Recent Trends in Management of Unresectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
|
|
|
- Rhoda Curtis
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.23, No.4, December 2001 Recent Trends in Management of Unresectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Jalal Al-Maskati, MBChB, ABIM * Lung cancer is a major health problem worldwide. It is etiologically related to smoking, the incidence is high and increasing in many countries, in both men and women. The treatment is so far not ideal and the results of various modalities of treatment available have reduced mortality only slightly. This is a review of the role of chemotherapy in treatment of lung cancer, with emphasis on the role of newer cytotoxic drugs in management of locally advanced and metastatic Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); when definite curative surgery is not feasible. Bahrain Med Bull 2001;23(4): NSCLC is a significant health problem around the world. In the USA, NSCLC is the second most common cancer in both men and women, and the leading cause of death in both groups 1. According to the publications of GCC cancer registry, lung cancer is the most common type of cancer among men in Bahrain and has the highest rate compared to other Gulf States with an Age Standardized Rate (ASR) at 22.6/100, This is a review of the role of chemotherapy in the treatment of lung cancer. Epidemiology Incidence rates of lung cancer is continuing to increase in most countries of the world. It increases with age and is steadily increasing in both industrialized and developing countries. While efforts in early detection and adequate treatment have failed to reduce mortality significantly, the major cause of this disease is known to be cigarette smoking. Primary prevention through control of cigarette smoking is the most important measure for combating the disease 3. Most patients with lung cancer are diagnosed between 35 to 75 years of age with a peak at years. More than 80% of lung cancer among men is related to cigarette smoking. The incidence and mortality rates from lung cancer among women are now rising faster than men and lung cancer is already the leading cause of cancer deaths among women in some countries * Consultant Medical Oncologist Department of Medicine Salmaniya Medical Complex & Deputy Chairman National Cancer Control Committee Ministry of Health State of Bahrain 1
2 Less than 10% of lung cancer patients survive 5 years and 80% are dead within a year of diagnosis 1. Cessation of cigarette smoking is followed by a decrease in the risk of lung cancer and the mortality rate from lung cancer would return to the level of nonsmoker within 20 years. In patients with metastatic disease, median survival is only 4 months for patients treated with best supportive care alone. Pathology Lung cancer usually originates from the epithelium of the primary and segmental bronchi and less frequently from the peripheral small bronchi. There are many histological types of lung cancer and currently it is divided into either Small Cell (20-25%) or Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (75-80%). This review is concerned only with NSCLC that includes many sub-types 3 : Squamous Carcinomas are the most common (40-50%), tend to be central and occur primarily in men. These may be highly differentiated with keratin formation or anaplastic. Adenocarcinomas make up 25-30%. They are often peripheral and may present as pleural effusion. They are less often associated with smoking than other types of lung cancer. Large Cell Carcinomas occur in only 10% of cases. They may appear either centrally or peripherally. Other types are uncommon, it include bronchiolo-alveolar carcinomas, carcinoid tumours and mucoepidermoid carcinomas. Staging of NSCLC TNM Clinical Classification system and stage Grouping. Table 1. Summary of TNM Clinical Classification System for NSCLC TX Positive cytology T1 3 cm T2 > 3 cm, main bronchus 2 cm or more from carina, invades visceral pleura, partial atelectasis T3 chest wall, diaphragm, pericardium, mediastinal pleura, main bronchus < 2 cm from carina, total atelectasis T4 Mediastinum, heart, great vessels, carina, trachea, oesophagus, vertebra; separate nodules in the same lobe, malignant effusion N1 Ipsilateral peribronchial, ipsilateral hilar 2
3 N2 N3 Ipsilateral mediastinal, subcarinal Contralateral mediastinal or hilar, scalene or supraclavicular M1 Includes separate nodule in different lobe T = Tumour (primary) N = Node M = Metastases Table 2. Stage Grouping for NSCLC Occult Carcinoma TX N0 M0 Stage 0 Tis N0 M0 Stage IA T1 N0 M0 Stage IB T2 N0 M0 Stage IIA T1 N1 M0 Stage IIB T2 N1 M0 T3 N0 M0 Stage IIIA T1 N2 M0 T2 N2 M0 T3 N1, N2 M0 Stage IIB Any T N3 M0 T4 Any N M0 Stage IV Any T Any N M1 Management of NSCLC Principles of Treatment: Surgery is the treatment of choice for early stage of NSCLC (T is, T 1 and T 2, N 0, M 0 ) with the hope of cure. Lobectomy is preferred when feasible. About 25% of all patients can have a resection with some hope of cure. Patients with T 2, N 1 lesions respond less favorably to surgical treatment. Recently, patients with clinical N 2 disease have been treated with cytotoxic drugs (Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy) prior to surgery and some responders have been converted to operable and thus possibly curable 1-3. In some patients, radiation therapy may be given with curative intent. These are usually patients for whom surgery is a risk. But radiation therapy may cause pulmonary fibrosis and cardiac damage. Radiation therapy is used for palliation of symptoms such as persistent cough, pain, haemoptysis and hoarseness. Radiotherapy is also utilized to relieve bronchial obstruction, superior vena cava compression and to control pain due to bone or brain 3
