Restrictive lung diseases
|
|
|
- Jocelyn Nelson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Restrictive lung diseases Characterized by reduced compliance of the lung. Prominent changes in the interstitium (interstitial lung disease). Important signs and symptoms: - Dyspnea. - Hypoxia. - With progressive severe hypoxia, respiratory failure and cor pulmonale. It can be: - Acute. - Chronic.
2 Chronic restrictive lung disease Are a heterogenous group with little uniformity regarding terminology and classification. Many entities are of unknown cause and pathogenesis. Similar clinical signs, symptoms, radiographic alterations and pathophysiologic changes. Account for about 15% of non-infectious diseases.
3 Chronic restrictive lung disease Major Categories of Chronic Interstitial Lung Disease -Fibrosing: Pneumoconiosis Usual interstitial pneumonia (idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis) Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia Associated with collagen vascular diseases Drug and Radiation Reactions -Granulomatous: Sarcoidosis -Eosinophilic Hypersensitibity pneumonitis. -Smoking related: Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease
4 Usual interstitial pneumonia (idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis) (cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis) UIP A clinicopathologic syndrome with characteristic radiologic, pathologic and clinical features. Characterized histologically by diffuse interstitial fibrosis and inflammation.
5 Pathogenesis Some form of alveolar wall injury result in interstitial edema and alveolitis. Type I pneumocyte is more susceptible to injury. Type II pneumocyte hyperplasia (regenerate). Fibroblast proliferation with progressive fibrosis of intra-alveolar exudate and interalveolar septa. IgG deposits are seen in alveolar wall. IL-8 leukotriens FGF, TGF-β, PDGF
6 Morphology of IPF Gross -The lungs are firm. -Pulmonary edema. The morphologic changes vary according to the stage of the disease. Early cases: -Intraalveolar exudate. -Hyaline membranes. -Infiltration of the alveolar septa with mononuclear cells. -Hyperplasia of type II pneumocytes -
7 Morphology of IPF Advancing disease: -Organization of the intraalveolar exudates by fibrous tissue. -Thickening of the alveolar septa owing to fibrosis and variable amounts of inflammation. -Alternating areas of fibrosis and normal tissue. -Geographic variation - Temporal variation In the end, the lung consists of spaces lined by cuboidal or columnar epithelium separated by inflammatory fibrous tissue (honeycomb lung).
8 Clinical features of IPF Males are affected more often than females. Most patients are between 40 &70 years old. Gradual onset of dyspnea with respiratory difficulty. Hypoxemia and cyanosis. Cor pulmonale and cardiac failure may result. The progression in individual cases is unpredictable. The median survival is about 3 to 5 years.
9 Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Diffuse interstitial lung disease of unknown etiology 2 patterns: cellular and fibrosing Pt. Present with dyspnea and cough Occur at 50 year of age Pt. Have better prognosis than UIP
10 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia (COP) brochiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia Pt. Present with cough and dyspensa with patchy areas of airspace consolidation radiographically. No interstitial fibrosis. Patient recover spontaneously or after oral steroids.
11 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
12 Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Smoking related Age : fourth decade Dyspnea and cough Complete recovery after cessation of smoking
13 Hypersensitivity pneumonitis An immunologically mediated inflammatory lung disease that primarily affects the alveoli and is therefore often called allergic alveolitis. Hypersensitivity to inhaled antigens in the form of organic such as moldy hay, e.g. farmer s lung, humidified lung or pigeon breeder s lung. May present either as an acute reaction with fever, cough, dypsnea and constitutional complains 4 to 8 hours after exposure or as a chronic disease with insidious onset of cough, dyspnea, malaise and weight loss.
14 Hypersensitivity pneumonitis Acute syndromes result from the combination of: - A direct irritant effect. - Activation of the alternate complement pathway. - Immune complex. The chronic form of the disease is mediated by delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
15 Selected cause of hypersensivity pneumonitis Syndrome Exposure Antigens Microbes contaminating vegetable matter of water. Farmer s lung Moldy hay Various Actinomycetes Aspergillus spp. Bagassosis Moldy pressed Thermophilic sugar cane Actinomycetes (bagasse) Maple bark disease Maple bark Cryptostroma Corticale Humidifier lung Cool-mist Thermophilic humidifier Actinomycetes Aureobasidium Animal products Pigeon breeder s lung Pigeons Pigeon serum proteins Chemicals Trimelitic anhydried Chemical industry Haptenated protein pneumonia
16 Morphology of hypersensitivity pneumonitis Mononuclear cell infiltrates in the alveoli and alveolar walls and around terminal bronchioles. Interstitial non-caseating granulomas reflecting type IV hypersensitivity reaction are present in more than two thirds of cases. Diffuse interstitial fibrosis. Clinical course is variable.
17
18 Pneumoconiosis Non-neoplastic lung reaction to inhalation of mineral dusts. Most common dusts are coal dust, silica, asbestos and beryllium. Pathogenesis: The development of pneumoconiosis is dependent on: - The amount of dust retained in the lung and airways. a. Concentration of the dust in the ambient air. b. Duration of the exposure. c. Effectiveness of the clearance mechanisms. - The size (1-5µ) shape. - Their solubility and physiochemical activity. - The possible additional effects of other irritants, tobacco smoking. The particles are impacted at alveolar duct macrophage, accumulate inflammatory response fibrosis.
