Case Study of Quality Improvement in Metrocrest Community Clinic Dallas, Texas August Diabetes Standard of Care Plan
|
|
|
- Avice Gillian Wilkerson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Study of Quality Improvement in Metrocrest Community Clinic Dallas, Texas August Diabetes Standard of Care Plan About the Clinic Page 1 Summary of Quality Improvement Project Page 2 General Q&A with Clinic Director Page 2 Q&A Specific to Quality Improvement Project Page 4 Appendicies of Supporting Documents - Appendix A. Metrocrest Patient Table Page 6 - Appendix B. Metrocrest Performance Improvement Evaluation Page 9 - Appendix C. Diabetic Education Checklist Page 11 About the Clinic Name of Clinic: Metrocrest Community Clinic Type of Clinic: Charitable Location: Dallas, TX Year Founded: 1993 (incorporated as 501(c)(3) in 1996) Budget: ~$300,000 Unduplicated patients: 2,164 Patient visits: 4,100 Paid staff: 5 FTEs: Executive Director 1 FTE; Physician 1 FTE; office manager 0.7 FTE, front office technician 1 FTE; certified medical assistant 1 FTE; and medical records technician 0.3 FTE Volunteers: 15 medical providers (Physicians: 9; Registered Nurses: 4; Ancillary personnel: 2). In addition, the clinic hosts externships for advanced practice nursing students (6 8 per year) and undergraduate nursing students from nearby college (up to 20 per year), as well as students from trade schools training for qualification as certified medical assistants, medical record management, and medical office management. Hours Open: 8:30 AM to 5:00 PM, Monday Friday, with one Saturday gynecology clinic per month. Specialty Clinics: Gynecology, 4 5 per month, by demand; Dermatology, one clinic per month (8 hours, 1:00 PM to 9:00 PM); Neurology clinic, 4 hour evening clinic once per month. Services: Internal medicine office visit; specialty clinics for gynecology, dermatology, neurology, and ear, nose, and throat; full laboratory; limited radiology testing; medical social services; patient and family education; language interpretation; health fairs, collaboration and referral to other services. Leadership: 18-member Board of Directors, Executive Director, and Medical Director For further information: Jane Hawkins, BS, RN jhawkins@metrocrestcommunityclinic.org Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 1
2 Summary of Quality Improvement Project The Problem: The increasing volume of patients with diabetes made it difficult to ensure that each client was being offered appropriate and equal service. The Approach: The clinic developed a standard, evidence-based plan of care for all diabetic patients. Each client newly enrolled in the diabetes management program is introduced to the plan of care, which sets forth what the client can expect from the program and the requirements for patient self-management. PDSA in Action: PLAN: A literature search of diabetes care was undertaken to identify the parameters of care in standard practice in the United States. DO: A planning committee was established to devise a standard plan of care for all diabetic patients. The written plan was implemented in Each current diabetic client was introduced to the program, including what the patient could expect from participating in the program and what level of participation was expected of the client. STUDY: The clinic tracks whether patient visits occur on a standardized schedule (i.e., every 3 months), the completeness of laboratory testing based on the national standard of care, and changes in physical findings. These results are compiled for individual patients and for all participants in the diabetes management program and then trended over time. The results are used to identify strengths and barriers to compliance with the program s parameters and patients ability to participate. ACT: The physicians utilize these findings to inform their provision of treatment modalities for each patient. Q & A i with Jane Hawkins, Executive Director, Metrocrest Community Clinic Quality Improvement Efforts at Your Clinic Q: What was the impetus for deciding to initiate improvement at your clinic? A: I was new to the field of non-profit health care delivery. As I began to learn about this brave new world, I had to have a system by which to measure the demands of operation and delivery of health care in a very lowbudget environment. Q: How were you able to achieve staff/provider/ volunteer/organizational buy-in to your QI initiative? A: I utilized information from my past clinical experience; collaboration with the team of amazing volunteer physicians, registered nurses, and community clinics; and literature searches. Q: What activities have been especially important to sustaining improvement? A: Continuous collection of data on individual patients, trended and utilized by the physician and care team, gives clear goals for future activities directed on the patient s behalf and the patient population in general. Q: Was leadership important to your improvement efforts? How so? A: As Executive/Clinical Director of the Metrocrest Community Clinic, it is my responsibility to devise programs of care and means of evaluation of the activities of our clinic operations, and report to the Medical Director and Board of Directors who oversee the clinic. I have the full support of the Board and Medical Director, who review these activities on a regular, formal basis. In addition, The Day Clinic Physician and the Medical Director participate in regular, informal conversations regarding the clinic operation, the focus of accurate measurement of clinic activity, and suggestions for focus studies. Q: Do you have an ongoing team that leads improvement in your organization? If so, please describe who is on it, how often they meet, and the structure for initiating improvements. A: Due to the small size of our clinic team of volunteers and employees, I have not been able to develop a consistent team to assist in the QI process. I have utilized college student volunteers to collect data and place information in various collection tools, such as spread sheets. With the time limitations of our volunteers, the quality of data collection has not always been consistent. In 2013, our clinic grew in volume and funding. We now have a 5 FTE staff. This excites me as the clinical leader. The processes for collection of all aspects of our clinic operation have been improved. The downside of the venture is that these employees have had no previous introduction to performance improvement (PI) through quality management or the many tools available for the process. The challenge is education and support in the early stages of a novice s experience. We are now at the point where almost everyone has been bitten by the PI Bug. i Questions were taken or adapted from Houck, S. (2004). What Works: Effective Tools and Case Studies to Improve Clinical Office Practice. Boulder, CO: HealthPress Publishing. Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 2
3 Q: How do you track and post results or outcomes? (These include operational, clinical, satisfaction, and financial) How do you select which metrics to use? Have you found it important to limit the number of metrics used? What metrics do you use? A: Microsoft Word and Excel are the system tools we use to record and evaluate information. We are still in the introductory phase of implementing Practice Fusion. This web-based EMR is useful and affordable. These elements are of equal importance in our budgetary situation. We will be fully operational as a paperless system in the future, but the timeline is subject to resources, both human and electronic. An accurate demographic database has been the most useful metric. Each client is registered in the system at the time of their first contact with our clinic. Any changes in their personal information, including adding a new diagnosis, change in allergy status, or simply a telephone number, are easily completed. This information is then available at each computer terminal. The various aspects of the EMR are populated as this information is available. Laboratory results are downloaded into the system at their point of origin. Q: What lessons have you learned during the QI process? If you were starting your improvement work now, what would you do differently? What would you do the same way? A: This is a hard question to answer. Each QI process in which I have participated has been both useful and challenging, for various reasons. Over some 20-plus years conducting Performance Improvement, Quality Management, I have learned how to cut to the chase when developing a QI study. Years ago, the entire process was quite intimidating. Now, when I see a need, I create a study tool and collect the information I need to make an accurate assessment of any situation. This is very useful when working with employees who have strong personal ideas and a narrow frame of vision. Utilization of the PI process can give structure to the team and minimize the issues that develop when everyone recognizes and problem or issue and tries to fix it by themselves. Q: To what do you attribute your success in your QI efforts? A: Perseverance. What started out as part of my job in the healthcare industry quite a few years ago now runs on autopilot in the background of my busy clinic, my busy life, and making future plans. Q: What advice do you have for other clinics that are new to QI? A: Sit down together and make a list of problems, ideas and goals. Take a little time to formulate this list before prioritizing the items. Be honest and ask the following questions: 1. Is this problem a People Problem? 2. Is this problem a Process Problem? 3. Is this problem a Resources Problem? 4. Is this problem a Permanent Concern? 5. Is this problem an Intermittent Problem? 6. Is this problem causing Harm? 7. Is this a problem that is a Need or just a Nuisance? 8. Is the problem one of time management, cost, or lack of proper training of the individuals performing the process? 9. How can the individuals participating in the QI/ PI/QM activity be inspired to properly participate in the activities required to conduct the study and activate the various steps of the measurement and improvement desired? Q: I ve heard clinics say, I don t have the time or I don t have the resources/staff to do QI. What would you say to a clinic that is reluctant to start using QI? A: 1. Start by answering the questions above, or similar concerns. 2. Create a simple tool for solving a simple problem with a quick turnaround to engage the team in finding an equitable and timely solution. 3. Implement the full Plan Do Study Act and continue to monitor the Act to evaluate the accuracy of the outcome study. Remember that the organized process of QI/PI/QM is quite intimidating to the novice. One must find value in the activity to usefully participate in and value the process. Q: What are the benefits and drawbacks of engaging in a QI process? A: The benefits of engaging in a QI process are many. The studies can be true indicators of outcome of effort. Outcomes measurement can be used to present an accurate picture of a problem, an accomplishment, or to promote a future goal. The drawbacks are the expense of time and personnel, especially when these commodities are in short supply. Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 3
