions
Chinese Journal of Traumatology 2009; 12(5):305-314. 305. Review Biomechanics of whiplash injury CHEN Hai-bin 陈 海 斌 *, King H YANG and WANG Zheng-guo 王 正 国 Despite a large number of rear-end collisions
Whiplash Testing and Assessment Summary of Current Activities in Europe
 136 B. Lorenz Federal Highway Research Institute (BASt), Passive Safety & Biomechanics, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany R. Sferco Ford Motor Company, Vehicle Safety, Automotive Safety Office (ASO), Köln, Germany
136 B. Lorenz Federal Highway Research Institute (BASt), Passive Safety & Biomechanics, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany R. Sferco Ford Motor Company, Vehicle Safety, Automotive Safety Office (ASO), Köln, Germany
NECK INJURIES IN CAR COLLISIONS - A REVIEW COVERING A POSSIBLE INJURY MECHANISM AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW REAR-IMPACT DUMMY
 NECK INJURIES IN CAR COLLISIONS - A REVIEW COVERING A POSSIBLE INJURY MECHANISM AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW REAR-IMPACT DUMMY M.Y. Svensson 1, O. Boström 4, J. Davidsson 1, H.-A. Hansson 2, Y. Håland
NECK INJURIES IN CAR COLLISIONS - A REVIEW COVERING A POSSIBLE INJURY MECHANISM AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW REAR-IMPACT DUMMY M.Y. Svensson 1, O. Boström 4, J. Davidsson 1, H.-A. Hansson 2, Y. Håland
Assessment of Whiplash Protection in Rear Impacts. Crash Tests and Real-life Crashes
 Assessment of Whiplash Protection in Rear Impacts Crash Tests and Real-life Crashes Maria Krafft, Anders Kullgren Folksam Anders Lie, Claes Tingvall Swedish National Road Administration June 24 Summary
Assessment of Whiplash Protection in Rear Impacts Crash Tests and Real-life Crashes Maria Krafft, Anders Kullgren Folksam Anders Lie, Claes Tingvall Swedish National Road Administration June 24 Summary
Influence of thoracic ramping on whiplash kinematics
 Clinical Biomechanics 2 (25) 119 128 www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Influence of thoracic ramping on whiplash kinematics Brian D. Stemper a,b, *, Narayan Yoganandan a,b, Raj D. Rao c, Frank A. Pintar
Clinical Biomechanics 2 (25) 119 128 www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Influence of thoracic ramping on whiplash kinematics Brian D. Stemper a,b, *, Narayan Yoganandan a,b, Raj D. Rao c, Frank A. Pintar
A Review of the Literature Refuting the Concept of Minor Impact Soft Tissue Injury (M.I.S.T.) Christopher J. Centeno, M.D.
 Centeno 1 A Review of the Literature Refuting the Concept of Minor Impact Soft Tissue Injury (M.I.S.T.) Christopher J. Centeno, M.D. Michael Freeman, PhD, M.P.H., D.C. Whitney L. Elkins, M.P.H. Short Title:
Centeno 1 A Review of the Literature Refuting the Concept of Minor Impact Soft Tissue Injury (M.I.S.T.) Christopher J. Centeno, M.D. Michael Freeman, PhD, M.P.H., D.C. Whitney L. Elkins, M.P.H. Short Title:
Proposing a 2D Dynamical Model for Investigating the parameters Affecting Whiplash Injuries
 Proposing a 2D Dynamical Model for Investigating the parameters Affecting Whiplash Injuries Seyed Mohammad Rajaai i, and Mohammad H Farahani ii ABSTRACT: This paper proposes a 2D dynamical model for evaluating
Proposing a 2D Dynamical Model for Investigating the parameters Affecting Whiplash Injuries Seyed Mohammad Rajaai i, and Mohammad H Farahani ii ABSTRACT: This paper proposes a 2D dynamical model for evaluating
Summary Report: Requirements and Assessment of Low-Speed Rear Impact Whiplash Dummies
 Summary Report: Requirements and Assessment of Low-Speed Rear Impact Whiplash Dummies WG12 report October 2008 Report published on the EEVC web site: www.eevc.org Report obtained from EEVC web site www.eevc.org
Summary Report: Requirements and Assessment of Low-Speed Rear Impact Whiplash Dummies WG12 report October 2008 Report published on the EEVC web site: www.eevc.org Report obtained from EEVC web site www.eevc.org
Correlating crash severity with injury risk, injury severity, and long-term symptoms in low velocity motor vehicle collisions
 Med Sci Monit, 2005; 11(10): RA316-321 PMID: 16192914 WWW.MEDSCIMONIT.COM Review Article Received: 2005.08.04 Accepted: 2005.09.02 Published: 2005.10.01 Correlating crash severity with injury risk, injury
Med Sci Monit, 2005; 11(10): RA316-321 PMID: 16192914 WWW.MEDSCIMONIT.COM Review Article Received: 2005.08.04 Accepted: 2005.09.02 Published: 2005.10.01 Correlating crash severity with injury risk, injury
Side Impact Causes Multiplanar Cervical Spine Injuries
 Side Impact Causes Multiplanar Cervical Spine Injuries 1 The Journal of Trauma, Injury, infection and Critical Care Volume 63(6), December 2007, pp 1296-1307 Maak, Travis G. MD; Ivancic, Paul C. PhD; Tominaga,
Side Impact Causes Multiplanar Cervical Spine Injuries 1 The Journal of Trauma, Injury, infection and Critical Care Volume 63(6), December 2007, pp 1296-1307 Maak, Travis G. MD; Ivancic, Paul C. PhD; Tominaga,
ADSEAT. An EU funded project within the 7th Framework Programme. Adaptive Seat to Reduce Neck Injuries for Female and Male Occupants
 ADSEAT An EU funded project within the 7th Framework Programme Adaptive Seat to Reduce Neck Injuries for Female and Male Occupants Citizens who annually suffer whiplash injuries in the EU 800 000 Socio-economic
ADSEAT An EU funded project within the 7th Framework Programme Adaptive Seat to Reduce Neck Injuries for Female and Male Occupants Citizens who annually suffer whiplash injuries in the EU 800 000 Socio-economic
Prognostic factors of whiplash-associated disorders: A systematic review of prospective cohort studies. Pain July 2003, Vol. 104, pp.