19 Coal worker s pneumoconiosis (CWP) Occurs in coal workers after many years of underground mine work. Two forms: - The simple form: - Focal aggregations of coal dust-laden macrophages (coal macules). - Patients have slight cough and blackish sputum. - The complicated form: With heavier pulmonary burdens of coal dust, fibrous scarring appears (complicated CWP) also callled progressive massive fibrosis (PMF).
20 Morphology: Simple CWP: Coal worker pneumoconiosis - Focal black pigmentations (macules), 1-2 mm up to 5 mm are scattered through the lung. - Mostly in the upper zones of the lower and upper lobes of the lungs. - Macules are composed of aggregations of coal dust-filled macrophages in close proximity to alveolar ducts.
21 Morphology: Complicated CWP: Coal worker pneumoconiosis -Black scars exceed 2 cm in diameter some times up to 10 cm -It consists of dense collagen and carbon pigments. -Cor pulmonale. -Miners who have rheumatoid arthritis and PMF are called Caplan s syndrome.
22 Silicosis Long exposure to silica particles. Nodular densely fibrosing pneumoconiosis. Encountered in a diversity of industries: mining of gold, tin, copper and coal, sandblasting, metal grinding, ceramic manufacturing. Silicosis does not predispose to lung cancer. Pathogenesis: Crystalline silica is highly fibrogenic. Scattered lymphocytes and macrophages are drawn rapidly with fibrosis. Some particles are transported to lymph nodes.
23 Morphology of Silicosis Tiny collagenous nodules that enlarge forming stony-hard large fibrous scars usually in the upper lobes. The lung parenchyma between the scars may be compressed or emphysematous. Calcifications may appear (eggshell calcification). Similar collagenous nodules within the lymph nodes. Fibrous pleural plaques may develop.
24 Morphology of Silicosis Micro: -Hyalinized collagen fiber surround an amorphous center (fibrous nodules). - Scarring progress to PMF. -Scarring extending and encroching the pulmonary arteries. -Cor pulmonale.
25 Asbestosis Inhalation of asbestos leads to: - Asbestos pneumoconiosis. - Pleural effusion. - Pleural adhesions. - Parietal pleural fibrocalcific plaques. - Increased incidence of mesothelioma, bronchogenic carcinoma, other cancer. These consequences occurs decades after exposure has ended. All types of asbestos (crocidolite and amosite) are fibrogenic but the crocidolite is the most carcinogenic. Characterized by scarring containing asbestos bodies.
26 scarring containing asbestos bodies.
27 Asbestosis In asbestosis, pt. develop progressively worsened dyspnea with cough and sputum progressing to cor pulmonale and death. Both bronchogenic carcinoma and mesothelioma develop in workers exposed to asbestos. The risk of bronchogenic carcinoma is fivefold and for mesothelioma is 1000 fold greater.
28
29
30
Pulmonary interstitium. Interstitial Lung Disease. Interstitial lung disease. Interstitial lung disease. Causes.
 Pulmonary interstitium Interstitial Lung Disease Alveolar lining cells (types 1 and 2) Thin elastin-rich connective component containing capillary blood vessels Interstitial lung disease Increase in interstitial
Pulmonary interstitium Interstitial Lung Disease Alveolar lining cells (types 1 and 2) Thin elastin-rich connective component containing capillary blood vessels Interstitial lung disease Increase in interstitial
Granulomatous diseases - Sarcoidosis - Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
 Interstitial Lung Diseases 2010 Mark Tuttle Characterized by: Expansion of the lung TLC FEV normal or proportionately reduced Occurs in: 1. Chest wall disorders 2. Acute/chronic interstitial disease Interstitial
Interstitial Lung Diseases 2010 Mark Tuttle Characterized by: Expansion of the lung TLC FEV normal or proportionately reduced Occurs in: 1. Chest wall disorders 2. Acute/chronic interstitial disease Interstitial
PARTICLE SIZE AND CHEMISTRY:
 Pneumoconioses LW/Please note: This information is additional to Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medicine. /Hierdie inligting is aanvullend tot Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medicine. Pneumoconioses
Pneumoconioses LW/Please note: This information is additional to Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medicine. /Hierdie inligting is aanvullend tot Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medicine. Pneumoconioses
Environmental Lung Disease (Pneumoconiosis) AGAINDRA K. BEWTRA M.D.