4 Quality Improvement Initiative: Diabetes Standard of Care Plan Q: Can you give us a before and after portrait of the problem you wanted to address? A: Our care team was continually frustrated by our inability to meet our client s needs and to meet the client s perception of their illness without valid plan of care or funding for the provision of expensive supplies and medication. The barriers facing patients are many. Medical understanding of the condition may be influenced by: Time since the onset of the condition; Previous diabetic education provided to the patient at the time of the diagnosis and the intervening time; Language barrier; Cultural barriers related to dietary needs; and Patient s ability to pay for the supplies (medication, blood glucose testing strips, funds for office visits) required to treat their condition Care of the diabetic is a significant challenge, requiring time, resources and significant patient participation and commitment. While these barriers are common knowledge, a true evaluation must include trending over time for the individual and the program as a whole. We now routinely collect and monitor HgbA1c levels, and these data are used to create and modify an individualized plan of care. Grants for the diabetes management program were secured so that all laboratory tests are offered at no cost to the patient. Q: What aims did you set to address your problem? Were they measurable? A: The gold standard for the measurement of the management of the blood sugar of a diabetic is the laboratory test HemoglobinA1C. This measurement is collected every three months. The laboratory standard for the diagnosis of diabetes is less than 6.5 for tight control of the patient s condition. Another point of measure is the BMI (body mass index) over time. While the initial HemoglobinA1C is important, the second test is the true marker of the challenges facing the client. The physician creates a plan of care with the first visit (modified by the first HgbA1c testing) but really uses the next three months activity by the patient to firm up a treatment plan. Some clients respond quickly to their medication regimen, and compliance with a meal plan, exercise, and regular blood glucose monitoring. Others require significant drilling down into their daily habits including: medications administered, time of medications, episodes of blood glucose monitoring, exercise, rest, and other activities of daily living. Written flow records and graphs are very useful in demonstrating to the client the impact of their daily health practices. Q: What did you need to change? A: We needed to first establish a study sample (list of appropriate clients), create a data collection tool, and collect data points from the study sample group over time. The tool was created in Microsoft Excel. Q: Who was involved in the QI process? Who were the key players? Was leadership important? How so? A: The clinical team (Medical Director, Day Clinic Director and Clinic Director) was directly involved. Leadership was important, as the tools used had to be an accurate measure of the patient management/ participation of the clients, utilizing a standardized set of measures. Actual grants were written to assist in funding our diabetic management program. Total grant funding dedicated to the diabetes management program exceeds $12,000 per year. Q: What tools/templates/worksheets/diagrams/ instruments/charts/data/metrics did you use in your improvement efforts (in each of the PDSA stages)? A: Collection and trending of the laboratory test, HgbA1C, guides our efforts. Improvement is measured and trended by patient and across the diabetic patient population. This information is a great teaching tool for the clinician/patient when discussing the treatment regimen and success of the treatment. Q: What did you propose to do (want to change) to address the problem? A: We created a standard of care plan as a way to inspire and educate the individual patient about the importance of their role in the treatment of diabetes. Q: How did you go about testing the change(s)? A: Evaluation of the clients health records, including documentation of educational processes, compliance with medication administration, utilization of their daily blood glucose testing records, as well as continued serial monitoring of the laboratory tests, especially the HemoglobinA1C. Q: What were the results of your intervention? Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 4
5 A: The patient trending over time yields a bell curve, with a large majority of clients making significant progress in reducing HbgA1c levels. Within a six-month period, many patients HgbA1c levels were less than 7.0. Unfortunately, fewer than 50% of clients were able to sustain their improvement over time. All patients who are faithful in clinic attendance and behaviors (such as taking prescribed medications, meal planning and exercise regimens) are included in the study sample. Q: How did you spread the change? What are the lessons learned? A: The change was spread over our clientele by having the patients meet with the diabetic educator on a regular basis about addressing their personal challenges. It also became very apparent that the entire family of a client with diabetes has an impact on their ability to achieve success in self-management. The educational process involves other family members and communication in the patient s primary language, whenever possible. Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 5
6 Appendix A. Metrocrest Patient Table Patient Count Age at Report Run Medical Home DM HTN Lipids Thyroid First Date Seen Last Date Seen Episodic Hemoglobin A1c Measurements 1 61 yrs X X 05/19/11 01/18/ yrs X X 01/02/13 01/28/ yrs X X X 01/28/13 02/19/ yrs X X X X 09/20/11 03/05/ yrs X X X X 09/24/12 03/22/ yrs X X X 03/02/11 04/01/ yrs X X X 05/07/ yrs X X X 09/27/12 05/12/ yrs X X X X X 07/20/12 01/08/ yrs X X X 08/30/11 05/23/ yrs X X X X 11/03/11 05/24/ yrs dup X 05/29/13 05/29/ yrs X X X X 01/22/13 06/11/ yrs X X X X X 09/28/11 06/21/ yrs X X 10/25/11 06/27/ yrs X X X X 07/09/ yrs X X X X 10/25/11 07/11/ yrs X X X 04/15/11 07/23/ yrs X X X 02/16/12 08/12/ yrs X X X 07/29/09 08/13/ yrs X X X X X 08/07/12 08/19/ yrs X X X 04/24/12 08/26/ yrs X X X 02/14/12 08/30/ yrs X X X 03/02/11 09/02/ yrs X X X 01/25/13 09/06/ yrs X X X 07/24/13 09/16/ yrs X X 05/13/13 09/16/ yrs X X X X 01/18/11 09/20/ yrs X X X X 09/25/ yrs X X X X 03/17/11 09/26/ yrs X X 03/14/13 09/30/ yrs X X X 02/14/12 09/30/ yrs X X X 08/20/12 10/01/ yrs X X X 09/20/13 10/15/ yrs X X X 10/26/11 10/15/ yrs X X yrs X X X 06/20/13 10/15/ yrs X X X X X 09/07/13 10/15/ /18/13 10/25/ Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 6
7 Patient Count Age at Report Run Medical Home DM HTN Lipids Thyroid First Date Seen Last Date Seen Episodic Hemoglobin A1c Measurements yrs X X 01/10/13 10/28/ yrs X X X X 10/02/13 10/30/ yrs X X X X X 05/17/13 11/14/ yrs X X X 02/28/12 11/15/ yrs X X X X 06/24/09 11/20/ yrs X X X X 01/04/13 11/25/ yrs X X X X 01/02/13 11/26/ yrs X X X X X 08/01/13 11/26/ yrs X X X X 04/23/12 11/26/ yrs X X X 09/13/12 11/26/ yrs X X X 05/30/13 12/02/ yrs X X X 05/09/13 12/02/ yrs X X X X 03/24/11 12/03/ yrs X X 03/27/10 12/03/ yrs X X X X 05/08/13 12/04/ yrs X X X X X 05/02/13 12/04/ yrs X X X X 11/07/13 12/05/ yrs X X X X 05/24/12 12/10/ yrs X X X 05/05/11 12/10/ yrs X X X X 12/15/11 12/10/ yrs X X X X 06/13/11 12/11/ yrs X X X X 06/09/10 12/11/ yrs X X X 02/06/13 12/11/ yrs X X X X 09/28/11 12/11/ yrs X X X X 11/12/13 12/12/ yrs X X X X 06/29/11 12/12/ yrs X X X X 06/29/11 12/12/ yrs X X X X 09/27/12 12/13/ yrs X X X 01/25/12 12/13/ yrs X X X X 09/11/13 12/13/ yrs X X X X 05/01/13 12/13/ yrs X X X X X 04/05/12 12/13/ yrs X X X 09/16/09 12/13/ yrs X X X X 09/25/12 12/16/ yrs X X X X 09/10/12 12/16/ yrs X X X X 09/08/09 12/17/ yrs X X X X 03/07/11 12/17/ yrs X X X X 03/02/12 12/18/ /18/13 10/25/ Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 7
8 Patient Count Age at Report Run Medical Home DM HTN Lipids Thyroid First Date Seen Last Date Seen Episodic Hemoglobin A1c Measurements yrs x x x 09/28/11 12/19/ yrs x x x 09/12/13 12/19/ yrs x x x 07/05/12 12/19/ yrs x x x x 04/02/09 12/20/ yrs x x x 09/27/12 12/20/ yrs x x x x 08/23/12 12/30/ Clients reaching <7> HgbA1c 50/61% Clients not reaching <7> HgbA1c 32/39% Total Patients Completing Study 82/100% Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 8