 Prognostic factors of whiplash-associated disorders: A systematic review of prospective cohort studies 1 Pain July 2003, Vol. 104, pp. 303 322 Gwendolijne G.M. Scholten-Peeters, Arianne P. Verhagen, Geertruida
Prognostic factors of whiplash-associated disorders: A systematic review of prospective cohort studies 1 Pain July 2003, Vol. 104, pp. 303 322 Gwendolijne G.M. Scholten-Peeters, Arianne P. Verhagen, Geertruida
Whiplash: a review of a commonly misunderstood injury
 1 Whiplash: a review of a commonly misunderstood injury The American Journal of Medicine; Volume 110; 651-656; June 1, 2001 Jason C. Eck, Scott D. Hodges, S. Craig Humphreys This review article has 64
1 Whiplash: a review of a commonly misunderstood injury The American Journal of Medicine; Volume 110; 651-656; June 1, 2001 Jason C. Eck, Scott D. Hodges, S. Craig Humphreys This review article has 64
Development of Whiplash Associated Disorders for Male and Female Car Occupants in Cars Launched Since the 80s in Different Impact Directions
 Development of Whiplash Associated Disorders for Male and Female Car Occupants in Cars Launched Since the 80s in Different Impact Directions Anders Kullgren, Helena Stigson and Maria Krafft Abstract The
Development of Whiplash Associated Disorders for Male and Female Car Occupants in Cars Launched Since the 80s in Different Impact Directions Anders Kullgren, Helena Stigson and Maria Krafft Abstract The
Long-term medical consequences to children injured in car crashes and influence of crash directions
 Long-term medical consequences to children injured in car crashes and influence of crash directions Katarina Bohman 1,2), Helena Stigson 2,3), Maria Krafft 3,4) 1) Autoliv Research, 2) Karolinska Institutet,
Long-term medical consequences to children injured in car crashes and influence of crash directions Katarina Bohman 1,2), Helena Stigson 2,3), Maria Krafft 3,4) 1) Autoliv Research, 2) Karolinska Institutet,
REAL-WORLD PERFORMANCE OF CITY SAFETY BASED ON SWEDISH INSURANCE DATA
 REAL-WORLD PERFORMANCE OF CITY SAFETY BASED ON SWEDISH INSURANCE DATA Irene Isaksson-Hellman If P&C Insurance Sweden Magdalena Lindman Volvo Car Corporation Sweden Paper Number 15-0121 ABSTRACT The number
REAL-WORLD PERFORMANCE OF CITY SAFETY BASED ON SWEDISH INSURANCE DATA Irene Isaksson-Hellman If P&C Insurance Sweden Magdalena Lindman Volvo Car Corporation Sweden Paper Number 15-0121 ABSTRACT The number
Influence of Gender, Height, Weight, Age, Seated Position and Collision Site related to Neck Pain Symptoms in Rear End Impacts
 Influence of Gender, Height, Weight, Age, Seated Position and Collision Site related to Neck Pain Symptoms in Rear End Impacts Astrid Linder, Stefan Olsén, Jenny Eriksson, Mats Y. Svensson, Anna Carlsson
Influence of Gender, Height, Weight, Age, Seated Position and Collision Site related to Neck Pain Symptoms in Rear End Impacts Astrid Linder, Stefan Olsén, Jenny Eriksson, Mats Y. Svensson, Anna Carlsson
THE EFFECT OF WHIPLASH PROTECTION SYSTEMS IN REAL-LIFE CRASHES AND THEIR CORRELATION TO CONSUMER CRASH TEST PROGRAMMES
 THE EFFECT OF WHIPLASH PROTECTION SYSTEMS IN REAL-LIFE CRASHES AND THEIR CORRELATION TO CONSUMER CRASH TEST PROGRAMMES Anders Kullgren Maria Krafft Folksam Research and Karolinska Institutet, Sweden Anders
THE EFFECT OF WHIPLASH PROTECTION SYSTEMS IN REAL-LIFE CRASHES AND THEIR CORRELATION TO CONSUMER CRASH TEST PROGRAMMES Anders Kullgren Maria Krafft Folksam Research and Karolinska Institutet, Sweden Anders
PERFORMANCE OF SEATS WITH ACTIVE HEAD RESTRAINTS IN REAR IMPACTS
 PERFORMANCE OF SEATS WITH ACTIVE HEAD RESTRAINTS IN REAR IMPACTS Liming Voo Bethany McGee Andrew Merkle Michael Kleinberger Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory United States of America
PERFORMANCE OF SEATS WITH ACTIVE HEAD RESTRAINTS IN REAR IMPACTS Liming Voo Bethany McGee Andrew Merkle Michael Kleinberger Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory United States of America
SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME
 SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME SUSTAINABLE SURFACE TRANSPORT (SST)-2008-RTD-1 ADSEAT Adaptive seat to reduce neck injuries for female and male occupants Project no. 233904 Summary from 1 st Periodic Report
SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME SUSTAINABLE SURFACE TRANSPORT (SST)-2008-RTD-1 ADSEAT Adaptive seat to reduce neck injuries for female and male occupants Project no. 233904 Summary from 1 st Periodic Report
DOCUMENT RETRIEVAL INFORMATION
 AUSTRALIAN TRANSPORT SAFETY BUREAU DOCUMENT RETRIEVAL INFORMATION Title and Subtitle Development of an Anti-Whiplash Seat Authors Michael Yuen, Mr. Lynne E. Bilston, Dr. Performing Organisation The Prince
AUSTRALIAN TRANSPORT SAFETY BUREAU DOCUMENT RETRIEVAL INFORMATION Title and Subtitle Development of an Anti-Whiplash Seat Authors Michael Yuen, Mr. Lynne E. Bilston, Dr. Performing Organisation The Prince
Head Position and Impact Direction in Whiplash Injuries: Associations with MRI-Verified Lesions of Ligaments and Membranes in the Upper Cervical Spine
 Head Position and Impact Direction in Whiplash Injuries: Associations with MRI-Verified Lesions of Ligaments and Membranes in the Upper Cervical Spine 1 Journal of Neurotrauma Volume 22, Number 11, November
Head Position and Impact Direction in Whiplash Injuries: Associations with MRI-Verified Lesions of Ligaments and Membranes in the Upper Cervical Spine 1 Journal of Neurotrauma Volume 22, Number 11, November
THE WHIPLASH INJURY IN REAR-END COLLISION USING 3-D HUMAN WHOLE BODY MODEL
 THE WHIPLASH INJURY IN REAR-END COLLISION USING 3-D HUMAN WHOLE BODY MODEL Yu-Bong KANG 1, Masatoshi TANAKA 1, Sadami TSUTSUMI 1 and Ken IKEUCHI 1 Dept. Medical Simulation Engineering, Research Center
THE WHIPLASH INJURY IN REAR-END COLLISION USING 3-D HUMAN WHOLE BODY MODEL Yu-Bong KANG 1, Masatoshi TANAKA 1, Sadami TSUTSUMI 1 and Ken IKEUCHI 1 Dept. Medical Simulation Engineering, Research Center
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options
 Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
GENDER ANALYSIS ON WHIPLASH SEAT EFFECTIVENESS: RESULTS FROM REAL-WORLD CRASHES
 GENDER ANALYSIS ON WHIPLASH SEAT EFFECTIVENESS: RESULTS FROM REAL-WORLD CRASHES Anders Kullgren * **, Maria Krafft * * Folksam Research ** Department for Public Health Science, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
GENDER ANALYSIS ON WHIPLASH SEAT EFFECTIVENESS: RESULTS FROM REAL-WORLD CRASHES Anders Kullgren * **, Maria Krafft * * Folksam Research ** Department for Public Health Science, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
COMPARISON OF BIORID INJURY CRITERIA BETWEEN DYNAMIC SLED TESTS AND VEHICLE CRASH TESTS
 COMPARISON OF BIORID INJURY CRITERIA BETWEEN DYNAMIC SLED TESTS AND VEHICLE CRASH TESTS David A. Aylor David S. Zuby Insurance Institute for Highway Safety United States Paper No. 11-235 ABSTRACT The Insurance
COMPARISON OF BIORID INJURY CRITERIA BETWEEN DYNAMIC SLED TESTS AND VEHICLE CRASH TESTS David A. Aylor David S. Zuby Insurance Institute for Highway Safety United States Paper No. 11-235 ABSTRACT The Insurance
EFFECTS OF HEAD RESTRAINT POSITION ON NECK INJURY IN REAR IMPACT
 EFFECTS OF HEAD RESTRANT POSTON ON NECK NJURY N REAR MPACT Michael Kleinberger, Emily Sun, James Saunders and Zaifei Zhou3 Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, MD, USA National Highway Traffic
EFFECTS OF HEAD RESTRANT POSTON ON NECK NJURY N REAR MPACT Michael Kleinberger, Emily Sun, James Saunders and Zaifei Zhou3 Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, MD, USA National Highway Traffic
On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash. Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199
 On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash 1 Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199 Nikolai Bogduk, MD, PhD FROM ABSTRACT Objective To summarize the evidence that implicates
On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash 1 Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199 Nikolai Bogduk, MD, PhD FROM ABSTRACT Objective To summarize the evidence that implicates
Manchester Claims Association Chronic Whiplash
 Manchester Claims Association Chronic Whiplash Thursday 03 rd July 2014 Scot Darling, Chief Medical Officer Premex Services Limited, Premex House, Futura Park, Middlebrook, Bolton BL6 6SX. T 01204 478300
Manchester Claims Association Chronic Whiplash Thursday 03 rd July 2014 Scot Darling, Chief Medical Officer Premex Services Limited, Premex House, Futura Park, Middlebrook, Bolton BL6 6SX. T 01204 478300
Finite Element Modelling of Biomechanical Dummies- The Ultimate Tool in Anti-Whiplash Safety Design?