4 metastases. However, the use of pre-operative irradiation does not improve the rate of resectability or curability of lung cancer. Chemotherapy, usually a platinum-based regimen, is appropriate for selected patients with unresectable, locally advanced and metastatic NSCLC. A detrimental effect on survival was observed with older alkylating agent-based regimens. In patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC, two or more cycles of cisplatin-based chemotherapy with or followed by radiation has been proven to enhance survival; ongoing maintenance chemotherapy is of unproven benefit. Chemotherapy should be administered for no more than eight cycles in patients with stage III or IV NSCLC. Delayed chemotherapy until symptoms develop may negate the survival benefits of treatment. There is no current evidence that second-line chemotherapy improves survival in patients with nonresponding or progressive NSCLC. Histological type of NSCLC is not an important prognostic factor in these patients and the role of newer prognostic factors (eg. P53 mutation) in clinical decision-making is investigational. Treatment of Unresectable NSCLC Chemotherapy in association with definitive-dose radiotherapy prolongs survival in patients with locally advanced and surgically unresectable NSCLC. These patients frequently have extensive disease and compromised performance status, often associated with significant co-morbid conditions. Physicians have an obligation to help patients make the right decision. The anticipated outcome, the potential toxicity and inconvenience of therapy is critical and should be discussed with the patients 6. Unresectable Stage III NSCLC Traditionally, such patients were treated with thoracic radiotherapy with 5-year survival rates of 4% to 8%. In a recent meta-analysis of all randomized trials of radiotherapy with or without cisplatin-based chemotherapy, the addition of chemotherapy led to a 13% reduction in death risk, although the absolute survival advantage at 2 years was a modest 4% 7. In a randomized trial in the early eightees, three times as many patients were alive at 5 years after combined modality compared with patients receiving radiation alone (17% versus 6%) 8, 9. Controlled studies of concurrent chemo-radiotherapy with daily low-dose, less toxic administration of drugs have been documented to prolong survival compared with radiation alone 10,11. Based on these data cisplatin-based chemotherapy regimens became the standard treatment for locally advanced NSCLC. Chemotherapy also demonstrated both improvement in cancer related symptoms and to be cost effective. The results of a recent meta-analysis of a large co-operative group experiences indicate survival is most improved with platinum based chemotherapy 7,16. Another recent metaanalysis addressed survival benefits of single agent chemotherapy compared with 4
5 combination chemotherapy and nine controlled trials that enrolled 1,493 patients were included in the analysis. The estimated pooled odds ratio was 0.80 in favor of combination chemotherapy 17. The best platinum based regimen is not well defined. Numerous combinations have been prospectively compared using older agents, with no single regimen emerging as the superior combination. Recently published prospective trials indicate relatively new drugs as vinorelbine or paclitaxel in combination with cisplatin can improve survival beyond that achieved with more established regimens such as cisplatin plus vindesine 14 or cisplatin plus etoposide 13, respectively. Regarding the selection of drugs, uncontrolled studies suggest that cisplatin and carboplatin may have comparable efficacy against NSCLC 25,26. Stage IV NSCLC Chemotherapy modestly improves median survival in patients with distant metastatic NSCLC compared with best supportive care, but is not curative. The results of three recently published meta-analyses indicate that cisplatin-based chemotherapy yields an improvement in median survival of approximately 6 to 8 weeks in stage IV NSCLC 6,7,12. The one year survival rate is increased from 15% to 25%. Compared with supportive care alone, cisplatin-based chemotherapy produced an absolute improvement in survival of 10% at one year 7. These meta-analyses do not include the most recent randomized data evaluating newer drugs. In a recent randomized trial, two dose levels of paclitaxel given in conjunction with cisplatin have produced significantly higher response rates and borderline survival improvement compared to etoposide with cisplatin. No survival advantage with higher dose, but more toxic with Paclitaxel regimen effect 13. Both single-agent vinorelbine (navelbine) and single-agent cisplatin have been found to produce survival rates inferior to cisplatin plus vinorelbine in two recently completed phase III trials. 14,15 These randomized trials show that one year survival rates of 35% to 40% are achieved with these newer regimens. Recently, a number of new non-platinum compounds have demonstrated activity in NSCLC, including paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine, navelbine, irinotecan and topotecan. Response rates for these new compounds have ranged from 12-42% in phase II and III trials Table 3. Summary of Phase I/II studies with non-platinum-based doublets in NSCLC Author Drugs Patients Response Other Rate Takeda 19 Tax/CPT % 1 yr survival=38% Herbst 20 Gem/Navel 56 42% MS=32.4 wks 5
6 Kourousis 21 Tax/Navel 46 37% 1 yr survival=24% Trillet-Lenoir 22 Tax/Navel 39 27% Krug 23 Tax/Navel 35 54% 1 yr survival=86% Rosen Paclitaxel/Gem -- 22% Second line Spiridonidis 24 Tax/Gem 21 43% Phase I Georgoulias 25 Tax/Gem % 1 yr survival=51% Tax = Taxotere, CPT-11 = Irinotecan, Gem = Gemcitabine, Navel = Navelbine, MS= Median Survival Investigators have developed many non-platinum -based doublets in the hope of maintaining activity with lower toxicity. In NSCLC, non-platinum- based doublets that have demonstrated interest include Taxotere Gemcitabine, Taxotere Navelbine, Gemcitabine Nabelbine, Taxotere Irinotecan and Gemcitabine Irinotecan. The results of many randomized phase I/II studies with non-platinum doublets showed high response rate ranging from 22% to 54% with survival advantage at one year (Table 3) CONCLUSION The overall management of lung cancer is multidisciplinary; the change noted recently in management of unresectable NSCLC is mostly with the introduction of newer cytotoxic drugs. These drugs are given in combination with or without cisplatin, which is considered the standard treatment. The response rates are improving but the results on survival rates are still modest. Further trials and efforts are needed to improve on overall survival and quality of life of these patients. REFERENCES 1. McVie JG. Cancer of the lung and pleura. In: Hossfeld DK, Sherman CD, eds. Manual of Clinical Oncology. 5 th ed. UICC: Springer-verlag, 1990: Cancer Incidence Summary GCC Countries. 1 st report from Gulf Center for Cancer Registration. KFSH, Riyad, Saudi Arabia: Hoogstraten B, et al. Lung Tumors: lung, mediastinum, pleura and chest wall (International Union Against Cancer) New York: Springer, Prorok PC, Miller AB, eds. Screening for Cancer. International Union against Cancer, Geneva (UICC) Technical Report Series, No 78, Sobin LH, Wittekind Ch. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours,UICC, New York: Wiley-Liss, 1997: Grilli R, Oxman AD, Jullian JA. Chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: How much Benefit is enough? J Clin Oncol 1993;11: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Collaborative Group. Chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis using updated data on individual patients from 52 randomized clinical trials. BMJ 1995;311:
7 8. Dillman RO, Seagren SL, Propert KJ, et al. A randomized trial of induction chemotherapy plus high-dose radiation versus radiation alone in stage III non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 1990;323: Dillman RO, Seagren SL, Herndon J, et al. Improved survival in stage III nonsmall cell lung cancer: Seven year follow-up of CALGB J Natl Cancer Inst 1996;88: Jeremic B, Shibamoto Y, Acimovic L, et al. Hyperfractionated radiation therapy with or without concurrent low-dose daily carboplatin/etoposide for stage III nonsmall-cell lung cancer: A randomized study. J Clin Oncol 1996;14: Schaake-Koning C, van den Bogaert W, Dalesio W, et al. Effects of concomitant cisplatin and radiotherapy on in-operable non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 1992;326: Souquet PJ, Chauvin F, Boissel JP, et al. Polychemotherapy in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Lancet 1993;342: Bonomi P, Kim K, Chang A, et al. Phase III trial comparing etoposide (E), cisplatin (C) versus Taxol (T) with cisplatin-g-csf (G) versus Taxol-cisplatin in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. An Eastern Cooperative Group (ECOG) trial [Abstract]. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1996;15: Le Chevalier T, Brisgard D, Douillard JY, et al. Randomized study of vinorelbine and cisplatin versus vindesine and cisplatin versus vinorelbine alone in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Results of a European multi-center trial including 612 patients. J Clin Oncol 1994;12: Wozniak AJ, Crowley JJ, Balcerzak SP, et al. Randomized phase II trial of cisplatin (CDDP) versus CDDP plus Navelbine (NVB) in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Report of the Southwest Oncology Group study (SWOG-9308) [Abstract]. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1996;15: Albain KS, Crowley JJ, Le Blanc M, et al. Survival determinants in extensivestage non-small cell lung cancer: The Southwest Oncology Group experience. J Clin Oncol 1991;9: Marino P, Preatoni A, Cantoni A, et al. Single-agent chemotherapy versus combination chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A quality and meta-analysis study. Lung Cancer 1995;13: Takeda K, et al. Phase I study of docetaxel and irinotecan(cpt-11) for previously untreated advanced non-small cell lung cancer [Abstract 2019]. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1999;18: Herbst RS, et al. Chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 1997;11:
8 20. Kourousis C, et al. First-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma with docetaxel and vinorelbine. Cancer 1998;83: Trillet-lenoir V. Interim results of a phase II study of docetaxel ( Taxotere) and vinorelbine in chemotherapy naïve patients with advanced non small cell lung carcinoma [Abstract 450P]. Ann Oncol 1996;7(Suppl 5): Krug LM, et al. Phase II trial of dose dense docetaxel plus vinorelbine with prophylactic fillgrastim (G-CSF) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [Abstract 1775]. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1999;18: Spiridonidis CH. Phase I study of docetaxel dose escalation in combination with fixed weekly gemcitabine in patients with advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol 1998;16;12: Georgoulias V. Front-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with docetaxel and gemcitabine: a multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 1999;17;3: Colvin M. Alkylating Agents and Platinum Antitumor Compounds. 3 rd edn. Philadelphia:Lea & Febiger, Calabresi P, Chabner BA. Chemotherapy of Neoplastic Disease. 9 th edn. New York: McGraw-Hill,
NCCN Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer V.1.2011 Update Meeting 07/09/10
 Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Stage IIIB disease includes patients with T4 tumors,
 Guidelines on Treatment of Stage IIIB Non-small Cell Lung Cancer* James R. Jett, MD, FCCP; Walter J. Scott, MD, FCCP; M. Patricia Rivera MD, FCCP; and William T. Sause, MD, FACR Stage IIIB includes patients
Guidelines on Treatment of Stage IIIB Non-small Cell Lung Cancer* James R. Jett, MD, FCCP; Walter J. Scott, MD, FCCP; M. Patricia Rivera MD, FCCP; and William T. Sause, MD, FACR Stage IIIB includes patients
SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of
 Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Stage I, II Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Stage I, II Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Best Results T1 (less 3 cm) N0 80% 5 year survival No Role Adjuvant Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Reduces Local Recurrence No Improvement in Survival 1 Staging Mediastinal
Stage I, II Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Best Results T1 (less 3 cm) N0 80% 5 year survival No Role Adjuvant Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Reduces Local Recurrence No Improvement in Survival 1 Staging Mediastinal
Management of stage III A-B of NSCLC. Hamed ALHusaini Medical Oncologist
 Management of stage III A-B of NSCLC Hamed ALHusaini Medical Oncologist Global incidence, CA cancer J Clin 2011;61:69-90 Stage III NSCLC Includes heterogeneous group of patients with differences in the
Management of stage III A-B of NSCLC Hamed ALHusaini Medical Oncologist Global incidence, CA cancer J Clin 2011;61:69-90 Stage III NSCLC Includes heterogeneous group of patients with differences in the
Stage 3 Lung Cancer - Know YourSurviving Conditions
 Survival of Stage IIIb and IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients on Best Supportive Care in Manitoba, Canada Erich Kliewer Alain Demers Sri Navaratnam Coreen Hildebrand Grace Musto Report for AstraZeneca
Survival of Stage IIIb and IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients on Best Supportive Care in Manitoba, Canada Erich Kliewer Alain Demers Sri Navaratnam Coreen Hildebrand Grace Musto Report for AstraZeneca
B. Dingle MD, FRCPC, Brian Yaremko MD,FRCPC, R. Ash, MD, FRCPC, P. Truong, MD, FRCPC
 Lung Cancer B. Dingle MD, FRCPC, Brian Yaremko MD,FRCPC, R. Ash, MD, FRCPC, P. Truong, MD, FRCPC EPIDEMIOLOGY The estimated incidence of lung cancer in Canada for 2007 is 23,300 with 12,400 occurring in