9 Appendix B. Metrocrest Performance Improvement Evaluation Evaluation of Patient Progress toward Goal: A Hemoglobin A1c sustained at or below 7.0 mg/dl over serial laboratory testing. Premise: Using the Gold Standard of the Hemoglobin A1c Test to evaluate the clients at Metrocrest Community Clinic who have a diagnosis of diabetes, requiring diet, exercise as well as medication to sustain blood sugar levels under 150 through the daily life functioning in a private setting. Our clients are considered to be their own physician, in that they determine the activities of daily living: Eating, sleeping, exercise, and adjuncts such as taking medication to stabilize their daily blood sugars. As facilitators: Our clients have access to their internal medicine physician on a regular basis, usually determined to be at least every three months. They will receive access to medicine, affordable, and appropriate for their condition. If the patient requires insulin, the clinic will assist the client in the application for pharmacy assistance. Low cost testing supplies for blood sugar determination will be available to all diabetic clients. When the client cannot afford the cost for these supplies, they will be provided through medication grant funding. The diabetic client will have access to educational resources, in their preferred language, with printed and audio resources. During their clinic visits with the physician, an interpreter will facilitate communication between the physician, the patient and their family/meaningful others. Laboratory testing is available without cost to the patient on the physician s order and timely evaluation of the results are available for the adjustment of the patient s medicine regime or other needs. Barrier to success in the program are fear, denial and inability to understand medical instructions as first presented. The clinic staff invite family members to participate in the support and care of the patient. They are also offered screening for diabetes as this is a familial disease process. Prevention of diabetic complications is predicated on early diagnosis and treatment of the condition. Evaluation of the efficacy of the diabetic of the diabetic who is successful in the diabetic protocol is both subjective and objective. Objective: Subjective: Laboratory testing Review of blood sugar testing results Review of food diaries Return demonstrations of use of diabetic testing supplies, administration and review of medication logs kept by the client, and matching blood sugar results to the log. Interviews with the diabetic patient, their family (food preparation and access to appropriate food, in timely manner.) Working with the client to meet their ethnic diversity related to food, life style, exercise pattern. Perception of selfimage. In the time that Metrocrest Community Clinic has actively recognized the diabetic population seeking care in the Day Clinic, the yearly trending of laboratory findings has remained in a similar bell curve, with a trend toward moderate control of the HgbA1c in our clientele. We have some long-term patients who have remained in a stable, moderate control classification, despite continued efforts to recharge their diabetic self-care. Food selection, life style and a level of access that is better that any they have previously experienced are factors that continually appear in evaluation of the physician/ client relationship. When the physician begins to speak of insulin therapy as an adjunct to their care, some will seek a review of their disease self-knowledge. The clinic has always focused on inspiring our clients to follow medical advice, rather than striking fear into their reality. Unfortunately, implementation of insulin into the treatment regime is becoming more common. The monitoring of the active diabetics who did present for at least two serial HemablobinA1c tests is attached for review. The previous years reflect similar trends, with smaller numbers of clients participating. Addendum: August, After a successful monitoring of the control of blood pressures in our clients, a monitor will begin on September 1, 2014, performing a standardized foot exam on all our diabetic clients. Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 9
10 Metrocrest Community Clinic Final evaluation of all MCC Clients who have been Followed For Diabetes in 2013, but did not met all criteria for enrollment in the Diabetic Clinic. Most of these clients have been satisfactorily enrolled in the program or have been referred elsewhere for future care. This includes the 128 clients who did not complete the program expectations. Patient with diagnosis of Diabetes, enrolled at Metrocrest Community Clinic. Has at least two data points ( HgbA1c) lab tests with last 12 months. Diabetes is a primary diagnosis, with prescription of diabetic medication, oral or parenteral. Patient has a glucose meter and tests the blood sugar or a regular or intermittent basis. Documentation of clinic visits are reflected in the medical record with physician notes, laboratory testing. Client may or may not show a positive trend in HgbA1c laboratory testing, but must reflect an effort to follow the physician s advice. A Hemoglobin A1c of 7.0 mg/dl or below is considered a patient with a controlled blood sugar. A Hemoglobin A1c of 7.5 mg/dl to 8.0 mg/dl is considered a patient who is marginally controlling their blood sugar. A Hemoglobin A1c of 8.5mg/dL or greater is considered an uncontrolled blood sugar. Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 10
11 Appendix C. Diabetic Education Checklist METROCREST COMMUNITY CLINIC Clínica de Medicina Familiar Metrocrest Comprehensive Diabetes Checklist Lista de verificación de la diabetes Patient Name: Nombre del paciente: Type of Diabetes: Tipo de Diabetes: Have you had any diabetic education: Ha recibido algún tipo de educación diabética: Date of Enrollment: Fecha de inscripción: Date of Diagnosis: Fecha de Diagnostico: When: Cuando: Enrollment in this educational service is a condition of patient care at Metrocrest Community Clinic. Attendance at the clinic at the interval requested by my physician is a condition of participation. I have been advised that I may request additional educational information regarding my medical condition and how to take care of myself. La inscripción en este servicio educativo es una condición de la atención al paciente en la Clínica de Medicina Familiar Metrocrest. La asistencia a la clínica en el intervalo solicitado por mi médico es una condición para la participación. Me han aconsejado que puedo solicitar información educativa adicional con respecto a mi estado de salud y cómo cuidar de mí mismo. TOPIC Tema Materials Materiales Date Fecha Verbalized Understanding Conocimiento Verbalizado Meal Planning Planificación de alimentos Create your own meal plan Crear propio plan de alimentos Discuss special foods and occasions Hablar sobre comida y ocasiones especiales Portion Control Control de porciónes Low cholesterol, low-fat guidelines Guías para bajo colesterol, baja grasa Fitting sugar into the meal plan Acomodando el azúcar en los alimentos Label reading Leer etiquetas de comida Alcohol Alcohol Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 11
12 Appendix C. Diabetic Education Checklist METROCREST COMMUNITY CLINIC Clínica de Medicina Familiar Metrocrest TOPIC Tema Materials Materiales Date Fecha Verbalized Understanding Conocimiento Verbalizado Self monitoring of blood glucose Auto supervisión de glucosa en la sangre Blood glucose goals Metas de glucosa en la sangre How to use a meter to guarantee accurate results Como usar el medidor para garantizar resultados precisos Monitoring schedule Monitorear su tiempo How to clean meter Como limpiar su medidor Storing supplies Artículos de almacenamiento Interpreting blood glucose values and making dedisions in diabetes treatment plan Interpretando valores de glucosa en la sangre y hacer decisiones en el tratamiento de diabetes Use of insulin or diabetes pills Uso de insulina o pastillas para la diabetes Action and side effects of medication Acción y efectos secundarios de medicamentos Timing and treatment schedule El tiempo y régimen de tratamiento Insulin injection technique Técnica de inyección de insulina Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 12
13 Appendix C. Diabetic Education Checklist METROCREST COMMUNITY CLINIC Clínica de Medicina Familiar Metrocrest TOPIC Tema Materials Materiales Date Fecha Verbalized Understanding Conocimiento Verbalizado Site rotation and schedule for injection Sitio de rotación y horario para la inyección Proper storage, refrigeration and disposal of supplies Forma adecuada para almacenar, refrigerar y desechar artículos What to do for missed doses Qué hacer con doces olvidadas Exercise Ejercicio Exercise guidelines: how long, how hard, how often and when? Guías de ejercicio: duración, intensidad, frecuencia y cuando? Snacking adjustments Ajustes de bocadillos Preventing high and low blood glucose Prevenir alta y baja glucosa en la sangre Knowledge of high and low blood glucose: Conocimiento de alta y baja glucosa en sangre Factors that cause high and low blood glucose Factores que causan alta y baja glucosa en la sangre Symptoms Síntomas Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 13
14 Appendix C. Diabetic Education Checklist METROCREST COMMUNITY CLINIC Clínica de Medicina Familiar Metrocrest TOPIC Tema Materials Materiales Date Fecha Verbalized Understanding Conocimiento Verbalizado How to treat Como tratar How to prevent Como prevenir When to call a healthcare provider Cuando llamar a un proveedor de salud Factors that cause high and low blood glucose Factores que causan alta y baja glucosa en la sangre Symptoms Síntomas How to treat Como tratar How to prevent Como prevenir When to call a healthcare provider Cuando llamar a un proveedor de salud Footcare Cuidado de los pies Daily foot care Cuidado diario de los pies Emergency treatment of cuts, sores, abrasions, blisters Tratamiento de emergencia para cortaduras, llagas, abrasiones, ampollas How to do a proper foot exam Como hacer un examen adecuado de los pies Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 14
15 Appendix C. Diabetic Education Checklist METROCREST COMMUNITY CLINIC Clínica de Medicina Familiar Metrocrest TOPIC Tema Materials Materiales Date Fecha Verbalized Understanding Conocimiento Verbalizado Proper footwear and sick day management Calzado adecuado y administración de días de enfermedad Preventing life-threatening problems La prevención de problemas amenazantes What to eat and drink Que comer y tomar Monitoring and medication schedule Horario de medicamento y monitoreo When to call the doctor Cuando llamar al doctor Urine testing for ketones (for insulin users only) Prueba de orina para detectar cetonas(para usuarios de insulina solamente) When and how to check for ketones Cuando y como revisar cetonas What ketones mean Significado de cetonas When to call the doctor Cuando llamar al doctor Special Topics Temas Especiales Meal Plan Plan alimenticio Skills in taking medicine Habilidades para tomar medicamentos Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 15