 Finite Element Modelling of Biomechanical Dummies- The Ultimate Tool in Anti-Whiplash Safety Design? Waldemar Z. Golinski The Nottingham Trent University Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering
Finite Element Modelling of Biomechanical Dummies- The Ultimate Tool in Anti-Whiplash Safety Design? Waldemar Z. Golinski The Nottingham Trent University Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering
Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury. Canadian Family Physician
 Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury 1 Canadian Family Physician Volume 32, September 1986 Arthur Ameis, MD Dr. Ames practices physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury 1 Canadian Family Physician Volume 32, September 1986 Arthur Ameis, MD Dr. Ames practices physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Reining in Whiplash. Better Protection for Europe s Car Occupants
 Reining in Whiplash Better Protection for Europe s Car Occupants Members Accident Research Unit - Medical University Hannover (D) Austrian Road Safety Board (KfV) (A) Automobile and Travel Club Germany
Reining in Whiplash Better Protection for Europe s Car Occupants Members Accident Research Unit - Medical University Hannover (D) Austrian Road Safety Board (KfV) (A) Automobile and Travel Club Germany
Clinical Biomechanics
 Clinical Biomechanics 2 (29) 699 77 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Clinical Biomechanics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Whiplash injury prevention with active head restraint
Clinical Biomechanics 2 (29) 699 77 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Clinical Biomechanics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/clinbiomech Whiplash injury prevention with active head restraint
Whiplash Associated Disorder
 Whiplash Associated Disorder The pathology Whiplash is a mechanism of injury, consisting of acceleration-deceleration forces to the neck. Mechanism: Hyperflexion/extension injury Stationary vehicle hit
Whiplash Associated Disorder The pathology Whiplash is a mechanism of injury, consisting of acceleration-deceleration forces to the neck. Mechanism: Hyperflexion/extension injury Stationary vehicle hit
T he terms whiplash and whiplash associated disorders
 97 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessing automobile head restraint positioning in Portland, Oregon A L Young, B T Ragel, E Su, C N Mann, E H Frank... Injury Prevention 2005;11:97 101. doi: 10.1136/ip.2004.006122
97 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessing automobile head restraint positioning in Portland, Oregon A L Young, B T Ragel, E Su, C N Mann, E H Frank... Injury Prevention 2005;11:97 101. doi: 10.1136/ip.2004.006122
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
SAE / Government Meeting. Washington, D.C. May 2005
 SAE / Government Meeting Washington, D.C. May 2005 Overview of the Enhancements and Changes in the CIREN Program History of Phase One Established 1997 (7 centers) Four Federal centers Three GM centers
SAE / Government Meeting Washington, D.C. May 2005 Overview of the Enhancements and Changes in the CIREN Program History of Phase One Established 1997 (7 centers) Four Federal centers Three GM centers
Pressure Effects in the Spinal Canal during Whiplash Extension Motion : A Possible Cause of Injury to the Cervical Spinal Ganglia
 I - 1 Pressure Effects in the Spinal Canal during Whiplash Extension Motion : A Possible Cause of Injury to the Cervical Spinal Ganglia M.Y. Svensson 1, B. Aldman 1, H.A. Hansson 2,4, P. Lövsund 1, T.
I - 1 Pressure Effects in the Spinal Canal during Whiplash Extension Motion : A Possible Cause of Injury to the Cervical Spinal Ganglia M.Y. Svensson 1, B. Aldman 1, H.A. Hansson 2,4, P. Lövsund 1, T.
NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
 WHIPLASH and WHIPLASH-ASSOCIATED DISORDERS AN EVIDENCE-BASED APPROACH Nikolai Bogduk Emeritus Professor of Pain Medicine University of Newcastle Australia NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST WHIPLASH and WHIPLASH-ASSOCIATED
WHIPLASH and WHIPLASH-ASSOCIATED DISORDERS AN EVIDENCE-BASED APPROACH Nikolai Bogduk Emeritus Professor of Pain Medicine University of Newcastle Australia NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST WHIPLASH and WHIPLASH-ASSOCIATED
Minutes. GTR No. 7 / BioRID TEG. Group of Experts Whiplash Injury Criteria Meeting
 Minutes GTR No. 7 / BioRID TEG Group of Experts Whiplash Injury Criteria Meeting Date & Timing: Location: Minutes drafted by: Participants: Documents: Monday September 8 th 2014, 13:00-17:30 (CET) and
Minutes GTR No. 7 / BioRID TEG Group of Experts Whiplash Injury Criteria Meeting Date & Timing: Location: Minutes drafted by: Participants: Documents: Monday September 8 th 2014, 13:00-17:30 (CET) and
INVESTIGATION OF LOWER SPINE COMPRESSION FRACTURES IN FRONTAL CRASHES
 INVESTIGATION OF LOWER SPINE COMPRESSION FRACTURES IN FRONTAL CRASHES Rodney W. Rudd, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Company Logo Here Overview Lower spine includes: 10 th through 12 th
INVESTIGATION OF LOWER SPINE COMPRESSION FRACTURES IN FRONTAL CRASHES Rodney W. Rudd, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Company Logo Here Overview Lower spine includes: 10 th through 12 th
WHAT ARE THE ODDS OF YOUR BEING INJURED IN A LOW SPEED COLLISION? KNOW YOUR RISK FACTORS. Meet Jennifer, the world s unluckiest driver.