Lung Cancer B. Dingle MD, FRCPC, Brian Yaremko MD,FRCPC, R. Ash, MD, FRCPC, P. Truong, MD, FRCPC EPIDEMIOLOGY The estimated incidence of lung cancer in Canada for 2007 is 23,300 with 12,400 occurring in
Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART
 Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART Goals Discuss treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer: New and old Discuss new developments in personalized
Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART Goals Discuss treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer: New and old Discuss new developments in personalized
Controversies in Management of. Inoperable NSCLC. Inoperable NSCLC. Introduction:
 Inoperable NSCLC Controversies in Management of Inoperable NSCLC Introduction: It is difficult to overemphasize the magnitude of lung cancer as Public Health Problem in our society. - In US, Lung cancer
Inoperable NSCLC Controversies in Management of Inoperable NSCLC Introduction: It is difficult to overemphasize the magnitude of lung cancer as Public Health Problem in our society. - In US, Lung cancer
Lung Cancer Treatment Guidelines
 Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
5. Non small Cell Lung Cancer
 5. Non small Cell Lung Cancer Introduction The cancer registry in Sweden shows a continuous increase of lung cancer cases from 867 in 1958 when the registry started to 2 846 in 2000. The Swedish cancer
5. Non small Cell Lung Cancer Introduction The cancer registry in Sweden shows a continuous increase of lung cancer cases from 867 in 1958 when the registry started to 2 846 in 2000. The Swedish cancer
Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians
 Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians Background The Cancer Institute New South Wales Oncology Group Lung (NSWOG Lung) identified the need for the development
Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians Background The Cancer Institute New South Wales Oncology Group Lung (NSWOG Lung) identified the need for the development
Table of Contents. Data Supplement 1: Summary of ASTRO Guideline Statements. Data Supplement 2: Definition of Terms
 Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary
 TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Lung Cancer. Public Outcomes Report. Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD
 Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
POLICY A. INDICATIONS
 Alimta (pemetrexed) Line(s) of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration Akamai Advantage Original Effective Date: 09/01/2007 Current Effective Date: 10/01/2015 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indications below
Alimta (pemetrexed) Line(s) of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration Akamai Advantage Original Effective Date: 09/01/2007 Current Effective Date: 10/01/2015 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indications below
Is the third-line chemotherapy feasible for non-small cell lung cancer? A retrospective study
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.1, 2004 19 Is the third-line chemotherapy feasible for non-small cell lung cancer? A retrospective study MUSTAFA ÖZDO AN, MUSTAFA SAMUR, HAKAN BOZCUK, ERKAN ÇOBAN,
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.1, 2004 19 Is the third-line chemotherapy feasible for non-small cell lung cancer? A retrospective study MUSTAFA ÖZDO AN, MUSTAFA SAMUR, HAKAN BOZCUK, ERKAN ÇOBAN,
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015
 Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
An Overview of Lung Cancer Symptoms, Pathophysiology, And Treatment Linda H. Yoder
 CE Objectives and Evaluation Form appear on page 235. An Overview of Lung Cancer Symptoms, Pathophysiology, And Treatment Linda H. Yoder Patients with lung cancer can provide treatment challenges for even
CE Objectives and Evaluation Form appear on page 235. An Overview of Lung Cancer Symptoms, Pathophysiology, And Treatment Linda H. Yoder Patients with lung cancer can provide treatment challenges for even
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer John delcharco, MD (Statistics based on CVMC data 2009-2013) Statistics Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer John delcharco, MD (Statistics based on CVMC data 2009-2013) Statistics Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC. Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai
 Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. IV. THERAPY. I. NON SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof.
 Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. IV. THERAPY. I. NON SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi TREATMENT OF LUNG CARCINOMA * overall treatment approach to
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. IV. THERAPY. I. NON SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi TREATMENT OF LUNG CARCINOMA * overall treatment approach to
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer. Mark A. Socinski, MD
 Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Extrapleural Pneumonectomy for Malignant Mesothelioma: Pro. Joon H. Lee 9/17/2012
 Extrapleural Pneumonectomy for Malignant Mesothelioma: Pro Joon H. Lee 9/17/2012 Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (Epidemiology) Incidence: 7/mil (Japan) to 40/mil (Australia) Attributed secondary to asbestos
Extrapleural Pneumonectomy for Malignant Mesothelioma: Pro Joon H. Lee 9/17/2012 Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (Epidemiology) Incidence: 7/mil (Japan) to 40/mil (Australia) Attributed secondary to asbestos
More than half of all lung cancer patients present with. New Combinations in the Treatment of Lung Cancer* A Time for Optimism
 New Combinations in the Treatment of Lung Cancer* A Time for Optimism Paul A. Bunn, Jr., MD; and Karen Kelly, MD Strides have been made in the treatment of lung cancer in the last decade that warrant a
New Combinations in the Treatment of Lung Cancer* A Time for Optimism Paul A. Bunn, Jr., MD; and Karen Kelly, MD Strides have been made in the treatment of lung cancer in the last decade that warrant a
CHAPTER 6: TREATMENT FOR SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
 CHAPTER 6: TREATMENT FOR SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER INTRODUCTION This chapter provides an overview of treatment for small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Treatment options are presented based on the extent of disease.
