Expression of ERCC1, Bcl-2, MT and their Clinical Significance in Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer Treated With Cisplatin-based Chemotherapy
|
|
|
- Cathleen Eaton
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Latin American Journal of Pharmacy (formerly Acta Farmacéutica Bonaerense) Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 28 (6): (2009) Original Article Received: March 20, 2009 Accepted: July 18, 2009 Expression of ERCC1, Bcl-2, MT and their Clinical Significance in Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer Treated With Cisplatin-based Chemotherapy Haiqing MA 1,3, Huanhuan SUN 2, Fuxi HUANG 3, Jing LI 4, Xiaolong CAO 3 * & Wenqi JIANG 5 1 State Key Laboratory of Oncology in Southern China and Department of Experimental Research, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, 561 Dongfeng East Road, Guangzhou, Guangdong, , People s Republic of China 2 Department of Pharmacology, Sun Yat-sen University, 74 Zhongshaner Road, Guangzhou, Guangdong, , People s Republic of China 3 Department of Medical Oncology and 4 Department of Pathology, Panyu People s Hospital, 93 Qiaodong Road, Panyu, Guangzhou, , People s Republic of China SUMMARY. The aim of this study was to determine the prognostic value of expression of Excision Repair Cross-complementation Group 1 (ERCC1), B cell lymphoma/lewkmia-2 (Bcl-2) and metallothionein (MT) by immunohistochemically staining tumor specimens from 78 patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The result showed that positive expression of ERCC1 was associated both with short survival (10.45 months vs months, log-rank p = 0.003) and poor response to cisplatin-based chemotherapy (p = 0.003) when compared with negative group. But expression of Bcl-2 and MT was not associated with response to chemotherapy and survival. Multivariate analysis confirmed that expression of ERCC1 was an independent variable related to overall survival (p = 0.013). These data support the role of RECC1 expression as a candidate predictor for the survival of patients with advanced NSCLC treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. INTRODUCTION Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is one of the commonest causes of cancer deaths worldwide 1,2. Although surgical resection plays a major role in curative treatments, not more than 20% of NSCLC patients were diagnosed in operable stage. Combination chemotherapy with cisplatin is considered a standard treatment for advanced NSCLC patients while only show a limit improvement in survival 3-6. The major reason for the failure of cisplatin-based chemotherapy is initial or acquired resistance. Unluckily, it is still not clear about the molecular mechanisms that underlie this chemoresistance. Possible mechanisms of acquired resistance to cisplatin include the following: reduced intracellular accumulation of cisplatin, increased repair activity of DNA damage, altered expression of oncogenes and regulatory proteins, and enhanced drug inactivation by metallothionine and glutathione 7. Recently, it seems to be helpful to identify some molecular markers, which could predict tumor response to chemotherapy, and then to optimize the treatment for the individual patient. In NSCLC, such prognostic factors would be useful in selecting those patients who are likely to benefit from cisplatin-based chemotherapy, thus preventing about 60% of patients who do not experience response to this treatment from the serious adverse effects. The aim of the present study was to investigate the predictive value of ERCC1, Bcl-2 and MT for response of cisplatin-based chemotherapy and survival in advanced NSCLC. KEY WORDS: Bcl-2, Cisplatin, ERCC1, MT, NSCL, Resistance * Authors to whom correspondence should be addressed. xiaolong_cao10@163.com. H. Ma and H. Sun contributed equally to this work. ISSN
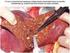
2 MA H., SUN H., HUANG F., LI J., CAO X. & JIANG W. METHODS Case Selection Microscopic slides from 78 randomly selected cases of advanced NSCLC from 2000 to 2005 were retrieved from Panyu People s Hospital, Guangzhou, China. There were 18 squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), 36 adenocarcinomas (AC), 7 adenosquamous carcinomas and 17 other histological types in the study group. These cases contained 51 men and 27 women. Tumors were staged in accordance with the UICC TNM classification, including p-stage IIIA, IIIB and IV tumors. Clinical follow-up data were obtained from the Medical Record Unit of the Panyu People s Hospital. All patients were treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. This research protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Hospital (Nº ). Data concerning clinicopathologic characteristics, including sex, age, smoking history, histologic type, pathologic stage and survival were obtained by thorough medical record review. Smoker is defined to people having smoked more than 400 cigarettes one year. Immunohistochemical staining for drug resistance-related proteins Immunohistochemical staining of formalinfixed, paraffin-embedded tumor tissue was performed using mouse anti-human monoclonal antibodies against Bcl-2 (clone 124, dilution 1:40, DAKO, Tokyo; Japan), ERCC1 (ERCC1 Ab- 2, dilution 1:100, Neomarkers, Fremont, CA, USA), and MT (MT Ab-1, dilution 1:100, Invitrogen, Camarillo, CA, USA). Sections were deparaffinized in xylene and rehydrated in graded alcohols and water. Endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked by treatment with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 10 min. Sections were treated with protein-blocking solution and then with primary antibodies overnight at 4 C. After several rinses in phosphate-buffered saline, the sections were incubated in the biotinylated secondary antibody. Bound antibodies were detected by the streptavidin-biotin method. Slides were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline, exposed to diaminobenzidine, and counterstained with Mayer s hematoxylin. The negative controls for these proteins were made by the omission of the primary antibody during the process of immunohistochemical staining. The slides were examined independently by two observers (LI J, CAO XL) blinded to both clinical and pathologic data. Expression of the drug resistance-related proteins was quantified using a visual grading system based on the extent of staining (percentage of positive tumor cells) (graded on a scale of 0-3; 0 = none, 1 = 1-9%, 2 = 10-49%, 3 = 50%) as well as the intensity of staining (graded on a scale of 0-3; 0 = no staining, 1 = weak staining, 2 = moderate staining, 3 = strong staining). The expression of these proteins was considered as positive (high expression) when both scores were 2 or above (Fig. 1). Figure 1. Representative immunohistochemical staining of drug resistance-related proteins in NSCLC ( 400). (A) High expression of ERCC1: nuclear staining (grade 3). (B) High expression of Bcl-2: cytoplasmic staining (grade 3). (C) High expression of MT: cytoplasmic staining (grade 3). (D) Low expression of ERCC1 (grade 0). Canon PowerShot A720 IS. Statistical analysis Overall survival (OS) was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method. OS was defined as the time from the date of histologic diagnosis to death; data on survivors were censored at the last follow-up. The differences between the survival curves were tested using the log-rank test. The Cox proportional-hazards regression model was used to determine the joint effects of several variables on survival. A comparison of clinicopathologic characteristics was evaluated with the chi-square test. All analyses were performed with SPSS for Windows 16.0 software and a p- value < 0.05 was considered significant. RESULTS Patient characteristics The clinicopathologic characteristics of the 78 patients are listed in Table