 WHAT ARE THE ODDS OF YOUR BEING INJURED IN A LOW SPEED COLLISION? KNOW YOUR RISK FACTORS Meet Jennifer, the world s unluckiest driver. Jennifer is a very fit 50-something babe, grooving to the beat in
WHAT ARE THE ODDS OF YOUR BEING INJURED IN A LOW SPEED COLLISION? KNOW YOUR RISK FACTORS Meet Jennifer, the world s unluckiest driver. Jennifer is a very fit 50-something babe, grooving to the beat in
STATUS REPORT. The seats and head restraints in many vehicles don t protect people s necks, but new designs show promise
 STATUS REPORT INSURANCE INSTITUTE Special issue: neck injuries in rear-end crashes Vol. 34, No. 5, May 22, 1999 FOR HIGHWAY SAFETY The seats and head restraints in many vehicles don t protect people s
STATUS REPORT INSURANCE INSTITUTE Special issue: neck injuries in rear-end crashes Vol. 34, No. 5, May 22, 1999 FOR HIGHWAY SAFETY The seats and head restraints in many vehicles don t protect people s
Spinal Anatomy. * MedX research contends that the lumbar region really starts at T-11, based upon the attributes of the vertebra.
 Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Relationship of Dynamic Seat/Head Restraint Ratings to Real-world Neck Injury Rates
 Relationship of Dynamic Seat/Head Restraint Ratings to Real-world Neck Injury Rates Charles M. Farmer, Laurie A. Hellinga, Jo Ann K. Wells, David S. Zuby Basic method Collect insurance claims for late
Relationship of Dynamic Seat/Head Restraint Ratings to Real-world Neck Injury Rates Charles M. Farmer, Laurie A. Hellinga, Jo Ann K. Wells, David S. Zuby Basic method Collect insurance claims for late
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders
 Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
From the Trenches Personal Injury Report Whiplash Injuries Review & Update on Facet Joint Trauma
 Quadra Chiropractic Frank McDiarmid, D.C., FRCCSS (Canada) (email: frank@quadrachiropractic.com) City Centre Chiropractic 2602 Quadra Street 2832 Leigh Road Victoria, B.C. Langford, B.C. V8T 4E4 V9B 4G3
Quadra Chiropractic Frank McDiarmid, D.C., FRCCSS (Canada) (email: frank@quadrachiropractic.com) City Centre Chiropractic 2602 Quadra Street 2832 Leigh Road Victoria, B.C. Langford, B.C. V8T 4E4 V9B 4G3
Case Report: Whiplash-Associated Disorder From a Low-Velocity Bumper Car Collision: History, Evaluation, and Surgery
 Case Report: Whiplash-Associated Disorder From a Low-Velocity Bumper Car Collision: History, Evaluation, and Surgery Spine: Volume 29(17) September 1, 2004 pp 1881-1884 Duffy, Michael F. MD; Stuberg, Wayne
Case Report: Whiplash-Associated Disorder From a Low-Velocity Bumper Car Collision: History, Evaluation, and Surgery Spine: Volume 29(17) September 1, 2004 pp 1881-1884 Duffy, Michael F. MD; Stuberg, Wayne
THE ANATOMY OF A WHIPLASH INJURY Samuel D. Hodge, Jr., Esquire Jack E. Hubbard, PhD, MD
 THE ANATOMY OF A WHIPLASH INJURY Samuel D. Hodge, Jr., Esquire Jack E. Hubbard, PhD, MD Nobody really knows when the term whiplash injury originated, and U.S. insurance companies, which each year pay out
THE ANATOMY OF A WHIPLASH INJURY Samuel D. Hodge, Jr., Esquire Jack E. Hubbard, PhD, MD Nobody really knows when the term whiplash injury originated, and U.S. insurance companies, which each year pay out
Evaluation of Seat Performance Criteria for Future Rear-end Impact Testing
 EEVC WG12 Report Document Number 578 final version Evaluation of Seat Performance Criteria for Future Rear-end Impact Testing May 2013 Authors Johan Davidsson, Chalmers University of Technology Anders
EEVC WG12 Report Document Number 578 final version Evaluation of Seat Performance Criteria for Future Rear-end Impact Testing May 2013 Authors Johan Davidsson, Chalmers University of Technology Anders
COMBINING CRASH RECORDER AND PAIRED COMPARISON TECHNIQUE: INJURY RISK FUNCTIONS IN FRONTAL AND REAR IMPACTS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO NECK INJURIES
 COMBINING CRASH RECORDER AND AIRED COMARISON TECHNIQUE: INJURY RISK FUNCTIONS IN FRONTAL AND REAR IMACTS WITH SECIAL REFERENCE TO NECK INJURIES Anders Kullgren, Maria Krafft Folksa Research, 66 Stockhol,