16 Appendix C. Diabetic Education Checklist METROCREST COMMUNITY CLINIC Clínica de Medicina Familiar Metrocrest TOPIC Tema Materials Materiales Date Fecha Verbalized Understanding Conocimiento Verbalizado Technique Técnica Treatment of high and low blood glucose Tratamiento de alta y baja glucosa en la sangre Sick day management Administración de días de enfermedad Risk factors for health problems Factores de riesgo para problemas de salud Foot Care Treatment Tratamiento de cuidado para los pies Tests you should have at least once a year or more Análisis que debe de tener al menos una vez al año o más A1C (2-4 times per year) A1C ( 2-4 veces al año) Kidney function Función de riñones Cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides (lipids) Colesterol, LDL, HDL, y triglicéridos (lípidos) Urinary microalbumin/creatinine ratio yearly Urinaria de micro albúmina / creatinina ración anual GFR ( Kidney function test) GFR (Examen de función renal) Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 16
17 Appendix C. Diabetic Education Checklist METROCREST COMMUNITY CLINIC Clínica de Medicina Familiar Metrocrest TOPIC Tema Materials Materiales Date Fecha Verbalized Understanding Conocimiento Verbalizado Dilated eye exam Examen de dilatación de pupilas Blood Pressure Presión arterial General Health Exam Examen de salud general Women: Pap test Mujeres: Papanicolaou Women: Breast Exam Mujeres: Examen de los senos Women: Mammogram: at age 40 and yearly thereafter Mujeres: Monograma: A los 40años y después cada año Men: Hombres: Foot Exam Examen de los pies I understand that I may receive these services in my community. Yo entiendo que puedo recibir estos servicios en mi comunidad. Metrocrest Community Clinic is a resource for diabetic care. La Clínica Medica Metrocrest esta un recursos para cuidado diabético. I will attend my medical appointment. Yo asistiré mi cita médica. I will follow the advice of my physician Yo voy a seguir los consejos de mi doctor. I will bring my meter and my medication to each clinic Yo voy a traer mi medidor y medicamento a cada clínica. I will bring my meter to the clinic for downloading at least once per month, or more often. Yo voy a traer mi medidor a la clínica para la descarga al menos una vez al mes o más. I will notify my clinic when I cannot afford to purchase my medication or testing strips. Yo avisare a mi clínica cuando no tenga los recursos para comprar mi medicamento o tiras de prueba. Name: Nombre: Date Signed: Fecha de la firma: Case Study: Metrocrest Community Clinic 17
INFORMATIONAL NOTICE
 Rod R. Blagojevich, Governor Barry S. Maram, Director 201 South Grand Avenue East Telephone: (217) 782-3303 Springfield, Illinois 62763-0002 TTY: (800) 526-5812 DATE: March 4, 2008 INFORMATIONAL NOTICE
Rod R. Blagojevich, Governor Barry S. Maram, Director 201 South Grand Avenue East Telephone: (217) 782-3303 Springfield, Illinois 62763-0002 TTY: (800) 526-5812 DATE: March 4, 2008 INFORMATIONAL NOTICE
I have diabetes. In case of emergency, please call: Healthcare Provider s Name. Name. Telephone. Address. Hospital. City. Pharmacy.
 Self-Care Diary Name Address City Healthcare Provider s Name Hospital State ZIP I have diabetes. In case of emergency, please call: Name Pharmacy Diabetes Educator s Name Address 1 Small Steps to Managing
Self-Care Diary Name Address City Healthcare Provider s Name Hospital State ZIP I have diabetes. In case of emergency, please call: Name Pharmacy Diabetes Educator s Name Address 1 Small Steps to Managing
Case Study of Quality Improvement in Shepherd s Hand Free Clinic Whitefish, Montana. Improving Care for Diabetic Patients
 Case Study of Quality Improvement in Shepherd s Hand Free Clinic Whitefish, Montana Improving Care for Diabetic Patients May 2014 1 2 3 4 5 About the Clinic Page 1 Summary of Quality Improvement Project
Case Study of Quality Improvement in Shepherd s Hand Free Clinic Whitefish, Montana Improving Care for Diabetic Patients May 2014 1 2 3 4 5 About the Clinic Page 1 Summary of Quality Improvement Project
Diabetes Health Plan Member Guide
 Diabetes Health Plan Member Guide Welcome UnitedHealthcare Diabetes Health Plan Welcome to the Diabetes Health Plan. Our goal is to ensure you are getting the most out of your program. Please use this
Diabetes Health Plan Member Guide Welcome UnitedHealthcare Diabetes Health Plan Welcome to the Diabetes Health Plan. Our goal is to ensure you are getting the most out of your program. Please use this
Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire
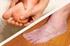 Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire Name: Date: Date of Birth: / / Gender: F M Address: Street City State Zip Phone: Home ( ) Work: ( ) Mobile: ( ) Ethnic Background: White/Caucasian Black/A-A Hispanic
Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire Name: Date: Date of Birth: / / Gender: F M Address: Street City State Zip Phone: Home ( ) Work: ( ) Mobile: ( ) Ethnic Background: White/Caucasian Black/A-A Hispanic
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
 Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
More information >>> HERE <<<
 More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/diabetes10/pdx/monc/ Tags: best way to get download todo
More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/diabetes10/pdx/monc/ Tags: best way to get download todo
Population Health Management Program
 Population Health Management Program Program (formerly Disease Management) is dedicated to improving our members health and quality of life. Our Population Health Management Programs aim to improve care
Population Health Management Program Program (formerly Disease Management) is dedicated to improving our members health and quality of life. Our Population Health Management Programs aim to improve care
DAMAR MEDICAL CENTER, INC
 PATIENT INFORMATION TODAY S DATE: / / (INFORMACION DEL PACIENTE) MES/DIA /AÑO: / / PATIENT S NAME: NOMBRE Y APELLIDO: D.O.B.: / / FECHA DE NACIMIENTO / / ADDRESS: CITY: ZIP CODE DIRECCION CIUDAD: CODIGO
PATIENT INFORMATION TODAY S DATE: / / (INFORMACION DEL PACIENTE) MES/DIA /AÑO: / / PATIENT S NAME: NOMBRE Y APELLIDO: D.O.B.: / / FECHA DE NACIMIENTO / / ADDRESS: CITY: ZIP CODE DIRECCION CIUDAD: CODIGO
UMA Diabetes Self-Care Log Book
 BRING THIS WITH YOU ON EVERY VISIT UMA Diabetes Self-Care Log Book Name MY INSTRUCTIONS FOR TESTNG MY BLOOD GLUCOSE My Doctor s name My Nurse s name Check your blood glucose: before breakfast before lunch
BRING THIS WITH YOU ON EVERY VISIT UMA Diabetes Self-Care Log Book Name MY INSTRUCTIONS FOR TESTNG MY BLOOD GLUCOSE My Doctor s name My Nurse s name Check your blood glucose: before breakfast before lunch
Medicare. Orientation Guide
 Medicare Orientation Guide Your Medicare Orientation Guide At MCS Classicare (HMO), we take care of you so you feel better every day. That s why we want to get you familiar and provide you with the tools
Medicare Orientation Guide Your Medicare Orientation Guide At MCS Classicare (HMO), we take care of you so you feel better every day. That s why we want to get you familiar and provide you with the tools
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Chapter 1 The Importance of Education in Diabetes
 Chapter 1 The Importance of Education in Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD DeAnn Johnson, RN, BSN, CDE INTRODUCTION Families and children need to understand as much as possible about diabetes. A shorter book,
Chapter 1 The Importance of Education in Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD DeAnn Johnson, RN, BSN, CDE INTRODUCTION Families and children need to understand as much as possible about diabetes. A shorter book,
D I D Y O U K N O W? D I A B E T E S R E S O U R C E G U I D E. Blindness Heart Disease Strokes Kidney Failure Amputation
 D I D Y O U K N O W? D I A B E T E S R E S O U R C E G U I D E Diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to Blindness Heart Disease Strokes Kidney Failure Amputation Diabetes kills almost 210,000 people
D I D Y O U K N O W? D I A B E T E S R E S O U R C E G U I D E Diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to Blindness Heart Disease Strokes Kidney Failure Amputation Diabetes kills almost 210,000 people
manage A TRUEinsight Guide High and Low Blood Glucose Levels
 monitor track manage A TRUEinsight Guide manage High and Low Blood Glucose Levels High and low blood glucose A TRUEinsight T M Guide to help you recognize and understand the symptoms of high and low blood
monitor track manage A TRUEinsight Guide manage High and Low Blood Glucose Levels High and low blood glucose A TRUEinsight T M Guide to help you recognize and understand the symptoms of high and low blood
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes
 MEETING YOUR GOALS An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes MEETING YOUR GOALS This brochure was designed to help you understand the health goals to live a healthy lifestyle with type
MEETING YOUR GOALS An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes MEETING YOUR GOALS This brochure was designed to help you understand the health goals to live a healthy lifestyle with type
type 2 diabetes and you Live Well with Diabetes
 type 2 diabetes and you Live Well with Diabetes Basic Guidelines for Good Diabetes Care Check your blood sugar regularly At every doctor visit: Review your blood sugar records Blood pressure Weight Foot
type 2 diabetes and you Live Well with Diabetes Basic Guidelines for Good Diabetes Care Check your blood sugar regularly At every doctor visit: Review your blood sugar records Blood pressure Weight Foot
Diabetes, Type 2. RelayClinical Patient Education Sample Topic Diabetes, Type 2. What is type 2 diabetes? How does it occur?