3 Latin American Journal of Pharmacy - 28 (6) Characteristics Number ( %) Age (years) Median 57.5 Range Gender Male 51 (65.4) Female 27 (34.6) Performance 0 5 (6.4) status 1 52 (66.7) (ECOG) 2 18 (23.1) 3 3 (3.8) Histologic type Squamous cell 18 (23.1) carcinomas Adenocarcinoma 36 (46.2) Adenosquamous 7 (9) carcinoma Others 17 (21.8) ERCC-1-41 (52.6) + 37 (47.4) Bcl-2-40 (51.3) + 38 (48.7) MT - 42 (53.8) + 36 (46.2) Chemotherapy Gemcitabine/ 33 (42.3) regimens cisplatin Navelbine/cisplatin 7 (9) Paclitaxel/cisplatin 39 (48.7) Stage 3 a 29 (37.2) 3 b 30 (38.5) 4 19 (24.4) Table 1. Characteristics of patients. ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Association of expression of drug resistance-related proteins with clinicopathologic characteristics Positive expression of ERCC1, Bcl-2, and MT was observed in 37 (47.4%), 38 (48.7%) and 36 (46.2%) patients, respectively. Examples of the immunohistochemical staining patterns are shown in Figure 1. Positivity of ERCC1 showed significant association with smoking (p = 0.001) and response of treatment (p = 0.003) (Table 2). No significant association was found between the positivity of ERCC1 with other clinicopathologic characteristics, including age, gender, ECOG, histologic type, stage, chemotherapy regimens, Bcl-2 and MT expression (Table 2). In addition, neither of positive expression of Bcl-2 and MT represented significant association with clinicopathologic characteristics (data not shown). Association of expression of drug resistance-related proteins with patient outcome The follow-up duration of patients was 22 months (range: 3-22 months), and the median follow-up duration was 11 months. 48 patients were dead at the time of analysis. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed the association between positive expression of ERCC1 and poor OS (1-year, 35% vs. 65.2%; p = 0.003) (Fig. 2A and Table 3), and in strata analysis, this statistic association was significant in adenocarcinoma (Fig. 2D) and other types of NSCLC (p = 0.009; p = 0.033), not in squamous cell carcinoma (Fig. 2E) or adenosquamous carcinoma (p = 0.919; p = 0.433). Besides, bad ECOG performance status and smoking were also associated with poor OS (1-year; 25.6%/59.0%, p = and 36.7%/ 65.0%, p = 0.029, respectively) (Table 3). However, positive expression of Bcl-2 and MT was not correlated with survival of patients (p = 0.672; p = 0.734) (Fig. 2B-C). Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that, among pretreatment characteristics, ECOG performance status (p=0.018) and ERCC1 (p = 0.013) expression were independent predictors of poor OS, while smoking failed to reach statistical significance (p = 0.283), although an association was observed (p = 0.030) in univariate analysis (Table 4). DISCUSSION In the present study, we investigated the expression of ERCC1, Bcl-2 and MT in advanced NSCLC and their relationship with response of cisplatin-based chemotherapy. As a result, negative expression of ERCC1 was associated with good response of cisplatin-based chemotherapy (p = 0.003). Moreover, in multivariate analysis, positive expression of ERCC1 (p = 0.013) was an independent poor prognosis factor for patients with advanced NSCLC. In addition, negative expression of ERCC1 showed significant association with longer survival in adenocarcinomas (p = 0.009). However, positive expression of Bcl-2 and MT did not show any correlation with response of chemotherapy and survival in overall NSCLC patients. These findings suggest that immunostaining of ERCC1 may be a useful marker for stratifying NSCLC patients into chemoresponsive and chemoresistant groups to cisplatinbased therapy. To date, cisplatin-based chemotherapy remains the standard treatment of advanced NSCLC. The nucleotide excision repair pathway 829
4 MA H., SUN H., HUANG F., LI J., CAO X. & JIANG W. Figure 2. Overall survival of patients with advanced NSCLC according to the expression of ER- CC1 (A), Bcl-2 (B), MT (C), ERCC1 in adenocarcinomas (D) and ER- CC1 in Squamous cell carcinomas (E). All graphics were performed with SPSS for Windows 16.0 software. Characteristics ERCC-1 expression (%) High Low p Age a (40.5) 24 (58.5) >57 22 (59.5) 17 (41.5) Gender Male 24 (64.9) 27 (65.9) Female 13 (35.1) 14 (34.1) Performance status 0,1 26 (70.3) 31 (75.6) (ECOG) 2,3 11 (29.7) 10 (24.4) Histologic type Squamous cell carcinoma 8 (21.6) 10 (24.4) Adenocarcinoma 18 (48.6) 18 (43.9) Adenosquamous carcinoma 3 (8.1) 4 (9.8) Others 8 (21.6) 9 (22) Bcl-2 expression + 16 (43.2) 22 (53.7) (56.8) 19 (46.3) MT expression + 16 (43.2) 20 (48.8) (56.8) 21 (51.2) Stage 3 a 12 (32.4) 17 (41.5) b 15 (40.5) 15 (36.6) 4 10 (27) 9 (22) Chemotherapy regimens Gemcitabine+cisplatin 19 (51.4) 14 (34.1) Navelbine+cisplatin 4 (10.8) 3 (7.3) Paclitaxel+cisplatin 14 (37.8) 24 (58.5) Smoking history Smoker 11 (29.7) 28 (68.3) Non-smoker 26 (70.3) 13 (31.7) Response of treatment CR, PR 25 (67.6) 14 (34.1) Others b 12 (32.4) 27 (65.9) Table 2. ERCC1 expression and clinicopathologic characteristics. ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; CR, complete response; PR, partial response; a Median age. b Stable disease, + progressive disease, not evaluable. 830
5 Latin American Journal of Pharmacy - 28 (6) Prognostic factors 1-year OS (%) p Age a > Gender Male Female 58.2 Performance status (ECOG) 0, , Chemotherapy regimens Gemcitabine+cisplatin Navelbine+cisplatin 42.9 Paclitaxel+cisplatin 45.1 Smoking history Smoker Non-smoker 36.7 ERCC-1 expression Bcl-2 expression MT expression Stage 3 a b Histologic type Squamous cell carcinoma Adenocarcinoma 43.5 Adenosquamous carcinoma 57.1 Others 61.4 Table 3. Kaplan-Meier analysis of overall survival. OS, overall survival; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. a Median age. b Stable disease, + progressive disease, not evaluable. manifests a central contribution in DNA repair and is proved to be involved in resistance to cisplatin-based chemotherapy ERCC1 displays a key role in nucleotide excision repair and removes cisplatin-induced DNA adducts Several clinical studies have shown that ERCC1 expression is associated with resistance to cisplatin-based chemotherapy and poor prognosis in several tumors, including NSCLC By immunohistochemistry, we also found that ERCC1 positive cases were more resistance to the cisplatin-based chemotherapy, and had a shorter overall survival than negative ones. Moreover, a significant correlation between positive expression of ERCC1 and poor outcome of NSCLC was observed only in some histologic types, especially in adenocarcinomas. In fact, to date, there are not many studies concerning about the association between histological type of NSCLC and resistance to cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Over recent years, it has become recognized that defects in the regulation of apoptosis occupies an outstanding role in the biology and treatment resistance of cancer 25. The anti-apoptotic proto-oncogene bcl-2 is concerned with apoptosis, by inhibiting programmed cell death (apoptosis) and prolonging cell survival by arresting cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. It has been reported that overexpression of Bcl-2 existed in approximate half of all NSCLC cases 26,27. Data from clinical studies suggest that Bcl-2 not only contributes to a more malignant NSCLC phenotype 28, but also confers resistance to chemotherapy in NSCLC 28,29. As one of the most frequent chemotherapeuticses in NSCLC treatment 30,31, cisplatin mediated its antitumor effect at least in part by inducing apoptosis 32,33. Bcl-2 overexpression confers resistance to cisplatin-induced apoptosis in many types of solid tumors and has been reported to correlate with poor response to cisplatin chemotherapy 7. Nevertheless, no unified conclusion were achieved 831