 Environmental Lung Disease (Pneumoconiosis) AGAINDRA K. BEWTRA M.D. Pneumoconiosis Originally pneumoconiosis (gr: Pneumo = lung; konis = dust). So it was those diseases caused by dust inhalation, but in
Environmental Lung Disease (Pneumoconiosis) AGAINDRA K. BEWTRA M.D. Pneumoconiosis Originally pneumoconiosis (gr: Pneumo = lung; konis = dust). So it was those diseases caused by dust inhalation, but in
Occupational Lung Disease. SS Visser Internal Medicine UP
 Occupational Lung Disease SS Visser Internal Medicine UP Classification Anorganic ( mineral ) dust/pneumoconiosis Fibrogenic - silica, asbestos, talc, silicates Non-fibrogenic - Fe, barium, tin Immunologic/Pharmcologic
Occupational Lung Disease SS Visser Internal Medicine UP Classification Anorganic ( mineral ) dust/pneumoconiosis Fibrogenic - silica, asbestos, talc, silicates Non-fibrogenic - Fe, barium, tin Immunologic/Pharmcologic
Disorders of Known Causes: Occupational Lung Diseases/Pneumoconioses andenvironmental Lung Disease
 Disorders of Known Causes: Occupational Lung Diseases/Pneumoconioses andenvironmental Lung Disease Restrictive lung diseases; low lung volumes WE KNOW the causes Asbestosis Silicosis Coal Worker s pneumoconiosis
Disorders of Known Causes: Occupational Lung Diseases/Pneumoconioses andenvironmental Lung Disease Restrictive lung diseases; low lung volumes WE KNOW the causes Asbestosis Silicosis Coal Worker s pneumoconiosis
Francine Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario 2003
 ASBESTOS Francine Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario 2003 Asbestosis Asbestosis is a model for other dust diseases as well as
ASBESTOS Francine Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario 2003 Asbestosis Asbestosis is a model for other dust diseases as well as
Occupational Health III.
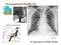 Occupational Health III. Asbestosis SU Department of Public Health Occupational respiratory diseases Dust Toxic Gases Silica dust SO 2 Asbestos dust NO x Coal dust Biologic reaction Inflammatory reaction
Occupational Health III. Asbestosis SU Department of Public Health Occupational respiratory diseases Dust Toxic Gases Silica dust SO 2 Asbestos dust NO x Coal dust Biologic reaction Inflammatory reaction
Occupational Lung Disease. David Perlman, MD
 Occupational Lung Disease David Perlman, MD What causes occupational lung diseases? Breathing bad stuff into your lung Mechanism of particle deposition Large particles (>0.5μM) Impaction Gravitational
Occupational Lung Disease David Perlman, MD What causes occupational lung diseases? Breathing bad stuff into your lung Mechanism of particle deposition Large particles (>0.5μM) Impaction Gravitational
Occupational Lung diseases. Dr Deepak Aggarwal Dept. Of Pulmonary Medicine
 Occupational Lung diseases Dr Deepak Aggarwal Dept. Of Pulmonary Medicine To be discussed. Pneumoconiosis Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis PNEUMOCONIOSIS Pneumoconioses are pulmonary diseases caused by mineral
Occupational Lung diseases Dr Deepak Aggarwal Dept. Of Pulmonary Medicine To be discussed. Pneumoconiosis Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis PNEUMOCONIOSIS Pneumoconioses are pulmonary diseases caused by mineral
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
LECTURES IN OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES
 LECTURES IN OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES الدكتورة سجال فاضل فرھود الجبوري M.B.Ch.B.(Babylon University) M.Sc.(Community Medicine-Al Nahrain) Asbestosis Asbestosis is a chronic inflammatory medical condition affecting
LECTURES IN OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES الدكتورة سجال فاضل فرھود الجبوري M.B.Ch.B.(Babylon University) M.Sc.(Community Medicine-Al Nahrain) Asbestosis Asbestosis is a chronic inflammatory medical condition affecting
Occupational lung diseases an overview 22:07:2013
 Occupational lung diseases an overview 22:07:2013 IIT MUMBAI 52/M Non smoker Worked in a bakery for > 30 years C/O Productive cough and exertional breathlessness since 2 years Treated with AKT on multiple
Occupational lung diseases an overview 22:07:2013 IIT MUMBAI 52/M Non smoker Worked in a bakery for > 30 years C/O Productive cough and exertional breathlessness since 2 years Treated with AKT on multiple
Occupational Lung Diseases
 13 Occupational Lung Diseases Occupational lung diseases are a broad group of diagnoses caused by the inhalation of dusts, chemicals, or proteins. Pneumoconiosis is the term used for the diseases associated
13 Occupational Lung Diseases Occupational lung diseases are a broad group of diagnoses caused by the inhalation of dusts, chemicals, or proteins. Pneumoconiosis is the term used for the diseases associated
PFF DISEASE EDUCATION WEBINAR SERIES. Welcome!
 PFF DISEASE EDUCATION WEBINAR SERIES Welcome! PFF CARE CENTER NETWORK EXPANSION Mridu Gulati, MD MPH Assistant Professor Associate Director, Yale-ILD Section of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine
PFF DISEASE EDUCATION WEBINAR SERIES Welcome! PFF CARE CENTER NETWORK EXPANSION Mridu Gulati, MD MPH Assistant Professor Associate Director, Yale-ILD Section of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids
 Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Male. Female. Death rates from lung cancer in USA
 Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Occupational Lung Diseases
 Occupational Lung Diseases OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASES The Major Types of Occupational Lung Diseases: Pneumoconioses, diseases caused by dust in the lungs Hypersensitivity
Occupational Lung Diseases OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASES The Major Types of Occupational Lung Diseases: Pneumoconioses, diseases caused by dust in the lungs Hypersensitivity
Defending the Rest Basics on Lung Cancer, Other Cancers and Asbestosis: Review of the B-Read and Pulmonary Function Testing
 Defending the Rest Basics on Lung Cancer, Other Cancers and Asbestosis: Review of the B-Read and Pulmonary Function Testing ASBESTOSIS November 2013 Bruce T. Bishop Lucy L. Brandon Willcox & Savage 440
Defending the Rest Basics on Lung Cancer, Other Cancers and Asbestosis: Review of the B-Read and Pulmonary Function Testing ASBESTOSIS November 2013 Bruce T. Bishop Lucy L. Brandon Willcox & Savage 440
HEALTH CARE FOR EXPOSURE TO ASBESTOS. 2010 The SafetyNet Centre for Occupational Health and Safety Research Memorial University www.safetynet.mun.