 What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
The Triple Aim. Two System Changes. PCMH Short Definition. Doctors Employed by Hospitals Exceed 100,000
 Doctors Employed by Hospitals Exceed 100,000 You May Be Hiring Physicians Is Your Primary Care Strategy Successful? 2004 64, 392 full time physicians were employed by hospitals In 2011 More than 100,000
Doctors Employed by Hospitals Exceed 100,000 You May Be Hiring Physicians Is Your Primary Care Strategy Successful? 2004 64, 392 full time physicians were employed by hospitals In 2011 More than 100,000
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes?
 Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
Using the Flip Chart to Teach
 Using the Flip Chart to Teach Learning Objectives: At the conclusion of this presentation, you should be able to: State being familiar and comfortable with the Diabetes Survival Skills Flip-Chart teaching
Using the Flip Chart to Teach Learning Objectives: At the conclusion of this presentation, you should be able to: State being familiar and comfortable with the Diabetes Survival Skills Flip-Chart teaching
To help stay on schedule, keep your own written record of when you get the tests and exams. Include your goals and test results.
 Oregon Diabetes Resource Bank Handouts to help people with diabetes 1 KNOW which tests, exams, and other care you should be getting. According to national standards for quality care for diabetes, there
Oregon Diabetes Resource Bank Handouts to help people with diabetes 1 KNOW which tests, exams, and other care you should be getting. According to national standards for quality care for diabetes, there
Borgess Diabetes Center PATIENT REGISTRATION/DEMOGRAPHICS
 Borgess Diabetes Center PATIENT REGISTRATION/DEMOGRAPHICS Please complete the following form by filling in the blanks or by circling the answer provided. Last Name: First Name M.I. Address: City, State,
Borgess Diabetes Center PATIENT REGISTRATION/DEMOGRAPHICS Please complete the following form by filling in the blanks or by circling the answer provided. Last Name: First Name M.I. Address: City, State,
MEDICARE MYSTERY. Taking the OUT OF. Your how-to guide for finding the right plan for your needs
 Taking the MYSTERY OUT OF MEDICARE Your how-to guide for finding the right plan for your needs S6506_071015_B01a CMS Accepted 08/15/2015 H0302_565_2016 CMS Accepted 08/15/2015 An independent licensee of
Taking the MYSTERY OUT OF MEDICARE Your how-to guide for finding the right plan for your needs S6506_071015_B01a CMS Accepted 08/15/2015 H0302_565_2016 CMS Accepted 08/15/2015 An independent licensee of
A Simplified Approach to Initiating Insulin. 4. Not meeting glycemic goals with oral hypoglycemic agents or
 A Simplified Approach to Initiating Insulin When to Start Insulin: 1. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels >250 mg/dl or 2. Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) >10% or 3. Random plasma glucose consistently >300 mg/dl
A Simplified Approach to Initiating Insulin When to Start Insulin: 1. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels >250 mg/dl or 2. Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) >10% or 3. Random plasma glucose consistently >300 mg/dl
Chronic Disease Initiative: Final Report February 2014
 U.S. Medical Assistance Program Chronic Disease Initiative: Final Report February 2014 Abstract Between vember 2011 and December 2013, the U.S. Medical Assistance Program at AmeriCares piloted an effort,
U.S. Medical Assistance Program Chronic Disease Initiative: Final Report February 2014 Abstract Between vember 2011 and December 2013, the U.S. Medical Assistance Program at AmeriCares piloted an effort,
manage A TRUEinsight Guide Blood Glucose Monitoring and Diabetes
 monitor track manage A TRUEinsight Guide manage Blood Glucose Monitoring and Diabetes The importance of monitoring This TRUEinsight T M guide provides useful information about blood glucose monitoring.
monitor track manage A TRUEinsight Guide manage Blood Glucose Monitoring and Diabetes The importance of monitoring This TRUEinsight T M guide provides useful information about blood glucose monitoring.
Fall 2015 Health & Family Newsletter
 Fall 2015 Health & Family Newsletter In This Issue Improving Services to Molina Healthcare Members... 1-2 Where to Find Answers to Drug Benefits...3 ID Cards...3 Protecting Your Privacy... 4-5 Prevent
Fall 2015 Health & Family Newsletter In This Issue Improving Services to Molina Healthcare Members... 1-2 Where to Find Answers to Drug Benefits...3 ID Cards...3 Protecting Your Privacy... 4-5 Prevent
Healthy at Heart FEELING GOOD. Reduce Your CV Risk. It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Issue 3
 Issue 3 Healthy at Heart Reduce Your CV Risk FEELING GOOD It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Inside: Tips for staying active and feeling good all over Speak to your healthcare provider before
Issue 3 Healthy at Heart Reduce Your CV Risk FEELING GOOD It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Inside: Tips for staying active and feeling good all over Speak to your healthcare provider before
Final Report Format. Follow-Up Activities to EHS/HS State/Territorial Oral Health Forum
 Final Report Format Follow-Up Activities to EHS/HS State/Territorial Oral Health Forum State /Territory: Maryland Person submitting report: Linda Zang Activities originally proposed and how they relate
Final Report Format Follow-Up Activities to EHS/HS State/Territorial Oral Health Forum State /Territory: Maryland Person submitting report: Linda Zang Activities originally proposed and how they relate
Let s Talk About Meters and Meds. Adapted for Upstate Medical University by: Kristi Shaver, BS, RN, CDE, MS-CNS Student (2014) January 2014
 Let s Talk About Meters and Meds Adapted for Upstate Medical University by: Kristi Shaver, BS, RN, CDE, MS-CNS Student (2014) January 2014 How to monitor diabetes control: Hemoglobin A 1 C, or just A 1
Let s Talk About Meters and Meds Adapted for Upstate Medical University by: Kristi Shaver, BS, RN, CDE, MS-CNS Student (2014) January 2014 How to monitor diabetes control: Hemoglobin A 1 C, or just A 1
REFUSAL OF CARE AND/OR TRANSPORTATION
 Page 1 REFUSAL OF CARE AND/OR TRANSPORTATION APPROVED: EMS Medical Director EMS Administrator 1. Purpose: 1.1 To determine when a person is identified as a patient in the EMS system. 1.2 To establish a
Page 1 REFUSAL OF CARE AND/OR TRANSPORTATION APPROVED: EMS Medical Director EMS Administrator 1. Purpose: 1.1 To determine when a person is identified as a patient in the EMS system. 1.2 To establish a
Diabetes The Basics. What is Diabetes? How does sugar get into your cells? Type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes. Why control Diabetes?