6 MA H., SUN H., HUANG F., LI J., CAO X. & JIANG W. Univariate analysis Prognostic factors Hazard ratio 95 % CI p All patients Age a > Histologic type Squamous cell carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenosquamous carcinoma Others Gender Male Female Performance status (ECOG) 0, , Chemotherapy regimens Gemcitabine+cisplatin Navelbine+cisplatin Paclitaxel+cisplatin Stage 3 a b ERCC Bcl MT Smoking history Smoker Non-smoker Multivariate analysis Performance status(ecog) 0, , Smoking ERCC-1 expression Table 4. The overall survival univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis. ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; CI, confidence interval. a Median age. b Stable disease, + progressive disease, not evaluable. with regard to the role of Bcl-2 expression in NSCLC 34. Several immunohistochemical studies have investigated the prognostic value of Bcl-2 expression in lung cancer. Most studies support the hypothesis of prolonged survival in Bcl-2- positive cases 35-42, but others do not agree In this present study, we did not find the correlation between Bcl-2 expression and survival. Metallothioneins (MT) are a group of lowmolecular weight, cysteine rich intracellular proteins, which are encoded by a family of genes containing at least 10 functional isoforms in hu- man. The expression and induction of these proteins have been associated with protection against DNA damage, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Moreover, MT may potentially activate certain transcriptional factors by donating zinc. Although MT is a cytosolic protein in resting cells, it can be translocated transiently to the cell nucleus during cell proliferation and differentiation 46. In previous study, it have been demonstrated that overexpression of MT can confer resistance to radiation 47 and antineoplastic drugs 48,49. It has been supposed that the ability of MT in de- 832
7 Latin American Journal of Pharmacy - 28 (6) creasing the efficacy of chemotherapeutic effects may be attributed to sequestrating free radicals, drugs or their metabolites, thus inhibiting the direct interaction of antineoplastic agents with their intracellular targets 46. In fact, the role of MT in the development of chemoresistance in the clinical setting is still debatable. The protective effect of MT overexpression against antineoplastic agents has been reported in human tumors such as ovarian, testicular and colon tumors 50-54, whereas there are other reports which do not support this perception 46. In this study, there was no evidence supporting the predictive value of MT expression in advanced NSCLC treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Although many studies have tried to identify a clinical indicator powerful enough to predict response to chemotherapy and outcome of patients with NSCLC, only TNM stage and performance status are used in clinical practice 55,56. Likewise, in this present study, we also found that bad performance status was an independent poor prognosis for patients with advanced NSCLC. In addition, there was also an unexpected finding that ERCC1 expression was associated with smoking, but failed to be an independent poor prognosis of NSCLC in multivariate analysis. The causal relationship between smoking and lung cancer has been accepted since the 1950s, and it has shown that carcinogenic compounds found in tobacco smoke can promote damage to the DNA 34. Does the DNA damage reversely promote the capacity of DNA repair and then result in the elevated expression of ERCC1 in lung cancer? It seems only feasible in theory but still need warranted. CONCLUSION In this study, we showed that ERCC1 could be a helpful biomarker to identify the subgroup of NSCLC patients most likely to benefit from cisplatin-based chemotherapy. However, before putting ERCC1 in daily practice for treatment making-decision, confirmatory retrospective analyses as well as prospective randomised trials are needed. REFERENCES 1. Jemal, A., T. Murray, A. Samuels, A. Ghafoor, E. Ward & M. J. Thun (2003) CA Cancer J. Clin. 53: Mountain, C. F. & C. M. Dresler (1997) Chest. 111: Shepherd, F. A. (1999) Semin Oncol. 26: Arriagada, R., B. Bergman, A. Dunant, T. Le Chevalier, J. P. Pignon & J. Vansteenkiste (2004) N. Engl. J. Med. 350: Winton, T., R. Livingston, D. Johnson, J. Rigas, M. Johnston, C. Butts, Y. Cormier, G. Goss, R. Inculet, E. Vallieres, W. Fry, D. Bethune, J. Ayoub, K. Ding, L. Seymour, B. Graham, M. S. Tsao, D. Gandara, K. Kesler, T. Demmy & F. Shepherd (2005) N. Engl. J. Med. 352: Douillard, J. Y., R. Rosell, M. De Lena, F. Carpagnano, R. Ramlau, J. L. Gonzales-Larriba, T. Grodzki, J. R. Pereira, A. Le Groumellec, V. Lorusso, C. Clary, A. J. Torres, J. Dahabreh, P. J. Souquet, J. Astudillo, P. Fournel, A. Artal- Cortes, J. Jassem, L. Koubkova, P. His, M. Riggi & P. Hurteloup (2006) Lancet Oncol. 7: Wang, G., E. Reed & Q.Q. Li (2004) Oncol Rep. 12: Rosell, R., M. Taron, V. Alberola, B. Massuti & E. Felip (2003) Lung Cancer. 41 Suppl 1: S Rosell, R., M. Taron, A. Barnadas, G. Scagliotti, C. Sarries & B. Roig (2003) Cancer Control. 10: Rosell, R., M. Taron, C. Camps & G. Lopez-Vivanco (2003) Drugs Today (Barc). 39: Rosell, R., L. Crino, K. Danenberg, G. Scagliotti, G. Bepler, M. Taron, V. Alberola, M. Provencio, C. Camps, F. De Marinis, J. J. Sanchez & R. Penas (2003) Semin. Oncol. 30: Sancar, A. (1994) Science 266: Mu, D., D.S. Hsu & A. Sancar (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271: Zamble, D.B., D. Mu, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar & S. J. Lippard (1996) Biochemistry 35: Ceppi, P., M. Volante, S. Novello, I. Rapa, K.D. Danenberg, P.V. Danenberg, A. Cambieri, G. Selvaggi, S. Saviozzi, R. Calogero, M. Papotti & G.V. Scagliotti (2006) Ann. Oncol. 17: Olaussen, K.A., A. Dunant, P. Fouret, E. Brambilla, F. Andre, V. Haddad, E. Taranchon, M. Filipits, R. Pirker, H. H. Popper, R. Stahel, L. Sabatier, J. P. Pignon, T. Tursz, T. Le Chevalier & J. C. Soria (2006) N. Engl. J. Med. 355: Simon, G.R., S. Sharma, A. Cantor, P. Smith & G. Bepler (2005) Chest 127: Dabholkar, M., J. Vionnet, F. Bostick-Bruton, J. J. Yu & E. Reed (1994) J. Clin. Invest. 94: Joshi, M.B., Y. Shirota, K. D.Danenberg, D.H. Conlon, D.S. Salonga, J.E. Herndon, 2nd, P.V. Danenberg & D.H. Harpole, Jr. (2005) Clin. Cancer Res. 11: Lord, R. V., J. Brabender, D. Gandara, V. Al- 833
8 MA H., SUN H., HUANG F., LI J., CAO X. & JIANG W. berola, C. Camps, M. Domine, F. Cardenal, J.M. Sanchez, P.H. Gumerlock, M. Taron, J.J. Sanchez, K.D. Danenberg, P.V. Danenberg & R. Rosell (2002) Clin. Cancer Res. 8: Metzger, R., C.G. Leichman, K.D. Danenberg, P.V. Danenberg, H. J. Lenz, K. Hayashi, S. Groshen, D. Salonga, H. Cohen, L. Laine, P. Crookes, H. Silberman, J. Baranda, B. Konda & L. Leichman (1998) J. Clin. Oncol. 16: Rosell, R., K.D. Danenberg, V. Alberola, G. Bepler, J.J. Sanchez, C. Camps, M. Provencio, D. Isla, M. Taron, P. Diz & A. Artal (2004) Clin. Cancer Res. 10: Shirota, Y., J. Stoehlmacher, J. Brabender, Y. P. Xiong, H. Uetake, K. D. Danenberg, S. Groshen, D. D. Tsao-Wei, P. V. Danenberg & H. J. Lenz (2001) J. Clin. Oncol. 19: Huang, P. Y., X.M. Liang, S.X. Lin, R.Z. Luo, J.H. Hou & L. Zhang (2004) Ai Zheng. 23: Reed, J. C. (2003) Cancer Cell 3: Ohmura, Y., M. Aoe, A. Andou & N. Shimizu (2000) Clin. Cancer Res. 6: Groeger, A. M., V. Esposito, A. De Luca, R. Cassandro, G. Tonini, V. Ambrogi, F. Baldi, R. Goldfarb, T. C. Mineo, A. Baldi & E. Wolner (2004) Histopathology 44: Herbst, R. S. & S. R. Frankel (2004) Clin Cancer Res. 10: 4245s-48s. 29. Han, J.Y., E.K. Hong, B.G. Choi, J.N. Park, K.W. Kim, J.H. Kang, J.Y. Jin, S.Y. Park, Y.S. Hong & K.S. Lee (2003) Med. Oncol. 20: Comer, A.M. & K.L. Goa (2000) Drugs Aging. 17: Green, M.R. (2002) Semin Oncol. 29: Chattopadhyay, S., R. Machado-Pinilla, C. Manguan-Garcia, C. Belda-Iniesta, C. Moratilla, P. Cejas, J. A. Fresno-Vara, J. de Castro-Carpeno, E. Casado, M. Nistal, M. Gonzalez-Baron & R. Perona (2006) Oncogene. 25: Grant, D.S., T.L. Williams, M. Zahaczewsky & A.P. Dicker (2003) Int. J. Cancer 104: Duarte, R.L. & M.E. Paschoal (2006) J. Bras. Pneumol. 32: Cox, G., R. A. Walker, S. Muller, K. R. Abrams, W. P. Steward & K. J. O Byrne (2000) Pathol. Oncol. Res. 6: Moldvay, J., P. Scheid, P. Wild, K. Nabil, J. Siat, J. Borrelly, B. Marie, G. Farre, T. Labib, G. Pottier, R. Sesboue, C. Bronner, J. M. Vignaud, Y. Martinet & N. Martinet (2000) Clin. Cancer Res. 6: Laudanski, J., L. Chyczewski, W.E. Niklinska, M. Kretowska, M. Furman, B. Sawicki & J. Niklinski (1999) Neoplasma 46: Athanassiadou, P., T. Dosios, E. Petrakakou, A. Liossi, C. Zerva & P. Athanassiades (1998) Diagn. Cytopathol. 19: Silvestrini, R., A. Costa, C. Lequaglie, C. Mochen, S. Veneroni, M. Leutner & G. Ravasi (1998) Virchows Arch. 432: Pastorino, U., S. Andreola, E. Tagliabue, F. Pezzella, M. Incarbone, G. Sozzi, M. Buyse, S. Menard, M. Pierotti & F. Rilke (1997) J. Clin. Oncol. 15: Higashiyama, M., O. Doi, K. Kodama, H. Yokouchi, S. Nakamori & R. Tateishi (1997) J. Surg. Oncol. 64: Ghosh, M., J. Crocker & A.G. Morris (1999) J. Pathol. 189: Cagini, L., M. Monacelli, G. Giustozzi, L. Moggi, G. Bellezza, A. Sidoni, E. Bucciarelli, S. Darwish, V. Ludovini, L. Pistola, V. Gregorc & M. Tonato (2000) J. Surg. Oncol. 