CHAPTER 6: TREATMENT FOR SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER INTRODUCTION This chapter provides an overview of treatment for small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Treatment options are presented based on the extent of disease.
REPORT ASCO 1998 LOS ANGELES : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group
 REPORT ASCO 1998 LOS ANGELES : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Educational session Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in
REPORT ASCO 1998 LOS ANGELES : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Educational session Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in
Summary of treatment benefits
 Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
Review article. Combined modality therapy of non-small cell lung cancers. A. Juretic, H. Sobat & M. Samija
 Annals of Oncology 10 (Suppl. 6): S93S98. 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Review article Combined modality therapy of nonsmall cell lung cancers A. Juretic, H. Sobat
Annals of Oncology 10 (Suppl. 6): S93S98. 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Review article Combined modality therapy of nonsmall cell lung cancers A. Juretic, H. Sobat
III. EXTENT OF DISEASE
 Advanced Abstracting Lung Cancer III. EXTENT OF DISEASE Staging Systems and Documentation 1 Source: AJCC Cancer Staging Illustrations from the AJCC Cancer Staging Atlas. Springer, 2007. Used with permission.
Advanced Abstracting Lung Cancer III. EXTENT OF DISEASE Staging Systems and Documentation 1 Source: AJCC Cancer Staging Illustrations from the AJCC Cancer Staging Atlas. Springer, 2007. Used with permission.
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof.
 Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMA Summary of treatment approach * limited
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMA Summary of treatment approach * limited
Survival analysis of 220 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer
 窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer
 Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline
 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Update on Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Welcome to Master Class for Oncologists Session 3: 2:45 PM - 3:30 PM Washington, DC March 28, 2009 Small Cell Lung Cancer: Best Practices & Recent Advances Speaker: Bruce E. Johnson, MD Professor of Medicine,
Welcome to Master Class for Oncologists Session 3: 2:45 PM - 3:30 PM Washington, DC March 28, 2009 Small Cell Lung Cancer: Best Practices & Recent Advances Speaker: Bruce E. Johnson, MD Professor of Medicine,
People Living with Cancer
 Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Emerging Drug List GEFITINIB
 Generic (Trade Name): Manufacturer: Gefitinib (Iressa ) formerly referred to as ZD1839 AstraZeneca NO. 52 JANUARY 2004 Indication: Current Regulatory Status: Description: Current Treatment: Cost: Evidence:
Generic (Trade Name): Manufacturer: Gefitinib (Iressa ) formerly referred to as ZD1839 AstraZeneca NO. 52 JANUARY 2004 Indication: Current Regulatory Status: Description: Current Treatment: Cost: Evidence:
How To Treat Lung Cancer At Cleveland Clinic
 Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma
 Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Non small-cell lung cancer, mesothelioma, and thymoma
 CHAPTER 7 Non small-cell lung cancer, mesothelioma, and thymoma Robert J. McKenna, Jr., MD, Benjamin Movsas, MD, Dong M. Shin, MD, and Fadlo R. Khuri, MD NSC LUNG In the United States, lung cancer has
CHAPTER 7 Non small-cell lung cancer, mesothelioma, and thymoma Robert J. McKenna, Jr., MD, Benjamin Movsas, MD, Dong M. Shin, MD, and Fadlo R. Khuri, MD NSC LUNG In the United States, lung cancer has
Lung Tumours. Dr Emil Beltchev 07/03/2007 1
 Lung Tumours Dr Emil Beltchev 07/03/2007 1 Lung Cancer Primary carcinoma of the lung was an uncommon cancer until the 1930s. At that time a dramatic increase in the incidence of lung cancer began that
Lung Tumours Dr Emil Beltchev 07/03/2007 1 Lung Cancer Primary carcinoma of the lung was an uncommon cancer until the 1930s. At that time a dramatic increase in the incidence of lung cancer began that
How To Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CHAPTER 7: TREATMENT FOR NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER INTRODUCTION This chapter provides an overview of treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Treatment options are discussed according to the
CHAPTER 7: TREATMENT FOR NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER INTRODUCTION This chapter provides an overview of treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Treatment options are discussed according to the
Small Cell Lung Cancer* State-of-the-Art Therapy 1994
 Small Cell Lung Cancer* State-of-the-Art Therapy 1994 Daniel C. Ihde, MD In the United States, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) accounts for about 20% of all cases of lung cancer. Without treatment, tumor
Small Cell Lung Cancer* State-of-the-Art Therapy 1994 Daniel C. Ihde, MD In the United States, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) accounts for about 20% of all cases of lung cancer. Without treatment, tumor
3.0 With final Comments for presentation at Sub Group Meeting 24. 24.11.10
 Guideline for the Treatment of Lung Cancer Version History 2.0 Endorsed by the Governance Committee as treatment of lung cancer 27.07.09 with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. 2.1 Re-written to include the
Guideline for the Treatment of Lung Cancer Version History 2.0 Endorsed by the Governance Committee as treatment of lung cancer 27.07.09 with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. 2.1 Re-written to include the
Non-small cell lung cancer, advanced or metastatic, switch-therapy after gemcitabine/carboplatin
 COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY TRACKING FORM DRUG: Docetaxel INDICATION: Non-small cell lung cancer, advanced or metastatic, switch-therapy after gemcitabine/carboplatin COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY REQUIREMENTS 1 Provide
COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY TRACKING FORM DRUG: Docetaxel INDICATION: Non-small cell lung cancer, advanced or metastatic, switch-therapy after gemcitabine/carboplatin COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY REQUIREMENTS 1 Provide
the standard of care 2009 5/1/2009 Mesothelioma: The standard of care take home messages PILC 2006 Jan.vanmeerbeeck@ugent.be Brussels, March 7, 2009
 Mesothelioma: The standard of care Jan.vanmeerbeeck@ugent.be Brussels, March 7, 2009 take home messages PILC 2006 All patients should receive adequate palliation of dyspnea and pain before starting chemotherapy
Mesothelioma: The standard of care Jan.vanmeerbeeck@ugent.be Brussels, March 7, 2009 take home messages PILC 2006 All patients should receive adequate palliation of dyspnea and pain before starting chemotherapy
How To Treat Lung Cancer
 The Lung Cancer Program at St. Joseph Hospital takes a comprehensive and individualized approach to patient care. We offer a wide range of services that include cancer prevention, CT lung cancer screening,
The Lung Cancer Program at St. Joseph Hospital takes a comprehensive and individualized approach to patient care. We offer a wide range of services that include cancer prevention, CT lung cancer screening,
Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness
 Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness Investigators: Paul G. Shekelle, MD, PhD, Director Alicia R. Maher, MD Clinical
Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness Investigators: Paul G. Shekelle, MD, PhD, Director Alicia R. Maher, MD Clinical
Summary ID# 13095. Clinical Study Summary: Study H3E-EW-B012
 Page 1 Summary ID# 13095 Clinical Study Summary: Study H3E-EW-B012 First-line Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer under Routine Conditions: Observational Study on Overall Survival Date summary electronically
Page 1 Summary ID# 13095 Clinical Study Summary: Study H3E-EW-B012 First-line Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer under Routine Conditions: Observational Study on Overall Survival Date summary electronically
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Survey on the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in England and Wales
 Eur Respir J 1997; 10: 1552 1558 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.97.10071552 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1997 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Survey on the treatment
Eur Respir J 1997; 10: 1552 1558 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.97.10071552 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1997 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Survey on the treatment
INTRODUCTION. liver neoplasms, adrenal gland neoplasms, non small-cell lung cancer, radionuclide imaging, bisphosphonates,
 VOLUME 22 NUMBER 2 JANUARY 15 2004 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY A S C O S P E C I A L A R T I C L E American Society of Clinical Oncology Treatment of Unresectable Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Guideline:
VOLUME 22 NUMBER 2 JANUARY 15 2004 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY A S C O S P E C I A L A R T I C L E American Society of Clinical Oncology Treatment of Unresectable Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Guideline:
Lung cancer LUNG CANCER. Box 1 Clinical signs
 22 LUNG CANCER Lung cancer Bronchial carcinoma refers to two distinct clinical entities small cell and non-small cell carcinoma. Although these conditions have much in common, with broadly similar presenting
22 LUNG CANCER Lung cancer Bronchial carcinoma refers to two distinct clinical entities small cell and non-small cell carcinoma. Although these conditions have much in common, with broadly similar presenting
Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
 Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research & Development Service Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research & Development Service Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
SYSTEMIC THERAPY FOR STAGE IV NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER: AMERICAN SOCIETY OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE UPDATE
 Which patients with stage IV NSCLC should be treated with chemotherapy? NSCLC with nonsquamous cell carcinoma, negative or unknown EGFR-sensitizing mutation and ALK gene rearrangement status, and PS 0-1
Which patients with stage IV NSCLC should be treated with chemotherapy? NSCLC with nonsquamous cell carcinoma, negative or unknown EGFR-sensitizing mutation and ALK gene rearrangement status, and PS 0-1
SMALL. 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org
 Understanding series SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient I TABLE OF CONTENTS ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS The following image shows different parts that make up
Understanding series SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient I TABLE OF CONTENTS ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS The following image shows different parts that make up
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Male. Female. Death rates from lung cancer in USA
 Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
SECOND-LINE CHEMOTHERAPY in advanced non
 Gemcitabine as Second-Line Treatment for Advanced Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase II Trial By Lucio Crinò, Anna Maria Mosconi, Giorgio Scagliotti, Giovanni Selvaggi, Silvia Novello, Massimo Rinaldi,
Gemcitabine as Second-Line Treatment for Advanced Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase II Trial By Lucio Crinò, Anna Maria Mosconi, Giorgio Scagliotti, Giovanni Selvaggi, Silvia Novello, Massimo Rinaldi,
The National Clinical Lung Cancer Audit (LUCADA)
 The National Clinical Lung Cancer Audit (LUCADA) DATA MANUAL Title: Version: 3.1.5 Date: September 2013 LUCADA Lung Cancer Audit VERSION HISTORY Version Date Issued Brief Summary of Change Owner s Name
The National Clinical Lung Cancer Audit (LUCADA) DATA MANUAL Title: Version: 3.1.5 Date: September 2013 LUCADA Lung Cancer Audit VERSION HISTORY Version Date Issued Brief Summary of Change Owner s Name
The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging
 The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging Peter Baik, DO Thoracic Surgery Cancer Treatment Centers of America Oklahoma Osteopathic Association 115th Annual Convention Financial Disclosures: None 2 Objectives
The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging Peter Baik, DO Thoracic Surgery Cancer Treatment Centers of America Oklahoma Osteopathic Association 115th Annual Convention Financial Disclosures: None 2 Objectives
Post-recurrence survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local recurrence
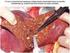 Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Recurrence Patterns, Prognostic Factors and Survival
 16 Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Recurrence Patterns, Prognostic Factors and Survival Jung-Jyh Hung and Yu-Chung Wu Division of Thoracic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Taipei Veterans General Hospital
16 Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Recurrence Patterns, Prognostic Factors and Survival Jung-Jyh Hung and Yu-Chung Wu Division of Thoracic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Taipei Veterans General Hospital
Management of Stage III, N2 NSCLC: A Virtual Thoracic Oncology Tumor Board
 Management of Stage III, N2 NSCLC: A Virtual Thoracic Oncology Tumor Board Abstract Introduction Management of stage III non small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is complex and requires careful work-up, staging,
Management of Stage III, N2 NSCLC: A Virtual Thoracic Oncology Tumor Board Abstract Introduction Management of stage III non small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is complex and requires careful work-up, staging,
Treatment of Stage III Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
 CHEST Supplement DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER, 3RD ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Treatment of Stage III Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer, 3rd ed: American College of
CHEST Supplement DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER, 3RD ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Treatment of Stage III Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer, 3rd ed: American College of
Is an evidence-based approach realistic in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)?