 Diabetes The Basics What is Diabetes? Diabetes is when there is too much sugar in your blood. Sugar from food you eat and drink stays in your blood instead of going into the cells in your body. The cells
Diabetes The Basics What is Diabetes? Diabetes is when there is too much sugar in your blood. Sugar from food you eat and drink stays in your blood instead of going into the cells in your body. The cells
UNDERSTANDING BLOOD SUGAR
 UNDERSTANDING BLOOD SUGAR The best way to stay healthy with diabetes is to control the level of sugar in your blood. The medical word for sugar in the blood or blood sugar is glucose. Your goal is to keep
UNDERSTANDING BLOOD SUGAR The best way to stay healthy with diabetes is to control the level of sugar in your blood. The medical word for sugar in the blood or blood sugar is glucose. Your goal is to keep
WhatHow To Choose A Good Looking Online Stock Broker
 Additional details >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/diabetes10/pdx/ftpl3343/ Tags: online, how to get todo lo que tengo
Additional details >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/diabetes10/pdx/ftpl3343/ Tags: online, how to get todo lo que tengo
Type 2 diabetes Definition
 Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Institute of Applied Health Sciences. University of Aberdeen DATABASE REVIEW. Grampian University. Hospitals NHS Trust GRAMPIAN DIABETES
 DATABASE REVIEW Grampian University Hospitals NHS Trust GRAMPIAN DIABETES SERVICES DATABASE Page 1 Contents Contents 2 Introduction 3 History 3 Overview of Database 3 Database Structure 4 Main Table Summary
DATABASE REVIEW Grampian University Hospitals NHS Trust GRAMPIAN DIABETES SERVICES DATABASE Page 1 Contents Contents 2 Introduction 3 History 3 Overview of Database 3 Database Structure 4 Main Table Summary
Nicholas C. Lambrou, M.D., LLC 6200 Sunset Drive, STE 502, Miami, Florida 33143 4306 Alton Road, 3 rd Floor, Miami Beach, Florida 33140
 DATE: Fecha: DRIVER'S LICENSE# Numero De Licencia De Conducir: PATIENT NAME: BIRTH DATE: Nombre del paciente Fecha de nacimiento HOME ADDRESS: SOCIAL SECURITY: Direccion del hogar: Seguro Social CITY/STATE/ZIP:
DATE: Fecha: DRIVER'S LICENSE# Numero De Licencia De Conducir: PATIENT NAME: BIRTH DATE: Nombre del paciente Fecha de nacimiento HOME ADDRESS: SOCIAL SECURITY: Direccion del hogar: Seguro Social CITY/STATE/ZIP:
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Health Professional s. Guide to INSULIN PUMP THERAPY
 Health Professional s Guide to INSULIN PUMP THERAPY Table of Contents Introduction Presenting Insulin Pump Therapy to Your Patients When Your Patient Chooses the Pump Estimates for Starting Insulin Pump
Health Professional s Guide to INSULIN PUMP THERAPY Table of Contents Introduction Presenting Insulin Pump Therapy to Your Patients When Your Patient Chooses the Pump Estimates for Starting Insulin Pump
Summary of Benefits. Blue Cross Community Integrated Care Plan (ICP) SM. January 1, 2015 - December 31, 2015
 Blue Cross Community Integrated Care Plan (ICP) SM Summary of Benefits January 1, 2015 - December 31, 2015 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Illinois, a Division of Health Care Service Corporation, a Mutual
Blue Cross Community Integrated Care Plan (ICP) SM Summary of Benefits January 1, 2015 - December 31, 2015 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Illinois, a Division of Health Care Service Corporation, a Mutual
Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1
 Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 What is type 1 diabetes mellitus? Type 1 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body produces little or no insulin. The lack of insulin causes the level of sugar in your
Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 What is type 1 diabetes mellitus? Type 1 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body produces little or no insulin. The lack of insulin causes the level of sugar in your
Your child has been scheduled for an appointment in Diabetes Clinic of the Children s Hospital University of Illinois
 To the Parent/Guardian of: Welcome to the Diabetes Clinic! Your child has been scheduled for an appointment in Diabetes Clinic of the Children s Hospital University of Illinois on: at: with: We have enclosed
To the Parent/Guardian of: Welcome to the Diabetes Clinic! Your child has been scheduled for an appointment in Diabetes Clinic of the Children s Hospital University of Illinois on: at: with: We have enclosed
after meals Monitoring: Control your the Power to bedtime before meals ActiveCare Basics ActiveCare Basics
 ActiveCare Basics This pamphlet is an educational resource published for participants in the Diabetes ActiveCare Program through Prescription Solutions. To order your diabetes testing supplies, call toll-free
ActiveCare Basics This pamphlet is an educational resource published for participants in the Diabetes ActiveCare Program through Prescription Solutions. To order your diabetes testing supplies, call toll-free
MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS
 BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
Analysis of the Impact Weekly Diabetes Education Class Has On the Health of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Analysis of the Impact Weekly Diabetes Education Class Has On the Health of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 By Trang Lu Master of Physician Assistant Practice (MPAP), 2014, Keck School of Medicine
Analysis of the Impact Weekly Diabetes Education Class Has On the Health of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 By Trang Lu Master of Physician Assistant Practice (MPAP), 2014, Keck School of Medicine
SCHOOL DISTRICT #22 VERNON DIABETES POLICY
 SCHOOL DISTRICT #22 VERNON DIABETES POLICY A student with diabetes does not automatically qualify for additional support. The student may qualify as a temporary D category (chronic health) after diagnosis
SCHOOL DISTRICT #22 VERNON DIABETES POLICY A student with diabetes does not automatically qualify for additional support. The student may qualify as a temporary D category (chronic health) after diagnosis
HealthCare Partners of Nevada. Heart Failure
 HealthCare Partners of Nevada Heart Failure Disease Management Program 2010 HF DISEASE MANAGEMENT PROGRAM The HealthCare Partners of Nevada (HCPNV) offers a Disease Management program for members with
HealthCare Partners of Nevada Heart Failure Disease Management Program 2010 HF DISEASE MANAGEMENT PROGRAM The HealthCare Partners of Nevada (HCPNV) offers a Disease Management program for members with
Gayle Curto, RN, BSN, CDE Clinical Coordinator
 Gayle Curto, RN, BSN, CDE Clinical Coordinator INTRODUCTION Historical Program Overview Leadership Team Mission Statement Diabetes Center Demographics for 2011 Older Adult Population HISTORICAL PROGRAM
Gayle Curto, RN, BSN, CDE Clinical Coordinator INTRODUCTION Historical Program Overview Leadership Team Mission Statement Diabetes Center Demographics for 2011 Older Adult Population HISTORICAL PROGRAM
Diabetes Self Management Training Insulin Pump Follow Up
 701 East Marshall Street, West Chester, PA 19380 www.chestercountyhospital.org 610.431.5000 Diabetes Self Management Training Insulin Pump Follow Up Patient Name: Visit Date: Time: To prepare for your
701 East Marshall Street, West Chester, PA 19380 www.chestercountyhospital.org 610.431.5000 Diabetes Self Management Training Insulin Pump Follow Up Patient Name: Visit Date: Time: To prepare for your
Medical Regimen Adherence in the Management of Diabetes: What Psychologists Need to Know
 Medical Regimen Adherence in the Management of Diabetes: What Psychologists Need to Know Suzanne Bennett Johnson Distinguished Research Professor Florida State University College of Medicine 2012 President,
Medical Regimen Adherence in the Management of Diabetes: What Psychologists Need to Know Suzanne Bennett Johnson Distinguished Research Professor Florida State University College of Medicine 2012 President,
Managing the Diabetes Patient. Dan Kremer, RN, BSN Diabetes Nurse Educator
 Managing the Diabetes Patient Dan Kremer, RN, BSN Diabetes Nurse Educator Objectives Referring & assessing the inpatient Address the needed diabetes education for the patients survival skills Problem solving
Managing the Diabetes Patient Dan Kremer, RN, BSN Diabetes Nurse Educator Objectives Referring & assessing the inpatient Address the needed diabetes education for the patients survival skills Problem solving
Anchor Bay School District Diabetic Medical Care Plan. Student Name Date Grade Teacher
 Rev: 4/2009 Anchor Bay School District Diabetic Medical Care Plan Place Child s Picture Here Student Name Date Grade Teacher Emergency Contact information (Please list in order to be called) #1 Parent
Rev: 4/2009 Anchor Bay School District Diabetic Medical Care Plan Place Child s Picture Here Student Name Date Grade Teacher Emergency Contact information (Please list in order to be called) #1 Parent