74: Greatens, T.M., G.A. Niehans, J.B. Rubins, J. Jessurun, R.A. Kratzke, M.A. Maddaus & D.E. Niewoehner (1998) Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 157: Anton, R.C., R.W. Brown, M. Younes, M.M. Gondo, M.A. Stephenson & P. T. Cagle (1997) Hum Pathol. 28: Cherian, M.G., A. Jayasurya & B.H. Bay (2003) Mutat. Res. 533: Bakka, A., L. Endresen, A.B. Johnsen, P.D. Edminson & H.E. Rugstad (1981) Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 61: Kelley, S.L., A. Basu, B.A. Teicher, M.P. Hacker, D.H. Hamer & J.S. Lazo (1988) Science 241: Satoh, M., M.G. Cherian, N. Imura & H. Shimizu (1994) Cancer Res. 54: Cherian, M.G. (1994) Environ. Health Perspect. 102 Suppl 3: Chin, J.L., D. Banerjee, S.A. Kadhim, T.E. Kontozoglou, P.J. Chauvin & M. G. Cherian (1993) Cancer 72: Dziegiel, P., J. Forgacz, E. Suder, P. Surowiak, J. Kornafel & M. Zabel (2003) Histol. Histopathol. 18: Germain, I., B. Tetu, J. Brisson, M. Mondor & M. G. Cherian (1996) Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 15: Ioachim, E.E., A.C. Goussia, N.J. Agnantis, M. Machera, E.V. Tsianos & A.M. Kappas (1999) J. Clin. Pathol. 52: Espinosa, E., J. Feliu, P. Zamora, M. Gonzalez Baron, J.J. Sanchez, A. Ordonez & J. Espinosa (1995) Lung Cancer 12: Borges, M., J.P. Sculier, M. Paesmans, M. Richez, G. Bureau, G. Dabouis, J. Lecomte, J. Michel, O. Van Cutsem, J. Schmerber, V. Giner, M.C. Berchier, R. Sergysels, P. Mommen & J. Klastersky (1996) Lung Cancer 16:
Is the third-line chemotherapy feasible for non-small cell lung cancer? A retrospective study
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.1, 2004 19 Is the third-line chemotherapy feasible for non-small cell lung cancer? A retrospective study MUSTAFA ÖZDO AN, MUSTAFA SAMUR, HAKAN BOZCUK, ERKAN ÇOBAN,
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.1, 2004 19 Is the third-line chemotherapy feasible for non-small cell lung cancer? A retrospective study MUSTAFA ÖZDO AN, MUSTAFA SAMUR, HAKAN BOZCUK, ERKAN ÇOBAN,
Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008
 Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Pharmacogenomic Approaches. Luis Paz-Ares Hospital Universitario Virgen del Rocio Seville, Spain
 Pharmacogenomic Approaches Luis Paz-Ares Hospital Universitario Virgen del Rocio Seville, Spain Pharmacogenetics & Pharmacogenomics Medicine tailored to the individual Genetic information, including the
Pharmacogenomic Approaches Luis Paz-Ares Hospital Universitario Virgen del Rocio Seville, Spain Pharmacogenetics & Pharmacogenomics Medicine tailored to the individual Genetic information, including the
L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal, D Landau, J Spicer
 Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Adjuvant Chemotherapy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Review Article 2012 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 Tanaffos 2012; 11 (1): 12-17 TANAFFOS Adjuvant Chemotherapy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Review Article 2012 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 Tanaffos 2012; 11 (1): 12-17 TANAFFOS Adjuvant Chemotherapy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: Scientific Discoveries and the Pursuit of Progress
 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: Scientific Discoveries and the Pursuit of Progress Lung Cancer Accounts for 14% of All New Cancer Diagnoses in the United States 1 Lung cancer is the second most common malignancy
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: Scientific Discoveries and the Pursuit of Progress Lung Cancer Accounts for 14% of All New Cancer Diagnoses in the United States 1 Lung cancer is the second most common malignancy
NCCN Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer V.1.2011 Update Meeting 07/09/10
 Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC. Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai
 Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
Emerging Drug List GEFITINIB
 Generic (Trade Name): Manufacturer: Gefitinib (Iressa ) formerly referred to as ZD1839 AstraZeneca NO. 52 JANUARY 2004 Indication: Current Regulatory Status: Description: Current Treatment: Cost: Evidence:
Generic (Trade Name): Manufacturer: Gefitinib (Iressa ) formerly referred to as ZD1839 AstraZeneca NO. 52 JANUARY 2004 Indication: Current Regulatory Status: Description: Current Treatment: Cost: Evidence:
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
Survival analysis of 220 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer
 窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
Molecular markers and clinical trial design parallels between oncology and rare diseases?
 Molecular markers and clinical trial design parallels between oncology and rare diseases?, Harriet Sommer Institute for Medical Biometry and Statistics, University of Freiburg Medical Center 6. Forum Patientennahe
Molecular markers and clinical trial design parallels between oncology and rare diseases?, Harriet Sommer Institute for Medical Biometry and Statistics, University of Freiburg Medical Center 6. Forum Patientennahe
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
 Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
New Trends & Current Research in the Treatment of Lung Cancer, Pt. II
 New Trends & Current esearch in the Treatment of Lung Cancer, Pt. II Howard (Jack) West, MD President & CEO, GACE Medical Director, Thoracic Oncology Program Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Cancer
New Trends & Current esearch in the Treatment of Lung Cancer, Pt. II Howard (Jack) West, MD President & CEO, GACE Medical Director, Thoracic Oncology Program Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Cancer
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
Pharmacogenomic markers in EGFR-targeted therapy of lung cancer
 Pharmacogenomic markers in EGFR-targeted therapy of lung cancer Rafal Dziadziuszko, MD, PhD University of Colorado Cancer Center, Aurora, CO, USA Medical University of Gdansk, Poland EMEA Workshop on Biomarkers,
Pharmacogenomic markers in EGFR-targeted therapy of lung cancer Rafal Dziadziuszko, MD, PhD University of Colorado Cancer Center, Aurora, CO, USA Medical University of Gdansk, Poland EMEA Workshop on Biomarkers,
CLINICAL POLICY Department: Medical Management Document Name: Opdivo Reference Number: CP.PHAR.121 Effective Date: 07/15
 Page: 1 of 6 IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration of generally accepted
Page: 1 of 6 IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration of generally accepted
Third-line or fourth-line chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with relatively good performance status
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 74 (2011) 209e214 Original Article Third-line or fourth-line chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 74 (2011) 209e214 Original Article Third-line or fourth-line chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with
ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials)
 ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials) 3 Integrated Trials Testing Targeted Therapy in Early Stage Lung Cancer Part of NCI s Precision Medicine Effort in
ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials) 3 Integrated Trials Testing Targeted Therapy in Early Stage Lung Cancer Part of NCI s Precision Medicine Effort in
Docteur Oswald VAN CUTSEM Pneumologue Chef de Service
 Docteur Oswald VAN CUTSEM Pneumologue Chef de Service Contacts secrétariat planning : 081. 20 96 61 secrétariat consultations : 081. 20 94 61 Diplômes : Doctorat UCL 1983 Diplôme de spécialiste en pneumologie
Docteur Oswald VAN CUTSEM Pneumologue Chef de Service Contacts secrétariat planning : 081. 20 96 61 secrétariat consultations : 081. 20 94 61 Diplômes : Doctorat UCL 1983 Diplôme de spécialiste en pneumologie
Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART
 Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART Goals Discuss treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer: New and old Discuss new developments in personalized
Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART Goals Discuss treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer: New and old Discuss new developments in personalized
Prognostic and Predictive Factors in Oncology. Mustafa Benekli, M.D.