 HEALTH CARE FOR PATIENTS WITH EXPOSURE TO ASBESTOS 2010 The SafetyNet Centre for Occupational Health and Safety Research Memorial University www.safetynet.mun.ca HEALTH CARE FOR PATIENTS WITH EXPOSURE
HEALTH CARE FOR PATIENTS WITH EXPOSURE TO ASBESTOS 2010 The SafetyNet Centre for Occupational Health and Safety Research Memorial University www.safetynet.mun.ca HEALTH CARE FOR PATIENTS WITH EXPOSURE
by Lee S. Newman, M.D., and Cecile S. Rose, M.D., M.P.H.
 OCCUPATIONAL ASBESTOSIS AND RELATED DISEASES by Lee S. Newman, M.D., and Cecile S. Rose, M.D., M.P.H. A 63-year-old man consulted an internist complaining of dyspnea on exertion. He reported the following:
OCCUPATIONAL ASBESTOSIS AND RELATED DISEASES by Lee S. Newman, M.D., and Cecile S. Rose, M.D., M.P.H. A 63-year-old man consulted an internist complaining of dyspnea on exertion. He reported the following:
Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary
 TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
Radiological Findings in BO
 Radiological Findings in BO BO-Meeting 2016 Schloss Johannisberg Geisenheim - Rheingau Germany Dr. Simon Martin Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology University Hospital Frankfurt Bronchiolitis
Radiological Findings in BO BO-Meeting 2016 Schloss Johannisberg Geisenheim - Rheingau Germany Dr. Simon Martin Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology University Hospital Frankfurt Bronchiolitis
Occupational Lung Diseases
 What are occupational lung diseases? Occupational lung disease is the number one cause of workrelated illness in the United States in terms of frequency, severity and preventability. Many occupational
What are occupational lung diseases? Occupational lung disease is the number one cause of workrelated illness in the United States in terms of frequency, severity and preventability. Many occupational
Interstitial Lung Diseases ACOI Board Review 2013
 Interstitial Lung Diseases ACOI Board Review 2013 Thomas F. Morley, DO, FACOI, FCCP, FAASM Professor of Medicine Director of the Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine UMDNJ-SOM Restrictive
Interstitial Lung Diseases ACOI Board Review 2013 Thomas F. Morley, DO, FACOI, FCCP, FAASM Professor of Medicine Director of the Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine UMDNJ-SOM Restrictive
Uses and Abuses of Pathology in Asbestos-exposed Populations
 Uses and Abuses of Pathology in Asbestos-exposed Populations Jerrold L. Abraham, MD Department of Pathology State University of New York Upstate Medical University Syracuse, NY, 13210 USA The term: Asbestosis,
Uses and Abuses of Pathology in Asbestos-exposed Populations Jerrold L. Abraham, MD Department of Pathology State University of New York Upstate Medical University Syracuse, NY, 13210 USA The term: Asbestosis,
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS about asbestos related diseases
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS about asbestos related diseases 1. What are the main types of asbestos lung disease? In the human body, asbestos affects the lungs most of all. It can affect both the spongy
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS about asbestos related diseases 1. What are the main types of asbestos lung disease? In the human body, asbestos affects the lungs most of all. It can affect both the spongy
Asthma - morphology ARDS. Acute restrictive lung disease. Diffuse pulmonary diseases. Pulmonary fibrosis, asbestosis and mesothelioma
 Diffuse pulmonary diseases Pulmonary fibrosis, asbestosis and mesothelioma 2012 by MB Obstructive Limitation of air flow, resulting from obstruction at any level (asthma airway narrowing; emphysema loss
Diffuse pulmonary diseases Pulmonary fibrosis, asbestosis and mesothelioma 2012 by MB Obstructive Limitation of air flow, resulting from obstruction at any level (asthma airway narrowing; emphysema loss
Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board
 Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board Year to date, numbers as of January 1, 2008 to December 31, 2008 Occupational disease fatalities are usually gradual in onset
Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board Year to date, numbers as of January 1, 2008 to December 31, 2008 Occupational disease fatalities are usually gradual in onset
NISG Asbestos. Caroline Kirton
 NISG Asbestos Caroline Kirton 1 The Control of Asbestos Regulations 2012, Regulation 10 requires every employer to ensure that adequate information, instruction and training is given to their employees
NISG Asbestos Caroline Kirton 1 The Control of Asbestos Regulations 2012, Regulation 10 requires every employer to ensure that adequate information, instruction and training is given to their employees
Inflammation and Healing. Review of Normal Defenses. Review of Normal Capillary Exchange. BIO 375 Pathophysiology
 Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Interstitial Lung Disease (Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease) Focusing on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Interstitial Lung Disease (Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease) Focusing on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis J. D Urbano, RCP, RRT Founder / CEO: BreathSounds, LLC E-Mail: [email protected] Mobile: (480)
Interstitial Lung Disease (Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease) Focusing on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis J. D Urbano, RCP, RRT Founder / CEO: BreathSounds, LLC E-Mail: [email protected] Mobile: (480)
CPT codes are for information only; consult your payer organization for reimbursement information.