Integrating Self Management Supports in Primary Care
 Integrating Self Management Supports in Primary Care Support for this product was provided by a grant from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation in Princeton, New Jersey, 2009 Objectives: To describe key
Integrating Self Management Supports in Primary Care Support for this product was provided by a grant from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation in Princeton, New Jersey, 2009 Objectives: To describe key
Blood Glucose Management
 Blood Glucose Management What Influences Blood Sugar Levels? There are three main things that influence your blood sugar: Nutrition Exercise Medication What Influences Blood Sugar Levels? NUTRITION 4 Meal
Blood Glucose Management What Influences Blood Sugar Levels? There are three main things that influence your blood sugar: Nutrition Exercise Medication What Influences Blood Sugar Levels? NUTRITION 4 Meal
Nutrition. Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT
 1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
POLICY. 2015 7513 1 of 5. Students ADMINISTRATION OF MEDICATION
 1 of 5 ADMINISTRATION OF MEDICATION The school's registered professional nurse may administer medication to a student during the school day under certain conditions. who have been determined by the school
1 of 5 ADMINISTRATION OF MEDICATION The school's registered professional nurse may administer medication to a student during the school day under certain conditions. who have been determined by the school
Fecha: 04/12/2010. New standard treatment for breast cancer at early stages established
 New standard treatment for breast cancer at early stages established London December 04, 2010 12:01:13 AM IST Spanish Oncology has established a new standard treatment for breast cancer at early stages,
New standard treatment for breast cancer at early stages established London December 04, 2010 12:01:13 AM IST Spanish Oncology has established a new standard treatment for breast cancer at early stages,
QUALITY OF LIFE WITH DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 QUALITY OF LIFE WITH DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney
QUALITY OF LIFE WITH DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney
Diabetes and Your Kidneys
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
Implementing Home Blood Pressure Monitoring In Your Practice A Practical Guide
 Implementing Home Blood Pressure Monitoring In Your Practice A Practical Guide Home blood pressure monitoring offers a useful tool for the management of blood pressure, for both patients and healthcare
Implementing Home Blood Pressure Monitoring In Your Practice A Practical Guide Home blood pressure monitoring offers a useful tool for the management of blood pressure, for both patients and healthcare
DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study
 DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What
DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes
 Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
The Joint Commission Advanced DSC Certification for Inpatient Diabetes Care
 The Joint Commission Advanced DSC Certification for Inpatient Diabetes Care November 12, 2013 Caroline Isbey RN, MSN, CDE Associate Director Teresa Gomez Associate Project Director Specialist-SSM Carol
The Joint Commission Advanced DSC Certification for Inpatient Diabetes Care November 12, 2013 Caroline Isbey RN, MSN, CDE Associate Director Teresa Gomez Associate Project Director Specialist-SSM Carol
2. What Should Advocates Know About Diabetes? O
 2. What Should Advocates Know About Diabetes? O ften a school district s failure to properly address the needs of a student with diabetes is due not to bad faith, but to ignorance or a lack of accurate
2. What Should Advocates Know About Diabetes? O ften a school district s failure to properly address the needs of a student with diabetes is due not to bad faith, but to ignorance or a lack of accurate
Health Plans That Fit Your Life 2016
 Health Plans That Fit Your Life 2016 Maine 121415-02-0004 Find the one that s right for you. Certified by the Health Insurance Marketplace My husband and I both work for ourselves so Health Options has
Health Plans That Fit Your Life 2016 Maine 121415-02-0004 Find the one that s right for you. Certified by the Health Insurance Marketplace My husband and I both work for ourselves so Health Options has
Instructor Application for Certificate Renewal
 Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) Promotor(a)/Community Health Worker Training and Certification Program Instructor Application for Certificate Renewal Note: There is no cost to renew your
Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) Promotor(a)/Community Health Worker Training and Certification Program Instructor Application for Certificate Renewal Note: There is no cost to renew your
Medical Administrative Assistant (Clinical and Administrative Support Team Member) 37.5 hours per week, permanent role
 Medical Administrative Assistant (Clinical and Administrative Support Team Member) 37.5 hours per week, permanent role South East Toronto Family Health Team South East Toronto Family Health Team (SETFHT)
Medical Administrative Assistant (Clinical and Administrative Support Team Member) 37.5 hours per week, permanent role South East Toronto Family Health Team South East Toronto Family Health Team (SETFHT)
How to get the most from your UnitedHealthcare health care plan.
 How to get the most from your UnitedHealthcare health care plan. Your UnitedHealthcare health care plan includes many features and benefits that help you get the care you need and enjoy better overall
How to get the most from your UnitedHealthcare health care plan. Your UnitedHealthcare health care plan includes many features and benefits that help you get the care you need and enjoy better overall
Myth vs. Reality: Diabetes Related
 Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
Kelly Goode, PharmD, BCPS, FAPhA, FCCP and Lisa Price Stevens, MD, MPH, FACP
 Kelly Goode, PharmD, BCPS, FAPhA, FCCP and Lisa Price Stevens, MD, MPH, FACP Objec&ves Describe Diabetes Awareness Program Provide Tools for Program Implementation at Other Sites Describe Shared Care Model
Kelly Goode, PharmD, BCPS, FAPhA, FCCP and Lisa Price Stevens, MD, MPH, FACP Objec&ves Describe Diabetes Awareness Program Provide Tools for Program Implementation at Other Sites Describe Shared Care Model
Meaningful Use. Michael L. Brody, DPM FACFAOM CCHIT Ambulatory Workgroup HITSP Physician Perspective Technical Committee NYeHC
 Meaningful Use Michael L. Brody, DPM FACFAOM CCHIT Ambulatory Workgroup HITSP Physician Perspective Technical Committee NYeHC What is Meaningful Use? Meaningful use is a term defined by CMS and describes
Meaningful Use Michael L. Brody, DPM FACFAOM CCHIT Ambulatory Workgroup HITSP Physician Perspective Technical Committee NYeHC What is Meaningful Use? Meaningful use is a term defined by CMS and describes
The Nursing Department of Central CUSD 301 provides nursing services that promote students ability to learn. Our goals are to:
 Date Dear (Parent / Guardian), The Nursing Department of Central CUSD 301 provides nursing services that promote students ability to learn. Our goals are to: o Assist students in learning how to take care
Date Dear (Parent / Guardian), The Nursing Department of Central CUSD 301 provides nursing services that promote students ability to learn. Our goals are to: o Assist students in learning how to take care
Diabetes and Blood Pressure PIP Care Coordinator Toolkit. Provided by: - 1 -
 Diabetes and Blood Pressure PIP Care Coordinator Toolkit Provided by: - 1 - Project Summary MSHO/MSC+/SNBC Community & Institutionalized Blood Pressure Control for Members with Diabetes 2010 Performance
Diabetes and Blood Pressure PIP Care Coordinator Toolkit Provided by: - 1 - Project Summary MSHO/MSC+/SNBC Community & Institutionalized Blood Pressure Control for Members with Diabetes 2010 Performance
Preventive Services Explained
 Preventive Services Explained Medicare covers many preventive care services without charge. Most of these services have been recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. However, which beneficiaries
Preventive Services Explained Medicare covers many preventive care services without charge. Most of these services have been recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. However, which beneficiaries
San Diego County. 2015 Benefit Highlights
 San Diego County Scripps Classic offered by SCAN Health Plan(HMO) Scripps Signature offered by SCAN Health Plan (HMO) Scripps Heart First offered by SCAN Health Plan (HMO SNP) 2015 Benefit Highlights San
San Diego County Scripps Classic offered by SCAN Health Plan(HMO) Scripps Signature offered by SCAN Health Plan (HMO) Scripps Heart First offered by SCAN Health Plan (HMO SNP) 2015 Benefit Highlights San