 Prognostic and Predictive Factors in Oncology Mustafa Benekli, M.D. NCI Definitions ESMO Course -Essentials of Medical Oncology -Istanbul 2 Prognostic factor: NCI Definition A situation or condition, or
Prognostic and Predictive Factors in Oncology Mustafa Benekli, M.D. NCI Definitions ESMO Course -Essentials of Medical Oncology -Istanbul 2 Prognostic factor: NCI Definition A situation or condition, or
ERCC1 as a Biological Marker Guiding Management in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.10.4117 RESEARCH ARTICLE ERCC1 as a Biological Marker Guiding Management in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Yasemin Benderli Cihan 1 *, Ahmet Ozturk², Alaettin
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.10.4117 RESEARCH ARTICLE ERCC1 as a Biological Marker Guiding Management in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Yasemin Benderli Cihan 1 *, Ahmet Ozturk², Alaettin
Avastin in Metastatic Breast Cancer
 Non-interventional study Avastin in Metastatic Breast Cancer ML 21165 / 2007 Clinical Study Report Synopsis ROCHE ML21165 / WiSP Project RH09 / V. 1.0 / 24.06.2013 ROCHE ML21165-2 - Name of Sponsor Roche
Non-interventional study Avastin in Metastatic Breast Cancer ML 21165 / 2007 Clinical Study Report Synopsis ROCHE ML21165 / WiSP Project RH09 / V. 1.0 / 24.06.2013 ROCHE ML21165-2 - Name of Sponsor Roche
Adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: new insights into
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published September 5, 2014 1 Adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: new insights into the effect on failure type via a multistate approach
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published September 5, 2014 1 Adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: new insights into the effect on failure type via a multistate approach
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies
 Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
Effects of Herceptin on circulating tumor cells in HER2 positive early breast cancer
 Effects of Herceptin on circulating tumor cells in HER2 positive early breast cancer J.-L. Zhang, Q. Yao, J.-H. Chen,Y. Wang, H. Wang, Q. Fan, R. Ling, J. Yi and L. Wang Xijing Hospital Vascular Endocrine
Effects of Herceptin on circulating tumor cells in HER2 positive early breast cancer J.-L. Zhang, Q. Yao, J.-H. Chen,Y. Wang, H. Wang, Q. Fan, R. Ling, J. Yi and L. Wang Xijing Hospital Vascular Endocrine
ORIGINAL ARTICLE THORACIC ONCOLOGY
 Ann Surg Oncol (2013) 20:1934 1940 DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2800-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE THORACIC ONCOLOGY Predictors for Locoregional Recurrence for Clinical Stage III-N2 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Nodal
Ann Surg Oncol (2013) 20:1934 1940 DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2800-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE THORACIC ONCOLOGY Predictors for Locoregional Recurrence for Clinical Stage III-N2 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Nodal
Summary ID# 13095. Clinical Study Summary: Study H3E-EW-B012
 Page 1 Summary ID# 13095 Clinical Study Summary: Study H3E-EW-B012 First-line Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer under Routine Conditions: Observational Study on Overall Survival Date summary electronically
Page 1 Summary ID# 13095 Clinical Study Summary: Study H3E-EW-B012 First-line Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer under Routine Conditions: Observational Study on Overall Survival Date summary electronically
Ovarian Cancer and Modern Immunotherapy: Regulatory Strategies for Drug Development
 Ovarian Cancer and Modern Immunotherapy: Regulatory Strategies for Drug Development Sanjeeve Bala, MD, MPH Ovarian Cancer Endpoints Workshop FDA White Oak September 3, 2015 Overview Immune agents from
Ovarian Cancer and Modern Immunotherapy: Regulatory Strategies for Drug Development Sanjeeve Bala, MD, MPH Ovarian Cancer Endpoints Workshop FDA White Oak September 3, 2015 Overview Immune agents from
Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know
 Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know AATS Focus in Thoracic Surgery 2014 David R. Jones, M.D. Professor & Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center I have no disclosures
Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know AATS Focus in Thoracic Surgery 2014 David R. Jones, M.D. Professor & Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center I have no disclosures
Future Directions in Clinical Research. Karen Kelly, MD Associate Director for Clinical Research UC Davis Cancer Center
 Future Directions in Clinical Research Karen Kelly, MD Associate Director for Clinical Research UC Davis Cancer Center Outline 1. Status of Cancer Treatment 2. Overview of Clinical Research at UCDCC 3.
Future Directions in Clinical Research Karen Kelly, MD Associate Director for Clinical Research UC Davis Cancer Center Outline 1. Status of Cancer Treatment 2. Overview of Clinical Research at UCDCC 3.
CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal
 CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal 1. STUDY TITLE: Longitudinal Assessment of Chronic Health Conditions: The Aging of Childhood Cancer Survivors 2. WORKING GROUP AND INVESTIGATORS:
CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal 1. STUDY TITLE: Longitudinal Assessment of Chronic Health Conditions: The Aging of Childhood Cancer Survivors 2. WORKING GROUP AND INVESTIGATORS:
A 70-year old Man with Pleural Effusion
 Mesothelioma Diagnosis: Pitfalls and Latest Updates S Klebe and DW Henderson Recommendations Indisputable malignant cells on cytomorphological criteria which demonstrate a mesothelial phenotype, which
Mesothelioma Diagnosis: Pitfalls and Latest Updates S Klebe and DW Henderson Recommendations Indisputable malignant cells on cytomorphological criteria which demonstrate a mesothelial phenotype, which
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015
 Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer. Mark A. Socinski, MD
 Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Clinical development of AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer
 Clinical development of AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer Rachael Lawrance (AstraZeneca) PSI One Day Meeting: The Innovative, Challenging and Diversified World of Respiratory Disease 13 Nov 2015 Overview
Clinical development of AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer Rachael Lawrance (AstraZeneca) PSI One Day Meeting: The Innovative, Challenging and Diversified World of Respiratory Disease 13 Nov 2015 Overview
micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved
 microrna 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions of target mrnas Act as negative
microrna 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions of target mrnas Act as negative
Gemcitabine, Paclitaxel, and Trastuzumab in Metastatic Breast Cancer
 Gemcitabine, Paclitaxel, and Trastuzumab in Metastatic Breast Cancer Review Article [1] December 01, 2003 By George W. Sledge, Jr, MD [2] Gemcitabine (Gemzar) and paclitaxel show good activity as single
Gemcitabine, Paclitaxel, and Trastuzumab in Metastatic Breast Cancer Review Article [1] December 01, 2003 By George W. Sledge, Jr, MD [2] Gemcitabine (Gemzar) and paclitaxel show good activity as single
Endpoint Selection in Phase II Oncology trials
 Endpoint Selection in Phase II Oncology trials Anastasia Ivanova Department of Biostatistics UNC at Chapel Hill aivanova@bios.unc.edu Primary endpoints in Phase II trials Recently looked at journal articles
Endpoint Selection in Phase II Oncology trials Anastasia Ivanova Department of Biostatistics UNC at Chapel Hill aivanova@bios.unc.edu Primary endpoints in Phase II trials Recently looked at journal articles
a Phase 2 prostate cancer clinical trial is ongoing. Table 2: Squalamine vs Standard-of-care literature
 PRODUCT FACT SHEET Spring 2007 MISSION STATEMENT Genaera Corporation is a biopharmaceutical company with a focus on metabolic and respiratory diseases. The compounds in the Genaera pipeline address signal
PRODUCT FACT SHEET Spring 2007 MISSION STATEMENT Genaera Corporation is a biopharmaceutical company with a focus on metabolic and respiratory diseases. The compounds in the Genaera pipeline address signal
Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma
 The Use of Kinase Inhibitors: Translational Lab Results Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Sheelu Varghese, Ph.D. H. Richard Alexander, M.D.
The Use of Kinase Inhibitors: Translational Lab Results Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Sheelu Varghese, Ph.D. H. Richard Alexander, M.D.