COMBINING CRASH RECORDER AND AIRED COMARISON TECHNIQUE: INJURY RISK FUNCTIONS IN FRONTAL AND REAR IMACTS WITH SECIAL REFERENCE TO NECK INJURIES Anders Kullgren, Maria Krafft Folksa Research, 66 Stockhol,
A MULTI-BODY MODEL OF THE WHOLE HUMAN SPINE FOR WHIPLASH INVESTIGATIONS
 A MULTI-BODY MODEL OF THE WHOLE HUMAN SPINE FOR WHIPLASH INVESTIGATIONS Volkan Esat Memis Acar Loughborough University United Kingdom Paper Number 7-437 ABSTRACT This paper presents whiplash simulations
A MULTI-BODY MODEL OF THE WHOLE HUMAN SPINE FOR WHIPLASH INVESTIGATIONS Volkan Esat Memis Acar Loughborough University United Kingdom Paper Number 7-437 ABSTRACT This paper presents whiplash simulations
The Biomechanics of "Whiplash" in Low Velocity Collisions
 1999-01-3235 The Biomechanics of "Whiplash" in Low Velocity Collisions Copyright 1999 Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc. Richard P. Howard, Richard M. Harding and Scott W. Krenric Biodynamic Research
1999-01-3235 The Biomechanics of "Whiplash" in Low Velocity Collisions Copyright 1999 Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc. Richard P. Howard, Richard M. Harding and Scott W. Krenric Biodynamic Research
Addressing Female Whiplash Injury Protection A Step Towards 50 th Percentile Female Rear Impact Occupant Models
 THESIS FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY in MACHINE AND VEHICLE SYSTEMS Addressing Female Whiplash Injury Protection A Step Towards 50 th Percentile Female Rear Impact Occupant Models A NNA C ARLSSON
THESIS FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY in MACHINE AND VEHICLE SYSTEMS Addressing Female Whiplash Injury Protection A Step Towards 50 th Percentile Female Rear Impact Occupant Models A NNA C ARLSSON
IIHS Head Restraint Ratings and Insurance Injury Claim Rates. November 2015. Rebecca E. Trempel. David S. Zuby. Marcy A. Edwards
 IIHS Head Restraint Ratings and Insurance Injury Claim Rates November 2015 Rebecca E. Trempel Highway Loss Data Institute David S. Zuby Insurance Institute for Highway Safety Marcy A. Edwards Insurance
IIHS Head Restraint Ratings and Insurance Injury Claim Rates November 2015 Rebecca E. Trempel Highway Loss Data Institute David S. Zuby Insurance Institute for Highway Safety Marcy A. Edwards Insurance
CHIROPRACTIC WELLNESS AWARENESS ONE FREE MASSAGE SESSION
 CHIROPRACTIC WELLNESS AWARENESS Do you want to have a healthy body? Do you like to maintain your high energy level? Do you want to be stress-less? Do you like to be pain free? Please call Conrad Nieh D.C.
CHIROPRACTIC WELLNESS AWARENESS Do you want to have a healthy body? Do you like to maintain your high energy level? Do you want to be stress-less? Do you like to be pain free? Please call Conrad Nieh D.C.
A METHOD TO ESTIMATE INJURY MEDICAL COST OF OCCUPANTS IN A CRASH TEST
 A METHOD TO ESTIMATE INJURY MEDICAL COST OF OCCUPANTS IN A CRASH TEST Ching-Huei Lai Ji-Liang Doong Department of Mechanical Engineering National Central University Taiwan Tso-Liang Teng Department of
A METHOD TO ESTIMATE INJURY MEDICAL COST OF OCCUPANTS IN A CRASH TEST Ching-Huei Lai Ji-Liang Doong Department of Mechanical Engineering National Central University Taiwan Tso-Liang Teng Department of
SpineFAQs. Whiplash. What causes this condition?
 SpineFAQs Whiplash Whiplash is defined as a sudden extension of the cervical spine (backward movement of the neck) and flexion (forward movement of the neck). This type of trauma is also referred to as
SpineFAQs Whiplash Whiplash is defined as a sudden extension of the cervical spine (backward movement of the neck) and flexion (forward movement of the neck). This type of trauma is also referred to as
The term whiplash was first used by H. E. Crowe
 Whiplash: A Review of a Commonly Misunderstood Injury Jason C. Eck, MS, Scott D. Hodges, DO, S. Craig Humphreys, MD Whiplash injury is a relatively common occurrence, but its mechanism and optimal treatment
Whiplash: A Review of a Commonly Misunderstood Injury Jason C. Eck, MS, Scott D. Hodges, DO, S. Craig Humphreys, MD Whiplash injury is a relatively common occurrence, but its mechanism and optimal treatment
The multitude of symptoms following a whiplash injury has given rise to much discussion because of the lack of objective radiological findings.