 CPT codes are for information only; consult your payer organization for reimbursement information. Coverage for Spirometry/Oximetry Spirometry is a component of pulmonary function testing (PFTs). PFTs
CPT codes are for information only; consult your payer organization for reimbursement information. Coverage for Spirometry/Oximetry Spirometry is a component of pulmonary function testing (PFTs). PFTs
Asbestos Related Diseases
 Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease Asbestosis and Mesothelioma (LUNG CANCER) Support Group 1800 017 758 www.amsg.com.au ii Helping you and your family through
Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease Asbestosis and Mesothelioma (LUNG CANCER) Support Group 1800 017 758 www.amsg.com.au ii Helping you and your family through
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board
 Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board Year to date, numbers as of December 31, 2014 Occupational disease fatalities are usually gradual in onset and result from exposure
Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board Year to date, numbers as of December 31, 2014 Occupational disease fatalities are usually gradual in onset and result from exposure
Asbestos and the diseases it causes
 Asbestos and the diseases it causes October 2013 Liz Darlison Mesothelioma UK University Hospitals of Leicester Contents What is asbestos Why is it such an issue in the UK Disease Statistics Asbestos Related
Asbestos and the diseases it causes October 2013 Liz Darlison Mesothelioma UK University Hospitals of Leicester Contents What is asbestos Why is it such an issue in the UK Disease Statistics Asbestos Related
UKRC 2015 Dr Michael Sproule Glasgow
 UKRC 2015 Dr Michael Sproule Glasgow Radiology of Asbestos Related Lung Disease General term given to a group of fibrous minerals containing silica and a variety of other elements. Asbestos: Derived
UKRC 2015 Dr Michael Sproule Glasgow Radiology of Asbestos Related Lung Disease General term given to a group of fibrous minerals containing silica and a variety of other elements. Asbestos: Derived
Asbestos Disease: An Overview for Clinicians Asbestos Exposure
 Asbestos Asbestos Disease: An Overview for Clinicians Asbestos Exposure Asbestos: A health hazard Exposure to asbestos was a major occupational health hazard in the United States. The first large-scale
Asbestos Asbestos Disease: An Overview for Clinicians Asbestos Exposure Asbestos: A health hazard Exposure to asbestos was a major occupational health hazard in the United States. The first large-scale
Treatment Guide Interstitial Lung Disease
 Treatment Guide Interstitial Lung Disease Since interstitial lung disease (ILD) is not a single disease but a group of more than 200 different pulmonary disorders, it can be confusing to understand exactly
Treatment Guide Interstitial Lung Disease Since interstitial lung disease (ILD) is not a single disease but a group of more than 200 different pulmonary disorders, it can be confusing to understand exactly
education Occupational lung disease CME Obstructive occupational airway disease PA Reid, 2 PT Reid
 CME http://dx.doi.org/10.4997/jrcpe.2013.111 2013 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Occupational lung 1 PA Reid, 2 PT Reid 1 Specialist Registrar in Respiratory Medicine, Department of Respiratory
CME http://dx.doi.org/10.4997/jrcpe.2013.111 2013 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Occupational lung 1 PA Reid, 2 PT Reid 1 Specialist Registrar in Respiratory Medicine, Department of Respiratory
Presented by: Donna M. Ringo, CIH. DMR & Associates, Inc., Louisville, Kentucky
 New Considerations for: If It s Silica It s Not Just Dust Presented by: Donna M. Ringo, CIH DMR & Associates, Inc., Louisville, Kentucky Honorable Mention OSHA / NIOSH updates Disclaimer : I am not a toxicologist.
New Considerations for: If It s Silica It s Not Just Dust Presented by: Donna M. Ringo, CIH DMR & Associates, Inc., Louisville, Kentucky Honorable Mention OSHA / NIOSH updates Disclaimer : I am not a toxicologist.
June 20, 2002. 2002.06.20: Wagner Testimony on Workplace Exposure to Asbestos. This is an archive page. The links are no longer being updated.