Genomic Medicine The Future of Cancer Care. Shayma Master Kazmi, M.D. Medical Oncology/Hematology Cancer Treatment Centers of America
 Genomic Medicine The Future of Cancer Care Shayma Master Kazmi, M.D. Medical Oncology/Hematology Cancer Treatment Centers of America Personalized Medicine Personalized health care is a broad term for interventions
Genomic Medicine The Future of Cancer Care Shayma Master Kazmi, M.D. Medical Oncology/Hematology Cancer Treatment Centers of America Personalized Medicine Personalized health care is a broad term for interventions
Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
 Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research & Development Service Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research & Development Service Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
Malignant Mesothelioma State of the Art
 Malignant Mesothelioma State of the Art Paul Baas The Netherlands Cancer Institute August 12, 2011, Carlsbad, CA Summary Diagnosis; epithelial type subdivided Pleiomorphic vs other Staging: IASLC-IMIG
Malignant Mesothelioma State of the Art Paul Baas The Netherlands Cancer Institute August 12, 2011, Carlsbad, CA Summary Diagnosis; epithelial type subdivided Pleiomorphic vs other Staging: IASLC-IMIG
The Whipple Operation for Pancreatic Cancer: Optimism vs. Reality. Franklin Wright UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds September 11, 2006
 The Whipple Operation for Pancreatic Cancer: Optimism vs. Reality Franklin Wright UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds September 11, 2006 Overview Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Pancreaticoduodenectomy
The Whipple Operation for Pancreatic Cancer: Optimism vs. Reality Franklin Wright UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds September 11, 2006 Overview Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Pancreaticoduodenectomy
HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer?
 Ask the Experts HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer? Bharat Jasani MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Marco Novelli MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Josef Rüschoff, MD Robert Y. Osamura, MD, FIAC
Ask the Experts HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer? Bharat Jasani MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Marco Novelli MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Josef Rüschoff, MD Robert Y. Osamura, MD, FIAC
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in East tasia Chia-Chi (Josh) Lin, MD, PhD 林 家 齊 Director of Phase I Center, e Department of Oncology, National Taiwan University Hospital Clinical Associate Professor, Department
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in East tasia Chia-Chi (Josh) Lin, MD, PhD 林 家 齊 Director of Phase I Center, e Department of Oncology, National Taiwan University Hospital Clinical Associate Professor, Department
Postoperative Adjuvant Chemotherapy, with or without Radiotherapy, in Completely Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 EBS 7-1-2 EDUCATION AND INFORMATION 2013 Evidence-based Series 7-1-2: EDUCATION AND INFORMATION- 2013 Postoperative Adjuvant Chemotherapy, with or without Radiotherapy, in Completely Resected Non-Small
EBS 7-1-2 EDUCATION AND INFORMATION 2013 Evidence-based Series 7-1-2: EDUCATION AND INFORMATION- 2013 Postoperative Adjuvant Chemotherapy, with or without Radiotherapy, in Completely Resected Non-Small
Introduction Objective Methods Results Conclusion
 Introduction Objective Methods Results Conclusion 2 Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is the most common form of mesothelioma a rare cancer associated with long latency period (i.e. 20 to 40 years),
Introduction Objective Methods Results Conclusion 2 Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is the most common form of mesothelioma a rare cancer associated with long latency period (i.e. 20 to 40 years),
The Value of Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 in Cytologic Preparations as a Marker for Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Lung Origin
 Anatomic Pathology / TTF-1 IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS The Value of Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 in Cytologic Preparations as a Marker for Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Lung Origin Jonathan L. Hecht, MD,
Anatomic Pathology / TTF-1 IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS The Value of Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 in Cytologic Preparations as a Marker for Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Lung Origin Jonathan L. Hecht, MD,
White paper Evaluation of BRAF (V600E) Mutation by Immunohistochemical Staining with anti-braf V600E (VE1) Antibody: A Comparison with Sanger
 White paper Evaluation of BRAF (V600E) Mutation by Immunohistochemical Staining with anti-braf V600E (VE1) Antibody: A Comparison with Sanger Sequencing 2 Evaluation of BRAF (V600E) Mutation by Immunohistochemical
White paper Evaluation of BRAF (V600E) Mutation by Immunohistochemical Staining with anti-braf V600E (VE1) Antibody: A Comparison with Sanger Sequencing 2 Evaluation of BRAF (V600E) Mutation by Immunohistochemical
The Kaplan-Meier Plot. Olaf M. Glück
 The Kaplan-Meier Plot 1 Introduction 2 The Kaplan-Meier-Estimator (product limit estimator) 3 The Kaplan-Meier Curve 4 From planning to the Kaplan-Meier Curve. An Example 5 Sources & References 1 Introduction
The Kaplan-Meier Plot 1 Introduction 2 The Kaplan-Meier-Estimator (product limit estimator) 3 The Kaplan-Meier Curve 4 From planning to the Kaplan-Meier Curve. An Example 5 Sources & References 1 Introduction
CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy
 CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy Joseph M. Tuscano, Jason Kato, David Pearson, Chengyi Xiong, Laura Newell, Yunpeng Ma, David R. Gandara,
CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy Joseph M. Tuscano, Jason Kato, David Pearson, Chengyi Xiong, Laura Newell, Yunpeng Ma, David R. Gandara,
Post-recurrence survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local recurrence
 Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Developments in Biomarker Identification and Validation for Lung Cancer
 Developments in Biomarker Identification and Validation for Lung Cancer Alexandre Passioukov, MD, PhD Alexandre.Passioukov@eortc.be Contents Introduction Lung cancer pathogenesis NSCLC treatment options
Developments in Biomarker Identification and Validation for Lung Cancer Alexandre Passioukov, MD, PhD Alexandre.Passioukov@eortc.be Contents Introduction Lung cancer pathogenesis NSCLC treatment options
Clinical Trial Designs for Incorporating Multiple Biomarkers in Combination Studies with Targeted Agents
 Clinical Trial Designs for Incorporating Multiple Biomarkers in Combination Studies with Targeted Agents J. Jack Lee, Ph.D. Department of Biostatistics 3 Primary Goals for Clinical Trials Test safety and
Clinical Trial Designs for Incorporating Multiple Biomarkers in Combination Studies with Targeted Agents J. Jack Lee, Ph.D. Department of Biostatistics 3 Primary Goals for Clinical Trials Test safety and
Cancer Treatments Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 18 September 2015. (minutes for web publishing)
 Cancer Treatments Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 18 September 2015 (minutes for web publishing) Cancer Treatments Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the
Cancer Treatments Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 18 September 2015 (minutes for web publishing) Cancer Treatments Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the