 HELPFUL PERSONAL INJURY INFORMATION COURTESY OF RIVERVIEW CHIROPRACTIC FROM ABSTRACT: Dynamic kine magnetic resonance imaging in whiplash patients Pain Research and Management 2009 Nov-Dec 2009;Vol. 14,
HELPFUL PERSONAL INJURY INFORMATION COURTESY OF RIVERVIEW CHIROPRACTIC FROM ABSTRACT: Dynamic kine magnetic resonance imaging in whiplash patients Pain Research and Management 2009 Nov-Dec 2009;Vol. 14,
MARTIN CHARLES HILLIER
 HEAD ACCELERATION AND ASSOCIATED PAIN FELT IN THE NECK REGION DURING A SIMULATED AUTOMOBILE LOW VELOCITY REAR-END COLLISION AS A FUNCTION OF SEAT BACK ANGLE By MARTIN CHARLES HILLIER A THESIS PRESENTED
HEAD ACCELERATION AND ASSOCIATED PAIN FELT IN THE NECK REGION DURING A SIMULATED AUTOMOBILE LOW VELOCITY REAR-END COLLISION AS A FUNCTION OF SEAT BACK ANGLE By MARTIN CHARLES HILLIER A THESIS PRESENTED
Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors
 1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
From the State of Florida Department of
 A Minor Accident Equals A Big Problem From the State of Florida Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles The following crash information is compiled from traffic crash reports (long form) submitted
A Minor Accident Equals A Big Problem From the State of Florida Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles The following crash information is compiled from traffic crash reports (long form) submitted
Whiplash Associated Disorder
 Whiplash Associated Disorder Bourassa & Associates Rehabilitation Centre What is Whiplash? Whiplash is a non-medical term used to describe neck pain following hyperflexion or hyperextension of the tissues
Whiplash Associated Disorder Bourassa & Associates Rehabilitation Centre What is Whiplash? Whiplash is a non-medical term used to describe neck pain following hyperflexion or hyperextension of the tissues
Epidemiology of Whiplash-Associated Disorders
 Epidemiology of Whiplash-Associated Disorders 2 Until recently, there was no consensus on the definition of whiplash. According to the Quebec Task Force (QTF) on whiplash-associated disorders (WAD), whiplash
Epidemiology of Whiplash-Associated Disorders 2 Until recently, there was no consensus on the definition of whiplash. According to the Quebec Task Force (QTF) on whiplash-associated disorders (WAD), whiplash
Low Velocity Impact, Vehicular Damage and Passenger Injury
 Back 916-786-4TMJ Advanced Dental Concepts 916-786-4TMJ CRANIO: THE JOURNAL OF CRANIOMANDIBULAR PRACTICE OCT.1998, VOL. 16, NO. 4 Low Velocity Impact, Vehicular Damage and Passenger Injury ABSTRACT: Low
Back 916-786-4TMJ Advanced Dental Concepts 916-786-4TMJ CRANIO: THE JOURNAL OF CRANIOMANDIBULAR PRACTICE OCT.1998, VOL. 16, NO. 4 Low Velocity Impact, Vehicular Damage and Passenger Injury ABSTRACT: Low
Synopsis of Causation. Whiplash
 Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Whiplash Authors: Dr Amanda Rashier, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham and Mr Jonathan Monk, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham Validator: Mr M Gargan, Bristol
Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Whiplash Authors: Dr Amanda Rashier, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham and Mr Jonathan Monk, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham Validator: Mr M Gargan, Bristol
A Systematic Approach for Improving Occupant Protection in Rollover Crashes
 SAE 2011 Government / Industry Meeting A Systematic Approach for Improving Occupant Protection in Rollover Crashes Jingwen Hu, PhD University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute King H. Yang,
SAE 2011 Government / Industry Meeting A Systematic Approach for Improving Occupant Protection in Rollover Crashes Jingwen Hu, PhD University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute King H. Yang,
1 REVISOR 5223.0070. (4) Pain associated with rigidity (loss of motion or postural abnormality) or
 1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
BRADLEY E HEINRICHS, MSc PEng PRINCIPAL, SENIOR ENGINEER
 Vancouver Los Angeles Toronto San Francisco BRADLEY E HEINRICHS, MSc PEng PRINCIPAL, SENIOR ENGINEER EDUCATION Master of Science, Mechanical Engineering, University of Manitoba, 1996. Bachelor of Applied
Vancouver Los Angeles Toronto San Francisco BRADLEY E HEINRICHS, MSc PEng PRINCIPAL, SENIOR ENGINEER EDUCATION Master of Science, Mechanical Engineering, University of Manitoba, 1996. Bachelor of Applied
Chicago Chiropractic & Sports Injury Centers
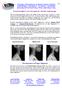 1of6 Cervical (Lordotic Lordotic) Curve Correction for `Anterior Head Carriage` The soft forward [lordotic] curve at the middle of the cervical spine is critical as a shock absorber for the full weight
1of6 Cervical (Lordotic Lordotic) Curve Correction for `Anterior Head Carriage` The soft forward [lordotic] curve at the middle of the cervical spine is critical as a shock absorber for the full weight
Soft-tissue injuries of the neck in automobile accidents: Factors influencing prognosis
 Soft-tissue injuries of the neck in automobile accidents: Factors influencing prognosis 1 Mason Hohl, MD FROM ABSTRACT: Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (American) December 1974;56(8):1675-1682 Five years
Soft-tissue injuries of the neck in automobile accidents: Factors influencing prognosis 1 Mason Hohl, MD FROM ABSTRACT: Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (American) December 1974;56(8):1675-1682 Five years
Umeå University. Access to the published version may require subscription.
 Umeå University This is an accepted version of a paper published in PM&R. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections or journal pagination. Citation for
Umeå University This is an accepted version of a paper published in PM&R. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections or journal pagination. Citation for
Curriculum Vitae Helena Stigson +46 (0) 70 284 96 97 helena.stigson@folksam.se
 Updated 2 October 2015 Page: 1 / 5 Department of Clinical Neuroscience Division of Insurance Medicine Curriculum Vitae Helena Stigson +46 (0) 70 284 96 97 helena.stigson@folksam.se Education 2005 2009
Updated 2 October 2015 Page: 1 / 5 Department of Clinical Neuroscience Division of Insurance Medicine Curriculum Vitae Helena Stigson +46 (0) 70 284 96 97 helena.stigson@folksam.se Education 2005 2009
Whiplash: Research and Case Management. Presented by: Ronald J. Farabaugh, D.C.