 Is an evidence-based approach realistic in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)? Authors Key words P.A. Coucke, N. Barthelemy, L. Bosquee, J.P. van Meerbeeck NSCLC, sequential and concomitant chemo-radiotherapy,
Is an evidence-based approach realistic in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)? Authors Key words P.A. Coucke, N. Barthelemy, L. Bosquee, J.P. van Meerbeeck NSCLC, sequential and concomitant chemo-radiotherapy,
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer APPROVED BY THE NHMRC ON 18 MARCH 2004 The Cancer Council Australia 2004 ISBN Print: 1 86496 312 3 Online: 1 86496
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer APPROVED BY THE NHMRC ON 18 MARCH 2004 The Cancer Council Australia 2004 ISBN Print: 1 86496 312 3 Online: 1 86496
How To Know When To Stage Lung Cancer
 WHITE PAPER - SBRT for Non Small Cell Lung Cancer I. Introduction This white paper will focus on non-small cell lung carcinoma with sections one though six comprising a general review of lung cancer from
WHITE PAPER - SBRT for Non Small Cell Lung Cancer I. Introduction This white paper will focus on non-small cell lung carcinoma with sections one though six comprising a general review of lung cancer from
Key words: chemotherapy; evidence-based medicine; guidelines; non-small cell lung cancer
 Chemotherapeutic Management of Stage IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer* Mark A. Socinski, MD, FCCP; David E. Morris, MD; Gregory A. Masters, MD, FCCP; and Rogerio Lilenbaum, MD Stage IV non-small cell lung
Chemotherapeutic Management of Stage IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer* Mark A. Socinski, MD, FCCP; David E. Morris, MD; Gregory A. Masters, MD, FCCP; and Rogerio Lilenbaum, MD Stage IV non-small cell lung
MOH Policy for dispensing NEOPLASTIC DISEASES DRUGS
 MOH Policy for dispensing NEOPLASTIC DISEASES DRUGS All prescriptions for antineoplastic drugs must be accompanied by the MOH special form. All the attachments mentioned on this form shall be submitted
MOH Policy for dispensing NEOPLASTIC DISEASES DRUGS All prescriptions for antineoplastic drugs must be accompanied by the MOH special form. All the attachments mentioned on this form shall be submitted
What is non-small-cell lung cancer?
 Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer What is non-small-cell lung cancer? Let us explain it to you. www.anticancerfund.org www.esmo.org ESMO/ACF Patient Guide Series based on the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines
Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer What is non-small-cell lung cancer? Let us explain it to you. www.anticancerfund.org www.esmo.org ESMO/ACF Patient Guide Series based on the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Out-Patient Chemotherapy for Lung Cancer
 Lung Cancer Out-Patient Chemotherapy for Lung Cancer Principles and practice JMAJ 46(12): 542 546, 2003 Shuichi YONEDA Director, Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Saitama Cancer Center Abstract: Recent
Lung Cancer Out-Patient Chemotherapy for Lung Cancer Principles and practice JMAJ 46(12): 542 546, 2003 Shuichi YONEDA Director, Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Saitama Cancer Center Abstract: Recent
Mesothelioma. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
 Mesothelioma William G. Richards, PhD Brigham and Women s Hospital Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma 2,000-3,000 cases per year (USA) Increasing incidence Asbestos (50-80%, decreasing) 30-40 year latency
Mesothelioma William G. Richards, PhD Brigham and Women s Hospital Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma 2,000-3,000 cases per year (USA) Increasing incidence Asbestos (50-80%, decreasing) 30-40 year latency
Lung cancer (non-small-cell)
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
REPORT PERSPECTIVES IN LUNG CANCER 2010 AMSTERDAM
 REPORT PERSPECTIVES IN LUNG CANCER 2010 AMSTERDAM Valerie Van Damme, Isabelle Wauters, Johan Vansteenkiste Univ. Hospital Leuven and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Introduction Perspectives in Lung Cancer (PILC)
REPORT PERSPECTIVES IN LUNG CANCER 2010 AMSTERDAM Valerie Van Damme, Isabelle Wauters, Johan Vansteenkiste Univ. Hospital Leuven and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Introduction Perspectives in Lung Cancer (PILC)
CHEMOTHERAPY FOR ADVANCED UROTHELIAL CANCER OF THE BLADDER. Walter Stadler, MD University of Chicago
 CHEMOTHERAPY FOR ADVANCED UROTHELIAL CANCER OF THE BLADDER Walter Stadler, MD University of Chicago Chemotherapy Doctor Terms Drugs used to treat cancer Will attack cancer no matter where it is located
CHEMOTHERAPY FOR ADVANCED UROTHELIAL CANCER OF THE BLADDER Walter Stadler, MD University of Chicago Chemotherapy Doctor Terms Drugs used to treat cancer Will attack cancer no matter where it is located
4.8 Lung cancer. 4.8.5 In the UK, three fractionation regimens are most commonly used:
 4.8 Lung cancer 4.8.1 In 2005, both NICE (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence) and SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network) published guidelines on the management of lung cancer.