20 Diagnostic Cytopathology, Vol 36, No 1 ' 2007 WILEY-LISS, INC.
 Utility of WT-1, p63, MOC31, Mesothelin, and Cytokeratin (K903 and CK5/6) Immunostains in Differentiating Adenocarcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Malignant Mesothelioma in Effusions Robert T. Pu,
Utility of WT-1, p63, MOC31, Mesothelin, and Cytokeratin (K903 and CK5/6) Immunostains in Differentiating Adenocarcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Malignant Mesothelioma in Effusions Robert T. Pu,
ERCC1 and topoisomerase I expression in small cell lung cancer: Prognostic and predictive implications
 2104 ERCC1 and topoisomerase I expression in small cell lung cancer: Prognostic and predictive implications MARIA SERENO 1*, PALOMA CEJAS 2*, VÍCTOR MORENO 2, CRISTÓBAL BELDA-INIESTA 2, ROCIO LÓPEZ 2,
2104 ERCC1 and topoisomerase I expression in small cell lung cancer: Prognostic and predictive implications MARIA SERENO 1*, PALOMA CEJAS 2*, VÍCTOR MORENO 2, CRISTÓBAL BELDA-INIESTA 2, ROCIO LÓPEZ 2,
Evaluating the Efficiency of Targeted Designs for Randomized Clinical Trials
 Vol. 0, 6759 6763, October 5, 004 Clinical Cancer Research 6759 Perspective Evaluating the Efficiency of Targeted Designs for Randomized Clinical Trials Richard Simon and Aboubakar Maitournam Biometric
Vol. 0, 6759 6763, October 5, 004 Clinical Cancer Research 6759 Perspective Evaluating the Efficiency of Targeted Designs for Randomized Clinical Trials Richard Simon and Aboubakar Maitournam Biometric
Update on Mesothelioma
 November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
PATHOLOGY. HercepTestTM. Product Information
 PATHOLOGY HercepTestTM Product Information CLINICAL TRIALS HercepTest The First and Foremost Dako s pharmdx HercepTest was the first FDA-approved assay developed exclusively to aid physicians in identifying
PATHOLOGY HercepTestTM Product Information CLINICAL TRIALS HercepTest The First and Foremost Dako s pharmdx HercepTest was the first FDA-approved assay developed exclusively to aid physicians in identifying
Role of taxanes in the treatment of advanced NHL patients: A randomized study of 87 cases
 Role of taxanes in the treatment of advanced NHL patients: A randomized study of 87 cases R. Shraddha, P.N. Pandit Radium Institute, Patna Medical College and Hospital, Patna, India Abstract NHL is a highly
Role of taxanes in the treatment of advanced NHL patients: A randomized study of 87 cases R. Shraddha, P.N. Pandit Radium Institute, Patna Medical College and Hospital, Patna, India Abstract NHL is a highly
Targeting angiogenesis in NSCLC: Clinical trial update Martin Reck Lung Clinic Grosshansdorf Grosshansdorf, Germany
 Targeting angiogenesis in NSCLC: Clinical trial update Martin Reck Lung Clinic Grosshansdorf Grosshansdorf, Germany This presentation was selected by the 15 th World Conference on Lung Cancer Program Committee
Targeting angiogenesis in NSCLC: Clinical trial update Martin Reck Lung Clinic Grosshansdorf Grosshansdorf, Germany This presentation was selected by the 15 th World Conference on Lung Cancer Program Committee
Adiuwantowe i neoadiuwantowe leczenie chorych na zaawansowanego raka żołądka
 Adiuwantowe i neoadiuwantowe leczenie chorych na zaawansowanego raka żołądka Neoadiuvant and adiuvant therapy for advanced gastric cancer Franco Roviello, IT Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for advanced
Adiuwantowe i neoadiuwantowe leczenie chorych na zaawansowanego raka żołądka Neoadiuvant and adiuvant therapy for advanced gastric cancer Franco Roviello, IT Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for advanced
Lung cancer. A guide for journalists on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and its treatment
 Lung cancer A guide for journalists on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Lung Cancer 4 i. Types of lung cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms
Lung cancer A guide for journalists on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Lung Cancer 4 i. Types of lung cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms
Translating DNA repair pathways into therapeutic targets: beyond the BRCA1/2 and PARP inhibitor saga. Jorge S Reis-Filho, MD PhD FRCPath
 Translating DNA repair pathways into therapeutic targets: beyond the BRCA1/2 and PARP inhibitor saga Jorge S Reis-Filho, MD PhD FRCPath Summary How do PARP inhibitors work? Synthetic lethality Potential
Translating DNA repair pathways into therapeutic targets: beyond the BRCA1/2 and PARP inhibitor saga Jorge S Reis-Filho, MD PhD FRCPath Summary How do PARP inhibitors work? Synthetic lethality Potential
Decision to Continue the Development of Tecemotide (L-BLP25) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to be Announced
 September 27, 2013 ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD. Corporate Communications Phone: +81-6-6263-5670 Decision to Continue the Development of Tecemotide (L-BLP25) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to be Announced
September 27, 2013 ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD. Corporate Communications Phone: +81-6-6263-5670 Decision to Continue the Development of Tecemotide (L-BLP25) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to be Announced
Personalized Predictive Medicine and Genomic Clinical Trials
 Personalized Predictive Medicine and Genomic Clinical Trials Richard Simon, D.Sc. Chief, Biometric Research Branch National Cancer Institute http://brb.nci.nih.gov brb.nci.nih.gov Powerpoint presentations
Personalized Predictive Medicine and Genomic Clinical Trials Richard Simon, D.Sc. Chief, Biometric Research Branch National Cancer Institute http://brb.nci.nih.gov brb.nci.nih.gov Powerpoint presentations
Lung Cancer: More than meets the eye
 Lung Cancer Education Program November 23, 2013 Lung Cancer: More than meets the eye Shantanu Banerji MD, FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Shantanu Banerji Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
Lung Cancer Education Program November 23, 2013 Lung Cancer: More than meets the eye Shantanu Banerji MD, FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Shantanu Banerji Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
REPORT PERSPECTIVES IN LUNG CANCER 2010 AMSTERDAM
 REPORT PERSPECTIVES IN LUNG CANCER 2010 AMSTERDAM Valerie Van Damme, Isabelle Wauters, Johan Vansteenkiste Univ. Hospital Leuven and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Introduction Perspectives in Lung Cancer (PILC)
REPORT PERSPECTIVES IN LUNG CANCER 2010 AMSTERDAM Valerie Van Damme, Isabelle Wauters, Johan Vansteenkiste Univ. Hospital Leuven and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Introduction Perspectives in Lung Cancer (PILC)
Development of Bone Metastases in Men With Prostate Cancer
 Development of Bone Metastases in Men With Prostate Cancer Explore the Causes Understand the Consequences Natural History of Prostate Cancer Progression Many prostate tumors may become castrate-resistant
Development of Bone Metastases in Men With Prostate Cancer Explore the Causes Understand the Consequences Natural History of Prostate Cancer Progression Many prostate tumors may become castrate-resistant
Stage IV Renal Cell Carcinoma. Changing Management in A Comprehensive Community Cancer Center. Susquehanna Health Cancer Center
 Stage IV Renal Cell Carcinoma Changing Management in A Comprehensive Community Cancer Center Susquehanna Health Cancer Center 2000 2009 Warren L. Robinson, MD, FACP January 27, 2014 Introduction 65,150
Stage IV Renal Cell Carcinoma Changing Management in A Comprehensive Community Cancer Center Susquehanna Health Cancer Center 2000 2009 Warren L. Robinson, MD, FACP January 27, 2014 Introduction 65,150
Clinical Indications and Results Following Chest Wall Resection
 Clinical Indications and Results Following Chest Wall Resection for Recurrent Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Ali SO, Burt BM, Groth SS, DaSilva MC, Yeap BY, Richards WG, Baldini EH and Sugarbaker DJ. Division
Clinical Indications and Results Following Chest Wall Resection for Recurrent Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Ali SO, Burt BM, Groth SS, DaSilva MC, Yeap BY, Richards WG, Baldini EH and Sugarbaker DJ. Division
REPORT ASCO 2002 ORLANDO : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group
 REPORT ASCO 2002 ORLANDO : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group In the 2002 edition of the ASCO meeting, a total of 315 abstracts in the field of respiratory
REPORT ASCO 2002 ORLANDO : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group In the 2002 edition of the ASCO meeting, a total of 315 abstracts in the field of respiratory
AIDS IN IDENTIFYING CANDIDATES FOR HER2-TARGETED THERAPY
 AIDS IN IDENTIFYING CANDIDATES FOR HER2-TARGETED THERAPY THE HERMARK BREAST CANCER ASSAY HERmark is based on our proprietary VeraTag technology that precisely quantifies HER2 proteins and protein complexes
AIDS IN IDENTIFYING CANDIDATES FOR HER2-TARGETED THERAPY THE HERMARK BREAST CANCER ASSAY HERmark is based on our proprietary VeraTag technology that precisely quantifies HER2 proteins and protein complexes
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Sur les nouveaux médicaments et les perspectives qu ils offrent (traitement à la carte et survie longue)
 Sur les nouveaux médicaments et les perspectives qu ils offrent (traitement à la carte et survie longue) Professeur Jean Trédaniel Unité de cancérologie thoracique Hôpital Saint-Louis Comparison of Four
Sur les nouveaux médicaments et les perspectives qu ils offrent (traitement à la carte et survie longue) Professeur Jean Trédaniel Unité de cancérologie thoracique Hôpital Saint-Louis Comparison of Four
The Impact of Palliative Care and Hospice Services in the Care of Patients with Advanced Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 The Impact of Palliative Care and Hospice Services in the Care of Patients with Advanced Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Richard C. Stephenson, MD Hospice & Palliative CareCenter Amy H. Hughes Forsyth
The Impact of Palliative Care and Hospice Services in the Care of Patients with Advanced Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Richard C. Stephenson, MD Hospice & Palliative CareCenter Amy H. Hughes Forsyth
Mechanism Of Action of Palbociclib & PFS Benefit
 A Phase II Randomized Controlled Trial of Palbociclib & Tamoxifen/Fulvestrant in Postmenopausal Women and Men With Hormone-Receptor Positive, HER2- Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC) Protocol Chair:
A Phase II Randomized Controlled Trial of Palbociclib & Tamoxifen/Fulvestrant in Postmenopausal Women and Men With Hormone-Receptor Positive, HER2- Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC) Protocol Chair:
A new predictive algorithm for aiding clinical decision-making in lung cancer
 Better Care. Faster A new predictive algorithm for aiding clinical decision-making in lung cancer Y Kogan, I Sela, Y Kheiffetz, M Kleiman, Z Agur, Optimata Ltd., O Liran, N Peled, Sheba hospital, I Lazarev,
Better Care. Faster A new predictive algorithm for aiding clinical decision-making in lung cancer Y Kogan, I Sela, Y Kheiffetz, M Kleiman, Z Agur, Optimata Ltd., O Liran, N Peled, Sheba hospital, I Lazarev,
What is the reference cytotoxic regimen in advanced gastric cancer?