 Whiplash: Research and Case Management Presented by: Ronald J. Farabaugh, D.C. Principle #1: The three pillars of LOSRIC: Accident reconstruction: weak science. Body kinematics: strong science. Risk Factors:
Whiplash: Research and Case Management Presented by: Ronald J. Farabaugh, D.C. Principle #1: The three pillars of LOSRIC: Accident reconstruction: weak science. Body kinematics: strong science. Risk Factors:
Correlating crash severity with injury risk, injury severity, and long-term symptoms in low velocity motor vehicle collisions
 Correlating crash severity with injury risk, injury severity, and long-term symptoms in low velocity motor vehicle collisions Medical Science Monitor, October 2005; 11(10): RA316-321 FROM ABSTRACT: Arthur
Correlating crash severity with injury risk, injury severity, and long-term symptoms in low velocity motor vehicle collisions Medical Science Monitor, October 2005; 11(10): RA316-321 FROM ABSTRACT: Arthur
Neck Exercises for Car Accident Victims 3 Steps to a Healthier Neck
 Neck Exercises for Car Accident Victims 3 Steps to a Healthier Neck DR BARRY L. MARKS CHIROPRACTOR AUTHOR LECTURER Neck Exercises for Car Accident Victims 3 Steps to a Healthier Neck 2012 Dr. Barry L.
Neck Exercises for Car Accident Victims 3 Steps to a Healthier Neck DR BARRY L. MARKS CHIROPRACTOR AUTHOR LECTURER Neck Exercises for Car Accident Victims 3 Steps to a Healthier Neck 2012 Dr. Barry L.
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report
 Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Modeling of Whiplash Injuries using CFD
 Modeling of Whiplash Injuries using CFD FENG LIU JUNFENG YANG Department of Applied Mechanics Division of Fluid Dynamics / Division of Vehicle Safety CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Göteborg, Sweden
Modeling of Whiplash Injuries using CFD FENG LIU JUNFENG YANG Department of Applied Mechanics Division of Fluid Dynamics / Division of Vehicle Safety CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Göteborg, Sweden
from whiplash injuries?
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 17-21 Do head-restraints protect the neck from whiplash injuries? F. MORRIS Accident and Emergency Department, Oldchurch Hospital, Romford, Essex, England SUMMARY
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 17-21 Do head-restraints protect the neck from whiplash injuries? F. MORRIS Accident and Emergency Department, Oldchurch Hospital, Romford, Essex, England SUMMARY
Digges 1 INJURIES TO RESTRAINED OCCUPANTS IN FAR-SIDE CRASHES. Kennerly Digges The Automotive Safety Research Institute Charlottesville, Virginia, USA
 INJURIES TO RESTRAINED OCCUPANTS IN FAR-SIDE CRASHES Kennerly Digges The Automotive Safety Research Institute Charlottesville, Virginia, USA Dainius Dalmotas Transport Canada Ottawa, Canada Paper Number
INJURIES TO RESTRAINED OCCUPANTS IN FAR-SIDE CRASHES Kennerly Digges The Automotive Safety Research Institute Charlottesville, Virginia, USA Dainius Dalmotas Transport Canada Ottawa, Canada Paper Number
ABSTRACTS OF STUDIES RELATED TO SOFT-TISSUE INJURIES IN AUTOMOBILE ACCIDENTS SUMMARY
 ABSTRACTS OF STUDIES RELATED TO SOFT-TISSUE INJURIES IN AUTOMOBILE ACCIDENTS 1. Bioengineering SUMMARY Study of Basic Physical Measurements related to Susceptibility to Cervical Hyperextension-Hyperflexion
ABSTRACTS OF STUDIES RELATED TO SOFT-TISSUE INJURIES IN AUTOMOBILE ACCIDENTS 1. Bioengineering SUMMARY Study of Basic Physical Measurements related to Susceptibility to Cervical Hyperextension-Hyperflexion
CITY SAFETY A SYSTEM ADDRESSING REAR-END COLLISIONS AT LOW SPEEDS
 CITY SAFETY A SYSTEM ADDRESSING REAR-END COLLISIONS AT LOW SPEEDS Martin Distner Mattias Bengtsson Thomas Broberg Lotta Jakobsson Volvo Cars Sweden Paper Number 09-0371 ABSTRACT Rear-end collisions account
CITY SAFETY A SYSTEM ADDRESSING REAR-END COLLISIONS AT LOW SPEEDS Martin Distner Mattias Bengtsson Thomas Broberg Lotta Jakobsson Volvo Cars Sweden Paper Number 09-0371 ABSTRACT Rear-end collisions account
THE EURO NCAP WHIPLASH TEST
 THE EURO NCAP WHIPLASH TEST Michiel van Ratingen James Ellway Euro NCAP Belgium Matthew Avery Thatcham United Kingdom Peter Gloyns VSC, on behalf of ICRT United Kingdom Volker Sandner ADAC Germany Ton
THE EURO NCAP WHIPLASH TEST Michiel van Ratingen James Ellway Euro NCAP Belgium Matthew Avery Thatcham United Kingdom Peter Gloyns VSC, on behalf of ICRT United Kingdom Volker Sandner ADAC Germany Ton
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