 Page 1 of 6 skip navigational links This is an archive page. The links are no longer being updated. Statement by Gregory R. Wagner, M.D. Director, Division of Respiratory Disease Studies National Institute
Page 1 of 6 skip navigational links This is an archive page. The links are no longer being updated. Statement by Gregory R. Wagner, M.D. Director, Division of Respiratory Disease Studies National Institute
Interstitial lung disease
 Interstitial lung disease William D Travis Abstract Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias represent an important group of interstitial lung diseases, encompassing seven entities: (1) usual interstitial pneumonia
Interstitial lung disease William D Travis Abstract Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias represent an important group of interstitial lung diseases, encompassing seven entities: (1) usual interstitial pneumonia
Asbestos: health effects and risk. Peter Franklin Senior Scientific Officer, EHD Senior Research Fellow, UWA
 Asbestos: health effects and risk Peter Franklin Senior Scientific Officer, EHD Senior Research Fellow, UWA What is asbestos Naturally occurring mineral that has crystallised to form long thin fibres and
Asbestos: health effects and risk Peter Franklin Senior Scientific Officer, EHD Senior Research Fellow, UWA What is asbestos Naturally occurring mineral that has crystallised to form long thin fibres and
Asbestos Related Diseases. Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease. connecting raising awareness supporting advocating
 Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease connecting raising awareness supporting advocating 1800 017 758 www.asbestosassociation.com.au Asbestos lagging was widely
Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease connecting raising awareness supporting advocating 1800 017 758 www.asbestosassociation.com.au Asbestos lagging was widely
Asbestos Diseases. What Is Asbestos?
 1 Asbestos Diseases What Is Asbestos? Asbestos is a term applied to a group of minerals formed into rock and mined in a similar way to coal. In this form, asbestos is made up of strong, fine and flexible
1 Asbestos Diseases What Is Asbestos? Asbestos is a term applied to a group of minerals formed into rock and mined in a similar way to coal. In this form, asbestos is made up of strong, fine and flexible
Environmental and Occupational Lung Disease. Claudia Corwin MD MPH University of Iowa Healthy Lung Expo May 13, 2016
 Environmental and Occupational Lung Disease Claudia Corwin MD MPH University of Iowa Healthy Lung Expo May 13, 2016 I have nothing to disclose that would create a conflict of interest. Objectives Understand
Environmental and Occupational Lung Disease Claudia Corwin MD MPH University of Iowa Healthy Lung Expo May 13, 2016 I have nothing to disclose that would create a conflict of interest. Objectives Understand
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Type III Hypersensitivity Response
 NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
OCCUPATIONAL LUNG CANCER
 OCCUPATIONAL LUNG CANCER Anwar Jusuf, Agus Dwi Susanto Department of Pulmonology & Respiratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine University Of Indonesia - Persahabatan Hospital-Jakarta INTRODUCTION Occupational
OCCUPATIONAL LUNG CANCER Anwar Jusuf, Agus Dwi Susanto Department of Pulmonology & Respiratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine University Of Indonesia - Persahabatan Hospital-Jakarta INTRODUCTION Occupational
Leanne M Poulos Patricia K Correll Brett G Toelle Helen K Reddel Guy B Marks Woolcock Institute of Medical Research, University of Sydney, NSW
 Lung disease in Australia Leanne M Poulos Patricia K Correll Brett G Toelle Helen K Reddel Guy B Marks Woolcock Institute of Medical Research, University of Sydney, NSW Prepared for Lung Foundation Australia
Lung disease in Australia Leanne M Poulos Patricia K Correll Brett G Toelle Helen K Reddel Guy B Marks Woolcock Institute of Medical Research, University of Sydney, NSW Prepared for Lung Foundation Australia
The Management of Asbestos at the University of Manitoba
 The Management of Asbestos at the University of Manitoba WHAT IS ASBESTOS? Asbestos is a name given to a group of minerals which occur naturally as masses of long silky fibres. Asbestos is known for its
The Management of Asbestos at the University of Manitoba WHAT IS ASBESTOS? Asbestos is a name given to a group of minerals which occur naturally as masses of long silky fibres. Asbestos is known for its
April 2015 CALGARY ZONE CLINICAL REFERENCE PULMONARY CENTRAL ACCESS & TRIAGE
 April 2015 CALGARY ZONE CLINICAL REFERENCE CENTRAL ACCESS & TRIAGE Introduction Pulmonary consulting services are organized through the Calgary Zone Pulmonary Central Access and Triage (PCAT). Working
April 2015 CALGARY ZONE CLINICAL REFERENCE CENTRAL ACCESS & TRIAGE Introduction Pulmonary consulting services are organized through the Calgary Zone Pulmonary Central Access and Triage (PCAT). Working
Survey of Mesothelioma Associated with Asbestos Exposure in Japan
 The research and development and the dissemination projects related to the 13 fields of occupational injuries and illnesses Survey of Mesothelioma Associated with Asbestos Exposure in Japan Clinical characteristics
The research and development and the dissemination projects related to the 13 fields of occupational injuries and illnesses Survey of Mesothelioma Associated with Asbestos Exposure in Japan Clinical characteristics
BE.104 Spring Evaluating Environmental Causes of Mesothelioma J. L. Sherley
 BE.104 Spring Evaluating Environmental Causes of Mesothelioma J. L. Sherley Outline: 1) Toxicological mechanisms and causation evaluations 2) An environetics case: Asbestos and Mesothelioma Toxicological
BE.104 Spring Evaluating Environmental Causes of Mesothelioma J. L. Sherley Outline: 1) Toxicological mechanisms and causation evaluations 2) An environetics case: Asbestos and Mesothelioma Toxicological
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Paul F. Simonelli, MD, Ph.D.