 What is the reference cytotoxic regimen in advanced gastric cancer? Florian Lordick Professor of Oncology Director of the University Cancer Center Leipzig (UCCL) Germany What we know from clinical research.
What is the reference cytotoxic regimen in advanced gastric cancer? Florian Lordick Professor of Oncology Director of the University Cancer Center Leipzig (UCCL) Germany What we know from clinical research.
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Analysis for Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_analysis_for_targeted_therapy_for_non_small_cell_lung_cancer
Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Analysis for Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_analysis_for_targeted_therapy_for_non_small_cell_lung_cancer
GUIDELINES ADJUVANT SYSTEMIC BREAST CANCER
 GUIDELINES ADJUVANT SYSTEMIC BREAST CANCER Author: Dr Susan O Reilly On behalf of the Breast CNG Written: December 2008 Agreed at CNG: June 2009 & June 2010 Review due: June 2011 Guidelines Adjuvant Systemic
GUIDELINES ADJUVANT SYSTEMIC BREAST CANCER Author: Dr Susan O Reilly On behalf of the Breast CNG Written: December 2008 Agreed at CNG: June 2009 & June 2010 Review due: June 2011 Guidelines Adjuvant Systemic
Malignant Mesothelioma: an Update
 Malignant Mesothelioma: an Update Nico van Zandwijk Asbestos Diseases Research Institute Bernie Banton Centre University of Sydney Australia Physicians Week RACP 19-5-2009 Health Risks of Asbestos Fibers
Malignant Mesothelioma: an Update Nico van Zandwijk Asbestos Diseases Research Institute Bernie Banton Centre University of Sydney Australia Physicians Week RACP 19-5-2009 Health Risks of Asbestos Fibers
Outline. Workup for metastatic breast cancer. Metastatic breast cancer
 Metastatic breast cancer Immunostain Update: Diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma, emphasizing distinction from GYN primary 1/3 of breast cancer patients will show metastasis 1 st presentation or 20-30
Metastatic breast cancer Immunostain Update: Diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma, emphasizing distinction from GYN primary 1/3 of breast cancer patients will show metastasis 1 st presentation or 20-30
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma
 Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
H. Richard Alexander, Jr., M.D. Department of Surgery and The Greenebaum Cancer Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Baltimore, Md
 Major Advances in Cancer Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment~ Why Mesothelioma Leads the Way H. Richard Alexander, Jr., M.D. Department of Surgery and The Greenebaum Cancer Center University of Maryland
Major Advances in Cancer Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment~ Why Mesothelioma Leads the Way H. Richard Alexander, Jr., M.D. Department of Surgery and The Greenebaum Cancer Center University of Maryland
18.5 Percent Overall Response Rate Observed in Pembrolizumab-Treated Patients with this Aggressive Form of Breast Cancer
 News Release Media Contacts: Annick Robinson Investor Contacts: Joseph Romanelli (514) 837-2550 (908) 740-1986 Stephanie Lyttle NATIONAL Public Relations (514) 843-2365 Justin Holko (908) 740-1879 Merck
News Release Media Contacts: Annick Robinson Investor Contacts: Joseph Romanelli (514) 837-2550 (908) 740-1986 Stephanie Lyttle NATIONAL Public Relations (514) 843-2365 Justin Holko (908) 740-1879 Merck
MEDICAL POLICY EFFECTIVE DATE: 07/20/06 REVISED DATE: 10/18/07, 10/23/08, 10/29/09, 10/28/10, 03/17/11, 02/16/12, 01/17/13, 01/16/14
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: HER-2 TESTING IN INVASIVE BREAST OR PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: HER-2 TESTING IN INVASIVE BREAST OR PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
Mesothelioma. 1. Introduction. 1.1 General Information and Aetiology
 Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
MOLOGEN AG. Q1 Results 2015 Conference Call Dr. Matthias Schroff Chief Executive Officer. Berlin, 12 May 2015
 Q1 Results 2015 Conference Call Dr. Matthias Schroff Chief Executive Officer Berlin, 12 May 2015 V1-6 Disclaimer Certain statements in this presentation contain formulations or terms referring to the future
Q1 Results 2015 Conference Call Dr. Matthias Schroff Chief Executive Officer Berlin, 12 May 2015 V1-6 Disclaimer Certain statements in this presentation contain formulations or terms referring to the future
Clinical Study Report
 An Open, Multi-Center, Phase II Clinical Trial to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of Taxol (), UFT, and Leucovorin in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer Clinical Study Report 4F, No. 156, Jiankang Rd.,
An Open, Multi-Center, Phase II Clinical Trial to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of Taxol (), UFT, and Leucovorin in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer Clinical Study Report 4F, No. 156, Jiankang Rd.,
Treatment Paradigm in NSCLC Treatment
 Treatment Paradigm in NSCLC Treatment Era of Targeted Therapy Aumkhae Sookprasert, MD Medicine Department, KKU Which factors taken to be account in NSCLC treatment? 1. Staging 2. ECOG performance status
Treatment Paradigm in NSCLC Treatment Era of Targeted Therapy Aumkhae Sookprasert, MD Medicine Department, KKU Which factors taken to be account in NSCLC treatment? 1. Staging 2. ECOG performance status
Transgene Presents Additional Positive Clinical Data from Phase 2b Part of TIME Trial with TG4010 at ESMO
 Transgene Presents Additional Positive Clinical Data from Phase 2b Part of TIME Trial with TG4010 at ESMO Statistically significant difference in progression-free survival continues to be seen in non-squamous
Transgene Presents Additional Positive Clinical Data from Phase 2b Part of TIME Trial with TG4010 at ESMO Statistically significant difference in progression-free survival continues to be seen in non-squamous
Breast and Lung Cancer Biomarker Research at ASCO: Changing Treatment Patterns
 July 2013 Edition Vol. 7, Issue 7 Breast and Lung Cancer Biomarker Research at ASCO: Changing Treatment Patterns By Julie Katz, MPH, MPhil Biomarkers played a prominent role in the research presented in
July 2013 Edition Vol. 7, Issue 7 Breast and Lung Cancer Biomarker Research at ASCO: Changing Treatment Patterns By Julie Katz, MPH, MPhil Biomarkers played a prominent role in the research presented in
Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins
 The American Journal of Surgery 190 (2005) 521 525 George Peter s Award Winner Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins Heather R. MacDonald,
The American Journal of Surgery 190 (2005) 521 525 George Peter s Award Winner Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins Heather R. MacDonald,
Targeted therapies and brain metastases in lung cancer patients. Benjamin Besse, MD, PhD. Medical Oncologist. 19 septembre 2014
 Targeted therapies and brain metastases in lung cancer patients Benjamin Besse, MD, PhD Medical Oncologist 19 septembre 2014 Targeted therapies and brain mets! Brain mets in NSCLC! Specific targeted therapies!
Targeted therapies and brain metastases in lung cancer patients Benjamin Besse, MD, PhD Medical Oncologist 19 septembre 2014 Targeted therapies and brain mets! Brain mets in NSCLC! Specific targeted therapies!
Dietary treatment of cachexia challenges of nutritional research in cancer patients
 Dietary treatment of cachexia challenges of nutritional research in cancer patients Trude R. Balstad 4th International Seminar of the PRC and EAPC RN, Amsterdam 2014 Outline Cancer cachexia Dietary treatment
Dietary treatment of cachexia challenges of nutritional research in cancer patients Trude R. Balstad 4th International Seminar of the PRC and EAPC RN, Amsterdam 2014 Outline Cancer cachexia Dietary treatment