4.8 Lung cancer 4.8.1 In 2005, both NICE (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence) and SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network) published guidelines on the management of lung cancer.
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Lung Practice Guideline Dr. Brian Dingle MSc, MD, FRCPC Approval Date: April 2007 Revised: November 2008 This guideline is a statement of consensus of the Thoracic Disease Site Team
Small Cell Lung Cancer Lung Practice Guideline Dr. Brian Dingle MSc, MD, FRCPC Approval Date: April 2007 Revised: November 2008 This guideline is a statement of consensus of the Thoracic Disease Site Team
Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners
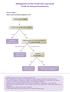 Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
Clinical Focus on Lung Cancer
 Clinical Focus on Lung Cancer A snapshot of lung cancer for Ontario health care providers and managers Driving quality, accountability and innovation throughout Ontario s cancer system TABLE OF CONTENTS
Clinical Focus on Lung Cancer A snapshot of lung cancer for Ontario health care providers and managers Driving quality, accountability and innovation throughout Ontario s cancer system TABLE OF CONTENTS
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies
 Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
 Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA
 Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Treatment Advances in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Veerle Surmont
 Treatment Advances in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Veerle Surmont Cover design: Divine De Baets; Rotterdam-Gent Impressions Lay-out: Optima Grafische Communicatie Rotterdam
Treatment Advances in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Veerle Surmont Cover design: Divine De Baets; Rotterdam-Gent Impressions Lay-out: Optima Grafische Communicatie Rotterdam
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
How To Know If You Have Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Lung cancer Lung cancer TABLE 85 1. MALIGNANT PULMONARY NEOPLASMS INCIDENCE (%) Common 99 Non small cell lung cancer ~75 Adenocarcinoma ~35 Squamous cell carcinoma ~30 Large cell carcinoma ~10 Small cell
Lung cancer Lung cancer TABLE 85 1. MALIGNANT PULMONARY NEOPLASMS INCIDENCE (%) Common 99 Non small cell lung cancer ~75 Adenocarcinoma ~35 Squamous cell carcinoma ~30 Large cell carcinoma ~10 Small cell
Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Complete Resection of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 REVIEW ARTICLE Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Complete Resection of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Eckart Laack, Carsten Bokemeyer, Dieter Kurt Hossfeld SUMMARY Introduction: In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
REVIEW ARTICLE Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Complete Resection of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Eckart Laack, Carsten Bokemeyer, Dieter Kurt Hossfeld SUMMARY Introduction: In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Characterization of lung cancer patients, their actual treatment and survival: experience in Slovenia
 Characterization of lung cancer patients, their actual treatment and survival: experience in Slovenia Lučka Debevec 1, Andrej Debeljak 1, Janez Eržen 2, Viljem Kovač 3, Izidor Kern 1 1 University Clinic
Characterization of lung cancer patients, their actual treatment and survival: experience in Slovenia Lučka Debevec 1, Andrej Debeljak 1, Janez Eržen 2, Viljem Kovač 3, Izidor Kern 1 1 University Clinic
Optimization of radiotherapy in locally advanced lung cancer
 Optimization of radiotherapy in locally advanced lung cancer Andreas Hallqvist 2012 Department of Oncology Institute of Clinical Sciences at Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg Correspondence
Optimization of radiotherapy in locally advanced lung cancer Andreas Hallqvist 2012 Department of Oncology Institute of Clinical Sciences at Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg Correspondence
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data
 Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC
 A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC Robert J. Korst, M.D. Director, Thoracic Surgery Medical Director, The Blumenthal Cancer Center The Valley Hospital Objectives Revised staging
A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC Robert J. Korst, M.D. Director, Thoracic Surgery Medical Director, The Blumenthal Cancer Center The Valley Hospital Objectives Revised staging
LUNG CANCER. FCDS 2011 Educational Webcast Series November 17, 2011
 LUNG CANCER FCDS 2011 Educational Webcast Series November 17, 2011 Judy Bonner, RN, MS, CTR and Lynne Pearson, CTR, LHRM Steven Peace, CTR Updated for 2011 Requirements and CSv02.03.02 1 Presentation Outline
LUNG CANCER FCDS 2011 Educational Webcast Series November 17, 2011 Judy Bonner, RN, MS, CTR and Lynne Pearson, CTR, LHRM Steven Peace, CTR Updated for 2011 Requirements and CSv02.03.02 1 Presentation Outline
Locoregional & advanced esophagus or esophagogastric junction cancer
 Eloxatin (oxaliplatin) Prior Authorization Request (For Maryland Only) Send completed form to: Case Review Unit CVS/caremark Specialty Programs Fax: 866-249-6155 CVS/caremark administers the prescription
Eloxatin (oxaliplatin) Prior Authorization Request (For Maryland Only) Send completed form to: Case Review Unit CVS/caremark Specialty Programs Fax: 866-249-6155 CVS/caremark administers the prescription