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Paul F. Simonelli, MD, Ph.D. Definition: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a broad range of conditions that have common clinical, physiological, and radiological features.
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Paul F. Simonelli, MD, Ph.D. Definition: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a broad range of conditions that have common clinical, physiological, and radiological features.
Diseases. Inflammations Non-inflammatory pleural effusions Pneumothorax Tumours
 Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Role of HRCT in Diagnosis of Asbestos Related Pleuro Pulmonary Disease
 Cairo University Role of HRCT in Diagnosis of Asbestos Related Pleuro Pulmonary Disease ESSAY Submitted for partial fulfillment of Master degree in Radio-diagnosis By Rania Adel Abd ElRahem Elghetany (M.B.B.CH.,
Cairo University Role of HRCT in Diagnosis of Asbestos Related Pleuro Pulmonary Disease ESSAY Submitted for partial fulfillment of Master degree in Radio-diagnosis By Rania Adel Abd ElRahem Elghetany (M.B.B.CH.,
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Defending Lung Cancer Claims A Primer for Young Lawyers
 Defending Lung Cancer Claims A Primer for Young Lawyers Michael W. Drumke Swanson, Martin & Bell, LLP 330 North Wabash Avenue, Suite 3300 Chicago, IL 60611-3604 (312) 321-9100 (312) 321-0990 [email protected]
Defending Lung Cancer Claims A Primer for Young Lawyers Michael W. Drumke Swanson, Martin & Bell, LLP 330 North Wabash Avenue, Suite 3300 Chicago, IL 60611-3604 (312) 321-9100 (312) 321-0990 [email protected]
NHS Barking and Dagenham Briefing on disease linked to Asbestos in Barking & Dagenham
 APPENDIX 1 NHS Barking and Dagenham Briefing on disease linked to Asbestos in Barking & Dagenham 1. Background 1.1. Asbestos Asbestos is a general name given to several naturally occurring fibrous minerals
APPENDIX 1 NHS Barking and Dagenham Briefing on disease linked to Asbestos in Barking & Dagenham 1. Background 1.1. Asbestos Asbestos is a general name given to several naturally occurring fibrous minerals
General Thoracic Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks. C34.11 Malignant neoplasm of upper lobe, right bronchus or lung
 ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
FIBROGENIC DUST EXPOSURE
 FIBROGENIC DUST EXPOSURE (ASBESTOS & SILICA) WORKER S MEDICAL SCREENING GUIDELINE Prepared By Dr. T. D. Redekop Chief Occupational Medical Officer Workplace Safety & Health Division Manitoba Labour & Immigration
FIBROGENIC DUST EXPOSURE (ASBESTOS & SILICA) WORKER S MEDICAL SCREENING GUIDELINE Prepared By Dr. T. D. Redekop Chief Occupational Medical Officer Workplace Safety & Health Division Manitoba Labour & Immigration
Sir William Osler: Listen to the patient; the patient tells you everything.
 Sir William Osler: Listen to the patient; the patient tells you everything. Jean-Martin Charcot: The patient is a liar. Epidemiology of Mesothelioma Jeffrey H. Mandel, MD, MPH Division of Environmental
Sir William Osler: Listen to the patient; the patient tells you everything. Jean-Martin Charcot: The patient is a liar. Epidemiology of Mesothelioma Jeffrey H. Mandel, MD, MPH Division of Environmental
Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia
 Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Lower Respiratory Tract Dr T Avenant Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Definitions Recurrent pneumonia more than two episodes of pneumonia in 18 months Persistent pneumonia
Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Lower Respiratory Tract Dr T Avenant Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Definitions Recurrent pneumonia more than two episodes of pneumonia in 18 months Persistent pneumonia
HEALTH EFFECTS. Inhalation
 Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Cystic Lung Diseases. Melissa Price Gillian Lieberman, MD Advanced Radiology Clerkship Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center November, 2008
 Cystic Lung Diseases Melissa Price Gillian Lieberman, MD Advanced Radiology Clerkship Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center November, 2008 How do we define a cyst of the lung? Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon
Cystic Lung Diseases Melissa Price Gillian Lieberman, MD Advanced Radiology Clerkship Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center November, 2008 How do we define a cyst of the lung? Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon
Primary reason asbestos is used, is its special resistance to heat. Asbestos fibers are also virtually indestructible.
 ASBESTOS AWARENESS Asbestos Awareness Asbestos is a serious health hazard commonly found in our environment today. This module is designed to provide initial education of asbestos and its associated hazards.
ASBESTOS AWARENESS Asbestos Awareness Asbestos is a serious health hazard commonly found in our environment today. This module is designed to provide initial education of asbestos and its associated hazards.
Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board
 Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board Year to date, numbers as of Occupational disease fatalities are usually gradual in onset and result from exposure to work-related
Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board Year to date, numbers as of Occupational disease fatalities are usually gradual in onset and result from exposure to work-related
Criteria for Attributing Lung Cancer to Asbestos Exposure
 Criteria for Attributing Lung Cancer to Asbestos Exposure Philip T. Cagle, MD The article by Mollo and coworkers 1 examines the criteria for attribution of lung cancers to asbestos exposure, suggesting
Criteria for Attributing Lung Cancer to Asbestos Exposure Philip T. Cagle, MD The article by Mollo and coworkers 1 examines the criteria for attribution of lung cancers to asbestos exposure, suggesting
fibrogenic minerals may be altered considerably
 Br. J. exp. Path. (1983) 64, 66 FAILURE OF MACROPHAGE ACTIVATION TO INDUCE PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN ASBESTOS-EXPOSED GUINEA-PIGS R. J. EMERSON* AND P. J. COLE Fromt the Host Defence Unit, Department of ]ledicine,
Br. J. exp. Path. (1983) 64, 66 FAILURE OF MACROPHAGE ACTIVATION TO INDUCE PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN ASBESTOS-EXPOSED GUINEA-PIGS R. J. EMERSON* AND P. J. COLE Fromt the Host Defence Unit, Department of ]ledicine,
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Christine Pham MD
 Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
TUBERCULOSIS PLEURAL EFFUSION - MANAGEMENT
 TUBERCULOSIS PLEURAL EFFUSION - MANAGEMENT Introduction : ETB 15-20% Pleural effusion 20% in non HIV Under reporting because of AFB negative in fluid In HIV patients: EPTB 20% PTB + EPTB 50% Pleural Effusion
TUBERCULOSIS PLEURAL EFFUSION - MANAGEMENT Introduction : ETB 15-20% Pleural effusion 20% in non HIV Under reporting because of AFB negative in fluid In HIV patients: EPTB 20% PTB + EPTB 50% Pleural Effusion
Lung cancer and asbestos
 Lung cancer and asbestos Bureau Veritas Training Bill Sanderson For the benefit of business and people To begin with.. There are known knowns, that is there are things we know that we know. There are known
Lung cancer and asbestos Bureau Veritas Training Bill Sanderson For the benefit of business and people To begin with.. There are known knowns, that is there are things we know that we know. There are known
Exploring the Role of Vitamins in Achieving a Healthy Heart
 Exploring the Role of Vitamins in Achieving a Healthy Heart There are many avenues you can take to keep your heart healthy. The first step you should take is to have a medical professional evaluate the
Exploring the Role of Vitamins in Achieving a Healthy Heart There are many avenues you can take to keep your heart healthy. The first step you should take is to have a medical professional evaluate the
What is Asbestos? Asbestos was also used in household items, such as: oven gloves ironing board pads simmer mats for stoves fire blankets.
 All About Asbestos Read this booklet to learn more about: identifying asbestos-containing material in your home the health risks of asbestos what you can do about asbestos. What is Asbestos? Asbestos is
All About Asbestos Read this booklet to learn more about: identifying asbestos-containing material in your home the health risks of asbestos what you can do about asbestos. What is Asbestos? Asbestos is
Asbestos in the Home MISAWA AB, JAPAN
 Asbestos in the Home MISAWA AB, JAPAN Asbestos Awareness OCCUPANT ACKNOWLEDGEMENT OF INFORMATION SIGNATURE UNIT NUMBER DATE Prepared by: 35 CES/CEV If you have further question about location of asbestos
Asbestos in the Home MISAWA AB, JAPAN Asbestos Awareness OCCUPANT ACKNOWLEDGEMENT OF INFORMATION SIGNATURE UNIT NUMBER DATE Prepared by: 35 CES/CEV If you have further question about location of asbestos
An introduction to claiming compensation: Industrial diseases Deafness, Dermatitis, HAVS, Silicosis, Latex allergies and Dermatitis
 An introduction to claiming compensation: Industrial diseases Deafness, Dermatitis, HAVS, Silicosis, Latex allergies and Dermatitis www.thompsons.law.co.uk Our pledge to you Thompsons Solicitors has been
An introduction to claiming compensation: Industrial diseases Deafness, Dermatitis, HAVS, Silicosis, Latex allergies and Dermatitis www.thompsons.law.co.uk Our pledge to you Thompsons Solicitors has been
ASBESTOS AWARENESS. For workers and building occupants
 ASBESTOS AWARENESS For workers and building occupants Asbestos Awareness Asbestos is a serious health hazard commonly found in our environment today. This module is designed to provide an overview of asbestos
ASBESTOS AWARENESS For workers and building occupants Asbestos Awareness Asbestos is a serious health hazard commonly found in our environment today. This module is designed to provide an overview of asbestos
Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board
 Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board Year to date, numbers as of 30, Occupational disease fatalities are usually gradual in onset and result from exposure to work-related
Occupational Disease Fatalities Accepted by the Workers Compensation Board Year to date, numbers as of 30, Occupational disease fatalities are usually gradual in onset and result from exposure to work-related
Apportionment in Asbestos-Related Disease for Purposes of Compensation
 Industrial Health 2002, 40, 295 311 Review Article Apportionment in Asbestos-Related Disease for Purposes of Compensation Tee L. GUIDOTTI Department of Public Health Sciences, University of Alberta, Faculty
Industrial Health 2002, 40, 295 311 Review Article Apportionment in Asbestos-Related Disease for Purposes of Compensation Tee L. GUIDOTTI Department of Public Health Sciences, University of Alberta, Faculty