Sales Presentation The Michigan Medicare Plans Designed Around YOU
 Sales Presentation The Michigan Medicare Plans Designed Around YOU HARBOR MEDICARE (HMO) HARBOR MEDICARE SELECT (HMO) H7960_003-2016 Approved WHAT YOU CAN EXPECT FROM THIS PRESENTATION PART 1 Introduction
Sales Presentation The Michigan Medicare Plans Designed Around YOU HARBOR MEDICARE (HMO) HARBOR MEDICARE SELECT (HMO) H7960_003-2016 Approved WHAT YOU CAN EXPECT FROM THIS PRESENTATION PART 1 Introduction
PEBTF s Get Healthy Program Know Your Numbers Wellness Screenings Frequently Asked Questions
 PEBTF s Get Healthy Program Know Your Numbers Wellness Screenings Frequently Asked Questions The Pennsylvania Employees Benefit Trust Fund (PEBTF) is pleased to offer the third annual Get Healthy Program
PEBTF s Get Healthy Program Know Your Numbers Wellness Screenings Frequently Asked Questions The Pennsylvania Employees Benefit Trust Fund (PEBTF) is pleased to offer the third annual Get Healthy Program
Diabetes. Living with. Better Health Guide. Anywhere, TN 11111. 1008 Main Street. Janet James. BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1
 BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1 Living with Diabetes Better Health Guide Janet James 1008 Main Street Anywhere, TN 11111 65109016-999-000000006 13810 Southeast Eastgate Way, Suite 200 Bellevue,
BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1 Living with Diabetes Better Health Guide Janet James 1008 Main Street Anywhere, TN 11111 65109016-999-000000006 13810 Southeast Eastgate Way, Suite 200 Bellevue,
Manage Your. Diabetes. Healthy Life. for a
 Manage Your Diabetes for a Healthy Life Know your ABCs! trying to control your A1C (blood sugar), Blood pressure, Cholesterol and stopping Smoking can help you to lower your chances of having a heart attack,
Manage Your Diabetes for a Healthy Life Know your ABCs! trying to control your A1C (blood sugar), Blood pressure, Cholesterol and stopping Smoking can help you to lower your chances of having a heart attack,
How your health insurance works
 How your health insurance works Important information about you and your membership in Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina As a member of Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina (BCBSNC),
How your health insurance works Important information about you and your membership in Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina As a member of Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina (BCBSNC),
Diabetes means you have too much sugar in
 WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes means you have too much sugar in your blood. The medical word for sugar in the blood or blood sugar is glucose, but most people just say sugar. Your body changes most of the
WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes means you have too much sugar in your blood. The medical word for sugar in the blood or blood sugar is glucose, but most people just say sugar. Your body changes most of the
Type 2 Diabetes. Type 1 Diabetes. What is Diabetes? Diabetes during Pregnancy Very Thirsty Very Tired
 FCD2-006 BINGO GAME To Prepare bingo game:!copy Picture Cards with pictures on one side and corresponding words on the other.!cut Bingo Cards apart, duplicate if you have more than ten players.!cut apart
FCD2-006 BINGO GAME To Prepare bingo game:!copy Picture Cards with pictures on one side and corresponding words on the other.!cut Bingo Cards apart, duplicate if you have more than ten players.!cut apart
DIABETES PACKET. To ensure your child s well-being, please provide the school with the following supplies:
 NSG-203A NORTH ROYALTON CITY SCHOOLS 6579 Royalton Road North Royalton, Ohio 44133 DIABETES PACKET Dear Parent/Guardian: You have indicated that your child has Diabetes. Please complete the attached SCHOOL
NSG-203A NORTH ROYALTON CITY SCHOOLS 6579 Royalton Road North Royalton, Ohio 44133 DIABETES PACKET Dear Parent/Guardian: You have indicated that your child has Diabetes. Please complete the attached SCHOOL
Pediatric Diabetic Teaching Guidelines/Checklist
 Pediatric Diabetic Teaching Guidelines/Checklist This teaching guideline contains the essential elements for teaching pediatric inpatients with diabetes. All teaching and patient/family responses should
Pediatric Diabetic Teaching Guidelines/Checklist This teaching guideline contains the essential elements for teaching pediatric inpatients with diabetes. All teaching and patient/family responses should
My life with Type 2-diabetes. English
 My life with Type 2-diabetes English 1 What is type 2 diabetes Diabetes is a disease where you have increased sugar content in the blood. If you have type 2-diabetes, you lack the ability of exploiting
My life with Type 2-diabetes English 1 What is type 2 diabetes Diabetes is a disease where you have increased sugar content in the blood. If you have type 2-diabetes, you lack the ability of exploiting
Section 504 Plan (pg 1 of 8)
 Section 504 Plan (pg 1 of 8) of Birth School Today s Section 504 Plan for: Disability: Diabetes School Year: Grade: Homeroom Teacher: Bus Number: Background Objectives The student has type diabetes. Diabetes
Section 504 Plan (pg 1 of 8) of Birth School Today s Section 504 Plan for: Disability: Diabetes School Year: Grade: Homeroom Teacher: Bus Number: Background Objectives The student has type diabetes. Diabetes
Diabetes. Emergency Checklists. From A Child in Your Care Has Diabetes. A Collection of Information. Copyright 2005 by Elisa Hendel, M.Ed.
 Diabetes Emergency Checklists From A Child in Your Care Has Diabetes. A Collection of Information. Copyright 2005 by Elisa Hendel, M.Ed. Hyperglycemia High Blood Sugar * Hyperglycemia occurs when the blood
Diabetes Emergency Checklists From A Child in Your Care Has Diabetes. A Collection of Information. Copyright 2005 by Elisa Hendel, M.Ed. Hyperglycemia High Blood Sugar * Hyperglycemia occurs when the blood
Simple Start TM Diabetes Log Book
 Calorie Sweetener Learn about Diabetes & Earn rewards at the same time Simple Start TM Diabetes Log Book our engagement and rewards program that Empowers you through Education Learn how to manage your
Calorie Sweetener Learn about Diabetes & Earn rewards at the same time Simple Start TM Diabetes Log Book our engagement and rewards program that Empowers you through Education Learn how to manage your
HARBOR ADVANTAGE (HMO) H7960-002-2015 Accepted
 HARBOR ADVANTAGE (HMO) H7960-002-2015 Accepted IMPORTANT This presentation is for the exclusive use of Authorized Plan Representatives of Harbor Advantage (HMO). Harbor Health Plan is an HMO plan with
HARBOR ADVANTAGE (HMO) H7960-002-2015 Accepted IMPORTANT This presentation is for the exclusive use of Authorized Plan Representatives of Harbor Advantage (HMO). Harbor Health Plan is an HMO plan with
MEDICATION RETRIEVAL FROM SCHOOLS
 Directive to Administrators (Specify which administrators) WAD (Wednesday) Publication Date WAD Notice Number No. of Pages All Administrators WAD Title (Limit to 4-6 Words) May 6, 2015 Date Due (if applicable)
Directive to Administrators (Specify which administrators) WAD (Wednesday) Publication Date WAD Notice Number No. of Pages All Administrators WAD Title (Limit to 4-6 Words) May 6, 2015 Date Due (if applicable)
Diabetes Care 2011-2012
 Clinical Innovations in the Patient Centered Medical Home to Improve Diabetes Care Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, FACP Chief Medical Officer & Senior Vice President Joslin Diabetes Center Harvard Medical School
Clinical Innovations in the Patient Centered Medical Home to Improve Diabetes Care Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, FACP Chief Medical Officer & Senior Vice President Joslin Diabetes Center Harvard Medical School
Medical Assistant s Diabetes Survey
 Medical Assistant s Diabetes Survey Instructions: Circle one answer for each question. Thank-you. Basic Knowledge 1. Risk factors for developing Type 2 diabetes include: a. Family members with diabetes
Medical Assistant s Diabetes Survey Instructions: Circle one answer for each question. Thank-you. Basic Knowledge 1. Risk factors for developing Type 2 diabetes include: a. Family members with diabetes
Healthy Solutions for Life
 Healthy Solutions for Life 2015 Presentation Overview About Healthy Solutions for Life Disease Management Health Coaching Model DM Programs TeleCare Monitoring 2013 Nurtur Health, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Healthy Solutions for Life 2015 Presentation Overview About Healthy Solutions for Life Disease Management Health Coaching Model DM Programs TeleCare Monitoring 2013 Nurtur Health, Inc. All Rights Reserved.

 Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE  More information >>> HERE
More information >>> HERE  Additional details >>> HERE
Additional details >>> HERE  More details >>> HERE
More details >>> HERE  Additional details >>> HERE
Additional details >>> HERE